#side effects of dupilumab
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Atopy and Alopecia Areata: A Leading Pair

#atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata#atopic alopecia#side effects of dupilumab#dupilumab for alopecia#dupilumab for atopic dermatitis#dupilumab efficacy atopic dermatitis
0 notes
Text
Atopic Dermatitis Market Trends, Size, Share, and Growth Forecasts Through 2030 Across Key Regions
The global Atopic Dermatitis Market is experiencing dynamic growth, driven by a rising prevalence of the condition, increasing awareness among patients and healthcare providers, and significant innovation in treatment modalities. As a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin disorder, atopic dermatitis affects millions of individuals worldwide—most commonly infants and young children, though adult cases are also rising. This report outlines the key market drivers, challenges, and regional revenue projections influencing the future landscape of atopic dermatitis therapeutics.

Key Market Drivers
1. Rising Global Prevalence of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis has witnessed a significant increase in global prevalence over the past two decades. According to the World Allergy Organization, up to 20% of children and 3% of adults are affected by AD. Urbanization, environmental changes, and genetic predisposition are contributing to the rising burden, particularly in developed economies. The rising patient population directly supports growing demand for more effective and long-lasting treatments.
2. Advancements in Biologic Therapies
A major driver of market expansion is the growing pipeline and approval of biologic drugs. Dupilumab (Dupixent) by Sanofi and Regeneron has set a precedent by targeting IL-4 and IL-13 pathways, showing significant efficacy with minimal side effects. Several other biologics, including tralokinumab and lebrikizumab, are progressing through clinical trials. These therapies are transforming moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis management and creating new revenue streams.
3. Increased Awareness and Diagnosis
The growing awareness among patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals is boosting diagnosis rates. Campaigns by organizations such as the National Eczema Association and improved access to dermatological services have enhanced early diagnosis and timely intervention, especially in North America and Europe. Additionally, teledermatology has emerged as a valuable tool in expanding access to dermatologic care in underserved regions.
4. Rising Investments in Research and Development
Pharmaceutical companies are significantly investing in R&D to develop more targeted therapies, including JAK inhibitors, PDE4 inhibitors, and novel biologics. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and EMA have provided fast-track and orphan drug designations to accelerate the approval process for promising drugs. These initiatives are fostering a more competitive and innovative market.
Market Barriers and Challenges
1. High Cost of Biologics and Advanced Therapies
The high cost of biologic drugs remains a major barrier to market penetration, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Even in developed markets, access to advanced therapies may be limited due to reimbursement constraints or out-of-pocket expenses, discouraging both patients and providers from adopting newer treatments.
2. Limited Access in Emerging Economies
While the disease burden is rising globally, access to specialized dermatological care and novel treatments remains limited in regions such as Latin America, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa. Weak healthcare infrastructure, low awareness, and limited insurance coverage are major obstacles to treatment uptake in these markets.
3. Side Effects and Long-Term Safety Concerns
Although newer therapies show promise, concerns around the long-term safety profile of JAK inhibitors and immunomodulators persist. Adverse effects such as infections, liver enzyme abnormalities, and malignancy risk may limit widespread adoption and hinder physician confidence in prescribing certain agents.
4. Generic Competition and Patent Expiry
As key branded products begin to lose patent protection, generic competition is likely to increase. While this may benefit cost-conscious markets, it could challenge the revenue streams of established players unless offset by new product launches or label expansions.
Revenue Projection by Region
1. North America
North America currently dominates the global atopic dermatitis market, driven by high diagnosis rates, favorable reimbursement policies, and widespread adoption of biologics. The U.S. alone accounts for over 40% of global revenue due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and presence of major pharmaceutical players. The regional market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 9% through 2030.
2. Europe
Europe holds the second-largest share in the AD market, with countries like Germany, France, and the U.K. leading in biologics adoption. Regulatory support from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and strong public healthcare systems contribute to stable market growth. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 8% over the forecast period.
3. Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a high-growth market, driven by increasing awareness, expanding healthcare access, and the growing burden of dermatological disorders. Countries like Japan, South Korea, China, and India are seeing accelerated adoption of advanced therapies, albeit at varying paces due to affordability issues. The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 10–11% through 2030, with China likely to become a major contributor.
4. Latin America
Latin America remains an underpenetrated market due to limited access to biologics and inadequate healthcare funding. However, urbanization, better access to dermatologists, and slow but steady regulatory reforms are improving the outlook. Brazil and Mexico are expected to lead growth, with the regional market expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6%.
5. Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa represent the smallest share but offer untapped potential due to increasing disease awareness and investments in private healthcare infrastructure. Market growth is likely to be modest but steady, supported by expanding pharmaceutical distribution networks and international health partnerships.
Conclusion
The global atopic dermatitis market is poised for sustained growth over the next decade, fueled by innovations in biologics, better disease awareness, and expanding treatment access. However, barriers such as high therapy costs, regional disparities in healthcare access, and safety concerns will require strategic navigation. Regional markets such as Asia-Pacific and North America will remain key drivers of revenue, while companies that invest in patient-centric approaches, affordability, and R&D will be well-positioned to lead the evolving landscape.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Most Effective Eczema Treatment for Your Skin Type

Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. While there is no permanent cure, choosing the right eczema treatment for your specific skin type can help manage symptoms effectively.This guide will help you understand different eczema treatments and how to select the best one for your needs.
Understanding Eczema and Skin Types
Eczema affects people of all skin tones. The treatment plan shifts if you’re dry, oily, combination or have sensitive skin.Determining what skin type you have is an important step to get the best eczema treatment that works for you. Dry Skin

The leading cause of eczema flare-ups is dry skin. When skin becomes dry, it can no longer effectively protect and repair itself.Best Treatment Options:- Ceramide and hyaluronic acid moisturizing creams and ointments can be effective in restoring hydration. - Fragrance-free emollients supplement the skin barrier and reduce irritation. - Prescription corticosteroids may be required for severe cases. Oily Skin Eczema can form on oily skin, causing irritation and itchiness.Best Treatment Options:- Non-clogging, lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated without blocking pores. - Gel-based corticosteroids to calm inflammation without excess oil. - Antibacterial cleansers to prevent secondary infections. Combination Skin Combination skin needs a balanced approach to avoid triggering flare-ups in the oily and dry zones.Best Treatment Options:- Hydrating serums for dry patches. - Non-comedogenic oil-free moisturizers to help reduce pore clogging on oily T-zone. - Mild steroid creams to control inflammation. Sensitive Skin

Sensitive skin is overly reactive skin that is easily irritated by skincare products.Best Treatment Options:- Hypoallergenic and fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe irritation. - Colloidal oatmeal-based creams to reduce redness and itching. - Topical calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus) as steroid alternatives. Key Eczema Treatment Methods 1. Topical Treatments - Regular use of thick creams and ointments helps lock in moisture. - Corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and control severe flare-ups. - Non-steroidal creams: Options like pimecrolimus or tacrolimus help treat eczema without the side effects of steroids. 2. Medications for Severe Eczema - Antihistamines: Help relieve itching and prevent scratching. - Used for short-term relief of severe symptoms. - Such as dupilumab, are prescribed for chronic eczema that doesn’t respond to other treatments. 3. Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments - Aloe vera gel: Soothes itching and inflammation. - Coconut oil: Provides hydration and has antibacterial properties. - Yoga and meditation can help reduce flare-ups caused by stress. Choosing the Right Treatment: Factors to Consider

- Mild cases may only require moisturizers, while severe eczema may need prescription treatments. - Choose products suitable for your skin type to prevent further irritation. - Ingredients: Avoid allergens such as fragrances, alcohol, and sulfates. - Doctor’s Recommendation: Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. Conclusion Selecting the most effective eczema treatment for your skin type involves understanding your skin’s needs and choosing treatments that provide relief while minimizing irritation.Pick topical creams, topical medications, or natural alternatives to control your eczema. Whatever you choose—all of the devices here are great—commit to regular skincare maintenance for optimal results.If you deal with chronic eczema, call an eczema expert today. They can assist you in developing a personalized care regimen to find what’s most effective for your skin.
FAQ
What is the best treatment for eczema? The best eczema treatment includes moisturizing regularly, using topical corticosteroids for inflammation, and avoiding triggers like allergens and harsh soaps. In severe cases, prescription medications or biologic treatments may be needed. What is the main cause of eczema? Eczema is primarily caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It occurs due to a weakened skin barrier that makes the skin more prone to irritation, dryness, and infections. Is eczema a fungal infection? No, eczema is not a fungal infection. It is an inflammatory skin condition caused by immune system dysfunction, though fungal infections can sometimes worsen eczema symptoms. What is the 3-minute rule for eczema? The 3-minute rule for eczema recommends applying a moisturizer within 3 minutes after bathing to lock in moisture and prevent skin dryness, which helps reduce flare-ups. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Managing Urticaria: Latest Medical and Natural Remedies
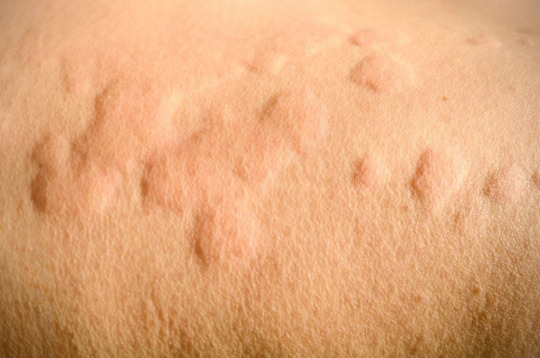
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts that appear suddenly on the skin. These welts can vary in size and may appear and fade repeatedly. For many, urticaria is a temporary issue, but for others, it can become a chronic problem affecting quality of life. Fortunately, both medical advancements and natural remedies offer effective ways to manage urticaria. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the latest treatment options.
What Causes Urticaria?
Urticaria occurs when the body releases histamine and other chemicals into the skin, often as an allergic response. Common triggers include:
Certain foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs)
Medications (e.g., antibiotics, NSAIDs)
Infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal)
Physical stimuli (pressure, temperature changes, sunlight)
Stress and autoimmune disorders
Latest Medical Treatments for Urticaria
1. Second-Generation Antihistamines
Modern antihistamines like cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine are the first-line treatment for urticaria. They are non-drowsy and can be taken daily to control symptoms.
2. Omalizumab (Xolair)
Omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody, is a game-changer for those with chronic spontaneous urticaria that doesn't respond to antihistamines. It works by targeting IgE antibodies involved in allergic responses.
3. Biologics and Immunosuppressants
In severe or resistant cases, cyclosporine or biologic drugs like dupilumab (approved for eczema but used off-label) may help reduce inflammation and immune overactivity.
4. Corticosteroids (Short-Term Use)
For acute flare-ups, short-term corticosteroid use can be effective. However, long-term use is discouraged due to serious side effects.
5. Allergen Immunotherapy
If a specific allergen is identified, allergen-specific immunotherapy can gradually desensitize the immune system.
Natural Remedies for Urticaria Relief
While not a replacement for medical care, natural remedies can provide symptom relief and reduce flare-ups:
1. Cold Compresses
Applying a cold compress to affected areas can reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
2. Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal soothes the skin and helps calm irritation. Add it to lukewarm bath water for a relaxing treatment.
3. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory and cooling properties. Apply directly to welts to soothe itching.
4. Turmeric
Known for its anti-inflammatory effects, turmeric can be consumed as a supplement or added to food to support immune health.
5. Probiotics
Improving gut health with probiotics may help regulate immune responses and reduce allergic reactions.
6. Vitamin D
Studies suggest that vitamin D supplementation can help reduce chronic urticaria symptoms in individuals who are deficient.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Urticaria
Identify and avoid triggers: Keep a diary to track food, medications, and environmental exposures.
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight clothing can aggravate skin irritation.
Manage stress: Stress is a known trigger; mindfulness, yoga, and therapy can help.
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush histamines from the body.
When to See a Doctor
If hives persist for more than six weeks, occur frequently, or are accompanied by symptoms like difficulty breathing or swelling of the lips or tongue, seek immediate medical attention. Chronic urticaria often requires a tailored treatment plan developed with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Managing urticaria involves a combination of medical urticaria treatment, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. With new therapies like biologics and a greater understanding of immune responses, individuals suffering from chronic hives have more options than ever before. If you’re struggling with recurring urticaria, consult a dermatologist or allergist for a personalized approach to relief.
0 notes
Text
Epidemiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Regional Insights and Global Trends by 2034

Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated disorder of the esophagus characterized by inflammation caused by the infiltration of eosinophils—a type of white blood cell—into the esophageal lining. This condition leads to symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, food impaction, heartburn, and chest pain, significantly affecting the quality of life of patients. EoE has been increasingly recognized as a major gastrointestinal disorder, with the number of diagnosed cases on the rise globally. The market for Eosinophilic Esophagitis treatments is expected to grow in response to the increasing prevalence, advancements in diagnostic techniques, and the introduction of novel therapies.
This article explores the market insights, epidemiology, and forecast for the Eosinophilic Esophagitis market, highlighting key trends, emerging treatments, and growth drivers up to 2034.
Market Insights
Increasing Diagnosis and Recognition: Eosinophilic esophagitis was once underdiagnosed, with many patients experiencing misdiagnoses for other gastrointestinal conditions. However, as awareness increases and diagnostic methods such as endoscopy with biopsy and serum eosinophil count become more widely available, diagnosis rates have surged. Eosinophil counts are now recognized as a key indicator for EoE, contributing to better identification of the condition.
Therapeutic Landscape: The treatment landscape for EoE is evolving, with both pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies employed. Current treatments typically focus on managing symptoms and reducing inflammation, with corticosteroids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and dietary management being commonly prescribed. However, challenges with long-term therapy and side effects have led to research into alternative therapies.
Topical Corticosteroids: Fluticasone and budesonide are used to treat inflammation in EoE. These drugs can be taken orally but are swallowed in a manner that targets the esophagus directly.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Though PPIs are more commonly used for acid reflux, they are sometimes effective for EoE patients, particularly in those where acid reflux and eosinophilic inflammation coexist.
Dietary Interventions: Avoidance of specific foods is often effective in managing EoE symptoms, with elimination diets (such as six-food elimination diet) showing promise for symptom reduction.
Emerging Therapies: The search for novel treatments is rapidly evolving, and multiple new therapies are expected to enter the market over the next decade. These include biologics and targeted therapies designed to modify the underlying immune mechanisms of EoE. Notable emerging treatments include:
Monoclonal Antibodies: Drugs targeting IL-4 and IL-13 (such as dupilumab) are showing promise in clinical trials, aiming to reduce eosinophilic inflammation by modulating the immune response.
Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: These are being explored as potential therapies for EoE, particularly for patients who are not responsive to conventional treatments.
Biologic Therapy: Other biologics, such as lebrikizumab and tezepelumab, are in advanced stages of clinical trials, targeting the key cytokines involved in eosinophil activation.
Market Expansion through Personalized Medicine: As understanding of the pathophysiology of EoE improves, the focus on personalized medicine is growing. Genomic, proteomic, and immunologic profiling of EoE patients can provide more precise treatment strategies tailored to individual responses. This shift toward precision therapies is expected to drive growth in the market, as patients benefit from treatments that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
Combination Therapies: The use of combination therapies, involving the integration of dietary interventions, topical steroids, and biologics, is being explored for more comprehensive management of EoE. Combining different therapeutic modalities may provide synergistic effects, especially for patients with severe or refractory disease.
Request for sample report @ Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market
Epidemiology
Eosinophilic esophagitis is increasingly recognized worldwide, though its prevalence varies by region. Historically, the disease was more common in developed countries, with a particularly high incidence in the United States, Europe, and Australia. Recent data suggests that EoE is becoming more recognized in developing regions as well, though it may still be underdiagnosed in some areas due to limited access to healthcare and diagnostic services.
Prevalence and Incidence: The prevalence of EoE in the United States is estimated to be between 55 and 75 cases per 100,000 individuals, with a higher incidence observed among children and young adults. The condition is more commonly seen in men than women, although recent studies suggest that gender disparity may be narrowing.
Age of Onset: The disease most commonly presents in adolescents and young adults, typically between the ages of 20-40, although it can occur at any age. It is also common in individuals with a history of other allergic conditions, such as asthma, eczema, and allergic rhinitis.
Geographic Variation: In North America and Europe, the rates of diagnosis and treatment are higher due to greater awareness and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, as global awareness grows, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, the number of diagnosed cases is expected to rise in these regions as well.
Market Forecast to 2034
The Eosinophilic Esophagitis market is expected to experience significant growth over the forecast period, driven by advancements in diagnostics, treatment options, and increased disease awareness. The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of approximately 6-8% from 2024 to 2034.
Several factors are contributing to this growth:
The introduction of biologic therapies and targeted treatments will revolutionize the management of EoE, particularly in patients with severe or refractory forms of the disease.
The growing availability of advanced diagnostic tools like endoscopic biopsy, biomarkers, and blood tests is expected to improve early diagnosis and patient outcomes.
Dietary therapies and patient support programs focused on lifestyle modification and adherence to treatment plans will contribute to better disease management, further driving market growth.
Increasing government funding and awareness programs for allergic diseases and esophageal disorders will contribute to market expansion.
The market is expected to reach USD 5-7 billion by 2034, with North America holding the largest share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. As the therapeutic pipeline advances, new biologics, combination therapies, and personalized treatments will play key roles in shaping the future of the EoE market.
Request for sample report @ Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market
Key Players in the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market
Several key players are involved in the development of therapies for eosinophilic esophagitis, including pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions. Some of the leading companies include:
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: Known for its work on dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4 and IL-13 for EoE treatment.
AstraZeneca: Involved in developing tezepelumab, which targets the epithelial thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) pathway in EoE patients.
Sanofi: Partnering with Regeneron to advance dupilumab for the treatment of EoE.
GlaxoSmithKline: Exploring benralizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting eosinophil trafficking.
Bristol-Myers Squibb: Involved in advancing immune-modulating biologics for EoE treatment.
Novartis: Developing therapies targeting eosinophilic pathways in EoE.
Request for sample report @ Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market
Conclusion
The eosinophilic esophagitis market is poised for substantial growth through 2034, driven by increased diagnosis, innovative therapies, and a growing understanding of the disease’s underlying mechanisms. The availability of biologic therapies, coupled with advancements in personalized medicine and diagnostic techniques, will transform how EoE is managed and treated, improving patient outcomes and significantly expanding the market. Continued investment in research and development, as well as global efforts to increase awareness, will be crucial in addressing the unmet needs in EoE treatment and providing better solutions for patients worldwide.
Latest Report Offered By DelveInsight: Benefits Of Robotics In Healthcare | Lewy Body Dementia | Energy Based Aesthetic Devices Market | Ependymoma Market | Fertility Monitoring Devices Market | Germ Cell Tumor Market | Hernia Repair Devices Market | Hot Flashes Market | Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market | Keloid Market | Orthopedic Power Devices Market | Pouchitis Market | Surgical Sealant Market | Transthyretin Amyloidosis Market | Vascular Graft Devices Market | Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer Market | Sinus Dilation Devices Market | Inguinal Hernia Market | Plaque Psoriasis Market | Plasmodium Vivax Malaria Market | Hdac Inhibitors Market | Peritoneal Dialysis Equipment Market | Adenosine Deaminase-severe Combined Immunodeficiency Market | Bone Resorption Market | Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Market
#Eosinophilic Esophagitis#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Forecast#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Companies#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Therapies#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Epidemiology#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Pipeline#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market Size#Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market Trends
0 notes
Text
Atopic Dermatitis Market: Trends, Growth, and Future Outlook
The Atopic Dermatitis Market Overview
The global Atopic Dermatitis market is poised for growth due to several factors, including increasing prevalence, advancements in treatment options, and greater awareness about the condition. The market can be segmented by drug type, route of administration, distribution channel, and geography.
By Drug Type:
Topical Treatments: These include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g., crisaborole), which are commonly prescribed to manage mild to moderate symptoms.
Systemic Treatments: Biologic drugs such as Dupilumab (Dupixent), which target specific pathways involved in inflammation, are gaining traction for moderate to severe AD. Systemic immunosuppressants and oral JAK inhibitors also offer alternative options.
Oral Medications: Oral antihistamines and corticosteroids are frequently used to control flare-ups and itching.
Emollients and Moisturizers: These are used for skin hydration, a key part of managing dry skin in AD patients.
By Route of Administration:
Topical: Topical drugs are preferred for treating mild to moderate AD and are available in creams, ointments, and lotions.
Injectable: Biologics, which are administered via injection, represent the latest advancement in treating severe cases of AD.
By Distribution Channel:
Hospital Pharmacies: These are critical distribution points, especially for more specialized treatments.
Retail Pharmacies: Widely accessible to consumers for over-the-counter treatments, like corticosteroids and emollients.
Online Pharmacies: Growing as a convenient alternative for purchasing over-the-counter and prescription medications.
Geography:
North America: Dominates the global market due to high awareness, favorable reimbursement policies, and access to advanced treatments.
Europe: The European market is expanding due to increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure and novel treatments.
Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing region, driven by rising awareness, improving healthcare infrastructure, and a growing middle class.
Key Drivers of Growth
Rising Prevalence: Atopic Dermatitis is increasingly common, particularly in industrialized countries. The prevalence of AD in children has surged in recent years, and the growing number of adult cases has further contributed to the expanding market.
Advancements in Treatment: The development of targeted biologic therapies, which specifically address the immune pathways involved in inflammation, has revolutionized the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. These biologics, such as Dupilumab (Dupixent), have garnered significant attention due to their ability to provide relief when traditional treatments fail.
Increased Awareness and Education: Healthcare campaigns, social media, and support groups have increased awareness of AD, leading to more people seeking medical advice and treatment. This awareness has led to more patients pursuing early diagnosis and intervention, expanding the market for both conventional and advanced therapies.
Improved Diagnostics: Enhanced diagnostic techniques and greater recognition of the condition among dermatologists have improved the diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis, enabling earlier and more effective treatment options.
Growing Investment in R&D: Pharmaceutical companies are heavily investing in research and development to create innovative treatments, such as biologics and novel oral drugs, to address the unmet needs of AD patients.
Market Challenges
Despite the optimistic growth prospects, the Atopic Dermatitis market faces some challenges:
High Treatment Costs: Biologic drugs, particularly those for moderate to severe AD, come with high price tags, which can be a barrier for patients in certain regions, especially in emerging economies.
Side Effects and Safety Concerns: While biologics and systemic treatments are effective, they may have side effects, and long-term safety data for some new treatments is still limited.
Access to Healthcare: In low-income regions, access to healthcare remains a significant challenge, hindering the adoption of newer, more effective treatments.
Compliance Issues: Due to the chronic nature of Atopic Dermatitis, patient adherence to long-term treatment regimens, including topical and systemic medications, can be inconsistent.
Emerging Trends in the Atopic Dermatitis Market
Biologic Drugs: Biologics are revolutionizing the treatment of AD, offering targeted, highly effective therapies. With the launch of new drugs, such as Tralokinumab (Adbry) and Lebrikizumab, the market is seeing a shift toward more personalized treatments.
Telemedicine: The rise of telemedicine allows dermatologists to consult with patients remotely, improving access to care for individuals in underserved regions.
Patient-Centered Care: There is a greater emphasis on holistic, individualized treatment approaches, combining pharmacological interventions with lifestyle and dietary recommendations.
Oral JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, like Upadacitinib (Rinvoq), are gaining attention as promising oral treatments for moderate-to-severe AD, offering convenience compared to biologics.
AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being explored to identify biomarkers for early diagnosis, predict disease flare-ups, and even personalize treatment plans.
The Future of the Atopic Dermatitis Market
The Atopic Dermatitis market is set for continued growth, driven by increasing awareness, rising patient numbers, and a growing pipeline of innovative treatments. The global market is expected to expand, with North America and Europe leading the charge, while the Asia-Pacific region promises significant potential due to improving healthcare infrastructure.
The next few years will likely witness a shift toward more personalized therapies, as precision medicine becomes an integral part of dermatology. As the demand for effective treatments grows, industry players must continue to innovate and overcome challenges related to treatment accessibility and affordability.
In conclusion, the Atopic Dermatitis market is undergoing transformation, presenting opportunities for pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and patients alike. With technological advancements, new treatment options, and greater patient awareness, the future of AD care looks brighter than ever.
For a detailed overview and more insights, you can refer to the full market research report by Mordor Intelligence
0 notes
Text
Eczema Clinical Trials: Progress and Promise in the Search for Better Treatments

Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, inflamed, itchy patches of skin that can become dry, cracked, and prone to infection. This condition can cause significant discomfort and disruption to everyday life, and for some, it leads to emotional and psychological distress due to its visibility and persistent nature. While treatments have evolved over the years, there remains a significant need for better, more effective, and safer options. Clinical trials are critical in this pursuit, offering insights into new therapies and a deeper understanding of the disease itself.
Understanding the Nature of Eczema
Before delving into the details of clinical trials, it’s essential to understand what eczema entails. Eczema is primarily a disorder of the immune system and skin barrier dysfunction. It causes the immune system to overreact to environmental triggers such as allergens, irritants, or stress, resulting in inflammation and itching. For some, eczema is a mild inconvenience, while for others, it becomes a severe, life-long condition requiring frequent medical intervention.
There are currently several types of treatments available, ranging from topical corticosteroids, emollients, and calcineurin inhibitors to more advanced systemic options like biologics. However, many patients fail to achieve full remission, or they experience side effects from existing medications. This gap in treatment options highlights the importance of continued research through clinical trials.
The Role of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a fundamental role in advancing medical research and bringing new treatments to market. They help determine the safety and effectiveness of new drugs, compare them to existing treatments, and explore new approaches to disease management. For eczema, clinical trials are indispensable in identifying innovative treatments that target the immune system, restore the skin barrier, or both.
The process of conducting a clinical trial is thorough and methodical, typically broken into several phases:
Phase I trials focus on assessing safety and dosage in a small group of healthy volunteers or patients.
Phase II trials expand the number of participants and focus on effectiveness and side effects.
Phase III trials involve even larger populations to confirm efficacy, monitor side effects, and compare the new treatment to standard therapies.
Phase IV trials occur after a treatment is approved, monitoring long-term effectiveness and potential risks in a larger population.
Clinical trials are often conducted by pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, or academic centers, working under the guidance of regulatory agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Recent Breakthroughs in Eczema Clinical Trials
Recent clinical trials have yielded several promising developments in the treatment of eczema, particularly through the use of biologic therapies. Biologics, which are drugs derived from living organisms, represent a new frontier in eczema treatment because they target specific molecules involved in the immune response.
One of the most significant advancements is the approval of dupilumab (Dupixent), a biologic drug that blocks certain proteins (IL-4 and IL-13) involved in the immune response that leads to eczema. Dupilumab has been approved for both adults and children with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and has shown remarkable results in reducing the severity and frequency of flare-ups. Clinical trials for dupilumab demonstrated significant improvement in skin clearance and reduction in itching, even for patients who had failed traditional treatments.
Another promising biologic in clinical trials is tralokinumab, an antibody that targets the IL-13 protein specifically. Tralokinumab has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve skin conditions in patients with atopic dermatitis. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant efficacy, with minimal side effects, offering an alternative for patients who may not respond to or tolerate other treatments.
Other innovative approaches being explored in clinical trials include Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. JAK inhibitors, such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, work by blocking specific pathways that lead to inflammation. These drugs have shown promising results in clinical trials, offering rapid relief of symptoms and a potential alternative to biologics.
Challenges and Considerations in Eczema Clinical Trials
Despite the encouraging progress, conducting clinical trials for eczema presents unique challenges. One major issue is the heterogeneity of the condition. Eczema manifests differently in each individual, with varying triggers, severity, and response to treatment. This variability can make it difficult to develop standardized treatments and test them in a diverse patient population.
Additionally, eczema clinical trials must carefully consider long-term safety. Since eczema is a chronic condition, many treatments, especially systemic ones like biologics or JAK inhibitors, may need to be taken over extended periods. Monitoring long-term effects, including immune suppression and risk of infections, is crucial.
Another challenge is recruitment. Although eczema is widespread, recruiting patients for clinical trials can be difficult. Many patients, particularly those with mild or moderate eczema, may be satisfied with existing treatments and may not be willing to participate in trials for experimental drugs. For those with more severe conditions, the burden of travel, frequent doctor visits, and time away from work or school can be prohibitive.
The Future of Eczema Treatment
While the road to better eczema treatments is not without obstacles, the future looks promising. With new biologics, small molecules, and topical agents in the pipeline, the landscape of eczema treatment is evolving rapidly. Personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to an individual’s specific immune profile or genetic makeup, may also play a more significant role as researchers learn more about the molecular mechanisms behind eczema.
Patient advocacy groups and international eczema research networks continue to push for more robust research, more inclusive trials, and faster development of effective therapies. For patients living with eczema, the ongoing clinical trials offer hope that safer, more effective treatments are on the horizon, improving their quality of life and reducing the burden of this chronic skin condition.
Conclusion
Clinical trials are at the heart of progress in eczema treatment, offering hope to patients who struggle with the limitations of current therapies. The breakthroughs achieved so far, particularly with biologics like dupilumab and emerging treatments such as JAK inhibitors, represent a significant shift in how eczema is managed. As research continues and more patients participate in clinical trials, the future of eczema treatment looks brighter, with the potential to revolutionize care for millions worldwide.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Pharma and Nutraceutical Synergy: Elevate Your Skin Health with Holistic Dermatology Solutions
In the realm of skincare, a holistic approach that integrates both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical solutions offers a powerful pathway to optimal skin health. At A.S. Pharmaceuticals, we believe that combining the precision of pharmaceutical treatments with the benefits of nutraceuticals can provide comprehensive care for your skin. This integrated strategy not only addresses immediate concerns but also supports long-term skin wellness. In this blog, we will delve into the benefits of this synergistic approach and explore how it can transform your skincare routine.
1. The Concept of Holistic Dermatology
Holistic dermatology is an approach that treats the skin as part of the whole body system. It considers both external treatments and internal support to promote overall skin health. By blending pharmaceutical treatments with nutraceuticals, we aim to address the underlying causes of skin issues while also managing visible symptoms.
Pharmaceutical Treatments involve scientifically proven medications and therapies designed to target specific skin conditions. These include topical treatments, systemic medications, and advanced therapies.
Nutraceuticals are dietary supplements that offer additional support to skin health. They include vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds that nourish the skin from within, enhancing its function and resilience.
2. The Benefits of Combining Pharma and Nutraceuticals
1. Enhanced Efficacy:
When used together, pharmaceutical treatments and nutraceuticals can complement each other, leading to enhanced overall efficacy. Pharmaceuticals may directly target symptoms, while nutraceuticals support systemic health and enhance the skin's ability to respond to treatment.
2. Comprehensive Skin Health:
Combining these approaches allows for a more comprehensive strategy that addresses both external and internal factors affecting skin health. Pharmaceuticals tackle acute issues, while nutraceuticals improve long-term skin health and support the body's natural repair processes.
3. Reduced Side Effects:
Integrating nutraceuticals can often reduce the need for higher doses of pharmaceuticals, potentially minimizing side effects. Nutraceuticals can support the skin's repair mechanisms, making it easier to manage skin conditions with lower pharmaceutical dosages.
4. Improved Skin Resilience:
Nutraceuticals enhance skin resilience by providing essential nutrients that support cellular function and reduce inflammation. This can lead to more durable and sustained improvements in skin health.
3. Key Pharmaceutical Treatments for Skin Health
1. Topical Treatments:
Topical Corticosteroids: Effective for reducing inflammation and managing symptoms of conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Available in various strengths to address different severities.
Topical Retinoids: These treatments, including tretinoin and adapalene, are used for acne and signs of aging. They promote cell turnover and improve skin texture.
Topical Antifungals: Address fungal infections like ringworm and athlete's foot with medications such as clotrimazole and ketoconazole.
2. Oral Medications:
Antibiotics: Prescribed for bacterial skin infections and severe acne. Common examples include doxycycline and minocycline.
Oral Retinoids: Used for severe acne and chronic skin conditions that are resistant to topical treatments. Isotretinoin is a well-known oral retinoid.
Systemic Corticosteroids: Provide relief for severe inflammation and flare-ups. Reserved for short-term use due to potential side effects.
3. Advanced Therapies:
Biologics: Target specific immune pathways involved in chronic conditions like psoriasis and eczema. Medications such as dupilumab offer significant relief for severe cases.
Phototherapy: Uses controlled ultraviolet light to treat conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo, reducing symptoms and improving skin appearance.
4. Essential Nutraceuticals for Skin Health
1. Vitamins:
Vitamin C: An antioxidant that protects the skin from oxidative stress and supports collagen synthesis, leading to brighter and more youthful skin.
Vitamin E: Helps to protect skin cells from damage and enhances hydration and repair.
Vitamin D: Plays a role in skin cell growth and repair, and can be beneficial for managing conditions like psoriasis.
2. Minerals:
Zinc: Supports skin healing, reduces inflammation, and regulates oil production, making it beneficial for acne-prone skin.
Selenium: Provides antioxidant protection and supports overall skin health.
3. Essential Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil and flaxseed oil, omega-3s reduce inflammation and support skin hydration, helping with conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Evening Primrose Oil: Rich in gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), which improves skin elasticity and reduces inflammation.
4. Herbal Extracts:
Green Tea Extract: Contains polyphenols that offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits, supporting skin health and reducing signs of aging.
Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can help manage conditions associated with inflammation, such as acne and eczema.
5. Integrating Pharma and Nutraceuticals into Your Routine
1. Consultation with Professionals:
Before starting any new treatment or supplement, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider. They can help tailor a regimen that incorporates both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical options based on your skin’s specific needs.
2. Balanced Routine:
Develop a skincare routine that includes both pharmaceutical treatments and nutraceuticals. For instance, use topical medications for immediate issues while taking supplements to support overall skin health.
3. Monitor and Adjust:
Keep track of your skin’s response to the combined treatments. Regular follow-ups with your dermatologist can help fine-tune your regimen and ensure that you are getting the best results.
4. Quality Matters:
Choose high-quality nutraceuticals from reputable sources to ensure effectiveness and safety. Likewise, ensure that pharmaceutical treatments are prescribed by a qualified healthcare provider.
6. Personalized Care at A.S. Pharmaceuticals
At A.S. Pharmaceuticals, we are dedicated to offering personalized care that integrates the best of both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical approaches. Our team of dermatologists and skincare experts works with you to create a customized treatment plan that addresses your unique skin concerns and promotes optimal health.
Consultation Services: We provide comprehensive consultations to assess your skin condition and recommend a tailored combination of pharmaceutical treatments and nutraceuticals.
Ongoing Support: Our team offers continuous support and guidance to help you navigate your skincare routine and achieve your skin health goals.
Educational Resources: We provide valuable information to help you understand how to effectively combine pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals for enhanced skin health.
Integrating pharmaceutical treatments with nutraceuticals offers a holistic approach to skincare that addresses both immediate and long-term needs. At A.S. Pharmaceuticals, we are committed to helping you achieve optimal skin health through this synergistic approach. Explore our range of products and consult with our experts to discover how combining pharma and nutraceuticals can elevate your skincare routine. Visit our website to learn more and take the first step towards healthier, more radiant skin.

0 notes
Text
The demand for Asthma Therapeutics was valued at USD 26184.20 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 40620.29 million in 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.00% between 2024 and 2032.Asthma, a chronic respiratory disease characterized by airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction, affects millions worldwide. The growing prevalence of asthma, coupled with increasing awareness of the disease and advancements in treatment options, is driving the global asthma therapeutics market. This article delves into the market's current landscape, key trends, growth drivers, and future outlook.
Browse the full report at https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/global-asthma-therapeutics-market
Market Overview
The global asthma therapeutics market is a rapidly evolving sector, fueled by the rising number of asthma patients, innovations in drug delivery systems, and a growing emphasis on personalized medicine. According to market research, the asthma therapeutics market was valued at approximately USD 20 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over USD 30 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-7%. The market's expansion is attributed to an increase in environmental pollution, lifestyle changes, and genetic predispositions that contribute to the disease's rising incidence.
Key Market Segments
The asthma therapeutics market is segmented based on drug class, route of administration, and distribution channels. The major drug classes include:
1. Bronchodilators: These medications, including short-acting beta agonists (SABAs) and long-acting beta agonists (LABAs), help relax airway muscles and are often used for quick relief during asthma attacks. 2. Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers are the most commonly used anti-inflammatory drugs. They help reduce airway inflammation, providing long-term control of asthma symptoms. 3. Biologics: Targeting specific components of the immune system, biologics are increasingly popular for treating severe asthma. Examples include omalizumab, mepolizumab, and dupilumab, which have shown significant effectiveness in reducing asthma exacerbations.
4. Combination Drugs: These include a combination of bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory agents, offering comprehensive management of asthma symptoms.
Route of Administration
Asthma drugs are primarily administered via inhalers, which provide direct delivery of medication to the lungs. Inhalers are preferred due to their rapid onset of action and lower systemic side effects compared to oral medications. Other routes include oral tablets, injectables, and nebulizers, which are used depending on the severity of the condition and patient preference.
Distribution Channels
The distribution of asthma therapeutics occurs through hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacies. With the rise of e-commerce, online pharmacies have gained popularity, offering patients convenience and often competitive pricing.
Key Trends Driving the Market
1. Advancements in Inhaler Technology: The development of smart inhalers equipped with sensors that monitor medication usage and provide feedback to patients is revolutionizing asthma management. These inhalers help improve adherence to treatment and optimize drug delivery, leading to better patient outcomes.
2. Personalized Medicine: With advances in genetic research, there is a growing focus on personalized asthma treatment. Biologics, for instance, are tailored to target specific pathways involved in severe asthma, offering a more effective approach than traditional therapies.
3. Rise of Biologics: Biologics have emerged as game-changers in asthma therapeutics, particularly for patients with severe, refractory asthma. These drugs target specific immune pathways, reducing inflammation and decreasing the frequency of asthma attacks.
4. Growing Awareness and Diagnosis: Increased awareness of asthma symptoms and improved diagnostic techniques are leading to earlier detection and treatment. Governments and health organizations are conducting awareness campaigns, further boosting the market.
Challenges
Despite the positive growth trajectory, the asthma therapeutics market faces challenges, such as the high cost of biologics, side effects associated with long-term use of corticosteroids, and limited access to advanced therapies in low-income regions. Moreover, the lack of adherence to prescribed medications remains a significant issue, affecting treatment outcomes.
Future Outlook
The future of the asthma therapeutics market looks promising, with ongoing research and development focusing on novel drug formulations, improved drug delivery systems, and gene therapy. The integration of digital health tools, such as mobile apps that track symptoms and medication use, will also enhance asthma management. Moreover, the expanding market presence of biosimilars is expected to make advanced therapies more affordable, further driving market growth.
Key Players
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
GSK plc
Merck & Co., Inc.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
AstraZeneca plc
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Sanofi S.A.
Koninklijke Philips N.V.
Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
Covis Pharma B.V.
Segmentation
By Drug Class
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS)
Muscle Relaxants
Combination Therapies (ICS/LABAs)
By Drug Class
Combination Therapies (ICS/LABAs)
Long-Acting Beta Agonists (LABAs)
Short-Acting Beta Agonists (SABAs)
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS)
Oral And Intravenous Corticosteroids
Leukotriene Modifiers
Other Drug Classes
By Treatment Type
Long-Term Asthma Control Drug Class
Quick-Relief (Rescue) Drug Class
By Route of Administration
Topical
Oral
Injectables
By Distribution Channel
Brick & Mortar
Hospital Pharmacies
E-Commerce
By End-use
Hospitals & Clinics
Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Homecare Settings
By Region
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
France
UK
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
South-east Asia
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
GCC Countries
South Africa
Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Browse the full report at https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/global-asthma-therapeutics-market
About Us:
Credence Research is committed to employee well-being and productivity. Following the COVID-19 pandemic, we have implemented a permanent work-from-home policy for all employees.
Contact:
Credence Research
Please contact us at +91 6232 49 3207
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
The atopic dermatitis market size was valued at USD 9.1 Billion in 2023 is expected to reach at a CAGR of 8.3%.
The atopic dermatitis market size was valued at USD 9.1 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach a market size of USD 18.6 Billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 8.3%.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects people of all ages, but it is particularly common in children. The market for atopic dermatitis treatments has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness, growing prevalence of the condition, and advancements in medical technology.
Market players are focusing on developing innovative therapies to address the unmet needs of patients, including improved efficacy, reduced side effects, and convenient administration routes.

Recent developments in the atopic dermatitis market include:
Biologic Therapies: The emergence of biologic therapies, such as dupilumab, has revolutionized the treatment landscape for atopic dermatitis. These therapies target specific pathways involved in the inflammatory response, providing effective relief for moderate to severe cases.
Topical Treatments: Pharmaceutical companies are investing in the development of novel topical treatments with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients, particularly those with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
Oral Medications: There is ongoing research and development of oral medications for atopic dermatitis, including Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. These drugs work by targeting the immune system’s response, offering an alternative treatment option for patients who may not respond to or tolerate other therapies.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy is emerging as a potential future treatment option for atopic dermatitis. Researchers are exploring the use of gene-editing techniques to target and modify genes associated with the condition, offering the possibility of long-term remission or even cure.
Top Companies are:
· Pfizer Inc.
· AbbVie Inc.
· Sanofi
· GALDERMA LABORATORIES, L.P.
· Eli Lilly and Company (Dermira)
· Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
· LEO Pharma Inc.
· Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
· Novartis AG
· Incyte Corporation
Market Segmentations:
Regional Analysis:
By Drug Class (2024–2032)
· Corticosteroids
· Calcineurin Inhibitors
· PDE4 Inhibitors
· Biologics
· Others
By Route of Administration (2024–2032)
· Topical
· Injectable
· Oral
By Age Group (2024–2032)
· Pediatric
· Adult
Key highlights of the report include:
1. The report delivers thorough Market analysis, furnishing valuable insights to guide strategic decision-making.
2. The comprehensive research outlined in the study enhances the depth of your presentations and marketing strategies.
3. By offering crucial insights into key market competitors, the study empowers businesses with a strategic edge.
4. It delivers a precise assessment of evolving market dynamics, ensuring readers stay abreast of the latest industry trends.
5. With meticulous breakdowns of various market niches, the report facilitates informed decision-making processes.
0 notes
Text
How Do Biologics Work for Atopic Dermatitis?
Millions of adults suffer from a form of eczema known as atopic dermatitis. Dallas, TX’s Dermatology Office of Dr. Ellen Turner explains that this condition is characterized by inflamed, itchy, and often painful skin lesions. These commonly occur on areas such as the elbows, knees, hands, feet, and face. Some of the other common symptoms associated with this disease are red or dry patches of skin, rashes that may ooze or bleed when you scratch them, and thickening or hardening of the skin. Moderate atopic dermatitis will affect around 10 percent of the surface area of the body, while severe atopic dermatitis will affect around 30 to 40 percent or more.
Double board-certified dermatologist Dr. Ellen Turner says, “Managing atopic dermatitis can be challenging, but there are various treatment options available to provide relief and improve the quality of life for those who suffer from this chronic inflammatory skin condition. Although it isn’t possible to cure eczema, certain treatment methods—such as a good skin care plan, trigger management, and topical medications—can help you to manage it. In recent years, biologic therapies have emerged as a promising treatment option for a variety of conditions such as atopic dermatitis. It’s likely that more biologics for this disease may be developed in the future.”
In this article, we will explore biologics and how they work for treating eczema.
What Are Biologics?
Biologics are highly targeted, breakthrough medications that are systemic, meaning they work throughout the body. One of the causes of atopic dermatitis is an overactive immune system that releases inflammatory molecules called cytokines when irritants are detected. Biologics work on the specific molecules that trigger inflammation as a way to provide relief from itching and help lead to clearer skin. This is opposed to other types of medications for atopic dermatitis, which simply lower inflammation in the body in a broad manner.
Patients who have a moderate to severe form of the disease and who aren’t responding well to other treatments may be good candidates for FDA-approved biologics, which are pills taken orally or injectables that patients can administer themselves and are available as prefilled syringes or pens. You can be taught how to give yourself these injections at home.
Another advantage of these treatments is that because they don’t suppress the immune system more broadly like immunosuppressants would, side effects are less likely. It is also believed that patients not likely be at risk of infection.
Individual results can vary, but the majority of patients will notice improvements within around four weeks. In most cases, this will be a continuous treatment, since it can’t cure the condition—but it will provide relief while you are taking it
Some examples of biologics include:
Dupilumab (Dupixent®): This is a prescription medication for adults and children aged six months and older that is given under the skin via injection for moderate to severe eczema.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq®): Rinvoq® is a pill that can be taken once a day to regulate an overactive immune system. It’s a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that blocks signals in the cells that trigger inflammation.
Which Other Treatments Are Effective for Atopic Dermatitis?
In addition to biologics, there are many conventional treatments that are used for atopic dermatitis. These include:
Emollients and Moisturizers
The cornerstone of managing atopic dermatitis is to maintain the skin's moisture. Applying emollients and moisturizers regularly can help prevent dryness and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are widely used to reduce inflammation and itching. They come in various strengths, with milder options suitable for the face and more potent formulations for other areas of the body. Long-term use of strong corticosteroids should be monitored closely by a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help relieve itching, but they are not a primary treatment for atopic dermatitis. They are often used in conjunction with other therapies to provide symptom relief.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy can be effective in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. It helps reduce inflammation and itching, but it requires regular sessions under the supervision of a dermatologist.
For more advice on the best treatments for atopic dermatitis, contact the Dallas, TX-based Dermatology Office of Dr. Ellen Turner. Call (214) 373-7546 or submit a contact form to request a consultation.
0 notes
Text
How Do You Treat Prurigo Nodularis? By Dr. Sunil Skin Specialist Hyderabad
Introduction:
Prurigo nodularis is a challenging and often distressing skin condition characterized by the development of itchy, hard, raised nodules on the skin's surface. Dr. Sunil, a leading skin specialist in Hyderabad, provides valuable insights into the treatment options available for prurigo nodularis to help alleviate symptoms and improve the patient's quality of life.
1. Topical Steroids:
Mild cases of prurigo nodularis may respond to topical corticosteroid creams or ointments. These can help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. However, long-term use of potent topical steroids should be carefully monitored to avoid side effects.
2. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
Calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus might be utilized as an option in contrast to steroids, especially in delicate regions or when long-haul steroid use isn't prudent. These drugs assist with stifling the resistant reaction in the skin.
3. Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
Phototherapy involves exposing the affected skin to controlled amounts of UVB or UVA light. This treatment can help reduce itching and inflammation in some cases.
4. Oral Antihistamines:
Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antihistamines can help alleviate itching and improve sleep. Non-drowsy options are available for daytime use.
5. Capsaicin Cream:
Topical capsaicin cream, derived from chili peppers, can be applied to prurigo nodularis nodules. It works by desensitizing nerve endings in the skin and may provide relief from itching.
6. Moisturizers:
Regular use of emollient moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching and irritation.
7. Topical Anesthetics:
Creams or ointments containing topical anesthetics, such as pramoxine, can provide temporary relief from itching and discomfort.
8. Oral Medications:
In more severe cases, oral medications may be necessary. These may include:
Oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching (short-term use).
Immune-suppressing medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate to control the immune response.
Opioid receptor antagonists like naltrexone to reduce itching.
9. Psychological Support:
Prurigo nodularis can have a significant impact on a patient's mental health due to chronic itching and discomfort. Psychiatric or psychological support may be beneficial to address the emotional toll of the condition.
10. Avoid Trigger Factors:
Identifying and avoiding trigger factors, such as specific allergens or irritants, can help prevent flare-ups.
11. Biologic Therapies:
In some cases, biologic therapies like dupilumab, which target specific immune system components, may be considered for treatment.
12. Cryotherapy or Excision:
In select cases, individual nodules may be treated with cryotherapy (freezing) or surgical excision to provide relief.
It's essential for individuals with prurigo nodularis to work closely with a dermatologist or skin specialist like Dr. Sunil to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the severity of their condition, medical history, and individual needs. Treatment approaches may vary, and a combination of therapies may be necessary to effectively manage the condition and improve the patient's quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments and ongoing care are essential for long-term management.
To know more information about Skin Specialist Hyderabad Visit: https://sowmyaskinclinic.com/skin-care/
0 notes
Text
Allergy Care Market Growth: Innovations Driving Global Expansion in Allergy Diagnostics and Treatments
Introduction
The global allergy care market is experiencing significant growth, propelled by a surge in allergic conditions and advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies. With over 20% of the global population affected by allergies, the demand for effective diagnostics and treatments has never been higher. Innovations in biologics, immunotherapy, digital health, and personalized medicine are transforming allergy care, offering new opportunities for market expansion and improved patient outcomes.

Biologic Therapies: A New Frontier in Allergy Treatment
Biologic therapies have emerged as a groundbreaking approach in managing severe allergic conditions. Monoclonal antibodies, such as omalizumab (Xolair), have shown significant promise in treating multiple food allergies by targeting immunoglobulin E (IgE), a key antibody involved in allergic reactions. Recent studies indicate that omalizumab can increase tolerance to allergens like peanuts, offering relief to patients with multiple food allergies .
Similarly, dupilumab (Dupixent), initially approved for eczema and asthma, is being explored for its potential to reverse severe allergies. These biologics represent a shift towards personalized medicine, addressing the underlying mechanisms of allergic responses and offering long-term relief .
Advancements in Immunotherapy: Enhancing Patient Compliance
Traditional allergen immunotherapy, involving subcutaneous injections, often requires prolonged treatment durations and frequent clinic visits. Emerging delivery methods aim to enhance patient compliance and convenience:
Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT): Administered as tablets or drops under the tongue, SLIT offers a non-invasive alternative with fewer side effects, making it suitable for children and individuals with severe allergies .
Intralymphatic Immunotherapy (ILIT): A novel approach involving direct allergen injections into lymph nodes, ILIT requires fewer sessions and has shown promising results in reducing allergic symptoms .
Innovative Delivery Platforms: Companies like Intrommune Therapeutics are developing unique delivery systems, such as toothpaste-based immunotherapy, to simplify administration and improve adherence .
Innovations in Allergy Diagnostics: Precision and Accessibility
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective allergy management. Recent advancements in diagnostic technologies are enhancing precision and accessibility:
Component-Resolved Diagnostics (CRD): CRD enables the identification of specific allergenic proteins responsible for allergic reactions, allowing for precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plans .
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI-driven platforms are now being used to analyze patient data, predict allergy risks, and recommend tailored treatments, improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency .
At-Home and Point-of-Care Testing: The development of at-home testing kits and point-of-care devices is making allergy diagnostics more accessible, especially in remote or underserved areas .
Digital Health and Telemedicine: Expanding Access to Allergy Care
The integration of digital health solutions is revolutionizing allergy care by enhancing patient access and engagement:
Telemedicine Platforms: Virtual consultations allow patients to receive expert allergy care without the need for in-person visits, increasing convenience and reducing barriers to access .
Mobile Health Applications: Apps for symptom tracking, medication reminders, and educational resources empower patients to manage their allergies proactively .
Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and remote monitoring tools enable continuous tracking of environmental exposures and physiological responses, facilitating timely interventions .
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to Individual Needs
Advances in genomics and biotechnology are paving the way for personalized medicine in allergy treatment. By analyzing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, healthcare providers can develop tailored treatment plans that enhance efficacy and reduce adverse effects .
Personalized approaches are particularly beneficial for patients with complex or multiple allergies, as they allow for targeted interventions that address specific triggers and immune responses.
Market Expansion in Emerging Regions
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, present significant growth opportunities due to increasing allergy prevalence, urbanization, and improved healthcare infrastructure. Factors contributing to market expansion include:
Rising Awareness: Educational initiatives and increased public awareness about allergic diseases are driving demand for diagnostic and therapeutic services .
Healthcare Investments: Governments and private sectors are investing in healthcare infrastructure, facilitating access to allergy care services .
Local Manufacturing and Distribution: Establishing local production facilities and distribution networks can reduce costs and improve the availability of allergy care products .
Conclusion
The allergy care market is poised for significant growth, driven by advancements in biologics, immunotherapy, diagnostics, digital health, and personalized medicine. These innovations are transforming allergy management, offering more effective, convenient, and patient-centered solutions. As awareness and demand continue to rise globally, particularly in emerging markets, stakeholders in the allergy care industry have the opportunity to expand their reach and improve patient outcomes worldwide.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Most Effective Eczema Treatment for Your Skin Type

Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. While there is no permanent cure, choosing the right eczema treatment for your specific skin type can help manage symptoms effectively.This guide will help you understand different eczema treatments and how to select the best one for your needs.
Understanding Eczema and Skin Types
Eczema affects people of all skin tones. The treatment plan shifts if you’re dry, oily, combination or have sensitive skin.Determining what skin type you have is an important step to get the best eczema treatment that works for you. Dry Skin

The leading cause of eczema flare-ups is dry skin. When skin becomes dry, it can no longer effectively protect and repair itself.Best Treatment Options:- Ceramide and hyaluronic acid moisturizing creams and ointments can be effective in restoring hydration. - Fragrance-free emollients supplement the skin barrier and reduce irritation. - Prescription corticosteroids may be required for severe cases. Oily Skin Eczema can form on oily skin, causing irritation and itchiness.Best Treatment Options:- Non-clogging, lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated without blocking pores. - Gel-based corticosteroids to calm inflammation without excess oil. - Antibacterial cleansers to prevent secondary infections. Combination Skin Combination skin needs a balanced approach to avoid triggering flare-ups in the oily and dry zones.Best Treatment Options:- Hydrating serums for dry patches. - Non-comedogenic oil-free moisturizers to help reduce pore clogging on oily T-zone. - Mild steroid creams to control inflammation. Sensitive Skin

Sensitive skin is overly reactive skin that is easily irritated by skincare products.Best Treatment Options:- Hypoallergenic and fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe irritation. - Colloidal oatmeal-based creams to reduce redness and itching. - Topical calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus) as steroid alternatives. Key Eczema Treatment Methods 1. Topical Treatments - Regular use of thick creams and ointments helps lock in moisture. - Corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and control severe flare-ups. - Non-steroidal creams: Options like pimecrolimus or tacrolimus help treat eczema without the side effects of steroids. 2. Medications for Severe Eczema - Antihistamines: Help relieve itching and prevent scratching. - Used for short-term relief of severe symptoms. - Such as dupilumab, are prescribed for chronic eczema that doesn’t respond to other treatments. 3. Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments - Aloe vera gel: Soothes itching and inflammation. - Coconut oil: Provides hydration and has antibacterial properties. - Yoga and meditation can help reduce flare-ups caused by stress. Choosing the Right Treatment: Factors to Consider

- Mild cases may only require moisturizers, while severe eczema may need prescription treatments. - Choose products suitable for your skin type to prevent further irritation. - Ingredients: Avoid allergens such as fragrances, alcohol, and sulfates. - Doctor’s Recommendation: Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. Conclusion Selecting the most effective eczema treatment for your skin type involves understanding your skin’s needs and choosing treatments that provide relief while minimizing irritation.Pick topical creams, topical medications, or natural alternatives to control your eczema. Whatever you choose—all of the devices here are great—commit to regular skincare maintenance for optimal results.If you deal with chronic eczema, call an eczema expert today. They can assist you in developing a personalized care regimen to find what’s most effective for your skin.
FAQ
What is the best treatment for eczema? The best eczema treatment includes moisturizing regularly, using topical corticosteroids for inflammation, and avoiding triggers like allergens and harsh soaps. In severe cases, prescription medications or biologic treatments may be needed. What is the main cause of eczema? Eczema is primarily caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It occurs due to a weakened skin barrier that makes the skin more prone to irritation, dryness, and infections. Is eczema a fungal infection? No, eczema is not a fungal infection. It is an inflammatory skin condition caused by immune system dysfunction, though fungal infections can sometimes worsen eczema symptoms. What is the 3-minute rule for eczema? The 3-minute rule for eczema recommends applying a moisturizer within 3 minutes after bathing to lock in moisture and prevent skin dryness, which helps reduce flare-ups. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
I was approved for Adtralza/Tralokinumab! I’ve been waiting since February to see if I could be approved for Dupilumab/Dupixent but the dermatologist who saw me said that one of the main side effects was face redness and my eczema extends to my face so she didn’t recommend it to me lol. But recently they started using Adtralza in Italy too so she wrote me up for that 🎉
1 note
·
View note
Text
New Case Report on Punctal Stenosis -A Rare Complication of Dupilumab Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis | Chapter 04 | New Horizons in Medicine and Medical Research Vol. 7
Background: Dupilumab is a biological medicine licenced for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) that has been shown in clinical trials to have a strong therapeutic effect and ability to improve quality of life. The most prevalent side effects of dupilumab therapy were upper respiratory tract infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, injection-site reaction, herpes viral infection, and conjunctivitis. Punctal stenosis, also known as dupilumab-induced lacrimal duct obstruction, is a rare and poorly understood side effect of the medicine.
Aim: To present a novel case of a young female with a history of Alzheimer's disease but no prior major ocular signs who developed right eye punctal stenosis after one year of Dupilumab medication.
Case Report: A 19-year-old female with a long history of Alzheimer's disease who developed severe punctal stenosis and continued tearing from her right eye in the last two months and was on dupilumab therapy for a year did not respond to conservative ophthalmological drugs, but completely improved after discontinuing dupilumab injection over a 6-month follow-up period.
Conjunctivitis is a well-known side effect of Dupilumab injections in people with Alzheimer's disease. If conjunctivitis and eye tears persist following ophthalmology treatment, punctal stenosis may be suspected, and dupilumab should be discontinued.
Author(S) Details
Waqas S. Abdulwahhab
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
Fatima Ibrahim Alamiri
Department of Ophthalmology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
Alaa S. Mehair
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
Fatma Abdulghaffar Qaderi
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Al Qassimi Hospital, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
View Book:-
https://stm.bookpi.org/NHMMR-V7/article/view/6662
0 notes