Transform Medical Devices into Connected-Care Solutions
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Unveiling the Transformative Benefits of IoT in Healthcare with Biot-Medical

In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering a multitude of transformative benefits that revolutionize patient care, operational efficiency, and healthcare outcomes. As a leading platform for connecting medical devices to the cloud, Biot-Medical is at the forefront of leveraging IoT in healthcare to unlock new possibilities and drive positive changes. Let's delve into the myriad benefits of IoT in healthcare and how Biot-Medical is spearheading this digital transformation.
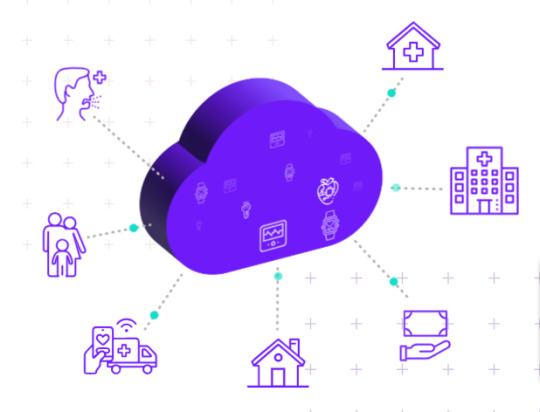
1. Remote Patient Monitoring
One of the standout benefits of IoT in healthcare is remote patient monitoring. IoT-enabled medical devices allow healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs, medication adherence, and overall health remotely and in real time. This continuous monitoring leads to early detection of health issues, timely interventions, and personalized care plans, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
IoT solutions streamline healthcare operations by automating processes such as inventory management, asset tracking, and equipment maintenance. This automation reduces manual errors, saves time for healthcare staff, and enhances overall operational efficiency, allowing organizations to focus more on delivering quality care to patients.
3. Data-driven Decision-making
IoT generates vast amounts of data, which, when analyzed using advanced analytics, provides valuable insights into patient health trends, treatment efficacy, and operational performance. These data-driven insights empower healthcare providers to make informed decisions, optimize treatment plans, and improve healthcare delivery.
4. Improved Patient Outcomes
By leveraging IoT for remote monitoring, personalized care, and predictive analytics, healthcare providers can achieve improved patient outcomes. IoT facilitates early disease detection, proactive interventions, and better management of chronic conditions, leading to healthier and more satisfied patients.
5. Telemedicine and Virtual Care
IoT plays a crucial role in enabling telemedicine and virtual care solutions. Through IoT-enabled devices and platforms, patients can access healthcare services remotely, receive medical consultations, and engage in virtual visits with healthcare providers. This expands access to care, especially for patients in rural or underserved areas, and improves overall healthcare accessibility.
Biot-Medical's Commitment to IoT in Healthcare
Biot-Medical is committed to harnessing the power of IoT in healthcare to drive positive changes and enhance patient care. Our platform seamlessly connects medical devices to the cloud, enabling real-time data access, advanced analytics, and interoperability across healthcare systems. Through our innovative solutions, we empower healthcare organizations to leverage IoT technology effectively and achieve better healthcare outcomes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Healthcare with IoT
In conclusion, the benefits of IoT in healthcare are profound and far-reaching. From remote patient monitoring to enhanced operational efficiency and improved patient outcomes, IoT has the potential to transform healthcare delivery. Biot-Medical continues to be a catalyst for this transformation, providing cutting-edge IoT solutions that empower healthcare providers, improve patient experiences, and shape the future of healthcare. Embrace the power of IoT with Biot-Medical and unlock new possibilities for a healthier tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
Setting a Standard for Cloud Computing in Medical Devices

In the last decade we have seen a growth in software-embedded medical devices. This, combined with a powerful off-the-shelf (OTS) software industry exploding around the world has forced regulatory bodies to re-think how to accommodate safety and risk requirements.
Then OTS Evolved into Cloud-based OTS SaaS Forcing Further Re-thinking
Cloud computing is both cost-effective and flexible, allowing for the quick scaling of computing resources and the provision of new services based on real-time demand. In many areas of industry, cloud computing has turned capital expenditures into operational expenditures, while increasing availability and cybersecurity. Moreover, companies delivering software in a SaaS model over the cloud also enjoy quick development and deployment cycles thanks to the advancement of Continuous Integration and Delivery techniques (CI/CD).
Within the SaaS industry, a PaaS industry of Off-the-shelf Platform software infrastructures has also evolved as a service that allows for the accelerated building of end-user-facing SaaS.
Cloud-based Medical Devices Using OTS SaaS Makes Perfect Sense
In the medical device arena, cloud computing allows for many beneficial applications, such as remote patient monitoring, data collection for medical research, as well as an emerging medical device architecture, where a significant proportion of the device functionality is executed on the cloud, rather than on the edge hardware. At BioT, we call this architecture a ‘distributed medical device.’
The benefits of the ‘distributed medical device’ architecture are great. It enables manufacturers to reduce the cost of the edge hardware by limiting the need for a strong CPU and memory. Manufacturers are able to introduce new capabilities more quickly, without the complexity related to firmware updates. Finally, it makes the device less exposed to cyber and privacy risks, because the IP (and in some cases, meaningful data) is not on the edge hardware anymore. With the option for slimmer, more affordable devices that can easily scale to the homes of patients, it seems evident that this is the future of medical devices.
Building a cloud-based medical device from scratch is an enormous and risky effort. Therefore, it makes perfect sense to utilize relevant OTS SaaS (we pronounce “OTSaaS” 😊) available, which can reduce the effort and risk to build by up to 95%. However, with OTSaaS new quality-oriented challenges rise.
The FDA Quality Regulation Does Not Address Cloud-based Medical Devices
In general, the FDA quality regulation requires that verification and validation (V&V) should take place whenever maintenance changes and new capabilities are introduced to a product baseline. This is to validate that the design structure and system logic are not negatively impacted anywhere in the device or in a way that increases patient risk or lowers efficacy.
The “validated state” as dictated by the FDA (and presented very nicely by our friends at Orthogonal), is proof that the medical software and quality systems are working as intended, and as affirmed by the previously accepted regulatory filings and the FDA’s quality management systems standards. This concept is the cornerstone of safe medical devices including Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), Digital Therapeutics (DTx), and connected medical device systems development. Without trust in the validation of the device software, there can be no trust in the ability of MedTech to improve health outcomes.
V&V processes must be consistently documented. When applied to a traditional hardware-based medical device, this is relatively straightforward as manufacturers have full control over each and every element of the software and computational environment.
With a cloud-based environment, the V&V process is much more challenging because the cloud is essentially a special form of OTSaaS. One challenge of OTSaaS is that not only does the device manufacturer lack full control over it, but the OTSaaS provider (e.g. cloud vendor) can regularly make updates to their technology stack, without prior notice – and without advanced customer approval.
The medical device manufacturer’s challenge is how to validate the software and maintain FDA validation without knowing when and what updates are being done by the cloud service provider. As with many other aspects of cloud computing, companies using the cloud weigh the tradeoff of having less control over their computing environment with the incredible economies of scale of public cloud vendors.
Cloud Change Control Now Gets Handled By AAMI
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) is an organization formed to set safety standards in both the design and usage of innovative medical devices. For cloud computing, the AAMI has a designated task group to focus on the issue of the appropriate use of public cloud computing for quality systems and medical devices.
Recently, this task group concluded that given the circumstances of cloud-based software, a continuously validated state cannot be achieved when using the cloud. In lieu of a continuously validated state, the task group considers the alternative: to achieve an intermittently validated state where the validation is periodically examined and re-confirmed.
An intermittently validated state
The types of validation that a medical device manufacturer needs to perform and the frequency with which these validations need to be conducted depends on the level of risk associated with the use of the cloud service for a particular device. Until a concrete standard or TIR (technical information report) is published on the subject, AAMI’s task force recommends that manufacturers take a risk-based approach to validation.
This requires manufacturers to ask themselves several questions:
What changes can occur between validations?
How will the change impact safety and effectiveness?
How can the change be detected?
How long will it take to correct an issue?
What harm could be caused by an unvalidated change?
The risk-based approach can be summed up as, ‘determining how a manufacturer can increase the chance of detecting a change and minimize the time taken to resolve it.’
The AAMI task force suggests that the following actions will help manufacturers to lower risk and meet the challenge of V&V:
Implement a set of automated testing that can be run at the frequency that will ensure the services remain in a validated state
Identify the intended function of the cloud computing resources within the product or service
Perform appropriate risk analysis to address potential issues specific to each individual device that may arise from cloud service changes or any malfunctioning of cloud services
Plan for the changes that may occur in real-time in the cloud, and respond thoughtfully and responsibly
For further reading about current action items, AAMI CR510:2021 provides the full details.
Clearly, a permanent solution is needed for the cloud change control challenge.
Introducing the AAMI TIR 115 Working Group SM-WG10
AAMI’s TIR 115 Working Group SM-WG10 was created by Randy Horton from Orthogonal and Pat Baird from Philips to address these issues. Bringing together a broad spectrum of stakeholders in the medical device and cloud ecosystem, this working group includes representatives from prominent cloud vendors, medical device companies, and the FDA, as well as innovative startups and platform vendors.
BioT is honored to be among the contributors to TIR 115, bringing the voice of platform vendors to the table. On one hand, as a PaaS (Platform as a Service), BioT is a user of cloud services, requiring BioT to maintain control measures to mitigate cloud vendor changes. On the other hand, as a PaaS provider, BioT is also required to provide such measures to the medical device companies we serve. This allows BioT a balanced perspective on the issues involved.
We invite anyone interested in cloud change control to be in touch and consider joining the AAMI TIR working group. Working together, we can shape industry standards, thereby improving patient outcomes, for years to come.
Interesting in Contributing to AAMI TIR 115? Contact Us
0 notes
Text
Transform Medical Devices into Connected-Care Solutions with BioT’s No-code Platform
1 note
·
View note