Text



Pennant-winged Nightjar (Caprimulgus vexillarius), male, family Caprimulgidae, order Caprimulgiformes, South Africa
photographs by Manfred Suter
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
I got to hold a 500,000 year old hand axe at the museum today.
It's right-handed
I am right-handed
There are grooves for the thumb and knuckle to grip that fit my hand perfectly
I have calluses there from holding my stylus and pencils and the gardening tools.
There are sharper and blunter parts of the edge, for different types of cutting, as well as a point for piercing.
I know exactly how to use this to butcher a carcass.
A homo erectus made it
Some ancestor of mine, three species ago, made a tool that fits my hand perfectly, and that I still know how to use.
Who were you
A man? A woman? Did you even use those words?
Did you craft alone or were you with friends? Did you sing while you worked?
Did you find this stone yourself, or did you trade for it? Was it a gift?
Did you make it for yourself, or someone else, or does the distinction of personal property not really apply here?
Who were you?
What would you think today, seeing your descendant hold your tool and sob because it fits her hands as well?
What about your other descendant, the docent and caretaker of your tool, holding her hands under it the way you hold your hands under your baby's head when a stranger holds them.
Is it bizarre to you, that your most utilitarian object is now revered as holy?
Or has it always been divine?
Or is the divine in how I am watching videos on how to knap stone made by your other descendants, learning by example the way you did?
Tomorrow morning I am going to the local riverbed in search of the appropriate stones, and I will follow your example.
The first blood spilled on it will almost certainly be my own, as I learn the textures and rhythm of how it's done.
Did you have cuss words back then? Gods to blaspheme when the rock slips and you almost take your thumbnail off instead? Or did you just scream?
I'm not religious.
But if spilling my own blood to connect with a stranger who shared it isn't partaking in the divine
I don't know what is.
104K notes
·
View notes
Text

Dendrogaster (a crustacean that parasitizes starfish)
56K notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm so sorry if you've talked about this already but I just saw it and you were the first person I thought of
Anyways have you seen this absolutely INSANE rove beetle
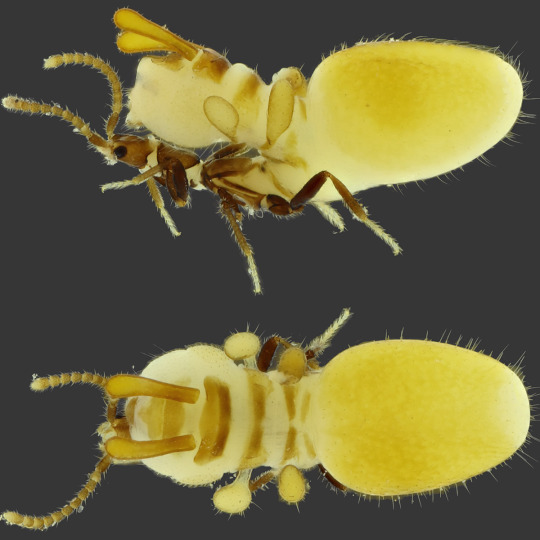

I HAVE HOPED TO SEE ACTUAL CLEAR PHOTOGRAPHS OF THIS FOR YEARS. I have seen nothing but scientific drawings and some microscopy slides!!! Oh my god it looks even sillier and more far-fetched than I thought it would. I want everyone to know before they carelessly continue scrolling that this is how the beetle pretends to be a termite and freeloads in termite society and the entire fake termite is just the beetle's abdomen. If you look closely you can see that's what it is, that it just has a massive weird butt so big it can hide entirely under its own butt and that it (the butt) is shaped like a different, inflatable decoy bug with fake antennas and fake legs.
Just four fake legs because it did not study entomology but luckily neither have the termites.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
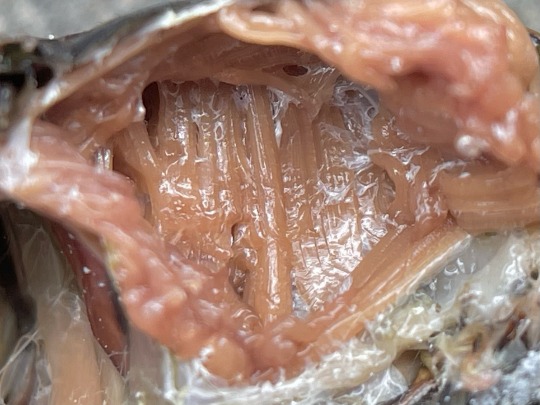
the paralyzed cicadas I picked up from a failed cicada killer nest are the perfect material to show off some cool features of insect anatomy! (although the wasp’s venom would keep them alive for her larvae to eat, I froze them to make sure they’re fully dead for dissection).
cicadas are powerful, fast fliers, and all of their thorax is taken up by a bulk of reddish, stringy flight muscles, which I’ll talk more about later. this cicada is a female, so her abdomen is full of white, elongated eggs that she will insert into tree bark with the bladed ovipositor at her rear.


the male cicada’s abdomen, however, is almost entirely empty, and that air-filled space is used as a resonator for his loud calls. the biggest structure visible there is a curved pair of muscles that deforms the tymbals, producing a click with every contraction.


here's a view of the complete muscle, and the tymbals themselves which look like overlapping plates on his belly. if you're curious what the white frosted appearance is, some Neotibicen have a coat of waxy powder or pruinescence; this male N. tibicen is particularly pruinose.
onto the flight muscles:
powered flight is a pretty complex mechanism in any organism, and is never so simple as just flapping wings up and down, but most insects power their flight in a really unintuitive way (at least for us vertebrates): they contract muscles in their thorax that aren’t even attached to the wings!
this method of flight is called indirect flight, in contrast to the direct flight of the dragonflies and mayflies where each of four wings is directly attached to a muscle and can flap on its own.
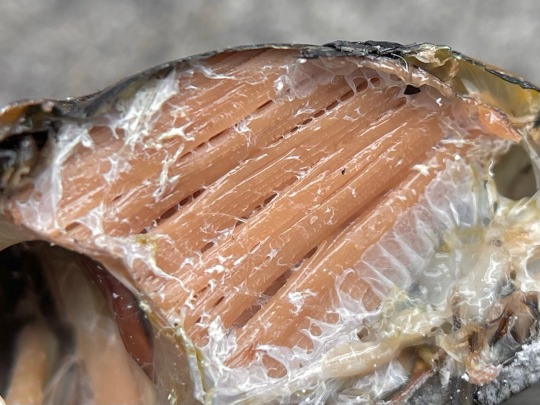

instead, most insects have a longitudinal (image 1 above, d below) pair and a vertical (2, c) pair of muscles that deform the shape of abdomen, pulling the upper segment of the thorax (notum) up and down, and this moves the wings which are attached to the notum. useful indirect flight gif from wikipedia found here
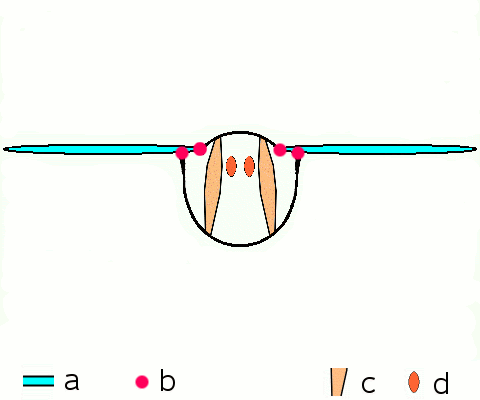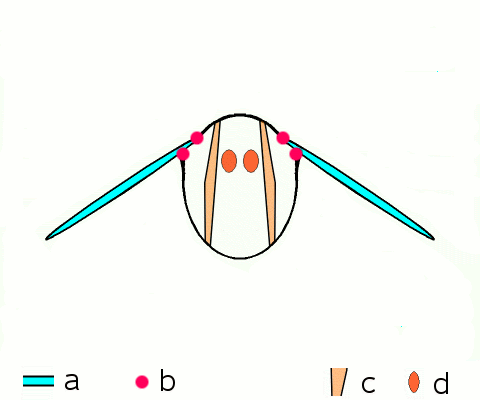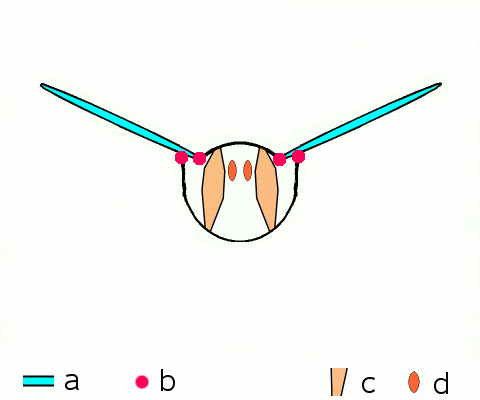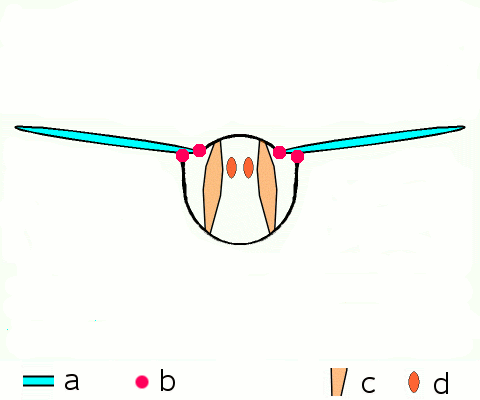
even if compressed manually, the dead cicadas "flap" their wings due to the motion of the notum:

insect flight is a lot more complicated than this simplified look at them, but I think these cicadas offer a pretty good look at how most insects get around essentially by squishing themselves internally!
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok y’all brace yourselves cuz I just learned about a new animal

Yes, that is an animal. Yes, scientists refer to it as the purple sock worm. No, that’s not it’s real name, silly, it’s real name is Xenoturbella!
When these deep-sea socks were first discovered, no one knew what the fuck they were looking at (and, really, can you blame them?). They have no eyes, brains, or digestive tracts. They are literally just a bag of wet slop. DNA analysis initially seemed to indicate that they were related to mollusks, until the scientists realized that DNA sample was from the clams they had recently eaten (yes, they can eat with no organs. We don’t know how.)
Scientists then analyzed the data again and tentatively placed them in the group that includes acorn worms, saying that their ancestors probably had eyes, brains, and organs, but simplified as a response to their deep sea ecosystems.
Later DNA testing has since shown that they are their own thing! Xenoturbella, along with another simple and problematic to place creature called acoelomorphs, belong to their own phylum called Xenacelomorpha! This places them as the sister group to all bilateral animals. So, they just never evolved brains, eyes, or organs. They are a glimpse at a very primitive form of animal that never bothered to change, because apparently what they do works. Rock on, purple sock worm.
37K notes
·
View notes
Text

This is the standard winged nightjar and it has one singular stupidly big feather on each wing... if you even care.
109K notes
·
View notes
Photo

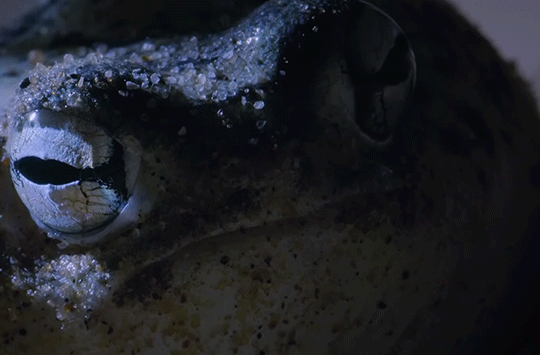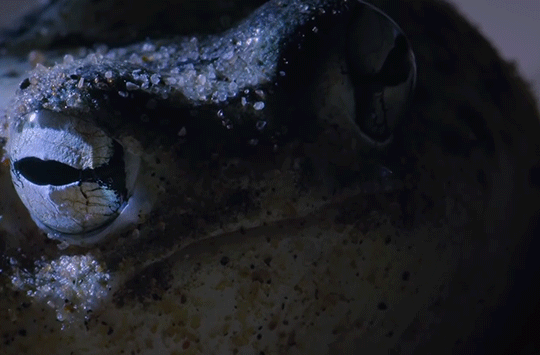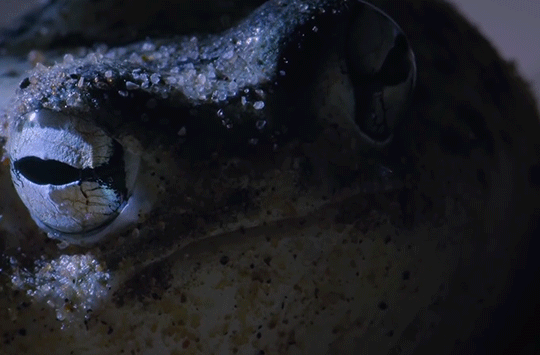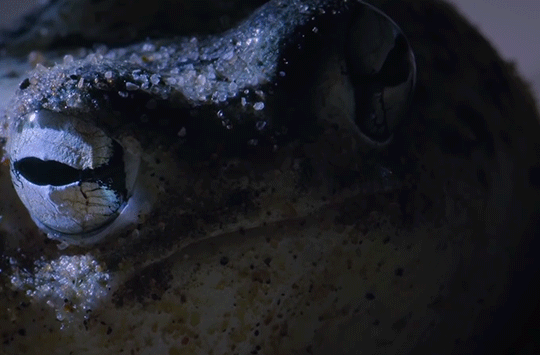


The desert rain frog is the size of a ping pong ball and may walk up to 50 yards in search of insects like termites to eat. BBC Earth
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

https://www.flickr.com/photos/vabbley/4758175680 In looking for good pictures of troglobites though I only just learned about the blind goby which is of course blind and colorless because it lives in the absolute darkness of subterreanean tunnels but that they don’t mean caves; these apparently live right on California coasts, they just absolutely never leave the burrows of mud shrimp they’re symbiotic with
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
The perfect being.




The sandhill frog [Arenophryne rotunda] is a plump little burrower native to the western coast of Australia. Unlike most burrowing frogs, who use their hind legs to dig, the sandhill frog buries itself face-first in the sand. These frogs will dig all the way to the moist layer beneath the sand and stay there during the day. At night, they emerge to hunt insects. Images by David Nelson.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
scientists in the 1990s, putting a Get More Purple gene attached to a harmless plant virus into an already purple petunia: please get more purple
the petunia, sensing an apparent honest to god Get More Purple Disease, using the previously undiscovered RNAi antiviral ability to shut down all other purple genes along with it just in case: you put VIRUS in petunia? you infect her with the More Purple?? oh! oh! her children shall bloom white! jail for mother, jail for mother for One Thousand Years!!!!
251K notes
·
View notes
Text
Being a scientist is just picking a tiny corner of existence and then spending the rest of your life seeking to know it as profoundly and intimately as you can. What greater act of love could there be?
I'm sure I've said this before but it's like so weird to me how people tend to think of scientific interest as antithetical to sentiment like noo.. What do you think drives people to study something so intently. Do you really think there's no passion behind it. Have you ever heard a scientist talk
28K notes
·
View notes
Link

This isn’t just the rediscovery of an animal thought to be extinct - there was serious debate as to whether the “Japanese axolotl” EVER existed! This is practically a cryptid!!
17K notes
·
View notes
Note
I’ve had a sucky week. I know you might not see this for a while but can I please have some weird animal facts when you get a chance to answer? :]
I’m sorry your week sucked, have some TURTLES.

Behold: one of nature’s best examples of min-maxing.
Armor plating isn’t uncommon in vertebrates. Pangolins, ankylosaurus, armadillos, and placoderms all share similar stat allocation to name a few.
Some, like pangolins, just throw all the keratin they can into their skin and end up with tough scales. That’s the same stuff fingernails and hair are made of, and also the stuff that makes our skin waterproof. Others, like ankylosaurs, also grow little bits of bone into their skin. A bunch do both. These are common, efficient, easy-to-evolve traits that occur multiple times in history.
Turtles said fuck all that.

I’m doing it my way.
(Well not ALL that, they do still have keratinized scaly skin on their limbs, but still)
They took their rib cage, sternum and spinal column- you know, things that normally go inside your body, and put ‘em on the outside instead. Shoulder blades and hip bones grow inside the rib cage, too. Then, as if that wasn’t enough, they covered the whole deal in keratin scales. Some turtles even have a hinge on their belly (plastron) that lets them close up completely. I promise, there’s a turtle in there.

What could go wrong reverse-engineering an exoskeleton onto a vertebrate?
Turns out, a lot.
Take a nice deep breath in, and exhale it out. Can you feel your ribs move? Feel them expand and contract, working with your diaphragm muscles to pull large quantities of air into your body?

Show-off.
Yeah, when all your ribs are fused into one big dome it turns out you lose a lot of lung function. The good news? With your body fully enclosed and stabilized in bone, it’s not like your abs and obliques are doing anything now. Might as well put them to work pumping your lungs. Except, not directly. Some muscles pull on the liver, which attaches to the right lung. Other muscles pull on the stomach, which pulls on the left lung. It’s pretty inefficient all around, so you may not get enough oxygen exchange to be a marathon runner, but as long as you don’t have to worry about predators you know what they say about slow and steady.
However that’s not always enough. What if, say, you did have to worry about predators a little. What if, hypothetically, you took a few points away from pure defense and gained a little more swim speed and mobility? You, like many semi-aquatic turtles, would need a backup source of oxygen. A breathing plan B.
In turtles, plan “B” stands for Butt. Some turtles (lots of freshwater semi-aquatic ones) can pump water in and out of their cloaca, which is sometimes enlarged and lined with specialized membranes that maximize surface area for gas exchange. Basically, improving any part of this fucked-up breathing apparatus is so difficult that it’s evolutionarily better to evolve proto-gills in the ass.

I was going to make a different joke here but these turtles are literally called “Northern Red-Bellied Cooters” and I really can’t top that
Turtles are cold-blooded, which of course means they don’t do shit in the winter. Turtles who are unfortunate enough to live in places that get winters bury themselves in the mud in a type of hibernation called ‘brumation’. You may wonder, how do they breathe THEN?
Easy, they don’t. They slow down their metabolism a crazy amount and spend the winter months doing anaerobic respiration. We can do this too, it’s why your muscles burn after working out. If your body doesn’t get oxygen, your cells can still burn fuel much less efficiently and produce a lot of lactic acid as a byproduct. Turtles can counteract the extreme acidity, buffering it and sequestering it with the bone in their shell. Literally, they leach calcium and magnesium out of their bones to prevent their acidic blood from killing them over the winter.
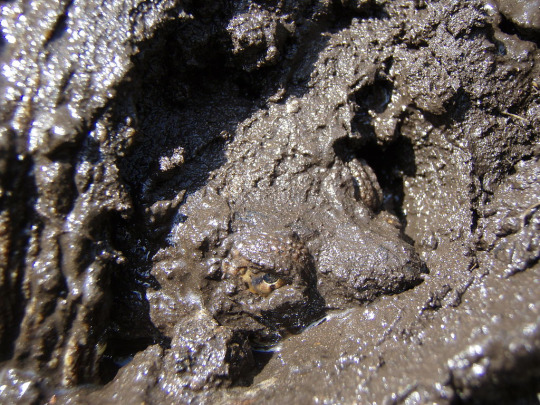

Just waking up from the winter, chock-full of acid and ready to snap.
The most infuriating thing, personally, is that all of this bullshit min-maxing works. Turtles are the longest-lived land vertebrates. The oldest recorded one lived to 187. There’s a little box turtle at my workplace that’s almost 90. This isn’t a glass cannon like a horse is, this janky tank build WORKS.
10K notes
·
View notes


