Text
Drugs for Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of the bite of female sand-fly phlebotomus. In the fly, the parasite exists exists in the flagellate extracellular form, while in man it is found in non flagellate (macrophage) form. Visceral leishmaniasis are fatal unless treated.
The drug that are currently employed to treat this infection are:
Sodium stibogluconateAmphotericin…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Drugs for Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis is micro aerophilic protozoan which causes vulvovaginitis. It is a common disease affecting. Several drugs are partly effective by vaginal application, but may not entirely clear the infection.
Metronidazole
Produce up to 90% cure.However, resistance is being reported.Some resistant cases respond to higher doses, especially tinidazole.Intravaginal treatment required in…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Drugs for Giardiasis
Giardia lambila is a flagellate protozoan which infects children and adults and mostly lives as commensal in intestine. Many drugs that are useful in amoebiasis are also effective to treat giardiasis.
Metronidazole
Drug of choice.Nearly !0% of the patients may not be cured.A second course or alternative drug maybe given.
Nitronidazole
Prodrug of PFOR enzyme inhibitor trinidazole.Treats…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
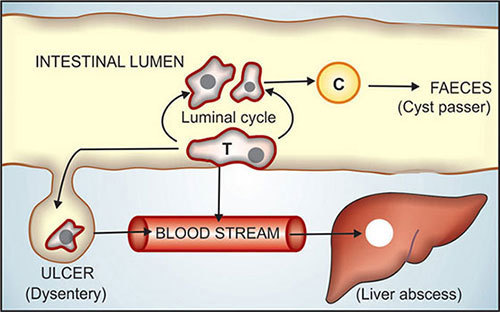
Antiamoebic Drugs
These drugs are useful in infection caused by Entamoeba histolytica.
Amoebic cysts reaches the intestine transforms into trophozoites that either:
Live on the surface of colonic mucosa as commensals-form cysts that pass into stools and serve to propagate the disease, orInvade the mucosa, form amoebic ulcers and cause acute dysentery of chronic intestinal amoebiasis.
Occasionally, the…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
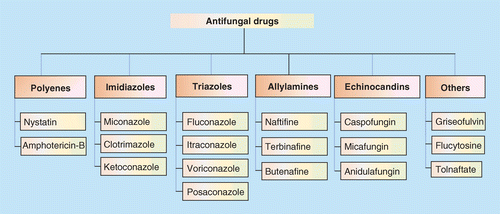
Antifungal Drugs
These are drugs used for superficial and deep fungal infections.
Classification of Drugs
Amphotericin B (AMB)
It is obtained from Streptomyces nodosus.
Chemistry and Mechanism of Action
Polyene antibiotic molecule is a macrocyclic ring, one side of which has several conjugated double bonds and is highly lipophilic, while the other side is hydrophilic with many -OH groups. A polar amino sugar…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antimalarial Drugs 1.3
Artemisinin Derivatives
Artemisinin is a sesquiterpene lactone endoperoxide active against Plasmodium falciparum resistant to all other anti malarial drugs as well as sensitive to other malarial species.
Potent and rapid blood schizonticide action is exerted producing quicker defervescence and parasitaemia clearance than CQ or any other drug. They have the broadest window of antimalarial…
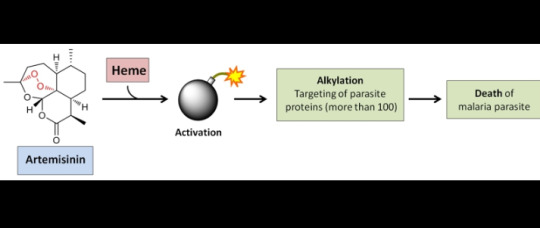
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antimalarial Drugs 1.2
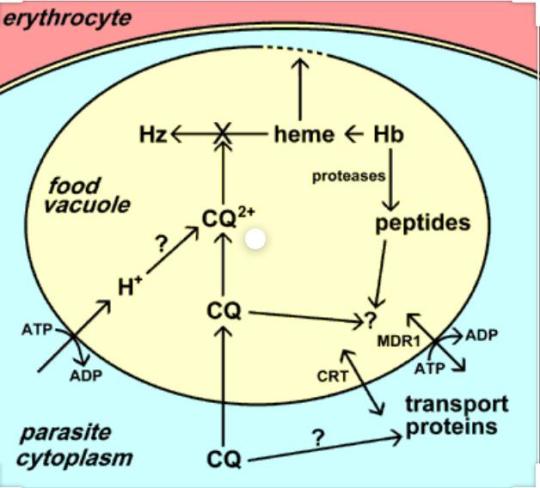
4-Aminoquinolines Chloroquine (CQ)
It is rapidly acting erythrocytic schizonticide against all species of plasmodia. Therapeutic plasma concentration is 15-30 ng/ml. It has no effect on primary and secondary hepatic stages of parasite, so does not prevent relapse in vivax and ovale malaria. No gametocidal activity.
Mechanism of Action
CQ is actively concentrated by sensitive…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antimalarial Drugs 1.1
These drugs are used in the prophylaxis, treatment and prevention of relapse of malaria.
Life Cycle of Malaria
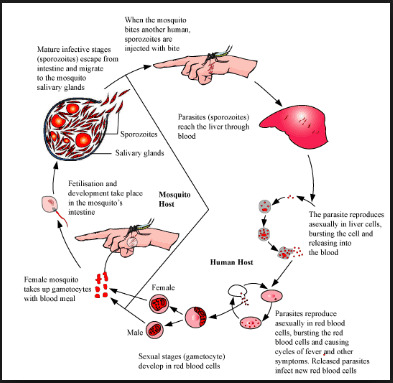
Objectives of Antimalarial Drugs
To prevent clinical attack of malaria.
To treat clinical attack of malaria.
To completely eradicate the parasite from the patient’s body.
To cutdown human to mosquitoe transmission.
These objectives are achieved by attacking the parasite at its…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Anti-retroviral Drugs 1.3
HIV Treatment Principles and Guidelines
Anti-retroviral therapy is only 30 years old and is still evolving. Highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) with combination of 3 or more drugs whenever indicated. Monotherapy is contraindicated.
Since no regimen can eradicate HIV from the body of the patient, the goal of the therapy is to maximally and durably inhibit viral replication so that…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Anti-retroviral Drugs 1.2
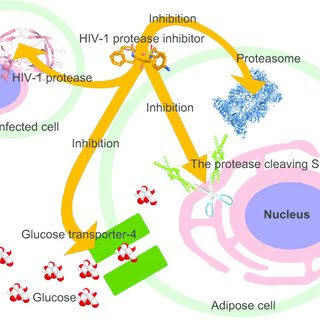
Protease Inhibitors (PIs)
An aspartic protease enzyme encoded by HIV is involved in the production of structural proteins and enzymes of the virus from large viral polyprotein synthesised by infected cell. The polyprotein is broken into various functional components by this protease enzyme. It acts at maturation of the new virus particles when RNA genome acquires core protein and enzymes.
M…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Anti-retroviral Drugs 1.1
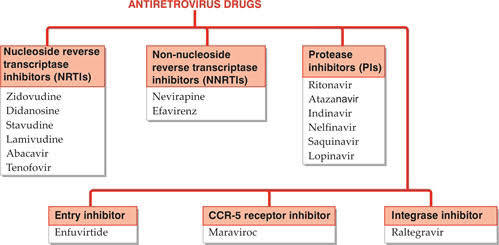
These drugs are useful in prolonging and improving the quality of life and postponing complications of AIDS or ARC but do not cure infection. Clinical efficacy of anti retroviral drugs is monitored by plasma HIV-RNA assay and CD4 lymphocyte count.
HIV is a single stranded RNA retrovirus which carries out reverse transcription of proviral DNA from viral RNA with the help of a viral RNA…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Anti Non-Retroviral Drugs 1.2
Anti Non-Retroviral Drugs 1.2
Anti-Hepatitis Virus Drugs For Hepatitis B
HBV virus is a DNA virus which integrates into the host chromosomal DNA and causes permanent infection.
The result of anti HBV drugs is improved liver function and reduction of risk for carcinoma. Sudden stoppage of these drugs can result in acute exacerbations of hepatitis.
Lamivudine
Nucleoside analogue active against HBV and HIV.
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Non-Retroviral Drugs 1.1
Viruses are the ultimate expression of obligate intracellular parasitism. They take nutrition from the host cell but also direct it’s metabolic machinery to synthesise new virus particles.
These are the drugs that are used to treat non retroviruses.
Classification of Non-Retroviral Drugs
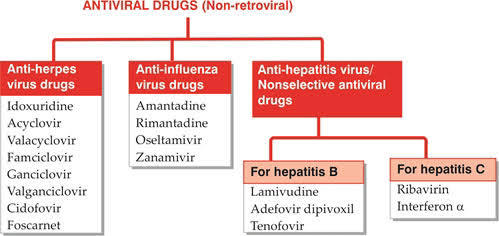
Anti Herpes Virus Drugs
These are active against the Herpes simplex virus-I (HSV-I), Herpes…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antileprotic Drugs 1.2
Treatment of Leprosy
Ridley and Jopling classification of leprosy is most widely used. They divided leprosy into Lepromatous (LL), Borderline lepromatous (BL), Borderline (BB), Borderline tuberculoid (BT) and Tuberculoid (TT).
Tuberculoid Leprosy
Anaesthetic patch.
Cell mediated immunity is normal.
Lepromin test is positive.
Bacilli rarely found in biopsy.
Prolonged remissions with periodic…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antileprotic Drugs 1.1
Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae, which was considered incurables since ages. But it curable now with antileprotic drugs but the deformities/defects already occured cannot be reversed.
Chaulmogra oil has weak antileprotic property and has been used in Indian medicine for centuries.
Classification of Antileprotic Drugs
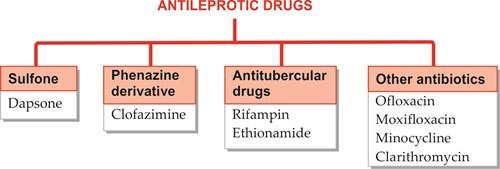
Dapsone
It is diamino diphenyl sulfone, the simplest,…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antitubercular Drugs 1.3
Treatment of Tuberculosis
Conventional therapy of tuberculosis was of 18-24 months but later a more effective and less toxic treatment reduced the duration to 6 months.
Biology of Tubercular Infection
M. tuberculosis is an aerobic organism that grows intermittently or remains dormant in unfavourable conditions. Examples are:
Rapidly growing with high bacillary load: In the wall of a…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antitubercular Drugs 1.2
Second Line Drugs
These are used when first line drugs when first line drugs cannot be used.
Kanamycin (Km), Amikacin (Am)
Similar to S.
Many S resistant strains and MDR strains of MDR strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis remains sensitive.
The RNTCP standardized regimen for MDR-TB includes Km, but Am is preferred because of less toxicity.
Cross resistance is between Km and Am.
Both…
View On WordPress
0 notes