Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
The Future of Print Marketing: Integrating AI for Maximum Impact
As digital transformation reshapes industries, print marketing remains a powerful channel that continues to evolve. With the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can enhance personalization, streamline production, and improve overall campaign effectiveness. AI is transforming print marketing by enabling smarter decision-making, optimizing content, and increasing engagement with targeted audiences.

The Role of AI in Print Marketing
AI-driven innovations allow businesses to leverage data insights, automate tasks, and create more compelling print materials. From predictive analytics to AI-powered design tools, print marketing is experiencing a revolution that enhances efficiency and maximizes ROI.
Personalization at Scale with AI
One of AI’s greatest contributions to print marketing is the ability to personalize content at an unprecedented scale. With AI-driven insights, businesses can:
Analyze consumer behavior to tailor messaging based on preferences and past interactions.
Generate variable data printing (VDP) to create unique, individualized print materials for different customer segments.
Enhance direct mail campaigns with dynamic, AI-curated content that resonates with recipients.
AI-Driven Print Design and Content Creation
AI is revolutionizing the creative process by automating and optimizing design. Some key AI-powered enhancements include:
Automated Layout Suggestions – AI tools analyze best-performing layouts and recommend design structures for optimal readability.
AI-Generated Copywriting – Content creation tools use machine learning to craft compelling and relevant print copy.
Smart Image Selection – AI selects and optimizes images for print, ensuring high quality and engagement.
Optimizing Print Campaign Targeting with AI
AI enhances targeting by refining audience segmentation and improving message delivery. Businesses can:
Use predictive analytics to determine the best recipients for print campaigns.
Employ machine learning models to analyze engagement data and improve response rates.
Integrate geolocation insights for hyper-targeted print marketing that aligns with customer locations and preferences.
Enhancing Print-Digital Integration
AI bridges the gap between print and digital marketing channels, allowing for seamless integration. Strategies include:
Personalized QR codes that drive users to digital platforms based on AI-driven recommendations.
Augmented reality (AR) experiences embedded in print materials to engage audiences interactively.
AI-powered tracking tools that monitor engagement with printed materials and inform future strategies.
Reducing Costs and Waste with AI-Powered Print Management
AI helps optimize print production, reducing waste and cost inefficiencies by:
Predicting print demand to minimize overproduction.
Automating supply chain management for improved resource allocation.
Enhancing print scheduling to streamline operations and maximize efficiency.
AI in Direct Mail Marketing
Direct mail continues to thrive with AI-driven improvements, including:
Dynamic Content Creation – AI tailors messages for specific recipients, increasing engagement.
Intelligent Address Validation – AI ensures mailing lists are accurate and up-to-date.
Post-Campaign Analytics – AI measures response rates and campaign success, refining future efforts.
The Future of AI in Print Marketing
As AI technology advances, the future of print marketing will include:
AI-powered real-time content generation for on-demand personalized prints.
Voice-assisted design tools that simplify print campaign creation.
Deep learning models that further refine targeting accuracy and predictive marketing.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing print marketing by enabling smarter targeting, improving personalization, and optimizing campaign efficiency. As businesses integrate AI into their print strategies, they gain the ability to enhance engagement, reduce costs, and drive higher ROI. The future of print marketing lies in the seamless combination of AI-driven insights and traditional print media, ensuring a more impactful and data-driven approach to marketing.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
A Guide to Addresses, Forward Geocoding & In-House Printing – Blogspot
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
Pinterest
0 notes
Text
Leveraging Machine Learning for Smarter Print Campaign Targeting
As businesses strive to maximize the impact of their marketing efforts, print campaigns continue to be a powerful tool. However, the effectiveness of print marketing can be significantly enhanced through the integration of machine learning. By leveraging data-driven insights, machine learning enables businesses to create highly targeted, efficient, and impactful print campaigns that resonate with specific audiences.

The Role of Machine Learning in Print Campaign Targeting
Machine learning allows businesses to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions that optimize campaign performance. By understanding customer behaviors, preferences, and demographics, print marketers can create more personalized and effective campaigns.
Data Collection and Analysis for Smarter Targeting
A successful machine-learning-powered print campaign starts with collecting and analyzing relevant data. Some key data sources include:
Customer Purchase History – Understanding past purchasing behavior helps predict future interests.
Demographic Information – Age, location, income, and occupation help tailor print materials.
Online Interactions – Website visits, social media activity, and email engagement provide insights into consumer interests.
Market Trends – Industry trends and competitor analysis help refine targeting strategies.
Predictive Analytics for Personalized Print Campaigns
Machine learning employs predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs and preferences. This enables businesses to:
Identify high-value customers most likely to respond to print marketing.
Create dynamic content that resonates with individual recipients.
Determine the best timing for sending printed materials to maximize engagement.
Segmentation and Audience Clustering
By segmenting audiences based on machine learning insights, businesses can create highly tailored print campaigns. Some segmentation techniques include:
Behavioral Segmentation – Grouping customers based on actions such as product purchases or service usage.
Geographic Segmentation – Customizing print materials based on location-specific trends.
Psychographic Segmentation – Targeting individuals based on values, lifestyle, and interests.
Lifetime Value Segmentation – Prioritizing customers with high lifetime value for personalized engagement.
Optimizing Print Material Design with AI Insights
Machine learning enhances the design process by analyzing engagement data to determine which formats, colors, and layouts drive the best results. Key considerations include:
Personalized Messaging – Customizing headlines and copy for different audience segments.
A/B Testing for Print – Testing different designs to identify the most effective layout.
Dynamic Content Generation – Automating the creation of personalized print materials.
Enhancing Direct Mail Campaigns with Machine Learning
Direct mail remains a powerful marketing tool, and machine learning enhances its effectiveness by:
Predicting the Best Mailing Lists – Identifying recipients most likely to engage with print content.
Optimizing Delivery Timing – Determining when customers are most receptive to printed materials.
Tracking and Measuring Impact – Using response rates and engagement data to refine future campaigns.
Integrating Print with Digital Marketing Strategies
Machine learning enables seamless integration between print and digital marketing strategies by:
Creating Omnichannel Experiences – Synchronizing print campaigns with online touchpoints.
Leveraging QR Codes and Personalized URLs – Encouraging recipients to engage with digital content.
Tracking Customer Journeys – Understanding how print materials influence online behavior.
Reducing Print Waste Through AI-Driven Efficiency
Sustainability is a growing concern, and machine learning helps reduce waste by:
Optimizing Print Runs – Printing only what is necessary based on demand predictions.
Improving Targeting Accuracy – Ensuring print materials reach the right audience to minimize unused prints.
Enhancing ROI Analysis – Evaluating campaign effectiveness to refine future print investments.
Challenges and Considerations in Machine Learning for Print Marketing
While machine learning offers significant benefits, businesses must address key challenges:
Data Privacy Compliance – Ensuring ethical data collection and adherence to privacy regulations.
Integration with Existing Systems – Aligning machine learning tools with traditional print workflows.
Balancing Personalization and Scale – Maintaining a balance between highly personalized content and production efficiency.
The Future of Machine Learning in Print Marketing
As technology evolves, machine learning will continue to refine print campaign targeting through:
Advanced AI-Powered Personalization – Enhancing real-time customization of printed materials.
Automated Print Production – Streamlining print processes for faster, cost-effective execution.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Print – Creating interactive print experiences that bridge the physical and digital worlds.
Conclusion
Machine learning is revolutionizing print marketing by enabling smarter targeting, optimizing design, and improving efficiency. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can create highly effective print campaigns that engage the right audiences, reduce waste, and maximize ROI. As AI and machine learning continue to advance, print marketing will become even more intelligent, personalized, and impactful.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
A Guide to Addresses, Forward Geocoding & In-House Printing – Blogspot
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
Pinterest
0 notes
Text
Essential Equipment and Tools for Effective In-House Printing
In today’s fast-paced business environment, In-House Printing has become a cost-effective and convenient solution for organizations that require frequent printing. Having the right equipment and tools is crucial to ensuring efficiency, high-quality output, and reduced long-term costs. Investing in the appropriate resources allows businesses to maintain control over their printing needs and eliminate dependency on external printing services.

The Importance of In-House Printing
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from In-House Printing, as it provides greater flexibility, faster turnaround times, and cost savings. By bringing printing operations in-house, organizations can customize materials, ensure confidentiality, and reduce reliance on third-party vendors.
Essential Equipment for In-House Printing
To establish an efficient In-House Printing setup, businesses need to invest in key equipment tailored to their specific printing needs. The following are the most essential tools for a successful in-house printing operation:
1. High-Quality Printers
Choosing the right printer depends on the type of printing required. Some of the most commonly used printers for In-House Printing include:
Laser Printers – Ideal for high-volume printing with crisp text and graphics.
Inkjet Printers – Suitable for high-resolution color prints and images.
All-in-One Printers – Combine printing, scanning, copying, and faxing functionalities for versatile use.
Large-Format Printers – Essential for businesses that need banners, posters, and other oversized materials.
2. Printing Paper and Specialty Media
Different printing tasks require different types of paper and media. Standard paper, glossy photo paper, cardstock, and adhesive labels are some of the most commonly used materials in In-House Printing operations.
3. Binding and Finishing Equipment
Binding and finishing tools enhance the professionalism of printed materials. Some important finishing equipment includes:
Laminators – Protect printed documents from wear and tear.
Binding Machines – Coil, comb, or thermal binding machines provide a polished look for reports and presentations.
Paper Cutters and Trimmers – Ensure clean and precise cuts for documents and marketing materials.
4. Graphic Design and Printing Software
Professional software is essential for designing and formatting documents. Some widely used programs for In-House Printing include:
Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign) – Industry-leading tools for graphic design and print media.
CorelDRAW – Another popular choice for creating high-quality printed materials.
Canva – User-friendly online design software for businesses with minimal design expertise.
5. Color Management Tools
Maintaining color accuracy is crucial for high-quality prints. In-House Printing setups should include:
Color Calibration Tools – Devices that adjust colors for consistent and accurate printing.
Pantone Color Guides – Ensure brand consistency across different print materials.
6. Print Management Software
For businesses with high printing demands, print management software helps track print jobs, reduce waste, and optimize printer usage. This software enhances efficiency by streamlining In-House Printing processes and preventing unnecessary printing.
Maintaining an Efficient In-House Printing Setup
A well-maintained In-House Printing setup ensures longevity and optimal performance. Key maintenance practices include:
Regular cleaning of printers to prevent ink and toner buildup.
Timely replacement of cartridges and paper to avoid disruptions.
Updating software and drivers for improved compatibility and security.
Proper storage of paper and media to prevent damage or curling.
Cost Considerations for In-House Printing
Although In-House Printing offers cost savings in the long run, initial investment costs should be carefully evaluated. Some key factors to consider include:
Equipment costs – Choosing the right printer and finishing tools within budget constraints.
Operating expenses – Ink, toner, paper, and maintenance costs.
Energy consumption – Efficient printers with energy-saving modes can reduce utility costs.
Staff training – Ensuring employees understand how to use printing equipment effectively.
Future Trends in In-House Printing
Technology continues to evolve, bringing innovations to In-House Printing. Some emerging trends include:
3D Printing – Expanding printing capabilities beyond traditional paper-based materials.
Eco-Friendly Printing – Using biodegradable inks and recycled paper for sustainability.
Cloud Printing – Enhancing remote printing accessibility and convenience.
AI-Powered Print Management – Automating print job distribution for greater efficiency.
Conclusion
Setting up a successful In-House Printing operation requires the right combination of equipment, software, and best practices. By investing in high-quality printers, finishing tools, and efficient management systems, businesses can achieve professional-grade printing at a fraction of the cost of outsourcing. As technology advances, businesses that embrace new printing trends will gain even greater control, efficiency, and sustainability in their printing operations.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
A Guide to Addresses, Forward Geocoding & In-House Printing – Blogspot
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
Pinterest
0 notes
Text
The Role of Forward Geocoding in Location Mapping and Navigation
In an increasingly digital world, accurate location mapping and navigation play a crucial role in various industries, from logistics and real estate to emergency services and urban planning. Forward geocoding, a fundamental process in geospatial technology, enables the conversion of text-based location data into geographic coordinates. This technology enhances location-based services, improves address accuracy, and ensures seamless navigation experiences.
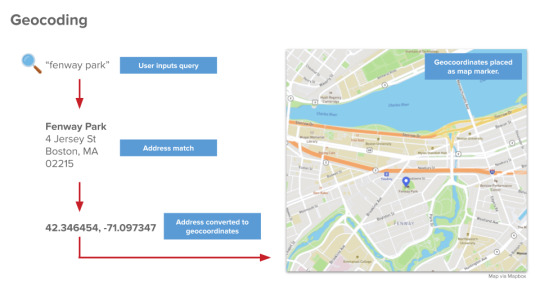
Understanding Forward Geocoding
Forward geocoding is the process of translating structured or unstructured address information into precise latitude and longitude coordinates. By leveraging a database of location data, this method helps map and navigation systems determine exact locations based on inputted addresses.
The Importance of Accurate Address Data in Forward Geocoding
The effectiveness of forward geocoding depends on the accuracy of the parts of an address provided. A complete and correctly formatted address ensures precise geolocation, reducing errors in mapping and navigation.
Key address components include:
Street Name and Number – The primary identifier of a location.
City or Municipality – Essential for narrowing down the location.
State or Province – Helps refine regional accuracy.
Postal Code – Enhances precision by limiting possible location variations.
Country – Crucial for distinguishing similar addresses in different nations.
Applications of Forward Geocoding in Location Mapping
Forward geocoding is widely used across multiple industries to improve mapping and navigation functionalities. Some of its key applications include:
1. Navigation and Routing Services
Navigation apps and GPS systems rely on forward geocoding to convert typed addresses into mappable locations. This allows users to receive step-by-step directions with optimized routes based on traffic and road conditions.
2. E-Commerce and Delivery Services
Online retailers and logistics providers use forward geocoding to ensure accurate deliveries. Address validation before shipment minimizes failed deliveries and enhances customer satisfaction.
3. Emergency Response and Public Safety
Emergency services utilize forward geocoding to pinpoint incident locations quickly. Accurate geolocation helps first responders reach emergencies faster, improving public safety outcomes.
4. Real Estate and Property Management
Real estate platforms integrate forward geocoding to map property listings accurately. Buyers and renters can view available properties based on precise geographic coordinates.
5. Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
City planners leverage forward geocoding to analyze geographic data for better infrastructure planning. It aids in zoning regulations, traffic management, and public transportation improvements.
Challenges in Forward Geocoding and Address Accuracy
Despite its advantages, forward geocoding faces challenges, particularly when address data is incomplete or incorrectly formatted.
1. Inconsistent Address Formatting
Differences in address formats across regions can lead to geolocation errors. Standardizing address inputs reduces discrepancies in mapping.
2. Ambiguous or Missing Address Components
If an address lacks key parts of an address, the system may return inaccurate or multiple location results. Address verification tools help mitigate these issues.
3. Data Quality and Database Limitations
Forward geocoding relies on extensive location databases. Incomplete or outdated databases can affect accuracy, making regular updates essential.
Improving Forward Geocoding Accuracy
To enhance the reliability of forward geocoding, organizations can implement various best practices:
Address Standardization – Using consistent formats ensures uniformity in geolocation results.
Validation Tools – Automated address verification software corrects errors and fills missing data.
Integration with GIS Systems – Geographic Information Systems (GIS) improve spatial data management and accuracy.
Regular Data Updates – Keeping location databases current ensures precise mapping.
The Future of Forward Geocoding in Location Technology
Advancements in AI and machine learning are revolutionizing forward geocoding. Predictive analytics and automation enhance accuracy, making location-based services more efficient and reliable.
Conclusion
Forward geocoding plays a vital role in location mapping and navigation, transforming address data into usable geographic coordinates. The accuracy of geolocation depends on the completeness of parts of an address, making standardization and validation essential for precision. As technology evolves, forward geocoding will continue to enhance navigation systems, logistics, and urban development, driving innovation in location-based services.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
A Guide to Addresses, Forward Geocoding & In-House Printing – Blogspot
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
Pinterest
0 notes
Text
Essential Parts of an Address: How to Format Addresses Correctly
Addresses are a fundamental part of communication, ensuring that mail and shipments reach the intended recipients efficiently. Properly formatting an address is crucial for reducing delivery errors and improving logistical efficiency. Understanding the essential parts of an address and adhering to standard formatting guidelines can help businesses and individuals avoid common mailing issues.

Understanding the Key Parts of an Address
A well-structured address consists of several essential components. Each part plays a critical role in guiding mail carriers and logistics providers to the correct destination.
Recipient’s Name – The name of the individual or business receiving the mail.
Street Address – The specific street number and name where the recipient is located.
Apartment, Suite, or Unit Number – Additional location details within a building or complex.
City or Town – The municipality where the address is located.
State or Province – The administrative division relevant to the address.
Postal Code or ZIP Code – A numeric or alphanumeric code that helps in sorting and delivering mail efficiently.
Country – Required for international addresses to ensure proper routing.
How to Format an Address Correctly
Different mailing systems and postal services have specific guidelines for address formatting. Here are some general formatting best practices:
Use a Clear, Legible Font – Ensuring that addresses are easy to read reduces misdelivery.
Avoid Punctuation – Many postal services recommend omitting periods and commas.
Write in All Capital Letters (Optional) – Some postal standards prefer uppercase letters for clarity.
Use Standard Abbreviations – Common abbreviations (e.g., “St” for Street, “Apt” for Apartment) help standardize addresses.
Place the Postal Code on the Last Line – Ensuring the postal code is correctly positioned enhances delivery accuracy.
Address Formatting for Different Mailing Needs
Residential Address Formatting
A standard residential address should include all necessary components while being concise and easy to read. Example:
John Smith 123 Main St Apt 4B Los Angeles, CA 90001 USA
Business Address Formatting
Business addresses may require additional details, such as department names or mail stops. Example:
ABC Corporation – Marketing Department 456 Elm Ave Suite 500 New York, NY 10022 USA
PO Box Address Formatting
Some individuals and businesses use PO boxes instead of street addresses. Example:
Jane Doe PO Box 789 Chicago, IL 60610 USA
Common Address Formatting Mistakes to Avoid
Incomplete Addresses – Missing any key part of an address can lead to misdelivery.
Incorrect Postal Codes – A wrong postal code can result in delivery to the wrong location.
Unnecessary Punctuation – Using excessive punctuation can slow down processing.
Illegible Handwriting – For handwritten addresses, clear writing is essential.
Incorrect Use of Abbreviations – Using non-standard abbreviations may cause confusion.
Why Address Formatting Matters in E-Commerce and Shipping
E-commerce businesses rely heavily on accurate address formatting to ensure timely deliveries. Address verification tools and standardized formats help reduce shipping errors, improve customer satisfaction, and lower costs associated with returns and undelivered packages.
International Address Formatting Differences
Different countries have varying address formats, so businesses and individuals sending international mail must be aware of these differences. For example:
UK Addresses: Typically include a county and a postcode in a different format.
Canadian Addresses: Use alphanumeric postal codes and may require bilingual labels.
Japanese Addresses: Start with the postal code and list the largest geographic area first.
Address Verification and Automation
Many businesses use address verification software to ensure accuracy before printing shipping labels. Automated tools can:
Detect missing or incorrect address components.
Standardize formatting based on postal service requirements.
Suggest corrections to prevent delivery issues.
Impact of Incorrect Address Formatting on Delivery Efficiency
Poorly formatted addresses can result in delayed or failed deliveries, increased costs, and dissatisfied customers. Ensuring every part of an address is correctly structured can streamline shipping operations and improve logistics management.
Conclusion
Proper address formatting is essential for ensuring accurate and efficient deliveries. By understanding and implementing correct formatting practices, individuals and businesses can minimize delivery errors, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Whether for residential, business, or international mailing, adhering to standard address structures is key to a seamless mailing experience.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
A Guide to Addresses, Forward Geocoding & In-House Printing – Blogspot
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
Pinterest
1 note
·
View note