danielmanlangit
4 posts
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
CHAPTER 5
COLLABORATIVE DEVELOPMENT IN ICT
TEAM STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS TEAM STRUCTURE - Is described as a less hierarchical organizational structure in which individuals are divided into teams. TEAM DYNAMICS - Is the unconscious, psychological forces that influence the direction of a team’s behavior and performance. COMMON PRINCIPLES OF COLLABORATION 1. Participation 2. Collective 3. Transparency 4. Independence 5. Persistence 6. Emergence 7. Strategy before Technology 8. Lead by Example 9. Create a Supportive Environment Participation - Encourage participation from across you organization wherein they belong as one. Collective - Each need to help the group reach a consensus and then take action collectively on the decision. Transparency - It is the feedback and trust are essential elements of collaboration. Independence - Ensure that group think goes not merge and that people are thinking for themselves. Persistence - To ensure that all content is kept within the community and easily accessible to all members. Emergence - Focus on the goal rather than worrying about hot it is achieved. “Companies should start to develop their collaboration capabilities before purchasing collaboration technology” - Dr. Graham Bill GROUP - Is a social community, consisting of two or more people who have something in common. TEAM - Is a special instance of a group in which the commonality is a shared goal. GROUP DYNAMICS - describes the way in which people in a group interact with one another. STRATEGIES TO STRENGTHEN TEAM’S DYNAMICS - Know your team. - Tackle problems quickly with good feedback. - Define roles and responsibilities. - Break down barriers. - Focus on communication. - Pay attention.
0 notes
Text
WYSIWYG What you see is what you get” - Is an editor or program that allows a developer to see what the end result will look like while the interface or document are being created. - WYSIWYG software runs on any windows computer. - You can make create background images on the fly. ONLINE TECHNOLOGIES - Include presentation programs, forms and the file management that are available over the internet. CLOUD COMPUTING - Is a term for the delivery of hosted services over the internet. - Goal is to apply traditional supercomputing or high-performance computing power MAIN BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING Self-service provisioning Elasticity Pay-per-use PRESENTATION TEMPLATES Prezi – Is a presentation resource that features a zoomable canvas unlike the box-type slides. Emaze – Is a presentation in which you can choose free presentation templates to easily create. It also features a proprietary state-of-the-art HTML5 presentation. Mind Map - Is a concept of using diagrams for representing tasks, words, concepts or items linked to and arranged around a central concept or subject. - Along with this is a file and project management. MIND MAPPING TOOLS Mind Meister – is an online mind mapping tool that allows users to create, develop and share ideas visually. Sibelius – is an online platform used for writing music. Google Forms – is a tool used form for creating surveys, tests or web input forms. Web Design Elements Links Following states of links: - Normal link - Visited link - Active link - Hover link Normal Link - This is the default state of a link(i.e., one that is not being hovered over or clicked or pointed to a URL that the user has already visited).
Visited Link - This is link that is not being hovered over or clicked but whose target has been visited by the user.

Active Link - An active link is one that is currently being clicked by the user. Most developers will replicate the hover state here if a style is not provided to them.
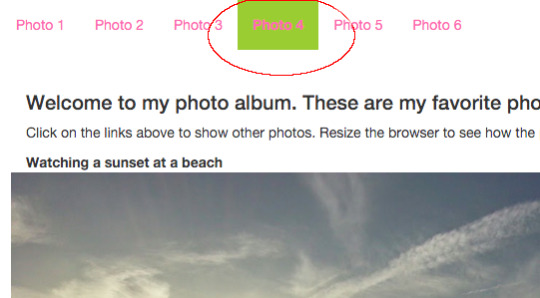
Hover Link - The hover state is what link look like when the user moves the mouse over it. This is the normal states are the ones most designer prepare for.
Forms
Two of the most important considerations when laying out a form are:
- Form label
- Input fields and labels
Form Label - Forms typically collect personal data that users are reluctant to give out. As such, properly informing user of the exact purpose of the form is wise.
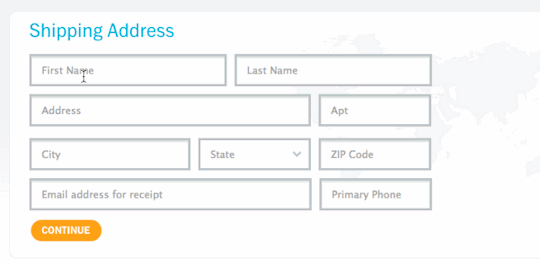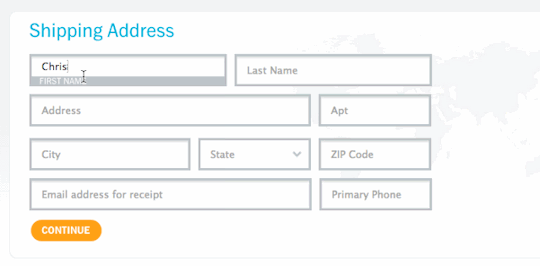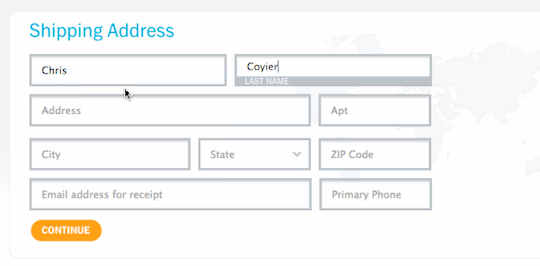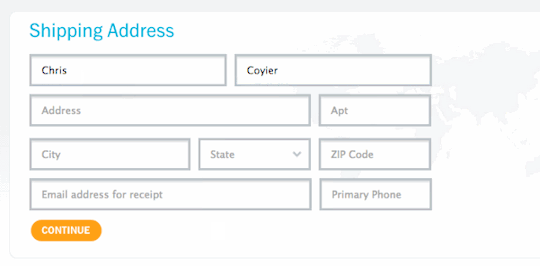
Input Fields and Labels - Plan on how the input fields of the form will be laid out on the page and how the labels for those fields will be styled and oriented relative to fields.

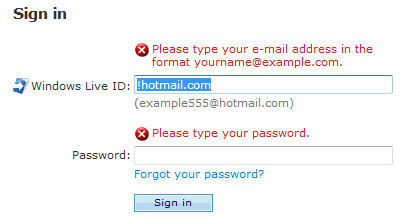
Form Validation - This is the critical point where the website communicates the user requirements and errors in a form. There are three core things to consider: Required fields Real – time validation Post back validation Required Fields - All the required fields should be indicated. This is done usually with an asterisk.
Real-Time Validation - Some validation can be done real-time as the user completes the form. This kind of validation informs the user as quickly as possible of any problems with the data they have inputted.

Post Back Validation - This kind of validation happens after the user has submitted the form. The style used for real-time validation is often repeated here, but another option is to group all errors into a single message.

Status messages: Errors, Warnings, Confirmation - User will usually need some sort of feedback after performing an action on your website. The most likely scenario is after submitting a form, but many other events could occur as well. Carefully consider your website and the action that user might take, and plan for the messages that the website will need to communicate.
Animations: Pop-ups, Tooltips, Transitions Tooltips - Those little pop-ups when user’s mouse hover over the elements.

Image rotators or sliders - Home page slide shows are all the range of option is available for transitions and styles.

Lightbox - You can style not only the lightbox itself, but also the transition to it.

WEB DESIGN ELEMENTS LINKS Following states of links: - Normal link - Visited link - Active link - Hover link Normal Link - This is the default state of a link(i.e., one that is not being hovered over or clicked or pointed to a URL that the user has already visited). Visited Link

- This link that is not being hovered over or clicked but whose target has been visited by the user. Active Link

- An active link is one that is currently being clicked by the user. Most developers will replicate the hover state here if a style is not provided to them. Hover Link

- The hover state is what link look like when the user moves the mouse over it. This is the normal states are the ones most designer prepare for. FORMS
Two of the most important considerations when laying out a form are:
- Form labeI
- Input fields and labels
Form Label

- Forms typically collect personal data that users are reluctant to give out. As such, properly informing user of the exact purpose of the form is wise.
Input Fields and Labels

- Plan on how the input fields of the form will be laid out on the page and how the labels for those fields will be styled and oriented relative to fields. Form Validation This is the critical point where the website communicates the user requirements and errors in a form. There are three core things to consider: - Required fields - Real – time validation - Post back validation Required Fields - All the required fields should be indicated. This is done usually with an asterisk. Real-Time Validation

Post Back Validation

- This kind of validation happens after the user has submitted the form. The style used for real-time validation is often repeated here, but another option is to group all errors into a single message. Status messages: Errors, Warnings, Confirmation

- User will usually need some sort of feedback after performing an action on your website. The most likely scenario is after submitting a form, but many other events could occur as well. Carefully consider your website and the action that user might take, and plan for the messages that the website will need to communicate. Animation: Pop-ups, Tooltips, Transition
Common places animations used are the following:
Tooltips
Image rotators or sliders
Lightbox
Tooltips

- Those little pop-ups when user’s mouse hover over the elements. Image rotators or sliders

- Home page slide shows are all the range of option is available for transitions and styles. Lightbox

- You can style not only the lightbox itself, but also the transition to it.
0 notes
Text
UNITY

- The sense of oneness of the elements that creates balance and harmony. REPITITION
- Describes the consistent and balanced repetition of a design or element. PROXIMITY

- Describes the organization and relationship of elements included in the design. CONTRAST

- Is the combination of opposing characteristics of an element. WHITESPACE

- Is the negative space or large margins that allow your design to breathe within the elements. INFOGRAPHIC - Is defined as a visual image such as a chart or diagram that is used to explain information or data. PRINCIPLES AND GUIDELINES IN CREATING AN INFORGRAPHIC Thesis/Story Data Simplicity Sources Branding/Shareability THESIS/STORY - The subject and the main idea of your infographic must be clear. DATA - Data must be well- organized and supports the main idea. SIMPLICITY - Style must be able to attract your readers so as not to make your infographic full of text. SOURCES - You must cite your resources so as to give credibility to your data. BRANDING/SHAREABILITY - Your infographic must be creative and innovative. IMAGE FILE FORMATS JOINT PHOTOGRAPHIC EXPERTS GROUP JPEG - JPEG IS THE MOST POPULAR IMAGE FORMAT USED ON THE WEB. JPEG FILES ARE USED MOSTLY BY PHOTOGRAPHERS, ARTISTS, GRAPHIC DESIGNERS, MEDICAL IMAGING SPECIALIST AND OTHERS BECAUSE IMAGE QUALITY AND COLOR FIDELITY IS IMPORTANT IN THE FIELD. GRAPHICS INTERCHANGE FORMAT GIF

- GIF IS LIMITED TO THE 8-BIT PALETTE WITH ONLY 256 COLORS. IT IS BEST USED FOR DIAGRAMS, CARTOONS. AND LOGOS WHICH USE FEW COLORS AND IS THE CHOSEN FORMAT FOR ANIMATION EFFECTS. BITMAP IMAGE FILE (BMP) OR DEVICE INDEPENDENT BITMAP (DIB)

BMP OR DIB - IT IS THE IMAGE USED IN THE MICROSOFT WINDOWS OPERATING SYSTEM. IT IS AN UNCOMPRESSED FILE AND IS MADE UP OF MILLION OF DOTS CALLED PIXELS, WITH DIFFERENT COLORS AND ARRANGEMENTS. TAGGED IMAGE FILE FORMAT

TIFF - IS A FILE FORMAT CREATED ORIGINALLY BY ALDUS CORPORATION FOR DESKTOP PUBLISHING.CONSIDERED AS A HIGH QUALITY IMAGE FORMAT. PORTABLE NETWORK GRAPHICS - PNG IS AN IMAGE FORMAT DEVELOP BY A GROUP OF GRAPHIC SOFTWARE DEVELOPERS AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO GIF FORMAT. PNG DOES NOT BEST WITH LINE ART, TEXT AND LOGO. PRINCIPLES AND BASIC TECHNIQUE IN IMAGE MANIPULATION CROPPING

- IT IS THE PROCESS OF REMOVING UNWANTED PARTS OF THE IMAGE FOCUSING ONLY ONB THE SUBJECT. COLOR BALANCE

- IN ANY IMAGE MANIPULATING PROGRAM, THIS COMMAND WILL ALLOW YOU TO MAKE CHANGES IN THE MIXTURE OF COLORS IN AN IMAGE. ADJUSTING THE BRIGHTNESS AND CONTRAST

- THIS COMMAND IS THE MOST BASIC TECHNIQUE WHEN ADJUSTING THE IMAGE TONES (HIGHLIGHTS, SHADOWS, AND MIDTONES). COMPRESSION AND RESIZING
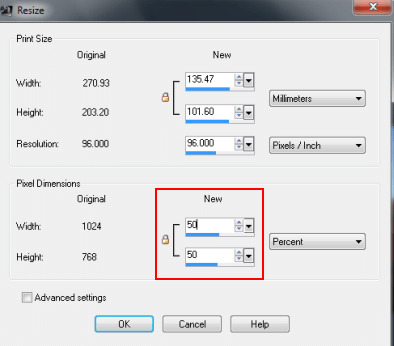
- COMPRESSING AND RESIZING IS IMPORTANT IN IMAGE MANIPULTAION. IMAGE TO BE UPLOADED IN THE WEB MUST BE OF THE STANDARD RESOLUTION OF 72 DPI (DOTS PER INCH) TO MAINTAIN ITS IMAGE SIZE OF 30-50 KB. COLOR BLENDING

- Use of the different special effects buttonavailable in the different image editing software. you can combine colors and commands that will give you a more dynamic image result. COMBINING MULTIPLE IMAGES

- Composition must be planned and conceptualized first so that you will be able to render the best image and message possible. ONLINE GRAPHICS SOFTWARE PICASA

- It is Google's free desktop image editing program. it can be downloaded and help you manage your photos and upload them to an online album. FOTOR

- IT IS A MULTIPLATFORM PHOTO EDITING WEBSITE. IT OFFERS A WIDE RANGE OF EFFECTS AND TOOLS FOR EDITING IMAGES. PIXLR

- IT IS ALSO A PLATFORM IMAGE EDITING PROGRAM. YOU CAN CHOOSE BETWEEN THE EDITOR FOR EDITING IMAGES OR CREATING AN ORIGINAL IMAGE RIGHT THROGH THE BROWSER. OTHER IMAGE EDITING SUITE THAT CAN BE DOWNLOADED FOR FREE: 1. PHOTOSCAPE 2. SERIF PHOTOPLUS STARTER EDITION 3. GIMP 4. PAINT.NET IMAGE HOSTING SITES IMGUR

- IT IS A FREE IMAGE HOSTING SITE WHEREIN YOU CAN UPLOAD IMAGES FROM YOUR COMPUTER. YOU CAN ALSO EDIT YOUR IMAGES BEFORE POSTING IT ONLINE. FLICKR

- IT IS AN IMAGE SOCIAL NETWORKING SITE. YOU CAN SAVE AND MANAGE YOUR PHOTOS FOR IT OFFERS A 1TB STORAGE CAPACITY IN YOUR ACCOUNT. PHOTOBUKCET

- IT HAS ALMOST SIMILAR FEATURES WITH FLICKR AS YOU CAN UPLOAD AND SHARE YOUR IMAGES OVER THE INTERNET THROUGH YOUR ACCOUNT. SLICKPIC

- IT IS AN ONLINE IMAGE HOSTING SERVICE THAT ALLOWS YOU TO UPLOAD AND STORE AN UNLIMITED NUMBER OF PHOTOS ONLINE. YOU CAN CREATE AS MANY ALBUMS, AND IT ALSO OFFERS PROFESSIONAL EDITING OF IMAGE. ZENPOLIO

- IT IS AN ONLINE IMAGE HOSTING SITE THAT DOES NOT ONLY ALLOW YOU TO UPLOAD IMAGE BUT ALSO LETS YOU CREATE AN ONLINE IMAGE WEBSITE FOR YOUR IMAGES.
CHAPTER 4
WEB DESIGN PRINCIPLES
-
According to Cleverism, “Web design is a concept of planning, creating, and maintaining websites.”
- It is the process of creatively designing and constructing a website and updating it regularly to incorporate changes.
PRINCIPLES IN DESIGNING YOUR WEB PAGE OR SITE
1. VISUAL HIRARCHY

- This explains the order in which human eye perceives what it sees. 2. PROPORTION

- You can make use of the golden ratio, magical number approximately equal to 1.618 that makes all things proportioned so as to make a design aesthetically pleasing. Then there is also the Fibonacci sequence where each term is defined as the sum of the two previous terms: 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,and so on.
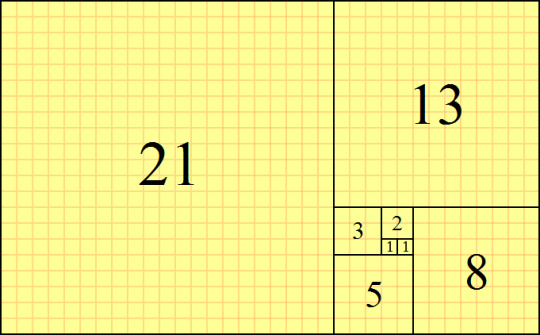
3. HICK’S LAW

- This law can be considered as a guideline for decision making in a viewer’s perspective.
- states that “with every additional choice, the time required to make a decision increases.” 4. FITT’S LAW

- According to this law, the time needed to move to a target is dependent upon the size of the target as well as the distance to the target. 5. ACCESSBILITY

- When a visitor enters the website, he or she must be able to access each bit of information in the easiest manner. 6. VISIBLE LANGUAGE

- A web page design should communicate with the users clearly and in an engaging manner. 7. WHITE SPACE AND SIMPLE DESIGN
- White space helps divide the web page into several distinct parts or areas that make it simpler for the users to process information. The following are some of the other things that can be considered as part of a simple design: Grid-based layout – The content of this layout is divided into columns, boxes, and different sections.

F-pattern design - Design a web page or website in a way that complements the natural reading behavior of the visitors like the “F-pattern.”

Conventional designs - Conventional or Conservative designs still work well as far as visitor response or likeability is concerned.

8. REGULAR TESTING

- Test Early and Test Often (TETO), is another web design principle that all designers and website owners must consider.
EVALUATION - Choose 1 or 2 Principles to follow in effectively designing you web page or site. Prepare to share it in class.
0 notes
Text
PORTFOLIO IN EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 1: INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY - Is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots. This field overlaps with electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mehcatronics, nanotechonology and bioengineering. CONTENT STANDARD
- The learners demonstrate an understanding of ICT in the context of global communication for specific professional track.
Performance Standards
- The learners shall be able to: at the end of the 2-week period independently compose an insightful reflection paper on the nature of ICT in the context of their lives, society, and professional tracks (Arts, Tech Vocational, Sports and Academic)
Most essential learning competencies
The learners should be able to:
1. Compare and contrast the nuances of varied online platforms, sites, and content to best achieve specific class objectives or address situational challenges.
2. Apply online safety, security, ethics, and etiquette standards and practice in the use of ICTs as it would relate to their professional tracks. 3. Use the internet as a tool for credible research and information gathering to best achieve specific class objectives or address situational.
1.1 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY

- ICT is the technology required for information processing, in particular, the use of the electronic computers, communication devices and software applications to convert, store, protect, process, transmit and retrieve information from anywhere, anytime.
- Information refers to the knowledge obtained from reading, investigation, study or research. The tools to transmit information are the telephone, television and radio. Information is knowledge and helps us to fulfill our daily tasks. - Communication is an act of transmitting messages. It is a process whereby information was exchanged between individuals using symbols, signs or verbal interactions. Communication is important in order to gain knowledge. Technology is the use of scientific knowledge, experience and resources to create processes products that fulfill human needs. Technology is vital in communication.
- ICT nowadays has also widened the horizon in developing new tools or emerging technologies. Mobile devices can communicate through wireless fidelity (Wifi), Bluetooth, third generation 3g & 4g, data services and dial up services and virtual private networks. EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES

- Artificial Intelligence (AI) - is the ability of a digital computer or computer controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings. The term is frequently applied to the project of developing systems endowed with the intellectual processes characteristics of humans, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize or learn from past experience. ROBOTICS

- Is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots. This field overlaps with electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mehcatronics, nanotechonology and bioengineering. BIOMETRICS
- Are a way to measure a person’s physical characteristics to verify their identity. These can include physiological traits, such as fingerprints and eyes, or behavioral characteristics, such as the unique way you’d complete a security-authentication puzzle. QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY

- Also called quantum encryption, applies principles of quantum mechanics to encrypt messages in a way that it is never read by anyone outside of the intended recipient. COMPUTER ASSISTED TRANSLATION

- Involves the use of software programs to translate both verbal and written texts. Also known as machine-assisted or machine aided translation. 3D IMAGING AND HOLOGRAPHY

- Is defined as a 3D projection that exists freely in space and is visible to everyone without the need for 3D glasses. VIRTUAL REALITY

- Refers to the computer generated simulation in which a person can interact within an artificial 3D environment using special electronic devices that can be similar to or completely different from the real world. ONLINE SAFETY

- Is the knowledge of maximizing the user’s personal safety and security and risk to private information, and self-protection from computer crime in general. 1. Know the scams - Learn about different kinds of scams and what you can do to avoid them.

2. Think before you click - Think twice, thrice and zillion time before click any link or buttons.

3. Safety Peruse - These sites may have an Address that’s very similar to a legitimate site, but the page can have misspelling, Bad Grammar, or low resolution Images.

4. Shop Safety - Don’t shop on a site unless it has “https” and a padlock icon on the left or right in the URL.

5. Kick-butt passwords - Use an Extremely uncrackable password One like “9&4thkel965#”.
6. Protect your info’s - Keep your guard up, Back up all your data on your computer, smartphone and tablet, theft or a cash.

7. Watch your Wi-Fi Connectivity - Protect your network by changing your router’s setting and making sure that you have the connection password protected.

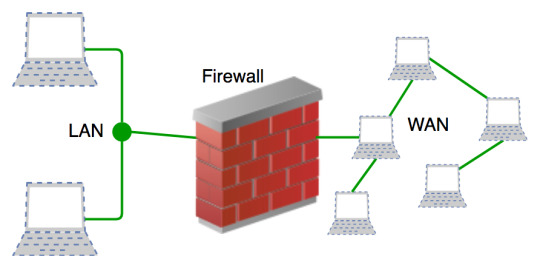
8. Install a Firewall - A firewall is a grate line of defense against cyber attracts.
9. Keep up to date - The best security updates automatically to protect your computer. - Use the manufacturer’s latest security patches to make regular updates and make that you have the software set to do routine scam.

10. Use your Noggin - Use your common sense while surfing the web.

COMMON ISSUES AND CRIMES IN THE INTERNET - CYBERBULLYING - HACKING - IDENTITY THEFT - PLAGIARISM - COPYRIGHT ISSUES CYBERBULLYING - Is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and Cyber Harassment are also known as online bullying. - Cyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims’ personal information, or pejorative labels. THE ANTI-BULLYING ACT OF 2013 ( RA 10627 )
(Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively “called cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1 RA 10627. Implementing Rules). THE REVISED PENAL CODE AND THE CYBERCRIME PREVENTION ACT. - One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art, 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175) Likers or shares of a post cannot be held liable under this law. - Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. Hence, a blind ite is not as actionable as a named-post in social media. HACKING

- Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system. - Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT

- Also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else. TYPES AND EXAMPLES OF IDENTITY THEFT 1. True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks. 2. Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person's existing accounts. PLAGIARISM

- Is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward. The following are considered plagiarism - turning in someone else's work as your own - copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit - failing to put a quotation in quotation marks - giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation - changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit - copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on "fair use" rules) Republic Act No. 8293 [An Act Prescribing the Intellectual Property Code and Establishing the Intellectual Property Office, Providing for Its Powers and Functions, and for Other Purposes]otherwise known as the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines. Intellectual property rights under the I. P. Code: The intellectual property rights under the Intellectual Property Code are as follows: 1. Copyright and related rights; 2. Trademarks and service marks; 3. Geographic indications; 4. Industrial designs; 5. Patents; 6. Layout designs [topographies] of integrated circuits; and 7. Protection of undisclosed information. The scheme of penalties for infringement has also been changed. From the previous fine of Php200 to Php2,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 year, the current range of penalties are as follows: - For first offenders - fine of PhP50,000 to PhP150,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 to 3 years - For second offenders - fine of PhP150,000 to PhP500,000 and/or imprisonment of 3 to 6 years - For third and subsequent offenders - fine of PhP500,000 to PhP1.5 Million and/or imprisonment of 6 to 9 years. - In case of insolvency, the offender shall furthermore suffer subsidiary imprisonment. NETIQUETTE - Is a combination of the word net and etiquette.It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource. - It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource. The Core Rules of Netiquette Rule 1. Remember the human. - Never forget that the person reading your mail or posting is, indeed, a person, with feelings that can be hurt. - Corollary 1 to Rule #1: It's not nice to hurt other people's feelings. - Corollary 2: Never mail or post anything you wouldn't say to your reader's face. - Corollary 3: Notify your readers when flaming. Rule 2. Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life. Corollary 1: Be Ethical Corollary Corollary 2: Breaking the law is bad Netiquette. Rule 3. Know where you are in cyberspace. Corollary 1: Netiquette varies from domain to domain. Corollary 2: Lurk before you leap. Rule 4. Respect other people's time and bandwidth. Corollary 1: It's OK to think that what you're doing at the moment is the most important thing in the universe, but don't expect anyone else to agree with you Corollary 2: Post messages to the appropriate discussion group.Corollary 3: Try not to ask stupid questions on discussion groups Corollary 4: Read the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) document Corollary 5: When appropriate, use private email instead of posting to the group Corollary 6: Don't post subscribe, unsubscribe, or FAQ requests Corollary 7: Don't waste expert readers' time by posting basic information Corollary 8: If you disagree with the premise of a discussion group, don't waste the time and bandwidth of the members by telling them how stupid they are.Just stay away Corollary 9: Conserve bandwidth when you retrieve information from a host or server. Rule 5. Make yourself look good online. Corollary 1: Check grammar and spelling before you post Corollary 2: Know what you're talking about and make sense Corollary 3: Don't post flame-bait Rule 6. Share expert knowledge. Corollary 1: Offer answers and help to people who ask questions on discussion groups Corollary 2: If you've received email answers to a posted question, summarize them and post the summary to the discussion group. Rule 7. Help keep flame wars under control. Corollary 1: Don't respond to flame-bait Corollary 2: Don't post spelling or grammar flames Corollary 3: If you've posted flame-bait or perpetuated a flame war, apologize Rule 8. Respect other people's privacy. - Don't read other people's private email. Rule 9. Don't abuse your power. - The more power you have, the more important it is that you use it well Rule 10. Be forgiving of other people's mistakes. CONTEXTUALIZED ONLINE SEARCH AND RESEARCH SKILLS

- Online search is the process of interactively searching for and retrieving requested information via a computer from databases that are online. Interactive searches became possible in the 1980s with the advent of faster databases and smart terminals. Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages: - Ability to obtain a large sample, which increases statistical power - Data is automatically coded so no data entry errors - Reduced cost of conducting research Disadvantages: Online is not totally secure and theft is one of the numerous danger it poses, researchers personal information is at risk of being access by rogue persons. - Some of the materials on the internet have not been evaluated by experts or thoroughly screened - Lack of accreditation and low quality
RESEARCH SKILLS “Research” sometimes just means finding out information about a topic.You can certainly develop advanced information retrieval skills in Working with Sources. However, in specific understandings of “research” carry a lot of weight. The classic definition is that “research” leads to an original contribution to knowledge in a particular field of inquiry by defining an important question or problem and then answering or solving it in a systematic way. - So you will need to read on to develop a relevant understanding of what research means in your subject. - Research skills can be anything from looking at competitors and seeing what they do well to producing a written report on how your department could work better. Doing research in the world of work is all about stepping back from your day-to-day work and looking at ways you can improve. Important aspects of research: - Research design covers the key issues in developing a successful research project. - Research methods takes you to resources on essential techniques for carrying out convincing research. - Working with data will provide resources on the use of statistics and other numerical skills in research. Improving Your Research Skills Online 1. Know your sources. Make sure to find the most reliable information which can be found in multiple sources or, better, to have the original source. 2. Use your web browser properly. Know the capabilities of your preferred browser to help make your search faster and easier. 3. Organize your bookmarks. It is to organize the links you have marked. 4. Learn to use advanced search engines. Practice using advanced search techniques which are available in Google. 5. Follow the web. Follow the web information in the web. Just make sure to read and be critical in every link you click. SIX STRATEGIES THAT CAN HELP ONLINE STUDENTS PRODUCE STRONGER RESEARCH. 1. Contact a librarian before getting stuck sifting through piles of online information. 2. Consider that when in doubt, it's wiser to over-cite sources than risk plagiarism. 3. Use Google and other reliable resources at the beginning of a research process, not the end. 4. Don't think that the Web is your only source of information. 5. Understand the professor's expectations for citation format. 6. Understand why professors still assign research projects. Some examples of research skills that you may have include: 1. Report writing. 2. Analyzing lots of information from different sources. 3. Finding information off the internet. 4. Critical thinking. CHAPTER 2 APPLIED PRODUCTIVITY TOOLS Productivity Tools - It is a tools that can be a freeware or shareware. Freeware - is copyrighted, which can be used for free and for an unlimited time. Shareware - is a commercial software that is copyrighted, which can be copied for trial but needs to be purchased for continued use. Advanced Techniques Using Microsoft Word Microsoft Office Word

- One of the software of Microsoft Office 2013 suite. - Offers a set of tools that is compared to its previous versions. - Along with its new features are advanced techniques including hyperlinks, macros and mail merge. Hyperlink
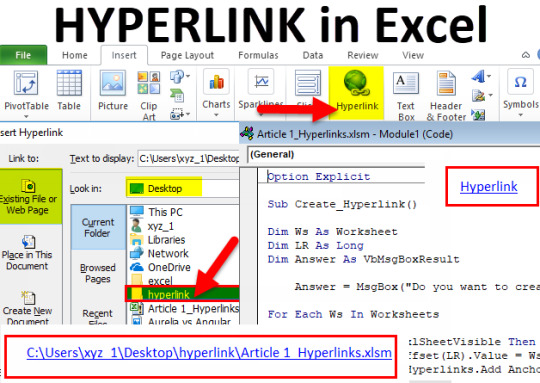
- A link that will direct you to another page or part of the same document. Creating a Hyperlink to an Existing Document - Suppose you are to link a part of your document to an existing document. - Click your mouse on the location in the document where you want to insert the hyperlink. - On the Insert Tab, click the Hyperlink button on the Links group. - On the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, click Existing File or Web Page and then select the File name where the source file is located and then hyperlink will be created on your document. - Press Ctrl+ click on the Hyperlink to open the linked file. Mail Merge
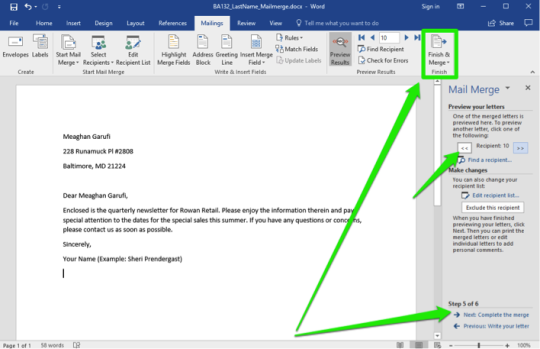
- Is a useful tool that allows you to quickly produce and send information, newsletter, resumes, or brochures to many people. Creating a Mail Merge 1. Open the word document that you want to Mail Merge. 2. On the Ribbon, click the Mailings tab, go to the Start Mail Merge group and click Start Mail Merge and select Step by Step Mail Merge Wizard. 3. The task pane will show the Mail Merge steps 1 to 6. PowerPoint

- It allows you to create slide show presentations wherein you can format the texts and images, adding also animations and other multimedia components interactively. Excel

- One of the applications created by Microsoft, used to simulate a paper worksheet.
- It is composed of cells that are represented in rows and columns design to perform basic arithmetic operations. - Widely used in accounting and financial applications, as well as statistics and engineering calculations. The following are the common Excel Functions: = SUM – Calculates the sum of the values of a range of cells = AVERAGE – Calculates the arithmetic mean of a range of cells = MAX - Gives the maximum value in a range of cells = MIN - Gives the minimum value in a range of cells = COUNT - Counts the number of cells in a range of cells BENIFITS OF ONLINE SOFTWARE Convenience - The applications should be intuitive and easy to use to ensure everyone can use them without spending a lot of time learning how. Scalability - The applications should be able to be used in all areas of your business and also work effectively no matter how much demand there is to use them or how much your business grows. Safety - All the applications should be safe to use with all existing systems and should have the ability to fully integrate with all other software and not inhibit the workers ability to do their job. Sustainability - All consumer-based software should be flexible and adaptable to have the ability to last for up to 10 years, but they must be able to expand functionally with other developments in software and operating systems. PRINCIPLES OF GRAPHICS AND DESIGN BALANCE UNITY MOVEMENT REPITITION PROXIMITY CONTRAST WHITESPACE BALANCE

- Describes the placement of elements of equal weight on the page. MOVEMENT

- Describes the flow of elements on the page.
1 note
·
View note