Audra Business is a robust internet controller with a combination of (a) Gateway device, (b) Cloud AI, and (c) Management app.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Monitor your children's internet activity

The modern digital era is a great moment to live in, but it also has the potential to be a scary one. Because there is so much cyberbullying and adult material on the internet, protecting children when using it has become one of the most important things that must be done.
Read More
0 notes
Text
Enhance Security and Protect your Data from cyber threats

If you keep up with the latest technological developments, you've probably noticed that privacy and cybersecurity have received much attention lately. The privacy policies of major corporations like Google and Facebook have been the subject of recent news coverage. It is essential to how firms deal with their data. In addition, sadly, there have been a lot of data breaches throughout the last year.
0 notes
Text
Five factors to consider while choosing internet security solutions

Internet connection is becoming extremely important for most companies and homes, making it on trend with other necessities like water and electricity. Most people no longer consider Wi-Fi a luxury; instead, it is an essential amenity for daily living. However, the internet is never a standard model for all users.
Read More
0 notes
Text
Prevent DDOS Attacks

A malicious effort to interfere with the accessibility of a target network, such as a website or program, to authorized end users is an example of a denial of service attack, often known as a DoS attack. At the same time, Distributed Denial of Service or DDoS attack is one of the most destructive weapons cybercriminals use to target websites and online services.
Read More
#ddos attack#cybersecurity#preventddosattacks#audrainternetcontroler#audra internet controller#audra
0 notes
Text
Cybersecurity Best Practices For Small Businesses

Cyberattacks on small businesses are getting more common. This is probably because smaller companies frequently have weaker security procedures than larger companies. Small business owners must therefore be informed of the most recent cybersecurity dangers and take action to safeguard their businesses.
It's important for small business owners to keep up with the most recent cybersecurity risks and apply best practices to safeguard their businesses. The following are some recommendations to help you.
Cyberattacks to be aware of -
Small firms must watch out for a range of cyberattacks, such as:
Phishing attacks: In such a phishing attack, thieves send emails that look like they are coming from a trustworthy source, such as the financial company or a well-known online marketplace. The email can have links or attachments and, when you click them, will infect your computer with malware or take you to a false page.
Malware: Malware is a program that is intended to harm or takedown systems. This can be distributed via web pages, USB drives, and sometimes email attachments.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: Through a denial-of-service attack, hackers try to overflow a website or server with activity in order to prevent regular users from accessing it.
SQL injection attacks: Through a SQL injection attempt, cybercriminals use faults in web-based programs to put malicious code into such a database. This program can then be completely disabled or sensitive data can be obtained by this code.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack: In such a MitM attack, thieves interrupt messages exchanged between two entities in order to get access to confidential data. A cybercriminal may, for instance, listen in on a discussion between a user and a company utilizing an open Wi-Fi connection.
Insider attack: A present or ex-employee who may have information about the company's network conducts an insider attack. Attackers of this kind can possess valid login information or have got entry using social engineering.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT): The APT is a type of cyberattack where a hacker infects a network without authorization and then uses that access to stay inaccessible for a sustained length of time. APTs are extremely challenging to protect against and are frequently brought out by state-sponsored entities.
Password Attack: During a password attack, a criminal employs a number of techniques to imagine or utilize brute force to gain access to a user's profile. Attacks on passwords can be conducted either manually or automatically using programs.
Zero-day exploit: A zero-day exploit is one that takes advantage of a weakness that has not previously been discovered. Since there was no fix accessible at the moment of the attack, most attacks are challenging to counter.
How to secure your small business from online threats:
It is important to take action to safeguard your organization against cyberattacks as more firms expand online. Here are a few recommendations:
Make sure to implement two-factor authentication as well as use unique passwords: Using strong, challenging passwords is among the strongest strategies to safeguard your resources. Additionally, wherever possible, you ought to activate two-factor authentication (2FA). By forcing you to use a code through your phone or some other device in relation to your password, 2FA offers an additional layer of protection.
Keeping your software updated: Security patches included in software upgrades can assist in defending your system against advanced threats. Install updates as fast as they become available, then.
Educate your staff: They should be knowledgeable about the most recent cybersecurity risks and how to counteract them. Make sure you routinely offer training.
Set a firewall: By preventing traffic coming from unauthorized sources, a firewall can actually protect your system from threats. It can also be applied to limit who has access to particularly sensitive information
Backup all of your data: Periodically backup your financial information to protect it in case your system is attacked. You may restore any deleted or corrupted files using this.
Differentiate workspace and personal passwords: It's essential to separate your work and personal passwords. All other accounts will thus be secure even if the first one is hacked.
Choose a secure network: Make sure to collaborate through a secure network, which includes HTTPS or a VPN, while retrieving sensitive information. This will reduce the risk that hackers will obtain your data.
Be careful when opening email attachments: Among the most popular techniques for malware to affect is through email attachments. Whenever opening any attachments, make sure to run a thorough antivirus scan on them.
Keep an eye on the activity logs: Keep an eye out for any strange activities in your activity logs. It can assist you in identifying an attack quickly and taking precautions to limit the impact.
Increase the complexity of your security procedures: Evaluate your security regulations and processes. Are they continually updated? Do they cover all of the most recent challenges? Ensure that all of your staff are aware of and comply with your policies and that they are reliable.
By taking these actions, you can defend your company against cyberattacks. It's necessary to keep in mind that no system is completely secure. So make sure to look out for any unexpected activity and keep an eye on your systems. Additionally, because cybersecurity is a sector that constantly changes, it's essential to keep up with the most recent threats and effective countermeasures.
0 notes
Text
5 Simple Ways To Spot a Phishing Email

A phishing email is one that has the looks of coming from a reliable source but is actually sent by a malicious party. An attachment or link in a phishing email is intended to deceive the receiver into downloading malware onto their machine. Additionally, important information including credit card details and login details can be stolen through phishing emails.
How can you identify a scam email?
You can detect a phishing email by keeping an eye out for the following signs:
The email address used by the sender does not belong to the name of the business or organization that they pretend to express.
The email contains grammatical mistakes or unusual word choices.
The email makes you feel compelled to act right away by expressing urgency or threatening penalties.
You weren't hoping the link or attachment was included in the email.
Simply speaking, the email appears suspicious because it was sent by an unknown source or has an uncomfortable subject line
1) The email address used by the spammer does not correlate to the name of the business or enterprise they tend to show.
Most frequently, phishing emails are sent using bogus email addresses that seem to be from a reliable source. The email address will typically differ somewhat from the authentic address even though the sender's identity may be accurate or the logo is slightly changed.
2) The email has grammatical mistakes or unusual word choices.
Phishing emails frequently have poor writing, including grammatical mistakes or strange wording, or numbering. This is due to the fact that non-native English speakers are typically the ones that generate them quickly. For instance, a phishing email can read: "Please fill this form", "To reactivate it, just click it." or some random numbers are added in a line to complete the mail.
3) The email makes you feel compelled to act right away or threatens you with negative outcomes if you don't.
By promising severe results if you fail to not take rapid action, phishing emails frequently induce a sense of pressure. For instance, a phishing email wants to sign in to your account via some link within a second and threatens to terminate your account whenever you don't clarify your login details in less than 7-14 days.
4) An unusual link or file is included in the email.
Phishing emails frequently contain unusual links or attachments. Such links and attachments can infect your computer with malware or lead you to a fraudulent website. Whenever you get an email with a link or file from an anonymous source, don't really click.
5) The email seems strange in context, for instance, the fact that it came from an untrusted source or had an irregular subject line.
An email is probably a phishing email if something appears questionable. Because authentic institutions don’t randomly send you emails with attachments, but instead direct you to download documents or files on their own website. Emails with strange subject lines or unidentified senders may fall under this category. For instance, a phishing email is one containing the subject line "Immediate! Your credit card or bank account has been hacked!"
How should you respond to a phishing email?
Avoid clicking any links or downloading any attachments from scam emails. You can get in touch with the business or group immediately to confirm an email's validity if you're not sure if it's real. In addition, you should remove the phishing email from your mailbox and inform your email service provider.
Which of the following phishing email formats are frequent?
Phishing emails typically come in the following forms:
Fabricated emails appear as coming from a reliable business or authority.
Emails threaten negative outcomes when you do not respond right away.
Emails containing files or links that download malware or take you to a harmful website.
Emails with strange subject lines or unidentified senders.
Emails that generally seem suspect
Concluding Views:
Cybercriminals frequently use phishing emails to obtain your personal details. There are strategies to recognize fraudulent emails even if they frequently symbolize actual emails quite closely. Avoid clicking any links or downloading any attachments from emails that appear questionable. Rather, file a complaint with the organization to which the email appears to belong.
0 notes
Text
10 Most Common Types Of Cyber-attacks And Tips To Prevent Them
What is a cyber-attack?
One or even more computers are used in a cyber-attack by hackers to launch a harmful incident against one and sometimes more systems, computer networks, organizations, or infrastructures. The intention is to steal confidential information or interrupt the victim's businesses' regular operations. Cyberattacks can reach a variety of targets, such as users, companies, government agencies, and essential services.
Most common types of cyber attacks
Ransomware, Phishing, SQL Injection, DoS and DDoS Attacks, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Man-in-the-Middle (MitM), Password Attacks, Insider Threat, DNS Tunneling, and Cryptojacking.
#1. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware virus that encrypts a victim's data from the computer, generating them inaccessible, and afterward claims payment in return for protected data. This kind of attack typically uses a Trojan that purpose is to identify a trustworthy file or program to fool the target into downloading and installing it. When activated, the ransomware encrypts any linked network drives as well as the files on the computer system. A ransom message is then displayed to the victim, usually requesting payment in Bitcoin or whatever cryptocurrency.
Guidelines for preventing Ransomware attacks
Effective measures for avoiding ransomware attacks include:
Start by frequently backing up your data and keeping backups offline. Consequently, backups can be deployed to restore encrypted data in the case of an attack.
Inform company personnel to stay away from fraudulent emails and website links.
Keep your security software updated and choose trusted applications.
Users' rights should be limited. Users should only be given access to the programs and data they require in order to do their activities.
#2. Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering in which the attacker uses tricks to get the victim to reveal confidential data like credit card details or login information. Email or instant messaging are frequently used in phishing attacks. In order to trick the victim, the hacker will forward an email or message that seems to be from a trustworthy source, like a bank or website. Usually, the message will contain a link to a false website that appears official. The attacker can gain access to accounts or steal information using the victim's login details or other confidential information.
How to stop phishing attempts
Employers may defend themselves from phishing attacks by having workshops on security awareness action for workers. Employees can learn how to identify phishing emails as well as what to respond to when they get one through this kind of training. Businesses can also adopt email filtering to stop phishing emails from getting to their staff.
#3. SQL Injection
Attackers can run harmful SQL queries on a database by using SQL injection. An input field, such as a login form, is attacked with malicious code that is then executed by the database. This could provide the attacker access to private information like customer information or credit card details. SQL injection can also completely erase data from the database or manipulate it.
How to stop attacks using SQL Injection
By employing parameterized queries, companies can defend against SQL injection attacks. This kind of query prevents harmful code execution by defining each input field as a parameter. Businesses can also utilize web application firewalls (WAFs) to find and stop attempts at SQL injection.
#4. DoS and DDoS Attacks
A cyberattack known as a denial-of-service (DoS) attack forbids users from using a service or system. A DoS attack known as a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack has various sources. Attacks such as DoS and DDoS are often carried out by overloading the target network with traffic, overflowing it, and denying access to authorized users. These kinds of cyberattacks can be carried out utilizing hacked computer systems and botnets under the command of the attacker.
Guidelines for defending DoS and DDoS attacks
By using rate-limiting, companies can defend themselves against DoS and DDoS attacks. Limiting the amount of traffic that is supplied to a system, this kind of security makes it harder for attackers to overload it. In order to stop harmful traffic, businesses can also employ firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS).
#5. Malware
Malware is a form of harmful software that has the ability to harm or take down networks, computers, and other devices. Malware, for instance, is capable of stealing sensitive information like credit card information or login details. Malware can also be used to take control of computers and utilize them to perform attacks like DDoS attacks. Malware comes in a wide variety of forms, such as viruses, worms, rootkits, and Trojan viruses.
The best way to stop malware attacks
Employing security software, including antivirus and anti-malware solutions, organizations may defend themselves against malware attacks. These tools are capable of finding and removing malware from networks and systems. Companies should also maintain their operating systems as well as software updated to avoid malware being able to take advantage of vulnerabilities.
#6. Man-in-the-Middle attacks
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks include the attacker monitoring two parties' discussions. The attacker can however monitor the communication or even manipulate the information being sent and received. There are numerous ways to conduct MitM attacks, including ARP spoofing and DNS poisoning.
Guidelines for defending Man-in-the-Middle attacks
Encryption can help companies defend against MitM attacks. Attackers find it more challenging to intercept conversations when there is this kind of security. In order to recognize and stop MitM attacks, companies can also deploy firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
#7. Password Attacks
An attack that tries to discover or brute force a password is known as a password attack. Passwords like "password" or "123456" can be used to guess passwords. Furthermore, attackers have the option of using brute force techniques to attempt every character arrangement until the right password is discovered. Malware and phishing emails can both be used in password attacks.
Defending against password attacks
By having stronger password regulations, businesses can defend themselves against password attacks. Workers should be required by these policies to use difficult-to-guess passwords. Companies can also utilize two-factor authentication (2FA), which calls for a secondary form of identification, such as a password and a one-time passcode.
#8. Insider Threats
A sort of attack that starts within a company is known as an insider threat. Insider threats can be caused by irresponsible insiders, including employees who mistakenly release data, or by information theft, such as dissatisfied employees. Given that the attackers have indeed gained access to the company's applications and networks, insider threats can be challenging to identify and prevent.
Detecting and avoiding Insider Threats
Security systems, such as operation tracking and data loss prevention (DLP) initiatives, can help organizations defend against insider threats. Such tools can assist businesses in identifying and stopping malicious or unintended data leaks. Businesses should also teach their workers about security processes to ensure effective security.
#9. DNS Tunneling
Data is tunneled over a network using DNS queries in a technique known as DNS tunneling. Bypassing firewalls or intrusion monitoring and risk reduction systems, this kind of assault can steal data from a business. Moreover, interacting with systems that are affected by malware is possible using DNS tunneling.
Methods to avoid DNS Tunneling
Companies can defend themselves against such DNS tunneling attacks by keeping an eye for odd activity in DNS traffic. Companies can also stop DNS traffic that does not originate from or travel via recognized DNS servers.
#10. Cryptojacking
Attackers who engage in cryptojacking utilize malware to take over a computer's capabilities in order to mine cryptocurrencies. The efficiency of a computer may be slowed down, and electrical costs may rise. Cryptjacking can also be used to fund other unethical operations or to make money for the attacker.
Methods to avoid Cryptojacking
By deploying security tools to find and stop malicious mining software, businesses may defend themselves from crypto jacking. In order to stop hackers from utilizing it to mine bitcoin, businesses can also disable JavaScript on PCs and other hardware.
Proper cyber hygiene practices to keep you safe online
Everyone should practice a few solid cyber hygiene practices in addition to the preventative strategies mentioned above to help keep themselves secure online. Among these behaviors are:
Avoid repeating passwords and always use strong ones.
As soon as it is possible, set up two-factor authentication (2FA).
Do not open attachments or click on links coming from unauthorized sources.
Update your program frequently.
When using open Wi-Fi networks, consider a VPN.
Whenever exchanging personal information online, use it carefully.
Maintain regular data backups.
Check your credit report frequently for unusual behavior.
Share sensitive information only if you are aware of who the receiver is.
Understand how to recognize social engineering attempts and be conscious of them.
You can take preventive measures against unauthorized efforts by outside parties to acquire your data and safeguard your privacy from people you wish not to share your details with by implementing a few straightforward modifications to your devices and accounts.
It's difficult to go a few days after reviewing the news without discovering a significant data breach that could have exposed the private information of millions of consumers to cybercriminals. Here Audra helps you prevent your personal information from falling into unwanted hands with many steps.
To conclude
You can defend yourself from falling a target of a cyber-attack by adapting to the preventive strategies and excellent cyber hygiene practices mentioned above. Furthermore, you can contribute to making the internet a comfortable place for everyone by keeping yourself updated on cybersecurity issues. If you want to learn more, contact us to secure your business or personal data from criminals.
0 notes
Text
Cybersecurity Best Practices For Small Businesses

Cybersecurity Best Practices For Small Businesses
Cyberattacks on small businesses are getting more common. This is probably because smaller companies frequently have weaker security procedures than larger companies. Small business owners must therefore be informed of the most recent cybersecurity dangers and take action to safeguard their businesses.
It's important for small business owners to keep up with the most recent cybersecurity risks and apply best practices to safeguard their businesses. The following are some recommendations to help you.
Cyberattacks to be aware of -
Small firms must watch out for a range of cyberattacks, such as:
Phishing attacks: In such a phishing attack, thieves send emails that look like they are coming from a trustworthy source, such as the financial company or a well-known online marketplace. The email can have links or attachments and, when you click them, will infect your computer with malware or take you to a false page.
Malware: Malware is a program that is intended to harm or takedown systems. This can be distributed via web pages, USB drives, and sometimes email attachments.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: Through a denial-of-service attack, hackers try to overflow a website or server with activity in order to prevent regular users from accessing it.
SQL injection attacks: Through a SQL injection attempt, cybercriminals use faults in web-based programs to put malicious code into such a database. This program can then be completely disabled or sensitive data can be obtained by this code.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack: In such a MitM attack, thieves interrupt messages exchanged between two entities in order to get access to confidential data. A cybercriminal may, for instance, listen in on a discussion between a user and a company utilizing an open Wi-Fi connection.
Insider attack: A present or ex-employee who may have information about the company's network conducts an insider attack. Attackers of this kind can possess valid login information or have got entry using social engineering.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT): The APT is a type of cyberattack where a hacker infects a network without authorization and then uses that access to stay inaccessible for a sustained length of time. APTs are extremely challenging to protect against and are frequently brought out by state-sponsored entities.
Password Attack: During a password attack, a criminal employs a number of techniques to imagine or utilize brute force to gain access to a user's profile. Attacks on passwords can be conducted either manually or automatically using programs.
Zero-day exploit: A zero-day exploit is one that takes advantage of a weakness that has not previously been discovered. Since there was no fix accessible at the moment of the attack, most attacks are challenging to counter.
How to secure your small business from online threats:
It is important to take action to safeguard your organization against cyberattacks as more firms expand online. Here are a few recommendations:
Make sure to implement two-factor authentication as well as use unique passwords: Using strong, challenging passwords is among the strongest strategies to safeguard your resources. Additionally, wherever possible, you ought to activate two-factor authentication (2FA). By forcing you to use a code through your phone or some other device in relation to your password, 2FA offers an additional layer of protection.
Keeping your software updated: Security patches included in software upgrades can assist in defending your system against advanced threats. Install updates as fast as they become available, then.
Educate your staff: They should be knowledgeable about the most recent cybersecurity risks and how to counteract them. Make sure you routinely offer training.
Set a firewall: By preventing traffic coming from unauthorized sources, a firewall can actually protect your system from threats. It can also be applied to limit who has access to particularly sensitive information.

Backup all of your data: Periodically backup your financial information to protect it in case your system is attacked. You may restore any deleted or corrupted files using this.
Differentiate workspace and personal passwords: It's essential to separate your work and personal passwords. All other accounts will thus be secure even if the first one is hacked.
Choose a secure network: Make sure to collaborate through a secure network, which includes HTTPS or a VPN, while retrieving sensitive information. This will reduce the risk that hackers will obtain your data.
Be careful when opening email attachments: Among the most popular techniques for malware to affect is through email attachments. Whenever opening any attachments, make sure to run a thorough antivirus scan on them.
Keep an eye on the activity logs: Keep an eye out for any strange activities in your activity logs. It can assist you in identifying an attack quickly and taking precautions to limit the impact.
Increase the complexity of your security procedures: Evaluate your security regulations and processes. Are they continually updated? Do they cover all of the most recent challenges? Ensure that all of your staff are aware of and comply with your policies and that they are reliable.
By taking these actions, you can defend your company against cyberattacks. It's necessary to keep in mind that no system is completely secure. So make sure to look out for any unexpected activity and keep an eye on your systems. Additionally, because cybersecurity is a sector that constantly changes, it's essential to keep up with the most recent threats and effective countermeasures.
0 notes
Text
5 Simple Ways To Spot a Phishing Email
5 Simple Ways To Spot a Phishing Email

A phishing email is one that has the looks of coming from a reliable source but is actually sent by a malicious party. An attachment or link in a phishing email is intended to deceive the receiver into downloading malware onto their machine. Additionally, important information including credit card details and login details can be stolen through phishing emails.
How can you identify a scam email?
You can detect a phishing email by keeping an eye out for the following signs:
The email address used by the sender does not belong to the name of the business or organization that they pretend to express.
The email contains grammatical mistakes or unusual word choices.
The email makes you feel compelled to act right away by expressing urgency or threatening penalties.
You weren't hoping the link or attachment was included in the email.
Simply speaking, the email appears suspicious because it was sent by an unknown source or has an uncomfortable subject line
1) The email address used by the spammer does not correlate to the name of the business or enterprise they tend to show.
Most frequently, phishing emails are sent using bogus email addresses that seem to be from a reliable source. The email address will typically differ somewhat from the authentic address even though the sender's identity may be accurate or the logo is slightly changed.

2) The email has grammatical mistakes or unusual word choices.
Phishing emails frequently have poor writing, including grammatical mistakes or strange wording, or numbering. This is due to the fact that non-native English speakers are typically the ones that generate them quickly. For instance, a phishing email can read: "Please fill this form", "To reactivate it, just click it." or some random numbers are added in a line to complete the mail.
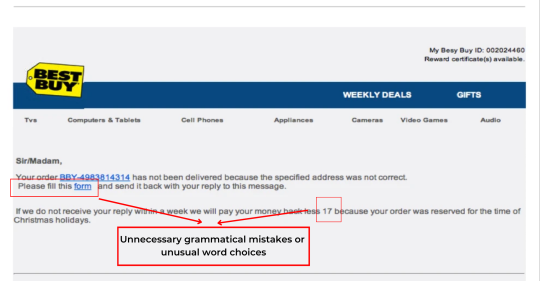
3) The email makes you feel compelled to act right away or threatens you with negative outcomes if you don't.
By promising severe results if you fail to not take rapid action, phishing emails frequently induce a sense of pressure. For instance, a phishing email wants to sign in to your account via some link within a second and threatens to terminate your account whenever you don't clarify your login details in less than 7-14 days.
4) An unusual link or file is included in the email.
Phishing emails frequently contain unusual links or attachments. Such links and attachments can infect your computer with malware or lead you to a fraudulent website. Whenever you get an email with a link or file from an anonymous source, don't really click.
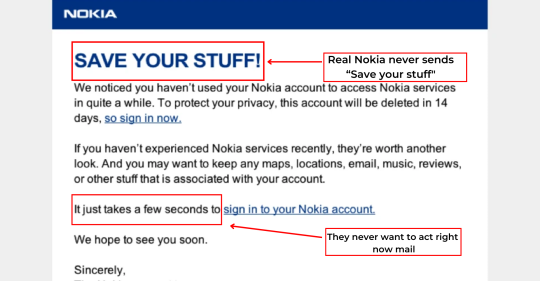
5) The email seems strange in context, for instance, the fact that it came from an untrusted source or had an irregular subject line.
An email is probably a phishing email if something appears questionable. Because authentic institutions don’t randomly send you emails with attachments, but instead direct you to download documents or files on their own website. Emails with strange subject lines or unidentified senders may fall under this category. For instance, a phishing email is one containing the subject line "Immediate! Your credit card or bank account has been hacked!"

How should you respond to a phishing email?
Avoid clicking any links or downloading any attachments from scam emails. You can get in touch with the business or group immediately to confirm an email's validity if you're not sure if it's real. In addition, you should remove the phishing email from your mailbox and inform your email service provider.
Which of the following phishing email formats are frequent?
Phishing emails typically come in the following forms:
Fabricated emails appear as coming from a reliable business or authority.
Emails threaten negative outcomes when you do not respond right away.
Emails containing files or links that download malware or take you to a harmful website.
Emails with strange subject lines or unidentified senders.
Emails that generally seem suspect
Concluding Views:
Cybercriminals frequently use phishing emails to obtain your personal details. There are strategies to recognize fraudulent emails even if they frequently symbolize actual emails quite closely. Avoid clicking any links or downloading any attachments from emails that appear questionable. Rather, file a complaint with the organization to which the email appears to belong.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Photo

Graw your business with maximum productivity.
#businessgrowth#grawyourbusiness#businesssolution#internetserviceprovider#InternetSecurity#audra#audrainternetcontroler
0 notes
Photo

Get the optimum speed from your both ISP lines.
0 notes
Photo

Protect your office network without any IT resources.
0 notes
Photo

Protect Your Office network with practical firewall.
#firewall#officenetwork#network security#audrainternetcontroler#audra#audrabusiness#internetserviceprovider
0 notes
Photo

Secure Your Office network with the simplest firewall.
0 notes
Photo

GET YOUR AUDRA HOMESHIELD TODAY
HomeShield Device+ 1 year subscription
1-year replacement warranty
Ships anywhere in Malaysia
Delivered within 3 days
0 notes