Text
Alligator Body Language and You, or: How To Know When An Alligator On Social Media is Being Stressed for Views
Alligators are wild animals. Despite the idiotic claims of animal abusers like Jay Brewer, they cannot be domesticated, which means they are always going to react on the same natural instincts they've had for millions of years. Habituated, yes. Tamed, yes. Trained, definitely. Crocodilians can form bonds with people- they're social and quite intelligent. They can solve problems, use tools, and they're actually quite playful. Alligators are also really good at communicating how they're feeling, but to somebody who doesn't spend much time around them, their body language can be a bit mystifying. And it doesn't help when social media influencers are saying shit like this:

That is not what a happy gator looks like.
That's a terrified, furious gator who isn't attacking because the ogre handling her has her in a chokehold. She's doing everything she can to express her displeasure, and he's lying about it because he knows his audience doesn't even know how to think critically about what he's doing. He knows that because his audience doesn't know anything about these animals, he can get away with it. This I think is why I hate him so much- he deliberately miseducates his audience. He knows what he's doing is factually inaccurate, he just doesn't care because attention means more to him than anything else in the world.
Let's change that! Here are two really important lessons for understanding alligator body language on social media.
Lesson 1: Alligators Don't Smile (in fact, most animals don't)
So what's going on in this video? Jay Brewer is aggressively choking his white alligator Coconut while scrubbing algae off of her with a toothbrush. And make no mistake, he is digging into the creature's throat while she is visibly distressed. He claims she's happy- but she's not. He is willfully misrepresenting what this animal is feeling. That's a problem, because people... well, we actually kind of suck at reading other species' body language. The reason for this is that we tend to overlay our own responses on their physical cues, and that's a problem. For example, let's look at an animal with a really similar face to ours, the chimpanzee. Check out Ama's toothy grin!

Wait, no. That's not a happy smile. That's a threat display. When a chimpanzee "smiles," it's either terrified and doing a fear grimace, or it's showing you its teeth because it intends on using them in your face.
How about a dog? Look at my smiling, happy puppy!
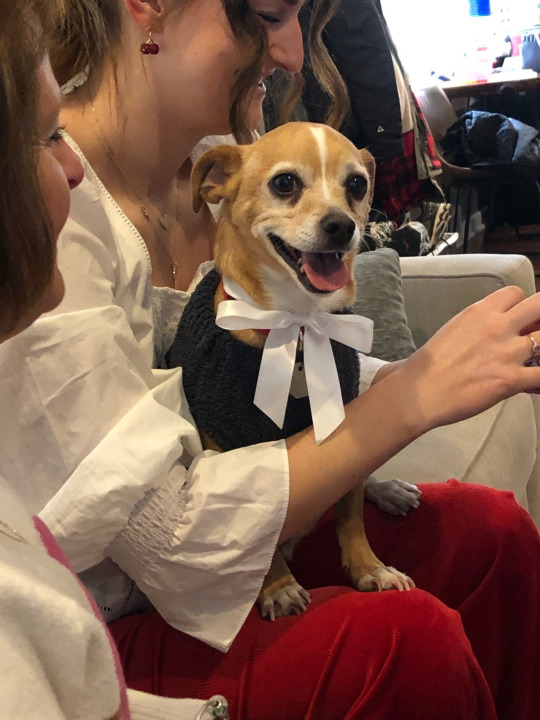

Oh wait no, this is a picture of Ryder when he was super overwhelmed by noise and people during a holiday party. He'd hopped up in my sister's lap to get away from stuff that was happening on the floor and was panting quite heavily. See the tension in the corners of his mouth and his eyes? A lot of the time when a dog "smiles," the smile isn't happy. It's stress! Why Animals Do The Thing has a nice writeup about that, but the point is, our body language is not the same as other species. And for reptiles, body language is wildly different.
For instance, look at these two alligators. Pretty cute, right? Look at 'em, they're posing for a Christmas card or something! How do you think they're feeling?

Well, I'll tell you how the normal one is feeling. He's annoyed! Why is he annoyed? Because the albino just rolled up, pushed another gator off the platform, and is trying to push this guy, too. I know this because I actually saw it happen. It was pretty funny, not gonna lie. He's not gaping all the way, but he was hissing- you can actually see him getting annoyed in the sequence I took right before this shot. Look at him in this first shot here- he's just relaxing, and you can see he isn't gaping even a little bit.
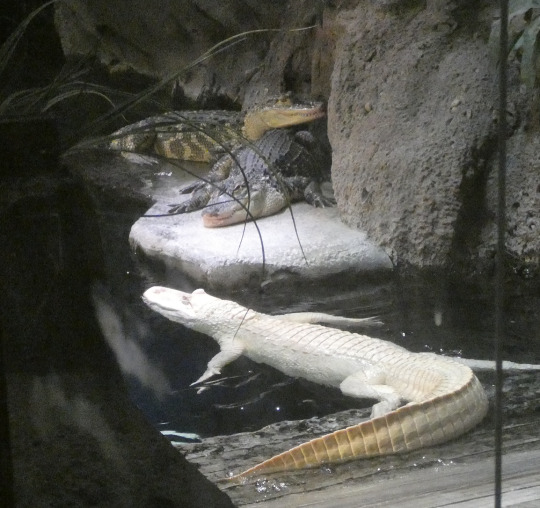
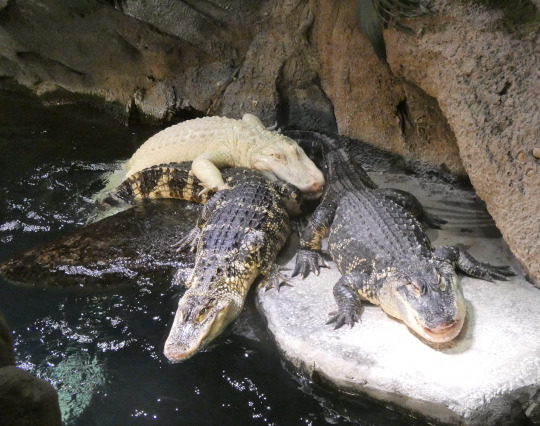



By the end, he's expressing displeasure, but not enough to actually do anything about it. He's annoyed, but he's comfy and that's where one of the best basking areas is, so he'll put up with it.
Reptiles open their mouths wide for a lot of reasons, but never because they are actively enjoying a sensation. Unless they're eating. No reptile smiles- they can't. They don't even have moveable lips. If a reptile is gaping, it's doing so because:
It is doing a threat display.
It is making certain vocalizations, all of which are threats. Alligators are one of the rare reptiles that do regularly vocalize, but most of their calls aren't made with a wide open mouth.
It is about to bite something delicious or somebody stupid. Check out this video- virtually all of the gaping here is anticipatory because these trained gators know darn well that the bowl is full of delicious snacks. (I have some issues with Florida's Wildest, but the man knows how to train a gator AND he is honest about explaining what they're doing and why, and all of his animals are healthy and well-cared for, and he doesn't put the public or his staff at risk- just himself.)
youtube
It's too hot and it has opened its mouth to vent some of that heat and thermoregulate. This is the main reason why alligators will often have their mouths part of the way open, but sometimes they'll open all the way for thermoregulation. This is what a thermoregulatory gape looks like- usually it's not all the way open, kinda more like < rather than V, but you can't say that 100% of the time. Additionally, a thermoregulatory gape... typically happens when it's hot out. If they're inside, maybe they've been under their basking light for too long. Heat's the dominant factor, is what I'm getting at.

There is another reason that a captive crocodilian might be gaping, and that's because it's doing so on command. Some places have their gators trained to gape on cue, like St. Augustine Alligator Farm and other good zoos. They have the animals do this in presentations that are genuinely educational. They ask the animals to open their mouths so that they can show off their teeth and demonstrate how their tongues seal off the back of their mouth. They'll also do it as part of routine healthcare, because looking at their teeth is important.
In this case, the animals aren't gaping because they're stressed, they're gaping because they know they're gonna get a piece of chicken or fish if they do it. And what's more, they're doing it on cue. They have a specific command or signal that tells them to open wide. It's not an instinctive response to a situation. It's trained. If the animal provides the behavior after a cue, the situation is much less likely to be negatively impactful.
It's also important to remember that there's a difference between a partially open mouth and a gape! As discussed above, alligators will often have their mouths a little bit open just to maintain temperature homeostasis. It helps them stay comfy, temperature-wise. These guys are all doing thermoregulatory open-mouthed behavior- that slight open and relaxed body posture is a dead giveaway. (That and it's the hottest spot in the enclosure.)

Lesson 2: A Happy Gator Is A Chill Gator
So if alligators don't smile or have facial expressions other than the :V that typically signifies distress, how else can you tell how they're feeling? One way is stillness. See, alligators subscribe to the philosophy of if it sucks... hit da bricks.

Basically, if they hate it, they'll leave. Unless, y'know, somebody has their meaty claws digging into their throat or is otherwise restraining them. (Restraint isn't always bad, btw. Sometimes the animal is going through a medical thing or needs to be restrained for their safety- which a responsible educator will explain.)
Let's look at a very similar scenario, in which a captive alligator is getting his back scrubbed.
As you can see, it's quite different. First, he's not being restrained at all. Second, look at how relaxed he is! He's just chilling there vibing! He could simply get up and leave if he wanted to, because he's not being held. Towards the end of the video, as he lifts his head, you can see that his respiratory rate is very even as his throat flutters a bit. I'm not sure what this facility is, so I can't comment on care/general ethics, but like. In this specific case, this is an alligator enjoying being scrubbed! And you can tell because he's not doing anything. A happy gator is content to be doing what they're doing.
Why Should I Listen To You?
Now, you should ask yourself, why should you listen to me? Why should you trust me, who does not own an alligator, versus Jay Brewer, who owns several?
Well, first off, there's no profit for me in telling you that what you're seeing on social media is in fact not what you're being told you're seeing. I'm not getting paid to do this. That's the thing with people who make social media content. The big names aren't doing it just for fun. They're doing it for money. Whether that's profit through partnerships or sponsorships, or getting more people to visit their facilities, or ad revenue, you can't ignore the factor of money. And this is NOT a bad thing, because it allows educators to do what they're passionate about! People deserve to be paid for the work that they do!
But the problem starts when you chase the algorithm instead of actually educating. A "smiling" alligator gets the views, and if people don't know enough to know better, it keeps getting the views. People love unconventional animal stories and they want those animals to be happy- but the inability to even know where to start with critically evaluating these posts really hinders the ability to spread real information. Like, this post will probably get a couple hundred notes, but that video of Coconut being scrubbed had almost 400,000 likes when I took that screenshot. Think about how many eyeballs that's reached by now. What I'm saying here is that it's just... really important to think critically about who you're getting your information from. What do dissenters say in the comments? What do other professionals say? You won't find a single herpetologist that has anything good to say about Prehistoric Pets, I can tell you that right now.
Another reason you can trust me is that my sources are not "just trust me bro," or "years of experience pretending my pet shop where animals come to die is a real zoo." Instead, here are my primary sources for my information on alligator behavior:
Dragon Songs: Love and Adventure among Crocodiles, Alligators, and Other Dinosaur Relations- Vladimir Dinets
The Secret Social Lives of Reptiles- J. Sean Doody, Vladimir Dinets, Gordon M. Burghardt
Social Behavior Deficiencies in Captive American Alligators (Alligator mississippiensis)- Z Walsh, H Olson, M Clendening, A Rycyk
Social Displays of the American Alligator (Alligator mississippiensis)- Kent Vliet
Social Signals and Behaviors of Adult Alligators and Crocodiles- Leslie Garrick, Jeffery Lang
Never smile at a crocodile: Gaping behaviour in the Nile crocodile at Ndumo Game Reserve, South Africa- Cormac Price, Mohamed Ezat, Céline Hanzen, Colleen Downs (this one's Nile crocs, not American alligators, but it's really useful for modeling an understanding of gape behaviors and proximity)
Thermoregulatory Behavior of Captive American Alligators (Alligator mississippiensis)- Cheryl S. Asa, Gary D. London, Ronald R. Goellner, Norman Haskell, Glenn Roberts, Crispen Wilson
Unprovoked Mouth Gaping Behavior in Extant Crocodylia- Noah J. Carl, Heather A. Stewart, Jenny S. Paul
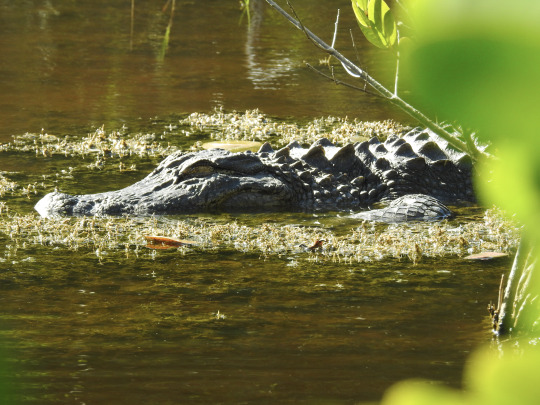
Thank you for reading! Here's a very happy wild alligator from Sanibel for your trouble.

34K notes
·
View notes
Text
love leopard seals. they are so dragon coded. that is an entire mammalian marine wyrm
67K notes
·
View notes
Text
The northern hairy-nosed wombat is the largest species in its family and one of the largest burrowing animals on the planet. Its stocky body—complete with muscular forearms for digging—can grow to be a metre in length (3.25 feet). It is also exceedingly rare, with only around 300 left in the wild.

6K notes
·
View notes
Text

What's this? A type of African antelope known as Jackson's hartebeest. Truly bizarre unless, of course, you are another Jackson's hartebeest.
263 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dragon Snake aka Javan Mud Snake (Xenodermus javanicus), family Xenodermidae, west Java, Indonesia
photograph by Mark Spence
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily fish fact #521
Spotfin lionfish!

While hunting, it approaches its prey slowly and then traps it via spreading out its fins as far as possible! Their prey includes small fish and crustaceans like crabs and shrimp.
199 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can you elaborate the story of the ”Free Willy” orca (forgot his name). From my understanding the orca couldn’t survive in the wild and imprinted on hunans to the point that he seeked out human compaionship
Oh Keiko. His is a sad story. In 1979, he was tragically captured from his native Icelandic waters as a calf and, after bouncing around for several years, was sold to an amusement park in Mexico City that would eventually become Six Flags Mexico. It was here that he found fame as the star of Free Willy, a very sweet and very fictional story (a favorite of mine as a child!) that later spawned a trilogy, all while convincing the public that it’s easy to free a whale.

The tank you see in the movie is the same tank Keiko lived in during his time in Mexico. Intended to house dolphins, it was incredibly undersized, and the water was far too warm for an orca. Worst of all, he was isolated from others of his kind, with only the companionship of his human caregivers and a few bottlenose dolphins. The years of poor husbandry took their toll on poor Keiko, and he was lethargic and in ill health when his story because known throughout the world.

Although many parties were involved in what happened next, Warner Bros. studios (the filmmakers behind Free Willy) and the Humane Society of the United States (HSUS, my beloathed) were at the forefront. Once it became public knowledge that the real Willy was not, in fact, returned to the wild to live with his family and was still living in that too-tiny pool, many of Keiko’s fans (mainly children) began writing letters asking for their favorite cetacean movie star to be released.

Doesn’t that warm your heart? *she says sarcastically*
Some time—and an incident in which Michael Jackson (yes, that Michael Jackson) tried to purchase the whale for his personal collection—later, Keiko’s owners relented. It was decided by the newly formed Free Willy-Keiko Foundation, founded by Warner Bros. and cell phone mogul Craig McCaw (and still in operation to this day, unfortunately), that it was time to make fantasy a reality and set Keiko free. In 1996, Keiko was transferred to the Oregon Coast Aquarium for rehabilitation, where he would spend two years.


Under the quality husbandry and veterinary care Keiko received in Oregon, his health began to improve. In my opinion, this beautiful habitat, with trainers who loved and cared for him, should’ve been his forever home. One would think this was the plan all along, considering his trainers were still doing waterwork with him. That doesn’t exactly scream “this animal is a candidate for release!”

But the HSUS and Free Willy-Keiko Foundation had promised the children of the world that Keiko would return to the wild. Think of the children, people.

In 1998, Keiko tasted the crisp saltwater of the Icelandic seas for the first time in nearly two decades. For the next four or so years, Keiko lived in a sea pen, with the intentions of gradually habituating him back to his native environment. Over time, his trainers took him on longer and longer “walks” in the open ocean. One day in 2002, the walk didn’t end.
Keiko was free.
15 months later, he was dead.
The cause of death was pneumonia, the most common disease of cetaceans both in the wild and in human care. He was 27 years old (average life expectancy of a male orca is about 30 years).
Perhaps it would’ve been worth it, had Keiko spent those last 15 months with his long-lost family. But he didn’t. Though he was occasionally observed trailing pods of orcas, Keiko never rejoined a wild pod. Instead, he spent those 15 months traveling the coasts of Iceland and Norway seeking out the only family he knew. Humans.

Keiko would approach swimming children, allowing them to ride on his back as he had with his trainers over the years. He would follow boats in search of food and companionship, as his caregivers had interacted with him from boats during his ocean walks. These escapades became so frequent that the local government passed ordinances to stop its citizens from interacting with the whale. Although the HSUS claimed otherwise, Keiko was never again a truly wild whale. He was a whale dependent on humans, humans who ignored the advice of experts and tried to bring fiction to life. In 2009, the journal Marine Mammal Science did a retrospective review of Keiko’s rehabilitation and release. They determined it was a failure.
Despite this, Keiko remains a poster child for anti-zoo activists. The still-hypothetical Whale Sanctuary Project (my even more beloathed) uses Keiko as an example of why their experiment is a good idea, tugging at heartstrings of well-meaning animal lovers like HSUS did all those years ago.

In reality, Keiko was quite possibly the worst candidate imaginable for release. He was a fully mature male, with a history of poor health, who had spent decades in the care of humans with absolutely no contact with others of his kind since he was basically a toddler. The decision to release him was made entirely on emotion and carried out by movie executives and animal rights activists. For further insight into the political and financial woes of the release, I highly recommend Killing Keiko by Mark Simmons, one of Keiko’s caregivers throughout the rehabilitation process.
RIP Keiko. You were a beautiful, sweet man who inspired millions 🐳

10K notes
·
View notes
Photo
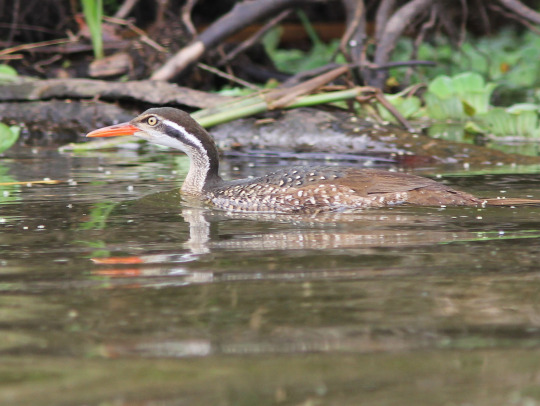

African Finfoot (Podica senegalensis)
Family: Finfoot Family (Heliornithidae)
IUCN Conservation Status: Least Concern
Found in flooded forests, mangrove swamps and vegetation-rich waterways throughout much of central, eastern and southern Africa, the African Finfoot is an unusual and extremely illusive species of aquatic bird notable for being one of only 3 living species of finfoots (a family of birds distantly related to cranes which are named for the fleshy fin-like lobes that extend from each of their toes.) Like other finfoots, the “finned” toes of the African Finfoot aid it in paddling as it swims along the surface but do not impair its ability to cling to branches or walk on land as fully webbed feet would. African Finfoots hunt in the water and feed mainly on aquatic or water-associated invertebrates such as mayflies, dragonflies and water snails, but may also catch small vertebrates such as frogs or venture onto land in search of terrestrial prey such as spiders. Due to their timid nature and preference for dense, inaccessible habitat little is known about this species’ life cycle but it has been observed that their breeding is associated with periods of heavy rainfall and that they build large, messy nests in branches overhanging water, with females returning to the nest to provide their chicks with prey until they are mature enough to join their mother on the water.
————————————————————————–
Image Source: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/62-Podica-senegalensis
428 notes
·
View notes
Text
*Teleports behind you*
Time to learn about gharials, kid.
965 notes
·
View notes
Photo








We’re only finding out recently that a lot of animals have colors and patterns that we cannot see because they’re outside of our visual range. It calls to attention how much of the world we can’t experience because our senses are limited.
When we shine UV lights on them, they glow pink or blue, but these are the colors that we CAN see…. they could be a bunch of different colors, which we SEE as all pink.
It’s also interesting to consider that most of these animals are not aware of having glowing patches on their bodies…. isn’t it also possible that we have skin or hair patterns that were not aware of?
.
.
(There is actually some research out there to support the idea that our own skin fluoresces as well and that there are gender differences in the pattern and glow.)
Other places to see my posts:
INSTAGRAM / FACEBOOK / ETSY / KICKSTARTER
193K notes
·
View notes
Text
TUMBLR I HAVE JUST LEARNED SOMETHING AMAZING AND MUST INFLICT IT IN YOU
There is a Japanese water beetle called Regimbartia attenuata. It has developed an incredible adaptation to be being eaten by pond frogs.
It walks out the frog’s butt.
The beetles get swallowed whole, and usually that would be considered Kinda Fatal, but this particular species is just like “DID YOU THINK A FROG’S DIGESTIVE TRACT COULD HOLD ME?!” and proceeds to walk through the frog’s intestines, then presumably stimulate the frog’s hind gut with its legs so that the frog poops. The beetles emerge headfirst and 93% of them survive and live on for weeks afterward.
Apparently some beetles can do this obstacle course in six minutes! (Usually takes a few hours, but some people will speedrun ANYTHING.)
Isn’t that COOL?!
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

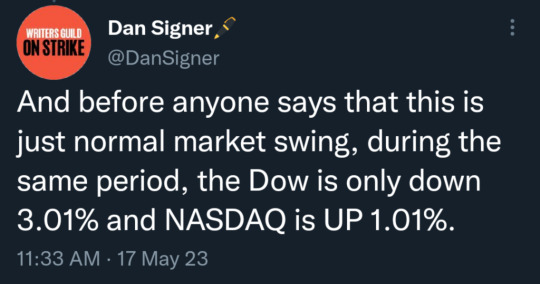
(link to first tweet)
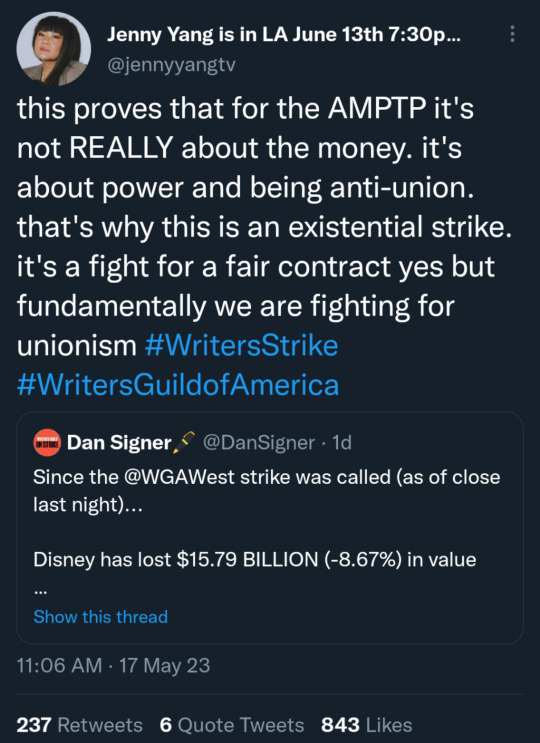
(link to tweet)

(link to tweet) They should be asking for more, ffs
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
i think if we’re going to have conversations about consent we should talk about how consenting to something doesn’t necessarily mean it’s going to be a good experience, and having a bad experience doesn’t necessarily mean someone violated your consent. this can apply to a lot of situations but the two i’m thinking of right now are sex and transition.
you’re getting it on with someone. you enthusiastically consent to having sex with them. afterward, you feel a little weird about it. maybe even distressed. maybe they did something you didn’t enjoy and in the moment you just didn’t say anything. maybe you just realized after the fact that you were not in a good headspace for sex and now your mental health is declining. that doesn’t inherently mean the person you had sex with violated your consent. sometimes it just means you need to take a break from sex or work on communicating your needs or boundaries better during sex.
and with transition, i feel like this is something that gets consistently overlooked but like. there will never be zero detransitioners. there will always be people who decide that actually transition wasn’t right for them. they could have had the best most thorough doctors in the world who did everything by the book and got full informed consent at every step. and some people are still going to decide they don’t like the changes and wish they hadn’t transitioned. that doesn’t mean that the doctors violated their consent, and that doesn’t mean that transition shouldn’t be available to anyone. it just means that we need to have more resources available for folks who detransition.
regret does not automatically mean someone did something wrong. regret is simply one possible result of having bodily autonomy, and i think we need to get more comfortable with that.
24K notes
·
View notes











