→We are two passionate Foreign Languages students who want to share with you particular facts and information on different topics that have had a great influence in the world. Our purpose with this blog is to help you enrich your vocabulary as well as your knowledge about these social and cultural phenomena. We hope you like it!←
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
WELCOME!!
HI EVERYONE! HOW IS IT GOING?

We are two Foreign Languages students from the University of Cartagena, Colombia. We are in 6th semester and due to Covid-19 we've been using social media and platforms in order to accomplish some projects and believe me or not, this is one of them!
The main reason why we decided to choose Tumblr to create this blog it's because it allows us to be as creative as we want by posting gifs, photos, music and videos. Our purpose with "Discovering the world of English" is not only to share relevant information and facts about certain topics that have had a great influence in the world but also to enrich you vocabulary, you will find new concepts, new ideas, unknown details that might help you to construct at the end of the day a whole new perspective.
We chose the name "Discovering the world of English" because as its name indicates, through this blog our intention is that you can be able to discover and learn new information about different academic topics and topics of everyday life that are part of the great world of English.
This is our final project, a blog that collects all the topics we have seen, read and analyzed during our semester. It contains many subjects focused on different contexts, such as culture, literature, musical genres and history.
At the very beginning you will find the title of the topic and therefore the information. We use images, gifs and videos in order to illustrate and help the reader to successfully understand.
We decided to attach songs related to the texts, we think you could listen to the music while you read in that way you can use your imagination and immerse yourself completely in the reading.
We thank you in advance to take some time to read it. We hope you enjoy it and like it, feel free to express yourself in the comments and if you have any doubts, please write us!
See you soon,
Victoria and Maria Camila.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
VICTORIAN ERA
THE VICTORIAN PERIOD IN FASHION: HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
In British history, the Victorian Era was the period between 1820 and 1914, corresponding to Queen Victoria’s reign (1837–1901). This phase was characterized by a class-based society, a great number of citizens were able to participate actively in social life decisions such as voting, and Britain’s status as the most powerful empire in the world.

Throughout the Victorian period, Britain was a high-power nation with a rich culture. It had a solid government, a growing state, and an expanding franchise. In addition, it managed a large empire. The reason why it was prosperous was that its level of industrialization and imperial possessions even though three-fourths or more of its population was working-class .
Notwithstanding the fact that this was the period of the world’s first Industrial Revolution, political reform, and social change, it is our pleasure to be able to focus this time on Victorian Era Women’s fashions and styles.
VICTORIAN ERA WOMEN’S FASHIONS AND STYLES

In spite of the prim and proper feminine goal, fashions of the Victorian Era set up pretty often a flamboyant and exaggerated look. Clothing items such as tight corsets, gigantic hoop-skirts, and outrageous bustles were the trend.
Clothing styles were imposed by decency. Stylish costumes were a sign of respect. The considerable amount of fabrics utilized in the creation of some Victorian skirts demonstrates that most women-owned few outfits.
The existence of detachable collars and cuffs allow a woman to change the look, having more variety. It is pretty obvious that wealthier women possessed more garments that were fabricated of finer fabrics as well as the use of more material in order to improve their look and make them more beautiful.
In that time, women lived at the benevolence of men- initially with their fathers or guardians and then with their husbands. It was expected a young lady to be docile and compassionate and to accept whatever their fathers or husband’s wishes were. A woman’s intelligence and percipience were restricted in social events as well as in conversation spaces.

EARLY VICTORIAN FASHION
There was a huge change from the Romantic style of dress in 1836. Women of a higher social class were expected to be modest and indolent as reflected by the restrictive dropped shoulder lines and corsets.
For instance:
Dreses in soft colors could be revived with detachable white collars and cuffs.
Extra flounces were attached to skirts and women wore a short over-skirt in day dressing in the 1840s. Skirts expanded as the hourglass silhouette became a popular look. Bodices had a V shape and the shoulder dropped a little bit more than usual.
Evening dresses showed the shoulders and neckline; corsets eliminated their shoulder straps. Sleeves were usually short.
However, women wore what we call “dresses”, many of these outfits were just a separate bodice and skirt.
Three-quarter length sleeves were used during the Victorian period and sleeves started to sprout bell shaped ruffles.
For most of the 19th century, bonnets were the clothing of choice.
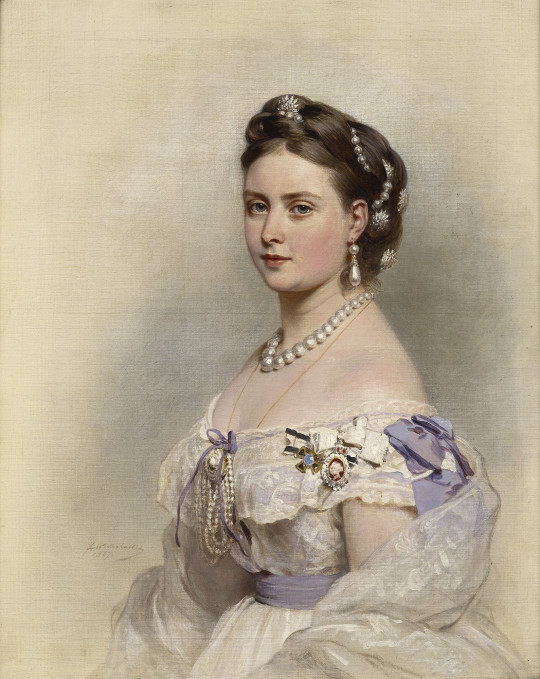

VICTORIAN ERA HAIR AND MAKEUP
Women’s hair in the Victorian Era was usually worn long and caught up in a bun. However, some curls dangled on each side of the head in the 1840s. At that time crimping the hair became very popular in the 1870s.
During this time, it was normal to worn false hairpieces and of course extensions. The use of artificial flowers, false leaves, and beaded butterflies often enhanced the whole costume, for example, Velvet Pansies and Roses, those were some headpieces.
On the other hand, Makeup was mainly used by theater people. The general appearance for those women back in the days was soft skin and rarely highlighted with blush on the cheeks.

THE VICTORIAN CORSET
We can define a corset such as an undergarment set that has strips that were made of whalebone at that time but they were replaced with steel. It was perceived as unhealthy and uncomfortable. Corsets were a fashion trend throughout the 19th-century allowing women social status and the idealized figure of youth.
They were often called “stays” from the French word “estayer” which means support. As you could imagine they provide support.
Some health professionals may criticize them since they can cause medical issues such as cancer, anemia, birth defects, miscarriages, and damage to internal organs.
The tight restriction of the body did reduce lung capacity and caused fainting.

As you can see this period was also characterized by the style and trends in the way women dress. The different outfits, ornaments, dresses, jewels also showed to which social class these women belong, while more ostentatious and exaggerated was the higher the social class. Many women set aside comfort to fit the demands of society.
I hope you have enjoyed a lot reading about the Victorian Era!
0 notes
Text
MIDDLE ENGLISH: FRENCH LOANWORDS
As we know every language accepts in its vocabulary several foreign words and expressions, often using them in their original meaning. It is always fascinating to contemplate the ‘limits’ of a language to signify things but especially thoughts, and why these foreign words were kept in their original form as if they were a better expression than an equivalent.
I do believe that you are pretty aware that we frequently use plenty of French words in English. However, did you know that English is so close to the “language of love” that around 30% of these words come from French? Amazing, right?
Few of these French cognates in English are directly borrowed from the French language whilst others derived from French origins.
A LITTLE BIT OF HISTORY
In order to understand the way French influenced the English language, you have to know a little bit about history because I am pretty sure you might be wondering, how did all of these French words get into English? Let’s take a look at the French influence on the English language, I hope you enjoy it!
The French influence on the English vocabulary had its greatest expansion in the period of Middle English (1150 – 1500). Over 10,000 French words were adopted into the English language and about 75% of these are still in use during that time. The very two reasons why this happened were that, first, the bilingualism in England due to the Norman Conquest in 1066 and second, at that time the English culture was considered inferior.
Even though these changes were essential for the improvement of the English language, there were also some disadvantages, for example, the loss of a lot of native words, the different Middle English dialects, and of course, the need for Standard English.

As I said before, due to the Norman Conquest in 1066 the French language was becoming more and more important. The Normans were descendants of the Danes and spoke French influenced by a Germanic dialect. Some of them lived in the north of France, they did not only speak the language but also adopted the french culture. The only reason why the French language was “superior” was because it was the language of the conquerors, it was not due to any cultural aspect.
It is incredible but, the Kings of England spoke French, took French wives, and lived mostly in France. The Normans became the new upper class since they dominated high positions in the society like the church, education, administration, etc. People who mostly were part of Gentry and whose native language was English had to acquire French if they wanted to get on in the world.

Taking into account the French influence on the vocabulary, we can divide the Middle English period into two stages. In the first stage (1150-1250) less french words were adopted into the English, around 900.
One of the main characteristics of this phase was that the loanwords had Anglo-Norman phonology and they were related from the different areas of nobility, for instance: servant, messenger.
Nevertheless, in the second phase (1250-1500), there was a quick change. Here, the Norman French developed its own features to the called Anglo-Norman dialect. Yet, this dialect was more old-fashioned and rustic compared to the Central French spoken in Paris.
youtube
Below, you will find the contributions of the French language in English according to the different contexts in social life.
FEUDALISM: Words from Anglo-Norman or Old French include terms related to:
Chivalry (homage, liege, peasant, seigniorage, suzerain, vassal, villain)
Institutions (bailiff, chancellor, council, government, mayor, minister, parliament)
Organization of religion (abbey, clergy, cloister, diocese, friar, mass, parish, prayer, preach, priest, sacristy, vestment, vestry, vicar)
The nobility (baron, count, dame, duke, marquis, prince, sir)
The art of war (armour, baldric, dungeon, hauberk, mail, portcullis, rampart, surcoat)
MILITARY: The vocabulary of warfare and the military include many words and expressions of French origin.
(accoutrements, aide-de-camp, army, artillery, battalion, bivouac, brigade, camouflage, carabineer, cavalry, cordon sanitaire, corps, corvette, dragoon, espionage, esprit de corps, état major, fusilier, grenadier, guard, hors-de-combat) among others.
FRENCH WORDS IN ENGLISH TODAY

As you can observe English has borrowed from and been influenced by many different languages, especially by French and Latin. French and Latin words make up 58 % of modern English vocabulary today. On their own, purely French words make up 29% of English.
It is thought that there are around 1,700 “true cognates” which means, words that not only look similar but have exactly the same meaning.
Let’s take a look some suffixes that are the same in French and English:
ation. Examples: nation/la nation ; information/l’information
tion. Examples: acceleration/l’accélération ; attention/attention
ssion. Examples: mission/une mission ; passion/la passion
able. Examples : capable/capable ; table/la table ; adorable/adorable
isme. Examples: Impressionism/l’impressionnisme ; racism/le racisme
if/ive. Examples: furtive/furtif/furtive; creative/créatif/créative
Not all of these words are identical down to the letter. But knowing that root words in both languages can have these suffixes added to them can be helpful.
FRENCH WORDS THAT ARE THE SAME IN ENGLISH
Now, you will find a list of French words that are the same or similar, both in spelling and meaning.
For example, food- and dining -related words:
à la carte : when you want to order individual dishes that are not part of a pre-established sequence of courses.
menu
apéritif
café (a type of restaurant)
picnic
salade
soupe
omelette
bon appétit
hors d’œuvre
vinaigrette
restaurant
alcool (This word was originally borrowed into French from Arabic, by way of Latin)
chef (This means boss in French and not only “cook”.)
British English speakers also often use some common French food words, including:
cornichon
gateau
courgette
aubergine

FASHION AND APPEARANCE WORDS
prêt-à-porter
chic
couture
silhouette
petite
faux (usually used to describe synthetic fur (faux fur), as opposed to fur from an animal)
ART AND CULTURE WORDS
Art Nouveau
avant-garde
bas-relief
film noir
matinee (Note that in French, this word is most commonly used as a way to say “morning”.)
papier mâché (For many English speakers, this is written slightly differently: papier mache)
trompe l’oeil
Many artistic movements are written in a similar way in French and English.
Impressionism/impressionnisme
Realism/réalisme
Surrealism/surréalisme
Cubism/cubisme}
All of these words are among the most noticeable French words in English because they haven’t changed from their original spellings and meanings. But what about the thousands of other French words that are supposed to make up the English language?
youtube
I hope you have enjoyed a lot reading about this subject!
0 notes
Text
HARLEM RENAISSANCE
THE ROLE OF BLACK WOMEN DURING THIS ERA AND IN LITERATURE
The Harlem Renaissance was a literary, artistic, and cultural movement among the African American community that lasted approximately from years 1918 to mid-1930s. Its roots were in Harlem, New York. Thanks to this movement African Americans were able to express themselves and prove that they were as capable as white Americans.

African Americans showed their reality and problems through many different art forms including music, drama, painting, sculpture, movies, but mainly literature. The Harlem Renaissance was the beginning of the change in the identity of black culture.
During all these years, the male role was reflected in all forms of expression of the moment. But, women were also part of this movement, on a much lower scale, but still, there was a way for them to shine with their own light.
According to Carole Marks, director of Black Studies and associate professor of sociology at the University of Delaware, women’s roles varied clearly from those of the men’s roles.
The normal and acceptable role of the female in the Harlem Renaissance was only as salon hostess or entertainer. Therefore, there were many women writers and others considered as "non-hostesses", that were ignored by many or forced to remain as shadows of men.

One of the most important features of this movement was the abundance of new literature by, and about, African-Americans. The quantity of black female writers, essayists, poets, novelists, and playwrights during this time was out of the ordinary, but it remained way less than those of the male figure.
Some of the women writers included Georgia Douglas Johnson, Nella Larsen, Jessie Fauset, Zora Neale Hurston, Anne Spencer, Gwendolyn Bennett, Helene Johnson, Alice Dunbar-Nelson, Elise Johnson McDougald, Dorothy West, and numerous others.
However, many of these texts and poems were criticized and labeled as "not good enough", this caused a notable difference between the perception of male and females. Sadly, society at that time was not capable of appreciating the effort and creativity of women.
According to the study “WOMEN ON WOMEN: THE BLACK WOMAN WRITER OF THE HARLEM RENAISSANCE“, made by Deborah Edith McDowell from Purdue University, women of that time suffered from two mainly stereotypes, they had to be always the sensual ones or the huge matriarch of the families.
The women writers expressed their unconformity to these stereotypes throughout their texts while attempting to create new and real images of women rather than the machista ones. They tried to show how women felt with these labels and give some importance to womanhood but they always were censored by critics and publishers.
For example, the poetry of Georgia Douglas Johnson embraced the aspects of love and womanhood which were deemed acceptable subjects for women to discuss.

And Anne Spencer’s poetry, on the other hand, labeled her a feminist.
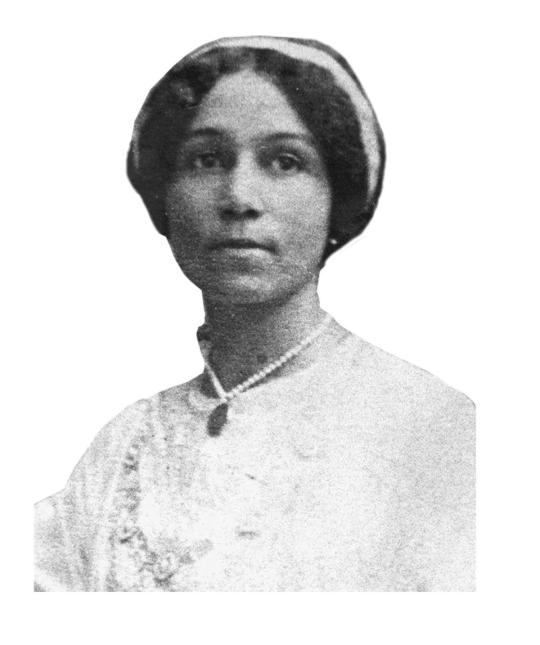

Evidently, being a woman during the Harlem Renaissance movement wasn’t easy. These women had to fight against discrimination and stereotypes from largely male society. But, in spite of everything, they found a way to shine through their writings, poems, paintings, songs, and many other art forms.
I hope you have enjoyed a lot reading about this movement!
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
FOLK TALES
A REVIEW OF RAGNAROK: THE FATE OF THE GODS
The stories that belong to the Norse mythology are diverse. There are stories of war, love, magic, betrayal, and more. These tales were the ones the Vikings recited at the great parties of that time. And that in some way, have been told from one generation to the other. Also, these stories provide some religious meanings for Vikings and all their culture.
The chronology of Norse mythology begins with the creation myth and ends in the tale of Ragnarok. The order of what happens in between those two tales is uncertain and doesn’t follow a linear course.
Ragnarok is, basically, the destruction of the cosmos and everything in it, including the gods. According to the website called “Norse Mythology for Smart People”, for the Vikings, this myth was a prophecy of what was to come in the future, but it had deeper results for how the Vikings understood the world in their own form.

The word “Ragnarok” comes from Old Norse “Ragnarök”, “Fate of the Gods.” In Norse mythology, the tale of Ragnarok describes a series of apocalyptic events that will define the end of the world, where the gods will fight against giants of frost and fire in a final battle that will end the planet earth, inundating it.
According to the myth, the world will resurface, the surviving gods will meet, and the world will be repopulated by two human survivors.
“Brothers will fight and kill each other, sisters' children will defile kinship. It is harsh in the world, whoredom rife —an axe age, a sword age —shields are riven— a wind age, a wolf age— before the world goes headlong. No man will have mercy on another.” Dronke (1997:19)
SIGNS OF THE APOCALYPSE
In the tale of Ragnarok, there are some signs that prove that the end is close. The first sign is a long and continuous cold winter that will last for a year, this is called the Fimbulvetr. Then, a red rooster called Fjalar will warn the Giants about the Ragnarok. A second rooster will warn all the dead that Ragnarok has begun. Finally, a third red rooster called Gullinkambi will warn all the gods about the beginning of the end.
SUMMARY OF THE TALE
After all the previous signs, the dead will get back to life and they will march to the realm called Vigrid, where the final battle will take place. The gods Baldr and Hod will also return from the dead to fight in this final battle. Loki and his horde, as well as the frost Giants, will sail to Vigrid in order to battle against the Aesir. All monsters and giants will create a powerful army against the gods. The result of the war will be that Thor and Odin and most of the gods will die and the dragons will release fire that will destroy all life on Earth.

But this is not the end. Things will start again with a new race. The first two mortals will be called Lif (woman) and Lifthrasir (man) and they will repopulate Earth. The gods Vali and Vidar, as well as the sons of Thor and Hoenir, who survive the battle, will go to Idavoll. The gods Baldr and Hoder will be returned to life and a new era will begin.
If yu are interested in reading the complete tale of Ragnarok, you will find a link below:
Link: https://norse-mythology.org/tales/ragnarok/
EXPLANATION
The apocalyptic story of Ragnarok shows the battle between gods and the consequences for both humans and the gods. This prophecy about the future tells a possible way of the end of the world. Maybe Ragnarok served as a model for human actions and how all can end if we act with malicious.
For Vikings, this tale served for realizing that the gods will one day die, so too will each individual human being. And just as the gods will face their destiny with honor, and courage, so too can humans.
I hope you have enyojed these new facts about Folk Tales!
youtube
0 notes
Text
GOSPEL MUSIC

BEGGINNINS
Gospel music is a genre of American Protestant music. Its roots come from the religious revivals of the19th century. This had as a result the development in different directions within the white (European American) and black (African American) communities of the United States.
Everything began when Rev. Jonathan Edwards (a New England preacher) started a religiously oriented revival labeled “The Great Awakening”. This movement started to move all the way down the eastern U.S. Here, African American slaves who were attending services together with their owners were surprised by the similarities between their fate and that of white people.
HISTORY
The African American slaves turned these hymns into their own religious songs that later became known as their “Negro Spirituals”, actually the first authentic American sacred music style.
Hidden in many of these songs were secret codes to deliver messages of freedom and hope. All through their difficult lives, slaves were using these religious songs for inspiration, inner strength, and courage.

You can find several kinds of Gospel Music, but the main significance of the Gospel was to spread the word of Christ. The Gospel was evolving stylistically, incorporating jazz and blues into the traditional African spirituals.
TYPES OF GOSPEL MUSIC
There are two types of gospel music, each one inspired and developed in a different way. Each one has different characteristics and different public.
BLACK GOSPEL MUSIC

The Negro spirituals lead this singing style and because of this, the result was the creation of many different Pentecostal churches in the USA. This was the foundation of Black Gospel Music, that later on was heavily influenced by early jazz and blues.
In Black Gospel, the soloist or the choir will repeat and/or answer the lyrics just sung by the other party, while the soloist can improvise around the theme.
2. WHITE SOUTHERN GOSPEL MUSIC

This is a style that leans heavily on bluegrass and country music and is characterized by close-harmony singing. The genre became very popular through the public thanks to movies and presentations.
If white musicians wanted to express their religion and spirituality in another way than singing traditional Christian hymns, they made it through this new style of music and transformed it into country music.
I hope you have enyojed this new information about Gospel Music!
youtube
0 notes
Text
CARIBBEAN ENGLISH
The Caribbean, a region of the Americas surrounded by immense beaches and islands, where gastronomy, nature, flora, and fauna are the main protagonists. However, what makes this region so special and multicultural is its history.

HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
From the early 1700s, thousands of people were transported as slaves to the Caribbean, particularly from West Africa, this resulted in a large number of pidgin languages being developed. We can define a pidgin language as a simplified language that is used and created by individuals from different communities who lack a common language. The majority of workers of the colonial plantations in the Caribbean would have spoken a variety of ethnic languages among them, using different sounds, vocabulary, and grammatical structures but slave owners would impose English. Thanks to this, nowadays we can say with certainty that the varieties of English spoken in the Caribbean give us a fascinating insight into the way language evolves due to the contact of different cultures.

FROM PIDGIN TO CREOLE
It is of the utmost importance to recognize that the pidgin language is not a mother tongue, this means that it has zero native speakers. Yet, if the pidgin language prevails as the main way of communication within a community for a long period of time, then it will become the very first language. For instance, on the plantations of the Caribbean.
This pidgin language begins to increase in its complexity due to it is spoken in a wide range of different contexts among the community. Once this process starts to taking place it is transformed into what we called a creole.
Creole is a new expanded in structure and vocabulary version of pidgin and has all the characteristics of other languages.
Throughout the Caribbean, for instance, Standard English, though a Caribbean version, is the language of education, although Jamaicans, Barbadians, and others are rightly proud of their local patois as an important expression of their cultural identity.

CARIBBEAN CREOLE
It can happen that sometimes the Caribbean creole could sound unintelligible for us, the outsiders. The same thing occurs with dialects since the presence of fine shades of differences between speakers, even though there are many elements that characterize most forms of Caribbean English.
Talking in this specific context, we can highlight certain aspects of the Caribbean creole for instance:
The little use of the verb “to be” in differents statements such as “She dreaming”. As Foreign Languages students, we know for sure that in Standard English it is “She is dreaming”.
Pronouns may not be marked for subject/object distinctions and verbs might not always carry a tense marker as in the statement “him tell me dat yesterday” for “he told me that yesterday”.
On the other hand, we can find certain elements that can be considered common in Caribbean vocabulary. For instance, the word “pickney”which means “young child”, what makes this word particularly special it is the fact that it is known to exist in several pidgin and creole languages across the world.

CARIBBEAN ENGLISH PHONOLOGY
You will find below several examples of speakers using different pronunciations and grammatical constructions that are typical of speech in the Caribbean.
All the audio clips were taken from recent BBC interviews and come from a spontaneous conversation that I found in this website: https://www.bl.uk/british-accents-and-dialects/articles/caribbean-english
They actually reflect the natural reflexes of Caribbean English. You can listen to them just by clicking on the sound file, here you will find an extract from a recording of a speaker using the target feature.
TH-STOPPING: In this extract in particular you will realize that the sound <TH> in words like “think” or “three” is pronounced using a <t> sound meanwhile in words such as “this” and “that” using a <d> sound.
youtube
H-DROPPING: The words that contain an “h” at the beginning are deleted. Words such as “happy” or “house”.
youtube
CONSONANT REDUCTION GROUP: Complex strings of consonants are generally simplified by excluding the final sound, in that order of ideas we can conclude that the word “best” becomes ‘bes’, “respect” becomes ‘respeck’ and “land” becomes ‘lan’.
youtube
RHOTICITY: The <r> sound is pronounced after a vowel in words like hard, corn and nurse.
youtube
UNREDUCED VOWEL PLACED IN WEAK SYLLABLES: The vowels situated in unstressed syllables are not reduced, to this extend speakers use a comparatively strong vowel on words such as about, bacon or arrival and even on grammatical function words, such as in the phrases lot of work, in a few days and in the kitchen.
LINK: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1MH9yRatSE8
FACE VOWEL: A similar vowel sound as this one is used by speakers in Scotland, Wales, and the North East of England on words such as game, tray, plain, they, and great.
LINK: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6N4Bj-b8D9A
GOAT VOWEL: A similar vowel sound as this one is used by speakers in Scotland, Wales and the North East of England on words. For instance, home, show, boat and toe.
LINK: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dxkPWBzR0Og
On the other hand, we have certain grammatical changes in Caribbean English:
NONEXISTENCE OF INDEFINITE ARTICLES: Articles such as “an” or “a” is often omitted.
LINK:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5bkSOw2B7wc
NO PAST TENSE INDICATOR: Some verbs do not have a past tense marker. However, some signals such as adverbs of time help you to understand about the timing of an event.
LINK:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KjpR1027Xpk
NO PLURAL SIGN: Nouns are left unmarked for plurality.
LINK:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P0RgJoa60KQ
If you haven’t been exposed to caribbean culture before, you may face some troubles when it comes to understand the dialect acroos the different islands even if you hear it in passing, or you're part of a full-blown conversation.
In order to avoid making mistakes, you will find below a short list that contains some familiar words and slangs. GOOD LUCK!!
1. "Pickney dem"→ Children/kids
"Dem yah pickney dem a drive mi mad!"→ These children/kids are driving me crazy!
2. "Deh'ya"→ Here
"Mi deh'ya a wait fi mi food done cook."→ I'm here waiting for my food to finish cooking.
3. "Lime" → Party
"Yes, man! We in di lime tonight."→ Yeah, dude. We're going to the party tonight.
4. "Pompasetting"→ Showing off
"Look pon di gyal pompasetting."→ Look at that chick showing off.
5. "Puppa Jeezas/Gawd"→ Father Jesus/God or My God!
"Puppa Jeezas/Gawd, mi nearly bun up di pot a rice."→ My God, I almost burned this pot of rice.
6. "Mi bumpsey"→ Oh shoot!
"Mi bumpsey, I nearly forgot mi keys"→ Oh shoot! I almost forgot my keys.
7. "Wah mek?"→ Why?
"Yuh neva nyam from mawning? Wah mek?→ Why didn't you eat this morning?
8. "Cheese on bread!"→ Wow!
"Cheese on bread! Mi phone just drop pon di ground"→ Oh wow! My phone just dropped on the ground.
9. "Sal up"→ Nasty/bad
"A nearly 20 dolla mi pay fi dis movie and it sal up!"→ I paid almost $20 for this movie and it was so bad.
youtube
I hope you have enjoyed a lot about this topic!
1 note
·
View note
Text
FANDOMS
Today, the term "Fandom" has become very popular in our society. This term describes communities that share the same delight about an aspect of popular culture, such as books, movies, TV shows, bands, sports, etc.

According to the website called “Fandoms para Jóvenes”, over the years, many kinds of fanaticism have developed, especially among young people, as they are the most passionate, dedicated, and with free-time. Today there exist hundreds of fan clubs around the world.
ADVANTAGES
Being part of a fandom is an entertaining activity and can have many advantages for you, like generating a lot of fun, it can provide entertainment and stress relief through cheering and socializing. Also, is special because it develops a passion for what you love, you can express your personality, and thanks to these groups your opinion is taken into account. However, it still brings with it a lot of work and a lot of dedication for the participants.
TYPES OF FANDOMS

Fandoms have characteristics that differentiate them from others and make them unique. That is why you need to know that there exist different types of fandoms:
Person fandoms: These are fandoms that usually follow a singer, actor, YouTuber, influencer, or any other celebrity.
Musical Group/Band fandoms: Instead of solo artist fandoms, these fandoms follow multiple people.
Musical Theater fandoms: They follow a certain musical, such as Hamilton. Liking the music is a must for entering these fandoms.
Video Game fandoms: This type of fandoms are one of the most popular, many people are interested in technology and apps. People of these groups can be considered as nerds or geek people.
Movie fandoms: These fandom members will go all out for loving a movie or character from the movie. They also tend to follow the actors they like.
Realistic TV show fandoms: They love to go on Netflix, Hulu etc. They bring up all the hype about shows like Game of Thrones, Stranger Things, and Riverdale.
Cartoon Show/Anime fandoms: They love cartoons either for the story or the visuals.
Lifestyle fandoms: These people don’t follow a certain thing, but mostly a culture or way of life. They all have something in common and can connect with each other.
PERCEPTION ABOUT FANDOMS

According to writer and professor Joli Jensen, there is a division between what is considered as being a “normal” fan, and being an “obsessed”. She said that there are stereotypes and negatives images made by today’s society about these groups, but that not everything is real.
Many people who don’t share the same love for this or don’t belong to a certain fandom can believe or misunderstand the expression "being a fan" to being a crazy fanatic. That is why not all people in today’s society share a positive opinion towards fandoms communities.
I hope you have enjoyed a lot reading about this movement!
youtube
0 notes
Text
TEXT TALK NOVELS
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION
A Text Talk Novel or Cell phone Novels (Japanese: 携帯小説) it is a literary work written, as you can infer, on a cellular phone via text messaging.

This phenomenon emerged almost 20 years ago and arrived in the English language world in 2008. It that way it began a new literary movement among thousands of young writers and readers all over the globe, first on Textnovel.com and now also on Wattpad.

We can say that this "not that new" literacy movement is a remarkably unique new form of writing, it is in fact, a fusing serialized online storytelling with a simple haiku-like poetic technique (a type of short-form poetry originally from Japan) and with prose narrative.
When it comes to the structure of these cell phone novels, each page or chapter is usually averaging around 50-100 words, implementing white space, fragments, deeply personal thoughts or ideas, or emotions. However, there are no restrictions on genres, form, style, or content.
THE ORIGINS
A young man named Yoshi, who originated from Japan, started writing a novel in his mobile phone including short chapters that could fit in an email message. He sent it to his closest friends and then forwarded, suddenly, this novel became worldwide known.
It is important to highlight that the different technological devices in Japan were more advanced than the Western counterparts back then. These tools were capable of 3G internet networks and email messaging and did not have SMS text limitations.
Since Yoshi’s “Deep Love” was known, more and more publishers and writers decided to embrace this new trend and as a consequence many Apps, as well as websites, were created in order to allow Japanese people not only to read them but also to publish their own stories online pen names and secret identities.

Inspiring a new generation of amateurs writers, the majority of them were high school students expressing very personal, emotional, existential, and controversial topics that may be considered taboo in the Japanese culture, topics such as bullying, rape, abortion, friendship using a colloquial vocabulary.
These books have then accumulated millions of reads and readership, published into print form and made into films, TV drama, anime and manga, and so on. The top five bestselling books each year in Japan are often cell phone novels. Some famous examples are: “Koizora” (Love Sky), “Akai Ito” (Red String of Fate), “Kimi No Sei” (It’s Your Fault), “Moshimo Kimi Ga” (If You) and more: http://hakaiya.com/20101204/movie-12945
THE WRITING STYLE
The concept set off the combination of narration and poetry, creating short chapters using white space, line breaks, fragments, poetic devices, and focusing on sensory, emotional, or dialogue content, you will find many cliffhangers. Each chapter is less than 200 words and averages around 50-100.
This type of style opens doors to creativity and imagination; it encourages young writers to reflect deeply about choosing the most accurate diction and layout and to think outside the box and at the same time to deliver the maximum potency in between the lines. In addition, it motives a haiku-style sentimental art form.

It actually allows writers to sound more sophisticated and literary beyond their age just by using their sensitivity and perception of their tiny moments in life. On the other hand, Text Talk Novels inspire to return to literature and poetry, even though its content is related to pop and youth culture in general.
What is amazing about this literary written work it's the fact that by using and bringing apps and social platforms it is widespread easily and everyone could have access. Due to social media writing or reading small chapters could be done between classes, during commutes, or even when you are lying in bed.
THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE MOVEMENT
Steve, K.T., or Takatsu, in 2008 introduced the English cell phone novel. After some research and reading, he realized that there was no such thing as English cell phone novels, and seeing the potential of this literary form, he came across Textnovel.com (the first site in North America to recognize cell phone novels).Since there were not actual cell phone stories on the website, some Japanese cell phone novels were translated.

Takatsu felt so inspired that he starts to experiment with his own original cell phone novel called “Secondhand Memories”. This novel became the very first English language cell phone novel in the West and in the world.
After publishing “Secondhand Memories” a lot of writers of all ages from all over the globe began to get involved in the community. After many years of work and leadership, these writers have been exploring and evolving the different possibilities and styles as well. Becoming more philosophical, artistic, and poetic or start to incorporate visual elements like changing fonts and sizes of fonts.

In 2015, the community also expanded as the Wattpad Cell Phone Novel Network.
“The goodness of inspiration and connecting from art to heart, one heart to another, one life to another, is epitomized in the cell phone novel form, its deeply personal subculture and spirit, and its globalization.”-Takatsu.
CELL PHONE NOVEL SAMPLES
Here are some samples from cell phone novels over the years.
Chapter 1, Secondhand Memories (2008) by Takatsu
It was July. She looked at me with a smile on her face. I smiled back. It was summer. School was off. I was in complete bliss. There was nothing better than this. With her beside me, nothing could go wrong. “Let’s go.” I heard myself say. She nodded.
Chapter 307, Secondhand Memories (2008) by TAKATSU
As we stood there, still in an embrace, all the color slowly returned to the world. The dark grey clouds above were scattering, golden sunlight released from Heaven’s gates above. Like honey, the grassy field in front of us turned colden, lit ablaze with vibrant color. The grass began to sway back and forth counting to a beat, dancing with the wind. I stood there, wide-eyed like a child in awe. Spring. Spring has come. Life. Life has returned.
Chizuru by EllieCue
Birds with the same feathers, flock together – I never knew what this adage means before. I mean, why do people group themselves according to “who” they are? Why can’t everyone just get along with each other? Like… …friends?
I hope you have enjoyed a lot reading about this literary movement!
youtube
2 notes
·
View notes