main is activatedamygdalate. artist and writer etc. "proshippers/anti-antis/pro-fiction" please DNI.
Last active 60 minutes ago
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Photo
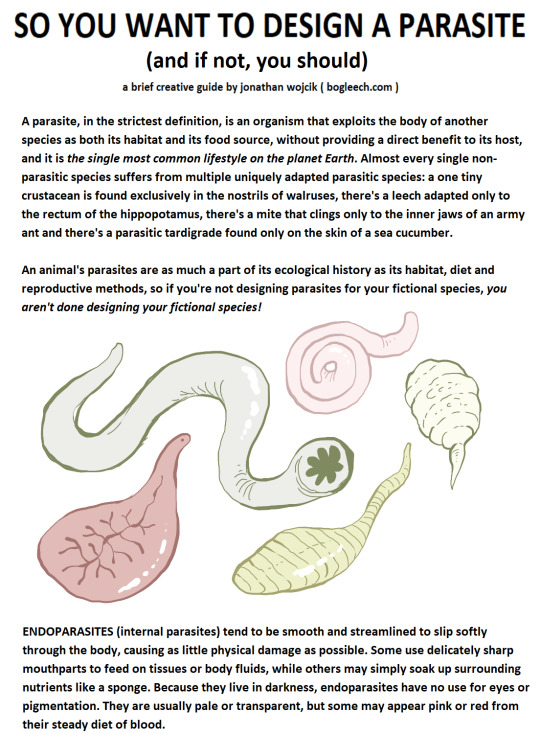
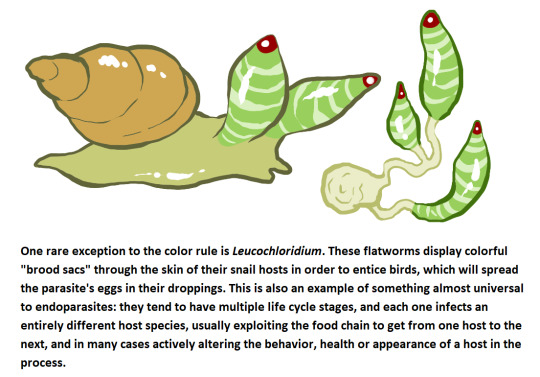




I took my second ADHD pill a little too late I guess because it was suddenly 4 am and I made this thing about why parasitic organisms are shaped like ways and how to consider that for your fiction settings. Raw text version below the cut for people with busted seeing:
Keep reading
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
WEIRDLY SPECIFIC BUT HELPFUL CHARACTER BUILDING QUESTIONS
What’s the lie your character says most often?
How loosely or strictly do they use the word ‘friend’?
How often do they show their genuine emotions to others versus just the audience knowing?
What’s a hobby they used to have that they miss?
Can they cry on command? If so, what do they think about to make it happen?
What’s their favorite [insert anything] that they’ve never recommended to anyone before?
What would you (mun) yell in the middle of a crowd to find them? What would their best friend and/or romantic partner yell?
How loose is their use of the phrase ‘I love you’?
Do they give tough love or gentle love most often? Which do they prefer to receive?
What fact do they excitedly tell everyone about at every opportunity?
If someone was impersonating them, what would friends / family ask or do to tell the difference?
What’s something that makes them laugh every single time? Be specific!
When do they fake a smile? How often?
How do they put out a candle?
What’s the most obvious difference between their behavior at home, at work, at school, with friends, and when they’re alone?
What kinds of people do they have arguments with in their head?
What do they notice first in the mirror versus what most people first notice looking at them?
Who do they love truly, 100% unconditionally (if anyone)?
What would they do if stuck in a room with the person they’ve been avoiding?
Who do they like as a person but hate their work? Vice versa, whose work do they like but don’t like the person?
What common etiquette do they disagree with? Do they still follow it?
What simple activity that most people do / can do scares your character?
What do they feel guilty for that the other person(s) doesn’t / don’t even remember?
Did they take a cookie from the cookie jar? What kind of cookie was it?
What subject / topic do they know a lot about that’s completely useless to the direct plot?
How would they respond to being fired by a good boss?
What’s the worst gift they ever received? How did they respond?
What do they tell people they want? What do they actually want?
How do they respond when someone doesn’t believe them?
When they make a mistake and feel bad, does the guilt differ when it’s personal versus when it’s professional?
When do they feel the most guilt? How do they respond to it?
If they committed one petty crime / misdemeanor, what would it be? Why?
How do they greet someone they dislike / hate?
How do they greet someone they like / love?
What is the smallest, morally questionable choice they’ve made?
Who do they keep in their life for professional gain? Is it for malicious intent?
What’s a secret they haven’t told serious romantic partners and don’t plan to tell?
What hobby are they good at in private, but bad at in front of others? Why?
Would they rather be invited to an event to feel included or be excluded from an event if they were not genuinely wanted there?
How do they respond to a loose handshake? What goes through their head?
What phrases, pronunciations, or mannerisms did they pick up from someone / somewhere else?
If invited to a TED Talk, what topic would they present on? What would the title of their presentation be?
What do they commonly misinterpret because of their own upbringing / environment / biases? How do they respond when realizing the misunderstanding?
What language would be easiest for them to learn? Why?
What’s something unimportant / frivolous that they hate passionately?
Are they a listener or a talker? If they’re a listener, what makes them talk? If they’re a talker, what makes them listen?
Who have they forgotten about that remembers them very well?
Who would they say ‘yes’ to if invited to do something they abhorred / strongly didn’t want to do?
Would they eat something they find gross to be polite?
What belief / moral / personality trait do they stand by that you (mun) personally don’t agree with?
What’s a phrase they say a lot?
Do they act on their immediate emotions, or do they wait for the facts before acting?
Who would / do they believe without question?
What’s their instinct in a fight / flight / freeze / fawn situation?
What’s something they’re expected to enjoy based on their hobbies / profession that they actually dislike / hate?
If they’re scared, who do they want comfort from? Does this answer change depending on the type of fear?
What’s a simple daily activity / motion that they mess up often?
How many hobbies have they attempted to have over their lifetime? Is there a common theme?
66K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Characters with a "Victim Mentality"

Victim Mentality - a type of mindset in which an individual believes they are a constant target of misfortune and have no control over their situation.
Individuals who adopt a victim mentality typically experienced a traumatic event that lowered their self-confidence.
Rather than coping with failure in a healthy and productive way, individuals with a victim mentality resort to chronic pessimism and defensive patterns of behavior.
By fostering self-pity and minimizing positive events, individuals with a victim mentality struggle to accept productive feedback and fail to adopt a growth mindset.
Signs of Victim Mentality
The main sign of victim mentality is a failure to assume personal responsibility.
Individuals who have a victim mentality have a hard time accepting accountability for their own actions in a situation.
Common behaviors associated with victim mentality include:
making excuses,
blaming others for misfortunes,
resenting other people’s accomplishments, and
believing nothing will change.
Catastrophizing bad things and refusing to develop solutions are also signs of victim mentality behavior.
Thought patterns associated with the victim complex cause individuals to view situations from an exaggerated and unrealistic standpoint.
Causes of Victim Mentality
Victim mentality is a learned behavior and personality trait that usually starts during childhood. Below are common causes of victim mentality:
Avoidance: Victim mentality is an emotional barrier that prevents individuals from displaying vulnerability. Individuals who fear and avoid vulnerability use the victim mentality as a way to distance themselves from their relationships and personal goals.
Betrayal: Repeated breaks in trust reduce an individual’s security and confidence in their relationships. Some people adopt a victim mentality after experiencing numerous forms of betrayal.
Manipulative tendencies: Individuals who seek constant validation from others employ their victim role for attention. Manipulative behavior and entitlement cause this form of victim mentality, as individuals use their sense of powerlessness to gain control over their loved ones.
Past trauma: Learned helplessness can develop from traumatic experiences that cause extreme feelings of helplessness. In some situations of abuse, adopting a victim mindset is a coping mechanism for handling physical or emotional pain.
Impact of Victim Mentality
Victimhood has a negative impact on your mental health and overall well-being.
Negative thinking can result in low self-esteem and self-sabotage behavior.
Allowing these thought patterns to persist can also make you feel frustrated, depressed, and isolated from friends and family members.
Addressing Victim Mentality
When addressing someone with a victim mentality, avoid using labels to describe their situation.
Remain open and calm as you support and guide them through finding help.
While you should validate their feelings, avoid outwardly agreeing with them.
The goal is to eventually reach a point where they feel comfortable taking actions that resolve their negative thinking and assume responsibility for their own life.
Source ⚜ More: Notes & References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
i wish i could remember who made the recommendation to "make a list of all the different ways someone could feel about a topic in your fictional setting and then make each of them a character" because it is a great technique and is also extremely fun
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to write characters that feel like real people and not NPCs in your brain
You ever read a book and think “this character would survive maybe five minutes in a real conversation”? Yeah. Let’s avoid that. Here’s how to make your fictional friends feel real:
everyone wants something
Even if it’s small. Even if it’s stupid. Every character—from your MC to the one-line barista—should want something. A promotion. Revenge. A nap. World domination. That want shapes how they act.
give them contradictions
Humans are messy. Let your characters be brave and terrified, kind but petty, loyal but deeply in denial. That tension? That’s where the magic lives.
let them make bad choices
If your character is right all the time, they’re either boring or a liar. People mess up. Let your character mess up in ways that feel true to them, not just to move the plot.
interior life > cool dialogue
Quippy one-liners are fun, but what’s going on underneath? What are they afraid to say out loud? What thoughts would they take to the grave? That’s what makes a character feel alive.
how do they show emotion?
Not everyone cries when sad. Some get mean. Some go quiet. Some rearrange their bookshelves obsessively. Find their emotional language.
backstory = spice, not soup
You don’t need a 12-page trauma dump to make a character real. Drip in bits of their past when it matters. Let it shape them quietly.
voice matters
Everyone shouldn’t sound like you. Think about how your character talks. What words do they overuse? Do they ramble? Are they blunt? What don’t they say?
tl;dr: believable characters aren’t perfect—they’re specific. They’ve got fears, flaws, favorite snacks, weird opinions, and conflicting goals. Make them messy. Make them human.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Realistic Injuries

References (Minor Injuries; Head Injuries; Broken Bones; Dislocated Joints; Cutting & Piercing; Blood Loss; Blunt Trauma; Burns)
WHAT'S "NORMAL"
For a normal, reasonably healthy adult the following reading are ‘normal’. Some variation is usual and what’s normal for one person may be abnormal for another.
Pulse Rate
Between 60-100 beats per minute
A fitter person will have a rate towards the slower end of the margin and a child or young person will have a naturally high rate.
Any drastic increase or decrease in pulse rate is cause for concern.
Blood Pressure
120-140 over 70-90
Can vary with the time of day, amount of stress and a number of other factors.
High blood pressure is not usually immediately dangerous but can cause long term damage.
Low blood pressure can cause faintness, dizziness and blackouts and is usually a sign that there is an underlying problem to be treated.
Body Temperature
36°C (98.6°F) to 37.5°C (99.5°F)
Relatively minor variations in temperature are cause for concern.
MINOR INJURIES
Bumps, bruises, cuts and grazes
All inconvenient.
But not incapacitating.
A blow to a bony part of a limb or to a joint
Hurts a lot at the time of impact (as anyone who’s banged their shin will agree) and may swell and stiffen.
The impact may also have the effect of temporarily disrupting the ‘power supply’ to the limb meaning the person getting hit is likely to lose their grip on anything they’re carrying and be unable to move the joint for a few minutes.
Bruises
Can take anything from a few seconds to over a day to appear and anything from a day to several weeks to fade away again.
Soft fleshy areas bruise much more colourfully.
Sprains and torn muscles/tendons etc.
Will stiffen, swell and become more painful after a few hours.
A bad sprain can be every bit as incapacitating as a broken bone.
HEAD INJURIES
Probably the most common injury in fiction.
From “let’s bash the bad guy over the head to stop him running after us” to those scenes where everyone gets thrown all over the flight deck by the first bit of turbulence and bounce their heads off consoles.
Minor Head injuries
The human skull is pretty robust and designed to take a fair amount of punishment. Consequently the occasional bump won’t do all that much damage.
A minor bump on the head may leave a character feeling dazed and suffering from a headache, blurred vision and ringing ears but will clear within a few minutes.
Facial bruising - quite uncommon, it takes quite a hard blow or a blow that impacts with the soft tissue around the eyes to leave a mark.
Minor cuts and lacerations on the scalp and face will hurt and bleed out of all proportion to their seriousness. [NOTE: A ‘laceration’ does not mean ‘a very bad cut’ – it is a term for a specific type of wound caused by the tearing rather than the slicing of the skin. It’s the sort of cut you get from being hit with a blunt object (or a fist).]
Medium Head Injuries
A more forceful blow (equivalent to a fall of several feet) can lead to complications of the injury.
Concussion (damage to the brain tissue) is quite common after a hard blow to the head and is often accompanied by temporary unconsciousness. (And it should be very temporary if you don’t want your character to be permanently damaged). This can also result in dizziness, nausea and, not surprisingly, a nasty headache.
Medium cuts and lacerations will be painful and messy but not dangerous. There may be scarring.
Severe Head Injuries
A blow to the head resulting in prolonged unconsciousness will almost certainly result in brain damage, possibly a fractured skull and bruising or bleeding within the brain itself. It can be fatal either straight away if the damage is extensive enough or later as the blood from the injury causes pressure to be put on the brain.
Severe cuts - can damage muscle and sinew and do permanent damage. The pain from such injuries would have most characters unable to concentrate on much else.
Concussion Symptoms
Confusion, disorientation, memory loss,
Dizziness, headache (lingering after the first few hours)
Nausea, vomiting,
Pupils uneven in size and/or reaction,
Sluggish reactions, sleepiness.
Any painkillers given to treat the headache must be non-narcotic and relatively mild. Otherwise it is difficult to tell if sleepiness is caused by a worsening of the injury or by the painkillers.
Someone suffering from a suspected head injury should be watched for at least 24 hours, and woken every few hours if they’re asleep, to check for the above symptoms.
BROKEN BONES
In general they hurt. A lot. Any character with a broken bone (with the possible exception of the ribs) is going to know about it and not be very happy. It is possible that if there is no displacement they might not hurt much at all, and it may not be immediately obvious that the bone is actually broken.
The initial shock and pain is often enough to cause unconsciousness. Keeping the limb immobile will minimise the pain but any pressure or movement is going to be extremely unpleasant.
Severe breaks (compound fractures) can cause part of the bone to protrude through the skin, this will also cause blood loss, which can be severe enough to be dangerous. Nerves and blood vessels can also be permanently damaged.
Smaller bones are obviously more likely to break than larger ones but they hurt every bit as much.
Distinguishing between breaks/sprains is not always easy with just 'it hurts to go on but as a guide… Lots of pain but some movement is a relatively good thing -- it indicates 'just' a tear. Less pain but very limited movement is a worry, because it can mean you've snapped something, and the joint becomes useless without surgery.
Broken Ribs
All sorts of nasty complications can arise here. For a start, though a character who has just broken a rib will feel winded and uncomfortable, the initial discomfort will pass quickly and they may feel fine for some hours afterwards. Possibly they may not even realise that they had broken anything.
After a few hours it will start to hurt badly and breathing may be impaired and painful. Problems can occur when the injured person is breathing only shallowly because of the pain and not expanding their lungs fully, lungs can collapse as a result, causing pneumonia. Interesting in a morbid kind of way is that the breathing difficulties of a collapsed lung aren't what gets you - it's the air pressure that builds up in the chest cutting of the blood flow to the heart.
Broken ribs can also puncture a lung or even the heart with fatal results. A punctured lung would result in death within 3-15 minutes if untreated.
DISLOCATED JOINTS
Hurt just as much as broken bones.
Can be forced back into place without medical facilities but it’s not recommended and will hurt a lot, probably enough to cause unconsciousness. On-the-hoof treatment is the same as for broken bones – imobilise and support the limb.
There are a few dislocations which can be life-threatening -- the sterno-clavicular joint (where the collarbone joins the breastbone) is one. It requires a lot of force to pop it (most people's collarbones will break before the joint goes), and the collarbone usually goes outwards, but if it displaces inwards, it can compress the airways. This joint can dislocate if you get slammed very hard into something like a wall and take the impact on the point of the shoulder. I can also say it hurts very badly and for a very long time.
CUTTING & PIERCING
most human beings come equipped with a healthy set of defensive reflexes to avoid it. If at all possible they will try to put something else (like hands) in the way of the blow. Most people injured in a stabbing have injuries on their hands and arms as well from trying to ward off their assailant.
The severity of the injury depends a great deal on its location:
Limbs
The arms and legs are not protected by much flesh so even a shallow cut or piercing injury here may damage bone and muscle and render the limb effectively useless.
Severe blood loss can occur if the major blood vessels in the inside of the upper arm and inner thigh are damaged.
Abdomen
Piercing injuries will bleed a lot and can easily do fatal damage, although unless a main artery is hit then it’s not going to be a quick death. A piercing more than 2 inches deep starts to get dangerous.
If the main descending aorta is hit, the character has seconds to live.
The femoral or renal arteries will lose a fatal amount of blood in 2 – 3 minutes.
Injury to internal organs would cause bleeding, infections and a nasty slow death if left untreated. Bleeding from the spleen or liver would cause death within 20 minutes. Less major damage to internal organs would cause death either from blood loss over several hours or up to several days later from infection and other complications.
Relatively slight cuts to the stomach area would affect breathing and damage muscles, More major cuts to this area can damage nerves and muscles, meaning the injured character would have no control over their legs. Not nice, when you’re trying to get away from the nutter who’s just sliced you up and suddenly your legs don’t work…
Extensive cuts here can also mean the insides are suddenly outside. Not pretty, not comfortable and, untreated, leaves the character with about 15 minutes to live and they’re going to wish it was much less. Quite apart from the pain (which is pretty horrific) the sight of their own insides tends to make most people quite hysterical.
BLOOD LOSS
Major blood loss will result in a fast weak pulse and accelerated respiratory rate.
For an average healthy person about a litre of blood lost is enough for shock to set in.
Loss of approximately a litre and a half to two litres or more will require transfusion.
Loss of more than 2 and a half litres will probably result in unconsciousness and, if transfusion is not given, death.
Symptoms of Blood Loss
Blood loss in litres < 0.75 || 0.750-1.5 || 1.5-2.0 || > 2.0
Percentage of blood lost < 15% || 15-30% || 30-40% || > 40%
Blood pressure Normal || Normal || Reduced || Low
Pulse rate (beats per minute) < 100 || > 100 || > 120 || > 140
Pulse pressure Normal || Decreased || Decreased || Decreased
Respiratory rate (breaths/min) 14-20 || 20-30 || 30-40 || > 35
Mental state Alert || Anxious || Confused || Lethargic
State of extremities Normal || Pale || Pale/Cool || Pale/Clammy
Amount of blood loss by injury
Severe blood loss, as a wound larger than a fist or that caused by a compound fracture. All figures are approximate and somewhat variable. They are meant as a rough guide only.
SITE OF INJURY || NORMAL BLOOD LOSS (Litres / %) || SEVERE || MAXIMUM
Shoulder: 0.85 / 17% || 1.25 / 25% || 2.1 / 42%
Arm: 0.4 / 8% || 0.85 / 17% || 1.25 / 25%
Elbow: 0.4 / 8% || 0.85 / 17% || 1.65 / 33%
Forearm: 0.4 / 8% || 0.85 / 17% || 1.25 / 25%
Wrist: 0.2 / 4% || 0.6 / 12% || 0.85 / 17%
Chest: 1.25 / 25% || 1.65 / 33% || 5.0 / 100%
Spleen/Liver: 1.25 / 25% || 1.65 / 33% || 5.0 / 100%
Pelvis: 1.25 / 25% || 1.65 / 33% || 5.0 / 100%
Thigh: 1.25 / 25% || 1.65 / 33% || 2.9 / 58%
Leg: 0.85 / 17% || 1.25 / 25% || 2.1 / 42%
Ankle: 0.85 / 17% || 1.25 / 25% || 2.1 / 42%
BLUNT TRAUMA
Getting hit…
Aside from the obvious risk of getting smacked upside the head or breaking bones (see above) there are assorted other injuries and complications which can arise.
Due to the elasticity of the ribcage getting smacked in the chest can cause a person to fly backwards some distance. Of course this means they can bounce off of something else and hurt themselves that way. At best they’re going to be winded and have difficulty breathing, which causes a certain amount of panic in most people. And it looks rather alarming.
Heavy blows to the back can damage the spine resulting in possible paralysis and death. Kidney injuries are also common when someone is hit in the small of the back. They can bleed and may shut down altogether. Kidney failure means the body can’t clear certain waste products from its system, if the waste products build up too far then coma and death can result.
Internal organs such as the liver and spleen can also be damaged by blunt trauma and bleed as detailed above. Other organs which may be injured are the pancreas and the intestines.
If the pancreas is damaged it may spill digestive enzymes which start to digest the person’s own insides. Obviously this is rather painful and unpleasant.
Damage to the intestines can result in blockages (causing pain, nausea and vomiting), bleeding, and the release of bacteria into the bloodstream resulting in septic shock (high fever followed by sudden drop in temperature and blood pressure – fatal if not treated) This can take 24 hours or more.
Usual treatment for internal injuries is IV feeding, antibiotics, painkillers and sometimes surgery.
BURNS
Burns are classified into degree by their seriousness.
1st degree burns – Red, sensitive skin, like a sunburn.
2nd degree burns – Blistering on the first layer of skin (the epidermis) only.
3rd degree burns – Damage to both the epidermis and dermis (the first two layers of skin), visible scars.
Burns over more than 70% of the body are life threatening due to dehydration and the risk of shock, kidney failure and infection.
Electrical shock
Physical marks can vary from none at all to severe tissue damage depending on the severity of the shock.
Internal damage can be done by electrical current traveling along the nerves and blood vessels.
Source: Leia Fee (with additions by Susannah Shepherd) Part 2 ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh my gosh. I just found this website that walks you though creating a believable society. It breaks each facet down into individual questions and makes it so simple! It seems really helpful for worldbuilding!
132K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes & References
Alchemy ⚜ Antidote to Anxiety ⚜ Attachment ⚜ Autopsy
Art: Elements ⚜ Principles ⚜ Photographs ⚜ Watercolour
Bruises ⚜ Caffeine ⚜ Color Blindness ⚜ Cruise Ships
Children ⚜ Children's Dialogue ⚜ Childhood Bilingualism
Dangerousness ⚜ Drowning ⚜ Dystopia ⚜ Dystopian World
Culture ⚜ Culture Shock ⚜ Ethnocentrism & Cultural Relativism
Emotions: Anger ⚜ Fear ⚜ Happiness ⚜ Sadness
Emotional Intelligence ⚜ Genius (Giftedness) ⚜ Quirks
Facial Expressions ⚜ Laughter & Humour ⚜ Swearing & Taboo
Fantasy Creatures ⚜ Fantasy World Building
Generations ⚜ Literary & Character Tropes
Fight Scenes ⚜ Kill Adverbs
Food: Cooking Basics ⚜ Herbs & Spices ⚜ Sauces ⚜ Wine-tasting ⚜ Aphrodisiacs ⚜ List of Aphrodisiacs ⚜ Food History ⚜ Cocktails ⚜ Literary & Hollywood Cocktails ⚜ Liqueurs
Genre: Crime ⚜ Horror ⚜ Fantasy ⚜ Speculative Biology
Hate ⚜ Love ⚜ Kinds of Love ⚜ The Physiology of Love
How to Write: Food ⚜ Colours ⚜ Drunkenness
Jargon ⚜ Logical Fallacies ⚜ Memory ⚜ Memoir
Magic: Magic System ⚜ 10 Uncommon ⚜ How to Choose
Moon: Part 1 2 ⚜ Related Words
Mystical Items & Objects ⚜ Talisman ⚜ Relics ⚜ Poison
Pain ⚜ Pain & Violence ⚜ Poison Ivy & Poison Oak
Realistic Injuries ⚜ Rejection ⚜ Structural Issues ⚜ Villains
Symbolism: Colors ⚜ Food ⚜ Numbers ⚜ Storms
Thinking ⚜ Thinking Styles ⚜ Thought Distortions
Terms of Endearment ⚜ Ways of Saying "No" ⚜ Yoga
Compilations: Plot ⚜ Character ⚜ Worldbuilding ⚜ For Poets ⚜ Tips & Advice
all posts are queued. will update this every few weeks/months. send questions or requests here ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Children's Dialogue
Language is extremely complex, yet children already know most of the grammar of their native language(s) before they are 5 years old.
BABBLING
Babbling begins at about 6 months and is considered the earliest stage of language acquisition
By 1 year babbles are composed only of the phonemes used in the language(s) they hear
Deaf babies babble with their hands like hearing babies babble using sounds
FIRST WORDS
After the age of one, children figure out that sounds are related to meanings and start to produce their first words
Usually children go through a holophrastic stage, where their one-word utterances may convey more meaning
Example: "Up" is used to indicate something in the sky or to mean “pick me up”
Most common first words (among the first 10 words uttered in many languages): “mommy,” “daddy,” “woof woof,” “no,” “bye,” “hi,” “yes,” “vroom,” “ball” and “banana”
WORD MEANINGS
When learning words, children often overextend a word’s meaning
Example: Using the word dog to refer to any furry, four-legged animal (overextensions tend to be based on shape, size, or texture, but never color)
They may also underextend a word’s meaning
Example: Using the word dog to refer only to the family pet, as if dog were a proper noun
The Whole Object Principle: When a child learns a new word, (s)he is likely to interpret the word to refer to a whole object rather than one of its parts
SYNTAX
At about two years of age, children start to put words together to form two-word utterances
The intonation contour extends over the two words as a unit, and the two-word utterances can convey a range of meanings:
Example: "mommy sock" = subject + object or possessive
NOTE: Chronological age is NOT a good measure of linguistic development due to individual differences, so instead linguists use the child’s mean length of utterance (MLU) to measure development
The telegraphic stage describes a phase when children tend to omit function morphemes such as articles, subject pronouns, auxiliaries, and verbal inflection
Examples: "He play little tune" or "Andrew want that"
Between 2;6 and 3;6 a language explosion occurs and children undergo rapid development
By the age of 3, most children consistently use function morphemes and can produce complex syntactic structures:
Examples: "He was stuck and I got him out" / "It’s too early for us to eat"
After 3;6 children can produce wh-questions, and relative pronouns
Sometime after 4;0 children have acquired most of the adult syntactic competence
PRAGMATICS
Deixis: Children often have problems with the shifting reference of pronouns
Children may refer to themselves as "you"
Problems with the context-dependent nature of deictic words: Children often assume the hearer knows who s/he is talking about
AUXILIARIES
In the telegraphic stage, children often omit auxiliaries from their speech but can form questions (with rising intonation) and negative sentences
Examples: "I ride train?" / "I not like this book"
As children acquire auxiliaries in questions and negative sentences, they generally use them correctly
SIGNED LANGUAGES
Deaf babies acquire sign language in the same way that hearing babies acquire spoken language: babbling, holophrastic stage, telegraphic stage
When deaf babies are not exposed to sign language, they will create their own signs, complete with systematic rules
IMITATION, REINFORCEMENT, ANALOGY
Children do imitate the speech heard around them to a certain extent, but language acquisition goes beyond imitation
Children produce utterances that they never hear from adults around them, such as "holded" or "tooths"
Children cannot imitate adults fully while acquiring grammar
Example:
Adult: "Where can I put them?" Child: "Where I can put them?"
Children who develop the ability to speak later in their childhood can understand the language spoken around them even if they cannot imitate it
NOTE: Children May Resist Correction
Example: Cazden (1972) (observation attributed to Jean Berko Gleason) – My teacher holded the baby rabbits and we patted them. – Did you say your teacher held the baby rabbits? – Yes. – What did you say she did? – She holded the baby rabbits and we patted them. – Did you say she held them tightly? – No, she holded them loosely.
Another theory asserts that children hear a sentence and then use it as a model to form other sentences by analogy
But while analogy may work in some situations, certainly not in all situations:
– I painted a red barn. – I painted a barn red. – I saw a red barn. – I saw a barn red.
Children never make mistakes of this kind based on analogy which shows that they understand structure dependency at a very young age
BIRTH ORDER
Children’s birth order may affect their speech.
Firstborns often speak earlier than later-born children, most likely because they get more one-on-one attention from parents.
They favor different words than their siblings.
Whereas firstborns gabble on about animals and favorite colors, the rest of the pack cut to the chase with “brother,” “sister,” “hate” and such treats as “candy,” “popsicles” and “donuts.”
The social dynamics of siblings, it would appear, prime their vocabularies for a reality different than the firstborns’ idyllic world of sheep, owls, the green of the earth and the blue of the sky.
MOTHER'S LEVEL OF EDUCATION
Children may adopt vocabulary quite differently depending on their mother’s level of education.
In American English, among the words disproportionately favored by the children of mothers who have not completed secondary education are: “so,” “walker,” “gum,” “candy,” “each,” “could,” “wish,” “but,” “penny” and “be” (ordered starting with the highest frequency).
The words favored by the children of mothers in the “college and above” category are: “sheep,” “giraffe,” “cockadoodledoo,” “quack quack,” the babysitter’s name, “gentle,” “owl,” “zebra,” “play dough” and “mittens.”
BOYS / GIRLS
One area of remarkable consistency across language groups is the degree to which the language of children is gendered.
The words more likely to be used by American girls than by boys are: “dress,” “vagina,” “tights,” “doll,” “necklace,” “pretty,” “underpants,” “purse,” “girl” and “sweater.”
Whereas those favored by boys are “penis,” “vroom,” “tractor,” “truck,” “hammer,” “bat,” “dump,” “firetruck,” “police” and “motorcycle.”
Tips for Writing Children's Dialogue (compiled from various sources cited below):
Milestones - The dialogue you write should be consistent with the child's developmental milestones for their age. Of course, other factors should be considered such as if the child has any speech or intellectual difficulties. Also note that developmental milestones are not set in stone and each child is unique in their own way.
Too "Cutesy" - If your child characters are going to be cute, they must be cute naturally through the force of their personality, not because the entire purpose of their existence is to be adorable.
Too Wise - It’s true kids have the benefit of seeing some situations a little more objectively than adults. But when they start calmly and unwittingly spouting all the answers, the results often seem more clichéd and convenient than impressive or ironic.
Unintelligent - Don’t confuse a child’s lack of experience with lack of intelligence.
Baby Talk - Don’t make a habit of letting them misuse words. Children are more intelligent than most people think.
Unique Individuals - Adults often tend to lump all children into a single category: cute, small, loud, and occasionally annoying. Look beyond the stereotype.
Personal Goals - The single ingredient that transforms someone from a static character to a dynamic character is a goal. It can be easy to forget kids also have goals. Kids are arguably even more defined by their goals than are adults. Kids want something every waking minute. Their entire existence is wrapped up in wanting something and figuring out how to get it.
Don't Forget your Character IS a Child - Most of the pitfalls in how to write child characters have to do with making them too simplistic and childish. But don’t fall into the opposite trap either: don’t create child characters who are essentially adults in little bodies.
Your Personal Observation - To write dialogue that truly sounds like it could come from a child, start by being an attentive listener. Spend time around children and observe how they interact with their peers and adults. You can also study other pieces of media that show/write about children's behaviour (e.g., documentaries, films, TV shows, even other written works like novels and scripts).
Context - The context in which children speak is crucial to creating realistic dialogue. Consider their environment, who they're speaking to, and what's happening around them. Dialogue can change drastically depending on whether a child is talking to a friend, a parent, or a teacher. Additionally, children's language can be influenced by their cultural background, family dynamics, and personal experiences. Make sure the context informs the dialogue, lending credibility to your characters' voices.
Sources and other related articles: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Writing Notes: On Children ⚜ Childhood Bilingualism More: Writing Notes & References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
didnt expect to be talking abt starbucks so much after i quit but it just keeps getting worse

8 human trafficking survivors are suing Starbucks, exposing years of forced labor and child labor. the article starts with the story of a man who was enslaved at age 16 and was just rescued last year. if nothing else has convinced you to boycott, please let this sway you...
it also says the NGO CoffeeWatch is filing a complaint with US Customs and Border Protection attempting to block these corporations from importing coffees produced wholly or in part by slave labor in Brazil.
but this isn't unique to Starbucks, this is the unspoken truth of many of our goods in the west, relying on the exploitation of people in the global south. i pray all the survivors secure a massive payout, but still.. i cant imagine anything would ever make up for this kind of treatment.
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Description Notes:
Updated 9th September 2024 More writing tips, review tips & writing description notes
Facial Expressions
Masking Emotions
Smiles/Smirks/Grins
Eye Contact/Eye Movements
Blushing
Voice/Tone
Body Language/Idle Movement
Thoughts/Thinking/Focusing/Distracted
Silence
Memories
Happy/Content/Comforted
Love/Romance
Sadness/Crying/Hurt
Confidence/Determination/Hopeful
Surprised/Shocked
Guilt/Regret
Disgusted/Jealous
Uncertain/Doubtful/Worried
Anger/Rage
Laughter
Confused
Speechless/Tongue Tied
Fear/Terrified
Mental Pain
Physical Pain
Tired/Drowsy/Exhausted
Eating
Drinking
Warm/Hot
47K notes
·
View notes
Text
If your plot feels flat, STUDY it! Your story might be lacking...
Stakes - What would happen if the protagonist failed? Would it really be such a bad thing if it happened?
Thematic relevance - Do the events of the story speak to a greater emotional or moral message? Is the conflict resolved in a way that befits the theme?
Urgency - How much time does the protagonist have to complete their goal? Are there multiple factors complicating the situation?
Drive - What motivates the protagonist? Are they an active player in the story, or are they repeatedly getting pushed around by external forces? Could you swap them out for a different character with no impact on the plot? On the flip side, do the other characters have sensible motivations of their own?
Yield - Is there foreshadowing? Do the protagonist's choices have unforeseen consequences down the road? Do they use knowledge or clues from the beginning, to help them in the end? Do they learn things about the other characters that weren't immediately obvious?
93K notes
·
View notes
Text
gentle psa to new comic artists about a problem i also suffered from: slow quiet pacing is totally fine BUT if that’s not what you’re deliberately going for, you CAN fit more Story Progression on the page. no, more than that. more than that even. i promise if you don’t want it to a single action doesn’t need to take a whole page to illustrate each of its steps, a lot of connecting magic happens in the gutters i /promise/ if you draw someone pulling up in a car then skip to them walking in the door with groceries we will Understand that they unloaded the car and unlocked the house you feel me
475 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips for Writing an Intersex Character with Grace
I’m an intersex person—and a novelist myself—who’s had the blessing of growing up in intersex support and activism communities. After 15 years immersed in these topics, I’ve built up a great deal of knowledge about what is and isn’t anatomically possible, politics and inter-community dynamics, which pop culture depictions go down smooth, and which leave a pit in the stomach. -Hans Lindahl, 2022
This resource webpage serves as a very informative starting point for those who wish to involve intersex characters or intersex themes in their storytelling! To emphasize their knowledge on the topic, Hans is expecting their intersex-focused debut graphic novel, I'm Going Through Something, to release in 2027! <3
614 notes
·
View notes
Text
All k9 dogs are abused hands down if you post any pro k9 stuff on my dash you’re unfollowed I don’t care if we’ve been mutuals for years, you can claim to be anti-cop or a leftist or whatever but if you post k9 dogs with like “a good doggo! A good boy!” fuck off, if I lose followers over this then good riddance
121K notes
·
View notes
Text
“Get his ass” Is so unreasonably funny to me. A huge win for the English language. Today’s version of “seize him” imo
134K notes
·
View notes
