#flash memory is widely used for storage and data transfer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Do you want to make your Phone more convenient? Are you tired of your Phone running out of memory? Do you want to keep enough Phone memory during your trip? Plug and Play, No Application Required! Never lose important documents, videos, photos again thanks to large and reliable Phone flash drives. Free up iPhone and iPad Memory Space Immediately If your iPhone or iPad has almost used up all the memory space, this iPhone USB storage flash drive can help alleviate 128GB of storage space. Whether you like to shoot short videos or take selfies, our iPhone memory stick are perfect for you. Quickly Backup Without Using iTunes or Cloud You can easily backup and manage files at any time. No need of iTunes or Cloud, manage files, pictures and videos through the mobile app to quickly backup to iPhone flash drive, save the storage space of the mobile phone, and at the same time, operations such as forwarding files on the USB drive can be performed. Plug and Play Share your photos, videos, songs and other files between iPhone picture stick easily. You don't have to pay extra for additional storage, just insert iPhone external storage and enjoy the extra space of your flash drive. High Transfer Speed Smart and upgraded chip with high efficiency and stability. read speed up to 30MB/s and write speed up to 15MB/s. The upgraded chip provides you with more efficient storage experience. How to Transfer for iPhone iPad Requires iOS 13 and higher: Simply insert the flash drive into your iPhone iPad, then go to the "Files" app to find "Untitled" and move files to your iPad or iPhone as needed. How to Transfer for Android Android phones need to support OTG, and flash drives can be found in the “File Manager” of most Android devices. 【Plug and Play, No Application Required, Instantly Increases iPhone and iPad Memory Space】If you almost used up all space on your iPhone or iPad, with 128GB of additional storage, this iPhone flash drive perfectly addresses memory shortages on your phone or iPad. Whether you're capturing short videos or selfies, simply plug the memory stick in your device, easily back up your photos, videos, and files, share your special moment with your friends and family on your social media with just one-click. No worries with the iPhone storage anymore! 【MFi Certified Flash Drive, Multi Port Design】Equipped with USB/USB-L/USB-C (with independent adapter), the phone storage flash drive supports a variety of devices for effortless plug and play operation. Quickly transfer data between different devices, significantly enhancing convenience. Allows you to get rid of the data cable and iTunes, iCloud, so you can easily organize your phone's storage space. Widely Compatible: iPhone 16/15/14/13/12/11/8/7/6S/SE/XR/XS/XS Max/X Series/iPad Air/Pro Series. Also support Android smartphones/Computers and other devices with USB-C Ports.(Tip: For iPhone system version requires iOS 13 or higher, For Android smartphones need to open OTG function) 【High Speed Transfer, Save Your Time】With read speeds up to 30MB/s and write speeds up to 20MB/s, this thumb drive is more efficient than traditional USB drive. Allowing you to quickly transfer files, photos, and videos, which help you save time and focus on the things you like. Enjoy the whole relaxing trip with never stuttering or buffering video play on the go. (Tip: No Third-Party Apps Required, Simply insert the flash drive into the iPhone iPad and go to "Files" app, while Android only needs to open your OTG function) 【Watch Movies, Photos and Play Music Directly From Phone Flash Drive】Store your favorite videos, audios and music on your iPhone's Photo Stick, then seamlessly plug and play on your iPhone or iPad anytime, anywhere. No more need for Internet or WiFi. This iPhone storage device plays videos in many different formats.Pictures stored on the Phone storage device also support different formats. Great way to store all your pictures and videos on an phone external storage device.
【How to transfer in iPhone iPad】Requires iOS 13 and higher: Simply insert the flash drive into your iPhone iPad, then go to the "Files" app to find "Untitled" and move files to your iPad or iPhone as needed. 【How to transfer in Android Phones】Android phones need to support OTG, and flash drives can be found in the “File Manager” of most Android devices. 【Kindly Note】1) For Flash Media Devices, 1 megabyte = 1 million bytes; 1 gigabyte = 1 billion bytes. Actual useable capacity may vary. Some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus is not available for data storage. 2) Up to 30MB/s read speed, write speed is lower. Based on internal testing; performance may be lower depending on the host devices and user’s settings and configurations. 【Reliable After-Sales Service】Experience the convenience of high-quality USB memory stick and enjoy our premium customer service at the same time. For the phone flash drive, if you have any questions, we are willing to provide help. (Note: The phone case may prevent the proper connection between a phone and a usb flash drive, which could result in the phone being unable to recognize the usb flash drive. In this situation, please do not conclude that the usb flash drive cannot be used, remove the phone case and try again) [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
SSD Processor Market: Segmentation by Type and Application 2025–2032

MARKET INSIGHTS
The global SSD Processor Market size was valued at US$ 4,230 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 8,670 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 10.78% during the forecast period 2025-2032. While the U.S. accounts for 35% of global demand with USD 5.4 billion market value in 2024, China is emerging as the fastest-growing region with projected revenues exceeding USD 6.1 billion by 2027.
SSD processors are specialized integrated circuits that manage data storage operations in solid-state drives, optimizing performance through functions like error correction, wear leveling, and flash translation layers. These processors come in three primary NAND flash configurations: SLL (Single Level Cell) for high-endurance applications, MLL (Multi Level Cell) for balanced performance, and TLL (Triple Level Cell) for cost-effective high-density storage solutions.
The market growth is driven by explosive demand for cloud computing infrastructure and enterprise storage solutions, which grew 24% year-over-year in 2023. Furthermore, the transition to PCIe 4.0/5.0 interfaces and adoption of NVMe protocols in data centers has created new opportunities. Industry leaders like Samsung and Western Digital captured 48% combined market share in 2023, with Marvell's new 7nm SSD controllers gaining significant traction in hyperscale data center deployments.
MARKET DYNAMICS
MARKET DRIVERS
Explosive Growth in Data Storage Needs Accelerates SSD Processor Demand
The global datasphere is projected to exceed 180 zettabytes by 2025, creating unprecedented demand for high-performance storage solutions. This explosive growth in data generation across sectors including cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and IoT is driving SSD adoption at a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15%. SSD processors, being the computational brains behind storage operations, are consequently experiencing parallel demand growth as they enable faster data transfer rates that can reach up to 7,000 MB/s in cutting-edge NVMe SSDs. The transition from traditional HDDs to SSDs in enterprise environments is particularly notable, with enterprise SSD shipments growing 25% year-over-year as organizations prioritize storage performance.
Advancements in Processor Architectures Fuel Performance Breakthroughs
Recent architectural innovations in SSD processor design are delivering substantial performance improvements. The shift from planar NAND to 3D NAND technology has enabled processor manufacturers to achieve storage densities exceeding 1 terabit per die while maintaining power efficiency. Cutting-edge controller designs now incorporate multiple ARM cores operating at frequencies above 1GHz, supported by advanced error correction algorithms that extend SSD lifespan by up to 300% compared to previous generations. These technological advancements are creating new market opportunities across hyperscale data centers, where endurance and throughput are critical. Leading manufacturers are reporting that their latest processor designs can sustain random write performance of up to 800,000 IOPS, meeting the demanding requirements of modern database applications.
➤ The industry is witnessing processor designs that can manage 128-layer 3D NAND flash while maintaining power envelopes below 5W, representing a 40% improvement in power efficiency compared to previous generations.
Emerging applications in edge computing and autonomous vehicles are creating additional demand for ruggedized SSD processors capable of operating in extreme environments. These specialized processors incorporate features such as wide temperature operation (-40°C to 105°C) and enhanced power loss protection, opening new vertical markets for SSD processor manufacturers.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Complexity in NAND Flash Integration Creates Technical Barriers
While SSD processors continue to advance, the growing complexity of NAND flash memory presents significant technical challenges. The transition to newer NAND generations requires complete redesigns of processor architectures to maintain compatibility, with each node shrink introducing new timing constraints and signal integrity issues. Current market dynamics show that controller development cycles have extended to 18-24 months for advanced nodes, creating critical timing-to-market pressures. Additionally, the industry is grappling with retention challenges in QLC (Quad-Level Cell) NAND, where SSD processors must implement increasingly sophisticated error correction algorithms that can consume up to 30% of total processor die area.
Supply Chain Constraints Impact Production Capacities
The semiconductor industry's ongoing supply chain challenges are particularly acute for SSD processors, which require advanced fabrication nodes typically between 12nm and 28nm. Foundry capacity allocation remains constrained, with lead times for certain wafer processing steps extending beyond six months. This situation is exacerbated by the concentrated nature of the NAND flash market, where just five manufacturers control over 95% of global production capacity. Recent geopolitical developments have further complicated matters, prompting manufacturers to implement costly supply chain diversification strategies that can add 15-20% to overall production costs.
These constraints are particularly impactful for smaller manufacturers attempting to compete in the enterprise SSD market, where validation cycles can exceed 12 months and require substantial engineering resources.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Thermal Management Becomes Critical Performance Limiter
As SSD processors push performance boundaries, thermal dissipation has emerged as a fundamental challenge. High-performance controllers in enterprise SSDs can generate heat loads exceeding 10W in sustained workloads, requiring sophisticated thermal throttling mechanisms that can reduce performance by up to 40% under worst-case conditions. The industry is responding with innovative packaging solutions such as embedded heat spreaders and advanced thermal interface materials, but these solutions add 10-15% to bill-of-material costs. Thermal challenges are particularly acute in emerging form factors like EDSFF (Enterprise and Data Center SSD Form Factor), where space constraints limit cooling options.
Additional Technical Challenges
Security Vulnerabilities Emerging attack vectors targeting SSD firmware require continuous investments in hardware-level security features. Recent vulnerabilities discovered in partition management functions have highlighted the need for more robust isolation architectures in processor designs.
Power Consumption Optimization Balancing performance and power efficiency remains an ongoing challenge, particularly for hyperscale applications where a 10% improvement in power efficiency can translate to millions in annual savings for large deployments.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
AI Workloads Create Demand for Specialized Acceleration
The exponential growth of AI applications is driving demand for storage solutions with computational capabilities. SSD processors are evolving to incorporate specialized AI acceleration blocks that can perform in-storage processing for tasks like data filtering and transformation. Early implementations demonstrate potential throughput improvements of 5-8x for specific database operations when leveraging these capabilities. The market for computational storage devices is projected to grow at over 35% CAGR through 2030, representing a significant adjacency opportunity for SSD processor manufacturers willing to invest in heterogeneous compute architectures.
Emerging Memory Technologies Open New Architectural Possibilities
Advances in storage-class memory technologies like MRAM and ReRAM are creating opportunities for SSD processor innovation. These next-generation memories promise access latencies 1000x faster than NAND flash, requiring fundamental rethinking of controller architectures. Prototype processors incorporating these technologies have demonstrated the ability to reduce transaction commit latency from milliseconds to microseconds, potentially revolutionizing database architectures. While still in early stages, these developments represent a strategic opportunity for forward-looking manufacturers to establish technical leadership in future storage hierarchies.
➤ Pilot implementations of computational SSD processors in financial trading applications have shown latency reductions of over 85% for certain analytic workloads compared to traditional storage architectures.
The transition to PCIe 5.0 and upcoming PCIe 6.0 interfaces presents another significant opportunity, with processor designs needing to support signaling rates up to 64 GT/s while maintaining signal integrity in dense server environments.
SSD PROCESSOR MARKET TRENDS
Rising Demand for High-Performance Computing Fuels SSD Processor Market Growth
The global SSD processor market, valued at approximately $5.2 billion in 2024, is witnessing robust growth due to increasing demand for high-performance computing across industries. Enterprise adoption of advanced SSD controllers with PCIe 4.0 and upcoming PCIe 5.0 interfaces is driving significant market expansion, particularly in data centers requiring ultra-low latency. Furthermore, the growing preference for NVMe technology, which offers up to 40% faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA interfaces, is reshaping storage infrastructure and creating new opportunities for processor innovation. Manufacturers are responding with multi-core controller designs capable of handling parallel workloads more efficiently.
Other Trends
Cloud Computing and Hyperscale Data Center Expansion
The accelerating shift toward cloud services and hyperscale data center deployments is fueling demand for enterprise-grade SSD processors capable of handling heavy, continuous workloads. Hyperscale operators now account for over 40% of total SSD processor purchases, prioritizing solutions with enhanced power efficiency and thermal management capabilities. This trend is particularly evident in North America and Asia-Pacific regions, where cloud infrastructure investments continue to surge. Processor manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing specialized controllers optimized for read-intensive and write-intensive workload profiles in cloud environments.
Advancements in NAND Technology Drive Processor Innovation
The transition to QLC (Quad-Level Cell) and emerging PLC (Penta-Level Cell) NAND flash is necessitating more sophisticated processors capable of managing increased endurance challenges. While TLC (Triple-Level Cell) currently dominates with over 65% market share, processors supporting higher density NAND are gaining traction in cost-sensitive applications. Modern SSD controllers now integrate advanced error correction (LDPC) and wear-leveling algorithms that can extend SSD lifespan by up to 30% compared to previous generations. These technological improvements are critical as industries increasingly adopt SSDs for mission-critical storage applications.
Edge Computing and IoT Applications Create New Opportunities
The rapid growth of edge computing deployments and IoT applications is driving demand for specialized SSD processors that balance performance with power efficiency. Processors designed for edge applications now feature low-power architectures that consume up to 50% less energy than traditional data center controllers, while still delivering sufficient throughput for real-time processing. This segment is particularly attractive for automotive, industrial IoT, and 5G infrastructure applications, where reliability under diverse environmental conditions is paramount. Manufacturers are responding by developing ruggedized controllers with extended temperature operation capabilities.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key Industry Players
Innovation and Strategic Partnerships Drive SSD Processor Market Competition
The global SSD processor market features a highly competitive environment dominated by semiconductor giants and specialized storage manufacturers. As of 2024, the market remains semi-consolidated, with the top five players collectively holding approximately xx% revenue share. Samsung Electronics leads the pack through its vertically integrated flash memory solutions and proprietary controller technology.
Western Digital and Micron Technology have strengthened their positions through aggressive R&D investments in NAND flash architectures and processor optimization algorithms. Both companies reported xx% year-over-year growth in SSD controller shipments during Q1 2024, reflecting strong demand from hyperscale data centers.
The market has seen intensified competition in the enterprise segment, where Marvell Technology and Intel Corporation are competing through customized SSD processors featuring advanced error correction and power management capabilities. Meanwhile, Toshiba Memory (now Kioxia) maintains technological leadership in high-endurance TLC processors through its BiCS FLASH™ 3D memory technology.
Emerging trends show companies focusing on three strategic areas to maintain competitiveness: (1) development of PCIe Gen 5 controllers, (2) integration of machine learning for wear-leveling optimization, and (3) partnerships with cloud service providers for customized solutions.
List of Key SSD Processor Manufacturers
Samsung Electronics (South Korea)
Toshiba/Kioxia (Japan)
Western Digital Corporation (U.S.)
Intel Corporation (U.S.)
Micron Technology, Inc. (U.S.)
Marvell Technology Group (U.S.)
Lite-On Technology Corporation (Taiwan)
SK Hynix Inc. (South Korea)
Kingston Technology (U.S.)
NetApp, Inc. (U.S.)
Market intelligence suggests that competitive positioning is increasingly determined by three key factors: (1) time-to-market for new storage interfaces, (2) die shrinkage capabilities (with leading players transitioning to 7nm and below processes), and (3) qualification cycles with major OEMs. The ongoing industry transition to QLC (Quad-Level Cell) and PLC (Penta-Level Cell) technologies is expected to further intensify competition through 2030.
Segment Analysis:
By Type
SLL (Single Level Cell) Segment Leads Due to Superior Speed and Efficiency in High-Performance Applications
The market is segmented based on type into:
SLL (Single Level Cell)
MLL (Multi Level Cell)
TLL (Triple Level Cell)
Others
By Application
Large Enterprises Dominate Market Share Due to Higher Adoption of Data-Intensive Storage Solutions
The market is segmented based on application into:
SMEs
Large Enterprise
Data Centers
Consumer Electronics
Others
By End-User Industry
Cloud Computing Services Drive Significant Demand for Advanced SSD Processors
The market is segmented based on end-user industry into:
IT & Telecom
Healthcare
BFSI
Retail & E-commerce
Others
By Architecture
3D NAND Architecture Gains Traction for Higher Storage Density Applications
The market is segmented based on architecture into:
Planar NAND
3D NAND
Others
Regional Analysis: SSD Processor Market
North America The North American SSD processor market is characterized by strong adoption of high-performance computing solutions across enterprise and data center applications. The U.S. dominates regional demand, driven by extensive cloud infrastructure deployments and the presence of major technology firms upgrading storage hardware. Recent shortages in semiconductor supply chains have impacted production, leading to strategic partnerships between SSD controller manufacturers and foundries. The market is transitioning toward PCIe Gen4 and upcoming Gen5 controllers, with Marvell and Intel leading innovations in this space. While enterprise adoption remains robust, consumer SSD demand has softened somewhat due to economic pressures.
Europe European markets emphasize energy-efficient storage solutions aligned with the EU's Green Deal initiatives. Germany and the UK show particularly strong demand for enterprise-grade SSD processors that balance performance with power efficiency. The region benefits from collaborative R&D between academic institutions and manufacturers on next-generation NVM (Non-Volatile Memory) controllers. However, strict data protection regulations have slightly slowed adoption of some advanced controller technologies requiring architectural modifications. Tier 2 manufacturers like Phison and Silicon Motion are gaining traction by offering competitive alternatives to dominant players.
Asia-Pacific This rapidly expanding market is led by China's semiconductor self-sufficiency push, evidenced by Yangtze Memory Technologies' growing SSD controller capabilities. Japan and South Korea maintain leadership in high-end controller IP development, while Southeast Asian nations emerge as manufacturing hubs. The consumer electronics boom and 5G infrastructure rollout drive demand across price segments. Interestingly, the region shows the fastest adoption of QLC (Quad-Level Cell) controllers despite technical tradeoffs, reflecting cost sensitivity in volume markets. Local champions like Huawei's HiSilicon division are reshaping competitive dynamics previously dominated by Western firms.
South America Market growth here faces infrastructure limitations, with Brazil accounting for over 60% of regional demand. Most SSD processors enter through imported storage devices rather than local controller assembly. Economic volatility discourages capital-intensive upgrades, keeping the market focused on value-oriented SATA and PCIe Gen3 solutions. However, developing digital banking sectors and government IT modernization programs create opportunities for mid-range enterprise storage solutions. The lack of local semiconductor expertise limits technological advancement, making the region dependent on global supply chains.
Middle East & Africa This emerging market shows divergent growth patterns - Gulf nations invest heavily in data center infrastructure requiring high-end controllers, while African markets rely on refurbished and entry-level SSDs. The UAE's focus on becoming a regional tech hub accelerates adoption of cutting-edge storage solutions. Meanwhile, economic constraints in other markets prolong dependence on HDDs, slowing SSD processor penetration. Infrastructure gaps in power reliability and connectivity further complicate deployments of advanced storage technologies. Long-term potential exists, particularly for modular and heat-tolerant controller designs suited to the climate.
Report Scope
This market research report provides a comprehensive analysis of the global and regional SSD Processor markets, covering the forecast period 2025–2032. It offers detailed insights into market dynamics, technological advancements, competitive landscape, and key trends shaping the industry.
Key focus areas of the report include:
Market Size & Forecast: Historical data and future projections for revenue, unit shipments, and market value across major regions and segments. The global SSD Processor market was valued at USD million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD million by 2032, at a CAGR of % during the forecast period.
Segmentation Analysis: Detailed breakdown by product type (SLL, MLL, TLL), technology, application (SMEs, Large Enterprises), and end-user industry to identify high-growth segments and investment opportunities.
Regional Outlook: Insights into market performance across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa, including country-level analysis where relevant. The U.S. market size is estimated at USD million in 2024, while China is to reach USD million.
Competitive Landscape: Profiles of leading market participants including Marvell, SAMSUNG, TOSHIBA, Western Digital, Intel, Micron Technology, Lite-On, Fusion-Io, Kingston Technology, and Netapp, covering their product offerings, R&D focus, and recent developments.
Technology Trends & Innovation: Assessment of emerging technologies in NAND flash memory, controller architectures, PCIe interfaces, and evolving industry standards like NVMe.
Market Drivers & Restraints: Evaluation of factors driving market growth such as cloud computing adoption and data center expansion, along with challenges like NAND flash pricing volatility.
Stakeholder Analysis: Insights for component suppliers, OEMs, system integrators, investors, and policymakers regarding the evolving storage ecosystem and strategic opportunities.
Primary and secondary research methods are employed, including interviews with industry experts, data from verified sources, and real-time market intelligence to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the insights presented.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
What is the current market size of Global SSD Processor Market?
-> SSD Processor Market size was valued at US$ 4,230 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 8,670 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 10.78% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
Which key companies operate in Global SSD Processor Market?
-> Key players include Marvell, SAMSUNG, TOSHIBA, Western Digital, Intel, Micron Technology, Lite-On, Fusion-Io, Kingston Technology, and Netapp, among others. The global top five players accounted for approximately % market share in 2024.
What are the key growth drivers?
-> Key growth drivers include increasing demand for high-performance storage solutions, cloud computing adoption, data center expansion, and the transition from HDD to SSD storage.
Which region dominates the market?
-> Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by semiconductor manufacturing in countries like China and South Korea, while North America remains a dominant market due to strong data center investments.
What are the emerging trends?
-> Emerging trends include PCIe 4.0/5.0 adoption, QLC NAND technology, computational storage solutions, and increasing SSD capacities.
Related Reports:https://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/hazardous-lighting-market-regional.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/mobile-document-reader-market-industry.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/gan-drivers-market-outlook-in-key-end.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/airbag-chip-market-research-report-and.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/computer-peripheral-device-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/single-ended-glass-seal-thermistor.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/commercial-control-damper-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/pcb-board-terminals-market-investment.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/bandpass-colored-glass-filter-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/video-surveillance-hardware-system.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/pfc-ics-market-technological.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/modulator-bias-controller-market-key.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/tubular-cable-termination-market-demand.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/logic-buffer-market-size-share-and.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/broadband-polarizing-beamsplitters.html
0 notes
Text
What are the key components of embedded devices?
Embedded devices are specialized computing systems designed to perform dedicated functions within a larger system. They are widely used in industries such as automotive, healthcare, consumer electronics, and industrial automation. The key components of embedded devices include:
Microcontroller/Microprocessor: This is the brain of the device, responsible for executing programmed instructions. Microcontrollers typically integrate a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals, while microprocessors often require external components.
Memory: Embedded devices utilize two primary types of memory: volatile memory (RAM) for temporary data storage during operation, and non-volatile memory (ROM, Flash) for storing firmware and persistent data.
Input/Output Interfaces: These enable communication between the device and the external environment. Examples include GPIO (General-Purpose Input/Output), UART, SPI, and I2C for data transfer with sensors, displays, or other peripherals.
Power Supply: A stable power source is critical for the functioning of embedded devices. This could be a battery, an external adapter, or a power management circuit.
Sensors and Actuators: Sensors collect data from the environment (e.g., temperature, pressure), while actuators perform actions such as motor control or sound generation.
Communication Modules: Many embedded devices include wired (Ethernet, USB) or wireless (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee) communication capabilities to interface with other devices or networks.
Software/Firmware: The functionality of embedded devices is determined by their firmware, which is tailored to specific applications. Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) are often employed for time-sensitive tasks.
Understanding these components is essential for designing efficient and reliable embedded devices. For those aspiring to specialize in this domain, an embedded system certification course can provide the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the field.
0 notes
Text
Random Access Memory
Pronounciation - ran·duhm ak·ses meh·mr·ee
Definition - Random access memory (RAM) is the hardware in a computing device that provides temporary storage for the operating system (OS), software programs and any other data in current use so they're quickly available to the device's processor.
Network Interface Card
Pronounciation - net·wrk in·tr·fays kaard
Definition - A hardware component, typically a circuit board or chip, installed on a computer so it can connect to a network.
Universal Serial Bus
Pronounciation - yoo·nuh·vur·suhl see·ree·uhl bus
Definition - The universal serial bus (USB) is a standard plug-and-play interface that allows computers and peripheral devices to connect with each other, transfer data, and share a power source.
Ethernet
Pronounciation - ee·thr·net
Definition - Ethernet is the traditional technology for connecting devices in a wired local area network (LAN) or wide area network.
Network
Pronounciation - net·wrk
Definition - an interconnected or interrelated chain, group, or system. a network of hotels. b. : a system of computers and peripherals that are able to communicate with each other.
System Unit
Pronounciation - si·stuhm yoo·nuht
Definition - the main box-like structure of a computer with all the essential components needed for the computer to work.
Solid State Drive
Pronounciation - saa·luhd staytdrive
Definition - store data permanently inside an integrated circuit, typically using flash memory.
Hard Disk Drive
Pronounciation - haard disk drive
Definition - A hard drive is the hardware component that stores all of your digital content.
Automatic Voltage Regulator
Pronounciation - aa·tuh·ma·tuhk vowl·tuhj reh·gyuh·lay·tr
Definition - Stabilises the mains power supply voltage to a load.
Mouse
Pronounciation - mows
Definition - A mouse is used to select items on the screen and to give instructions to your computer to perform tasks.
0 notes
Text
dubai data recovery,
dubai data recovery,
In the modern digital world, data loss can be a catastrophic event for both individuals and businesses. Whether it’s a corrupted file, accidental deletion, or a damaged hard drive, losing critical data can cause significant disruption. Fortunately, Dubai data recovery services provide the expertise and tools needed to retrieve lost data and ensure that your valuable information is safe.
What is Data Recovery?
Data recovery is the process of retrieving inaccessible, lost, or corrupted data from storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs, memory cards, or USB drives. This process is essential when normal methods (like opening files or using backups) fail to restore the data.
There are several reasons why data might become inaccessible:
Hardware failure: Physical damage to the storage device.
File corruption: Software malfunctions or viruses that alter the file system.
Accidental deletion: Files deleted unintentionally or after a system crash.
Human error: Incorrect formatting or mishandling of the device.
Natural disasters: Floods, fires, or other events that damage devices.
In Dubai, a variety of professionals and businesses specialize in recovering lost data from these situations, using cutting-edge technology and techniques to restore critical files, applications, and system configurations.
The Need for Data Recovery in Dubai
Dubai, known as a global business hub, sees countless organizations and individuals relying on digital tools for daily operations. The city has a thriving tech industry, with a growing demand for reliable IT services, including data recovery. Whether you're a small business owner, a large corporation, or an individual with precious personal data, the need for secure and efficient data recovery solutions is paramount.
Dubai’s tech-savvy population, which embraces advancements in cloud computing, mobile devices, and digital services, may find themselves needing data recovery services from time to time. For businesses, the loss of data can lead to halted operations, loss of customers, and even legal complications, making timely and effective recovery solutions crucial.
Data Recovery Services in Dubai
Dubai offers a wide range of data recovery services provided by experts who use advanced recovery tools and techniques to restore lost or inaccessible data. These services include:
Hard Drive Recovery: Hard drives are commonly used for storing data, but they are also susceptible to damage, both mechanical and electrical. Data recovery specialists in Dubai can retrieve data from damaged, corrupted, or failing hard drives using state-of-the-art equipment.
SSD Recovery: Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are becoming more popular due to their faster performance and reliability. However, they are still vulnerable to failure, and recovering data from SSDs requires specialized knowledge due to their unique structure.
RAID Data Recovery: RAID systems are commonly used in businesses to store large amounts of data across multiple drives. However, if a RAID array experiences a failure, it can be tricky to retrieve data. Dubai’s data recovery experts have the tools and experience needed to recover lost data from RAID systems, whether it's a simple single disk failure or a complex multi-drive failure.
Mobile Data Recovery: Many people store valuable data on their smartphones, from photos and videos to contacts and documents. Data recovery services in Dubai can help retrieve lost or deleted data from Android and iOS devices.
Cloud Data Recovery: Even cloud storage services are not immune to data loss. Whether due to account issues, system bugs, or human error, cloud data recovery services can help restore your information from cloud platforms.
Data Recovery for External Drives and Memory Cards: External hard drives, USB flash drives, and SD cards are commonly used to store and transfer data. These devices are also vulnerable to failure or corruption. Data recovery services in Dubai can retrieve lost data from these devices.
How Data Recovery Works
The data recovery process generally follows these steps:
Assessment: The first step is to evaluate the damage to the device. The recovery service team will determine the cause of the failure and whether data recovery is possible.
Backup: If the data is accessible, it is first backed up to a secure system or storage device.
Recovery: Using specialized software and tools, the data recovery team will attempt to recover as much lost data as possible.
Restoration: Once the data has been recovered, it is restored to the original device or transferred to a new one as required.
Testing: The restored data is tested to ensure its integrity and that it’s in usable condition.
Choosing the Right Data Recovery Service in Dubai
When selecting a data recovery provider in Dubai, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
Expertise and Experience: Choose a company with a proven track record and experienced technicians who are familiar with a wide range of devices and data recovery techniques.
Reputation: Check customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability and quality of the service.
Success Rate: A high success rate in data recovery is an important indicator of a company's ability to handle complex cases.
Security: Data confidentiality is crucial, especially for businesses. Make sure the provider offers secure recovery processes and handles your data with the utmost privacy.
Cost: While cost should not be the only consideration, it is important to ensure that the pricing is transparent and reasonable based on the level of service provided.
Why Choose Dubai for Data Recovery?
Dubai is home to highly trained professionals with access to the latest tools and technologies, making it an ideal location for reliable and effective data recovery. The city's strategic location as a business hub, combined with its advanced infrastructure, means that both individuals and businesses can access world-class services.
Whether you’re dealing with a personal data loss or a corporate disaster, Dubai’s data recovery services can help ensure that you don’t lose valuable information permanently.
Conclusion
Data loss doesn’t have to mean the end of the road for your valuable information. With the help of specialized data recovery services in Dubai, you can quickly restore your files and continue without missing a beat. By working with experienced professionals who understand the complexity of modern storage devices, you can rest assured that your data is in safe hands.
4o mini
0 notes
Text
The Rise of China Solid State Drives Manufacturer: Your Guide to Quality and Innovation
Micro Storage Electronics Technology Co., Limited As a manufacturer of NAND flash memory and DRAM modules, Micro Storage was founded in 2014. After 10 years of unremitting efforts, relying on excellent quality, powerful resources, and professional services as development support, it has achieved a good reputation in the commercial and industrial fields. Today, we will forge ahead and continue to provide higher quality services and comprehensive solutions for end users and industry leaders in the consumer, commercial, and industrial fields.
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, data storage solutions have become a crucial component for both consumers and businesses. As the demand for faster, more reliable storage solutions increases, many companies are turning to China Solid State Drives Manufacturer to meet their needs. This article delves into the benefits of partnering with Chinese manufacturers, the different types of solid-state drives (SSDs) available, and what to consider when selecting the right manufacturer for your business.
1. Understanding Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Before we explore the advantages of collaborating with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer, it’s important to understand what SSDs are and why they are preferred over traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Speed and Performance: SSDs offer significantly faster data access speeds compared to HDDs. This speed is crucial for applications that require quick read and write operations, such as gaming and data processing.
Durability and Reliability: SSDs have no moving parts, making them less susceptible to mechanical failures. This durability makes them ideal for mobile devices and rugged environments.
Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume less power, which translates to longer battery life in laptops and reduced energy costs for enterprises.
Compact Size: The smaller form factor of SSDs allows for more design flexibility in laptops and other electronic devices.
2. Advantages of Partnering with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer
Choosing a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer offers numerous benefits that can help businesses optimize their storage solutions.
Cost Efficiency: Manufacturers in China often provide competitive pricing due to lower labor and production costs. This affordability can significantly impact your bottom line without compromising on quality.
Diverse Product Range: Chinese manufacturers typically offer a wide variety of SSDs, including SATA, NVMe, and PCIe drives, ensuring that businesses can find products tailored to their specific needs.
Quality Assurance: Many reputable manufacturers in China adhere to strict quality control standards, which ensures that their SSDs meet international quality benchmarks.
Technological Advancements: China is a global leader in technology, with manufacturers continuously innovating to stay ahead in the SSD market. This commitment to R&D translates into better products for customers.
Customization Options: Many manufacturers allow for customization of SSDs, enabling businesses to specify storage capacity, branding, and other essential features.
3. Types of Solid State Drives Offered by Chinese Manufacturers
A China Solid State Drives Manufacturer typically provides various types of SSDs to meet different requirements:
SATA SSDs: The most common type of SSD, SATA drives are widely used in consumer laptops and desktops. They offer a good balance between performance and cost.
NVMe SSDs: Known for their exceptional speed, NVMe drives connect directly to the motherboard, providing significantly faster data transfer rates than SATA SSDs. These drives are ideal for high-performance tasks like gaming and professional applications.
M.2 SSDs: M.2 drives are compact and designed for ultra-thin devices. They can support both SATA and NVMe protocols, offering flexibility in performance.
PCIe SSDs: Utilizing the PCIe interface, these SSDs deliver high-speed data transfers, making them suitable for applications requiring quick read and write speeds.
Industrial SSDs: Built to withstand harsh environments, industrial SSDs are suitable for use in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where durability and reliability are paramount.
4. Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer
When selecting a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure you make the best choice for your business:
Reputation and Experience: Research the manufacturer’s background, focusing on their experience in the industry and customer reviews. A well-established manufacturer is more likely to deliver reliable products.
Quality Certifications: Look for manufacturers that hold international quality certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE, which demonstrate compliance with recognized quality standards.
Technological Capabilities: Assess the manufacturer’s commitment to research and development. Companies that invest in R&D are more likely to offer cutting-edge products.
Production Capacity: Ensure that the manufacturer has the capacity to meet your volume needs. A reliable manufacturer should be able to handle both small and large orders efficiently.
Customization Services: Check if the manufacturer offers customization options, such as specific storage capacities or branding features, to align with your business requirements.
Customer Support: Reliable after-sales support is critical for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase. Choose a manufacturer that provides robust customer service and warranty options.
5. Leading China Solid State Drives Manufacturers
Several prominent manufacturers in China have established themselves as leaders in the SSD market. Here are a few noteworthy companies:
a. Kingston Technology
Kingston is a globally recognized brand known for its high-quality memory and storage solutions. Their SSD offerings include a wide range of products designed for both consumers and enterprises.
b. ADATA Technology Co., Ltd.
ADATA specializes in high-performance memory and storage solutions. Their SSDs are known for their reliability and performance, catering to various user needs.
c. Longsys Electronics Co., Ltd.
Longsys focuses on developing innovative storage solutions, including SSDs that are widely used in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
d. Netac Technology Co., Ltd.
Netac offers a diverse range of SSDs, including consumer and enterprise solutions, with a strong emphasis on quality and performance.
e. Team Group Inc.
Team Group provides a variety of SSD products, including budget-friendly options, making them a popular choice for both individual consumers and businesses.
6. Challenges When Working with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer
While partnering with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer presents many benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
Quality Variability: The quality of SSDs can vary significantly among manufacturers. It's crucial to conduct thorough research and request samples to ensure you receive reliable products.
Communication Barriers: Language and cultural differences can sometimes lead to misunderstandings. Establishing clear communication channels is essential to overcome this challenge.
Logistical Complications: International shipping can introduce delays and complications. Working with manufacturers experienced in global logistics can help streamline the process.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the manufacturer adheres to international regulations regarding product safety and environmental standards.
7. The Future of SSD Manufacturing in China
The future of SSD manufacturing in China looks promising, driven by several emerging trends:
Increased Investment in R&D: Chinese manufacturers are expected to continue investing in research and development to innovate and improve their product offerings.
Rising Demand for Data Storage Solutions: With the increasing reliance on cloud computing and big data analytics, the demand for high-performance SSDs is projected to rise significantly.
Sustainability Initiatives: Many manufacturers are likely to adopt eco-friendly practices, responding to the growing global demand for sustainable products.
Expansion into Emerging Markets: As the adoption of SSDs grows in sectors such as automotive, healthcare, and IoT, Chinese manufacturers will likely broaden their product offerings to cater to these diverse needs.
8. Steps to Establish a Successful Partnership with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer
To effectively collaborate with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer, consider the following steps:
Conduct Thorough Research: Investigate potential manufacturers, focusing on their reputation, product offerings, and customer feedback.
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate the quality and performance of the SSDs.
Negotiate Terms Clearly: Discuss pricing, payment options, and delivery schedules to ensure both parties are aligned on expectations.
Visit Manufacturing Facilities: If feasible, visiting the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their production capabilities and quality control measures.
Establish Effective Communication: Set up direct communication channels for ongoing interactions to ensure alignment on expectations and address any concerns promptly.
Monitor Orders and Provide Feedback: Keep track of your orders and maintain open communication to address issues promptly and provide feedback on product performance.
9. Conclusion: The Path to Reliable Data Storage Solutions
In conclusion, partnering with a China Solid State Drives Manufacturer can significantly enhance your business's data storage capabilities. With numerous advantages, including cost efficiency, a diverse product range, and technological innovation, Chinese manufacturers are well-positioned to meet the growing demand for high-quality SSDs.
By understanding the types of SSDs available, evaluating key factors when choosing a manufacturer, and being aware of the challenges, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their technological needs. Embracing the partnership with a reliable manufacturer will not only lead to improved efficiency and performance but also set a solid foundation for future growth in a data-driven world. As technology continues to advance, the role of SSDs will become increasingly critical, and choosing the right manufacturing partner is essential for success.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the KLMCG4JETD-B041: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to KLMCG4JETD-B041
When it comes to data storage solutions, finding the right fit for your needs can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. That's where the KLMCG4JETD-B041 comes into play. This compact yet powerful storage device is designed to meet the growing demand for reliable, high-performance data storage. But what exactly makes the KLMCG4JETD-B041 stand out in a crowded market? In this article, we’ll dive deep into its features, benefits, and how it compares to other storage options available today. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a professional seeking the best storage solutions, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision.
What is KLMCG4JETD-B041?
The KLMCG4JETD-B041 is a type of embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC), which is a storage technology widely used in mobile devices, tablets, and some compact PCs. An eMMC like the KLMCG4JETD-B041 integrates flash memory and a flash memory controller in a single package, simplifying the storage interface in electronic devices. This model, in particular, offers a blend of speed, capacity, and durability, making it an ideal choice for modern electronics that require efficient and reliable storage solutions.
Technical Specifications
To truly appreciate what the KLMCG4JETD-B041 brings to the table, let's take a closer look at its technical specifications:
Storage Capacity: Typically available in multiple configurations, the KLMCG4JETD-B041 usually comes in a 32GB or 64GB variant, providing ample space for operating systems, applications, and user data.
Interface: It utilizes an 8-bit parallel interface, which allows for faster data transfer rates compared to its predecessors.
Read/Write Speed: The device offers high read and write speeds, making it suitable for applications that require quick access to data, such as gaming and video streaming.
NAND Type: It is built with 3D NAND technology, which stacks memory cells vertically, allowing for higher density and better reliability.
Operating Temperature: The KLMCG4JETD-B041 is designed to operate efficiently within a wide temperature range, making it suitable for various environments and applications.
Features of KLMCG4JETD-B041
The KLMCG4JETD-B041 comes packed with features that set it apart from other storage devices:
High Performance: With its high read/write speeds and efficient data handling capabilities, the KLMCG4JETD-B041 ensures smooth operation even under demanding workloads.
Durability: Built to last, this eMMC device is designed to handle numerous read/write cycles, making it a durable option for long-term use.
Compact Size: Its small form factor makes it ideal for use in compact devices where space is a premium.
Low Power Consumption: Designed with energy efficiency in mind, the KLMCG4JETD-B041 helps extend battery life in portable devices, a crucial factor for mobile and battery-operated gadgets.
How Does the KLMCG4JETD-B041 Work?
Understanding how the KLMCG4JETD-B041 works can help you better utilize it in your devices. The eMMC operates by combining a flash memory controller with NAND flash memory in a single package. The controller manages data storage and retrieval processes, optimizing performance and reliability. This setup reduces the complexity of storage management for device manufacturers and improves overall system performance by providing a seamless interface between the device’s processor and its storage.
Applications of KLMCG4JETD-B041
The KLMCG4JETD-B041 is versatile and finds applications in various devices and systems, including:
Smartphones and Tablets: Its compact size and efficiency make it a popular choice in mobile devices, where space and battery life are critical.
Automotive Systems: Used in infotainment systems and other vehicle control units, the KLMCG4JETD-B041 can withstand harsh operating conditions and provide reliable performance.
Wearable Devices: Due to its low power consumption and small form factor, it is ideal for use in wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers.
Embedded Systems: It’s also a great fit for industrial and consumer embedded systems, providing robust performance in a wide range of applications.
Advantages of Using KLMCG4JETD-B041
There are several benefits to using the KLMCG4JETD-B041 in your devices:
Reliability: It offers high reliability with built-in error correction and wear leveling features that enhance data integrity and prolong the lifespan of the device.
Ease of Integration: With its standardized interface and compact form factor, integrating the KLMCG4JETD-B041 into existing designs is straightforward, reducing development time and costs.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other storage technologies, eMMCs like the KLMCG4JETD-B041 are more affordable, providing a cost-effective solution for high-capacity storage needs.
High Capacity: Provides sufficient storage for most consumer and industrial applications, accommodating growing data requirements.
Limitations and Considerations
While the KLMCG4JETD-B041 is a great storage solution, it does come with some limitations:
Speed Limitation: While it offers good speed for most applications, it may not be suitable for use cases requiring extremely high-speed data transfers, such as professional video editing or high-performance computing.
Non-Upgradable: As with most eMMC storage devices, the KLMCG4JETD-B041 is soldered onto the motherboard, making it non-upgradable and non-replaceable.
Limited Lifespan: Like all flash memory devices, eMMC has a finite number of write cycles, which can affect its lifespan, especially in write-intensive applications.
Comparison with Other Storage Devices
How does the KLMCG4JETD-B041 stack up against other storage devices? Let’s take a look:
Compared to SSDs: While SSDs offer faster speeds and higher capacities, they are also more expensive and consume more power. The KLMCG4JETD-B041 is a more cost-effective and power-efficient solution for applications that do not require extreme performance.
Compared to HDDs: Hard drives provide more storage capacity at a lower cost but are significantly slower, larger, and more prone to physical damage. The KLMCG4JETD-B041 offers a better balance of speed, durability, and compactness.
Compared to Other eMMCs: The KLMCG4JETD-B041 provides competitive performance and features compared to other eMMC devices, particularly in terms of reliability and energy efficiency.
Integration and Compatibility
Integrating the KLMCG4JETD-B041 into your device is straightforward due to its compatibility with a wide range of operating systems and hardware configurations. Its standardized interface ensures seamless communication with most modern processors and chipsets, making it a versatile choice for various electronic applications.
Performance Optimization Tips
To get the most out of your KLMCG4JETD-B041, consider the following optimization tips:
Firmware Updates: Keep the device firmware updated to the latest version to ensure optimal performance and security.
Avoid Overloading: Maintain a healthy amount of free space on the device to prevent performance degradation caused by overloading.
Heat Management: Ensure proper ventilation and cooling to prevent overheating, which can affect the device’s lifespan and performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While the KLMCG4JETD-B041 is designed for reliability, you may encounter some common issues:
Slow Performance: This can often be resolved by clearing cached data or freeing up storage space.
Device Not Recognized: Ensure proper installation and check for driver updates.
Data Corruption: Regular backups and using built-in error correction features can mitigate the risk of data corruption.
Future Trends in Storage Technology
The future of storage technology is ever-evolving. Trends such as 3D NAND technology, advancements in flash memory, and increasing integration of AI for data management are expected to shape the future of devices like the KLMCG4JETD-B041. As devices continue to demand more storage and better performance, technologies like eMMC will continue to innovate to meet these needs.
Buying Guide: What to Look For
When considering the KLMCG4JETD-B041 or similar storage devices, keep the following factors in mind:
Capacity Needs: Determine the storage capacity you require based on your intended use.
Read/Write Speed: Choose a device that meets your performance needs, especially for applications that require fast data access.
Durability: Look for features like wear leveling and error correction that enhance the device’s reliability and lifespan.
Compatibility: Ensure the storage device is compatible with your existing hardware and software configurations.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The KLMCG4JETD-B041 eMMC storage device offers a compelling blend of performance, reliability, and affordability, making it a great choice for a wide range of applications, from mobile devices to industrial systems. While it has some limitations, its advantages make it a strong contender in the world of embedded storage solutions. Whether you’re building a new device or upgrading an existing one, understanding the capabilities and limitations of the KLMCG4JETD-B041 will help you make an informed decision.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Do you want to make your Phone more convenient? Are you tired of your Phone running out of memory? Do you want to keep enough Phone memory during your trip? Plug and Play, No Application Required! Never lose important documents, videos, photos again thanks to large and reliable Phone flash drives. Free up iPhone and iPad Memory Space Immediately If your iPhone or iPad has almost used up all the memory space, this iPhone USB storage flash drive can help alleviate 128GB of storage space. Whether you like to shoot short videos or take selfies, our iPhone memory stick are perfect for you. Quickly Backup Without Using iTunes or Cloud You can easily backup and manage files at any time. No need of iTunes or Cloud, manage files, pictures and videos through the mobile app to quickly backup to iPhone flash drive, save the storage space of the mobile phone, and at the same time, operations such as forwarding files on the USB drive can be performed. Plug and Play Share your photos, videos, songs and other files between iPhone picture stick easily. You don't have to pay extra for additional storage, just insert iPhone external storage and enjoy the extra space of your flash drive. High Transfer Speed Smart and upgraded chip with high efficiency and stability. read speed up to 30MB/s and write speed up to 15MB/s. The upgraded chip provides you with more efficient storage experience. How to Transfer for iPhone iPad Requires iOS 13 and higher: Simply insert the flash drive into your iPhone iPad, then go to the "Files" app to find "Untitled" and move files to your iPad or iPhone as needed. How to Transfer for Android Android phones need to support OTG, and flash drives can be found in the “File Manager” of most Android devices. 【Plug and Play, No Application Required, Instantly Increases iPhone and iPad Memory Space】If you almost used up all space on your iPhone or iPad, with 128GB of additional storage, this iPhone flash drive perfectly addresses memory shortages on your phone or iPad. Whether you're capturing short videos or selfies, simply plug the memory stick in your device, easily back up your photos, videos, and files, share your special moment with your friends and family on your social media with just one-click. No worries with the iPhone storage anymore! 【MFi Certified Flash Drive, Multi Port Design】Equipped with USB/USB-L/USB-C (with independent adapter), the phone storage flash drive supports a variety of devices for effortless plug and play operation. Quickly transfer data between different devices, significantly enhancing convenience. Allows you to get rid of the data cable and iTunes, iCloud, so you can easily organize your phone's storage space. Widely Compatible: iPhone 16/15/14/13/12/11/8/7/6S/SE/XR/XS/XS Max/X Series/iPad Air/Pro Series. Also support Android smartphones/Computers and other devices with USB-C Ports.(Tip: For iPhone system version requires iOS 13 or higher, For Android smartphones need to open OTG function) 【High Speed Transfer, Save Your Time】With read speeds up to 30MB/s and write speeds up to 20MB/s, this thumb drive is more efficient than traditional USB drive. Allowing you to quickly transfer files, photos, and videos, which help you save time and focus on the things you like. Enjoy the whole relaxing trip with never stuttering or buffering video play on the go. (Tip: No Third-Party Apps Required, Simply insert the flash drive into the iPhone iPad and go to "Files" app, while Android only needs to open your OTG function) 【Watch Movies, Photos and Play Music Directly From Phone Flash Drive】Store your favorite videos, audios and music on your iPhone's Photo Stick, then seamlessly plug and play on your iPhone or iPad anytime, anywhere. No more need for Internet or WiFi. This iPhone storage device plays videos in many different formats.Pictures stored on the Phone storage device also support different formats. Great way to store all your pictures and videos on an phone external storage device.
【How to transfer in iPhone iPad】Requires iOS 13 and higher: Simply insert the flash drive into your iPhone iPad, then go to the "Files" app to find "Untitled" and move files to your iPad or iPhone as needed. 【How to transfer in Android Phones】Android phones need to support OTG, and flash drives can be found in the “File Manager” of most Android devices. 【Kindly Note】1) For Flash Media Devices, 1 megabyte = 1 million bytes; 1 gigabyte = 1 billion bytes. Actual useable capacity may vary. Some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus is not available for data storage. 2) Up to 30MB/s read speed, write speed is lower. Based on internal testing; performance may be lower depending on the host devices and user’s settings and configurations. 【Reliable After-Sales Service】Experience the convenience of high-quality USB memory stick and enjoy our premium customer service at the same time. For the phone flash drive, if you have any questions, we are willing to provide help. (Note: The phone case may prevent the proper connection between a phone and a usb flash drive, which could result in the phone being unable to recognize the usb flash drive. In this situation, please do not conclude that the usb flash drive cannot be used, remove the phone case and try again) [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
KingDian SSD: Revolutionizing Data Storage
KingDian SSD: Revolutionizing Data Storage KingDian, a professional SSD (Solid State Drive) and DDR memory manufacturer based in China, has been focusing on SSDs and DDR memories since 00. With strong design and R&D capabilities, KingDian quickly provides customers with customized services such as OEM and ODM.Get more news about Kingdian Ssd,you can vist our website!
KingDian’s SSD product series include NVME series (PCIe Genx; PCIe Genx), SATA series, SATA series, M-SATA series, and NGFF (M.) series. DDR memory includes DDR5 series, DDR series, and DDR series. They also have RGB with Heat Sink and Heat Sink series specially developed for gamers. Their products are widely used in PCs, notebooks, all-in-one machines, advertising machines, thin clients, and POS machines, providing professional storage solutions for various industries.
One of the standout products in KingDian’s lineup is the KingDian External Solid State Drive P. KingDian Portable SSDs offer blazing-fast data transfer speeds, several times faster than traditional hard drives or USB flash drives. With a maximum sequential read/write speed of up to 0MB/s, transferring a large 5GB document takes just ten seconds. Offering multiple capacity options to meet user needs.
Another notable product is the .5 Inch SATA S70 Series SSD. This SSD is compatible with SATA (6.0Gb/s), and also with SATA (.0Gb/s). It operates efficiently in temperatures ranging from 0 to 70 degrees Celsius. The S70 series offers a wide range of capacities, from 6GB to TB, and is compatible with various systems including Windows, Unix, Linux, and Mac.
KingDian’s commitment to quality and innovation is evident in their production capacity, which is more than 600K per month. They have a professional quality control engineer team, professional equipment, and efficient and rigorous processes. KingDian has 8 abroad branch offices to provide efficient service to customers around the world without time difference. With years of professional industry experience, they have a 6000+ square meters factory, professional production equipment, professional practitioners, to provide customers with professional products and services.
In conclusion, KingDian is not just a manufacturer of SSDs and DDR memories. They are a company that is dedicated to providing professional storage solutions for customers in various industries. Whether you are a gamer looking for high-performance SSDs with heat sinks, or a business in need of reliable and efficient data storage solutions, KingDian has a product that can meet your needs.
0 notes
Text
The Benefits of SSD Hosting for Faster Website Performance
You have come across the phrase "solid state drive hosting" or "SSD hosting" when you are in the market for web hosting. The question is, what exactly is solid-state drive (SSD) hosting, and why is it so vital for your website? This article will provide an in-depth explanation of solid-state drive (SSD) hosting and the reasons why it is the most suitable option for your website.
The foundation of a website that loads quickly is a solid-state drive (SSD) hosting service. In addition to the performance advantages, solid-state drive (SSD) hosting is far more reliable than web hosting which is powered by traditional moving part drives. Continue reading to learn more about solid-state drive (SSD) hosting and the reasons why it offers website owners such a wide range of benefits.

What is SSD Hosting the why is the Best Option for Your Website?
Solid state drives, as opposed to the more conventional hard disk drives, are utilized in the process of SSD hosting, which is a sort of web hosting. In contrast to hard disk drives, which store data on spinning disks, solid state drives, often known as SSDs, do not have any mechanical components and instead store data on flash memory chips that are connected to one another. Since solid-state drives (SSDs) are faster and more reliable than hard disk drives (HDDs), they are a great option for web hosting.
When compared to typical HDD hosting solutions, SSD hosting provides a substantial number of advantages. It is not difficult to understand why solid-state drive (SSD) hosting is rapidly becoming the norm for high-performance web hosting solutions. SSD hosting offers a number of advantages, including faster recovery times, better speed and durability, improved reliability, reduced latency, and easier transfer of websites.
Why is hosting on solid-state drives (SSD) so important?
Speed
Think of it as being similar to needing to fast-forward through a video cassette as opposed to simply selecting a scene that you want to fast-skip through on a DVD. There are two ways to find the proper place: one is pretty much instant, and the other takes a lot of time. If you or one of your visitors are surfing your website, a website that is supported by solid-state drive (SSD) web space will be able to locate and provide the pages considerably more quickly than a website that is supported by a normal hard drive.
Regardless of how well your photos are optimized and how few plugins are utilized, if your website files are kept on a standard old hard drive, your website will always be slower than the identical website that is powered by solid-state drive (SSD) hosting. Without solid-state drive (SSD) hosting, your website is already at a disadvantage, and it will continue to be at a disadvantage even before you have completed constructing it.
Reliability
Solid-state drives (SSD) are extremely durable, and they are far less susceptible to physical shocks. These drives also have fewer moving components, which means there are less things that may wear out or go wrong with them. The files on your website are less likely to be lost as a result of these factors, in comparison to the situation in which they would be hosted on conventional hard drives of the past.
Advantages of Solid-State Drives (SSD) for Web Hosting-
Increased Times of Loading
When it comes to web hosting, solid-state drives (SSD) storage come with a number of advantages, one of the most important being the astonishing boost in website loading speed. Solid-state drives (SSDs) make use of flash memory, which enables them to retrieve data almost instantly, in contrast to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which rely on spinning disks and moving elements. By minimizing the amount of time it takes for content to load, your website visitors will be able to access material more quickly, which will improve user happiness and reduce bounce rates.
Optimized Experience for the User
When it comes to the success of any website, a great user experience is absolutely necessary. The use of solid-state drives (SSD) allows web pages to load quickly, hence reducing the amount of time that visitors have to wait and the amount of irritation they experience. There is a correlation between improved website responsiveness and seamless navigation, which contributes to a smooth and delightful browsing experience, which in turn increases user engagement and drives greater conversion rates.
Reduced amount of downtime
Periods of downtime can have a significant impact on both your online visibility and the operations of your business. Because of its greater reliability and faster data access, solid-state drive (SSD) storage reduces the likelihood of experiencing downtime. When you select web hosting that is based on solid-state drives (SSD), you may lessen the likelihood of server failures and make certain that your website is accessible to users at all times of the day and night.
Reliability is Improved
In comparison to hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs) are less likely to experience mechanical problems. Solid-state drives (SSDs) are less likely to be damaged by physical shocks or vibrations since they do not have any moving elements. Because of this increased reliability, your website will continue to function normally even during times of high traffic, preventing any potential loss of revenue and ensuring that users continue to have a great experience.
Application compatibility with contemporary software
To achieve the highest possible level of performance, contemporary online applications and content management systems (CMS) require storage solutions that are both efficient and effective. Since solid-state drives (SSDs) are able to handle the extensive read and write operations that are required by content management systems (CMS), e-commerce systems, and dynamic online content, they are an excellent choice for hosting applications of this nature. By utilizing solid-state drive (SSD) storage, you can guarantee that your website will have trouble-free compatibility and dependable performance.
Enhancement of Data Protection
Data security is an extremely important topic for those who operate websites. SSDs provide an additional layer of protection for the data you hold. Due to the absence of mechanical components, solid-state drives (SSDs) are less likely to have data corruption as a result of physical failures. Additionally, a large number of solid-state drives (SSDs) make use of sophisticated encryption methods, which allows them to protect the privacy of important data that is kept on your web hosting server.
Employing Resources in an Effective Manner
As a result of their quicker read and write speeds, solid-state drives (SSDs) enable web hosting servers to efficiently manage a greater number of simultaneous requests. A better server performance is the outcome of this enhanced utilization of the available resources. Websites are able to accommodate increased visitor volumes without compromising speed or responsiveness thanks to this technological advancement.
Scalability and flexibility
The use of solid-state drives (SSD) for web hosting provides increased scalability and flexibility. Hosting that is based on solid-state drives (SSD) makes it possible to easily upgrade and expand your website as it grows and demand increases. Solid-state drives (SSDs) provide smooth scaling without compromising performance or user experience because of their capacity to manage higher volumes of data and traffic.
The Benefits of SEO
Optimization for search engines, also known as SEO, is an essential component in boosting the visibility of your website and obtaining organic visitors. Solid-state drive (SSD) storage makes an indirect contribution to search engine optimization (SEO) by improving the performance and speed of websites. By using solid-state drives (SSD) storage, you may boost the search engine rankings of your website, which will ultimately result in increased organic traffic and improved online exposure. Search engines like Google give priority to websites that load quickly.
Efficiency in terms of cost
There was a time when solid-state drive (SSD) storage was regarded to be expensive; however, the cost has dramatically fallen over the years. It is more than worth the initial expenditure because of the several advantages it provides, which include enhanced performance, dependability, and energy efficiency levels. This makes SSD-based web hosting plans a cost-effective choice for individuals and businesses that are looking for high-quality hosting solutions. As a result of growing competition in the market, SSD-based web hosting plans have become more affordable.
Reduce the Latency
The amount of time that passes between a user's request and the server's response is referred to as latency. By faster data access and retrieval, solid-state drive (SSD) storage enables a significant reduction in latency. When there is less latency, the interactive components of your website, such as shopping carts, forms, and real-time communication, are able to function more effectively, resulting in a more seamless experience for the user.
Reduced Consumption of Electricity
Hard disk drives (HDDs) are substantially more power-hungry than solid-state drives (SSDs). Because there are no moving parts, there is less friction and less energy wasted, which leads to cheaper electricity costs and a smaller carbon footprint. When you choose solid-state drive (SSD) storage for your web hosting requirements, you not only reap the benefits of enhanced performance, but you also make a contribution to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable environment.
Conclusion-
The benefits of solid-state drives (SSD) storage in web hosting cannot be refuted. The web hosting market has been revolutionized by solid-state drives (SSDs) due to its capacity to have faster load times, increased dependability, enhanced data security, and effective resource utilization. An amazing user experience, increased search engine rankings, and smooth compatibility with modern applications are all potential outcomes that might result from selecting web hosting that is based on solid-state drives (SSD).

Dollar2host Dollar2host.com We provide expert Webhosting services for your desired needs
Facebook Twitter Instagram YouTube
0 notes
Text
Understanding iPhone Data Recovery: A Lifesaver for Your Lost Data

our smartphones, particularly iPhones, hold vast amounts of personal and professional data. From cherished photos and videos to important contacts and emails, the data stored on our iPhones is invaluable. But what happens when this data is lost due to accidental deletion, software malfunction, or hardware failure? This is where data recovery comes into play, providing a solution to retrieve lost information. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of iPhone data recovery, the methods involved, and the expertise of professional recovery services like Apple Expert.
Introduction to Data Recovery
Data recovery refers to the process of salvaging inaccessible, lost, corrupted, or formatted data from storage devices. This can include hard drives, solid-state drives, USB flash drives, and, notably, smartphones. The process of data recovery can range from simple software solutions to complex hardware repairs, depending on the nature and extent of the data loss.
iPhone Data Recovery
iPhone data recovery specifically addresses the challenges associated with retrieving lost data from Apple's mobile devices. Given the sophisticated technology and security features integrated into iPhones, the recovery process can be more intricate compared to other devices. Common scenarios requiring iPhone data recovery include accidental deletion of files, iOS update failures, water damage, and system crashes.
The Mechanism of iPhone Data Recovery
The mechanism of iPhone data recovery involves several steps, each tailored to address different types of data loss. Here's a detailed look at the process:
Initial Assessment: The first step involves diagnosing the iPhone to determine the cause of data loss and assess the extent of the damage. This can include checking for physical damage, software issues, and ensuring the device is recognized by recovery tools.
Data Extraction: Depending on the diagnosis, data extraction can be performed using specialized software or hardware tools. For software-related issues, recovery software can scan the device’s storage to locate and retrieve lost files. In cases of hardware failure, more advanced techniques may be required, such as accessing the phone's internal memory directly.
Data Repair and Reconstruction: Sometimes, recovered data might be corrupted or incomplete. Data recovery professionals use specialized tools to repair and reconstruct the data to make it usable again.
Data Restoration: The final step involves restoring the recovered data to the device or transferring it to a secure backup location. This ensures that the data is safely stored and easily accessible to the user.
Methods of iPhone Data Recovery
Several methods can be employed for iPhone data recovery, each suited to different types of data loss scenarios:
Using iTunes Backup: If regular backups have been made via iTunes, data can be restored from the latest backup. This method is straightforward but requires that backups have been made prior to data loss.
Using iCloud Backup: Similar to iTunes, data can be restored from iCloud backups. This method is convenient as it does not require a physical connection to a computer but relies on having recent backups.
Third-Party Recovery Software: Various third-party applications are designed to recover data from iPhones. These tools can scan the device for lost data and allow users to selectively restore files.
Professional Data Recovery Services: For more severe cases, professional data recovery services, such as those provided by Apple Expert, offer advanced solutions. These services can handle complex recovery scenarios that standard software cannot address.
Beneficial Software for iPhone Data Recovery
Several software solutions are beneficial for iPhone data recovery:
Dr.Fone - Data Recovery (iOS): A popular tool that can recover data directly from the iPhone, iTunes backup, or iCloud backup. It supports a wide range of data types including photos, messages, contacts, and more.
EaseUS MobiSaver: Known for its user-friendly interface, EaseUS MobiSaver can recover lost data from iPhones, iTunes, and iCloud backups efficiently.
iMobie PhoneRescue: This software specializes in retrieving lost data and fixing iOS issues that may cause data loss. It supports a variety of data types and recovery scenarios.
Professional iPhone Data Recovery at Apple Expert
The professional crew at Apple Expert excels in providing comprehensive iPhone data recovery services. Here’s what sets them apart:
Expertise and Experience: Apple Expert's team comprises skilled professionals with extensive experience in data recovery. Their expertise ensures a high success rate in recovering lost data.
Advanced Tools and Techniques: The team utilizes state-of-the-art tools and techniques to handle both simple and complex recovery tasks. This includes sophisticated software for logical recovery and specialized hardware for physical recovery.
Personalized Service: Apple Expert offers personalized service tailored to each client's specific needs. They conduct a thorough assessment to determine the best approach for recovery, ensuring that clients receive the best possible outcome.
Confidentiality and Security: Data privacy is a top priority at Apple Expert. The team follows strict protocols to ensure that all recovered data is handled securely and confidentially.
Comprehensive Support: From the initial consultation to post-recovery support, Apple Expert provides comprehensive assistance to ensure clients are fully satisfied with the service.
Losing data from your iPhone can be a distressing experience, but with the right tools and professional help, it is often possible to recover lost information. Understanding the mechanisms and methods of iPhone data recovery can empower users to take the right steps in case of data loss. For those in Calgary, Apple Expert offers reliable and professional iPhone data recovery services, ensuring your valuable data is in safe hands.
Tags: iPhone Data Recovery, Data Recovery Services, iPhone Backup, Data Retrieval, Apple Expert Calgary
0 notes
Text
Investigate SSD Types: SATA, NVMe, M.2, U.2, and PCIe

SSD Types
For anyone looking to improve performance and efficiency in data handling and storage, solid-state drives (SSDs) have completely changed the data storage industry and are now necessary components. An SSD can significantly increase system responsiveness by cutting down on loading times.
Games and video editing require SSD types with non-volatile memory express (NVMe) technology since these SSDs can read and write data at over 7,000 MB/s. Because M.2 SSDs enable more elegant and effective computing solutions, the design of ultrabooks and tiny PCs is changing. With their versatility and scalability, U.2 SSDs fill the void left by conventional 2.5-inch SATA drives and PCIe-based NVMe storage. Professional data processing skills are being revolutionised by PCIe SSDs, which leverage the high-bandwidth PCIe interface to provide unparalleled storage performance.
Now let’s examine the various SSD varieties, including the well-known SATA, the cutting-edge NVMe drive, the small M.2, the adaptable U.2, and the high-performance PCIe versions.
Comprehending the subtle differences between SSD types enables you to fully utilise contemporary data storage options, be it for updating computers in your company or setting up a data centre. In order to meet a range of storage requirements, each SSD types has unique benefits.
Different Types of SSDs and How They Work for Storage
Utilising flash memory technology rather than the moving parts found in hard drives, SSDs offer different data access and endurance. For applications that require high-performance data storage, SSD types are an excellent choice because of these capabilities.
Varied SSD types form factors for varied performance and space needs are available for solid-state drives. To choose a drive that meets the device’s physical specifications and the application’s performance requirements, it is essential to comprehend SSD form factors. Compactness, ease of use, compatibility with current hardware setups, and fast data transfer are just a few of the benefits that each form factor offers.
What Is SATA SSD?
Solid-state drive technology can be easily accessed through SATA SSDs, also known as serial ATA solid-state drives. The majority of current systems can be used with these drives because they make use of the SATA interface, a common connection protocol used in most PCs and laptops. NVMe and other more recent SSD technologies outperform SATA SSDs in terms of raw performance, despite the fact that SATA SSDs have revolutionised storage by considerable speed improvements over traditional hard drives.
ATA SSDs are widely used for everyday computer operations such as installing operating systems, playing games, and using general productivity apps. They outperform traditional hard drives in terms of performance. In terms of performance, however, NVMe SSDs exceed them because to a more advanced interface that allows for even greater data transfer rates and lower latency.
A popular option for cost-conscious businesses and individuals, SATA SSDs can be easily integrated into current systems and are reasonably priced, even with their performance restrictions. Their broad compatibility and simplicity of installation make them a cost-effective upgrade option for outdated hardware or adding more storage to newly installed systems.
What Is NVMe SSD?
With their extremely low latency and rapid speeds, NVMe SSDs revolutionised storage performance. NVMe fully realises the potential of solid-state technology by leveraging the PCIe interface created especially for flash-based SSD storage, in contrast to SATA interfaces. NVMe M.2 is one of the form factors that this storage type can be used to.
Server settings, data-intensive apps, and video editing are just a few of the demanding workloads that NVMe SSDs thrive in. For consumers that need the best possible performance and responsiveness from their storage devices, their high throughput and low latency are invaluable.
What Is M.2 SSD?
The compact shape and superior performance of M.2 SSDs make them a popular small, high-speed storage option for usage in contemporary computers.
M.2 SSDs, which measure 22mm (.87 inches) wide and vary in length, plug directly into a motherboard slot, making them excellent for laptops and small-form-factor PCs with little space.
SATA or PCIe interfaces can be used with M.2 SSDs. Nonetheless, compared to conventional SATA SSDs and hard drives, those that use the PCIe interface especially with NVMe support offer better data transfer rates.
When it comes to high-demand applications like gaming, multimedia editing, and data analysis, this speed boost significantly increases system boot times, programme loading times, and file transfer speeds.
The fact that M.2 SSDs connect directly to the motherboard, saving extra power and data cords and simplifying internal computer layouts, is another advantage of these drives. Installing them involves motherboard M.2 slot type, size, and interface compatibility checks.
Which is a PCIe SSD?
PCIe SSDs perform well due to their high bandwidth. These SSDs can transmit data quickly by directly connecting to the PCIe bus, making them excellent for high-speed applications.
PCIe connects high-speed electronics to the motherboard. PCIe supports x2 or x4 data lanes for M.2 SSDs, offering better bandwidth than SATA. This speeds up data transfer, boosting system booting, software launches, and huge file manipulations.
Performance-critical devices like gaming rigs, enterprise servers, and high-end workstations frequently have PCIe SSDs installed. Unmatched responsiveness and efficiency are guaranteed by their capacity to utilise PCIe lanes to their fullest.
What’s U.2 SSD?
NVMe PCIe SSDs and 2.5-inch SATA SSDs converge in U.2 SSDs. Their U.2 interface combines hot-swappable drive bays with NVMe’s speed boosts.
U.2 SSDs excel in enterprise and data centre environments focused on performance, scalability, and durability. They have NVMe SSD-like data transfer rates and lower latency than SATA drives. They are attractive to enterprises looking to improve storage without rebuilding the system because they work with existing infrastructure.
Comparable to conventional SATA drives, U.2 SSDs have the advantage of fitting into normal drive bays. This lessens the need for major changes and allows for simple incorporation into current server architectures.
Additionally, U.2 SSDs may be hot-swapped, which is a vital capability for mission-critical applications when downtime is not an option. This allows administrators to upgrade or replace drives on the fly without stopping systems or disrupting functions.
Organisations can attain a finely balanced combination of performance and adaptability by adopting U.2 SSDs. Along with guaranteeing compatibility and simplicity of deployment inside pre-existing infrastructure, these drives provide the speed and responsiveness required for demanding applications. Enterprise environments are increasingly prioritising agility and efficiency in their IT operations, and U.2 SSDs are a practical option for fostering storage innovation.
Let’s examine the numerous varieties of NAND flash storage now that we’ve discussed SSD types.
Types of NAND storage
NAND flash memory powers SSD storage. The four types of NAND flash are SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC. Their variations affect performance, endurance, and cost-effectiveness. They also differ in the amount of bits held in each memory cell.
SLB
Although SLC NAND costs more per gigabyte, it delivers the maximum performance and longevity. Although SLC SSDs are more expensive per gigabyte than other NAND types, they are perfect for enterprise applications where reliability and constant performance are critical. The single bit of data that each memory cell retains enables greater dependability and faster read and write rates.
MDL
The combination of excellent performance, long life, and affordability is achieved by MLC NAND. MLC SSDs provide increased storage capacity and affordability with reasonable performance and reliability thanks to the two bits that each memory cell stores. Consumer-grade SSDs typically contain this kind of NAND, which offers a strong balance between speed and affordability.
Taking Care
Three bits are stored in each memory cell of TLC NAND, which is optimised for financial savings by sacrificing some endurance in favour of higher storage density. For common consumer applications like laptops and desktops, TLC SSDs are a good fit since they provide greater capacities at more affordable prices.
QLC
Cheap SSDs aimed at large-scale storage applications typically contain QLC NAND. As the least expensive NAND type per gigabyte, QLC NAND maximises storage density by storing four bits per memory cell. QLC SSDs are the best option for low-cost mass storage applications where speed is not as important, such data archiving and secondary storage, because of their higher density at the sacrifice of performance and endurance.
NAND in 3D Vertical
Higher capacities and better performance are possible with 3D vertical NAND (V-NAND) technology than with conventional planar NAND. V-NAND stacks NAND cells vertically in many layers. 3D V-NAND SSDs are a popular option for high-performance computing and enterprise applications because of their design, which permits increasing density without losing reliability or speed. It is more space-efficient and scalable to fulfil the needs of contemporary data storage solutions because of the vertical stacking of cells, which minimises the footprint.
Handling Environmental Concerns and SSD Longevity in Balance
SSD types longevity and dependability are greatly increased by overprovisioning, the process of assigning extra NAND flash capacity above and beyond claimed storage. Although overprovisioning extends the lifespan of SSD types, it also raises concerns about resource consumption and environmental impact. A comparison of the benefits and prospective environmental costs is necessary to assess the sustainability of overprovisioning benefits.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#ssd#nvmessd#pciessd#satassd#qlcssd#nandssd#nandflashmemory#tlcssd#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Unleashing the Power of the 32GB USB Pen Drive
Introduction
In today's digital age, where data rules supreme, the humble USB pen drive has emerged as an indispensable tool for storage, transfer, and backup purposes. Among the plethora of options available in the market, the 32GB USB pen drive stands out as a versatile and reliable solution for individuals and businesses alike. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the myriad features, benefits, and applications of the 32GB USB pen drive.
Understanding the 32GB USB Pen Drive
The 32GB USB pen drive, also known as a flash drive or thumb drive, is a portable storage device that utilizes flash memory to store data. With a storage capacity of 32 gigabytes (GB), it offers ample space to accommodate various types of files, including documents, photos, videos, music, and software applications.
Key Features
High Storage Capacity: The 32GB USB pen drive provides a generous storage capacity, allowing users to store large volumes of data conveniently.
Compact and Portable: One of the primary advantages of the USB pen drive is its compact size, making it highly portable and easy to carry around.
Plug-and-Play Functionality: The plug-and-play feature enables seamless connectivity to computers and other compatible devices without the need for additional drivers or software installations.
Compatibility: The 32GB USB pen drive is compatible with a wide range of devices, including laptops, desktop computers, tablets, and multimedia players, irrespective of the operating system.
Durability: Built with sturdy materials, USB pen drives are resistant to physical damage, such as shocks, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring the safety of stored data.
Data Security: Many USB pen drives come equipped with advanced security features, such as password protection and encryption, to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Fast Data Transfer Speeds: With the latest USB 3.0 technology, 32GB USB pen drives offer high-speed data transfer rates, allowing users to quickly copy or transfer large files within seconds.
Applications
Data Storage and Backup: The primary function of a USB pen drive is to store and backup data, serving as a reliable alternative to traditional storage methods like hard drives and optical discs.
File Transfer: USB pen drives facilitate the swift transfer of files between different devices, making them ideal for sharing documents, presentations, photos, and videos.
Portable Workspace: Users can carry essential software applications, utilities, and documents on a USB pen drive, effectively transforming it into a portable workspace that can be accessed from any computer.
Bootable Drive: USB pen drives can be used to create bootable drives for installing operating systems, troubleshooting system issues, and running diagnostics.
Multimedia Playback: With their plug-and-play functionality, USB pen drives can be connected to compatible multimedia devices, such as smart TVs, gaming consoles, and car stereos, for playing music, movies, and videos.
Presentation Tool: Professionals and students can store their presentations on a USB pen drive and deliver them directly from the device, eliminating the need for cumbersome laptops or projectors.
Data Recovery: In case of system failure or data loss, USB pen drives can be used to retrieve and restore backed-up files, ensuring minimal downtime and productivity loss.
Best Practices To maximize the utility and longevity of a 32GB USB pen drive, consider the following best practices:
Safely Eject: Always eject the USB pen drive from the computer using the "Safely Remove Hardware" option to prevent data corruption or loss.
Keep Backup: Regularly backup the data stored on the USB pen drive to avoid the risk of accidental deletion or device failure.
Protect with Password: Enable password protection and encryption to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Avoid Physical Damage: Handle the USB pen drive with care and avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures, moisture, or magnetic fields.
Update Firmware: Periodically check for firmware updates for the USB pen drive to ensure compatibility and performance optimization.
Scan for Malware: Use antivirus software to scan the USB pen drive for malware and viruses regularly, especially when transferring data between multiple devices.
Use Quality Brands: Invest in USB pen drives from reputable brands known for their reliability, performance, and customer support.
Conclusion
The 32GB USB pen drive is a versatile and indispensable tool for storing, transferring, and backing up data in today's digital landscape. With its high storage capacity, compact design, and plug-and-play functionality, it offers convenience, portability, and reliability to users across various domains. By understanding its features, applications, and best practices, individuals and businesses can harness the full potential of the 32GB USB pen drive to streamline their data management needs and enhance productivity.
0 notes
Text

Sometimes, when making your own devices on microcontrollers, there is a need to display huge amounts of information on a display and to use a bigger screen for ease of perception. Unfortunately, there are no ready-made and budget-friendly solutions for this task on the market. LCD displays with the ability to connect to a microcontroller are usually tiny and pricy.
But at the same time, there is a wide selection of legacy LCD monitors with a VGA interface. Models with a diagonal of 15 to 19 inches can be purchased in perfect working condition for a very low price, or one can even get one for free. This especially applies to monitors with a 4:3 aspect ratio. In addition, such models are usually quite reliable.
Most older monitors only have a VGA connector for connecting to a computer. Sometimes there is an additional DVI port (on more expensive models). The HDMI connector is more common on modern devices.
Thus, with a probability close to 100%, we'll get just a VGA on an older monitor. In order to display an image on such a monitor, it is enough to work with only five signals: analog R (red), G (green), and B (blue), responsible for the brightness of each color component, as well as digital HS (horizontal sync) and VS (vertical sync), providing synchronization. Analogue signal levels should range from 0 to 0.7 V, where 0 V corresponds to no light at all and 0.7 V to maximum brightness. Digital signals HS and VS are short pulses with a TTL level of negative polarity. The timings of these signals can be found, for example, here: http://tinyvga.com/vga-timing/640x480@60Hz.
Typically, special controllers, or FPGAs, are used to generate video signals, and many FPGA development boards are already equipped with a VGA connector. However, FPGAs are often expensive and require many additional components. I was looking for a simpler and cheaper solution. As a result, the decision was made to use CPLD. CPLDs have fewer available logic gates (LEs) than FPGAs but are less expensive. For example, the MAX II Altera EPM240 development board is sold on Aliexpress: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256804686276488.html for only $8.12 (excluding shipping), and the kit even includes a programmer. The chips themselves can be purchased for $1.6–2.1 (for nice knockoffs).

Plain text mode was chosen for implementation because it is easier for a slow microcontroller but at the same time quite informative. Some graphics elements can be implemented using pseudo-graphics symbols, as was often done in the days of DOS. The introduction of a graphics mode would require transferring a large amount of data from the microcontroller and additional efforts to create it, which is not always possible, especially for weak cores.
CPLD has a built-in Flash ROM (User Flash Memory block, UFM), which can be used as a character ROM. However, its capacity is very limited—only 8 kbit, or 1 KB. This amount of storage is only sufficient for characters with a resolution of 5×7 pixels, and only if we discard non-displayable, insignificant, and visually identical characters from the ASCII table. In addition, the use of UFM will require the use of logic gates (LE), of which there are already a few. Despite the attractiveness of this option, I had to abandon it and use an external ROM chip, which can be salvaged from an old motherboard. Choosing a microchip with a supply voltage of 3.3 V will eliminate problems with matching voltage levels for the CPLD. The capacity of such ROMs is quite large: 2, 4, or 8 Mbit, or at least 256 to 1024 KB, which allows one to store a large number of different fonts with a decent resolution of 8x16 pixels.
To store the screen image, you will also need a RAM chip. Let's estimate the approximate size required for this. If we plan on using an 8×16 pixel font on a screen with a resolution of 640×480 pixels, we will end up with 80 characters per line and 30 lines on the screen. Thus, saving the screen image will require 80 × 30 = 2400 bytes. This number is somewhat inconvenient because it is just slightly larger than the nearest power of two, 2048. The memory use in this case is inefficient—only 58%, since the next power of two is 4096. By the way, this is exactly why text mode with 80×25 symbols became popular since there are 5 fewer lines on the screen. In this case, only 2000 bytes of memory are needed, which easily fits into 2 KB.
However, modern memory chips have significant storage sizes, and saving memory is not so critical nowadays. Moreover, one can deliberately choose to waste memory in order to simplify the decryption logic and save CPLD logic elements. Then you will need at least 4096 bytes (2^12, 12 address bits), which can be divided as follows: 5 address bits are allocated to the row address on the screen (30 of 32 will be used) and 7 bits to the column or position address characters in the string (80 out of 128 will be used).
4096 bytes are required only for storing ASCII symbols. The same amount of memory will be taken by the symbol attribute page. Attributes must include character color (3 bits), background color (3 bits), underline, and blinking. So, a memory of at least 8 KB is required.
Of the most affordable options, the best one is static RAM (used as cache memory), also salvaged from old devices or motherboards. It should be noted that this memory can only operate at 5 V. However. If it is a CMOS-type memory, it can take 3.3 V, but this will require timing correction.
So, we got the following diagram:.
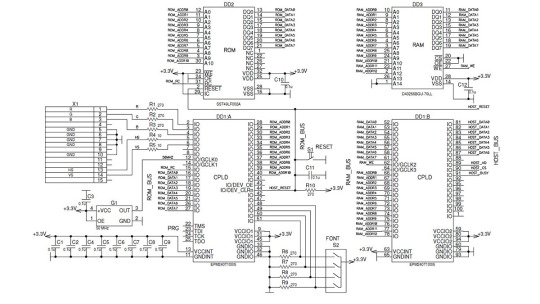
The circuit includes only three microchips and a minimum number of external components. Using the aforementioned Altera EPM240 development board as a base, all you need are ROM chips, RAM chips, and a DSUB header with five resistors. Connecting signals to the CPLD is just an approximation, since almost all of its pins are equivalent (with the exception of Global CLK, one of which requires connecting a signal from a clock generator). When the chip is repeatedly reprogrammed for a new device, almost all of its signals can be reassigned. Currently, the device is assembled on a breadboard and can be left aside.
The device communicates with the microcontroller via a parallel 8-bit interface (in the diagram, signals with the HOST prefix), which is logically almost identical to the widely used display interface on the 1602 and similar controllers. The only difference is the addition of a BUSY signal directed from the device to the microcontroller. Its necessity is due to the fact that access to the RAM chip is provided only during the backward sweep period. The rest of the time, the chip is busy (pun intended) executing CPLD logic. The BUSY signal also acts like an interrupt request (IRQ) function. When it's changed, the controller can automatically start writing to the screen buffer.
Interface description:
DATA[7:0] – eight bits of data, unidirectional port, intended exclusively for writing to the device
CS – chip select; 0 for chip is selected, 1 for chip is not selected. On the positive edge of the CS signal, the data is latched for writing.
AD – address/data, during a write operation: 0 – data is being transferred; 1 – address is being transferred.
BUSY – device busy state; 0 – free; 1 – busy. If the device is busy, the write operation to RAM is ignored. Writing is only possible to the address register.
RESET – device reset. 0 – reset; 1 – work. A hard reset can be used to turn off the screen immediately. When this signal is activated, the image output to the monitor stops. Resetting does not affect the contents of the RAM chip.
Writing data from the microcontroller to RAM is possible only during the backward sweep of the frame scan, when the RAM chip is not occupied by the CPLD logic. This time interval is 1.440 milliseconds. Despite the significant duration of this interval, when using slow microcontrollers, there may not be enough time to completely rewrite the entire memory space. For example, an AVR microcontroller, when operating at a frequency of 11.0592 MHz, is capable of recording only three full-screen lines with all the attributes. If one does not update the attributes (as is usually the case in real-life applications, attributes are written once when the program starts), then six full rows can be written in this time. Perhaps optimizing the code and rewriting it in assembly language can significantly speed up the process of updating data. Otherwise, it may take from 5 cycles (if updating only the data) to 15 cycles (if updating the attributes) to completely rewrite the screen. At 60 fps, it will take 1/12 to 1/4 of a second. Those who have ever worked on IBM PC/XT or IBM PC/AT computers with processor clock speeds around 4 to 12 MHz may notice the experience of refreshing the screen to be familiar.
If you don’t want to wait for the next vertical pulse and want to record all the data at once, you can use the RESET signal. When activated, the internal logic of the CPLD stops and is disconnected from the RAM chip, allowing the microcontroller to directly access the memory. Registers for working with RAM are not affected by the reset signal.
In general, the write operations are as follows: you need to wait until the BUSY signal becomes zero, then put the desired data on the data bus, set the data type (address or data) AD, and set the CS signal first to 0, then to 1. When this signal changes from 0 to 1, the data is stored in memory. During a vertical pulse, the RAM chip is directly connected to the microcontroller's HOST signals, so maintaining the timings during writes becomes the responsibility of the microcontroller. However, since static RAM is a fairly fast device and typically has timings significantly smaller than the maximum speed of an average microcontroller driving its I/O lines, this task is not difficult.
The RAM chip D43256BGU-70LL is connected to the CPLD's output pins, with the lines having a 'RAM' prefix on the diagram. These signals include an 8-bit bidirectional data bus and a 13-bit address bus. Of the control signals, only the WE signal is used. Since there is only one chip on the RAM bus and both buses (address and data) are completely under its control, the OE and CS signals are not used, equal 0, and connected to GND.
The SST49LF002A ROM chip is connected similarly (signals with the 'ROM' prefix), except that the data bus in this case is unidirectional. The OE and WE signals of this IC are also not used and are directly connected to 0 (GND) and 1 (VCC), respectively.
Jumpers are connected to the available CPLD pins to select the current font. Since the ROM chip is large enough, it allows one to store several different fonts, including national alphabets, and switch to them by installing jumpers.
The DSUB VGA port is connected to the CPLD using only 5 resistors. Resistors in the HS and VS circuits are primarily for protection and can be ditched. Resistors in circuits R, G, and B are selected in such a way that, together with the input resistance of the monitor (75 Ohms), they form a voltage divider that reduces the voltage at the monitor input to 0.7 V.
The power leads are shunted with ceramic capacitors, and the clock signal with a frequency of 50 MHz from a crystal is supplied to the GCLK0 pin. These parts were on the breadboard originally.
A resistor, a capacitor, and a button are connected to the RESET signal, forming it. However, if the signal is generated by a microcontroller, these components are redundant.
After creating the main part of the CPLD operating logic, it became clear that the number of logic elements (LEs) used was slightly over half of the available ones. In this regard, the idea arose to complexify the logic and add more features. First of all, the number of colors can be increased to 16 by adding three additional CPLD pins and three resistors. This won't significantly complicate the scheme, but it will add eight more colors. In this case, the RAM page with attributes will have to be completely devoted to color, and another page with attributes will have to be added, increasing the RAM address bus by 1 bit. In the second page of attributes, you can implement font selection, underlining, character and background flickering, and so on.
The new scheme looks similar to the previous one.
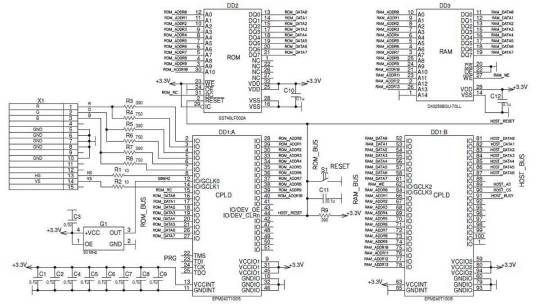
As the number of colors increases, the question is: which palette to choose? With only 8 colors, there is no such question; all colors are different combinations of the three primary colors: red, green, and blue (2^3 = 8). When there are more colors, different options are possible. For example, the 16-color EGA palette: https://moddingwiki.shikadi.net/wiki/EGA_Palette:
As can be seen from the presented palette, the 4th bit in the color number stands for brightness. However, the halves of the table are not evenly separated by brightness. The first half is set to 2/3 brightness (byte AAH = 170 = 2/3 × 256). In the second half, another 1/3 of brightness is added (byte 55H = 85 = 1/3 × 256), and the colors in this part are called "bright."
Interestingly, color No. 6 (yellow/brown) in this scheme deviates from the expected AAAA00 and is specifically set to AA5500. This was done to replace the unattractive, dirty yellow color with the more appealing brown. This is a known feature of EGA video cards and monitors. Some monitors took this into account, while others did not implement this feature in order to simplify the circuit. Some models added a BROWN ADJ knob so that the user could set the desired shade of that color. That is why the color in the table is indicated as yellow/brown.
Nonlinear separation by brightness level automatically leads to two shades of gray showing up: light gray and dark gray, which are widely used.
In the 16-color VGA palette: https://lospec.com/palette-list/microsoft-vga, the situation is slightly different: the colors are divided exactly in two halves by brightness (80H = 128 = 1/2 × 256):

There is also a noticeable outlier in this palette: light gray (С0С0С0), which should be black, duplicating an existing color. Additionally, this color swapped places with the dark gray color (808080). This was done intentionally to ensure compatibility between the VGA and EGA 16-color palettes, making them almost identical.
In our case, when the R, G, and B signals are generated in hardware using resistors, it is more convenient to use the EGA palette. So, it is necessary to make a software correction only for one color, No. 6. All other colors are generated automatically. Switching to the VGA palette would require not only a program change but also an additional group of resistors to be added to create the light gray color (C0C0C0). The resistors should be picked so that one group provides a brightness level of 1/3, the second is 2/3, and together they provide full brightness. By simple calculations using Ohm's law, we get the following values: 390 Ohms and 750 Ohms.
The signal generation logic for a static image like the one with test color bars is quite simple. However, if it is necessary to generate a dynamic image, the task becomes more complicated. It is necessary to organize a logical interface with RAM and ROM. At the same time, data exchange should occur not just quickly but lightning-fast! Let's first evaluate whether the selected chips can keep up with operating like this.
So, the resolution is 640x480. Pixel output frequency is 25 MHz (the standard specifies 25.175 MHz, but rounding to 25 MHz is acceptable since VGA, like many other analog standards, allows a significant spread of parameters). The frame refresh rate is 60 Hz (actually 59.5 Hz), and the line refresh rate is 31.46875 kHz (actually 31.25 kHz). Thus, the output time of one pixel is 40 ns, and the output time of an 8-bit character is 320 ns. During this time, the ASCII code of the character (one byte), the color code (one byte), and the attributes (one byte) should be read from RAM, and then, using the ASCII code as an address, we should read the bit mask of the character from ROM. Only then will the CPLD logic have all the necessary information to begin imaging.
According to the technical description (datasheet), for the selected D43256BGU-70LL chip, a full read cycle takes 70 ns. Considering the use of the chip at reduced voltage, the read cycle takes longer—let's say, 100 ns. Thus, in 320 ns, we will have enough time to read three bytes from RAM: ASCII code, color code, and character attributes. Great. The situation with ROM is more complicated: the address is written to it in two steps—in rows and columns—and, according to the manual, the read cycle takes 270 ns. Not the highest speed, but within the required 320 ns, even with time to spare.
The problem is that we can't start issuing the ROM address until we know at least the ASCII code, which takes 100 ns. This sums up to 370 ns. What saves us is the fact that each RAM or ROM read cycle individually fits within the allowed interval, and we can simply spend two additional cycles reading data. To add these two loops during data preparation, it is necessary to shift the character display area, creating an additional blanking area 2 characters wide at the beginning of the line and reducing the same area at the end of the line by 2 characters. This is quite simple to do: we simply shift the horizontal blanking pulse by 640 ns (accordingly, the horizontal sync pulse also shifts). From the monitor's point of view, there is no difference.
To better understand when and what to write and read, it is handy to create a timing diagram. At the beginning, all the timings were in my head, but creating a paper diagram and giving it another look allowed me to significantly optimize read cycles and even reduce the number of registers used.
The cycle begins by setting the RAM address of the ASCII character byte on the bus. After 80 ns, the requested byte appears on the RAM data bus, which is instantly used to generate the byte read address from the character generator ROM. At the 100 ns mark, we set the address of the symbol attributes byte to the RAM address bus. At 140 ns (60 ns after setting the address), we latch the first part of the ROM address. After another 60 ns, we set the second part of the address on the ROM address bus. At this point, there should be a byte of data on the RAM data bus with character attributes, where 5 bits correspond to the font and are included in the second part of the ROM address. The remaining 3 bits of data are stored in temporary register 2. After another 60 ns, we latch the second part of the ROM address. Data will appear on the ROM data bus 120 ns after this event, already during the second cycle. To prevent loop intersections, we write this data to temporary register 1 at 80 ns. And finally, at 300 ns, all the prepared data is written to the working registers. The character bitmask from temporary register 1 is copied into the rom_reg register, and the stored attribute bits are applied to the color byte that has been read at that time.
Thus, by the end of the second loop, all the data will be ready for outputting the symbol.
Writing data from the microcontroller to RAM is carried out as follows. We wait until the BUSY signal becomes zero, after which we set the starting addresses in the registers where data will be written. Typically, this is address 0, corresponding to the start of the data page, but a random address can also be chosen if only a few bytes need to be changed. Then we record the data. After each byte is written, the address is automatically incremented. When the edge of the screen is reached (the 80th character in a line), the address of the character position in the line is automatically reset to zero, and the line address is incremented by 1. After the entire page of data is written, the address is automatically adjusted to the attribute page entries and then the color page entries. After writing all three pages, the address is also automatically reset, and the process begins again with writing to the data page. Thus, the start address is set only once, and then only data is written. This saves a few microseconds on address setting and simplifies the code when all data can be transferred in one cycle.
Data format for writing data (AD=0):
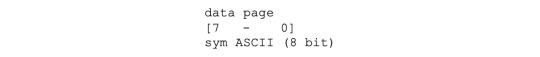
The data page stores ASCII character codes.

The attributes page stores symbol attributes. The lower two bits are responsible for the hardware-driven blinking of a character or background, and the third bit is for the underline. The upper 5 bits select the font. Accordingly, you can display characters from different fonts mixed in any combination. 5 digits for selecting the font allow one to store 32 different fonts, which can include any symbols of national alphabets as well as tiles for displaying an image.

The color page contains the character color and the background color. Color can be anything from the 16-color palette.
There are three address registers. The choice of which particular one to write to is defined by the most significant bits of the data byte. If the most significant bit [7] is 0, then the position register in the row (column) is written. If it is 1, then the line number register (line) and RAM page number register (ASCII code, attributes, or color) are written. If the three most significant bits are equal to 1, then a special control register is written, bits [4] and [3] of which determine the position of the hardware-generated line when the underscore bit is turned on, and bits [2–0] are reserved for future settings.
Data format for writing address (AD = 1):
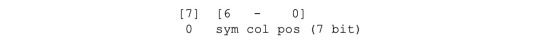
A register stores the position in a string.
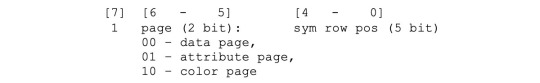
The register stores the line number and page selection.

If you set an address outside the range of 0-79 for a column and 0-29 for a row, then data will begin to be written to the shadow memory area, which is not displayed on the screen. There is nothing wrong with this; after passing the address 127, the data will again be written to the visible area.
Internal CPLD registers (some):

The register contains the current horizontal scan position. It is clocked at a frequency of 50 MHz, which is two times the required 25 MHz, so the least significant bit (tact bit) is not used. Accordingly, bits 1 to 3 indicate the position within the character, and bits 4 to 10 indicate the position of the character in the string. When the value reaches 1600, the register is reset to zero, and the value in the vreg register is increased by 1.
The register contains the current vertical scan position. Clocked from the hreg register. Bits 0 to 3 indicate the line within the character, and bits 4 to 8 indicate the line on the screen. Bit 9 is not used. When the value reaches 525, the register is reset to zero.
The registers contain the current address value for accessing RAM (16 KB in total). The lower 7 bits are the character address in the line (column), then 5 bits are the line address, and 2 bits are the page address (ASCII code, attributes, or color). There are two of these registers: one for internal use by the CPLD logic, and the second is controlled externally by the microcontroller.
The ROM address register is written in two stages. It contains the character string address, the character's ASCII code, and the font address. These addresses are located in such a way that one can flash standard DOS *.fnt font files into the ROM without any additional processing, just one after another. You can combine several fonts into one file for firmware using any file editing program. Just make sure that the fonts have a resolution of 8x16.

Color output register. This register is connected directly to the CPLD pins, supplying the R, G, and B signals to the monitor. The lower 3 bits provide a signal with 2/3 of a brightness level (they must be connected to 390 Ohm resistors); the highest ones provide a signal with a brightness level of 1/3 (they must be connected to 750 Ohm resistors).
Photos to illustrate:



0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] The jump drive is made of aluminum alloy, light weight, just like the size of a lipstick, looks premium and is easy to carry, no matter where you are. It can accompany you whenever you need it. 【Free up phone and iPad memory space immediately】: If your Phone or iPad has almost used up all the memory space, this phone usb storage flash drive can help alleviate 512GB of storage space. Whether you like to shoot short videos or take selfies, our phone memory stick are perfect for you. You don't have to pay extra for additional storage space, just plug in the external storage space of your phone. Enjoy the extra space (512GB) of the phone flash drive. 【Securing Personal Files】: The phone photo transfer stick provides a separate password function to encrypt the file information in the app. You can set a password to effectively protect your private files and protect the whole storage or selected parts. In this way, you can use the phone thumb drive with confidence and enjoy a more comfortable and secure file storage experience. 【One-click backup】: Back up your files, photos, videos and Phone book with just one click. Our phone photo stick is easy to use and comes with an APP that allows you to back up your data quickly and easily. Our phone usb flash drive supports sharing photos to social media such as: Facebook, Twitter, etc., and you can even take photos or videos on our jump drive and save them directly to the zip drive. With 512GB of storage space, you'll have more space and time to do what you love. 【High transfer speed】: Transfer photos, videos, and files in seconds with our USB stick. With a write speed of up to 20 MB/s and a read speed of up to 25 MB/s, our flash drive for phone have higher performance than conventional usb storage flash drive. Save time and get more done with phone photo storage stick. (Tip: phone/iPad needs to download "EASYFLASH PRO" APP from APP Store when using memory stick; Android phone/PC no need to download APP). 【High compatibility】: Our thumb drive is designed for use with a wide range of devices, including Phone 15, 15 Plus, 15 Pro, 15 Pro Max, Phone 14, 14 Pro, 14 Pro Max, 14 Plus, Phone 13, 13 Pro max, 13 Pro, 13 mini, 12 Pro max, 12 Pro, 12, 12 mini, 11 Pro max, 11 Pro, 11, XS MAX, XS, XR, X, 8, 7, 6, 6s, 5s (System Version 8.2 Or higher). The photo stick supports Android smartphones (Need to open OTG function). Our USB storage drives also support computers and other devices with USB ports. [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
AV 64G USB Memory Flash Drive: Speed, Style, and Storage Excellence
AV 64G USB Memory Flash Drive

Picture: Flash Drive
Introduction:
Introduce the article by talking about how, in the digital era, there is a growing need for high-capacity, portable storage. Present the AV 64G USB Memory Flash Drive as a flexible option that blends speed, design, and large storage.
Product Specifications:
Hardware Interface: USB 2.0
Special Feature: Lightweight
Write Speed: 15 Megabyte Per Second
Read Speed: 15 Megabyte Per Second
Color: Silver
Technical Specifications:
Support System: Windows/XP/Linux
Support USB Version: USB 1.0 and 2.0
Product Description:
The AV 64G USB Flash Drive is designed to meet your portable storage needs seamlessly. With a sleek silver finish, it not only offers a stylish look but also delivers optimal performance. The lightweight design ensures easy portability without compromising on storage capacity.
Key Features:
Lightweight Design: Emphasize the AV 64G's unique lightness. Its small size and smooth silver finish not only make it look good, but they also make it easier to carry around, making it perfect for people who are always on the go.
Fast Data Transfer: Learn more about how the AV 64G can send information quickly. With 15 megabytes per second of write and read speeds, the AV USB 2.0 Flash Drive makes sure that data is sent quickly and easily.
Versatile Capacities: Available storage sizes include 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, and 64GB. Because it is so flexible, users can pick the storage size that works best for them, making the AV 64G useful for many tasks.
Compatibility: The AV 64G flash drive works with a lot of different file types. Make sure to stress that it works with Windows, XP, and Linux so that it can serve a wide range of users. It works with both USB 1.0 and 2.0, so it can connect to a wide range of products.
Conclusion:
The AV USB 2.0 Flash Drive is a dependable and effective storage solution that provides various storage capacities and high-speed data transmission rates. The lightweight design enhances its attractiveness, making it essential for those looking for both elegance and functionality in their portable storage devices. Enhance your storage capabilities with the AV USB 2.0 Flash Drive, which offers a combination of high performance and mobility.
#computervision#technology#computer#technical#LaptopSale#pc#computerscience#electronics#computersetup#pcgamingsetup#abdullahventures#dealership#distributorship#deals gadgetshop#geek#apple#techy#hacks#windows#photoofthedayday#software#AIO#AI#allinonepc#av#AV#Abacus#PCS#laptop#startup
0 notes