#openshift pipelines using tekton
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Streamline Your DevOps Workflow with DO400: CI/CD with Jenkins, Git, and TDD
In today's fast-paced world of software development, speed without quality is a risk. That's where DevOps practices like Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD), Git version control, and Test-Driven Development (TDD) come into play. Red Hat’s DO400 course—Red Hat DevOps Pipelines and Processes—is designed to help developers and DevOps professionals master these practices using industry-standard tools like Jenkins, Git, and Red Hat OpenShift.
What is DO400?
DO400 is an advanced Red Hat training course that focuses on modern DevOps workflows. It helps participants build, test, and deploy applications through CI/CD pipelines while incorporating automation and quality checks. It’s a hands-on course that teaches you how to build scalable, testable, and automated application delivery pipelines on OpenShift.
Key Skills You'll Gain in DO400
✅ CI/CD Pipelines with Jenkins and OpenShift Learn how to set up and manage Jenkins pipelines integrated with Red Hat OpenShift for smooth application delivery.
✅ Version Control with Git Use Git effectively for source code management, collaboration, and integration into your DevOps pipeline.
✅ Test-Driven Development (TDD) Write tests first, code second. Improve software quality and reduce bugs with TDD workflows.
✅ Pipeline as Code Use Jenkinsfiles and OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton) to define CI/CD processes as code for better maintainability and reuse.
✅ Containerized Builds Leverage container-native CI/CD workflows, speeding up builds and deployments while maintaining consistency across environments.
Who Should Take DO400?
This course is ideal for:
DevOps Engineers
Site Reliability Engineers (SREs)
Application Developers working in CI/CD environments
Platform Engineers managing OpenShift pipelines
A working knowledge of OpenShift and basic container concepts (preferably completion of DO180 and DO288) is recommended before starting this course.
Why DO400 is a Game-Changer for DevOps Teams
Faster Release Cycles: Automate testing and deployment to release features faster and with confidence.
Reduced Errors in Production: Incorporate automated tests and rollback mechanisms.
Improved Collaboration: Git-based workflows make it easy for teams to collaborate, review, and track changes.
Scalable and Reusable Pipelines: Templates and code-based pipelines simplify reuse across projects.
Real-World Use Case
Imagine deploying a microservice to OpenShift. With DO400 skills, you can:
Push code to Git
Automatically trigger a Jenkins build
Run unit tests using TDD
Package the app in a container
Deploy it to staging or production with minimal manual effort
All of this, monitored and controlled through OpenShift and Jenkins dashboards.
Final Thoughts
DO400 isn’t just a training course. It’s a blueprint for building modern, resilient DevOps practices in your organization. Whether you're just starting with CI/CD or want to level up your automation game, DO400 will equip you with the skills and confidence to streamline software delivery using Red Hat technologies.
Ready to embrace automation and ship better code, faster? Visit - www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
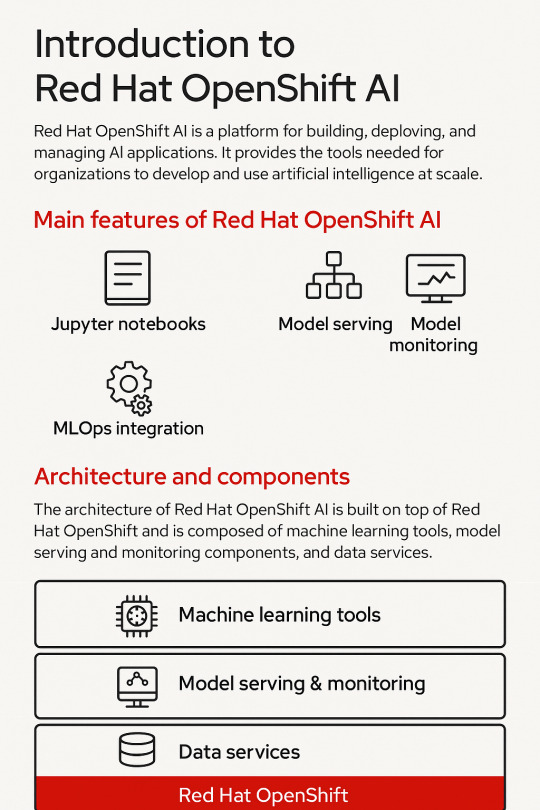
Introduction to Red Hat OpenShift AI: Features, Architecture & Components
In today’s data-driven world, organizations need a scalable, secure, and flexible platform to build, deploy, and manage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models. Red Hat OpenShift AI is built precisely for that. It provides a consistent, Kubernetes-native platform for MLOps, integrating open-source tools, enterprise-grade support, and cloud-native flexibility.
Let’s break down the key features, architecture, and components that make OpenShift AI a powerful platform for AI innovation.
🔍 What is Red Hat OpenShift AI?
Red Hat OpenShift AI (formerly known as OpenShift Data Science) is a fully supported, enterprise-ready platform that brings together tools for data scientists, ML engineers, and DevOps teams. It enables rapid model development, training, and deployment on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
🚀 Key Features of OpenShift AI
1. Built for MLOps
OpenShift AI supports the entire ML lifecycle—from experimentation to deployment—within a consistent, containerized environment.
2. Integrated Jupyter Notebooks
Data scientists can use Jupyter notebooks pre-integrated into the platform, allowing quick experimentation with data and models.
3. Model Training and Serving
Use Kubernetes to scale model training jobs and deploy inference services using tools like KServe and Seldon Core.
4. Security and Governance
OpenShift AI integrates enterprise-grade security, role-based access controls (RBAC), and policy enforcement using OpenShift’s built-in features.
5. Support for Open Source Tools
Seamless integration with open-source frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, and ONNX for maximum flexibility.
6. Hybrid and Multicloud Ready
You can run OpenShift AI on any OpenShift cluster—on-premise or across cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
🧠 OpenShift AI Architecture Overview
Red Hat OpenShift AI builds upon OpenShift’s robust Kubernetes platform, adding specific components to support the AI/ML workflows. The architecture broadly consists of:
1. User Interface Layer
JupyterHub: Multi-user Jupyter notebook support.
Dashboard: UI for managing projects, models, and pipelines.
2. Model Development Layer
Notebooks: Containerized environments with GPU/CPU options.
Data Connectors: Access to S3, Ceph, or other object storage for datasets.
3. Training and Pipeline Layer
Open Data Hub and Kubeflow Pipelines: Automate ML workflows.
Ray, MPI, and Horovod: For distributed training jobs.
4. Inference Layer
KServe/Seldon: Model serving at scale with REST and gRPC endpoints.
Model Monitoring: Metrics and performance tracking for live models.
5. Storage and Resource Management
Ceph / OpenShift Data Foundation: Persistent storage for model artifacts and datasets.
GPU Scheduling and Node Management: Leverages OpenShift for optimized hardware utilization.
🧩 Core Components of OpenShift AI
ComponentDescriptionJupyterHubWeb-based development interface for notebooksKServe/SeldonInference serving engines with auto-scalingOpen Data HubML platform tools including Kafka, Spark, and moreKubeflow PipelinesWorkflow orchestration for training pipelinesModelMeshScalable, multi-model servingPrometheus + GrafanaMonitoring and dashboarding for models and infrastructureOpenShift PipelinesCI/CD for ML workflows using Tekton
🌎 Use Cases
Financial Services: Fraud detection using real-time ML models
Healthcare: Predictive diagnostics and patient risk models
Retail: Personalized recommendations powered by AI
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance and quality control
🏁 Final Thoughts
Red Hat OpenShift AI brings together the best of Kubernetes, open-source innovation, and enterprise-level security to enable real-world AI at scale. Whether you’re building a simple classifier or deploying a complex deep learning pipeline, OpenShift AI provides a unified, scalable, and production-grade platform.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
Mastering OpenShift Clusters: A Comprehensive Guide for Streamlined Containerized Application Management
As organizations increasingly adopt containerization to enhance their application development and deployment processes, mastering tools like OpenShift becomes crucial. OpenShift, a Kubernetes-based platform, provides powerful capabilities for managing containerized applications. In this blog, we'll walk you through essential steps and best practices to effectively manage OpenShift clusters.
Introduction to OpenShift
OpenShift is a robust container application platform developed by Red Hat. It leverages Kubernetes for orchestration and adds developer-centric and enterprise-ready features. Understanding OpenShift’s architecture, including its components like the master node, worker nodes, and its integrated CI/CD pipeline, is foundational to mastering this platform.
Step-by-Step Tutorial
1. Setting Up Your OpenShift Cluster
Step 1: Prerequisites
Ensure you have a Red Hat OpenShift subscription.
Install oc, the OpenShift CLI tool.
Prepare your infrastructure (on-premise servers, cloud instances, etc.).
Step 2: Install OpenShift
Use the OpenShift Installer to deploy the cluster:openshift-install create cluster --dir=mycluster
Step 3: Configure Access
Log in to your cluster using the oc CLI:oc login -u kubeadmin -p $(cat mycluster/auth/kubeadmin-password) https://api.mycluster.example.com:6443
2. Deploying Applications on OpenShift
Step 1: Create a New Project
A project in OpenShift is similar to a namespace in Kubernetes:oc new-project myproject
Step 2: Deploy an Application
Deploy a sample application, such as an Nginx server:oc new-app nginx
Step 3: Expose the Application
Create a route to expose the application to external traffic:oc expose svc/nginx
3. Managing Resources and Scaling
Step 1: Resource Quotas and Limits
Define resource quotas to control the resource consumption within a project:apiVersion: v1 kind: ResourceQuota metadata: name: mem-cpu-quota spec: hard: requests.cpu: "4" requests.memory: 8Gi Apply the quota:oc create -f quota.yaml
Step 2: Scaling Applications
Scale your deployment to handle increased load:oc scale deployment/nginx --replicas=3
Expert Best Practices
1. Security and Compliance
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define roles and bind them to users or groups to enforce the principle of least privilege.apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: myproject name: developer rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods", "services"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete"]oc create -f role.yaml oc create rolebinding developer-binding --role=developer [email protected] -n myproject
Network Policies: Implement network policies to control traffic flow between pods.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-same-namespace namespace: myproject spec: podSelector: matchLabels: {} policyTypes: - Ingress - Egress ingress: - from: - podSelector: {} oc create -f networkpolicy.yaml
2. Monitoring and Logging
Prometheus and Grafana: Use Prometheus for monitoring and Grafana for visualizing metrics.oc new-project monitoring oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-monitoring-view -z default -n monitoring oc apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/kube-prometheus/main/manifests/setup oc apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/kube-prometheus/main/manifests/
ELK Stack: Deploy Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana for centralized logging.oc new-project logging oc new-app elasticsearch oc new-app logstash oc new-app kibana
3. Automation and CI/CD
Jenkins Pipeline: Integrate Jenkins for CI/CD to automate the build, test, and deployment processes.oc new-app jenkins-ephemeral oc create -f jenkins-pipeline.yaml
OpenShift Pipelines: Use OpenShift Pipelines, which is based on Tekton, for advanced CI/CD capabilities.oc apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tektoncd/pipeline/main/release.yaml
Conclusion
Mastering OpenShift clusters involves understanding the platform's architecture, deploying and managing applications, and implementing best practices for security, monitoring, and automation. By following this comprehensive guide, you'll be well on your way to efficiently managing containerized applications with OpenShift.
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#information technology#docker#container#linux#kubernetes#containerorchestration#containersecurity#dockerswarm#aws
0 notes
Text
https://youtu.be/3OfS5QYo77M
#openshiftpipelinesusingtekton #openshift4 #tektonpipelines #CICDpipelines #continuousintegration openshift pipelines using tekton,openshift pipelines using tektonan,openshift,installing openshift pipelines,openshift pipelines based on tekton,tekton,kubernetes,openshift pipelines using tektonic,openshift pipelines tutorial using…
View On WordPress
#application using tektoncd pipelines#ci cd pipelines in openshift#cicd#cli tekton pipelines operator#cloud-native#containers#continuous integration#installing openshift pipelines#kubernetes#openshift#openshift pipelines based on tekton#openshift pipelines tutorial using tekton#openshift pipelines using tekton#openshift pipelines using tektonan#openshift pipelines using tektonic#pipeline#pipelines#pipelines on red hat openshift#red hat#tekton#tekton-pipelines#tektoncd
0 notes
Text
🚀 DO288 – Master OpenShift Application Development
If you're aiming to become a Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Application Development, DO288 is the course that gets you there. It's not just about learning OpenShift — it's about learning how to build, deploy, and manage containerized applications the Red Hat way.
🧠 What is DO288?
DO288: Red Hat OpenShift Development II: Containerizing Applications is designed for developers who want to:
Move from traditional application deployment to Kubernetes-native development.
Learn how to use OpenShift for CI/CD, scaling, and secure application rollout.
Build container images, define app builds using S2I (Source-to-Image), and use OpenShift Templates and Helm Charts.
🔧 What You’ll Learn
Here’s a quick snapshot of what DO288 teaches:
🔹 Creating containerized services using Podman and Buildah
🔹 Configuring OpenShift builds using Source-to-Image (S2I)
🔹 Deploying apps using Templates and Helm Charts
🔹 Managing app environments, secrets, and configuration maps
🔹 CI/CD integration using OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton)
🔹 Securing applications using Service Accounts and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
🧰 Prerequisites
To make the most out of DO288, you should already know the basics of containers and OpenShift. Ideally, you’ve completed DO180 (Red Hat OpenShift I: Containers & Kubernetes).
If you're not there yet — start with DO180 and then move on to DO288. That combo gives you the foundation to become a Red Hat Certified Developer: OpenShift Application Development.
🎯 Who Should Take This?
Developers transitioning to container-native workflows
DevOps engineers working in OpenShift/Kubernetes environments
Application teams using CI/CD for microservices
Anyone preparing for the Red Hat certification exam EX288
🏆 Certification Outcome
Once you finish DO288, you’ll be ready to attempt the EX288 certification exam. Passing this exam makes you a Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Application Development.
That’s a powerful credential for anyone working in enterprise DevOps, cloud-native development, or platform engineering roles.
✍️ Final Thoughts
OpenShift isn’t just another Kubernetes platform — it’s the enterprise-ready standard trusted by governments, banks, telcos, and global enterprises. Learning to build on OpenShift sets you apart.
So if you’re serious about containerized app development, DO288 is the course to take. refer www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Developing and Deploying AI/ML Applications on Red Hat OpenShift AI (AI268)
As artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) continue to transform industries, organizations are striving not just to build smarter models — but to operationalize them at scale. This is exactly where Red Hat OpenShift AI steps in as a powerful enterprise platform, combining the flexibility of open-source tooling with the scalability of Kubernetes.
The AI268 course – Developing and Deploying AI/ML Applications on Red Hat OpenShift AI – is a deep-dive training designed for data scientists, ML engineers, and developers who want to go beyond notebooks and deploy real-world ML solutions with confidence.
🔍 What the Course Covers
AI268 equips professionals to build robust ML workflows within a cloud-native architecture. You'll start with model development in a secure, collaborative environment using Jupyter notebooks. From there, you’ll dive into containerizing your ML workloads to make them portable and reproducible across environments.
The course also explores automated ML pipelines using Tekton (OpenShift Pipelines), allowing seamless orchestration of model training, validation, and deployment. You’ll also learn how to serve models at scale using ModelMesh and Seldon, enabling high-performance inference with dynamic model loading and efficient resource utilization.
🌟 The Power of OpenShift AI
What makes OpenShift AI unique is its native integration with Kubernetes, allowing you to scale AI workloads efficiently while applying modern DevOps principles to ML workflows. It supports GPU acceleration, version control for data and models, and secure, role-based access — everything needed to move ML into production, faster and smarter.
This environment allows teams to collaborate across development, data, and operations — breaking down the traditional silos that stall many ML initiatives.
💡 Real-World Applications
Imagine building a pipeline that automatically retrains your model whenever new data arrives. Or deploying hundreds of models for different customer segments and loading them only when needed to save memory and cost. With the skills learned in AI268, these aren’t just possibilities — they’re your new baseline.
You also learn to integrate GitOps-style CI/CD for model lifecycle management, allowing automated versioning, promotion, rollback, and monitoring — all within the OpenShift ecosystem.
🧠 Why It Matters
MLOps is not just a buzzword — it's a necessity for any organization scaling AI efforts. The AI268 course arms you with practical tools and skills to not only develop models but to run them reliably in production. It’s ideal for teams aiming to modernize their AI/ML stack while adhering to enterprise standards for security, governance, and scalability.
🎯 Final Thoughts
Red Hat OpenShift AI provides the foundation, and AI268 shows you how to build on it. Whether you're modernizing legacy workflows or deploying cutting-edge models into production, this course helps you bridge the gap between experimentation and enterprise-ready ML operations.
If you're serious about delivering value with AI in a secure, automated, and scalable way — AI268 is the course to take.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Mastering OpenShift at Scale: Red Hat OpenShift Administration III (DO380)
In today’s cloud-native world, organizations are increasingly adopting Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift to power their modern applications. As these environments scale, so do the challenges of managing complex workloads, automating operations, and ensuring reliability. That’s where Red Hat OpenShift Administration III: Scaling Kubernetes Workloads (DO380) steps in.
What is DO380?
DO380 is an advanced-level training course offered by Red Hat that focuses on scaling, performance tuning, and managing containerized applications in production using Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. It is designed for experienced OpenShift administrators and DevOps professionals who want to deepen their knowledge of Kubernetes-based platform operations.
Who Should Take DO380?
This course is ideal for:
✅ System Administrators managing large-scale containerized environments
✅ DevOps Engineers working with CI/CD pipelines and automation
✅ Platform Engineers responsible for OpenShift clusters
✅ RHCEs or OpenShift Certified Administrators (EX280 holders) aiming to level up
Key Skills You Will Learn
Here’s what you’ll master in DO380:
🔧 Advanced Cluster Management
Configure and manage OpenShift clusters for performance and scalability.
📈 Monitoring & Tuning
Use tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and the OpenShift Console to monitor system health, tune workloads, and troubleshoot performance issues.
📦 Autoscaling & Load Management
Configure Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA), Cluster Autoscaler, and manage workloads efficiently with resource quotas and limits.
🔐 Security & Compliance
Implement security policies, use node taints/tolerations, and manage namespaces for better isolation and governance.
🧪 CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Automate application delivery using Tekton pipelines and manage GitOps workflows with ArgoCD.
Course Prerequisites
Before enrolling in DO380, you should be familiar with:
Red Hat OpenShift Administration I (DO180)
Red Hat OpenShift Administration II (DO280)
Kubernetes fundamentals (kubectl, deployments, pods, services)
Certification Path
DO380 also helps you prepare for the Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Scaling and Performance (EX380) exam, which counts towards the Red Hat Certified Architect (RHCA) credential.
Why DO380 Matters
With enterprise workloads becoming more dynamic and resource-intensive, scaling OpenShift effectively is not just a bonus — it’s a necessity. DO380 equips you with the skills to:
✅ Maximize infrastructure efficiency
✅ Ensure high availability
✅ Automate operations
✅ Improve DevOps productivity
Conclusion
Whether you're looking to enhance your career, improve your organization's cloud-native capabilities, or take the next step in your Red Hat certification journey — Red Hat OpenShift Administration III (DO380) is your gateway to mastering OpenShift at scale.
Ready to elevate your OpenShift expertise?
Explore DO380 training options with HawkStack Technologies and get hands-on with real-world OpenShift scaling scenarios.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Integrating ROSA Applications With AWS Services (CS221)
As organizations increasingly adopt Kubernetes for container orchestration, Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) has become a go-to managed Kubernetes solution. ROSA combines the power of Red Hat OpenShift with AWS infrastructure, offering seamless integrations, enterprise support, and scalability.
In CS221, we explore the design and implementation of intelligent systems. Integrating ROSA with AWS services enhances the capabilities of these systems, allowing real-time data ingestion, model deployment, logging, security, and scalable storage. In this blog, we’ll dive into how ROSA applications can be integrated with key AWS services to build production-ready, intelligent applications.
Why ROSA + AWS?
ROSA provides:
Managed OpenShift with built-in CI/CD, monitoring, and developer tooling.
Native integration with AWS IAM, VPCs, EBS/EFS, and security policies.
Ease of hybrid/multi-cloud deployments.
AWS provides:
A rich suite of services like S3, RDS, SageMaker, Lambda, CloudWatch, and more that extend OpenShift’s capabilities.
1. Storage Integration: Using Amazon S3 and EFS
🎯 Use Case:
Store unstructured data (e.g., ML datasets, logs, user uploads) from ROSA applications.
🔧 How to Integrate:
Use AWS Service Broker or OpenShift Operators to provision and bind S3 buckets.
Mount EFS volumes into ROSA pods for shared file systems.
2. Deploying ML Models With SageMaker
🎯 Use Case:
Train and deploy ML models using AWS SageMaker, then consume them in ROSA apps.
🔧 How to Integrate:
Build and train models in SageMaker.
Deploy as SageMaker Endpoints.
Connect from ROSA microservices using REST calls or AWS SDK.
💡 Tip:
Use Amazon EventBridge to trigger SageMaker workflows based on OpenShift events or Kafka topics.
3. Logging and Monitoring With CloudWatch
🎯 Use Case:
Centralize log and metrics collection from ROSA to AWS CloudWatch for visibility and alerting.
🔧 How to Integrate:
Use Fluent Bit/Fluentd DaemonSets in OpenShift to forward logs to CloudWatch Logs.
Leverage CloudWatch Container Insights for performance metrics.
4. Identity and Access Management With AWS IAM
🎯 Use Case:
Ensure secure, fine-grained access control for services running inside ROSA.
🔧 How to Integrate:
Use IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) via OpenShift.
Map OpenShift service accounts to IAM roles using OIDC.
Security Benefit:
Avoid hardcoding AWS credentials in containers. Use temporary credentials via role assumption.
5. Event-Driven Architectures With AWS Lambda
🎯 Use Case:
Trigger backend logic from ROSA applications (e.g., image processing, webhook handling).
🔧 How to Integrate:
Use Amazon SNS/SQS to decouple communication.
ROSA sends messages, and Lambda functions process them asynchronously.
🚀 Example Flow:
ROSA app publishes message to SNS.
Lambda listens via an SQS queue.
Lambda processes the event and stores the result in S3 or DynamoDB.
6. Databases With Amazon RDS and DynamoDB
🎯 Use Case:
Persistent storage of structured data like user profiles, system metadata.
🔧 How to Integrate:
Provision Amazon RDS databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL) and connect via VPC peering or service endpoints.
Use DynamoDB for NoSQL needs such as session storage or real-time counters.
DevOps Integration
CI/CD with OpenShift Pipelines and AWS:
Automate build/test/deploy via Tekton Pipelines in ROSA.
Store artifacts in Amazon ECR.
Use AWS CodeBuild/CodePipeline to trigger downstream services.
Best Practices
✅ Use Secrets Manager or Parameter Store for credentials management.
✅ Monitor costs using AWS Budgets when autoscaling ROSA workloads.
✅ Regularly scan container images with Amazon Inspector or Quay Security Scanner.
✅ Enable auto-scaling and HPA with AWS CloudWatch metrics.
Conclusion
ROSA allows developers to run OpenShift-native applications with the power of AWS services. Whether you're building scalable web services, training ML models, or setting up observability, integrating ROSA with AWS transforms your architecture into a modern, secure, and intelligent system.
In CS221, where systems need to learn, adapt, and scale, this integration empowers us to bring intelligent agents to life in real-world cloud environments.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
Developing and Deploying AI/ML Applications on Red Hat OpenShift AI with Hawkstack
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are driving innovation across industries—from predictive analytics in healthcare to real-time fraud detection in finance. But building, scaling, and maintaining production-grade AI/ML solutions remains a significant challenge. Enter Red Hat OpenShift AI, a powerful platform that brings together the flexibility of Kubernetes with enterprise-grade ML tooling. And when combined with Hawkstack, organizations can supercharge observability and performance tracking throughout their AI/ML lifecycle.
Why Red Hat OpenShift AI?
Red Hat OpenShift AI (formerly Red Hat OpenShift Data Science) is a robust enterprise platform designed to support the full AI/ML lifecycle—from development to deployment. Key benefits include:
Scalability: Native Kubernetes integration allows seamless scaling of ML workloads.
Security: Red Hat’s enterprise security practices ensure that ML pipelines are secure by design.
Flexibility: Supports a variety of tools and frameworks, including Jupyter Notebooks, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and more.
Collaboration: Built-in tools for team collaboration and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD).
Introducing Hawkstack: Observability for AI/ML Workloads
As you move from model training to production, observability becomes critical. Hawkstack, a lightweight and extensible observability framework, integrates seamlessly with Red Hat OpenShift AI to provide real-time insights into system performance, data drift, model accuracy, and infrastructure metrics.
Hawkstack + OpenShift AI: A Powerful Duo
By integrating Hawkstack with OpenShift AI, you can:
Monitor ML Pipelines: Track metrics across training, validation, and deployment stages.
Visualize Performance: Dashboards powered by Hawkstack allow teams to monitor GPU/CPU usage, memory footprint, and latency.
Enable Alerting: Proactively detect model degradation or anomalies in your inference services.
Optimize Resources: Fine-tune resource allocation based on telemetry data.
Workflow: Developing and Deploying ML Apps
Here’s a high-level overview of what a modern AI/ML workflow looks like on OpenShift AI with Hawkstack:
1. Model Development
Data scientists use tools like JupyterLab or VS Code on OpenShift AI to build and train models. Libraries such as scikit-learn, XGBoost, and Hugging Face Transformers are pre-integrated.
2. Pipeline Automation
Using Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton), you can automate training and evaluation pipelines. Integrate CI/CD practices to ensure robust and repeatable workflows.
3. Model Deployment
Leverage OpenShift AI’s serving layer to deploy models using Seldon Core, KServe, or OpenVINO Model Server—all containerized and scalable.
4. Monitoring and Feedback with Hawkstack
Once deployed, Hawkstack takes over to monitor inference latency, throughput, and model accuracy in real-time. Anomalies can be fed back into the training pipeline, enabling continuous learning and adaptation.
Real-World Use Case
A leading financial services firm recently implemented OpenShift AI and Hawkstack to power their loan approval engine. Using Hawkstack, they detected a model drift issue caused by seasonal changes in application data. Alerts enabled retraining to be triggered automatically, ensuring their decisions stayed fair and accurate.
Conclusion
Deploying AI/ML applications in production doesn’t have to be daunting. With Red Hat OpenShift AI, you get a secure, scalable, and enterprise-ready foundation. And with Hawkstack, you add observability and performance intelligence to every stage of your ML lifecycle.
Together, they empower organizations to bring AI/ML innovations to market faster—without compromising on reliability or visibility.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Developing and Deploying AI/ML Applications on Red Hat OpenShift AI (AI268)
As artificial intelligence and machine learning continue to drive innovation across industries, the need for scalable, enterprise-ready platforms for building and deploying models is greater than ever. Red Hat OpenShift AI (formerly Red Hat OpenShift Data Science) rises to this challenge by providing a fully integrated, Kubernetes-based environment for end-to-end AI/ML workflows.
In this blog, we’ll explore the essentials of Red Hat’s AI268 course – Developing and Deploying AI/ML Applications on Red Hat OpenShift AI – and how it empowers data scientists and ML engineers to accelerate the path from model development to production.
🎯 What is AI268?
AI268 is a hands-on training course designed by Red Hat to help professionals learn how to use OpenShift AI (a managed service on OpenShift) to:
Build machine learning models in Jupyter notebooks.
Train and fine-tune models using GPU/CPU resources.
Collaborate with teams in a secure and scalable environment.
Deploy models as RESTful APIs or inference endpoints using OpenShift tools.
Automate workflows using Pipelines and GitOps practices.
This course is ideal for:
Data Scientists
ML Engineers
DevOps/Platform Engineers supporting AI/ML workloads
🚀 Key Capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift AI
Here’s what makes OpenShift AI a game-changer for enterprise ML:
1. Jupyter-as-a-Service
Spin up customized Jupyter notebook environments with pre-integrated libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, and more. Users can develop, experiment, and iterate on models—all in a cloud-native environment.
2. Model Training at Scale
Access to elastic compute resources including GPUs and CPUs ensures seamless training and hyperparameter tuning. OpenShift AI integrates with distributed training frameworks and supports large-scale jobs.
3. MLOps Integration
Leverage Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton) and OpenShift GitOps (Argo CD) to bring CI/CD principles to your ML workflows, ensuring model versioning, automated testing, and deployment consistency.
4. Secure Collaboration
Enable data science teams to collaborate across workspaces, with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), quotas, and isolated environments ensuring governance and security.
5. Flexible Deployment Options
Deploy trained models as containers, REST endpoints, or even serverless workloads using OpenShift Service Mesh, Knative, and Red Hat OpenShift Serverless.
🛠️ Course Highlights
The AI268 course typically covers:
Setting up and accessing OpenShift AI
Managing projects, notebooks, and data connections
Using Git with Jupyter for version control
Building and deploying models using Seldon or KFServing
Creating Pipelines for ML workflows
Monitoring deployed services and gathering inference metrics
The course is lab-intensive and designed around real-world use cases to ensure practical understanding.
💼 Why It Matters for Enterprises
Organizations looking to scale AI initiatives often struggle with fragmented tooling, inconsistent environments, and lack of collaboration. OpenShift AI brings the power of Kubernetes together with Red Hat’s robust ecosystem to create a unified platform for data-driven innovation.
With OpenShift AI and skills from AI268, teams can:
Accelerate time to market for AI solutions
Maintain model reproducibility and traceability
Enable continuous delivery of AI/ML capabilities
Improve collaboration between data science and IT/DevOps teams
📚 Ready to Upskill?
If you're ready to bridge the gap between data science and production deployment, AI268 is your launchpad. It prepares teams to leverage OpenShift AI for building scalable, reproducible, and secure ML applications.
👉 Talk to us at HawkStack Technologies for:
Corporate Training
Red Hat Learning Subscription (RHLS)
AI/ML Training Roadmaps
🔗 Get in touch to learn more about Red Hat AI/ML offerings or to schedule your team's AI268 session. www.hawkstack.com
#RedHat #OpenShiftAI #MachineLearning #DevOps #MLOps #DataScience #AI268 #OpenShift #Kubernetes #RHLS #HawkStack #AITools #EnterpriseAI #CloudNativeAI
0 notes
Text
Mastering AI on Kubernetes: A Deep Dive into the Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a buzzword—it's a foundational technology across industries. From powering recommendation engines to enabling self-healing infrastructure, AI is changing the way we build and scale digital experiences. For professionals looking to validate their ability to run AI/ML workloads on Kubernetes, the Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift AI certification is a game-changer.
What is the OpenShift AI Certification?
The Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift AI certification (EX480) is designed for professionals who want to demonstrate their skills in deploying, managing, and scaling AI and machine learning (ML) workloads on Red Hat OpenShift AI (formerly OpenShift Data Science).
This hands-on exam tests real-world capabilities rather than rote memorization, making it ideal for data scientists, ML engineers, DevOps engineers, and platform administrators who want to bridge the gap between AI/ML and cloud-native operations.
Why This Certification Matters
In a world where ML models are only as useful as the infrastructure they run on, OpenShift AI offers a powerful platform for deploying and monitoring models in production. Here’s why this certification is valuable:
🔧 Infrastructure + AI: It merges the best of Kubernetes, containers, and MLOps.
📈 Enterprise-Ready: Red Hat is trusted by thousands of companies worldwide—OpenShift AI is production-grade.
💼 Career Boost: Certifications remain a proven way to stand out in a crowded job market.
🔐 Security and Governance: Demonstrates your understanding of secure, governed ML workflows.
Skills You’ll Gain
Preparing for the Red Hat OpenShift AI certification gives you hands-on expertise in areas like:
Deploying and managing OpenShift AI clusters
Using Jupyter notebooks and Python for model development
Managing GPU workloads
Integrating with Git repositories
Running pipelines for model training and deployment
Monitoring model performance with tools like Prometheus and Grafana
Understanding OpenShift concepts like pods, deployments, and persistent storage
Who Should Take the EX267 Exam?
This certification is ideal for:
Data Scientists who want to operationalize their models
ML Engineers working in hybrid cloud environments
DevOps Engineers bridging infrastructure and AI workflows
Platform Engineers supporting AI workloads at scale
Prerequisites: While there’s no formal prerequisite, it’s recommended you have:
A Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) or equivalent knowledge
Basic Python and machine learning experience
Familiarity with OpenShift or Kubernetes
How to Prepare
Here’s a quick roadmap to help you prep for the exam:
Take the RHODS Training: Red Hat offers a course—Red Hat OpenShift AI (EX267)—which maps directly to the exam.
Set Up a Lab: Practice on OpenShift using Red Hat’s Developer Sandbox or install OpenShift locally.
Learn the Tools: Get comfortable with Jupyter, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Git, S2I builds, Tekton pipelines, and Prometheus.
Explore Real-World Use Cases: Try deploying a sample model and serving it via an API.
Mock Exams: Practice managing user permissions, setting up notebook servers, and tuning ML workflows under time constraints.
Final Thoughts
The Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift AI certification is a strong endorsement of your ability to bring AI into the real world—securely, efficiently, and at scale. If you're serious about blending data science and DevOps, this credential is worth pursuing.
🎯 Whether you're a data scientist moving closer to DevOps, or a platform engineer supporting data teams, this certification puts you at the forefront of MLOps in enterprise environments.
Ready to certify your AI skills in the cloud-native era? Let OpenShift AI be your launchpad.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
🔧 Migrating from Jenkins to OpenShift Pipelines: 8 Steps to Success
As organizations modernize their CI/CD workflows, many are moving away from Jenkins towards Kubernetes-native solutions like OpenShift Pipelines (based on Tekton). This transition offers better scalability, security, and integration with GitOps practices. Here's a streamlined 8-step guide to help you succeed in this migration:
✅ Step 1: Audit Your Current Jenkins Pipelines
Begin by reviewing your existing Jenkins jobs. Understand the structure, stages, integrations, and any custom scripts in use. This audit helps identify reusable components and areas that need rework in the new pipeline architecture.
✅ Step 2: Deploy the OpenShift Pipelines Operator
Install the OpenShift Pipelines Operator from the OperatorHub. This provides Tekton capabilities within your OpenShift cluster, enabling you to create pipelines natively using Kubernetes CRDs.
✅ Step 3: Convert Jenkins Stages to Tekton Tasks
Each stage in Jenkins (e.g., build, test, deploy) should be mapped to individual Tekton Tasks. These tasks are containerized and isolated, aligning with Kubernetes-native principles.
✅ Step 4: Define Tekton Pipelines
Group your tasks logically using Tekton Pipelines. These act as orchestrators, defining the execution flow and data transfer between tasks, ensuring modularity and reusability.
✅ Step 5: Store Pipelines in Git (GitOps Approach)
Adopt GitOps by storing all pipeline definitions in Git repositories. This ensures version control, traceability, and easy rollback of CI/CD configurations.
✅ Step 6: Configure Triggers for Automation
Use Tekton Triggers or EventListeners to automate pipeline runs. These can respond to Git push events, pull requests, or custom webhooks to maintain a continuous delivery workflow.
✅ Step 7: Integrate with Secrets and ServiceAccounts
Securely manage credentials using Secrets, access control with ServiceAccounts, and runtime configs with ConfigMaps. These integrations bring Kubernetes-native security and flexibility to your pipelines.
✅ Step 8: Validate the CI/CD Flow and Sunset Jenkins
Thoroughly test your OpenShift Pipelines. Validate all build, test, and deploy stages across environments. Once stable, gradually decommission legacy Jenkins jobs to complete the migration.
🚀 Ready for Cloud-Native CI/CD
Migrating from Jenkins to OpenShift Pipelines is a strategic move toward a scalable and cloud-native DevOps ecosystem. With Tekton’s modular design and OpenShift’s robust platform, you’re set for faster, more reliable software delivery.
Need help with migration or pipeline design? HawkStack Technologies specializes in Red Hat and OpenShift consulting. Reach out for expert guidance! For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
20 project ideas for Red Hat OpenShift
1. OpenShift CI/CD Pipeline
Set up a Jenkins or Tekton pipeline on OpenShift to automate the build, test, and deployment process.
2. Multi-Cluster Management with ACM
Use Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management (ACM) to manage multiple OpenShift clusters across cloud and on-premise environments.
3. Microservices Deployment on OpenShift
Deploy a microservices-based application (e.g., e-commerce or banking) using OpenShift, Istio, and distributed tracing.
4. GitOps with ArgoCD
Implement a GitOps workflow for OpenShift applications using ArgoCD, ensuring declarative infrastructure management.
5. Serverless Application on OpenShift
Develop a serverless function using OpenShift Serverless (Knative) for event-driven architecture.
6. OpenShift Service Mesh (Istio) Implementation
Deploy Istio-based service mesh to manage inter-service communication, security, and observability.
7. Kubernetes Operators Development
Build and deploy a custom Kubernetes Operator using the Operator SDK for automating complex application deployments.
8. Database Deployment with OpenShift Pipelines
Automate the deployment of databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB) with OpenShift Pipelines and Helm charts.
9. Security Hardening in OpenShift
Implement OpenShift compliance and security best practices, including Pod Security Policies, RBAC, and Image Scanning.
10. OpenShift Logging and Monitoring Stack
Set up EFK (Elasticsearch, Fluentd, Kibana) or Loki for centralized logging and use Prometheus-Grafana for monitoring.
11. AI/ML Model Deployment on OpenShift
Deploy an AI/ML model using OpenShift AI (formerly Open Data Hub) for real-time inference with TensorFlow or PyTorch.
12. Cloud-Native CI/CD for Java Applications
Deploy a Spring Boot or Quarkus application on OpenShift with automated CI/CD using Tekton or Jenkins.
13. Disaster Recovery and Backup with Velero
Implement backup and restore strategies using Velero for OpenShift applications running on different cloud providers.
14. Multi-Tenancy on OpenShift
Configure OpenShift multi-tenancy with RBAC, namespaces, and resource quotas for multiple teams.
15. OpenShift Hybrid Cloud Deployment
Deploy an application across on-prem OpenShift and cloud-based OpenShift (AWS, Azure, GCP) using OpenShift Virtualization.
16. OpenShift and ServiceNow Integration
Automate IT operations by integrating OpenShift with ServiceNow for incident management and self-service automation.
17. Edge Computing with OpenShift
Deploy OpenShift at the edge to run lightweight workloads on remote locations, using Single Node OpenShift (SNO).
18. IoT Application on OpenShift
Build an IoT platform using Kafka on OpenShift for real-time data ingestion and processing.
19. API Management with 3scale on OpenShift
Deploy Red Hat 3scale API Management to control, secure, and analyze APIs on OpenShift.
20. Automating OpenShift Cluster Deployment
Use Ansible and Terraform to automate the deployment of OpenShift clusters and configure infrastructure as code (IaC).
For more details www.hawkstack.com
#OpenShift #Kubernetes #DevOps #CloudNative #RedHat #GitOps #Microservices #CICD #Containers #HybridCloud #Automation

0 notes
Text
Optimizing OpenShift for Enterprise-Scale Deployments: Best Practices & Pitfalls to Avoid
Introduction
As enterprises increasingly adopt containerization and Kubernetes-based platforms, OpenShift has emerged as a powerful solution for managing large-scale deployments. However, scaling OpenShift efficiently requires strategic planning, optimization, and adherence to best practices. In this blog, we explore key strategies to optimize OpenShift for enterprise-scale environments while avoiding common pitfalls.
Optimizing Cluster Performance
1. Resource Allocation & Autoscaling
Efficient resource allocation ensures that workloads run smoothly without unnecessary resource consumption. Utilize Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) to dynamically adjust resource usage based on workload demands. OpenShift’s Cluster Autoscaler can also help manage node scaling effectively.
2. Efficient Scheduling
Leverage OpenShift’s scheduler to distribute workloads intelligently across nodes. Utilize taints and tolerations, affinity rules, and resource quotas to optimize workload distribution and prevent resource contention.
3. Persistent Storage Management
For stateful applications, ensure proper use of OpenShift Container Storage (OCS) or other CSI-compliant storage solutions. Implement storage classes with appropriate policies to balance performance and cost.
Security Best Practices
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implement least privilege access using OpenShift’s RBAC policies. Define roles and bindings to restrict access to critical resources and avoid security loopholes.
2. Secure Container Images
Use Red Hat Quay or OpenShift’s built-in registry to store and scan container images for vulnerabilities. Automate security policies to prevent the deployment of unverified images.
3. Network Policies & Encryption
Enforce OpenShift Network Policies to limit pod-to-pod communication. Utilize mTLS encryption with OpenShift Service Mesh to secure inter-service communication.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
1. Tekton Pipelines for Kubernetes-Native CI/CD
Leverage Tekton Pipelines for a scalable and Kubernetes-native CI/CD workflow. Automate builds, tests, and deployments efficiently while maintaining pipeline security.
2. GitOps with ArgoCD
Use ArgoCD to implement GitOps workflows, ensuring continuous delivery with declarative configurations. This enhances traceability and allows seamless rollbacks in case of failures.
Networking & Service Mesh
1. OpenShift Service Mesh for Microservices
OpenShift Service Mesh, based on Istio, provides traffic management, observability, and security for microservices. Implement circuit breakers, rate limiting, and traffic mirroring to enhance reliability.
2. Ingress Controllers & Load Balancing
Optimize external access using HAProxy-based OpenShift Router or third-party ingress controllers like NGINX or Traefik. Ensure proper DNS configuration and load balancing for high availability.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
1. Configuration Drift
Use GitOps methodologies with ArgoCD to maintain consistency across environments and prevent manual misconfigurations.
2. Performance Bottlenecks
Monitor resource utilization with Prometheus & Grafana and implement proactive autoscaling strategies.
3. Compliance & Governance
Use OpenShift Compliance Operator to enforce industry standards like CIS Benchmarks and NIST guidelines across clusters.
Final Thoughts & Future Trends
Optimizing OpenShift for enterprise-scale deployments requires a balance of performance, security, and automation. As hybrid cloud adoption grows, OpenShift’s capabilities in multi-cloud and edge computing environments will continue to expand. By following these best practices and avoiding common pitfalls, organizations can achieve scalability, security, and operational efficiency with OpenShift.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
OpenShift DO380: Mastering Enterprise Kubernetes Scaling
As enterprises increasingly adopt containerized workloads, managing and scaling Kubernetes deployments efficiently becomes crucial. Red Hat’s OpenShift DO380: Red Hat OpenShift Administration III – Scaling Kubernetes Deployments in the Enterprise is designed to help IT professionals and DevOps engineers enhance their OpenShift expertise. This course focuses on performance tuning, cluster scaling, and advanced deployment strategies for large-scale Kubernetes applications.
Why OpenShift DO380 Matters
For organizations running business-critical applications on OpenShift, ensuring high availability, reliability, and optimal performance is non-negotiable. OpenShift DO380 equips administrators with the knowledge and skills to:
Optimize OpenShift clusters for better resource utilization.
Implement advanced deployment patterns for large-scale applications.
Manage workload automation using GitOps methodologies.
Ensure security and compliance in large enterprise environments.
Key Topics Covered in OpenShift DO380
1. Cluster Performance and Scalability
Understanding how to scale OpenShift efficiently is essential. DO380 covers:
Horizontal and vertical pod scaling.
Cluster autoscaling to handle variable workloads.
Optimizing resource allocation with CPU and memory tuning.
2. Advanced Deployment Strategies
Modern enterprises need flexible and robust deployment methodologies. In this course, you will learn:
Blue-Green and Canary deployments for seamless application updates.
Managing multi-cluster environments for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Using Helm and Operators for automated application deployment.
3. Security and Compliance
Securing Kubernetes workloads is critical in enterprise environments. DO380 teaches:
Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) and security policies.
Enhancing container security using OpenShift Security Context Constraints (SCCs).
Monitoring and auditing compliance with OpenShift tools.
4. GitOps and CI/CD Automation
Integrating DevOps practices with OpenShift enables automated and reliable deployments:
Leveraging ArgoCD for GitOps-based deployment automation.
Building resilient CI/CD pipelines using OpenShift Pipelines (Tekton).
Managing configurations with Kustomize and Helm charts.
Who Should Take OpenShift DO380?
This course is ideal for:
OpenShift administrators looking to enhance cluster performance and scalability.
DevOps engineers implementing automation in enterprise Kubernetes environments.
IT professionals responsible for managing large-scale OpenShift deployments.
Final Thoughts
Red Hat OpenShift DO380 is an essential course for IT professionals who want to scale, optimize, and secure Kubernetes workloads efficiently. By mastering these advanced OpenShift administration skills, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, resilience, and automation in their cloud-native deployments.
At HawkStack Technologies, we specialize in DevOps solutions and OpenShift consulting. If you’re looking to implement enterprise-grade Kubernetes deployments, get in touch with us today!
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Powering Up Your Workflow: OpenShift's Latest Developer Experience Enhancements
Introduction:
In today's fast-paced world of software development, a seamless and efficient workflow is paramount. Red Hat understands this, and the latest OpenShift updates reflect a strong commitment to empowering developers with enhanced tools and experiences. Let's delve into the key improvements that are streamlining the development process and boosting productivity.
Red Hat Developer Hub: Your Centralized Development Portal:
Imagine having a single pane of glass for all your development needs. That's the vision behind the Red Hat Developer Hub. This platform continues to evolve, providing developers with a centralized portal to access resources, documentation, and tools. Recent enhancements focus on:
Improved discoverability: Finding the right resources and templates is now easier than ever, reducing the time spent searching and increasing time spent coding.
Enhanced customization: Tailor your development environment to your specific needs, creating a personalized and efficient workspace.
Seamless integration: Red Hat Developer Hub integrates deeply with other OpenShift tools, creating a cohesive and streamlined experience.
OpenShift Dev Spaces: Cloud-Native Development at Your Fingertips:
OpenShift Dev Spaces brings the power of cloud-native development directly to your browser. Recent updates have focused on:
Faster startup times: Get your development environment up and running quicker, minimizing delays and maximizing productivity.
Enhanced debugging capabilities: Debugging your applications is now more intuitive and efficient, allowing you to identify and fix issues faster.
Improved performance: Experience a smoother and more responsive development environment, even with complex applications.
OpenShift Console: Refining the User Interface:
The OpenShift Console remains a crucial tool for developers, and recent improvements have focused on enhancing usability:
Tekton Pipelines Logs Enhancements: Working with Tekton pipelines is now more efficient with improved log viewing and analysis. Developers can quickly identify issues and track pipeline progress.
YAML Editing Improvements: Editing YAML files, a common task in Kubernetes environments, is now more streamlined with enhanced editing features and validation. This helps to reduce errors and improve configuration accuracy.
General UI/UX improvements: Red Hat is continuously refining the OpenShift console to make it more intuitive and user-friendly.
Podman Desktop: Bridging the Gap:
Podman Desktop is gaining traction as a powerful tool for container development, and recent updates are making it even more valuable.
Improved Kubernetes Integration: Podman Desktop continues to improve its integration with Kubernetes, making it easier to deploy and manage containerized applications.
Enhanced User Experience: The Podman Desktop team is focused on improving the overall user experience, making it easier to use for both new and experienced container developers.
Plugin Ecosystem: The plugin ecosystem is growing, allowing users to customize and extend the functionality of Podman Desktop.
Conclusion:
Red Hat's commitment to improving the developer experience is evident in the latest OpenShift updates. By focusing on tools like Red Hat Developer Hub, OpenShift Dev Spaces, the OpenShift Console, and Podman Desktop, Red Hat is empowering developers to build and deploy applications faster and more efficiently. Embrace these enhancements and unlock your full development potential with Red Hat OpenShift.
For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes