Upon the encouragement of my dearest Brother/Creative editor I have created this blog to reflect my own creativity.
Last active 2 hours ago
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
The video literally uses the word darning lmao
reposting this on here because I enjoy this account and because this is a really useful visual depiction of how to mend using thread.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oira!
Let me try this
So let the wheel decide your Japanese first-person pronoun
Note: descriptions may be inaccurate.
14K notes
·
View notes
Text

Ever feel like your characters are holding out on you? Like there’s something lurking beneath the surface... but they’re just sitting there, being cryptic?
We’ve got some new templates to help you discover their emotional arcs, relationships, and backstories!
Character Arc Planning Template: Growth, self-destruction, spiralling into chaos at the first sign of trouble... Track how your character changes (or refuses to).
Character Relationship Template: Friends, enemies, lovers, ex-lovers-who-are-now-rivals-with-awkward-sexual-tension... Explore relationship dynamics and define how your characters connect.
Emotional Wound Template: Uncover concealed motivations, and craft character-defining backstory with depth and care.
You can find them in Ellipsus—head over to the blog to read more!
- the Ellipsus Team xo
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Merry ORV MPreg Xmas" - a friend of mine
thank you sleepy-c -nim for this gift
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Show, don’t tell
"Show, don’t tell" means letting readers experience a story through actions, senses, and dialogue instead of outright explaining things. Here are some practical tips to achieve that:
1. Use Sensory Details
Tell: "The room was cold."
Show: "Her breath puffed in faint clouds, and she shivered as frost clung to the edges of the window."
Tell: "He was scared."
Show: "His hands trembled, and his heart thudded so loudly he was sure they could hear it too."
2. Focus on Actions
Tell: "She was angry."
Show: "She slammed the mug onto the counter, coffee sloshing over the rim as her jaw clenched."
Tell: "He was exhausted."
Show: "He stumbled through the door, collapsing onto the couch without even bothering to remove his shoes."
3. Use Dialogue
What characters say and how they say it can reveal their emotions, intentions, or traits.
Tell: "She was worried about the storm."
Show: "Do you think it'll reach us?" she asked, her voice tight, her fingers twisting the hem of her shirt.
4. Show Internal Conflict Through Thoughts or Reactions
Tell: "He was jealous of his friend."
Show: "As his friend held up the trophy, he forced a smile, swallowing the bitter lump rising in his throat."
5. Describe the Environment to Reflect Mood
Use the setting to mirror or hint at emotions or themes.
Tell: "The town was eerie."
Show: "Empty streets stretched into the mist, and the only sound was the faint creak of a weathered sign swinging in the wind."
6. Let Readers Infer Through Context
Give enough clues for the reader to piece things together without spelling it out.
Tell: "The man was a thief."
Show: "He moved through the crowd, fingers brushing pockets, his hand darting away with a glint of gold."
7. Use Subtext in Interactions
What’s left unsaid can reveal as much as what’s spoken.
Tell: "They were uncomfortable around each other."
Show: "He avoided her eyes, pretending to study the painting on the wall. She smoothed her dress for the third time, her fingers fumbling with the hem."
8. Compare to Relatable Experiences
Use metaphors, similes, or comparisons to make an emotion or situation vivid.
Tell: "The mountain was huge."
Show: "The mountain loomed above them, its peak disappearing into the clouds, as if it pierced the heavens."
Practice Example:
Tell: "The village had been destroyed by the fire."
Show: "Charred beams jutted from the rubble like broken ribs, the acrid smell of ash lingering in the air. A child's shoe lay half-buried in the soot, its leather curled from the heat."
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Non-Lethal Injuries to Add Pain to Your Writing
If you need a simple way to make your characters feel pain, here are some ideas:
1. Sprained Ankle
A common injury that can severely limit mobility. This is useful because your characters will have to experience a mild struggle and adapt their plans to their new lack of mobiliy. Perfect to add tension to a chase scene.
2. Rib Contusion
A painful bruise on the ribs can make breathing difficult, helping you sneak in those ragged wheezes during a fight scene. Could also be used for something sport-related! It's impactful enough to leave a lingering pain but not enough to hinder their overall movement.
3. Concussions
This common brain injury can lead to confusion, dizziness, and mood swings, affecting a character’s judgment heavily. It can also cause mild amnesia.
I enjoy using concussions when you need another character to subtly take over the fight/scene, it's an easy way to switch POVs. You could also use it if you need a 'cute' recovery moment with A and B.
4. Fractured Finger
A broken finger can complicate tasks that require fine motor skills. This would be perfect for characters like artists, writers, etc. Or, a fighter who brushes it off as nothing till they try to throw a punch and are hit with pain.
5. Road Rash
Road rash is an abrasion caused by friction. Aka scraping skin. The raw, painful sting resulting from a fall can be a quick but effective way to add pain to your writing. Tip: it's great if you need a mild injury for a child.
6. Shoulder Dislocation
This injury can be excruciating and often leads to an inability to use one arm, forcing characters to confront their limitations while adding urgency to their situation. Good for torture scenes.
7. Deep Laceration
A deep laceration is a cut that requires stitches. As someone who got stitches as a kid, they really aren't that bad! A 2-3 inch wound (in length) provides just enough pain and blood to add that dramatic flair to your writing while not severely deterring your character.
This is also a great wound to look back on since it often scars. Note: the deeper and wider the cut the worse your character's condition. Don't give them a 5 inch deep gash and call that mild.
8. Burns
Whether from fire, chemicals, or hot surfaces, burns can cause intense suffering and lingering trauma. Like the previous injury, the lasting physical and emotional trauma of a burn is a great wound for characters to look back on.
If you want to explore writing burns, read here.
9. Pulled Muscle
This can create ongoing pain and restrict movement, offering a window to force your character to lean on another. Note: I personally use muscle related injuries when I want to focus more on the pain and sprains to focus on a lack of mobility.
10. Tendonitis
Inflammation of a tendon can cause chronic pain and limit a character's ability to perform tasks they usually take for granted. When exploring tendonitis make sure you research well as this can easily turn into a more severe injury.
This is a quick, brief list of ideas to provide writers inspiration. Since it is a shorter blog, I have not covered the injuries in detail. This is inspiration, not a thorough guide. Happy writing! :)
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Check out the rest of Quillology with Haya; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors!
Instagram Tiktok
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
Resources For Describing Physical Things

Setting
Abandoned Mine
Airplane
Airport Check-in
Alley
Amusement Park
Attic
Bakery
Bank
Basement
Bathroom (home)
Barn
*GE* Barn 2 (Dairy Focus)
Beach
Bedrooms
Birthday Party
Bonfire
Bowling Alley
Bridge
Bookstore
Cafeteria
Casino
*GE* Catacombs
Cave
Church
City Park
Classroom
Closet
Coffee House
Courtroom
Cruise Ship
*GE* Cryogenic Sleep Chamber
Daycare
Desert
Diner
Dragon’s Lair
Dungeon (Caution Graphic Description)
*GE* Egyptian Pyramids
Elevator
Farms
Forest
Frozen Tundra
Gallows
Garage
Garage Sale
Garden
Graveyard
*GE* GLOBAL WARMING (dystopian)
Grocery Store
Halloween Party
Haunted House
Herbalist Shop (fantasy)
High School Hallway
Hospital
Hotel Room
House Fire
House Party
Kitchen
*GE* Laboratory
*GE* Laboratory (secret genetic)
Lake
Library
Locker Room
Meadow
Medieval Castle Armory
Medieval Marketplace
Middle School Dance (informal)
*GE* Mindscape (Mind Magic)
Mountains
Movie Theatre
Night Club
Nursery
Ocean/Sea Bed
Old Pick-Up Truck
Pirate Ship
Playground
Pond
Pool Hall
Prison Cell
Pub
Public Pool (Outdoor)
Rainforest/Jungle
Ranch
Restaurant
River
School Bus
School Office
Shopping Mall
Sleep-Away Camp
*GE* Spaceport
*GE* Spaceship
Stands at a Sporting Event
Storm Sewer
Subway Station
Swamp
Taxi cab
Teacher’s Lounge
Toolshed
*GE* Trailer
Treehouse
*GE* Tropical Island City
Urban Street
Video Arcade
Waiting Room
Waterfall
Water Slide Park
Wedding Ceremony (Church)
Woods at Night
Zoo
Weather
Air Pollution
Avalanche
Blizzard
Breeze
Clouds
Dew
Drought
Dusk
Dust or Sand Storm
Earthquake
Eclipse
Fall
Falling Star
Flood
Forest Fire
Frost
Hailstorm
Heat Wave
Hurricane/Typhoon
Lightning
Mirage
Mist or Fog
Moonlight
Mudslide
Rain
Rainbow
Sky
Sleet
Snow
Spring
Summer
Sunrise
Sunshine
Sunset
Thunderstorm
Tornado
Vortex
Wind
Winter
Color, Texture, & Shape
Color
Black
Blue
Brown
Gray
Gold
Green
Orange
Pink
Purple
Red
Silver
Spotted
Striped
Transparent
White
Yellow
Texture
Bumpy
Barbed/Spined
Crackled
Crumbly
Crusty
Foamy/Spongy
Fuzzy
Gritty
Pitted
Powdery
Prickly
Saw-edged/Serrated
Slimy
Smooth
Sticky
Shape
Arch
Circular/Sphere
Crescent
Heart
Oval & Oval-like
Rectangle
Spiral
Star
Square
Triangular
Tube
Wavy
Support Wordsnstuff!
Request A Writing Help Post/Themed Playlist/Writing Tips!
Send Me Poetry To Feature On Our Instagram!
Receive Updates & Participate In Polls On Our Twitter!
Like us and share on Facebook!
Read More On Our Masterlist & See our Frequently Asked Questions!
Tag What You Want Me To See With #wordsnstuff!
Participate in monthly writing challenges!
25K notes
·
View notes
Text
Different types of water and their magickal uses:

Sea water: good for curse/hex breaking, cleansing, healing, banishing and protection spells.
Dew water: beauty, love and fertility spells, as well as delicate magick. Also Good for Fae work.
Storm water: is great for spells and rituals that has to do with emotional strength, confidence, charge, motivation and force. It’s known for strengthening spells. Also good for curses.
Snow water: Spells and rituals that focus on purity, endings and change, as well as slow working spells.
River water: Good for creating changes, moving on and letting go of negativity, warding and focusing energy.
Rain water: Very multi-purpose, but specifically great for growth and rebirth spells. Great for spells that you want to keep gaining power over time.
Spring water: Growth, holy water, cleansing, protection, prosperity
Moon water: Depending on the moon phase it was created in, it can have different properties.
Sun Water: protection, healing, clairvoyance, courage, strength, prosperity, luck, self-love, cleansing and creativity.
Swamp Water: Used for banishing and binding.
tip-jar
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Herb's Properties
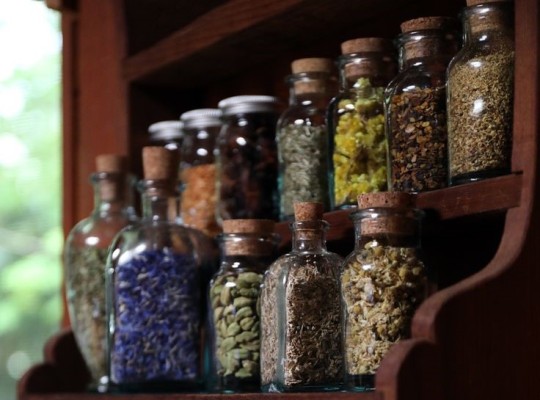
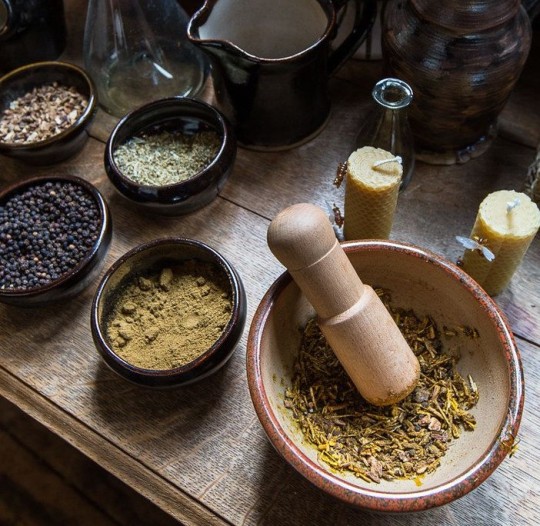


Basil: money, luck, prosperity, happiness
Bay Leaf: energy, cleansing, can be charged with almost any intention
Camomile: Caring, kindness, luck, growth, self-love growth, confidence, avoiding negativity, happiness
Cinnamon: passion, quick success, fire magick
Chia seeds: Growth, health, kindness, Property
Chilli flakes: Pride, confidence, power, strength, Passion
Cumin: Courage, bravery, protection, loyalty
Dandelion: wishes, charisma, success, good luck
Dill: sexual love, luck, protection
Eucalyptus: cleansing, healing, purifying, relaxing, comfort
Fennel: hate, anger
Flax seeds: Prosperity, growth, new beginnings
Ginger: fiery passion, success, and personal power
Jasmine: love, dreams, sensuality, luxury and kindness
Lavender: love and attraction, purification, relaxation, restful sleep
Nutmeg: luck, Health, Fidelity, Love, Prosperity, comfort, loyalty
Oregano: comfort, love, warmth
Paprika: Pride, confidence, power, strength
Parsley: Cleansing. purification
Peppermint: healing, purification, love and energy, cleansing, prosperity
Poppy seeds: protection, intuition, self-assurance, hexing and cursing
Rose: love, beauty, harmony, romance, attraction
Rosemary: cleansing, purification, wisdom, protection
Sesame seeds: Prosperity, growth, health, nurturing
Spearmint: love, cleansing, renewal, blessing
Sunflower seeds: happiness, growth, joy
Thyme: beauty, strength, courage
Turmeric: confidence, creativity, energy
Vanilla: love and sexuality
tip jar
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Surviving the Wilderness: Writing Realistic 'Lost in the Woods' Scenarios

The wilderness, with its vastness and unpredictability, can turn from serene to menacing in an instant. For writers, depicting a character who is lost in the woods offers a rich tapestry of emotions, challenges, and survival instincts to explore. But to do so effectively requires a blend of authenticity, attention to detail, and understanding the real-world repercussions of such an event.
Whether your character is an experienced outdoorsman or a city dweller thrown into the wild, this guide will help you craft a realistic narrative that resonates with readers.
1. Setting Up the Scenario
A. Choosing the Right Wilderness Environment
The first step in creating a believable lost-in-the-woods scenario is choosing the appropriate setting. Different types of wilderness present different challenges, and the environment you choose will shape the narrative.
Type of Forest: Consider the differences between dense forests, temperate rainforests, boreal woods, and tropical jungles. A dense forest might offer limited visibility and a disorienting array of trees, while a tropical jungle could present humidity, dangerous wildlife, and thick undergrowth. Each environment comes with unique hazards and characteristics that will impact your character’s journey.
Seasonal Considerations: The time of year plays a significant role in the story. In winter, your character might face snow, freezing temperatures, and the challenge of finding food. In summer, they might struggle with dehydration, heat exhaustion, or the difficulty of navigating through thick foliage. The season will also affect the availability of resources, like water and shelter.
Location-Specific Details: Consider the unique features of the chosen location. Is it known for dangerous wildlife, such as bears or wolves? Does the terrain include steep cliffs, rivers, or swamps? Researching the specific area can add layers of realism to your story, providing challenges that are true to the environment.
B. Character Background
The character’s background is crucial in determining how they will respond to being lost. Their level of experience, purpose for being in the woods, and psychological state all influence their actions.
Experience Level: Are they an experienced hiker with survival skills, or are they a city dweller with little knowledge of the outdoors? An experienced character might know how to build a shelter and find water, while an inexperienced one might make dangerous mistakes. Balancing their skills with the challenges they face can create tension and interest.
Purpose of the Trip: Why is your character in the woods? Whether they’re on a leisurely hike, conducting research, or fleeing from danger, their purpose will affect their preparedness and mindset. A hiker might have a map and supplies, while someone fleeing might have nothing but the clothes on their back.
Psychological State: Consider the character’s mental condition before they get lost. Are they overconfident, stressed, or fearful? Their psychological state will influence their decisions—overconfidence might lead to risky choices, while fear could cause them to panic. Understanding their mindset will help you write a more nuanced and realistic portrayal.
C. The Catalyst: How They Get Lost
The moment when a character realizes they are lost is a critical point in the narrative. How this happens can be gradual or sudden, depending on the story you want to tell.
Common Triggers: Characters can become lost for various reasons, such as deviating from a marked trail, encountering sudden weather changes, sustaining an injury, or simply having poor navigation skills. Each trigger offers different narrative possibilities—an injury might limit their mobility, while poor navigation could lead them deeper into danger.
Pacing: Decide how quickly your character realizes they are lost. It could be a slow realization as they fail to find familiar landmarks, or it could be immediate, such as after an unexpected event like a storm or injury. The pacing of this moment will set the tone for the rest of the story.
2. Writing the Experience of Being Lost
A. The Initial Panic
When a character first realizes they are lost, their initial reactions are often driven by panic. This moment is crucial for establishing the tone of the story and the character’s mental state.
Physical Reactions: Describe the character’s immediate physical responses, such as an elevated heart rate, adrenaline rush, sweating, and shortness of breath. These physiological reactions are the body’s natural response to fear and uncertainty.
Mental Reactions: Mentally, the character might experience denial, anxiety, or confusion. They might try to convince themselves that they aren’t really lost or that they’ll find their way back soon. This denial can lead to irrational decisions, like wandering in circles or making impulsive choices.
Immediate Actions: The character’s first actions after realizing they’re lost are critical. They might attempt to retrace their steps, call for help if they have a phone signal, or check the time to gauge how long they’ve been lost. These actions are often driven by the hope of quickly resolving the situation.
B. The Descent into Survival Mode
Once the character accepts that they are truly lost, the story shifts from panic to survival. This is where the character’s skills, or lack thereof, come into play.
Acceptance of the Situation: The character moves from panic to a more rational state of mind. They begin to assess their situation and prioritize their needs. This shift marks the beginning of their survival journey.
Basic Needs: The character will need to address their most immediate survival needs: shelter, water, food, and fire. Describe their efforts to find or create shelter, locate water sources, forage for food, and start a fire. Each of these tasks presents its own challenges and dangers.
Navigational Challenges: As the character tries to find their way, they will face navigational challenges. Dense foliage, fog, and the lack of clear landmarks can make it difficult to maintain a sense of direction. The character might struggle with the disorientation that comes from being surrounded by identical trees or losing sight of the sun.
C. Emotional and Psychological Effects
The emotional and psychological toll of being lost is significant and should be explored in depth.
Isolation and Fear: The character’s sense of isolation can amplify their fear. The fear of predators, injuries, or never being found can become overwhelming. This fear might cause the character to make rash decisions, or it could paralyze them, preventing them from taking action.
Hope vs. Despair: The character’s emotional journey will likely fluctuate between moments of hope and despair. They might find something that gives them hope, such as a sign of civilization or a source of water, only to be crushed when they realize it was a false lead.
Hallucinations and Delusions: In extreme situations, such as severe dehydration or starvation, the character might experience hallucinations or delusions. These can add an element of psychological horror to the narrative and further illustrate the severity of their situation.
D. Interaction with Nature
The character’s interaction with the natural environment is a key aspect of their survival story.
Wildlife Encounters: Depending on the location, the character might encounter dangerous wildlife, such as bears, wolves, or snakes. Describe these encounters realistically, focusing on the character’s fear and the steps they take to avoid or confront these animals.
Environmental Hazards: The natural environment presents its own set of dangers, such as quicksand, poisonous plants, and unstable terrain. The character might have to navigate these hazards while dealing with their growing exhaustion and fear.
Natural Resources: The character can use nature to their advantage by finding water, edible plants, or materials for building a shelter. This not only adds realism to the story but also gives the character moments of small victories that can keep them going.
3. Survival Tactics: What Works and What Doesn't
A. Basic Survival Skills
Understanding and depicting basic survival skills is crucial for writing a realistic lost-in-the-woods scenario.
Finding Water: Water is the most critical resource for survival. Describe how the character identifies potential water sources, such as streams or dew on leaves, and how they purify water to make it safe to drink. If they can’t find water, their condition will deteriorate rapidly, leading to severe dehydration.
Building Shelter: The character needs shelter to protect themselves from the elements. Whether they find a natural shelter, like a cave, or build one from branches and leaves, this task is essential for their survival. The process of building shelter also gives the character a sense of purpose and control over their situation.
Starting a Fire: Fire is essential for warmth, cooking, and protection from predators. Describe the challenges of starting a fire in the wild, especially if the wood is wet or the character lacks the proper tools. The ability to start and maintain a fire can be a turning point in the character’s survival story.
Foraging for Food: Finding food in the wild is difficult and dangerous. The character might forage for berries, roots, or small animals. Describe the risks of eating unknown plants or the difficulty of catching and preparing small game.
B. Navigational Techniques
Navigation is a critical aspect of survival, and the character’s ability to orient themselves can mean the difference between life and death.
Reading the Environment: The character might use the sun, stars, or natural landmarks to navigate. Describe how they attempt to determine their direction, and the challenges they face if the sky is cloudy or if they’re in a dense forest where the canopy blocks out the sun. Their ability to read the environment will depend on their prior knowledge and experience.
Using Makeshift Tools: If the character has access to materials like sticks, rocks, or even a piece of reflective metal, they might create makeshift tools like a compass or use shadows to determine direction. These improvisational skills can add a layer of resourcefulness to the character’s survival tactics.
Trail Marking: If the character decides to explore the area in hopes of finding a way out, they might mark their trail to avoid walking in circles. They could use stones, branches, or even carve symbols into trees. This tactic not only helps with navigation but also adds to the tension if they realize they’ve returned to a previously marked spot, indicating they’ve been moving in circles.
C. Mistakes and Misconceptions
Realistic survival stories often include mistakes that characters make, especially if they are inexperienced.
Following Streams Incorrectly: A common misconception is that following a stream will always lead to civilization. While it can lead to water sources, it might also take the character deeper into the wilderness. Highlight the risks of relying on this tactic without proper knowledge.
Overestimating Stamina: Characters might push themselves too hard, assuming they can keep going without rest. Overestimating their stamina can lead to exhaustion, injuries, or even fatal mistakes. Describing the physical toll of these decisions can add realism and tension to the narrative.
Eating Dangerous Plants: Foraging for food can be deadly if the character lacks knowledge of the local flora. Describe how they might mistake poisonous plants for edible ones, leading to illness or hallucinations. This mistake can be a significant plot point, demonstrating the dangers of the wilderness.
4. Realistic Repercussions of Being Lost
A. Physical Consequences
Being lost in the wilderness for an extended period can have severe physical repercussions.
Dehydration and Starvation: The longer the character is lost, the more their body will deteriorate. Dehydration can set in within a few days, leading to confusion, dizziness, and eventually death. Starvation takes longer but will cause weakness, muscle loss, and an inability to think clearly.
Injuries: Describe any injuries the character sustains, such as sprains, cuts, or broken bones. These injuries will hinder their ability to move and survive. If left untreated, even minor injuries can become infected, leading to serious complications.
Exposure: Depending on the environment, the character might suffer from exposure to the elements. Hypothermia can occur in cold conditions, while heatstroke is a risk in hot climates. Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate attention.
B. Psychological Consequences
The psychological toll of being lost is often as severe as the physical consequences.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Even after being rescued, the character might suffer from PTSD, experiencing flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. Describe how their ordeal has changed them, affecting their ability to return to normal life.
Survivor’s Guilt: If the character was lost with others who didn’t survive, they might experience survivor’s guilt. This emotional burden can be overwhelming, leading to depression and difficulty coping with their survival.
Long-Term Anxiety: The fear of being lost again can cause long-term anxiety and phobias. The character might avoid certain environments or experience panic attacks in similar situations.
C. Legal Consequences
There are also legal and financial repercussions to consider, especially if the character’s actions led to their getting lost.
Search and Rescue Costs: In many places, the cost of search and rescue operations can be billed to the person who was lost, especially if they were negligent or broke the law. This can be a significant financial burden and add a layer of realism to your story.
Negligence and Liability: If the character’s actions endangered others, such as leaving a marked trail or ignoring warnings, they might face legal consequences for negligence. This could include fines, community service, or even jail time, depending on the severity of their actions.
Impact on Relationships: The ordeal of getting lost can strain relationships with family and friends. Describe how their loved ones react—do they blame the character, or are they just relieved they’re safe? The legal and financial consequences can also impact these relationships, leading to tension and conflict.
5. Writing Tips: Making It Believable
Crafting a realistic and compelling lost-in-the-woods narrative requires attention to detail and an understanding of the human experience in such extreme situations. Here are some tips to make your story believable:
A. Research and Authenticity
Understand the Terrain: Before writing, research the specific environment where your character will be lost. Whether it's a dense forest, a mountainous region, or a desert, understanding the flora, fauna, and climate will help you create an authentic setting. Pay attention to details like the types of trees, animals, weather patterns, and geographical features.
Learn Basic Survival Techniques: Familiarize yourself with basic survival skills, such as building a shelter, finding water, and starting a fire. Even if your character is inexperienced, knowing the correct methods will allow you to portray their struggles accurately.
Incorporate Local Myths and Folklore: If your story is set in a particular region, consider integrating local myths or folklore about the wilderness. This can add depth to the narrative and give the environment a more ominous or mystical feel.
B. Character Realism
Establish Their Skills Early: If your character has any survival skills, establish them early in the story. This could be through flashbacks, previous experiences, or hints in their background. This will make their actions in the woods more believable.
Show Their Vulnerability: Even the most prepared individuals can make mistakes. Show your character’s vulnerability by having them face setbacks, make poor decisions, or struggle with their emotions. This makes them more relatable and human.
Reflect Their Mental State: The character's psychological state should evolve throughout the story. Show how their thoughts shift from initial panic to determination, despair, and finally, either acceptance or a desperate push for survival. Use internal monologue, dreams, or hallucinations to illustrate their mental state.
C. Plot and Pacing
Balance Action with Reflection: While the physical actions of survival are crucial, so is the internal journey of the character. Balance scenes of intense activity, like building a shelter or escaping a predator, with quieter moments of reflection or memory.
Use Sensory Details: Engage the reader’s senses by describing the environment through sights, sounds, smells, and even touch. The rustling of leaves, the scent of pine, or the rough bark of a tree can immerse readers in the setting and heighten the tension.
Avoid Convenient Resolutions: Survival stories are often about struggle and perseverance. Avoid giving your character an easy way out, such as a sudden rescue or finding a cabin with supplies. Instead, focus on their gradual adaptation and the hard choices they have to make.
D. Dialogue and Interactions
Internal Dialogue: In situations where the character is alone, internal dialogue becomes crucial. Use it to explore their fears, hopes, and regrets. This can also be a way to explain their thought process and decision-making.
Flashbacks and Memories: If your character is alone, use flashbacks or memories to develop their backstory and explain their motivations. These can also serve as a contrast to their current situation, highlighting how far they’ve come or what they’ve lost.
Interactions with the Environment: Treat the wilderness as a character in itself. The environment should interact with the character, creating obstacles, providing resources, and affecting their mood and decisions.
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Are you an author looking for writing tips and tricks to better your manuscript? Or do you want to learn about how to get a literary agent, get published and properly market your book? Consider checking out the rest of Quillology with Haya Sameer; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors! While you’re at it, don’t forget to head over to my TikTok and Instagram profiles @hayatheauthor to learn more about my WIP and writing journey!
333 notes
·
View notes
Text
hot artists don’t gatekeep
I’ve been resource gathering for YEARS so now I am going to share my dragons hoard
Floorplanner. Design and furnish a house for you to use for having a consistent background in your comic or anything! Free, you need an account, easy to use, and you can save multiple houses.
Comparing Heights. Input the heights of characters to see what the different is between them. Great for keeping consistency. Free.
Magma. Draw online with friends in real time. Great for practice or hanging out. Free, paid plan available, account preferred.
Smithsonian Open Access. Loads of free images. Free.
SketchDaily. Lots of pose references, massive library, is set on a timer so you can practice quick figure drawing. Free.
SculptGL. A sculpting tool which I am yet to master, but you should be able to make whatever 3d object you like with it. free.
Pexels. Free stock images. And the search engine is actually pretty good at pulling up what you want.
Figurosity. Great pose references, diverse body types, lots of “how to draw” videos directly on the site, the models are 3d and you can rotate the angle, but you can’t make custom poses or edit body proportions. Free, account option, paid plans available.
Line of Action. More drawing references, this one also has a focus on expressions, hands/feet, animals, landscapes. Free.
Animal Photo. You pose a 3d skull model and select an animal species, and they give you a bunch of photo references for that animal at that angle. Super handy. Free.
Height Weight Chart. You ever see an OC listed as having a certain weight but then they look Wildly different than the number suggests? Well here’s a site to avoid that! It shows real people at different weights and heights to give you a better idea of what these abstract numbers all look like. Free to use.
330K notes
·
View notes
Text
burning text gif maker
heart locket gif maker
minecraft advancement maker
minecraft logo font text generator w/assorted textures and pride flags
windows error message maker (win1.0-win11)
FromSoftware image macro generator (elden ring Noun Verbed text)
image to 3d effect gif
vaporwave image generator
microsoft wordart maker (REALLY annoying to use on mobile)
you're welcome
267K notes
·
View notes
Text

u can call ur skull-head deer oc literally anything else u don't even have to change the design
69K notes
·
View notes
Text
Inner Conflict Prompts
Have a character wrestle with guilt over a past mistake.
Introduce a scenario where a character must choose between two equally important things.
Show a character struggling with their own identity or sense of self.
Have a character battle their own fears or phobias.
Introduce a moral dilemma that challenges the character’s values.
Show a character torn between loyalty to their friends and their personal ambitions.
Reveal a character’s internal struggle with jealousy or envy.
Have a character grapple with feelings of inadequacy or imposter syndrome.
Show a character dealing with the aftermath of a traumatic event.
Have a character question their own sanity or reality.
2K notes
·
View notes