Text
Scene vs. Summary & When to Use Which

When I was a young writer, I didn’t fully understand what a scene was and what a summary was. Later, when I understood the difference, I wasn’t always sure when to use which. These days, I occasionally help writers with the same things. They may use summary for what should have been a scene, or they may write a whole scene for what really should have been summary. Understanding the difference and when to use which can be key when writing a successful novel.
Sure, some of it is subjective.
But what might be surprising to some, is that most of the time, one is more … “correct” than the other.
Scene
A scene is a structural unit that tends to have these qualities:
- Happens in Real Time
A scene will largely happen in real time. This means we “watch” the characters move, act, and talk, as if it were happening in real life.
- Dramatizes (Shows > Tells)
A scene dramatizes. It uses showing more than telling. If a character is angry with a friend, we see that anger in action and conversation. We may witness her yell or kick a rock, for example. It’s like watching a stage play.
- Concrete
Because it is dramatized, a scene will usually be more concrete. It will more likely appeal to our senses and the physical world and experience.
- Characters Acting in a Specific Location
A scene will have characters in a location (in some very rare cases, the setting or society may act as characters). They might be talking on a train ride, or exploring a cave, or dueling in the snow.
Scene Examples
(Because a full scene often lasts pages, these examples are passages from specific scenes.)
“This won’t take long, Andrew,” said the doctor.
Ender nodded.
“It’s designed to be removed. Without infection, without damage. But there’ll be some tickling, and some people say they have a feeling of something missing. You’ll keep looking around for something, something you were looking for, but you can’t find it, and you can’t remember what it was. So I’ll tell you. It’s the monitor you’re looking for, and it isn’t there. In a few days that feeling will pass.”
The doctor was twisting something at the back of Ender’s head. Suddenly a pain stabbed through him like a needle from his neck to his groin. Ender felt his back spasm, and his body arched violently backward; his head struck the bed. He could feel his legs thrashing, and his hands were clenching each other, wringing each other so tightly that they arched.
“Deedee!” shouted the doctor. “I need you!” The nurse ran in, gasped. “Got to relax these muscles. Get it to me, now! What are you waiting for!”
Something changed hands; Ender could not see. He lurched to one side and fell off the examining table. “Catch him!” cried the nurse.
“Just hold him steady–”
“You hold him, doctor, he’s too strong for me–”
“Not the whole thing! You’ll stop his heart–”
Ender felt a needle enter his back just above the neck of his shirt. It burned, but wherever in him the fire spread, his muscles gradually un-clenched. Now he could cry for the fear and pain of it.
“Are you all right, Andrew?” the nurse asked.
- Ender’s Game by Orson Scott Card
Mrs. Reed occupied her usual seat by the fireside; she made a signal to me to approach; I did so, and she introduced me to the stony stranger with the words: “This is the little girl respecting whom I applied to you.”
He, for it was a man, turned his head slowly towards where I stood, and having examined me with the two inquisitive-looking grey eyes which twinkled under a pair of bushy brows, said solemnly, and in a bass voice, “Her size is small: what is her age?”
“Ten years.”
“So much?” was the doubtful answer; and he prolonged his scrutiny for some minutes. Presently he addressed me—“Your name, little girl?”
“Jane Eyre, sir.”
In uttering these words I looked up: he seemed to me a tall gentleman; but then I was very little; his features were large, and they and all the lines of his frame were equally harsh and prim.
“Well, Jane Eyre, and are you a good child?”
- Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Summary
A summary has these qualities:
- Condensed Time
Summaries condense time. They may cover a month in a single sentence. They may talk about recurring events over a time period, within one paragraph. They may relay a past event (or in some cases, a future event) within a brief moment. They don’t happen in real time.
- Explains through Telling
Since the moment isn’t happening in real time, the audience is told more than shown what happened. This gives summary a stronger, guiding, narrative hand. Rather than experiencing the passage like the character, it’s more like the audience is being guided by a storyteller (generally speaking).
- More Abstract
For those reasons, telling is more abstract. It’s more likely to express ideas and concepts, rather than specific experiences.
- Characters and/or Setting may Change Swiftly (or Maybe Not Even Be Present In Some Cases)
A summary may not focus on a specific character or stay in the same setting. It may move quickly through settings or may not even mention a specific setting.
Summary Examples
Mother came home and commiserated with Ender about the monitor. Father came home and kept saying it was such a wonderful surprise, they had such fantastic children that the government told them to have three, and now the government didn’t want to take any of them after all, so here they were with three, they still had a Third … until Ender wanted to scream at him, I know I’m a Third, I know it, if you want I’ll go away so you don’t have to be embarrassed in front of everybody. - Ender’s Game by Orson Scott Card
John had not much affection for his mother and sisters, and an antipathy to me. He bullied and punished me; not two or three times in the week, nor once or twice in the day, but continually: every nerve I had feared him, and every morsel of flesh in my bones shrank when he came near. There were moments when I was bewildered by the terror he inspired, because I had no appeal whatever against either his menaces or his inflictions; the servants did not like to offend their young master by taking my part against him, and Mrs. Reed was blind and deaf on the subject: she never saw him strike or heard him abuse me, though he did both now and then in her very presence, more frequently, however, behind her back.
- Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë

When to Use Which
Most novels are better written with more scene than summary. Scenes dramatize the story, so that the audience feels like they are experiencing and participating in it. Scenes are more impactful. Scenes are more likely to stir emotions. Because they are more concrete, they are more likely to stick in the reader’s memory.
However, this is not to say all novels are better with more scene than summary. You can indeed find successful books with more summary. This can be particularly useful in books with huge casts and many viewpoint characters, books that take place over a long period of time (such as a character’s entire life), or books with powerful, present omniscient narrators. Not all books that rely on summary more than scene are bad.
But most books are better told largely through scene than summary.
And pretty much all novels need some of both.
So when do we use which?
Sometimes I edit passages that are weakened because they are summarized instead of dramatized. Other times I read scenes that offer very little dramatic value and should have been summarized.
Scenes
A good rule of thumb is the more significant the moment, the more likely it needs to be rendered as a scene.
Big turning points and climactic moments should almost always be a scene–whether that turning point relates to character arc, plot, or theme.
This means that the climactic moments of the beginning, middle, and end, should almost always be a scene.
Anything we’ve been building up to in the primary plotline related to the arc, events, or theme, should probably be a scene.
Keep reading
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dialogue tips that actually work:
You are not writing a movie (ignore this if you are). The reader doesn't need to know every word the characters say for the duration of the story. Less is more.
Dialogue can happen within the prose. "And they awkwardky discussed the weather for five minutes" is way better than actually writing five pages of dialogue about the weather.
Balance your dialogues. Surprise yourself with a monosyllabic answe to a dialogue that's ten sentences long. Don't be afraid of letting your character use half a page for a reply or nothing at all!
Don't write accents phonetically, use slang and colloquialisms if needed.
Comma before "said" and no caps after "!?" unless it's an action tag. Study dialogue punctuation.
Learn the difference between action tags and dialogue tags. Then, use them interchangeably (or none at all).
Don't be afraid to use said. Use said if characters are just saying things, use another word if not. Simple. There's no need to use fancy synonyms unless absolutely necessary.
Not everyone talks the same way so it makes sense for your characters to use certain words more often than others. Think of someone who says "like" to start every sentence or someone who talks really slow. Be creative.
Use prose to slow down the pace during a conversation.
Skip prose to speed up the pace during a conversation.
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm allowed to be unpalatable and weird, right? i'm in my head about it now
0 notes
Text
Physical pain is not only itself resistant to language but also actively destroys language, deconstructing it into the pre-language of cries and groans. To hear those cries is to witness the shattering of language.
The Body in Pain, Elaine Scarry
A well-known philosopher includes cries in the category of silence — cries, moans and curses form “a silent substance.” The substance of this underworld is evil. Sitting on her throne, the countess watches the tortures and listens to the cries.
The Bloody Countess, Alejandra Pizarnik, tr. Alberto Manguel
[The Count] hates music even more that he hates mathematics but he loves to listen to screaming. “The entropic rhetoric of the scream”, he calls it. Madame Schreck screeches for him sometimes at night, to augment his pleasure if we girls have screamed ourselves hoarse and cannot make any more noise. […]
When the Count beats me and I scream, he says: “Now you’re talking! Who needs words?”
We are his harem and also his finishing school. The curriculum is divided into three parts. First, we learn how to forget; second, we forget how to speak; third, we cease to exist.
The Scarlet House, Angela Carter
[A]side from murder there is but one trait the libertines themselves possess and never share, in any form whatever: speech. The master is he who speaks, who disposes of the entirety of language; the object is he who is silent. […]
The scream is the victim’s mark. […] Yet this scream which distinguishes the victim is also, contradictorily, nothing but the attribute, the accessory, the amorous supplement, bombast. Whence the value of a machine to isolate the scream and deliver it to the libertine as a delightful part of the victim’s body, i.e., as a sonorous fetish.
Sade, Fourier, Loyala, Roland Barthes, tr. Richard Miller
401 notes
·
View notes
Text

le suicidé, édouard manet, circa 1877
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
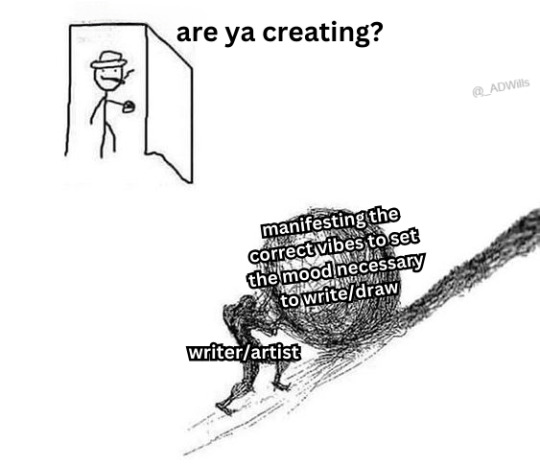

35K notes
·
View notes
Text
Saw this advice on Twitter today, and I think it's going to end up being useful for me. 🥹 Thought I'd share it with y'all, too.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
i am still playing with possibilities, but which would you find more compelling?
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
listen. men covered in their own blood. women covered in other people's blood. it's not difficult
22K notes
·
View notes




