#industry-specific estimating
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top Industries That Benefit from a Specialized Cost Estimating Service
A cost estimating service plays a vital role in helping businesses manage budgets, control project costs, and reduce financial risks. While almost any industry involved in construction or production can gain from accurate estimates, some sectors benefit more than others due to the complexity, scale, or frequency of their projects. In this article, we explore the top industries where a specialized cost estimating service is not just helpful but often essential for project success.
1. Construction Industry
The construction sector is perhaps the most obvious beneficiary of cost estimating services. Whether the project is residential, commercial, or industrial, precise estimating is crucial to ensure the feasibility and profitability of the job. In construction, a small miscalculation in materials or labor can lead to significant budget overruns or even legal disputes. Specialized estimators help builders and contractors manage resources, evaluate bids, and deliver more accurate proposals to clients.
2. Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies, especially those that deal with custom parts, large machinery, or complex product lines, rely heavily on detailed cost estimates. Estimating services assist with determining the cost of raw materials, labor, machining, assembly, and overhead. This is particularly useful when bidding on contracts or planning new production lines. A specialized service helps manufacturers remain competitive while protecting profit margins.
3. Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry involves large-scale projects with substantial budgets, such as pipeline installations, refineries, and offshore platforms. Specialized cost estimating services are critical in this field due to the high stakes and strict regulatory requirements. Estimators must account for environmental concerns, equipment logistics, safety protocols, and fluctuating energy prices. Accurate forecasting can make the difference between a successful project and a financial failure.
4. Infrastructure and Civil Engineering
Public works such as bridges, highways, water treatment plants, and railways demand detailed and accurate estimates before any work begins. These projects often rely on government funding, making transparency and budget control essential. Cost estimating services provide civil engineers and planners with the breakdown they need to justify spending and meet compliance requirements. The complexity and long timelines of these projects make specialized estimating services particularly valuable.
5. Energy and Utilities
Renewable energy installations, power plants, and utility networks are capital-intensive ventures with long-term returns. A specialized cost estimating service helps energy companies plan projects efficiently, allocate resources wisely, and maintain regulatory compliance. These estimates must include not just initial construction costs but also lifecycle costs such as maintenance, upgrades, and eventual decommissioning.
6. Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sectors, precision and compliance are non-negotiable. Estimating services in these industries go beyond basic cost planning to include complex systems analysis, government procurement rules, and strict quality standards. Given the size and sensitivity of most aerospace and defense contracts, accurate estimating is vital to both competitiveness and legal conformity.
7. Healthcare Facilities Development
Hospitals, clinics, and research facilities require highly specialized construction and equipment installation. These projects often involve a mix of architectural work, mechanical systems, and regulatory compliance with health codes. Estimating services help healthcare developers plan for construction, technology integration, and operating costs. Misestimating even one element—such as medical gas systems or imaging equipment—can result in costly delays.
8. Telecommunications
As networks expand and digital infrastructure becomes more essential, telecommunications companies depend on precise estimating for towers, data centers, fiber optic installations, and 5G rollouts. Specialized cost estimators assist with planning labor, equipment, permitting, and material procurement, ensuring these complex systems are installed efficiently and within budget.
9. Hospitality and Retail Development
Hotels, resorts, and retail centers require tailored estimating due to their unique design and function. Developers must account for aesthetic finishes, custom installations, and branded environments, all of which can vary greatly in cost. A cost estimating service helps manage these variances, ensuring the project meets both brand standards and financial expectations.
10. Education and Institutional Projects
Schools, universities, and government buildings also benefit from professional estimating. These projects typically involve public funding, community oversight, and long-term usage. Estimators help align the project scope with available budgets and assist in planning phased development over multiple years.
The Value of Industry-Specific Expertise
What makes a specialized cost estimating service different is its understanding of the specific challenges and requirements of each industry. A general estimator might miss key cost drivers or regulatory factors that are obvious to someone experienced in a particular field. By choosing a service with knowledge tailored to their industry, companies reduce the risk of financial surprises and improve project outcomes.
Specialized estimating services also stay up to date with relevant materials, labor rates, and industry trends. This allows them to provide more accurate and actionable insights, which are especially important in sectors where pricing can change rapidly or where delays can incur heavy penalties.
Conclusion
While many industries can benefit from cost estimating, some rely on it as a core part of their business planning and execution. Sectors such as construction, manufacturing, energy, and healthcare face unique challenges that demand specialized knowledge and tools. A cost estimating service tailored to these industries not only improves accuracy but also enhances efficiency, transparency, and long-term profitability. As projects grow more complex and budgets tighten, specialized estimating continues to be a strategic asset in high-stakes sectors.
#Cost Estimating Service#construction estimating#bid preparation#project budgeting#cost planning#quantity takeoff#estimating accuracy#industry-specific estimating#construction costs#project cost control#material takeoff#labor estimates#subcontractor pricing#budget forecasting#estimating software#commercial estimating#residential estimating#industrial estimating#cost breakdown#capital project planning#feasibility analysis#proposal estimating#estimation support#contractor bids#estimating consultants#job costing#cost overrun prevention#infrastructure budgeting#project cost analysis#accurate estimates
0 notes
Text
What you need to know about home water filtration.
Emergency Plumbing: Your Trusted Water Filtration Experts in North Shore and Northwest Chicago Suburbs.
With the most affordable deals for water filtration projects of all sizes, our services include:
Water Softeners.
Full-House Filtration Systems.
Well Water Filtration.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems.
Ultraviolet (UV) Water Purification.
Carbon Filters.
Why Choose Emergency Plumbing?
At Emergency Plumbing, we believe everyone deserves access to clean, safe, and affordable water. Our expert team is committed to:
Top-Quality Products: We partner with industry-leading brands for reliable performance.
Affordable Pricing: Transparent, competitive pricing with no hidden fees.
Custom Solutions: Tailored systems to meet your household’s specific needs.
Expert Installation and Maintenance: Trust our licensed professionals to do the job right.
Schedule Your Consultation Today.
Ready to improve your water quality? Contact Emergency Plumbing for a free consultation and estimate. We proudly serve the North Shore and Northwest Chicago suburbs and are here to ensure your family enjoys clean, safe water at an unbeatable value.
Your perfect water solution is just a call away!
Phone 224-754-1984
www.emergencyplumbing.biz
#What you need to know about home water filtration.#Emergency Plumbing: Your Trusted Water Filtration Experts#in North Shore and Northwest Chicago Suburbs.#With the most affordable deals for water filtration projects of all sizes#our services include:#1. Water Softeners.#2. Full-House Filtration Systems.#3. Well Water Filtration.#4. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems.#5. Ultraviolet (UV) Water Purification.#6. Carbon Filters.#Why Choose Emergency Plumbing?#At Emergency Plumbing#we believe everyone deserves access to clean#safe#and affordable water. Our expert team is committed to:#• Top-Quality Products: We partner with industry-leading brands for reliable performance.#• Affordable Pricing: Transparent#competitive pricing with no hidden fees.#• Custom Solutions: Tailored systems to meet your household’s specific needs.#• Expert Installation and Maintenance: Trust our licensed professionals to do the job right.#Schedule Your Consultation Today.#Ready to improve your water quality? Contact Emergency Plumbing for a free consultation and estimate. We proudly serve the North Shore and#safe water at an unbeatable value.#Your perfect water solution is just a call away!#Phone#224-754-1984#www.emergencyplumbing.biz
0 notes
Text
Frustrated that people continued to consume so much alcohol even after it was banned, federal officials had decided to try a different kind of enforcement. They ordered the poisoning of industrial alcohols manufactured in the United States, products regularly stolen by bootleggers and resold as drinkable spirits. The idea was to scare people into giving up illicit drinking. Instead, by the time Prohibition ended in 1933, the federal poisoning program, by some estimates, had killed at least 10,000 people. [...] By mid-1927, the new denaturing formulas included some notable poisons—kerosene and brucine (a plant alkaloid closely related to strychnine), gasoline, benzene, cadmium, iodine, zinc, mercury salts, nicotine, ether, formaldehyde, chloroform, camphor, carbolic acid, quinine, and acetone. The Treasury Department also demanded more methyl alcohol be added—up to 10 percent of total product. It was the last that proved most deadly. The results were immediate, starting with that horrific holiday body count in the closing days of 1926. Public health officials responded with shock. “The government knows it is not stopping drinking by putting poison in alcohol,” New York City medical examiner Charles Norris said at a hastily organized press conference. “[Y]et it continues its poisoning processes, heedless of the fact that people determined to drink are daily absorbing that poison. Knowing this to be true, the United States government must be charged with the moral responsibility for the deaths that poisoned liquor causes, although it cannot be held legally responsible.” His department issued warnings to citizens, detailing the dangers in whiskey circulating in the city: “[P]ractically all the liquor that is sold in New York today is toxic,” read one 1928 alert. He publicized every death by alcohol poisoning. He assigned his toxicologist, Alexander Gettler, to analyze confiscated whiskey for poisons—that long list of toxic materials I cited came in part from studies done by the New York City medical examiner’s office. Norris also condemned the federal program for its disproportionate effect on the country’s poorest residents. Wealthy people, he pointed out, could afford the best whiskey available. Most of those sickened and dying were those “who cannot afford expensive protection and deal in low grade stuff.” And the numbers were not trivial. In 1926, in New York City, 1,200 were sickened by poisonous alcohol; 400 died. The following year, deaths climbed to 700. These numbers were repeated in cities around the country as public-health officials nationwide joined in the angry clamor. Furious anti-Prohibition legislators pushed for a halt in the use of lethal chemistry. “Only one possessing the instincts of a wild beast would desire to kill or make blind the man who takes a drink of liquor, even if he purchased it from one violating the Prohibition statutes,” proclaimed Sen. James Reed of Missouri.
This isn't particularly relevant to anything specific. I just wanted to remind everyone this is something the US government did.
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Off-Duty - Dr. Jack Abbot x wife!reader



Summary: 1k words. Jack comes into the Pitt on his day off with no intention of working. One of his little guests has an affinity for raising his father’s blood pressure and adding to his gray hair. Part 2, Hung The Stars here!
Warnings: unnecessarily long sentences, so sweet it’ll rot your teeth fluff. Poking fun at the U.S. military industrial complex (specifically the Marines). Whitaker catching strays.
a/n: Allow me to contribute to the Girl Dad Abbot Agenda. I gave him fraternal twins here, but his new baby is also a girl. So. The Abbot household will be 3-2 girls-boys because feminism. Divider credit!

If looks could kill, Whitaker would be a dead man.
The med student was approaching the provider dictation desk, about to sit down in a padded rolling chair for the first time all shift when Doctor Abbot firmly gripped the back of the chair seconds before Whitaker could reach for it.
“Oh, uh, sir- I was just gonna sit down and do some charting,” the med student explained in a rush with his perpetual terrified ghost of a Victorian child look.
“You can stand.” Dr. Abbot deadpanned, snatching the chair and whisking it towards the peds ED room.
“Wha-” Whitaker stood, mouth slightly parted. The kid was intelligent and had come into his own throughout his emergency medicine rotation, but some things and some people still never ceased to shock him. He watched through the glass door as Dr. Abbot got far closer to a woman, whom he assumed was the peds patient’s mother, than was professionally necessary.
The woman came into full view, displaying the swell of her belly. The student raised his eyebrows. It was a bold move, even for Dr. Abbot. He estimated the woman to be at the end of her second trimester, if not well into her third.
A toddler bounced from behind the woman and quickly attached herself to Abbot’s leg (the flesh one, anyway). The attending smiled—perhaps for the first time in recorded human history, thought Whitaker—before picking up the child and propping her up on his hip, pressing a kiss to her forehead.
The mother turned to Abbot and smiled, pressing a kiss to his lips while he massaged her lower back with his free hands. His wedding band stuck out against the woman’s lighter shirt. Ah. The wife. A moan that definitely wasn’t appropriate for the workplace escaped the woman, seemingly unknowingly, leaving Abbot with a subtle smirk on his face.
Jack guided his wife into the comfortable chair he’d commandeered. Whitaker envied the relief on her face. The lumbar support cushion and ergonomic design could’ve made him cry. His body was aching for relief after hours on his feet, but he conceded that the woman needed it more than he did.
With a barely audible whimper, the med student went back to his original task. He’s startled when a foldable plastic chair, the ones that are typically kept in patient rooms for guests, unceremoniously clatters down next to him, brought over by none other than the stoic night shift attending.
“My wife said she’s sorry for stealing your seat. I’m not.” Dr. Abbot provided no further context before heading straight back to the room he came from. Some of the surrounding ED staff caught wind of the interaction and glanced up at the status board.
PEDS RM 1. 3 YRS 5 MOS MALE J. ABBOT. FOREIGN BODY INGESTION
Understanding hums sounded out before everyone went back to work.
It was rare to see Jack in anything other than black scrubs at the hospital. Today, he was in full Dad mode. The pink glitter nail polish on his fingers matched his daughter’s. His white New Balance sneakers and cargo shorts allowed a clear view of his prosthetic, which his son had decorated with dinosaur stickers. If you looked close enough, you could see a small apple sauce stain on his shirt.
You relaxed further into the chair and closed your eyes once Jack came back to witness your daughter Ellie toddling around the exam room. At 30 weeks pregnant, rest and comfort were becoming increasingly difficult to come by, especially when raising 3-year-old twins.
Dr. Collins caught Jack sitting at the end of the gurney with his son when she waltzed in, tailed by Matteo.
“What brings you all in today? It’s a pleasure to see the Abbot family. Some members more than others…” Heather teased, making a show out of whispering to Jack’s wife and tickling Ellie.
“Jacob here ate some crayons. Maybe some other stuff too. I want imaging of the GI tract to rule out any other foreign bodies or obstructions,” Jack rattled off, never taking his eyes off his son. The doctor’s leathered, weathered hand dwarfed his son’s small leg. Jack had a tough time letting go of his kids, especially when they were hurt or sick.
“Maybe he’s got a future career in the Marines,” Matteo joked.
“Watch it.” Jack warned with an even glare. The intense look on his face didn’t last long; his wife’s giggle brought a small smile to his face as he glanced toward her.
You winced when the baby delivered a particularly strong jab to your ribs. Jack’s smile quickly turned to concern before you shook your head to reassure him and ran a hand over your bump. Collins and Matteo didn’t miss the silent communication between the couple.
It made sense for the two of you. You were so in sync—always had been. The Pitt staff rarely got to see Jack’s wife, which you supposed was a good thing. Jack tried to keep his personal and professional life separate, but he’d become known for loving you and your little family so much. He would take your calls in the middle of a shift, routinely add more photos of his family to his locker, and occasionally show up to work with glittery nail polish if he forgot to remove it before clocking in.
Doctor Collins high-fived little Jacob, who was the spitting image of his father, after he tolerated the physical exam.
“No guarding or tenderness. Bowel sounds are hypoactive but present. Has he been NPO otherwise?” The physician glanced between the parents.
“We had breakfast around 8,” you supplied, exhaling when you got another sharp kick straight to the bladder.
“Alright. I’ll put in the imaging orders. Radiology will come and grab you guys soon,” Dr. Collins waved goodbye to the toddlers.
Matteo kept a stash of stickers in his scrub pocket for the kiddos that came into the Pitt. Jacob gladly accepted one and promptly stuck it on Jack’s prosthetic. Matteo blinked a couple of times, watching the exchange.
Jack was unfazed. His children seldom went a day without leaving their mark on him. If painted nails and a decorated prosthetic leg made them happy and preserved their innocence, he was happy to be a canvas.
The racecar was a fun addition to the dinosaurs anyway.

a/n: Please let me know what you think! Reblogs & comments keep me motivated <3
Companion piece: Hung The Stars
master list | post notifications @thesewordsxupdates
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The world of corporate intelligence has quietly ballooned into a market valued at over $20 billion. The Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) market alone, valued at around $9.81 billion in 2024. This exponential growth reflects an important shift: intelligence gathering, once the exclusive domain of nation-states, has been privatized and commodified. [...] The methods these firms employ have evolved into a sophisticated doctrine that combines centuries-old espionage techniques with new technology. Understanding their playbook is important to grasping how democracy itself is being undermined. [...] This practice is disturbingly widespread. A report by the Center for Corporate Policy titled “Spooky Business” estimated that as many as one in four activists in some campaigns may be corporate spies. The report documented how “a diverse array of nonprofits have been targeted by espionage, including environmental, anti-war, public interest, consumer, food safety, pesticide reform, nursing home reform, gun control, social justice, animal rights and arms control groups.” The psychological doctrine these firms follow was laid bare in leaked Stratfor documents. Their manual for neutralizing movements divides activists into four categories, each with specific tactics for neutralization: 1. Radicals: Those who see the system as fundamentally corrupt. The strategy is to isolate and discredit them through character assassination and false charges, making them appear extreme and irrational to potential supporters. 2. Idealists: Well-meaning individuals who can be swayed by data. The goal is to engage them with counter-information, confuse them about facts, and gradually pull them away from the radical camp toward more “realistic” positions. 3. Realists: Pragmatists willing to work within the system. Corporations are advised to bargain with them, offering small, symbolic concessions that allow them to claim victory while abandoning larger systemic changes. 4. Opportunists: Those involved for personal gain, status, or excitement. These are considered the easiest to neutralize, often bought off with jobs, consulting contracts, or other personal benefits. [...] Some firms have industrialized specific tactics into product offerings. According to industry sources, “pretexting” services — where operatives pose as someone else to extract information — run $500-$2,000 per successful operation. Trash collection from target residences (“dumpster diving” in industry parlance) is billed at $200-$500 per retrieval. Installing GPS trackers runs $1,000-$2,500 including equipment and monitoring. The most chilling aspect is how these costs compare to their impact. For less than a mid-level executive’s annual salary, a corporation can fund a year-long campaign to destroy a grassroots movement. For the price of a Super Bowl commercial, they can orchestrate sophisticated operations that neutralize threats to their business model. Democracy, it turns out, can be subverted for less than the cost of a good law firm.
94 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! Love your blog, it's such a brilliant resource, thanks so much for writing it.
So, I'm looking for more information on ways that someone would go about breaking someone else's neck. Long story short, it's for a murder mystery situation where I need the investigators to be able to look at the injury on the victims (in an autopsy context, not necessarily on casual examination) and go 'oh, that's a specific technique and it suggests our killer has military or similar how-to-kill-people combat training'. Any suggestions?
A shovel through the spine at the base of the skull?
So, the headlock neck break is basically a fantasy. The amount of force you'd need to actually shatter someone's neck in the way presented would be superhuman. (Which does mean there's probably examples as industrial accidents, but industrial accidents are a somewhat uncommon murder method. Mostly because they're not especially portable.)
Hilariously, there are multiple attempted murder cases, where the would-be killers tried to replicate that neck break, only succeeding in annoy their victims, and telegraphing their intention. So, someone were to try to snap someone's neck that way, it would be an excellent indicator that they had no training what so ever.
There are ways that someone can kill with a headlock, such as a blood choke, but nothing that's going to concretely point the finger at someone with a military background.
Similarly, stab wounds can be very informative about the killer. But all you'll really gather is how familiar they are with human anatomy, and how comfortable they are with cutting people-shaped meat. This won't help you distinguish between someone who's done this before, and someone who's done this before for their country. (Incidentally, “people-shaped meat,” isn't strictly a joke. There are lot of potential careers and backgrounds where you could become pretty comfortable cutting into animals, either live or recently deceased. So, in this specific case, that's more about the mindset. Someone uncomfortable with that level of physicality, is like to leave behind hesitation wounds. These are smaller cuts, sometimes in the main wound channel, indicating that they're not really comfortable with what they're doing.)
So far as it goes, I'm more a fan of just ramming a blade into an artery, rather than slitting their throat. The latter is a lot more work, but the former requires you actually know where to find someone's arteries quickly and efficiently. Which isn't necessarily a sure thing.
Even tool selection won't necessarily tell you much. Someone who's using a military knife might be ex-military, or they could be someone who uses surplussed equipment because it's cheap and relatively reliable. And that's assuming you can concretely identify the knife from the wounds it leaves. Which is also not especially reliable. You can tell how far the blade penetrated, and roughly how large it is, but that won't tell you if it was a bayonet or some cheap gas station hunting knife of a similar size.
Firearms present a similar problem. Once you can track down the gun (if there were any intact bullets to compare, which isn't a certainty), you might be able to match the gun to the wounds. But, examining the wounds on their own (especially if the bullets are gone, or buried deep in the corpse) will only give you an estimate of the bullet's size. Here's a problem with this, did you know that .38, .380, and .357 magnum are all 9mm rounds? They're different cartridges, but the bullets they spit out are very similarly sized. You might be able to make some educated guesses based on the wound channel and burns, but these all fire a round that's roughly the same size. So, when someone looks at a wound and definitively says it was a .38, they don't know that. (Unless they found the shell casing. But even then, you're not likely to find a .38 or .357mag shell casing unless the attacker specifically dropped their spent brass and reloaded, as those are revolver cartridges. .380 is a semi-auto round, so those will get kicked out after each shot. And, yes, before someone complains, there is .357 SIG, that's a semi-auto cartridge. It's 9x22mm.)
Also worth remembering, you can't, specifically match a shotgun's ballistics, assuming the shell was loaded with shot, and not slugs. You may be able to match the mechanical wear on the casing itself to a model (or multiple models in some cases), but not a specific gun.
So, how do you know it was someone with military training? You don't. Learning that someone's been trained to kill is a bit easier to pin down, but the information isn't that useful. That doesn't tell you if they're ex-military, ex-police, or even just the product of an extremely messed up homelife with a prepper parent. Or, even just they got extremely lucky (or unlucky) with a single stab.
Now, it isn't pointless to try to determine that, as it can be helpful later to demonstrate that the eventual suspect had the training to kill in the method that the victim experienced. But it doesn't do much to narrow the suspect pool on its own.
Ironically, the killer not having combat training. So, with things like defensive and hesitation wounds, can be far more useful for narrowing the suspect pool. As an investigator, when you're talking to someone that you're sure has been certified in knife combat, isn't likely to be especially messy with their stabbings. (Though, to be fair, even a trained knife fighter might stab their victim many times, to ensure a faster bleedout, and not all of those hits are going to be especially artful.)
So, that's a long way from, “you can't really break someone's neck like you see in the movies.” You can kill people, and as an investigator, you can make a lot of educated guesses based on what you find at the crime scene. But, “this method means they were militarily trained,” doesn't really mean they were trained by the military.
-Starke
This blog is supported through Patreon. Patrons get access to new posts three days early, and direct access to us through Discord. If you’re already a Patron, thank you. If you’d like to support us, please consider becoming a Patron.
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
BoyBoy book club⭑.ᐟ
These books have either been mentioned or recommended by the boys, list made to the best of my memory, some notes added for context + little abstract. [(A.) = Aleksa's rec; (L.) = Lucas' rec; (Al.) = Alex's rec] Reply or reblog to add more to update the list thanks!
⊹ Caliban and the Witch: Women, the Body and Primitive Accumulation - Silvia Federici (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: Also 'Caliban and the Witch' by Silvia Federicci is brilliant. It's a great marxist-feminist retelling of the European witch-hunts, it's really really cool. It completely flipped my view of the birth of capitalism... She posits that capitalism is a reaction to a potential peasant revolution in Europe that never succeeded, and situates the witch-hunt as a tool of the capitalist class to break peasant social-ties and discipline women into their new role as reproducers of workers.] || Is a history of the body in the transition to capitalism. Moving from the peasant revolts of the late Middle Ages to the witch-hunts and the rise of mechanical philosophy, Federici investigates the capitalist rationalization of social reproduction. She shows how the battle against the rebel body and the conflict between body and mind are essential conditions for the development of labor power and self-ownership, two central principles of modern social organization.
⊹ The Age of Surveillance Capitalism - Shoshana Zuboff (A.) || This book looks at the development of digital companies like Google and Amazon, and suggests that their business models represent a new form of capitalist accumulation that she calls "surveillance capitalism". While industrial capitalism exploited and controlled nature with devastating consequences, surveillance capitalism exploits and controls human nature with a totalitarian order as the endpoint of the development.
⊹ Anti-Oedipus: Capitalism and Schizophrenia - Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari (L.) || In this book , Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari set forth the following theory: Western society's innate herd instinct has allowed the government, the media, and even the principles of economics to take advantage of each person's unwillingness to be cut off from the group. What's more, those who suffer from mental disorders may not be insane, but could be individuals in the purest sense, because they are by nature isolated from society.
⊹ Open Veins of Latin America - Eduardo Galeano (A.) (Intro to LATAM history, infuriating but good.) (Personal recommendation if you know nothing about LATAM.) || An analysis of the impact that European settlement, imperialism, and slavery have had in Latin America. In the book, Galeano analyzes the history of the Americas as a whole, from the time period of the European settlement of the New World to contemporary Latin America, describing the effects of European and later United States economic exploitation and political dominance over the region. Throughout the book, Galeano analyses notions of colonialism, imperialism, and the dependency theory.
⊹ The Origin of Capitalism - Ellen Wood (A.) || Book on history and political economy, specifically the history of capitalism, written from the perspective of political Marxism.
⊹ If We Burn - Vincent Bevins (L.) || The book concerns the wave of mass protests during the 2010s and examines the question of how the organization and tactics of such protests resulted in a "missing revolution," given that most of these movements appear to have failed in their goals, and even led to a "record of failures, setbacks, and cataclysms".
⊹ The Jakarta Method - Vincent Bevins (A.) [Aleksa’s recommendation for leftists friends] || It concerns U.S. government support for and complicity in anti-communist mass killings around the world and their aggregate consequences from the Cold War until the present era. The title is a reference to Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66, during which an estimated one million people were killed in an effort to destroy the political left and movements for government reform in the country.
⊹ The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company - William Dalrymple (L.) [Not read by the boys yet, but wanted to read.] || History book that recounts the rise of the East India Company in the second half of the 18th century, against the backdrop of a crumbling Mughal Empire and the rise of regional powers.
⊹ The Triumph of Evil: The Reality of the USA's Cold War Victory - Austin Murphy (A.) || Contrary to the USA false propaganda, this book documents the fact that the USA triumph in the Cold War has increased economic suffering and wars, which are shown to be endemic to the New World Order under USA capitalist domination.
⊹ Technofeudalism: What Killed Capitalism - Yanis Varoufakis (L.) || Big tech has replaced capitalism’s twin pillars—markets and profit—with its platforms and rents. With every click and scroll, we labor like serfs to increase its power. Welcome to technofeudalism . . .
⊹ The History of the Russian Revolution - Leon Trotsky (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: This might be misconstrued since I'm not a massive fan of Trotsky... but... his book "History of the russian revolution" is amazing. It's so unique to have such a detailed history book compiled by someone who was an active participant in the events, and he's surprisingly hilarious. Makes some great jokes in there and really captures the revolutionary spirit of the time.] || The History of the Russian Revolution offers an unparalleled account of one of the most pivotal and hotly debated events in world history. This book presents, from the perspective of one of its central actors, the profound liberating character of the early Russian Revolution.
⊹ Rise of The Red Engineers - Joel Andreas (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: It's a sick history book, focusing on a single university in China following it's history from imperial china, through the revolution and to the modern day. It documents sincere efforts to revolutionize the education system, but does it from a very detailed, on-the-ground view of how these cataclysmic changes effect individual students and teachers at this institution.] || In a fascinating account, author Joel Andreas chronicles how two mutually hostile groups—the poorly educated peasant revolutionaries who seized power in 1949 and China's old educated elite—coalesced to form a new dominant class.
⊹ Adults in the Room: My Battle with the European and American Deep Establishment - Yanis Varoufakis (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: The book I mentioned earlier - "adults in the room" - is amazing. There's a great description of Greece's role in the European economy [as an archetype for other, small European countries] and the Union's successful attempts to discipline smaller countries to keep their monetary policy in line with the interest of central European bankers. I'd definitely reccommend it!] || What happens when you take on the establishment? In Adults in the Room, the renowned economist and former finance minister of Greece Yanis Varoufakis gives the full, blistering account of his momentous clash with the mightiest economic and political forces on earth.
Edit: Links added when possible! If they stop working let me know or if you have a link for the ones missing.
#IDK if anyone else is interested in this but in case anyone finds it useful <3#boy boy#aleksa vulović#alex apollonov#ididathing#ngl most of this r aleksa/lucas recs.... idk if any of them are alex sorry i forgot?#bb book club
168 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! I just read your post about your opinion on "AI" and I really liked it. If it's no bother, what's your opinion on people who use it for studying? Like writing essays, solving problems and stuff like that?
I haven't been a fan of AI from the beginning and I've heard that you shouldn't ask it for anything because then you help it develop. But I don't know how to explain that to friends and classmates or even if it's true anymore. Because I've seen some of the prompts it can come up with and they're not bad and I've heard people say that the summaries AI makes are really good and I just... I dunno. I'm at a loss
Sorry if this is a lot or something you simply don't want to reply to. You made really good points when talking about AI and I really liked it and this has been weighing on me for a while :)
on a base level, i don't really have a strongly articulated opinion on the subject because i don't use AI, and i'm 35 so i'm not in school anymore and i don't have a ton of college-aged friends either. i have little exposure to the people who use AI in this way nor to the people who have to deal with AI being used in this way, so my perspective here is totally hypothetical and unscientific.
what i was getting at in my original AI post was a general macroeconomic point about how all of the supposed efficiency gains of AI are an extension of the tech CEO's dislike of paying and/or giving credit to anyone they deem less skilled or intelligent than them. that it's conspicuous how AI conveniently falls into place after many decades of devaluing and deskilling creative/artistic labor industries. historically, for a lot of artists the most frequently available & highest paying gigs were in advertising. i can't speak to the specifics when it comes to visual art or written copy, but i *can* say that when i worked in the oklahoma film industry, the most coveted jobs were always the commercials. great pay for relatively less work, with none of the complications that often arise working on amateur productions. not to mention they were union gigs, a rare enough thing in a right to work state, so anyone trying to make a career out of film work wanting to bank their union hours to qualify for IATSE membership always had their ears to the ground for an opening. which didn't come often because, as you might expect, anyone who *got* one of those jobs aimed to keep it as long as possible. who could blame em, either? one person i met who managed to get consistent ad work said they could afford to work all of two or three months a year, so they could spend the rest of their time doing low-budget productions and (occasionally) student films.
there was a time when this was the standard for the film industry, even in LA; you expected to work 3 to 5 shows a year (exact number's hard to estimate because production schedules vary wildly between ads, films, and tv shows) for six to eight months if not less, so you'd have your bills well covered through the lean periods and be able to recover from what is an enormously taxing job both physically and emotionally. this was never true for EVERYONE, film work's always been a hustle and making a career of it is often a luck-based crapshoot, but generally that was the model and for a lot of folks it worked. it meant more time to practice their skills on the job, sustainably building expertise and domain knowledge that they could then pass down to future newcomers. anything that removes such opportunities decreases the amount of practice workers get, and any increased demand on their time makes them significantly more likely to burn out of the industry early. lower pay, shorter shoots, busier schedules, these aren't just bad for individual workers but for the entire industry, and that includes the robust and well-funded advertising industry.
well, anyway, this year's coca-cola christmas ad was made with AI. they had maybe one person on quality control using an adobe aftereffects mask to add in the coke branding. this is the ultimate intended use-case for AI. it required the expertise of zero unionized labor, and worst of all the end result is largely indistinguishable from the alternative. you'll often see folks despair at this verisimilitude, particularly when a study comes out that shows (for instance) people can't tell the difference between real poetry and chat gpt generated poetry. i despair as well, but for different reasons. i despair that production of ads is a better source of income and experience for film workers than traditional movies or television. i despair that this technology is fulfilling an age-old promise about the disposability of artistic labor. poetry is not particularly valued by our society, is rarely taught to people beyond a beginner's gloss on meter and rhyme. "my name is sarah zedig and i'm here to say, i'm sick of this AI in a major way" type shit. end a post with the line "i so just wish that it would go away and never come back again!" and then the haiku bot swoops in and says, oh, 5/7/5 you say? that is technically a haiku! and then you put a haiku-making minigame in your crowd-pleasing japanese nationalist open world chanbara simulator, because making a haiku is basically a matter of selecting one from 27 possible phrase combinations. wait, what do you mean the actual rules of haiku are more elastic and subjective than that? that's not what my english teacher said in sixth grade!
AI is able to slip in and surprise us with its ability to mimic human-produced art because we already treat most human-produced art like mechanical surplus of little to no value. ours is a culture of wikipedia-level knowledge, where you have every incentive to learn a lot of facts about something so that you can sufficiently pretend to have actually experienced it. but this is not to say that humans would be better able to tell the difference between human produced and AI produced poetry if they were more educated about poetry! the primary disconnect here is economic. Poets already couldn't make a fucking living making poetry, and now any old schmuck can plug a prompt into chatgpt and say they wrote a sonnet. even though they always had the ability to sit down and write a sonnet!
boosters love to make hay about "deskilling" and "democratizing" and "making accessible" these supposedly gatekept realms of supposedly bourgeois expression, but what they're really saying (whether they know it or not) is that skill and training have no value anymore. and they have been saying this since long before AI as we know it now existed! creative labor is the backbone of so much of our world, and yet it is commonly accepted as a poverty profession. i grew up reading books and watching movies based on books and hearing endless conversation about books and yet when i told my family "i want to be a writer" they said "that's a great way to die homeless." like, this is where the conversation about AI's impact starts. we already have a culture that simultaneously NEEDS the products of artistic labor, yet vilifies and denigrates the workers who perform that labor. folks see a comic panel or a corporate logo or a modern art piece and say "my kid could do that," because they don't perceive the decades of training, practice, networking, and experimentation that resulted in the finished product. these folks do not understand that just because the labor of art is often invisible doesn't mean it isn't work.
i think this entire conversation is backwards. in an ideal world, none of this matters. human labor should not be valued over machine labor because it inherently possesses an aura of human-ness. art made by humans isn't better than AI generated art on qualitative grounds. art is subjective. you're not wrong to find beauty in an AI image if the image is beautiful. to my mind, the value of human artistic labor comes down to the simple fact that the world is better when human beings make art. the world is better when we have the time and freedom to experiment, to play, to practice, to develop and refine our skills to no particular end except whatever arbitrary goal we set for ourselves. the world is better when people collaborate on a film set to solve problems that arise organically out of the conditions of shooting on a live location. what i see AI being used for is removing as many opportunities for human creativity as possible and replacing them with statistical averages of prior human creativity. this passes muster because art is a product that exists to turn a profit. because publicly traded companies have a legal responsibility to their shareholders to take every opportunity to turn a profit regardless of how obviously bad for people those opportunities might be.
that common sense says writing poetry, writing prose, writing anything is primarily about reaching the end of the line, about having written something, IS the problem. i've been going through the many unfinished novels i wrote in high school lately, literally hundreds of thousands of words that i shared with maybe a dozen people and probably never will again. what value do those words have? was writing them a waste of time since i never posted them, never finished them, never turned a profit off them? no! what i've learned going back through those old drafts is that i'm only the writer i am today BECAUSE i put so many hours into writing generic grimdark fantasy stories and bizarrely complicated werewolf mythologies.
you know i used to do open mics? we had a poetry group that met once a month at a local cafe in college. each night we'd start by asking five words from the audience, then inviting everyone to compose a poem using those words in 10 to 15 minutes. whoever wanted to could read their poem, and whoever got the most applause won a free drink from the cafe. then we'd spend the rest of the night having folks sign up to come and read whatever. sometimes you'd get heartfelt poems about personal experiences, sometimes you'd get ambitious soundcloud rappers, sometimes you'd get a frat guy taking the piss, sometimes you'd get a mousy autist just doing their best. i don't know that any of the poetry i wrote back then has particular value today, but i don't really care. the point of it was the experience in that moment. the experience of composing something on the fly, or having something you wrote a couple days ago, then standing up and reading it. the value was in the performance itself, in the momentary synthesis between me and the audience. i found out then that i was pretty good at making people cry, and i could not have had that experience in any other venue. i could not have felt it so viscerally had i just posted it online. and i cannot wrap up that experience and give it to you, because it only existed then.
i think more people would write poetry if they had more hours in a day to spare for frivolities, if there existed more spaces where small groups could organize open mics, if transit made those spaces more widely accessible, if everyone made enough money that they weren't burned the fuck out and not in the mood to go to an open mic tonight, if we saw poetry as a mode of personal reflection which was as much about the experience of having written it as anything else. this is the case for all the arts. right now, the only people who can afford to make a living doing art are already wealthy, because art doesn't pay well. this leads to brain drain and overall lowering quality standards, because the suburban petty bouge middle class largely do not experience the world as it materially exists for the rest of us. i often feel that many tech CEOs want to be remembered the way andy warhol is remembered. they want to be loved and worshipped not just for business acumen but for aesthetic value, they want to get the kind of credit that artists get-- because despite the fact that artists don't get paid shit, they also frequently get told by people "your work changed my life." how is it that a working class person with little to no education can write a story that isn't just liked but celebrated, that hundreds or thousands of people imprint on, that leaves a mark on culture you can't quantify or predict or recreate? this is AI's primary use-case, to "democratize" art in such a way that hacks no longer have to work as hard to pretend to be good at what they do. i mean, hell, i have to imagine every rich person with an autobiography in the works is absolutely THRILLED that they no longer have to pay a ghost writer!
so, circling back around to the meat of your question. as far as telling people not to use AI because "you're just helping to train it," that ship has long since sailed. getting mad at individuals for using AI right now is about as futile as getting mad at individuals for not masking-- yes, obviously they should wear a mask and write their own essays, but to say this is simply a matter of millions of individuals making the same bad but unrelated choice over and over is neoliberal hogwash. people stopped masking because they were told to stop masking by a government in league with corporate interests which had every incentive to break every avenue of solidarity that emerged in 2020. they politicized masks, calling them "the scarlet letter of [the] pandemic". biden himself insisted this was "a pandemic of the unvaccinated", helpfully communicating to the public that if you're vaccinated, you don't need to mask. all those high case numbers and death counts? those only happen to the bad people.
now you have CEOs and politicians and credulous media outlets and droves of grift-hungry influencers hard selling the benefits of AI in everything everywhere all the time. companies have bent over backwards to incorporate AI despite ethics and security worries because they have a fiduciary responsibility to their shareholders, and everyone with money is calling this the next big thing. in short, companies are following the money, because that's what companies do. they, in turn, are telling their customers what tools to use and how. so of course lots of people are using AI for things they probably shouldn't. why wouldn't they? "the high school/college essay" as such has been quantized and stripmined by an education system dominated by test scores over comprehension. it is SUPPOSED to be an exercise in articulating ideas, to teach the student how to argue persuasively. the final work has little to no value, because the point is the process. but when you've got a system that lives and dies by its grades, within which teachers are given increasingly more work to do, less time to do it in, and a much worse paycheck for their trouble, the essay increasingly becomes a simple pass/fail gauntlet to match the expected pace set by the simple, clean, readily gradable multiple choice quiz. in an education system where the stakes for students are higher than they've ever been, within which you are increasingly expected to do more work in less time with lower-quality guidance from your overworked teachers, there is every incentive to get chatgpt to write your essay for you.
do you see what i'm saying? we can argue all day about the shoulds here. of course i think it's better when people write their own essays, do their own research, personally read the assigned readings. but cheating has always been a problem. a lot of these same fears were aired over the rising popularity of cliffs notes in the 90s and 2000s! the real problem here is systemic. it's economic. i would have very little issue with the output of AI if existing conditions were not already so precarious. but then, if the conditions were different, AI as we know it likely would not exist. it emerges today as the last gasp of a tech industry that has been floundering for a reason to exist ever since the smart phone dominated the market. they tried crypto. they tried the metaverse. now they're going all-in on AI because it's a perfect storm of shareholder-friendly buzzwords and the unscientific technomythology that's been sold to laymen by credulous press sycophants for decades. It slots right into this niche where the last of our vestigial respect for "the artist" once existed. it is the ultimate expression of capitalist realism, finally at long last doing away with the notion that the suits at disney could never in their wildest dreams come up with something half as cool as the average queer fanfic writer. now they've got a program that can plagiarize that fanfic (along with a dozen others) for them, laundering the theft through a layer of transformation which perhaps mirrors how the tech industry often exploits open source software to the detriment of the open source community. the catastrophe of AI is that it's the fulfillment of a promise that certainly predates computers at the very least.
so, i don't really know what to tell someone who uses AI for their work. if i was talking to a student, i'd say that relying chatgpt is really gonna screw you over when it comes time take the SAT or ACT, and you have to write an essay from scratch by hand in a monitored environment-- but like, i also think the ACT and SAT and probably all the other standardized tests shouldn't exist? or at the very least ought to be severely devalued, since prep for those tests often sabotages the integrity of actual classroom education. although, i guess at this point the only way forward for education (that isn't getting on both knees and deep-throating big tech) is more real-time in-class monitored essay writing, which honestly might be better for all parties anyway. of course that does nothing to address research essays you can't write in a single class session. to someone who uses AI for research, i'd probably say the same thing as i would to someone who uses wikipedia: it's a fine enough place to start, but don't cite it. click through links, find sources, make sure what you're reading is real, don't rely on someone else's generalization. know that chatgpt is likely not pulling information from a discrete database of individual files that it compartmentalizes the way you might expect, but rather is a statistical average of a broad dataset about which it cannot have an opinion or interpretation. sometimes it will link you to real information, but just as often it will invent information from whole cloth. honestly, the more i talk it out, the more i realize all this advice is basically identical to the advice adults were giving me in the early 2000s.
which really does cement for me that the crisis AI is causing in education isn't new and did not come from nowhere. before chatgpt, students were hiring freelancers on fiverr. i already mentioned cliffs notes. i never used any of these in college, but i'll also freely admit that i rarely did all my assigned reading. i was the "always raises her hand" bitch, and every once in a while i'd get other students who were always dead silent in class asking me how i found the time to get the reading done. i'd tell them, i don't. i read the beginning, i read the ending, and then i skim the middle. whenever a word or phrase jumps out at me, i make a note of it. that way, when the professor asks a question in class, i have exactly enough specific pieces of information at hand to give the impression of having done the reading. and then i told them that i learned how to do this from the very same professor that was teaching that class. the thing is, it's not like i learned nothing from this process. i retained quite a lot of information from those readings! this is, broadly, a skill that emerges from years of writing and reading essays. but then you take a step back and remember that for most college students (who are not pursuing any kind of arts degree), this skillset is relevant to an astonishingly minimal proportion of their overall course load. college as it exists right now is treated as a jobs training program, within which "the essay" is a relic of an outdated institution that highly valued a generalist liberal education where today absolute specialization seems more the norm. so AI comes in as the coup de gras to that old institution. artists like myself may not have the constitution for the kind of work that colleges now exist to funnel you into, but those folks who've never put a day's thought into the work of making art can now have a computer generate something at least as good at a glance as basically anything i could make. as far as the market is concerned, that's all that matters. the contents of an artwork, what it means to its creator, the historic currents it emerges out of, these are all technicalities that the broad public has been well trained not to give a shit about most of the time. what matters is the commodity and the economic activity it exists to generate.
but i think at the end of the day, folks largely want to pay for art made by human beings. that it's so hard for a human being to make a living creating and selling art is a question far older than AI, and whose answer hasn't changed. pay workers more. drastically lower rents. build more affordable housing. make healthcare free. make education free. massively expand public transit. it is simply impossible to overstate how much these things alone would change the conversation about AI, because it would change the conversation about everything. SO MUCH of the dominance of capital in our lives comes down to our reliance on cars for transit (time to get a loan and pay for insurance), our reliance on jobs for health insurance (can't quit for moral reasons if it's paying for your insulin), etc etc etc. many of AI's uses are borne out of economic precarity and a ruling class desperate to vacuum up every loose penny they can find. all those billionaires running around making awful choices for the rest of us? they stole those billions. that is where our security went. that is why everything is falling apart, because the only option remaining to *every* institutional element of society is to go all-in on the profit motive. tax these motherfuckers and re-institute public arts funding. hey, did you know the us government used to give out grants to artists? did you know we used to have public broadcast networks where you could make programs that were shown to your local community? why the hell aren't there public youtube clones? why aren't there public transit apps? why aren't we CONSTANTLY talking about nationalizing these abusive fucking industries that are falling over themselves to integrate AI because their entire modus operandi is increasing profits regardless of product quality?
these are the questions i ask myself when i think about solutions to the AI problem. tech needs to be regulated, the monopolies need breaking up, but that's not enough. AI is a symptom of a much deeper illness whose treatment requires systemic solutions. and while i'm frustrated when i see people rely on AI for their work, or otherwise denigrate artists who feel AI has devalued their field, on some level i can't blame them. they are only doing what they've been told to do. all of which merely strengthens my belief in the necessity of an equitable socialist future (itself barely step zero in the long path towards a communist future, and even that would only be a few steps on the even longer path to a properly anarchist future). improve the material conditions and you weaken the dominance of capitalist realism, however minutely. and while there are plenty of reasons to despair at the likelihood of such a future given a second trump presidency, i always try to remember that socialist policies are very popular and a *lot* of that popularity emerged during the first trump administration. the only wrong answer here is to assume that losing an election is the same thing as losing a war, that our inability to put the genie back in its bottle means we can't see our own wishes granted.
i dunno if i answered your question but i sure did say a lot of stuff, didn't i?
#sarahposts#ai#ai art#chatgpt#llm#genai#capitalism#unions#labor#workers rights#capitalist realism#longpost#sarahAIposts
112 notes
·
View notes
Note
⭕️👋Hi I’m new, I really like your character analysis, world lore analysis etc,…I think they’re very accurate and provide more insight into the twisted wonderland world,
do you think NRC gets enough funding cause they’ve been losing to RSA for like almost 100 years now and the Magift incident where the recruiter’s and scouts probably didn’t really pay attention to most of the players cause of Malleus .I know they probably get funding and tuition and stuff from affluent parents who care about the quality of education & environment of their children but is that really enough? Is Crowley secret Stressed about funding cause of their losing streak to RSA???
I just wondered what your thoughts were on the matter

Hello and thank you very much ^^ It always warms my heart to hear that people enjoy my more analytical writings!
Now to answer your question, I don’t think NRC is hurting for money. Like, at all.
You did bring up a fair point about NRC’s almost a 100 year loss streak to RSA + the lack of interested Spelldrive/Magical Shift scouts in book 2, but that’s not enough of the big picture. RSA is only one rival magic school out of several. Just because NRC is not doing well against one other school doesn’t mean that NRC is suddenly deemed “lesser”—NRC is still considered a top arcane academy and eclipses other magical institutions like Noble Bell College.
In regards to the pro recruiters, I don’t think it has a huge impact?? Sports is only one sector at NRC; they’re still doing relatively well outside of it, such as in academics, extracurriculars, and connections for internships in the grand scheme of things. (Vargas actually does state in Vargas Camp that NRC is still an "athletic powerhouse" and has been "rocketing up the ranks in our division". This indicates to me that NRC is dominating against other arcane academies, but just falters with RSA specifically.)

Update: Trein states in his vignettes that NRC is falling behind RSA in academics, which isn’t great news—but again, RSA is but one school for comparison. NRC still ranks above several other magic schools. Things like not winning VDC and not being noticed by scouts seems to only really impact the career prospects of students who were interested in the entertainment/sports industries (and even then, I still think there would be recruiters interested since NRC is still a top performer, just perhaps not THE top performer); I doubt that this would seriously hurt whatever funding NRC is receiving.
Night Raven College is a private school, so they are most likely receiving money from tuition and not the government. Though tuition is not explicitly mentioned in TWST (at least not that I am aware of), if we assume the average cost for one student to attend a British boarding school—for which NRC is modeled after—that means 25,000 pounds per person, PER YEAR. Let us assume that NRC had only 800 students (this is the rough estimate TWST provides us). That means, from one year’s worth of tuition alone, the school is raking in 20,000,000 pounds or 4,058,310,000 madol. Note that this is just money in, not yet factoring for expenditures, taxes, etc.
The school also receives 10% of Mostro Lounge’s proceeds, and while we cannot put an exact number to that, we do know that most menu items range from 600 to 1500 madol. The lounge must also make significant enough money to pay for its ingredients, nice silverware (something which Azul stresses to give customers a high class experience), and even provide pay to workers (Ruggie would not be doing labor for free and refers to his time at Mostro Lounge as “a job”; see: his Ceremonial Robes vignettes). While this doesn’t make up a large part of NRC’s money, it’s still a nice little bonus to account for.



NRC also has many, MANY wealthy students, including literal celebrities and royalty. In fact, the upper middle class to flat-out rich make up the majority of the main cast (close to like 70-75%). If this is also the case for the regular mob students, then there are many other ways for the school to get huge donations. In the main story alone, two significant donations are mentioned: Kalim's dad gave enough money for NRC to completely renovate Scarabia and the Shroud parents paid for all the damages caused to the school's buildings. Additionally, Crowley says that the Shrouds made "substantial contributions toward expanding [NRC's] facilities."
Please note that this is just donations from current students’ families. Think about potential donations coming from NRC alumni too!!



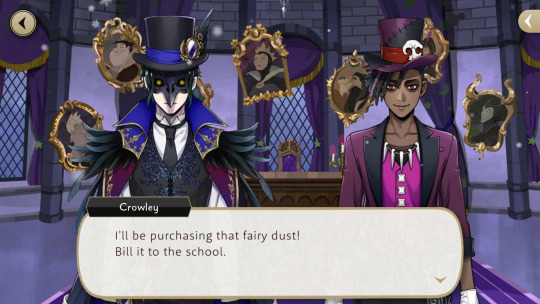
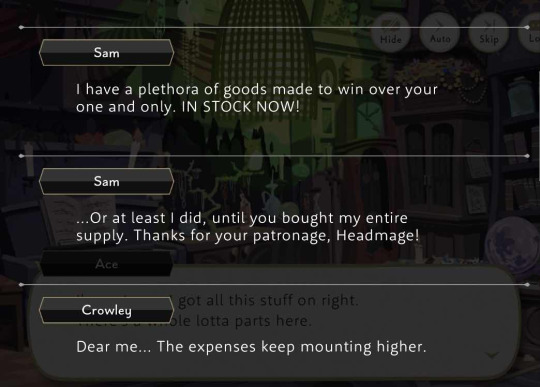
It should be noted that NRC has the financial power to spend liberally, and no one really says that this will put the school in a touch spot. For example, all students are provided free uniforms (school, dorm, PE, robes, labwear, etc.; even the birthday outfits are said to be provided by the school), but they have to pay for replacements if they fuck up their first one(s). Crowley literally buys up Sam's entire stock of goods during Ghost Marriage... and if you know anything about Sam, it's that he can magically keep things "IN STOCK NOW!!" Crowley even indicates in one of his voice lines that he is in constant competitions to buy out Sam's stock and has scarcely managed to one-up him--so the fact that Crowley does buy out Sam during an event is meaningful and speaks to how much of the school's money he is throwing to save it. He also tells Sam to bill the school for the cost of the fairy dust in Fairy Gala.

Both times, Crowley complains about how he would rather not spend money, but he does so anyway. This in of itself does NOT prove that NRC is in need of money, this is just proof of Crowley's cheapness. (We see many other examples of this greed and stinginess of his; he guilts Yuu for spending money on them, constantly tries to get free food and souvenirs from his students, and cuts costs for Halloween candy.) If NRC were truly hurting financially though, then they would not be able to throw lavish events or donate back to the community, both of which still happen multiple times. For example, NRC holds a huge Halloween event every year in which they open their campus to outsiders. This event is entirely free and involves a budget large enough for each dorm to create intricate decorations and costumes for 800ish students. There is also enough money to throw a celebration party for the students at the end of it—and let’s remember, NRC has the money to afford five star ghost chefs to regularly cater, serve in the cafeteria, AND teach their Culinary Crucibles/Master Chef courses.
While explaining the nature of the Halloween events, Crewel cites that NRC has survived this long in part due to the "While explaining the nature of the Halloween events, Crewel cites that NRC has survived this long in part due to the "understanding, cooperation, and subsistence of Sage's Island locals." This implies that the immediate community on the island also supports NRC in some ways. Perhaps it isn't financially, but it's clear that NRC still has social capital and a good reputation in spite of its losses to RSA.



In Port Fest, Crowley states that setup, food supplies, and all other expenses will be covered by the school. Half of the proceeds will then be donated to charity and the other half will be granted to the students to celebrate their hard work. Again, would NRC be giving away this money if they really needed it for the institution itself? They're not obligated to give money to the students, yet Crowley easily agreed when Azul asked for an incentive.



And let's not forget the school cultural festival, which was largely open for the public to attend. If they choose to spend on additional things (such as food and drink or VDC tickets, which are a "hot commodity"), that's on the individual. The school itself is hosting the event for free.
Yuu is offered a large sum of money (if the NRC tribe wins VDC)... and Ramshackle renovations (from Crowley) in book 5 in exchange for letting the boys host their training camp in their dorm. Look at how old and run-down Ramshackle is; there is no doubt that such repairs would be pretty expensive—but Crowley doesn't complain about the cost, he's not above bribing someone to make himself and his school look good.
Crowley caring about his reputation isn't new either, it's a pattern. We see him getting upset at NRC's loss in book 5 and lamenting bad publicity/being excited about good publicity in numerous events (Ghost Marriage, Wish Upon a Star, etc.) The school has been under his care for a long time, so naturally he will feel proud and/or slighted whenever NRC is involved.
This leads me to the conclusion that Crowley, the figurehead and headmaster of NRC, and his own personality quirks are being misconstrued as an indication that NRC is in a bad financial spot. His own fixation on triumphing over their rival school, acquiring and maintaining material goods for himself, and wanting positive attention do not reflect the state of the school. Notice how no one but Crowley whines about the financials and how while Crowley still complains about spending money, he has no qualms with spending lavishly himself on school events and holidays. This means NRC has money to spare, but Crowley is just stingy about how those funds are allocated.
#twisted wonderland#twst#Dire Crowley#disney twisted wonderland#disney twst#book 5 spoilers#Yuu#notes from the writing raven#question#fairy gala spoilers#ghost marriage spoilers#port fest spoilers#wish upon a star spoilers#Divus Crewel#terror is trending spoilers#ruggie ceremonial robes vignette spoilers#Ruggie Bucchi#book 2 spoilers#twst analysis#twisted wonderland analysis#Ashton Vargas#vargas camp spoilers
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
Official Commission Info Post
(Updated July 8, 2024. Copied over from my main website.)
Pay me to write about a topic of your choice!
Provide me with a topic related to my areas of interest, and I’ll share my expertise, opinions, and insights. My areas of interest/expertise include speculative fiction (sci-fi/fantasy), fiction writing, literature studies, television & film studies, media censorship, animation, and pop/fandom culture.
Note: You choose the topic, not the angle. You can’t pay me to write any amount on the topic, “why Ren’s favorite thing is actually bad,” or, “why Ren’s least-favorite politician is actually a superhero.” I reserve the right to refuse any commission for any reason, with money refunded where necessary. I retain full credit and ownership of my writing—meaning I don’t do homework and I don’t do ghostwriting.
Examples of my work can be found at this link. Further info below the cut.
Rates
$25 USD for 500 words.
Up to 3k words @ $0.05 USD per word.
Over 3k words @ $0.15 per word.
Over 5k words @ $0.20 per word.
Rates calculated using the IWW Freelance Journalists Union rate sheet. Writers of the world unite!
Payment processed via PayPal or Venmo. Final product will be emailed to you as a PDF, and cross-posted to my tumblr and Patreon page along with other platforms as I see fit.
Email me at [email protected] to commission today!
Turnaround Times
I’m disabled and have inconsistent energy levels, so turnaround times may vary depending on my health. At minimum, 500 word essays typically take me about a week, 3k takes about two weeks, and 5k papers take about a month. If there are any unexpected delays to my work, health-related or otherwise, I will email you with an updated turnaround estimate as needed.
À La Carte
Can’t think of a topic but still want to hire me? Here’s a list you can choose from!
General 500 Word Topics
500 words doesn’t give me much space, so these commissions are great for getting my basic thoughts and opinions on a topic. You can use the following list as simple prompts on their own, or as a springboard to come up with your own, more specific prompt.
Science Fiction
Fantasy
Worldbuilding
Self-Publishing
Animation
Tabletop Gaming
Cosplay and Costuming
Media Representation
Media Preservation
Media Piracy
Censorship
Purity Culture
Labor Rights in the Entertainment Industry
Queer Media History
Fandom
3k Essay Prompts:
These topics require a little more space to dig into, so I need at least 3,000 words to do them justice. You can also request any of the prompts from the 500 word prompt list for a more robust essay on the topic.
Always Watch the Background Actors: How Learning Stage Combat Improved My Moviegoing Experience
Animation and Musicals: Misunderstood Non-Genres
Draw from the Heart: Using Familiar Settings to Craft New Worlds
Worldbuilding: Avoiding the Planet of Hats Trope
Worldbuilding: Utilizing Elements of Culture
5k Research Paper Topics:
These are the big topics that will require research, citations, and several long weeks of work. I can write as much on the topic as you want, but it must be at least 5,000 words. You can also request any of the prompts from the 500 word or 3k word prompt lists for more robust essays on the topic.
Killing the Cat: Violence Against the Vulnerable as Sloppy Narrative Shorthand
It Wasn't a Damn Door: Why Jack Dawson Had to Die
Bury Your Gays on Solstheim: Queer Representation in the Elder Scrolls
Invisibility or the Freakshow: Intersex Representation on American Television
The Nuke in the Room: Political Allegory in Samurai Jack
Payment Installments & Discount Options
Times are rough for everyone. If you would like to hire me but can’t afford to pay all at once, please don’t hesitate to reach out to me about paying in installments! Details can be discussed on an individual basis.
For a 15% discount, you may also email me with proof that you have requested my short story, The Queen of Cups, at your local library! For a 25% discount, submit proof that you have requested both my short story, The Queen of Cups, and my wife’s novel, The Last Girl Scout.
329 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sorry if this is not the kind of ask you want to get but several people in this post argued about the benefit of legalizing prostitution and it sounds very convincing? What do you think? https://www.tumblr.com/prismatic-bell/757101438415601664/i-still-remember-learning-the-following-factoid?source=share
Hi! This is exactly the sort of ask I like to get!
So, I think the reason why this sounds convincing is because they are partially correct. However, the third individual is wrong on a very crucial part, which I will explain.
---
Policies regarding prostitution range from full legalization (all related activities are legal and incorporated into the legitimate economy) to full criminalization (all related activities are illegal and exist only in an underground economy).
The first thing to understand – and what the individuals in that post got right – is that full criminalization does not help the people trapped in either "voluntary" prostitution or sex trafficking victims. This stakeholder report [1] discusses various issues that result for human trafficking victims (including children) as a result of full criminalization. This is focused on trafficking victims, rather than all prostitutes, but in truth, the line between these categories is blurry at best. (There certainly isn't a reliable way for the legal system to differentiate between them.)
So, in this way, the first two individuals are correct. Arresting women and children for "selling sex" does significant harm. It also doesn't appear to be effective at reducing trafficking, child sexual exploitation, or exploitation by pimps.
---
However, each poster appears to be making the leap that because full criminalization is harmful to the vulnerable women and children in prostitution, the best alternative is full legalization or decriminalization. (To clarify between these two, consider the case of marijuana: legalized marijuana often entails taxation and other governmental involvement in the industry whereas decriminalization means it is still illegal remains but the government doesn't actively pursue people involved with marijuana.)
This assumption is erroneous.
There is well documented evidence that full legalization/decriminalization does not significantly reduce (and may increase) harm to prostituted women and children.
The alternative option, is a partial decriminalization. Specifically, decriminalizing the "supply" ("selling sex"), while maintaining criminalization of the demand ("buying sex") and third-party organization (pimps, traffickers, etc.). This option results in the most harm reduction (as endorsed by those posters!). This option is often referred to as the "Nordic Model" (as it originated in a Nordic country).
I'll expand on these points below.
---
Innumerable studies have shown that full legalization results in an increase in sex trafficking. Here is a selection:
These comparisons on several European countries find that full legalization leads to an increase in trafficking, in comparison to both full criminalization and the Nordic model. [2, 3]
This review discusses how "evidence supports the theory that legal prostitution is associated with increased trafficking." When the article was written (2009) an estimated "80% of all women in German and Dutch prostitution are trafficked". In New Zealand's largest city, "A 200-400% increase in street prostitution has been reported since prostitution was decriminalized in 2003." and "25% of those interviewed said that they entered the sex industry because it had been decriminalized". [4]
This paper highlights how "fighting sex trafficking using the criminal justice system may even be harder in the legalized prostitution sector". [5]
This EU commissioned study found that both full legalization and full decriminalization was associated with twice the number of trafficking victims as full criminalization or the Nordic model. [6]
This article discusses how legalization promotes trafficking, expands demand, increases the illegal market, increases child prostitution/trafficking, and doesn't protect the women/children in prostitution [7].
In addition:
This paper provides a thorough debunking of Amnesty International's support for decriminalization. They discuss how "the best available evidence indicates that decriminalization of prostitution would: increase sex trafficking, leave prostituted women or 'sex workers' more vulnerable to violence, and reduce access to healthcare, protection, and services." [8]
This paper's title is particularly apt: "Prostitution, Trafficking, and Cultural Amnesia: What We Must Not Know in Order To Keep the Business of Sexual Exploitation Running Smoothly". In particular, it discusses how prostitution is extremely violent, linked to prejudice, linked to trafficking, and harmful to women and society at large. [9]
This study of 150 countries finds legalization "does not help liberate victims of human trafficking" and doesn't protect victims. [10]
I have searched for any evidence that (as claimed by the third poster) that the "growth rate of trafficking in [Germany, following legalization] went down" and found ... nothing. I can't actually find any sources about the "growth rate" of trafficking in either direction. That being said, the above sources all clearly indicate that traffickers find Germany (and other countries with legalized prostitution) to be profitable (i.e., people are still being trafficked through and into Germany).
Further, while it is likely that victims find it easier to escape under a fully legalized than a fully criminalized model (as discussed above), that doesn't change the fact that more women are being trafficked in the first place. It also doesn't change the fact that there is a better alternative (i.e, the Nordic model, which retains the ability for women to escape trafficking while also reducing trafficking and the overall demand for prostitution).
To expand, many papers have provided empirical support for the Nordic model. These papers [11-15] all discuss the various advantages and disadvantageous of the different systems. Papers [13-15] all explicitly recommend the Nordic model as the best (if still flawed) option.
And here [16] is an additional discussion of both the benefits and issues (primarily implementation problems) with the Nordic model. They describe the reduction in prostitution and trafficking and positive change sin public opinion, but also discuss the additional services and protections needed to realize the full potential of this policy.
---
All in all, I actually agree that "harm reduction is always good". However, the greatest amount of harm reduction is afforded by the Nordic model. This model legalizes/decriminalizes "selling sex" while criminalizing "buying sex" and "organization" (e.g., pimps, brothels). It results in reduced demand, reduced trafficking, and reduced overall harm. Simply legalizing "sex work" is not harm reduction; on the contrary, it causes significant harm.
References under the cut:
International Women’s Human Rights Clinic, et al. Criminalization of Trafficking Victims. 2015, https://www.law.cuny.edu/wp-content/uploads/page-assets/academics/clinics/hrgj/publications/Criminalization-of-Trafficking-Victims.pdf.
Marinova, Nadejda K., and Patrick James. “The Tragedy of Human Trafficking: Competing Theories and European Evidence1: The Tragedy of Human Trafficking.” Foreign Policy Analysis, vol. 8, no. 3, July 2012, pp. 231–53. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-8594.2011.00162.x.
Osmanaj, Egzone. “The Impact of Legalized Prostitution on Human Trafficking.” Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, June 2014. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.5901/ajis.2014.v3n2p103.
Farley, Melissa. “Theory versus Reality: Commentary on Four Articles about Trafficking for Prostitution.” Women’s Studies International Forum, vol. 32, no. 4, July 2009, pp. 311–15. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsif.2009.07.001.
Huisman, Wim, and Edward R. Kleemans. “The Challenges of Fighting Sex Trafficking in the Legalized Prostitution Market of the Netherlands.” Crime, Law and Social Change, vol. 61, no. 2, Mar. 2014, pp. 215–28. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1007/s10611-013-9512-4.
Di Nicola, Andrea. The differing EU Member States’ regulations on prostitution and their cross-border implications on women’s rights. European Union, 2021.
Raymond, Janice G. "Ten reasons for not legalizing prostitution and a legal response to the demand for prostitution." Journal of Trauma Practice 2.3-4 (2004): 315-332.
Geist, Darren. (2016). Dignity: A Journal on Sexual Exploitation and Violence. Vol. 1, Issue 1, Article 6. DOI:10.23860/dignity.2016.01.01.06. Available at http://digitalcommons.uri.edu/dignity/Vol1/Iss1/6.
Farley, Melissa. "Prostitution, trafficking, and cultural amnesia: What we must not know in order to keep the business of sexual exploitation running smoothly." Yale JL & Feminism 18 (2006): 109.
Cho, Seo-young (2013) : Liberal coercion? Prostitution, human trafficking and policy, MAGKS Joint Discussion Paper Series in Economics, No. 44-2013, Philipps-University Marburg, Faculty of Business Administration and Economics, Marburg
Curiel, Angelica. Informing United States Sex Trafficking Policies: A Comparative Analysis of Sweden, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Chile, and South Korea. Diss. California State University San Marcos, 2016.
Tomlinson, Alexia, Mary Haggerty, and Caroline Rini. "A global study of prostitution policy." Wis. JL Gender, & Soc'y 37 (2022): 23.
Rowe, Kathryn, "Regulating Sex Work: United States' Policy and International Comparisons" (2018). Honors Theses. 522. https://egrove.olemiss.edu/hon_thesis/522
Tate Santana, Madison. "Trafficked in Texas: Combatting the sex-trafficking epidemic through prostitution law and sentencing reform in the lone star state." Vand. L. Rev. 71 (2018): 1739.
Joulaei, Hassan, et al. "Legalization, Decriminalization or Criminalization; Could We Introduce a Global Prescription for Prostitution (Sex Work)?." International Journal of High Risk Behaviors and Addiction 10.3 (2021).
Waltman, Max. "Sweden's prohibition of purchase of sex: The law's reasons, impact, and potential." Women's Studies International Forum. Vol. 34. No. 5. Pergamon, 2011.
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Daily updates!)
By Adam Piore
A new study from researchers at Mass General Brigham suggests racial disparities and the difficulty in diagnosing the condition may be leading to a massive undercount.
Almost one in four Americans may be suffering from long COVID, a rate more than three times higher than the most common number cited by federal officials, a team led by Boston area researchers suggests in a new scientific paper.
The peer-reviewed study, led by scientists and clinicians from Mass General Brigham, drew immediate skepticism from some long COVID researchers, who suggested their numbers were “unrealistically high.” But the study authors noted that the condition is notoriously difficult to diagnose and official counts also likely exclude populations who were hit hardest by the pandemic but face barriers in accessing healthcare.
“Long COVID is destined to be underrepresented, and patients are overlooked because it sits exactly under the health system’s blind spot,” said Hossein Estiri, head of AI Research at the Center for AI and Biomedical Informatics at Mass General Brigham and the paper’s senior author.
Though the pandemic hit hardest in communities of color where residents had high rates of preexisting conditions and many held service industry jobs that placed them at high risk of contracting the virus, the vast majority of those diagnosed with long COVID are white, non-Hispanic females who live in affluent communities and have greater access to healthcare, he said.
Moreover, many of the patients who receive a long COVID diagnosis concluded on their own that they have the condition and then persuaded their doctors to look into it, he said. As a result, the available statistics we have both underestimate the true number of patients suffering from the condition and skew it to a specific demographic.
“Not all people even know that their condition might be caused or exacerbated by COVID,” Estiri said. “So those who go and get a diagnosis represent a small proportion of the population.”
Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that long COVID can cause hundreds of different symptoms, many of which are difficult to describe or are easily dismissed, such as sleep problems, headaches or generalized pain, Estiri said. According to its formal definition, long COVID occurs after a COVID-19 infection, lasts for at least three months, affects one or more organ systems, and includes a broad range of symptoms such as crushing fatigue, pain, and a racing heart rate.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggested that in 2022 roughly 6.9 percent of Americans had long COVID. But the algorithm developed by Estiri’s team estimated that 22.8 percent of those who’d tested positive for COVID-19 met the diagnostic criteria for long COVID in the 12 months that followed, even though the vast majority had not received an official diagnosis.
To calculate their number, Estiri’s team built a custom artificial intelligence tool to analyze data from the electronic health records of more than 295,000 patients served at four hospitals and 20 community health centers in Massachusetts. The AI program pulled out 85,000 people who had been diagnosed with COVID through June 2022, and then applied a pattern recognition algorithm to identify those that matched the criteria for long COVID in the 12 months that followed.
Some researchers questioned the paper’s conclusions. Dr. Eric Topol, author of the 2019 book “Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again,” said the medical field is still divided over precisely what constitutes long COVID, and that complicates efforts to program an accurate AI algorithm.
“Since we have difficulties with defining long Covid, using AI on electronic health records may not be a way to make the diagnosis accurately,” said Topol, who is executive vice president of Scripps Research in San Diego. “I’m uncertain about this report.”
Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development at the VA St. Louis Health Care System, and an expert on long COVID, called the 22.8 percent figure unrealistically high and said the paper “grossly inflates” its prevalence.
“Their approach does not account for the fact that things happen without COVID (not everything that happens after COVID is attributable to COVID)— resulting in significant over-inflation of prevalence estimate,” he wrote via email.
Estiri said the research team took several measures to validate its AI algorithm, retroactively applying it to the charts of 800 people who had received a confirmed long COVID diagnosis from their doctor to see if it could predict the condition. The algorithm accurately diagnosed them more than three quarters of the time.
The algorithm scanned the records for patients who had a COVID diagnosis prior to July 2022, then looked for a constellation of symptoms that could not be explained by other conditions and lasted longer than two months. To refine the program, they conferred with clinicians and assigned different weights to different symptoms and conditions based on how often they are associated with long COVID, which made them more likely to be identified as potential sufferers.
Now that the initial paper has been published, the team is building a new algorithm that can be trained to detect the presence of long COVID in the medical records of patients without a confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis so the condition can be confirmed by clinicians and they can get the care they need, Estiri said.
But the most exciting part of the new research, Estiri said, is its potential to facilitate follow-up research and help refine and individualize treatment plans. In the months ahead, Estiri and his co-principal investigator Shawn Murphy, chief research information officer at Mass General Brigham, plan to ask a wide variety of questions by querying the medical records in their sample. Does vaccination make a patient more or less likely to develop the condition? How about treatment with Paxlovid? Do the symptoms patients develop differ based on those factors? What are the genomic characteristics of patients who are suffering from cardiovascular symptoms as opposed to those whose symptoms are associated with lung function or those who crash after exercising? Can they identify biomarkers in the bloodstream that could be used for diagnosis?
They have already prepared studies on vaccine efficacy, the effect of age as a risk factor, and whether the risk of long COVID increases with the fourth and fifth infection, Estiri said. “We were waiting for this paper to come out,” he said. “So now we can actually go ahead with the follow-up studies. With this cohort we can do things that no other study has been able to do, and I’m hoping it can really help people.”
Study link: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666634024004070
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#covid#wear a respirator#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
This story originally appeared on Vox and is part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
Odorless and colorless, methane is a gas that is easy to miss—but it’s one of the most important contributors to global warming. It can trap up to 84 times as much heat as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, though it breaks down much faster. Measured over 100 years, its warming effect is about 30 times that of an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide.
That means that over the course of decades, it takes smaller amounts of methane than carbon dioxide to heat up the planet to the same level. Nearly a third of the increase in global average temperatures since the Industrial Revolution is due to methane, and about two-thirds of those methane emissions comes from human activity like energy production and cattle farming. It’s one of the biggest and fastest ways that human beings are warming the Earth.
But the flip side of that math is that cutting methane emissions is one of the most effective ways to limit climate change.
In 2021, more than 100 countries including the United States committed to reducing their methane pollution by at least 30 percent below 2020 levels by 2030. But some of the largest methane emitters like Russia and China still haven’t signed on, and according to a new report from the International Energy Agency, global methane emissions from energy production are still rising.
Yet the tracking of exactly how much methane is reaching the atmosphere isn’t as precise as it is for carbon dioxide. “Little or no measurement-based data is used to report methane emissions in most parts of the world,” according to the IEA. “This is a major issue because measured emissions tend to be higher than reported emissions.” It’s also hard to trace methane to specific sources—whether from natural sources like swamps, or from human activities like fossil fuel extraction, farming, or deforestation.
Researchers are gaining a better understanding of where methane is coming from, surveilling potential sources from the ground, from the sky, and from space. It turns out a lot of methane is coming from underappreciated sources, including coal mines and small oil and gas production facilities.
The report also notes that while there are plenty of low-cost tools available to halt much of this methane from reaching the atmosphere, they’re largely going unused.
The United States, the world’s third largest methane-emitting country, has seen its methane emissions slowly decline over the past 30 years. However, the Trump administration is pushing for more fossil fuel development while rolling back some of the best bang-for-buck programs for mitigating climate change, which will likely lead to even more methane reaching the atmosphere if left unchecked.
Where Is All This Methane Coming From?
Methane is the dominant component of natural gas, which provides more than a third of US energy. It’s also found in oil formations. During the drilling process, it can escape wells and pipelines, but it can also leak as it’s transported and at the power plants and furnaces where it’s consumed.
The oil and gas industry says that methane is a salable product, so they have a built-in incentive to track it, capture it, and limit its leaks. But oil developers often flare methane, meaning burn it off, because it’s not cost-effective to contain it. That burned methane forms carbon dioxide, so the overall climate impact is lower than just letting the methane go free.
And because methane is invisible and odorless, it can be difficult and expensive to monitor it and prevent it from getting out. As a result, researchers and environmental activists say the industry is likely releasing far more than official government estimates show.
Methane also seeps out from coal mines—more methane, actually, than is released during the production of natural gas, which after all is mostly methane. Ember, a clean-energy think tank, put together this great visual interactive showing how this happens.
The short version is that methane is embedded in coal deposits, and as miners dig to expose coal seams, the gas escapes, and continues to do so long after a coal mine reaches the end of its operating life. Since coal miners are focused on extracting coal, they don’t often keep track of how much methane they’re letting out, nor do regulators pay much attention.
According to Ember, methane emissions from coal mines could be 60 percent higher than official tallies. Abandoned coal mines are especially noxious, emitting more than abandoned oil and gas wells. Added up, methane emitted from coal mines around the world each year has the same warming effect on the climate as the total annual carbon dioxide emissions of India.
Alarmed by the gaps in the data, some nonprofits have taken it upon themselves to try to get a better picture of methane emissions at a global scale using ground-based sensors, aerial monitors, and even satellites. In 2024, the Environmental Defense Fund launched MethaneSAT, which carries instruments that can measure methane output from small, discrete sources over a wide area.
Ritesh Gautam, the lead scientist for MethaneSAT, explained that the project revealed some major overlooked methane emitters. Since launching, MethaneSAT has found that in the US, the bulk of methane emissions doesn’t just come from a few big oil and gas drilling sites, but from many small wells that emit less than 100 kilograms per hour.
“Marginal wells only produce 6 to 7 percent of [oil and gas] in the US, but they disproportionately account for almost 50 percent of the US oil and gas production-related emissions,” Gautam said. “These facilities only produce less than 15 barrels of oil equivalent per day, but then there are more than half a million of these just scattered around the US.”
There Are Ways to Stop Methane Emissions, but We’re Not Using Them
The good news is that many of the tools for containing methane from the energy industry are already available. “Around 70 percent of methane emissions from the fossil fuel sector could be avoided with existing technologies, often at a low cost,” according to the IEA methane report.
For the oil and gas industry, that could mean something as simple as using better fittings in pipelines to limit leaks and installing methane capture systems. And since methane is a fuel, the sale of the saved methane can offset the cost of upgrading hardware. Letting it go into the atmosphere is a waste of money and a contributor to warming.
Capturing or destroying methane from coal mines isn’t so straightforward. Common techniques to separate methane from other gases require heating air, which is not exactly the safest thing to do around a coal mine—it can increase the risk of fire or explosion. But safer alternatives have been developed. “There are catalytic and other approaches available today that don’t require such high temperatures,” said Robert Jackson, a professor of earth system science at Stanford University, in an email.
However, these methods to limit methane from fossil fuels are vastly underused. Only about 5 percent of active oil and gas production facilities around the world deploy systems to zero out their methane pollution. In the US, there are also millions of oil and gas wells and tens of thousands of abandoned coal mines whose operators have long since vanished, leaving no one accountable for their continued methane emissions.
“If there isn’t a regulatory mandate to treat the methane, or put a price on it, many companies continue to do nothing,” Jackson said. And while recovering methane is ultimately profitable over time, the margins aren’t often big enough to make the up-front investment of better pipes, monitoring equipment, or scrubbers worthwhile for them. “They want to make 10 to 15 percent on their money (at least), not save a few percent,” he added.
And rather than getting stronger, regulations on methane are poised to get weaker. The Trump administration has approved more than $119 million to help communities reclaim abandoned coal mines. However, the White House has also halted funding for plugging abandoned oil and gas wells and is limiting environmental reviews for new fossil fuel projects. Congressional Republicans are also working to undo a fee on methane emissions that was part of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act. With weaker incentives to track and limit methane, it’s likely emissions will continue to rise in the United States. That will push the world further off course from climate goals and contribute to a hotter planet.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump reportedly warned domestic automakers not to raise prices before saying he “couldn’t care less” if foreign car prices rise
In the days leading up to President Donald Trump's April 2 implementation of 25% tariffs on imported automobiles and auto parts, Fox News and Fox Business personalities dismissed looming price increases the new import taxes are expected to unleash on American consumers. These auto-specific tariffs, combined with 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum and another 25% tariff on Canadian and Mexican imports, are estimated by economists and industry analysts to raise vehicle prices by up to double-digit percentage points and potentially up to $15,000 per vehicle.
The Wall Street Journal reported that earlier in March, Trump privately warned U.S. automakers not to raise prices in response to the tariffs, even though they will be subjected to them. When confronted with this story in a March 29 NBC News interview, Trump denied telling U.S. automakers not to raise prices before saying of foreign car makers: “I couldn’t care less. I hope they raise their prices, because if they do, people are gonna buy American-made cars.” He continued: “I couldn’t care less, because if the prices on foreign cars go up, they’re going to buy American cars.”
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from CBS News:
Extreme heat caused by emissions from 111 fossil fuel companies cost an estimated $28 trillion between 1991 and 2020, according to researchers at Dartmouth College.
Their study, which was published Wednesday in "Nature," presents a peer-reviewed method for tying emissions to specific climate harms. Their goal is to help hold companies liable for the cost of extreme weather, similar to holding the tobacco industry liable for lung cancer cases or pharmaceutical companies liable for the opioid crisis.
The research firm Zero Carbon Analytics counts 68 lawsuits filed globally about climate change damage, with more than half of them in the United States.
"We argue that the scientific case for climate liability is closed," wrote the study's authors, Christopher Callahan, who received his PhD from Dartmouth College, and Justin Mankin, a Dartmouth Department of Geography professor.
About a third of the total cost was attributed to five companies, which can be tied to more than $9 trillion in climate damage, according to the study.
These are the top-emitting companies and the dollar amount the researchers estimate they are responsible for:
Saudi Aramco: $2.05 trillion
Gazprom: $2 trillion
Chevron: $1.98 trillion
ExxonMobil: $1.91 trillion
BP: $1.45 trillion
The researchers figured that every 1% of greenhouse gas put into the atmosphere since 1990 has caused $502 billion in damage from heat alone, which doesn't include the costs incurred by other extreme weather such as hurricanes, droughts and floods. Emissions data is taken from the public Carbon Majors database, they said.
They used 1,000 different computer simulations to translate those emissions into changes for Earth's global average surface temperature by comparing it to a world without that company's emissions.
Using this approach, they determined that pollution from Chevron, for example, has raised the Earth's temperature by .045 degrees Fahrenheit.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Why did you do that?!”
Tenes shuffles uneasily in the background, biting his lip as he clenches his fingers over the clipboard. He casts a glance at Thrasus, who looks angry, and it’s kind of scary, even though the anger isn’t aimed at him. Tenes would rather that his supervisor be upset with him, though, because the current reality is even worse: Thrasus is angry with Titania.
Titania, the first of the Iron Cavalry. The bioweapon that was specifically designed to lead and command the legions of cloned soldiers against the Swarm.
Behind the thick layer of reinforced glass, Titania floats quietly in the blue-green experimental liquid. It casts an eerie color over her naked body –as if the solid black limbs morphing into human flesh wasn’t enough of an eerie sight already. And there were also those antennae atop her head. Tenes is almost glad that Titania has never opened her eyes before, because if it’s the same as those beady eyes of the bug-aliens, then he thinks that he might have nightmares for a week.
[I do not understand your question, Thrasus.] The speakers connected to the audio device acting as Titania’s ‘voice’ suddenly come to life. The voice is feminine, but very clearly artificial and robotic all the same.
(Personally, Tenes has never really understood the choice; wouldn’t it be easy enough to designate a more realistic-sounding voice to translate Titania’s signals? Wasn’t enough already that Titania looked half-bug alien, what was the point in making her seem half-machine lifeform, too? … More nightmare fuel, as if the entire world wasn’t enough of a nightmare already?)
“You were designed with the pinnacle of Glamoth’s intelligence, don’t play dumb.” Thrasus’ voice is harsh and unamused. “Why did you withdraw the Iron Cavalry from Pandaisia?”
[The forces stationed there were not enough to overcome the increased numbers of the Swarm. Engaging in combat would not have yielded meaningful results, and so I deemed that the Iron Cavalry would be better utilized in–]
“So you just gave up on Pandaisia?!” Thrasus roars.
[Correction: Temporary retreat.] Titania remains unmoving amid the hundreds of wires that she’s connected to. For all intents and purposes, she appears to be peacefully sleeping –which strikes a strong contrast against Thrasus’ anger. [Pandaisia is a nonessential area with low strategic value. It would be better to reclaim Phaenna first, before mounting any efforts to target–]
“The Council specifically ordered for Pandaisia to be reclaimed by the end of this month,” the scientist hisses. “Do you not understand the boost it would be for morale? Pandaisia’s agricultural industry once had the highest output in Glamoth with its fertile lands. If we can tell people that Pandaisia is ours once again, if we can let them know that there’s hope even despite the ongoing resource crisis–”
[Pandaisia’s lands have already been ravaged by the Swarm. It is unlikely that the fertility of the land will produce any bountiful crop yields. Estimated time of recovery is–]
“It’s not just about the goddamned resources! We need a meaningful victory that people can rally behind and cheer for!” Thrasus groans, running a hand through his hair. “Gods, resources are thin enough already, and if the Council decides to pull their support, then we–”
“Let me deal with the Council, Thrasus.”
Thank gods Chief Scientist Polus is here. Tenes quietly closes and hides his communicator –the one he’d used to notify the Chief Scientist of what was going on here. Then, he does his best to make himself small and disappear into a corner of the room.
“… Polus.” It’s either the Chief Scientist’s sudden appearance or the fact that Thrasus has already gotten most of the anger out of his system through shouting that has the man swiftly calming down again. “You aren’t worried at all by what this might mean for us?”
“The Council won’t decommission the Iron Cavalry,” the Chief Scientist shakes his head. “The Iron Cavalry is the hope of Glamoth. It’s only been a short time since Titania was activated, and we’re already starting to see results with the Swarm being pushed back in various locations all over Glamoth. The Council is just being too hasty.”
“Whatever. I’ll leave the political talk to you, then,” Thrasus grumbles.
The Chief Scientist nods, then turns towards the immobile bioweapon floating in her containment chamber.
[Hello, Polus.]
“Hello there, Titania.” Chief Scientist Polus checks a few of the readings on the side panels, then nods in apparent satisfaction at what he sees. “How are you doing?”
[I am well. All systems are online and operational.]
“Good,” the Chief Scientist nods, stepping backwards. He pulls out a holographic screen, and begins tapping away through them, his fingers a blue. “And, Titania –none of us here are military officers or strategists, so we can’t help you in matters of the battlefield. But, we’re still here to support you. Don’t be too concerned about losing your soldiers.”
There is a slight pause this time, before Titania responds again. [… I do not understand. Is there not an ongoing resource crisis?]
Thrasos snorts and folds his arms across his chest, muttering, “This is the one resource that there’s plenty of. Accursed bug aliens…”
“It’s fine, Titania,” Chief Scientist Polus replies, ignoring his fellow researcher and not even pausing to glance up from his growing cluster of holographic screens. “Don’t worry about it. We can just make more of them.”
#Writing#zenith of stars au#titania au#honkai star rail#more on this particular plot bunny!#guys if i write more about this does it mean i'll pull firefly before i hit hard pity#/jk#good luck to everyone pulling for firefly in their gacha pulls!
79 notes
·
View notes