Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
CRITICAL REFLECTION
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/10aT7skImbVGpSm9Q85BwiSAIRaFO6h7T_AZm4-dEPDA/edit
0 notes
Text
WEEK 24 - Post Production
Sequencing of the video
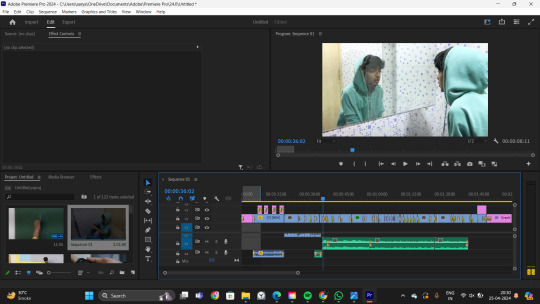
2. Adding the transition

0 notes
Text
WEEK 27 - Final Draft
Here is the final draft of my 2 min opening scene .
Good to go
0 notes
Text
WEEK 25 - Editing
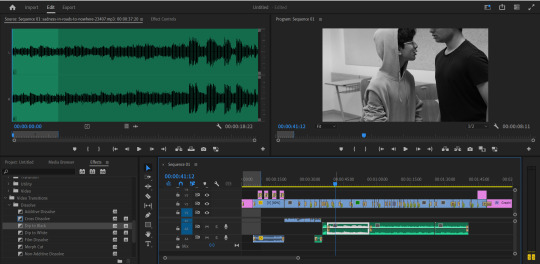
Editing in media is like magic! It takes your raw footage and turns it into a polished final product. You pick the best parts, arrange them in order, and add special touches like music or sound effects to bring your story to life.
This week we focused on editing of the video and sound
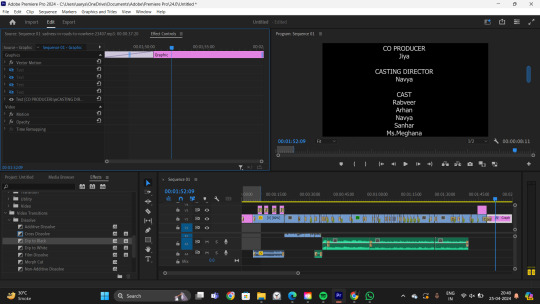
All the transitions and the credits including the title were added in the editing process.
0 notes
Text
WEEK 26 - Rough Draft
Here is the rough draft made for the 2 min opening scene after which I added a few more scenes
0 notes
Text
WEEK 23 - Shoot Day 1
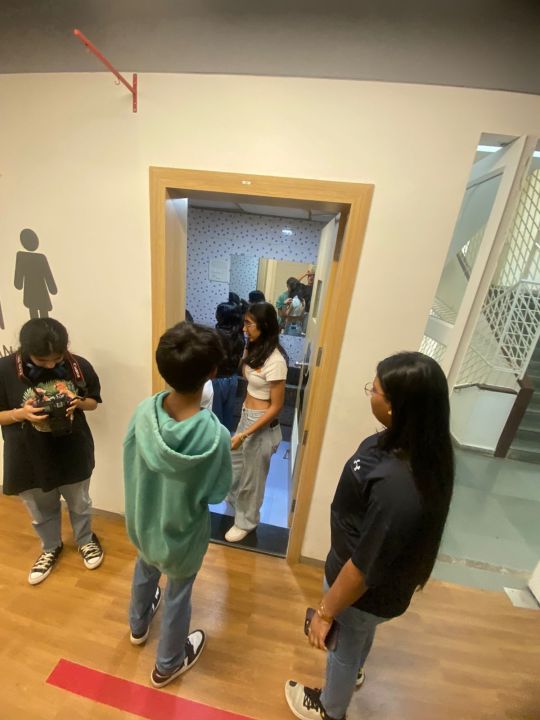

The above picture showcases how we're setting up the blood scene in the bathroom.


0 notes
Text
WEEK 21 - Actors PPT
After finalising our script, storyline,and screenplay we started to work on our actors ppt, which is basically what we have to send to the actors before the shoot so they know their roles and requirements. The ppt consists of the character, the characters background, his behaviour arc, the kind of clothes he wears the accessories he has and the proposed cast. This helps the actors learn more about their characters and get in character better.




0 notes
Text
WEEK 19 - Screenwriting for the opening scene
For this week we worked on the screenplay for our film


0 notes
Text
WEEK 18 - Story Board
Storyboards are sequential art like comic books which show the linear progression of a film's action as described in the script.
STORYBOARD:
Storyboards have truly changed the way I navigate my media studies journey. Drawing inspiration from filmmaking, they break down complex ideas, making them easier to grasp. As an art student, storyboards engage me, empowering me to understand and share media knowledge more effectively.

0 notes
Text
WEEK 15 - Scriptwriting
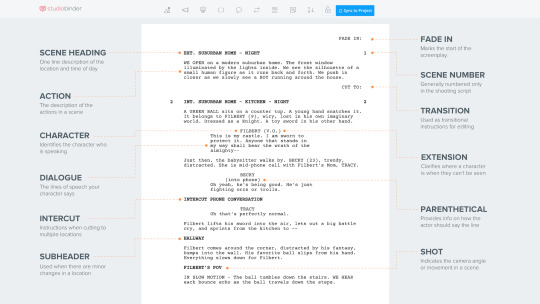
Scriptwriting for media:
Format: Learn the basic script layout (scene headings, action lines, dialogue). Free online resources can help.
Story: Start with a cool idea and strong characters. Plot it out simply (beginning, middle, end).
Types: Films (short/long), TV shows (pilots), commercials, documentaries (use scripts for narration).
Tips: Read existing scripts, write short ones to practice, get feedback, and explore genres.
0 notes
Text
WEEK 14 - Screen Play
SCREENPLAY:
To me, screenplays are more than just blueprints; they showcase the art of storytelling, dialogue delivery, action, and symbolism. They offer insights into visual language, societal contexts, and cultural commentary, letting us celebrate creativity and the timeless connection fostered through storytelling.
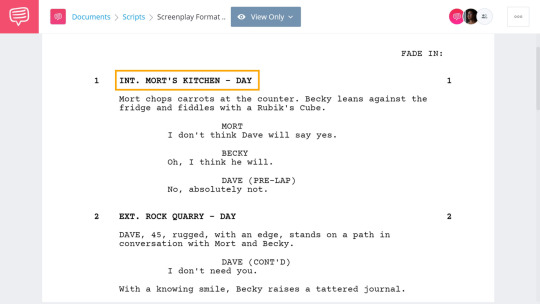
There are 2 types of screenplays that we were taught :
Actor's screenplay and Director's screenplay
Director's screenplay: The director's screenplay is about what the shoot will be. What will happen and how everything will work on the set. this screenplay is in detail and has lots of technical terms
Actor's screenplay: The actor's screenplay has everything that an actor is required to do in the shot
0 notes
Text
WEEK 13 - Story Writing
Story writing refers to the method of writing in which the writer narrates a series of events that have led to a problem, the progression of the same and the end result that has led to the current situation of the characters in the story.


0 notes
Text
WEEK 12 - Clip Analysis
Here's a breakdown of what we typically analyze in a clip:
Visual elements:
Framing (Camera shots): How the shot is composed (close-up, wide shot, etc.) and what it reveals about the subject or scene.
Camera angles: How the camera is positioned concerning the subject (low angle, high angle, etc.) and the effect it has on the viewer's perception.
Camera movements: How camera moves can show more of a scene, follow action, or build suspense.(pan, tilt, tracking, etc.)
Mise-en-scene: The arrangement of everything within the frame, including props, set design, costumes, and actors.
Audio elements:
Dialogue: What the characters are saying and how it conveys information, personality, and relationships.
Sound effects: Sounds added in post-production to create a sense of realism or atmosphere.
Music: The soundtrack and how it creates mood, tension, or foreshadows events.
Editing techniques:
Cuts: How shots are transitioned from one to another.
Pace: The speed at which the clip unfolds.
0 notes
Text
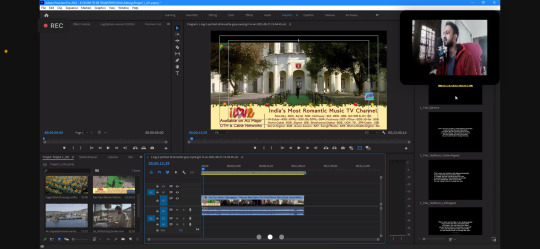
WEEK 11 - Editing(Learning how to use Adobe Premier Pro)
We were taught how to use the software Adobe Premier Pro over a few classes, where we learnt editing. Video editing software is like a toolbox for working with videos. It lets you cut, trim, and rearrange clips to improve the flow of your video. You can also use it to add effects and adjust colours to make your video look its best.: here are a few screenshots of our classes
how to import clips

how to add them in our timeline, split and crop them

how to add audio/music and sync it with the video
And how to colour correct
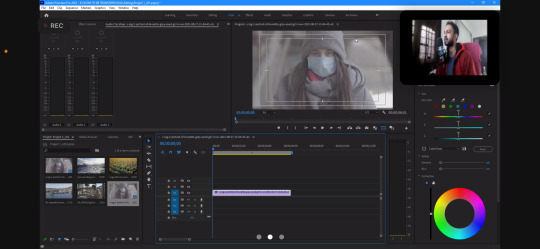

0 notes
0 notes
Text
WEEK 10 - Sound

Sound enhances the audience's emotional experience. Helps you to identify the character's type, the unspoken thought of the character. It creates meaning by setting the location, and the period, building a sense of continuity.
I wasn’t present when sounds were introduced in class, but I read the notes and on the internet about it. Diegetic sounds are sounds that are taken from a video or a clip they can come from an on-screen or off-screen subject but it’s in sync with what action is happening on the stage. example water falling an actor saying his dialogues or playing an instrument. Non-diegetic are the ones that are separated sounds and don’t originally exist in any clip. They are sounds the audience can hear but characters can’t, such as narration.
0 notes