This blog documented findings from the old ROBLOX client search: specifically the clients from the years 2004, 2005, 2006, and 2007. Formerly ran by DirtPiper. Please go to https://robloxopolis.com/ for new info.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
The clientsearch has moved!
Please go to https://robloxopolis.com/ for any new posts regarding Roblox lost media archival. This blog is retired.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discord Back I guess
Don’t be too noisy
https://discord.gg/CHFK7eXXMY
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Announcing the closure of the public clientsearch discord server
After some thought, I have decided that the clientsearch’s official discord server was proving to be more trouble than it was worth. The topic of discussion rarely approached something on topic and there was no progress being made in any respect towards finding new material.
As such, I have closed the public discord, and have consolidated all of the more experienced and relevant members into a smaller, private group, in the hopes to being able to remain on-topic and make actual progress in our effort of finding undiscovered clients.
Further updates on our projects will be available here and on our official wiki, over at https://clientsearch.fandom.com/.
The discord server will be completely closed to new discussion in a week, however it will not be deleted so that it may be archived.
-DirtPiper
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHOOPS I FORGOT TO UPDATE THE BLOG
The past YEAR of developments in the clientsearch have been highly interesting. Despite there still being a depressing lack of actual studio builds from before August 2007, oodles of information about the elusive 2004-2005 roblox beta have been uncovered, as well as some unknown bits and pieces from 06, so keep reading and I’ll regale you a year’s worth of fascinating discoveries, starting with the most shocking:
PHYSICALCHARACTERS
Remember when everyone thought that 2004-2005 was completely devoid of actual playable characters, and the only models that could be controlled had to be rigged with motors? Remember how many people would scream at idiots who made poorly-made “2005 recreations” that assumed that the figures were actual player models?
Whoops! Turns out the idiots were right! (sort of)
A bizarre piece of Roblox trivia that some scripters and veterans might be aware of is the existance of a pseudo-class named “PhysicalCharacter.” When trying to insert it in studio (whether through the insert objects dialog of pre-2008 studios or through Instance.new()), an Object of the class “Model” would instead be created. It has essentially languished in obscurity for years, with nobody really caring enough about its existence, until CloneTrooper1019 told me it might be worthwhile to actually take a closer look.
I pulled Toolbox’s original blue figure model from 2005, opened the rbxm in Notepad++, and found that not only was the classname of the model containing the entire figure given as PhysicalCharacter, but that class also had some particularly interesting qualities:
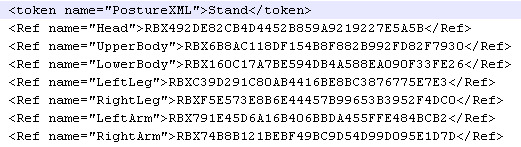
After crosschecking with “Chassis with Figure,” another 2005 model which features the blue figure in a seated position, and seeing that in that model the figure’s “PostureXML” is set to “Sit”, this dud class suddenly became a lot more interesting.
For starters, here’s the figure shown in both confirmed poses:

This discovery did finally serve to answer two questions, one practically ancient and the other about a year old - What “this model is posable” means and what the little character sitting/standing/climbing buttons on the 04 site were for.


It appears that during the transitionary period from 05 to 06, PhysicalCharacter was phased out in favor of Humanoid (or possibly even reworked into them). Given what is known about gameplay from this time, it can with some confidence be determined that these Characters couldn’t jump, strafe, or do much beside spin around and move forward/backward. Speaking of Humanoids,
DEPRECATED HUMANOID PROPERTIES
Once again, these were found by searching through old rbxms from 2006, and they show some interesting development history for the Humanoid class, as it was in March 2006:

And December 2006:

As it seems, Humanoids in early 2006 lacked any form of Health property whatsoever, with some added properties for setting walking, jumping, and falling sounds. By December, humanoid properties were now including health, as well as a boolean property for Jumping (added by Telamon himself in mid-06), and some properties related to movement: WalkRotate, WalkX, and WalkZ. WalkRotate vanished for a while before apparently returning in 2008 as WalkRotationalVelocity*, while WalkX and WalkZ were merged together into the Vector3 value WalkDirection.
It’s interesting to note just how rapidly Humanoids were being altered in their early development, as well as how much they were possibly derived from an earlier class.
2005 ERA UI CODE
youtube
Through some basic Hex editing, I have been able to ‘restore’ 05-era UI elements in the 2007 client. Currently I’ve only gotten as far as replacing existing buttons, but it’s possible to add more, and NT_x86 has been hard at work doing so. So far, every element added works completely, whether they be build tools, camera controls, or even the big green ‘GO’ button. Expect an update on this in the coming weeks.
KING ARTHUR’S CASTLE

Shown in one of the three color screenshots of Roblox on Morgan Mcguire’s website, King Arthur’s Castle is generally considered lost, as whatever place ID was associated with it is lost to history, and most likely a 404 anyways. However, as it turns out, certain assets from the castle still exist, as the towers and gate appear in none other than the original crossroads castle:

As shown in the following side-by-side comparison of the crossroads castle and my attempted recreation of the castle based on the original screenshot, the resemblance is more than uncanny - the crossroads castle is made with the exact same assets as King Arthur’s Castle.

As for the difference in colors, Roblox’s color set in 2005 was vastly different to the palette of BrickColors used in 06 and beyond, meaning that whenever importing an 05 era model/rbxl into 06 clients, the colors will not display properly. For example, here’s what Toolbox’s Blue Figure looks like rendered in its original colors (mind the wonky lighting on the head):

Expect some more frequent updates in the near future, not only on recent findings, but also on the 2005 recreation project!
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Restoring the 2004 site
The 2004 edition of the roblox website has been something of a mess for a while now. Save for two archived screenshots, the only archive of the site in the wayback machine lacks functional CSS or javascript, as well as displaying no pictures whatsoever. I personally have tried to fix what’s available but to no great success. The archived images are displayed below:


Earlier today, a user by the name of Ktoby found two critical archives: the original 2004 landing page and the roblox.css file from 2004. Not only were these both yet undiscovered, they are also now the oldest confirmed archives of the roblox website, being from August 2004, which puts them slightly after archives of the earliest Roblox forum posts.
Anyways, armed with the correct css and landing page, I set forth to finally fix the 2004 webpage.

It took a bit of finagling, but the end result is functional and visually faithful to the two previously known screenshots.
That isn’t all, though. For months I have known that the 2004 site contains elements making it nigh-certain that gameplay with the 2004 client required some site-based input, but now that I have corrected the site’s display errors I can finally confirm exactly how that input would have looked:

As an added bonus, here’s a (chronologically inaccurate) rendition of what roblox gameplay might have looked like in this era, using the G3D 2005 remake.

You can play around with the restored site for yourself here.
-DirtPiper
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healthy reminder: We’re still looking for 2006!
The last client to have been discovered was August 2007, and that was a little over a year ago now.
The search isn’t over! We’re still trying to find an 06 client!
If you or someone you personally know has or might have a harddrive they might have played roblox on in 2006, please contact us at [email protected] or join our discord!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
History of Roblox, 2003-2006
This post will be updated over time as more information is found.
2003

Roblox, Dynablox, and Goblox domains are registered by Jim Stevens.
2004
Up to July
Erik Cassel, Keith, and David Baszucki are Roblox’s primary developers.
Builds of roblox from this time were most likely attached* to the browser. The 3D view would show some general information, but build tools were contained in an html panel on the website.
*full ability to use the program required input from buttons on the roblox website, rather than in a UI hardcoded into the exe. Think of how the oldschool Toolbox worked: it was a webpage rendered inside the game window that could send special function calls to the program to insert content, use certain building tools, manipulate bricks, etc. This technique was abandoned by 2006 at the latest.
Surfaces and Joints existed. “Bumps”, a surface type resembling studs but later superseded by Glue, would create raised square bumps on the entire face of any surface it was applied to. To this day, trying to set a part’s surface to “Bumps” will instead turn it into a Glue surface.
Cards - A section of properties for parts and models. Would display in the upper right-hand corner of the screen whenever a part or model with set cards was selected. The text could be set by the user. The properties were Title, Description, Color, Image, Row0, Row1, Row2, Row3, and Row4.
Early evidence of planning for humanoids and multiplayer - Humanoids in the form of ‘PhysicalCharacter’, a subInstance of Models intended for models such as the red/blue figures, with support for Posing (sit, stand, and climb) and Control.
Roblox Website and forums are created. Client could be installed from the website.
In-game camera controlled by arrow keys, right mouse button, and scroll wheel.
2005
Up to the patent build (May)

Builds at this time, while not known if standalone or still required use of the browser, did not rely as much on build tools in an html side panel. All tools used for manipulating the level were contained within the 3D view, as well as a toolbox on the bottom of the screen for inserting parts and models, changing part colors, adding hopperbins, applying ControllerSchemes, and changing surface types. On the top of the screen were six drop-down menus: File, Edit, View, Insert, Format, and Run. A panel on the Left-hand side of the screen Contained basic build tools, from top to bottom: Go, Drag, Axis Drag, Resize, Rotate, Tilt, Group, Ungroup, Duplicate, and Delete. A Camera control cluster in the Lower right-hand corner of the screen could be used to tilt, zoom, pan, and focus the camera.
The property “className” was instead called “Keywords”.
Surfaces worked differently - each face of a part had 5 sub-properties: Type - the type of surface that face would use (Smooth or Bumps), Constraint - the type of rotating joint that would be used if any (Hinge, Motor, None, or SteppingMotor), SurfaceInput - the InputType for any rotating joints (LeftTread, RightTread, Steer, Throtle, Updown, Action1-5, Sin, and Constant), ParamA -the first parameter for any rotating joints, and ParamB - the second input for any rotating joints.
A mysterious surface called “Spawn” existed until early 06, used in models such as “Electron Gun” and “Figure with spawn gun.” Presumably, it would regularly respawn any object attached to it at intervals set by ParamA/ParamB. The cursor used when applying the ‘Spawn’ surface to a part is still in content/Textures up through at least 2008.
Motors were applied in a different way - one could choose from “LeftHandMotors” or “RightHandMotors” which would automatically set the surface’s input parameters to “LeftTread” or “RightTread” respectively. Another option, “OscillateMotor”, would set the input parameter to “sin”, allowing the motor to oscillate back and forth rather than constantly rotating. The tools for applying these motor types are, apparently, still in modern builds of studio.
Another, now long gone, service named “Level” with the following properties: SplashHTML - an unknown feature, though likely a window or text that would appear when a level was loaded to provide instructions, DragExtents - a constraint on where parts could be placed in the level, Messages - WinMessage and LoseMessage respectively, which would be displayed when the game reached either a win state or an end state, HighScoreIsGood - presumably to determine whether it’s better to have a low or high score (think golf), RunOnOpen - determined whether the game would being immediately upon being opened, InitialTimerValue - the amount of time the user would have to complete the level, InitialScore - the score the user would start with, TimerUpAction - what would happen if the timer ran out (Draw, Lose, Nothing, Pause, or Win), and TimerAffectsScore - how the timer would change the score (Decrease, Increase, or NoChange).
Parts had some more properties, too: HasOnTouch - a boolean to set whether the part would perform some action when touched, Color - still exists though hidden in the properties menu up until modern builds of Roblox - contains the Color3 value of the part’s BrickColor, Offset/RotVel - older names for “Position” and “RotVelocity” respectively, CanSelect - older name for “locked”, CanUngroup - sets whether the part/model can be ungrouped, NameShown - sets whether the name of the part/model would be displayed above it in the 3D space (code likely later reused for humanoids), Action - the action to be done when touched if HasOnTouch is set to true (Draw, Lose, Nothing, Pause, or Win), Sound - the sound to be played when touched if HasOnTouch is set to true (Boing, Bomb, Break, Click, Clock, NoSound, Page, Ping, Slingshot, Snap, Splat, Step, StepOn, Swoosh, or Victory), ChangeScore - the amount to be added to/subtracted from the score if touched when HasOnTouch is set to true, ChangeTimer - the amount to be added to/subtracted from the timer if touched when HasOnTouch is set to true, SingleShot - a boolean to set whether the OnTouch events can be triggered more than once, KeywordFilter - sets whether the part should look for all parts with a certain Keyword or without a certain Keyword (Exclude, Include) and Keyword - the Keyword to look for, TouchesToTrigger - the amount of times the part has to be touched to trigger the OnTouched actions, and UniqueObjects - How many unique objects have to touch the part to trigger the OnTouched actions.
Hopperbins were contained in the Hopper service and were not scriptable. Instead, users could select from the following “commands”: Clone, Grab, and Hammer. Grab could drag entire models or single ungrouped parts, and instead of displaying the chassis/yellow brick it does now, it simple displayed the click cursor with the blue text “grab”. Artifacting from this text is still slightly visible in current versions of the icon. Hopperbins could be added to a Level if building was required in order to complete it. HopperBins also had two other properties: “Cost” - the score the play would have to achieve before being granted the ability to use that HopperBin, and “Quantity” - unknown.
Chase and Follow ControllerSchemes.
Camera control keys possibly changed from Arrow cluster to UHJK, as the two known ControllerFlag schemes from this time were WASD and the Arrow cluster. Plausible that the behavior of Format>Camera View at the time was such that using WASD when the camera was focused on a model would not break that focus, thus allowing KeyboardLeft to be used without interfering with the camera.
Addition of the ability to view Properties of instances - a Properties window could either be shown by selecting it from the drop-down “View” menu or would appear whenever a part of model was double-clicked.
Undo function added.
Cards deprecated(?)
Up to the Morgan McGuire builds (October)
“Run” menu removed.
2006
Up to march

The 3D view for edit mode was placed into a Visual-Studio styled IDE initially referred to as the “roblox developer’s environment.” Build tools were removed from the in-game UI and relocated to the topbar, as well as the 5 dropdown menus. An explorer window was added to view the child hierarchy of the entire Level (now referred to as “game”) and the Property of any instance currently selected would display below that.
Humanoids are added, allowing for models (specifically player models with a certain structure) to be controlled by ControllerFlags without the use of motors. In conjunction with this, the “Player” ControllerScheme is added, as well as the Players service, and the Player instance. This occurred during Fall 2005. Mike Rayhawk was commissioned to make designs for characters that were ultimately never used, though he did design the bulk of Roblox’s classic badge Icons.
A Lua virtual machine was incorporated with its own API specifically for interacting with roblox, resulting in the addition of scripts and scriptable hopperbins. An output and command bar were added for better interaction with the Lua VM. This occurred during Fall 2005.
Explosions are added, and display as big red orbs. The hopperbin gets another four pre-scripted options: Rocket, Slingshot, Laser, and GameTool.
The UHJK ControllerScheme is added, and the studio camera is again controlled via the arrowkeys. It is unknown when WASD becomes an option for controlling the camera.
When the surface tools were added to the topbar, the motor tool was taken from the old “Right-Hand Motor tool”, resulting in all motors being automatically given the “RightHandTread” surface input.
At this time the lighting service is now visible (might always have been, unknown), and has the following properties: TopAmbient2 - how the areas of parts facing toward the sun will be shaded, BottomAmbient2 - how the areas of parts facing away from the sun will be shaded, Spotlight2 - the color of sunlight, and ClearColor - the color to be displayed in lieu of the skybox if the quality level is too low to render it.
Up to June

All or most 04/05-era properties of parts and other instances, such as the “Level” service, are removed or renamed, leaving them more or less as they are until 08.
Multiplayer was added, bringing with it the NetworkServer and NetworkClient services, as well as the chat bar and chatlog. Early multiplayer games were hosted on dedicated roblox servers and user-made games were restricted to singleplayer.
Telamon joins the roblox team, becoming their fourth engineer. He gives humanoids the ability to jump and begins working on AI.
Up to October
User-made games, now called “places”, may be played in multiplayer.
Beyond
In January of 2007, ‘Hopper’ is renamed to ‘StarterPack’ to better reflect its intended purpose, and a dummy ‘Hopper’ class is added purely to ensure that, when loading older levels with HopperBins stored under ‘Hopper’, they would all be dumped into the StarterPack. The dummy class would then delete itself.
In May of 2009, Controllers were rewritten - the ‘Player’ ControllerType was hard-coded into whatever model was set as the Player’s character, and all the Controller functionality involving motors was reworked into VehicleSeats, resulting in some loss of functionality, as individual Hinges/Motors could no longer be set to rotate with specific inputs.
-DirtPiper
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Origin of Roblox’s Rendering
ROBLOX was not built from scratch. It relies on several libraries and engines to achieve what it does: in 2007, these were the FMOD sound system, Lua 5.0, Scintilla (the program used for writing and editing scripts in-studio), and the Graphics3D innovation engine by Morgan Mcguire, aka “G3D”.
The most important one here is G3D.
G3D is made to allow for better ease of use with OpenGL when programming in C++. It has built-in skybox, sun, lens flare, and simple UI functionality implemented, which ROBLOX made full use of when G3D was used as the primary rendering method, from 2003 to 2007, and when G3D was available as an option, from 2007 to 2010.

ROBLOX’s default skybox from 2003-2009 was lifted directly from the G3D demo, with ROBLOX relying on version 6.09 from ~2007-2010.
And there you have it, a simple explanation of ROBLOX’s legacy rendering system.
But that’s not the interesting part.
Since you can still find all the G3D versions on sourceforge, and since we now know enough about how ROBLOX functioned from 2004-2005 through nearly a year of research from the patents and mcguire’s 3 color screenshots, we here at the clientsearch decided it would be feasible (and fun) to create a functioning replica of roblox using G3D.
So that’s what we’ve been doing.
To start off with, we’ve been sourcing as much information as we can find. There are 5 color screenshots of roblox from 2004-2005, with 2 being from 2004 and the other 3 being from 2005.
There are also 18 black and white screenshots of ROBLOX sourced from the original patents, with 5 being screenshots of the properties of various instances and 13 being screenshots of the actual 3D editor.

Morgan McGuire’s 3 color screenshots are the most high-quality, and from them we were able to make pixel-perfect measurements of the original UI.

There were also two very low-res screenshots from 2004, giving a glimpse of a version of ROBLOX with a much simpler UI, though far too low-res to be used as a basis.

From all these screenshots, we have begun making our rebuild.
And it’s been going smoothly.
youtube
While features like surfaces, physics, shadows, and the toolbox are still unfinished, what we have now has a lot of promise for future development.
We even have a github!
Stay tuned for further updates.
-DirtPiper
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
February 2018: From Metamodding to OpenGL shaders
The 07 client has been public for some time now, and there has been a corresponding “classlist.txt” alongside it to simplify the use of the insert basic object box, but there were a few classes that could not be inserted.
This, of course, was due to the fact that these classes lacked documentation in the ReflectionMetadata - the list of classes that the roblox client uses to keep track of things like the class’s icon, their description in the object browser, what order to display different classes in the explorer, etc.

To put things simply, I spent roughly a single afternoon modding the 2007 client’s reflectionmetadata until I managed to get most classes insertable or viewable in studio, which led to a few interesting discoveries. I also did this same treatment to the 08 client, at which point I found out about the first of these discoveries: LocalBackpackItems.
youtube
Used internally by roblox to handle the UI for the player’s backpack, LocalBackpackItems can be used to create simple HUDs, like an FPS counter or a position indicator. They come with two caveats though, in that clicking on them when they are placed in a child of guiroot will crash the game, and trying to select a tool while there are LocalBackpackItems in the player’s relativepanel will also crash the game.

The next discovery was the nature of StockSounds - up until their removal in 2014 or so, StockSounds were invisible to the explorer and were only accessible through scripts. The soundscape by default contains a slew of them, each one set to make a different noise - these stocksounds are used by the roblox studio to handle the sounds that are played when deleting an instance, scrolling the camera, using the fill tool, etc.
After the hype of hidden classes had died down, andreja6 made known to me a certain quirk of the “Texture” property of tools/hopperbins:
youtube
When the texture of a tool/hopperbin is set to a file that shares it’s location with other files with the same name but “_dn”, “_ds”, or “_ovr” appended to them, then those textures will automatically be used whenever the tool/hopperbin is clicked on, disabled, or being moused over, respectively.
Then, I started working on a project, using images with this feature found in the 07 client, to make a rough reconstruction of 2005-era minigame tools, as can bee seen here:
youtube
The next and potentially most amazing thing to be found occurred just last night: the discovery of OpenGL shaders in the 07 client.
youtube
MusicalProgrammer, using cheatengine and hex editing, found unused code in the 07 client that was used in 06 to render a bloom effect on bright areas of the screen - something that we had presumed to be photoshopped whenever we saw it in images of 06 clients. About an hour later, he found another shader for a depth of field effect, also seen in 06 era screenshots. Zeuxcg himself had previously stated that such shaders were impossible in this era of OpenGL.
If you want to find out more about these discoveries and perhaps even use them yourself, feel free to check out the clientsearch discord - the link can be found in the “contact” tab of this blog.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Controllers: an in-depth examination.

Controllers, while never explicitly documented and rarely mentioned by the ROBLOX staff, were a fundamental element of ROBLOX gameplay from 2004-2005, and were still usable up until 2009, when whatever functionality they had was reworked into VehicleSeats.
They were a hardcoded input/control method, taking the keystrokes of the WASD or UHJK keys (as well as space bar and 1-5) and directly controlling the rotation and direction of motor instances, as well as the movement of the character. In order to use them, one would have to set the face of a part to either “Motor” or “SteppingMotor.” After this has been done, view the part’s Properties and in the behavior section you will find a setting named “Controller.” These are its settings.

Up to early or mid 2007, there also existed purpose-built tools for setting the Controller for models in studio:

The Controllertype “Player” is reserved for the player to control their character, and will not respond to input otherwise. “KeyboardRight” and “KeyboardLeft” are for UHJK and WASD control schemes, respectively. “Joypad1″ and “Joypad2″ are presumably nonfunctional. “Chase” and “Flee” are more complicated, and will be discussed later in the post.
Once you set the Controller of a part with a motor on it, the grey ring around the base of the motor will change color -

Each control scheme has its own color with exception to the Joypads; the rings will be Purple for “Player”, Blue for “KeyboardRight”, Red for “KeyboardLeft”, Black for “Chase” and Yellow for “Flee”.
The actual function of the motor itself can be fine-tuned in the “Surface Inputs” subsection of the part’s properties.

There are 3 settings for every face of the part, making for a total of 18 settings under this subsection.
When using Controllers, ParamA will set the speed the motor will turn when moving ‘forwards’, and ParamB will set the speed of the motor when turning ‘backwards’. SurfaceInput is slightly more complicated.

The full list of options cannot be shown, but the ones excluded are “Action5”, “Constant”, and “Sin”.
“LeftTread” will make the motor respond to input as if it were on the left wheel of a vehicle, while likewise “RightTread” will make the motor respond to input as if it were on the right.
“Steer” will make the motor respond exclusively to A/D or H/K input, while ““Throtle”“ will make the motor respond exclusively to W/S or U/J input.
“UpDown” Will spin the motor forward when spacebar is held down, and stop otherwise.
Action1-4 will spin the motor forward when 1, 2, 3, or 4 are pressed on the keyboard. Action5 spins forward if 3 is pressed, and backward if 4 is pressed.
“Constant” and “Sin” are unrelated to Controllers, with “Constant” making the motor spin at a constant rate as defined by “ParamB” and “Sin” spinning the motor at a constant rate defined by ParamA, and changing the direction at intervals defined by ParamB.
Just like using hinges with VehicleSeats, the motors must be on the wheels/part to be turned, which are then attached to the frame/chassis of a Vehicle/Contraption.
In order to control a model, the motorized parts must all have their “Controller” set to the same control scheme, as well as the model itself. However, whenever running a game in 2008 or later, the model’s “Controller” will have to be re-set or else it will be non-functional. This can be easily achieved by having a simple script set the control scheme of the model whenever a game is run (you don’t have to do this in ‘07!) .

Whenever a model with a Controller correctly set to “KeyboardRight” or “KeyboardLeft” is in the workspace, the above GUIs, referred to internally as ‘ButtonBindingWidgets’, will appear in the upper right corner of the screen, and the individual keys will turn red to indicate when the game recognizes that they are being pressed. The flags correspond to the motor color of the control scheme. You can also click on them with your mouse, and they will have the same effect as pressing the corresponding key. For KeyboardLeft, this includes moving the camera or character.
“Chase” and “Flee” were slightly more complicated - models with these control schemes would try to rotate themselves such that their ‘front’ (as set by Format > Set Model Front) was facing away (flee) from or towards (chase) the nearest model with a different controller set. At one point these two Controllers were fully compatible with Humanoids, and they were even used in public models such as “figure with spawn gun”. However, they became broken at some point in late 2006 or early 2007, and remained totally non-functional until late 2008 when, somehow, they regained the ability to make Humanoids rotate in place, without being able to walk towards or away from their targets.
So what is a “Controllerflag” in the first place?
All model/part instances have a Boolean option named “ControllerFlagShown”. from 2004 to mid-2007, when this option was checked and the controller of a model was set, the model would have a 3D flag attached to it, with a color matching that of its control scheme. The flags were rendered as attached at their base to the model’s Primary Part, and would face away from whatever direction was set as their model’s ‘front’ (using Format > Set Model Front). These were for making it easier for the player to identify what models they could control in-game, and lingered for a while after minigames were otherwise made defunct - they can even be seen in one of Fleskhjerta’s videos.
(Skip to the 4 minute mark to see the relevant footage)
youtube

Of course, Controllers were not without their glaring flaws, which is why they were eventually reworked into VehicleSeats in 2009.
The biggest problem is that Controllers were not friendly with multiplayer games - since they were designed and implemented when ROBLOX was still strictly singleplayer, they were not built in a way that, say, one could specify, given a group of players on a server, which player has the ability to control which model. As such, “KeyboardRight” and “KeyboardLeft” are non-functional in multiplayer games (with their ButtonBindingWidgets being greyed out), though “Chase,” “Flee,” and “Player” all work as intended.
Another issue was that using Controllers was simply too complicated for the majority of ROBLOX users at the time, which was made worse by ROBLOX having no documentation of their functionality present. They would eventually be reworked into the more user-friendly VehicleSeats in 2009, which, while lacking some of the functionality Controllers presented, were well-documented and much simpler to configure and use.
Controllers, due to their obscurity and lack of documentation, were never utilized much beyond simple vehicles up until their removal from ROBLOX in 2009. Very few users knew or cared about their existence, as vehicles driven by scripted tools would quickly come to be the norm while Controllers remained unused and unupdated, outside of a few models uploaded to the toolbox by users. It wasn’t until 2017, eight years after their removal from ROBLOX, that any elements of their functionality beyond simply setting the Controller of a model became more widely known and documented.
Controllers remain as a footnote in ROBLOX’s history, only seeing widespread use during a time when ROBLOX was still a singleplayer minigame site, and remaining in the client as a ‘ghost feature’ until they were reworked into a more user-friendly mechanic. Their current use remains restricted to a handful of members of the old ROBLOX community interested in tinkering around with old clients, though their potential is still being explored to this day.
youtube

-DirtPiper
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Hello!
I, Bitl, have found a interesting feature in 2007 that allows you to create a instance of a player, allowing you to create player bots!
To create a player, use this script:
local newplayer = Instance.new("Player", game.Players) newplayer.Name = "Player" newplayer:LoadCharacter()
Then, to move the player around, use this:
game.Players.[your player's name].Character.Humanoid:MoveTo([the Vector3 position] , [target part] )
With this, you can create pretty complex humanoids in 2007 that replicate real players!
-Bitl
6 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Documentation of the now-removed “Controller” feature.
This feature was available from 2004 until May 5th 2009.
youtube
Here’s a demonstration of a simple game made using Controllers.
-DirtPiper
0 notes
Text
History of the clientsearch
A quick and simple history of our search.
2012 - The 2008 client installer (3.809) is found on the roblox servers, and is then shared by users on the forums. Many users begin to speculate whether older clients could be found using similar methods. RBLXDev development begins using this client as a base.
2013 - All old roblox versions are removed from c5.roblox.com, including the mid-2008 installer. The clientsearch pores over the wayback archive, but no archives of clients were made beside 3.809. RBLXDev becomes public, and the old roblox revival community begins its steady growth. The mid-2010 client is also found at this point. A link to a “2007″ client that was supposedly hosted on c5.roblox.com goes dead - this client was later confirmed to most likely be a fake, as the version number did not match what is now known about 2007 clients.
2014 - The archives of the 2005 and 2006 roblox site become more widely known, though no files are found on them besides various pictures. Old models and places still available on roblox are dug up in an attempt to deduce certain things about old roblox, notably toolbox’s models.
2015 - Few new discoveries of note are made.
2016 - A broken 2007 installer is found, but does not become widely known. RBLXDev dies, marking the end of the four-year lifespan of the first roblox revival. It ends up living on through nobelium.
2017 - Finobe is founded, as well as the clientsearch getting an official discord, tumblr, and a page in the lostmedia wiki. The search gains a ton of new members, as well. The broken 2007 installer becomes more widely known, and another broken installer is also found. The earliest roblox forum posts are discovered, the controller function was thoroughly documented, several veteran members of the roblox community are contacted (with no new leads), and DHTML is discovered as a removed feature of roblox from 2007. More screenshots from 2006 are found, revealing that 2006 had built-in shaders, making the client even more in-demand. A slew of previously-unreleased archived pages are made available on the wayback archive, including lost article from the roblox wiki detailing more lost features. The original roblox wiki is also found.
-DirtPiper
1 note
·
View note
Text
The oldest forum posts available - most of which are from before multiplayer.
The oldest forum thread currently known to mankind. It was made in 2004, when roblox was not even public.
Roblox changed their servers in mid-2004.
Keith requesting some additional camera controls.
Keith requests an undo button.
Keith requests a tool to rotate bricks. (this may be what the “velocity” tool was intended to be, however all versions of roblox currently available have this tool unselectable.)
Keith requesting the creation of what we now know as the “explorer”.
Keith mentions roblox being addictive.
First mention of “Cars” (see my video on the controller method), “Games” (later changed to ‘Places’), and a “lose condition”, most likely part of roblox’s minigame functionality.
First to mention the on-site “high score”, which ‘Woodgie’ would later attain.
Keith requests a link to the main site on the forum.
Keith says that he needs to disable his firewall in order to get ROBLOX to work properly.
Documentation on the “Five second jewel” in toolbox’s models.
erik.cassel mashes his keyboard.
Some info on how roblox was downloaded - not much has changed!
Woodgie asks for a “chatroom.” At the time, ROBLOX was still strictly singleplayer.
Some info on early roblox contests. Users could submit their “solutions” to a specific minigame to the site, which other users could also view. Once the contest was over, whoever had the best solution won the contest and was awarded a sum of “Roblox points.”
Request for the ability to save one’s own solutions to a minigame.
Earliest mention of shadows and antialiasing.
Roblox moved servers again in 2006.
Erik Cassel’s forum profile.
Keith’s forum profile. Forum profiles were apparently available up until 2010.
Some posts by David Baszuki - while most of the threads here are long gone, there is still some interesting information shown.
All of these except for threads ‘10′ and ‘106′ were previously undiscovered/undocumented.
-DirtPiper
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why we want 2007 so badly
Throughout the various iterations of ROBLOX, features have come and gone: Custom Meshes were removed, then readded, PlayerGui was added, Controller was removed, etc. While all of the features I have listed have been documented, not all were so lucky to be recorded before they were removed - two big ones being DHTML and OpenGL Stable/Legacy.
The first one, DHTML, has almost no documentation, with it only being mentioned by ROBLOX themselves 3 times and the wiki pages pertaining to it having been long since removed. What does remain of DHTML are a handful of scripts available through free models that used DHTML before its removal. So, what was DHTML?
DHTML was implemented through two instances: HtmlService and HtmlWindow. Scripts could call a function called :NewWindow() on HtmlService and create an HtmlWindow. Through the function :setBody(), one could have the Window load a block of Html, or they could use :navigate() to have the window load a URL. The HtmlWindow itself was a seperate window that opened, similar to the old help menu. Certain games used DHTML for shops, tutorials, intros, et cetera, with a famous example being Clockwork’s “Dodge the Teapots of doom.” DHTML was used by game creators as GUIs are used now, and when they were removed people were not pleased. The :NewWindow() function of HtmlService was locked, trying to insert an HtmlWindow would crash the game, and the two instances were left in as deprecated shells of their former selves up until June of 2008. DHTML was removed for making it too easy for people to exploit, though the exact incident that prompted its removal is unknown. DHTML, despite barely being mentioned by ROBLOX at all, was apparently important enough of a feature that people complained for years after it was removed - most of the information I could find about it was forum posts from 2008-2011 by nostalgic users.
The second one is much less elusive: OpenGL Stable, which was ROBLOX’s default rendering engine from 2005-2007, and remained an option (renamed as OpenGL Legacy in 2009) until 2010. OpenGL Stable was the only rendering engine ROBLOX has ever had that supported AntiAliasing, and handled the shading of round objects much better than Direct3D.

OpenGL Stable also has support for a few other features which are now useless, such as the “shiny” and “specular” properties of decals and textures. OpenGL also supported shadows, however by 2008 the ability to enable them was (most likely unintentionally) removed: the decision to change the way shadows were enabled in settings from a checkbox to a menu made it so OpenGL couldn’t tell if shadows were enabled or not, so they always defaulted to “off.” From what we can see by looking at screenshots of roblox from 2006-2007, OpenGL Stable with shadows was something truly beautiful.
Both of these features will remain forever as nothing more than words on a blog post unless we can find a working 2007 client - and that is why we are so hell-bent on finding one.
1 note
·
View note