Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
References:
• https://www.lung.org •https://www.healthline.com/health/copd •https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/chronic-diseases/chronic-respiratory-diseases/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-copd.html •https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd) •https://goldcopd.org

0 notes
Text
The American Lung Association Airways Clinical Research Centers Network is the nation's largest not-for-profit network of clinical research centers dedicated to asthma and COPD treatment research. The ACRC conducts large clinical trials that directly impact patient care for COPD and asthma. Current COPD trials include a study on the effects of Losartan (a blood pressure medication) on emphysema and another on the relationship between anxiety, health status, and prognosis, to inform appropriate treatment strategies.
0 notes
Text

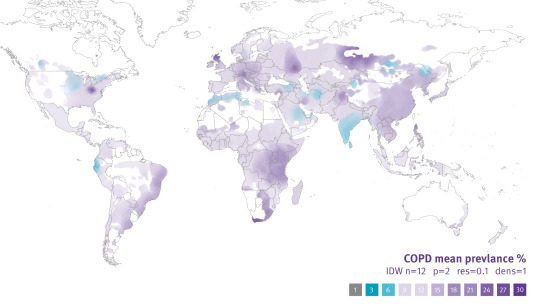
More than 65 million people around the world have moderate or severe COPD, and experts predict that this number will continue to rise worldwide over the next 50 years.
0 notes
Text

COPD symptoms progressively compromise the patient's ability to function normally in terms of their day-to-day activities and physical activity, and can impair sleep quality. Moreover, increased COPD symptom burden is associated with comorbid anxiety and depression. Common medications used to help COPD are: Fluticasone (Flovent), Budesonide (Pulmicort), Prednisolone.
0 notes
Text
Over time, exposure to irritants that damage your lungs and airways can cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The main cause of COPD is smoking, but nonsmokers can get COPD too. Indoor and outdoor pollutants can cause COPD in people who don't smoke. Air pollution inside the home and in certain filed of work force are the most common cause of COPD among people who don't smoke. Genetics may play a role in contracting COPD, and it may create a greater risk for obtaining the disease but it is not hereditary and it is not the main cause of COPD.

0 notes
Text
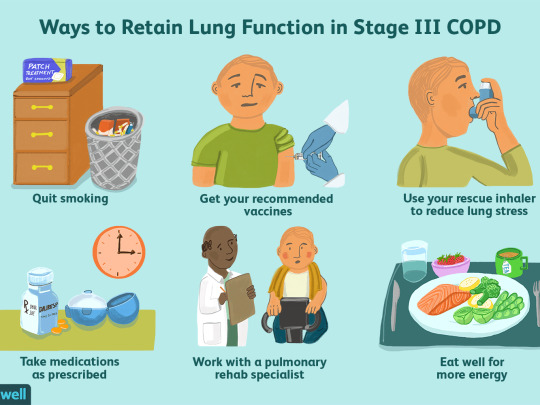
There's currently no cure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but treatment can help slow the progression of the condition and control the symptoms. Treatments include: stopping smoking, oxygen therapy, take prescribed inhalers and or medicines, lung/physical exercises

0 notes
Text


Your lungs rely on the natural elasticity of the bronchial tubes and air sacs to force air out of your body. COPD causes them to lose their elasticity and over-expand, which leaves some air trapped in your lungs when you exhale. The chronic inflammation in COPD involves the infiltration of the major inflammatory cells including neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages, and lymphocytes into the airway and lung tissue, and these can be detected in bronchoalveolar fluid and induced sputum.
0 notes
Text

Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production and wheezing. It's typically caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. People with COPD are at increased risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer and a variety of other conditions.
0 notes
Text

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease primarily affects the population age 35 years and older, it has been thought of as a predominately male-dominated condition, but that though is wrong! Records record that now a days mainly women are effected by copd! The cultural group affected most by copd are Caucasian’s.
0 notes
Text

In year 1814, British physician Charles Badhamidentified chronic bronchitis as a disabling health condition and part of COPD. He was the first person to use the term “catarrh” to describe the ongoing cough and excessive mucus that COPD produces. In 1821, the inventor of the stethoscope, physician René Laënnec, recognized emphysema as another component of COPD.
0 notes
Text

What is ”COPD” you might ask, well chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems. It includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
1 note
·
View note