Text
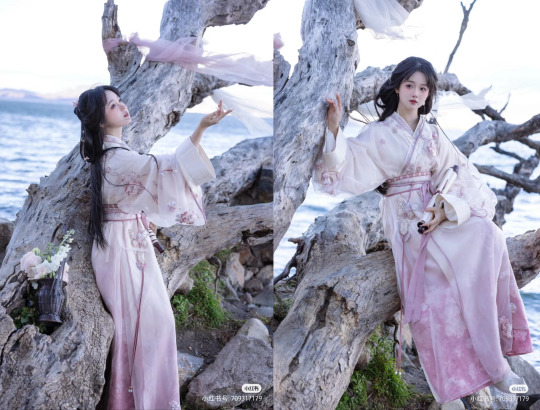
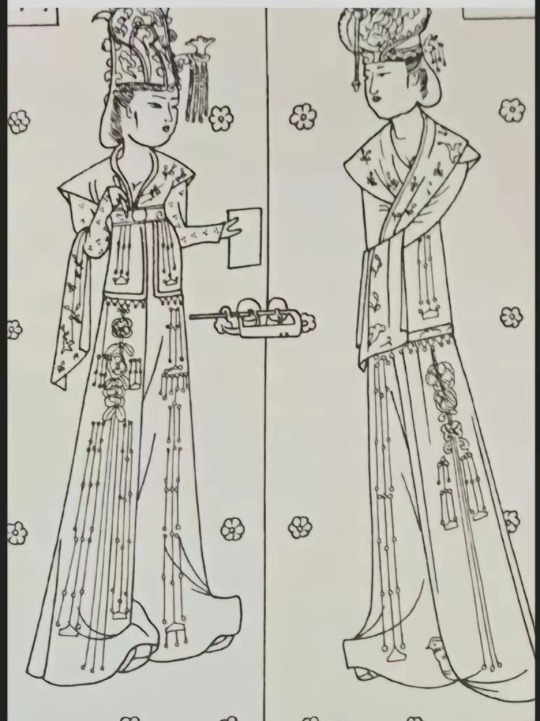
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Late Warring States period(475–221 BC) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Based On Based On Chu (state)Historical Artifacts
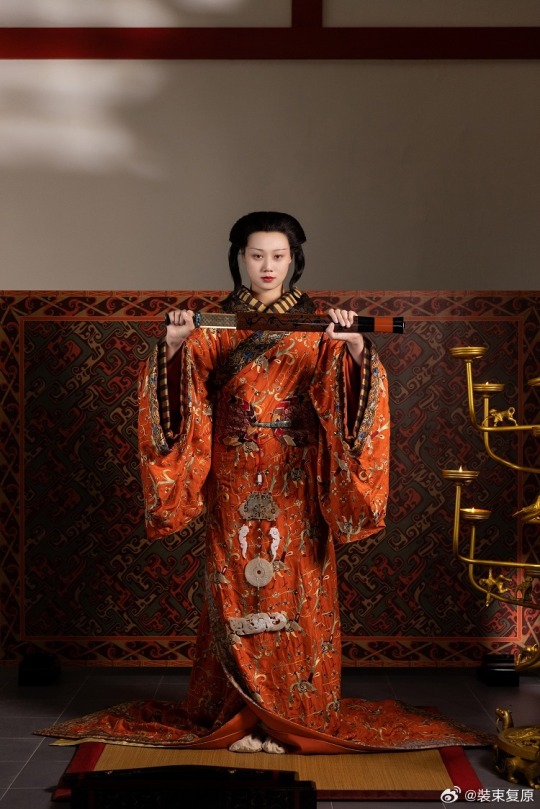
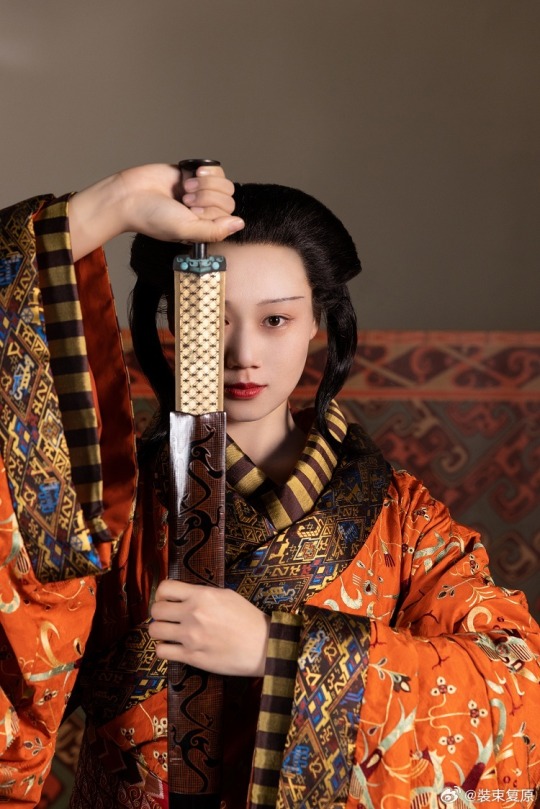





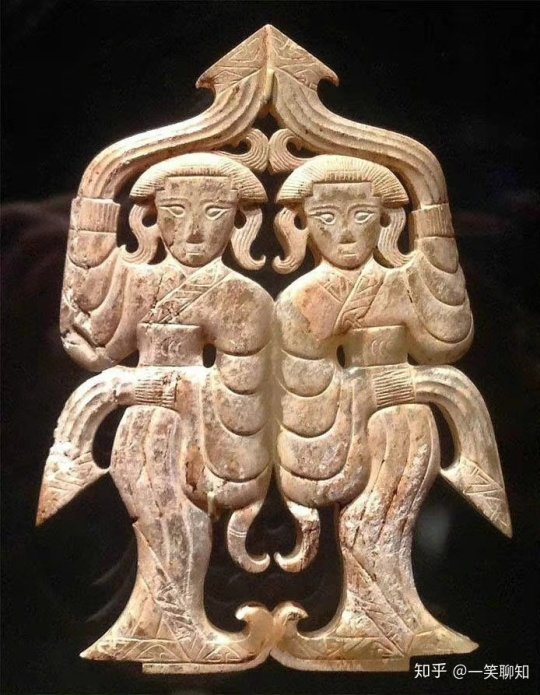
【Historical Artifact Reference】:
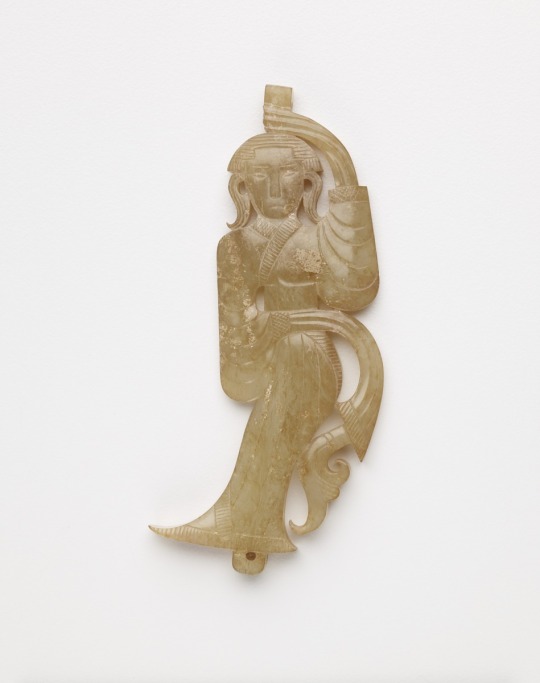
Late Warring States period(475–221 BC):Two conjoined jade dancers unearthed from Jincun, Luoyang,collected by Freer Museum of Art

A similar jade dancer was also unearthed from the tomb of Haihunhou, the richest royal family member in the Han Dynasty, and was one of his treasures.
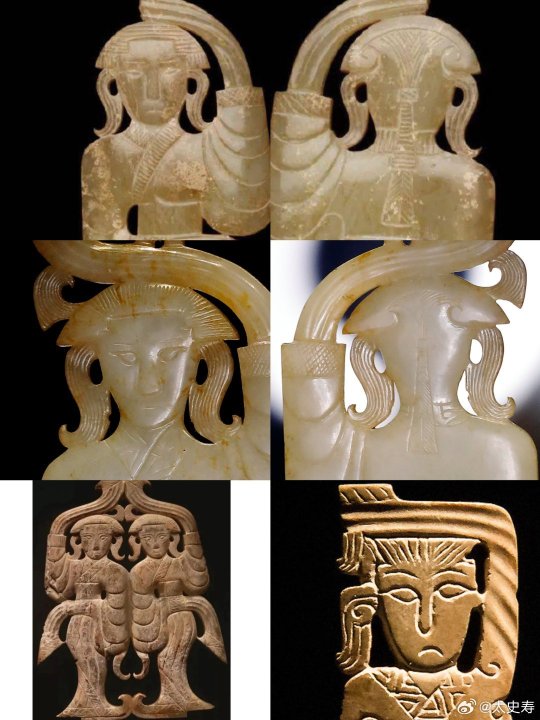

Warring States period, Eastern Zhou dynasty, 475-221 BCE,jade dancer by Freer Gallery of Art Collection.

Warring States period(475–221 BC)·Silver Head Figurine Bronze Lamp.Unearthed from the Wangcuo Tomb in Zhongshan state during the Warring States Period and collected by the Hebei Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology
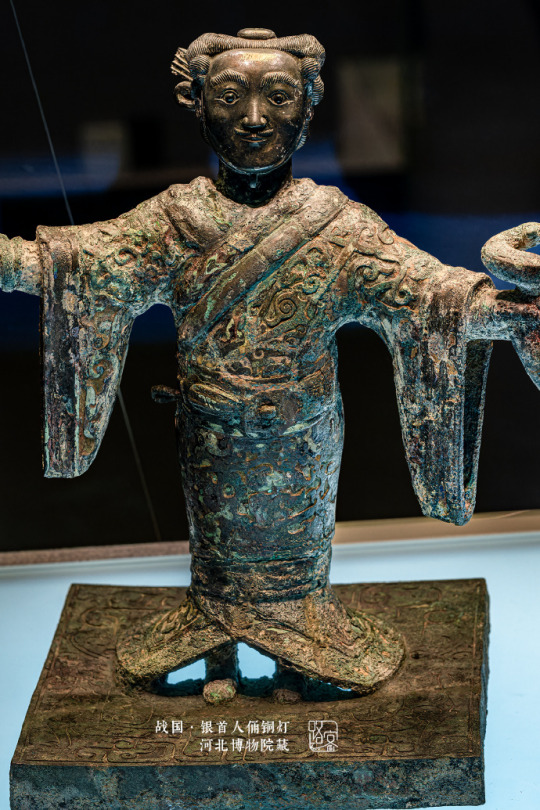
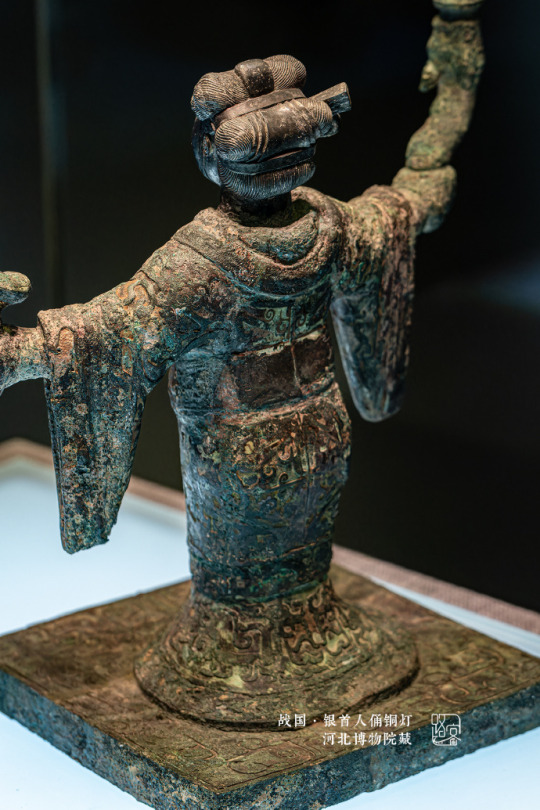



The figurine of a man dressed as a woman holds a snake in his hand, and 3 snakes correspond to 3 lamps.
Sword of Goujian/越王勾践剑:
The Sword of Goujian (Chinese: 越王勾践剑; pinyin: Yuèwáng Gōujiàn jiàn) is a tin bronze sword, renowned for its unusual sharpness, intricate design and resistance to tarnish rarely seen in artifacts of similar age. The sword is generally attributed to Goujian, one of the last kings of Yue during the Spring and Autumn period.
In 1965, the sword was found in an ancient tomb in Hubei. It is currently in the possession of the Hubei Provincial Museum.

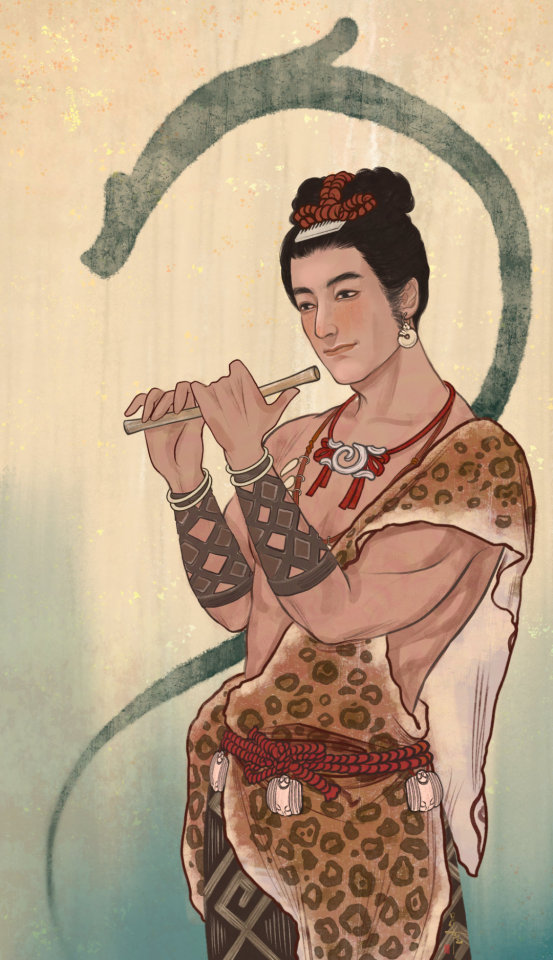
【Histoty Note】Late Warring States Period·Noble Women Fashion
The attire of noblewomen in the late Warring States period, as reconstructed in this collection, is based on a comprehensive examination of garments and textiles unearthed from the Chu Tomb No. 1 at Mashan, Jiangling, as well as other artifacts from the same period.
During the late Warring States period, both noble men and women favored wearing robes that were connected from top to bottom. These garments were predominantly made of gauze, silk, brocade, and satin, with silk edging. From the Chu Tomb No. 1 at Mashan, there were discoveries of robes entirely embroidered or embroidered fragments. The embroidery technique employed was known as "locked stitches," which gave the patterns a three-dimensional, lively appearance, rich in decoration.
The two reconstructed robes in this collection consist of an inner robe made of plain silk with striped silk edging, and an outer robe made of brocade, embroidered with phoenixes and floral patterns, with embroidered satin edging. Following the structural design of clothing found in the Mashan Chu Tomb, rectangular fabric pieces were inserted at the junction of the main body, sleeves, and lower garment of the robe. Additionally, an overlap was made at the front of the main body and the lower garment to enlarge the internal space for better wrapping around the body curves. Furthermore, the waistline of the lower garment was not horizontal but inclined upward at an angle, allowing the lower hem to naturally overlap, forming an "enter" shape, facilitating movement.
The layered edging of the collars and sleeves of both inner and outer robes creates a sense of rhythm, with the two types of brocade patterns complementing each other, resulting in a harmonious effect. Apart from the robes, a wide brocade belt was worn around the waist, fastened with jade buckle hooks, and adorned with jade pendants, presenting an elegant and noble figure.
The reconstructed hairstyle draws inspiration from artifacts such as the jade dancer from the late Warring States period unearthed at the Marquis of Haihun Tomb in Nanchang, and the jade dancer from the Warring States period unearthed at Jin Village in Luoyang. It features a fan-shaped voluminous hairdo on the crown, with curled hair falling on both sides, and braided hair gathered at the back. The Book of Songs, "Xiao Ya: Duren Shi," vividly depicts the flowing curls of noblewomen during that period. Their images of curly-haired figures in long robes were also depicted in jade artifacts and other relics, becoming emblematic artistic representations.
The maturity and richness of clothing art in the late Warring States period were unparalleled in contemporary world civilizations, far beyond imagination. It witnessed the transition of Chinese civilization into the Middle Ages. The creatively styled garments and intricate fabric patterns from the Warring States period carry the unique essence, mysterious imagination, and ultimate romanticism of that era, serving as an endless source of artistic inspiration.
--------
Recreation Work by : @裝束复原
Weibo 🔗:https://weibo.com/1656910125/O6cUMBa1j
--------
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
This really poisonous, inhumane, maniac, & nastily haughty bitch animal really makes me shame & ill feel upon her maniacal things she did prior. Feels like I want to repeat the maniacal sadistic maiming against this animal bitch & then tear out her animal bitch heart alive from her fucking breasts so that I can see how this animal bitch dying horribly.
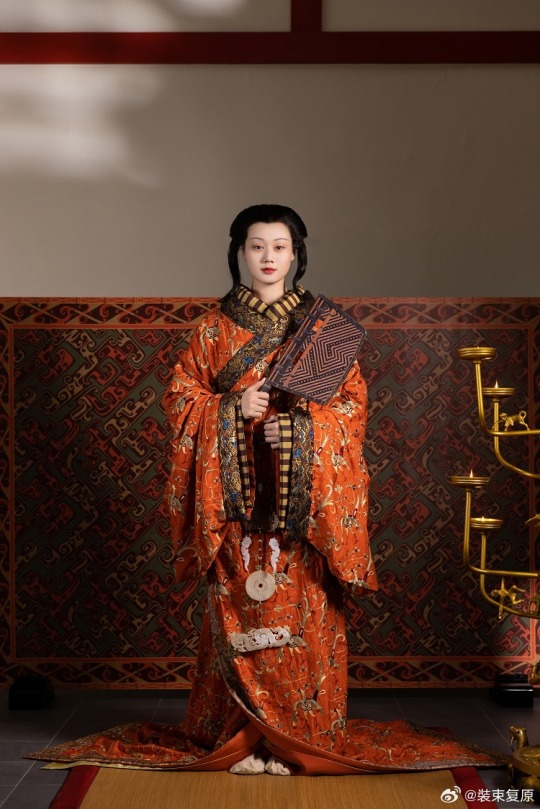
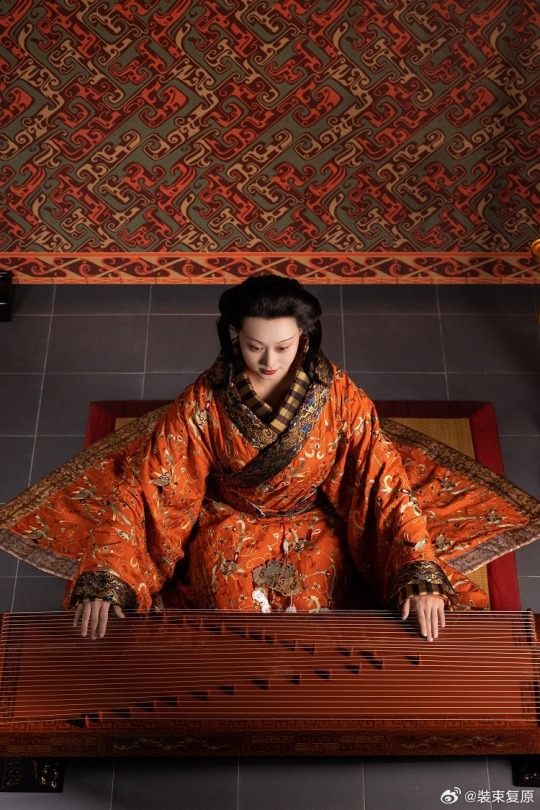
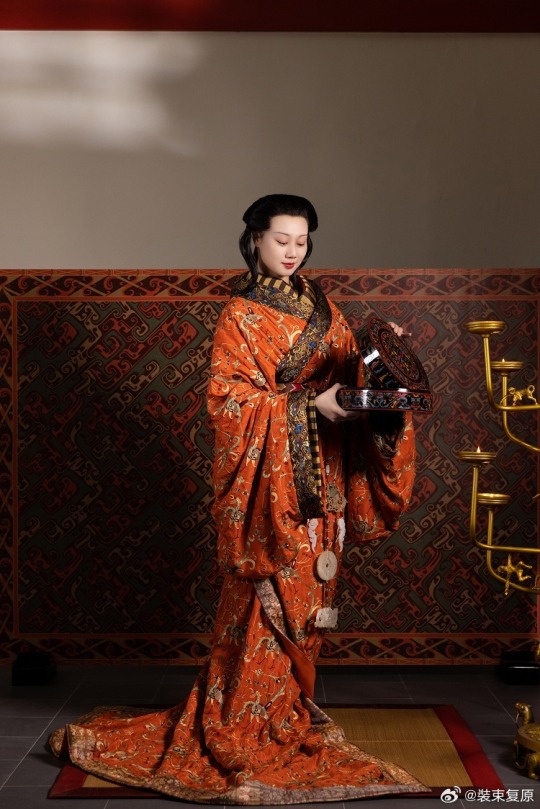
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
“这个位子 我有何坐不得?”
“我欲问鼎天下,试问谁与争锋”
"Why can't I sit in this seat?"
"I want to conquer the world, who can compete with me?"
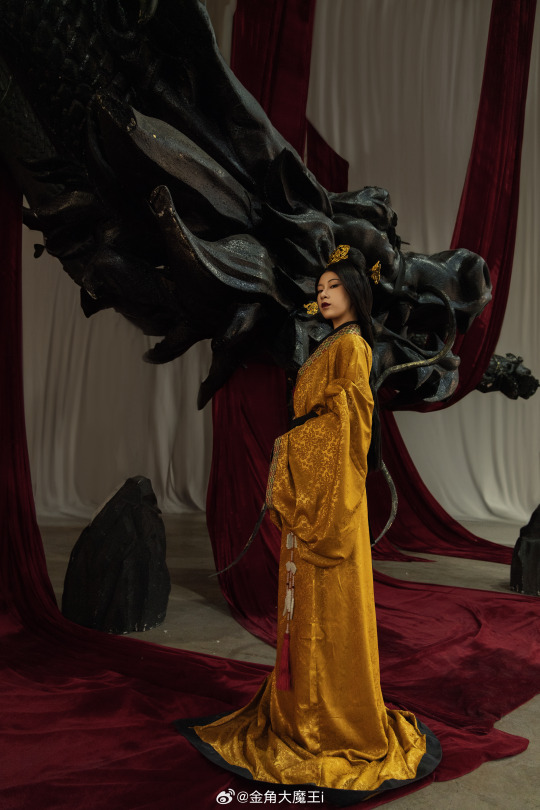
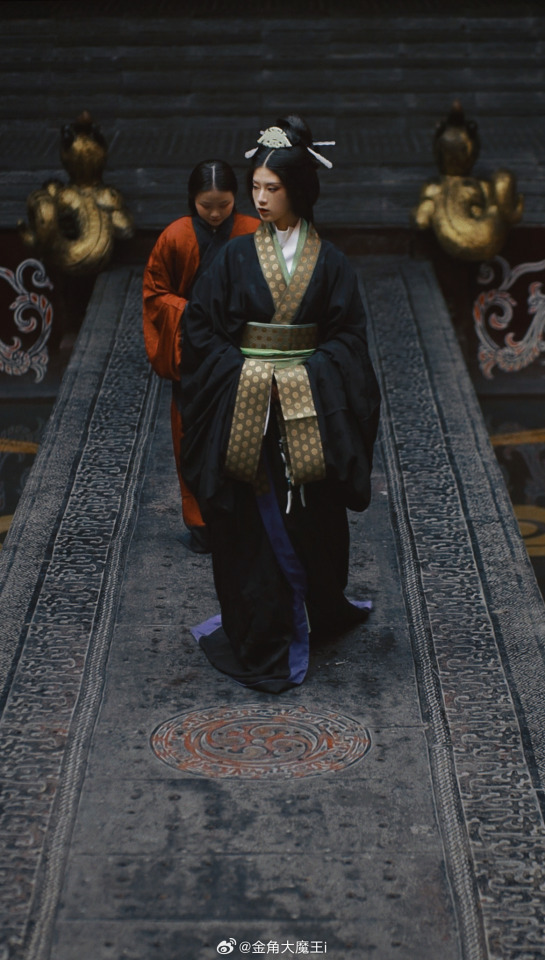
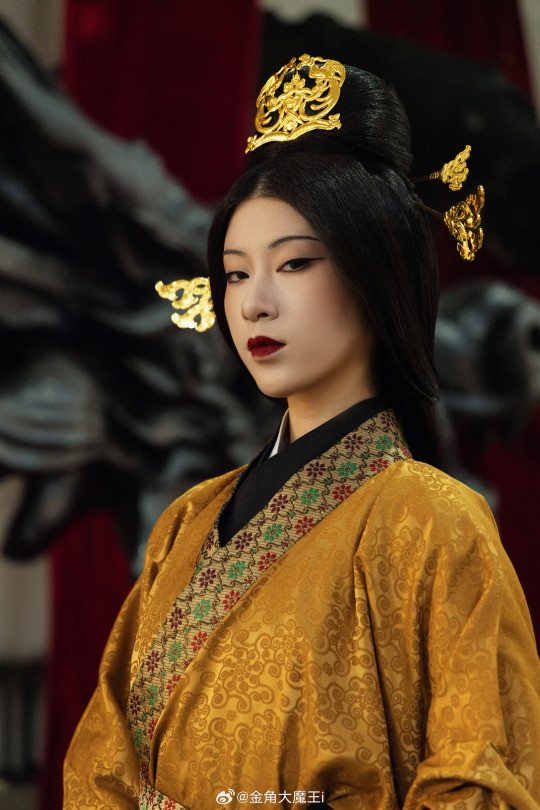
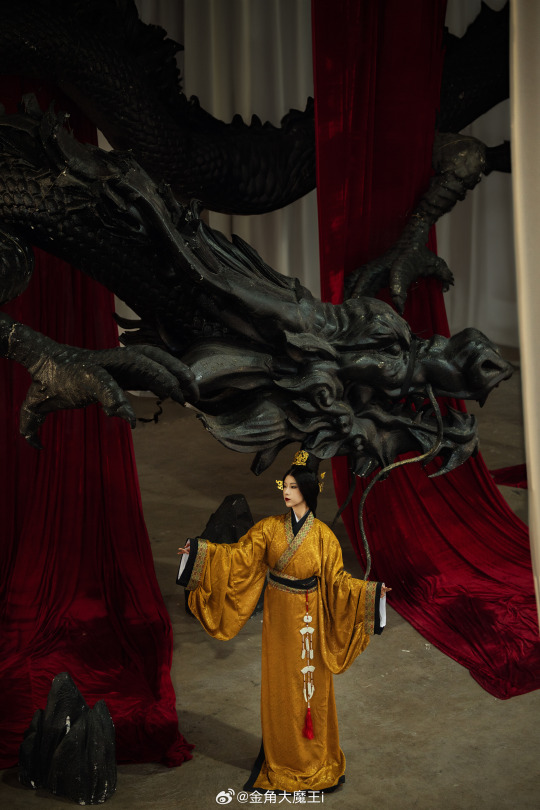
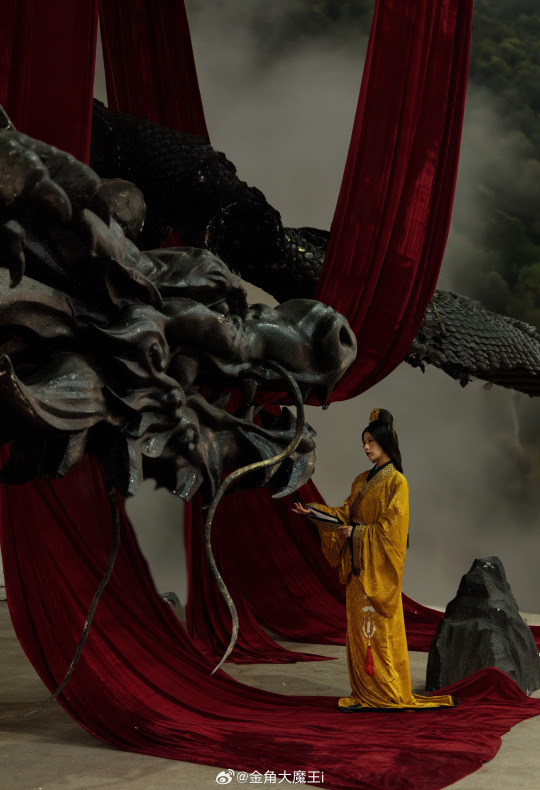








【About The First Empress of the Han Dynasty Empress Lü:Lǚ zhì(吕雉)】
Lü Zhi (241–18 August 180 BC), courtesy name E'xu (娥姁) and commonly known as Empress Lü (traditional Chinese: 呂后; simplified Chinese: 吕后; pinyin: Lǚ Hòu) and formally Empress Gao of Han (漢高后; 汉高后; Hàn Gāo Hòu), was the empress consort of Gaozu, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. They had two known children, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han) and Princess Yuan of Lu. Lü was the first woman to assume the title Empress of China and paramount power. After Gaozu's death, she was honoured as empress dowager and regent during the short reigns of Emperor Hui and his successors Emperor Qianshao of Han and Liu Hong (Emperor Houshao).
She played a role in the rise and foundation of her husband, Emperor Gaozu, and his dynasty, and in some of the laws and customs laid down by him. Empress Lü, even in the absence of her husband from the capital, killed two prominent generals who played an important role in Gaozu's rise to power, namely Han Xin and Peng Yue, as a lesson for the aristocracy and other generals. In June 195 BC, with the death of Gaozu, Empress Lü became, as the widow of the late emperor and mother of the new emperor, Empress Dowager (皇太后, Huángtàihòu), and assumed a leadership role in her son's administration. Less than a year after Emperor Hui's accession to the throne, in 194 BC, Lü had one of the late Emperor Gaozu's consorts whom she deeply hated, Concubine Qi, put to death in a cruel manner. She also had Concubine Qi's son Liu Ruyi poisoned to death. Emperor Hui was shocked by his mother's cruelty and fell sick for a year, and thereafter no longer became involved in state affairs, and gave more power to his mother. As a result, Empress dowager Lü held the court, listened to the government, spoke on behalf of the emperor, and did everything (臨朝聽政制, "linchao ting zhengzhi"). With the untimely death of her 22-year-old son, Emperor Hui, Empress dowager Lü subsequently proclaimed his two young sons emperor (known historically as Emperor Qianshao and Emperor Houshao respectively). She gained more power than ever before, and these two young emperors had no legitimacy as emperors in history; the history of this 8-year period is considered and recognized as the reign of Empress Dowager Lü. She dominated the political scene for 15 years until her death in August 180 BC, and is often depicted as the first woman to have ruled China. While four women are noted as having been politically active before her—Fu Hao, Yi Jiang, Lady Nanzi, and Queen Dowager Xuan—Lü was the perhaps first woman to have ruled over united China.
Lü Zhi was born in Shanfu County (單父; present-day Shan County, Shandong) during the late Qin Dynasty. Her courtesy name was Exu (Chinese: 娥姁; pinyin: Éxǔ). To flee from enemies, her father Lü Wen (呂文) brought their family to Pei County, settled there, and became a close friend of the county magistrate. Many influential men in town came to visit Lü Wen. Xiao He, then an assistant of the magistrate, was in charge of the seating arrangement and collection of gifts from guests at a banquet in Lü Wen's house, and he announced, "Those who do not offer more than 1,000 coins in gifts shall be seated outside the hall." Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han), then a minor patrol officer (亭長), went there bringing a single cent and said, "I offer 10,000 coins." Lü Wen saw Liu Bang and was so impressed with him on first sight, that he immediately stood up and welcomed Liu into the hall to sit beside him. Xiao He told Lü Wen that Liu Bang was not serious, but Liu ignored him and chatted with Lü. Lü Wen said, "I used to predict fortunes for many people but I've never seen someone so exceptional like you before." Lü Wen then offered his daughter Lü Zhi's hand in marriage to Liu Bang and they were wed. Lü Zhi bore Liu Bang a daughter (later Princess Yuan of Lu) and a son, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han).
Liu Bang later participated in the rebellion against the Qin Dynasty under the insurgent Chu kingdom, nominally-ruled by King Huai II. Lü Zhi and her two children remained with her father and family for most of the time during this period.
Even after Emperor Gaozu (Liu Bang)'s victory over Xiang Yu, there were still unstable areas in the empire, requiring the new government to launch military campaigns to pacify these regions thereafter. Gaozu placed Empress Lü Zhi and the crown prince Liu Ying (Lü Zhi's son) in charge of the capital Chang'an and making key decisions in court, assisted by the chancellor Xiao He and other ministers. During this time, Lü Zhi proved herself to be a competent administrator in domestic affairs, and she quickly established strong working relationships with many of Gaozu's officials, who admired her for her capability and feared her for her ruthlessness. After the war ended and Emperor Gaozu returned, she remained in power and she was always influential in many of the country's affairs.
In his late years, Emperor Gaozu started favouring one of his younger consorts, Concubine Qi(戚夫人), who bore him a son, Liu Ruyi, who was instated as Prince of Zhao in 198 BC, displacing Lü Zhi's son-in-law Zhang Ao (Princess Yuan of Lu's husband). Gaozu had the intention of replacing Liu Ying with Liu Ruyi as crown prince, reasoning that the former was too "soft-hearted and weak" and that the latter resembled him more. Since Lü Zhi had strong rapport with many ministers, they generally opposed Gaozu's decision but the emperor seemed bent on deposing Liu Ying. Lü Zhi became worried and she approached Zhang Liang for help, and the latter analysed that Gaozu was changing the succession on grounds of favouritism. Zhang Liang invited the "Four Whiteheads of Mount Shang", a group of four reclusive wise men, to persuade Gaozu to change his decision. The four men promised to assist Liu Ying in future if he became emperor, and Gaozu was pleased to see that Liu Ying had their support. Gaozu told Concubine Qi, "I wanted to replace (the crown prince). Now I see that he has the support of those four men; he is fully fledged and difficult to unseat. Empress Lü is really in charge!" This marked the end of the dispute over the succession and affirmed Liu Ying's role as crown prince.
In June 195 BC, Emperor Gaozu died and was succeeded by Liu Ying, who became historically known as Emperor Hui of Han. Lü Zhi was honoured by Emperor Hui as empress dowager. She exerted more influence during the reign of her son than she had when she was empress, and she became the powerful and effective lead figure in his administration.
Lü Zhi did not harm most of Gaozu's other consorts and treated them according to the rules and customs of the imperial family. For example, consorts who bore male children that were instated as princes were granted the title of "Princess Dowager" (王太妃) in their respective sons' principalities. One exception was Concubine Qi, whom Lü Zhi greatly resented because of the dispute over the succession between Liu Ruyi (Qi's son) and Liu Ying. Liu Ruyi, the Prince of Zhao, was away in his principality, so Lü Zhi targeted Concubine Qi. She had Qi stripped of her position, treated like a convict (head shaved, in stocks, dressed in prison garb), and forced to do hard labour in the form of milling rice.
Roles in the deaths of Concubine Qi and Liu Ruyi
Lü Zhi then summoned Liu Ruyi, who was around the age of 12 then, to Chang'an, intending to kill him together with his mother. However Zhou Chang (周昌), the chancellor in Liu Ruyi's principality, whom Lü Zhi respected because of his stern opposition to Emperor Gaozu's proposal to make Liu Ruyi crown prince, temporarily protected Liu Ruyi from harm by responding to Lü Zhi's order that, "The Prince of Zhao is ill and unfit for travelling over long distances." Lü Zhi then ordered Zhou Chang to come to the capital, had him detained, and then summoned Liu Ruyi again. Emperor Hui tried to save Liu Ruyi by intercepting his half-brother before the latter entered Chang'an, and kept Liu Ruyi by his side most of the time. Lü Zhi refrained from carrying out her plans for several months because she feared that she might harm Emperor Hui as well.
One morning in the winter of 195-194 BC, Emperor Hui went for a hunting trip and did not bring Liu Ruyi with him because the latter refused to get out of bed. Lü Zhi's chance arrived, so she sent an assassin to force poisoned wine down Liu Ruyi's throat. The young prince was dead by the time Emperor Hui returned. Lü Zhi then had Concubine Qi killed in an inhumane manner: she had Qi's limbs chopped off, eyes gouged out, ears sliced off, nose sliced off, tongue cut out, forced her to drink a potion that made her mute, and had her thrown into a latrine. She called Qi a "human swine" (人彘). Several days later, Emperor Hui was taken to view the "human swine" and was shocked to learn that it was Concubine Qi. He cried loudly and became ill for a long time. He requested to see his mother and said, "This is something done not by a human. As the empress dowager's son, I'll never be able to rule the empire" From then on, Emperor Hui indulged himself in carnal pleasures and ignored state affairs, leaving all of them to his mother, and this caused power to fall completely into her hands.
When Lu first came to the court, she planned to establish the Lu family members as "kings (nobles)". This was not only to commemorate her deceased relatives, but also to strengthen her power in the court. However, Wang Ling, the prime minister at the time, immediately pointed out that the great ancestor Liu Bang(Husband of Lu, founding emperor of Han Dynasty)once killed the white horse and agreed that "if someone who are not Liu family be come the king, the whole world should attack them." Therefore, the move of establishing a foreign surname as the king violated the ancestral system established by Liu Bang and was really inappropriate.
Faced with the obstruction of the royal mausoleum, Empress Lu responded by deposing him and insisting on honoring her deceased father and two brothers as King Lu Xuan, King Wu Wu, and King Zhao Zhao. After setting this precedent, Lu was out of control. She not only named her three nephews Lu Tai, Lu Chan, and Lu Lu as King Lu, King Liang, and King Zhao respectively, but also named her grandnephew Lu Tong. He was the King of Yan, and his grandson Zhang Yan was granted the title of King of Lu.
In addition, there are also quite a few people with the surname Lu who have been granted the title of marquis. As a result, it can be said that many princes surnamed Lu appeared in the court in the blink of an eye. They controlled the government and became the cornerstone and support for Empress Lu to control the right to speak in the court.
Empress Lu's life was emblematic of the intricate power dynamics of the Han Dynasty in ancient China. Born into a modest family, Lu rose to prominence through her marriage to Emperor Gaozu. Her astute political acumen and strategic alliances allowed her to wield significant influence behind the throne. As the mother of several emperors, she orchestrated their ascensions and manipulated court politics to consolidate power for her family. However, her ruthless pursuit of control and elimination of rivals earned her both admirers and enemies. In the end, her ambitions led to her downfall, as her unchecked power and manipulation of succession angered the nobility.As a result, after her death, the Lu family was retaliated and killed by the nobles and courtiers who supported the Han Dynasty, and the family was almost exterminated.Empress Lu's life illustrates the delicate balance of power, ambition, and intrigue in ancient Chinese imperial courts.
________________
📸Photo & Model :@金角大魔王i
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/NFVOXthxX
________________
180 notes
·
View notes
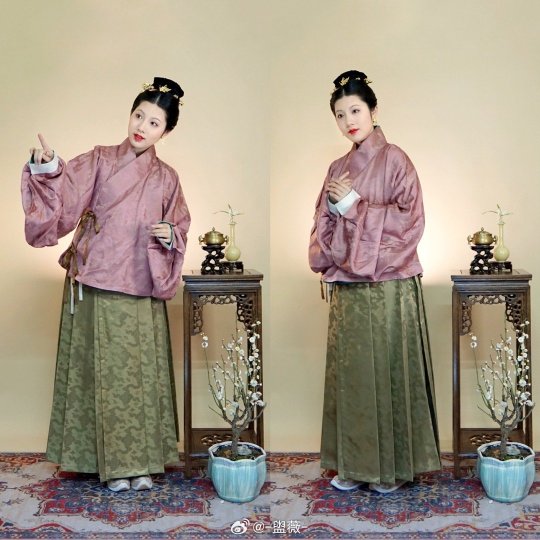
Photo
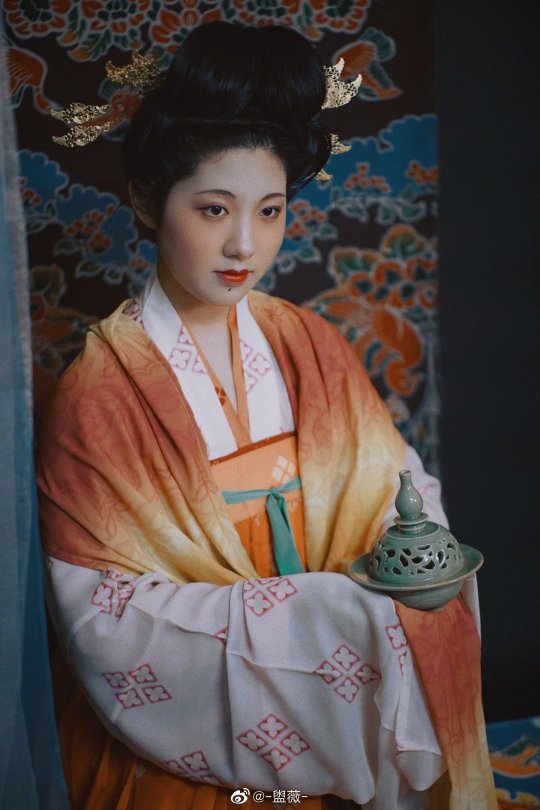
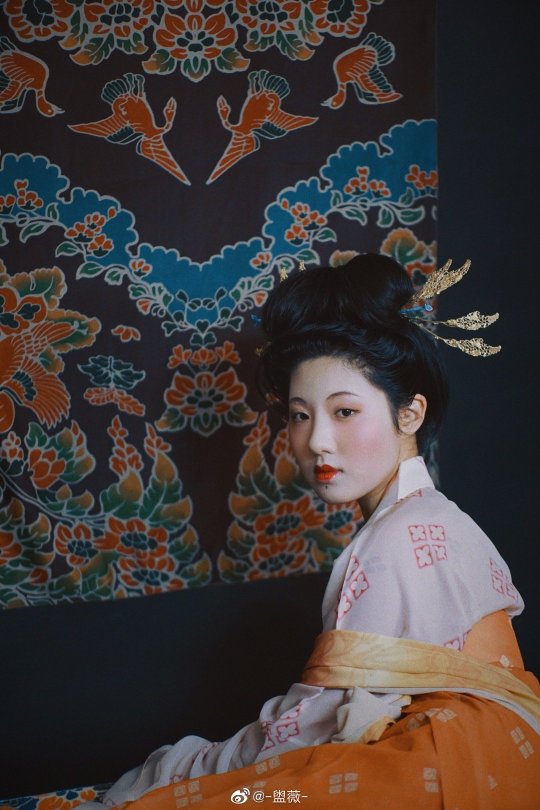
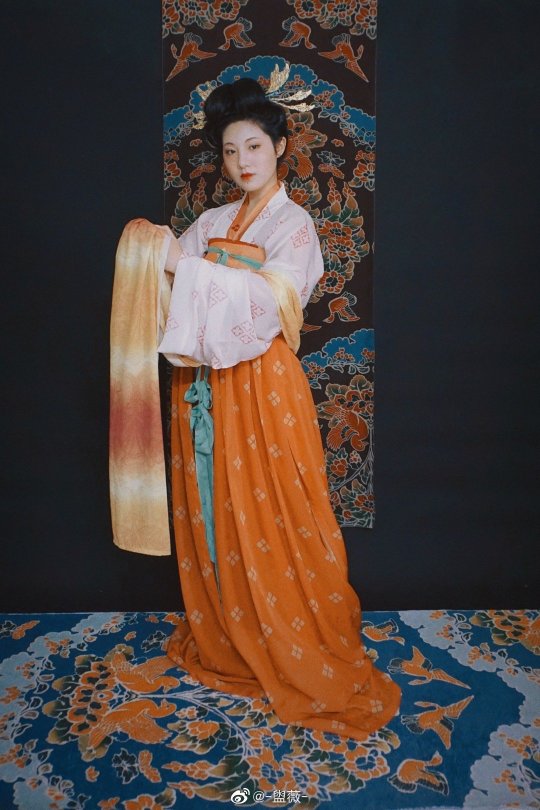
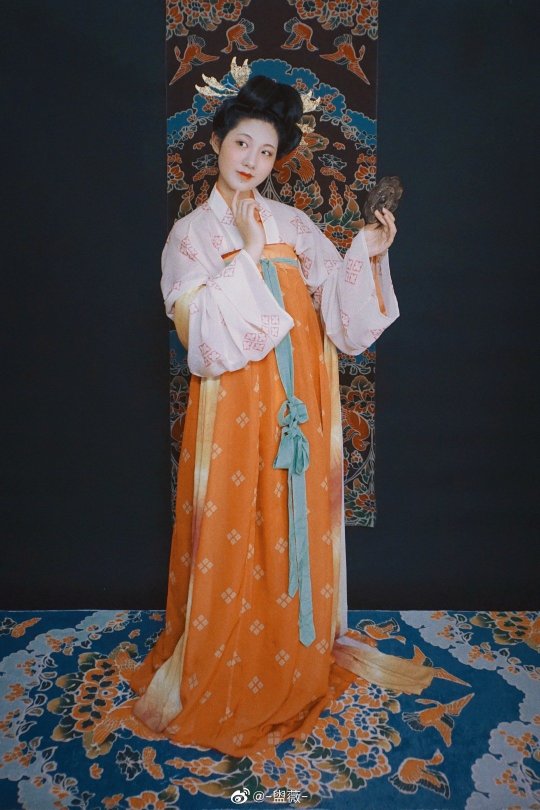










【Hairstyle Reference Artifacts】
Tang Dynasty Female Figurines & Dunhuang Mogao Grottoes Cave 231,Parents of Yin Chu Shi

[Hanfu · 漢服]China Tang Dynasty Chinese Traditional Clothing Hanfu & Hairstyle Photoshoots
Women’s Clothing and Hairstyles in the Mid-Tang Peirod
_______
📸Photo & Model:@-盥薇-
Carpet : @暮秋山行传统服饰
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/3942003133/MdkLBwX86
_______
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Historical immortal Hanfu Based On Yuan Dynasty Taoist Temple Mural<永乐宫/Yongle Palace>
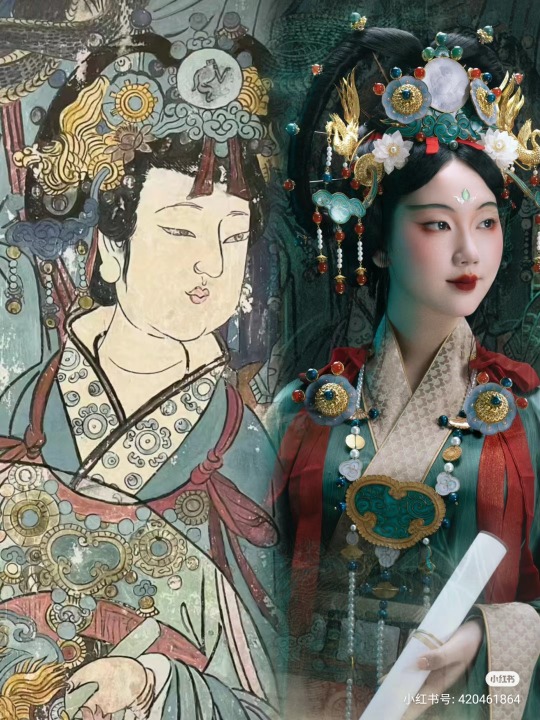
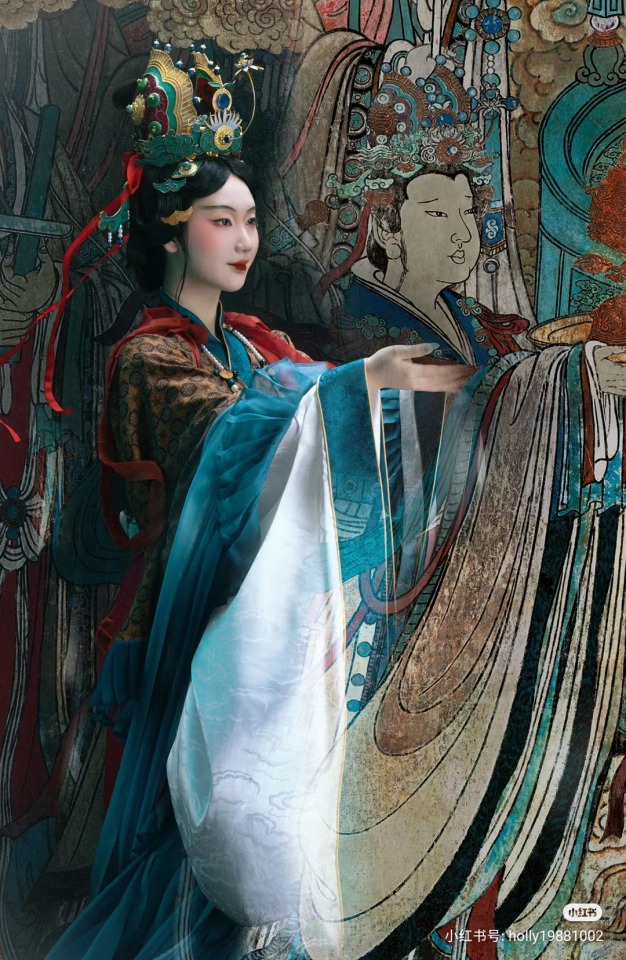
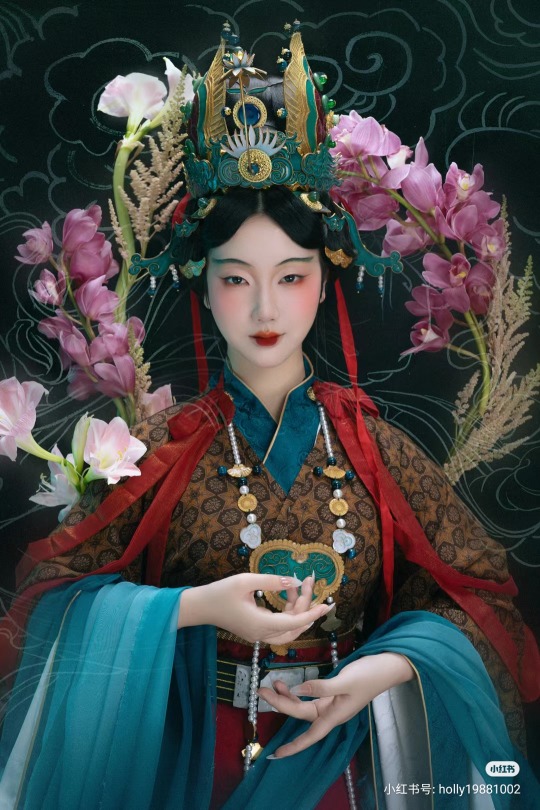
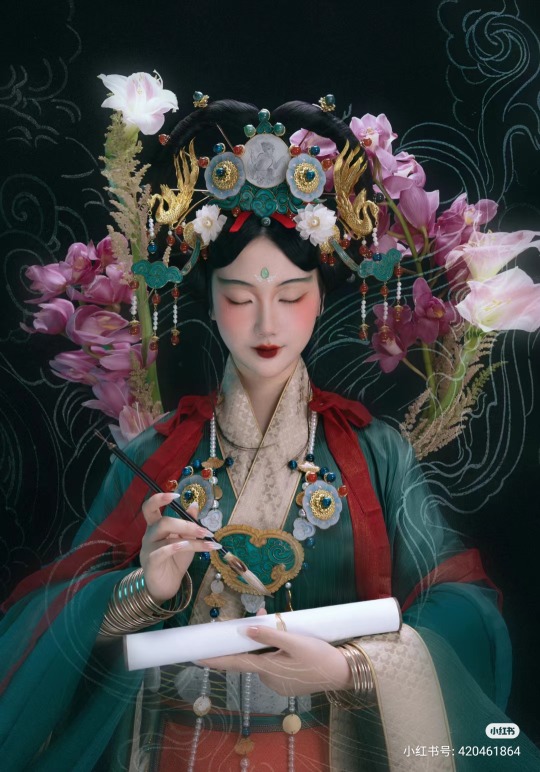
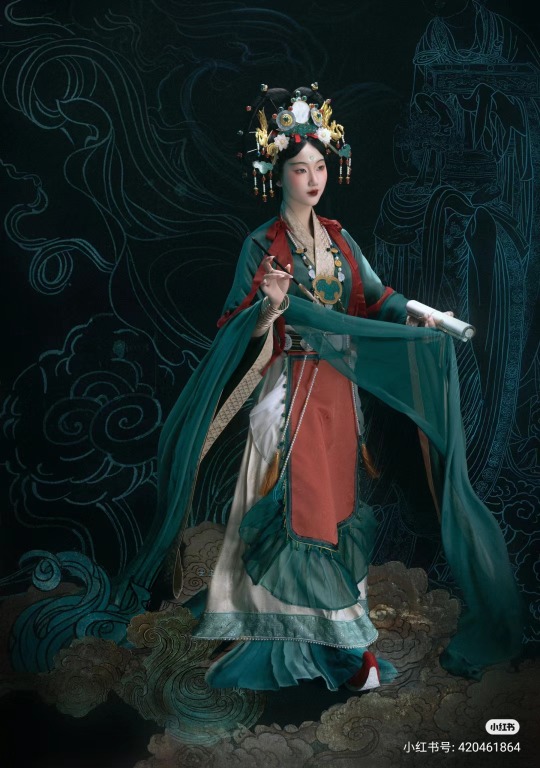
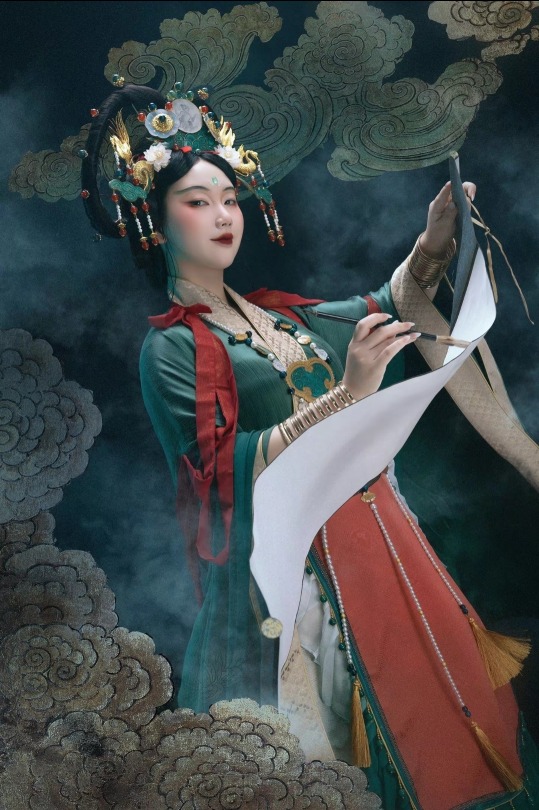
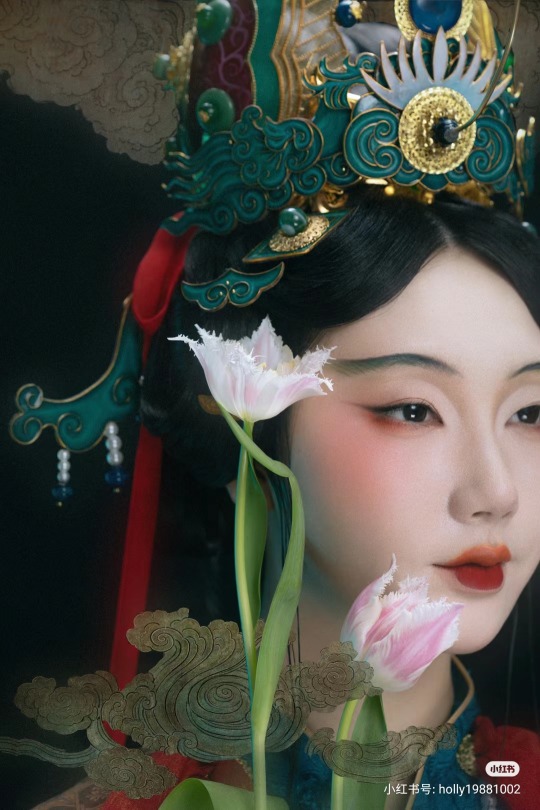
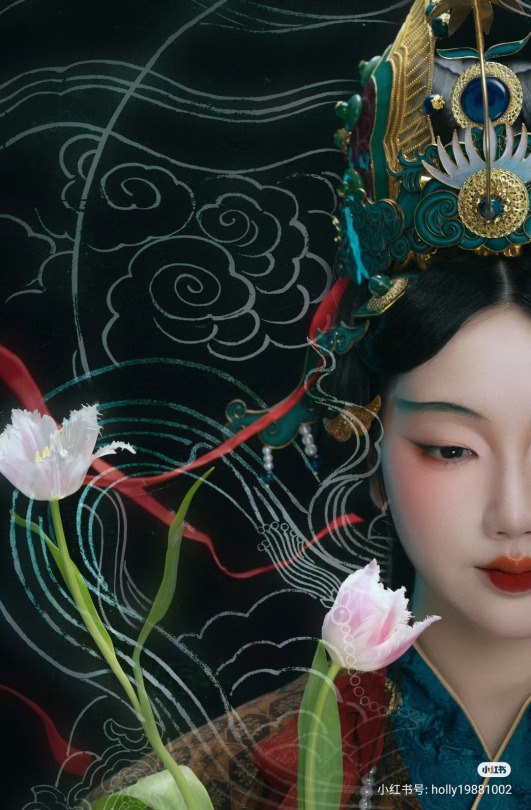

















【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
▶ China Yuan Dynasty Taoist Temple 永乐宫/Yongle Palace Mural
<水星神>:The "Statue of Water Stars God" is located among the gods on the east wall of the north wall of the Sanqing Hall of Yongle Palace. It is one of the five elements of Taoist statues of Water Stars God. According to Taoist norms, Water Stars is a female statue of a scribe wearing an ape crown. It belongs to the monkey god of the zodiac and is used as a written document.

<奉宝玉女>:The immortal attendant who presented the treasure.

————————
📸Photography post-production :@小何力
👗Hanfu:@雁鸿Aimee
💄 Makeup:百丽 (临溪摄影)
👭Model:@清音音音音
🔗 Weibo:https://weibo.com/1615560544/NDD5YEY5x
————————
402 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 A.D.) Traditional Clothing Hanfu with Actor Liu Tao/刘涛
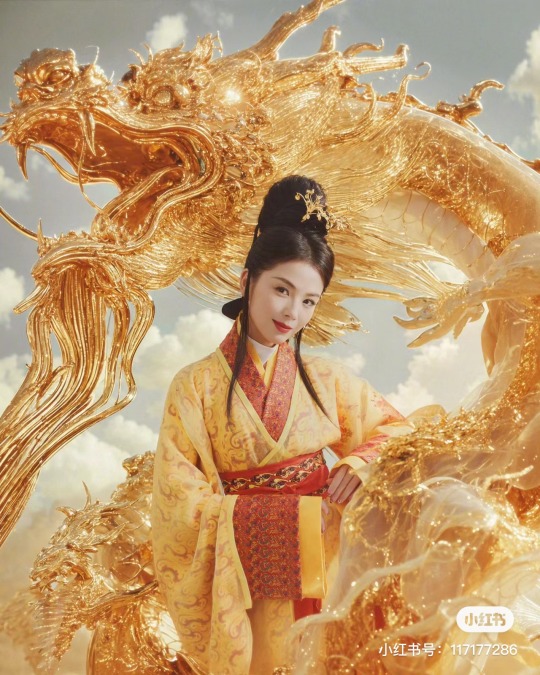
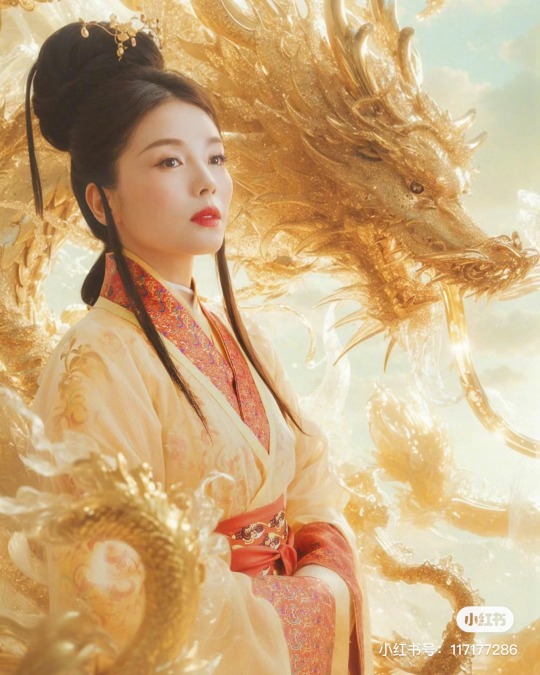
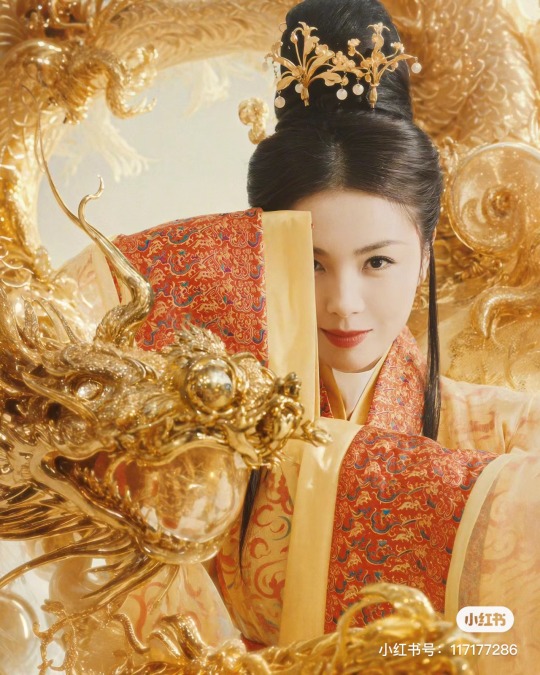
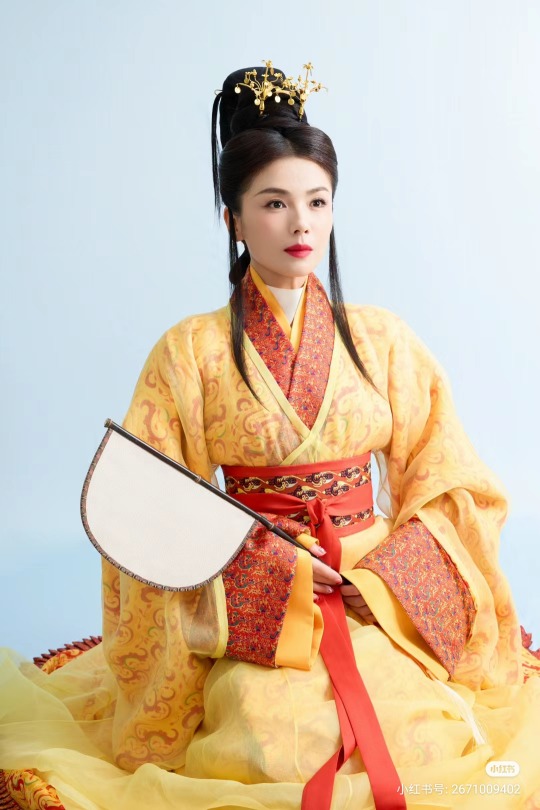
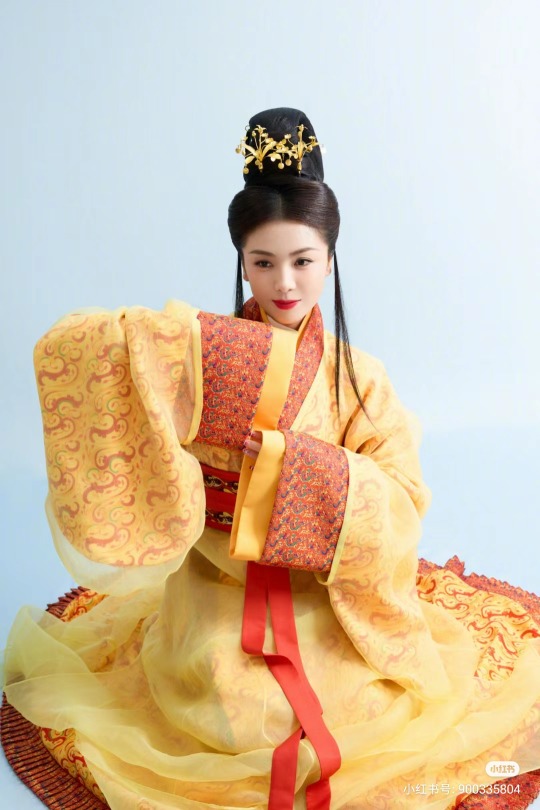
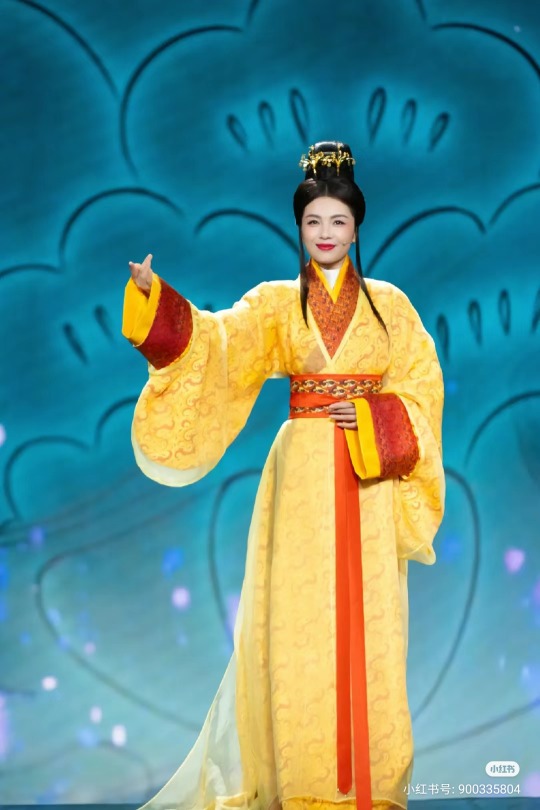
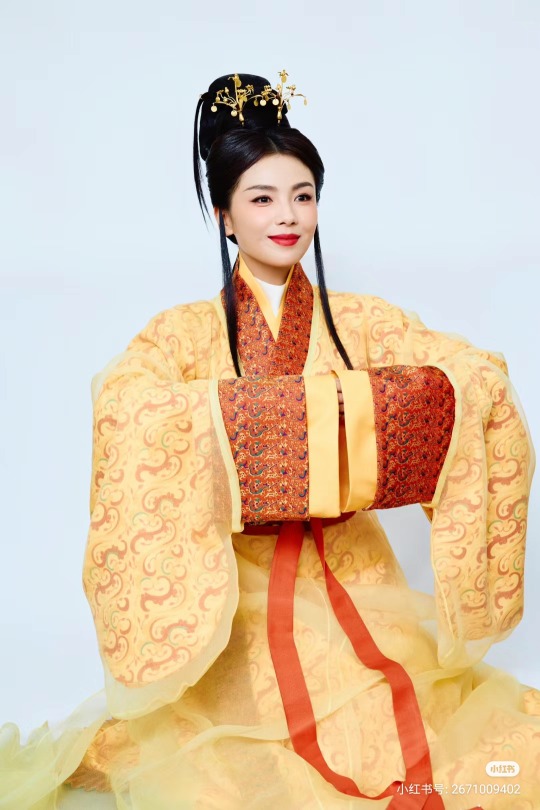
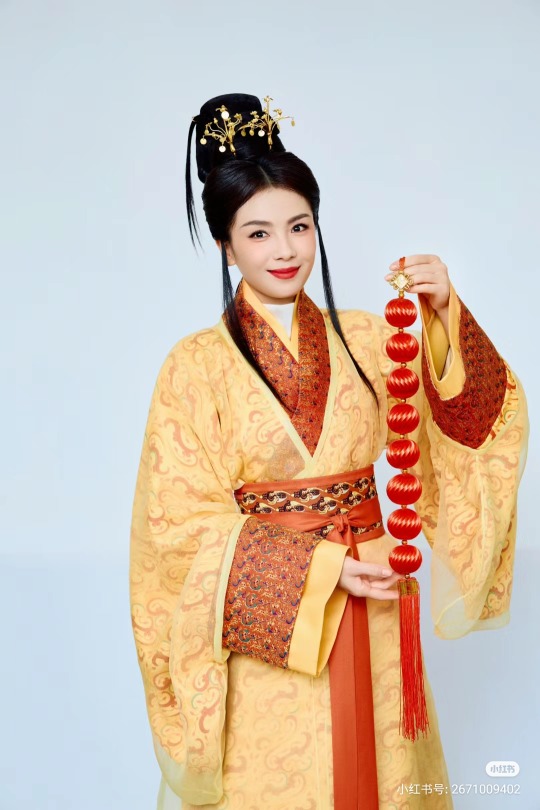
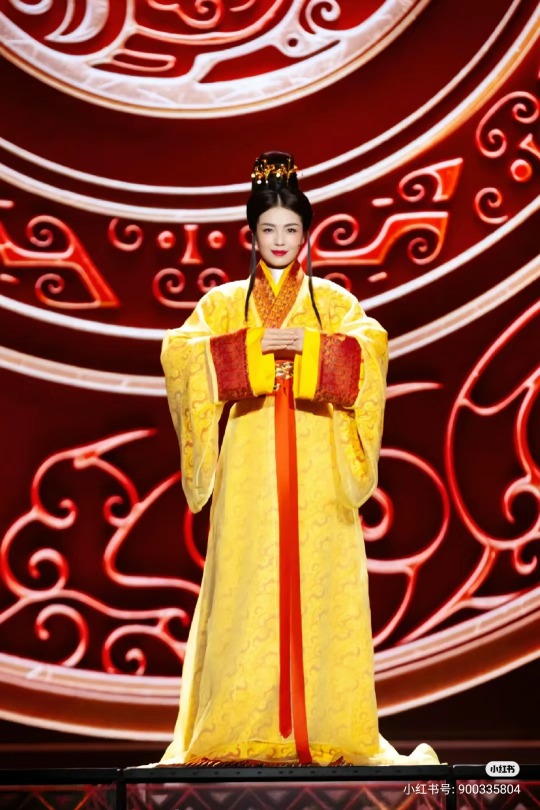
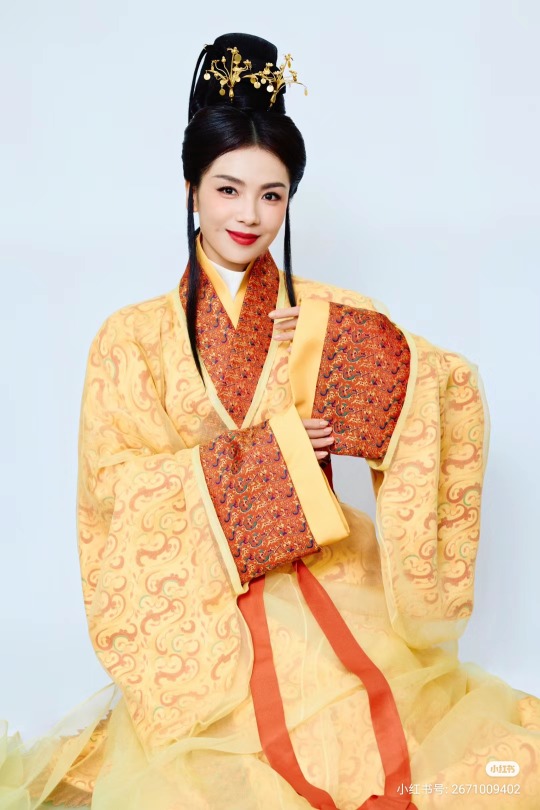
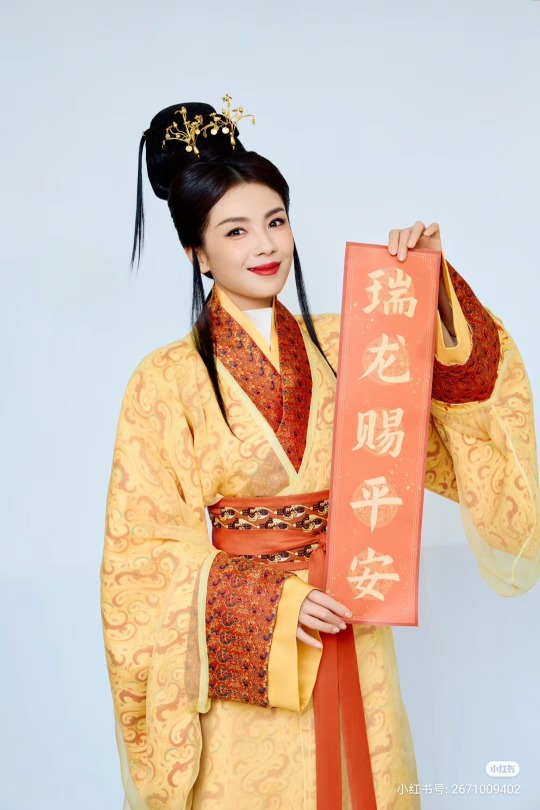
















【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
▶China Han Dynasty Murals<Part of the person holding the halberd and sword>, Luoyang Museum Collection.

▶China Jin Dynasty Painting By Gu Kaizhi (Chinese: 顧愷之,344–406)


202 notes
·
View notes
Text
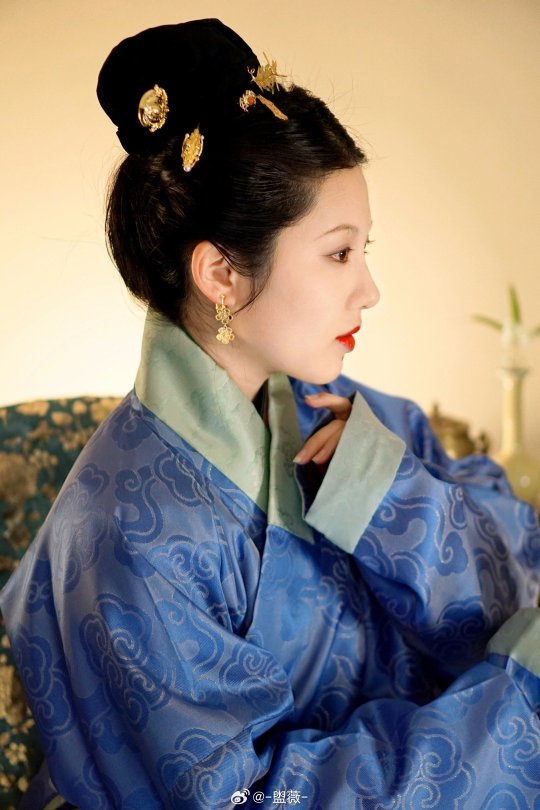
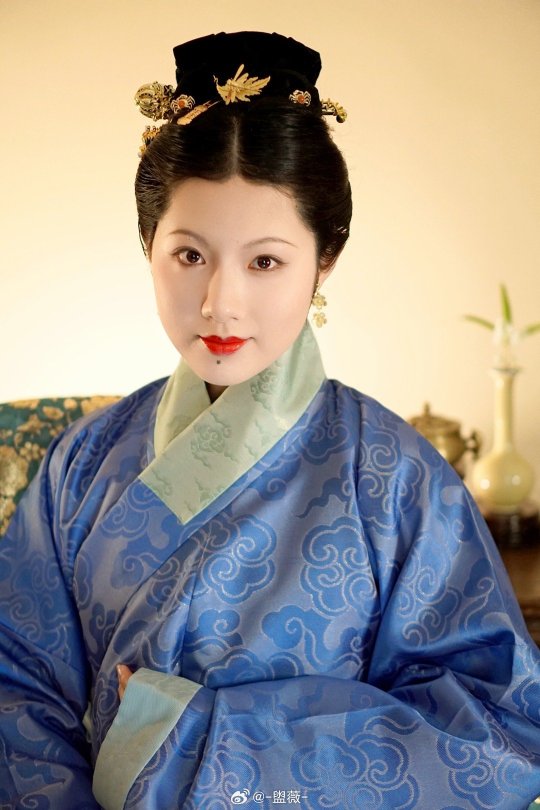
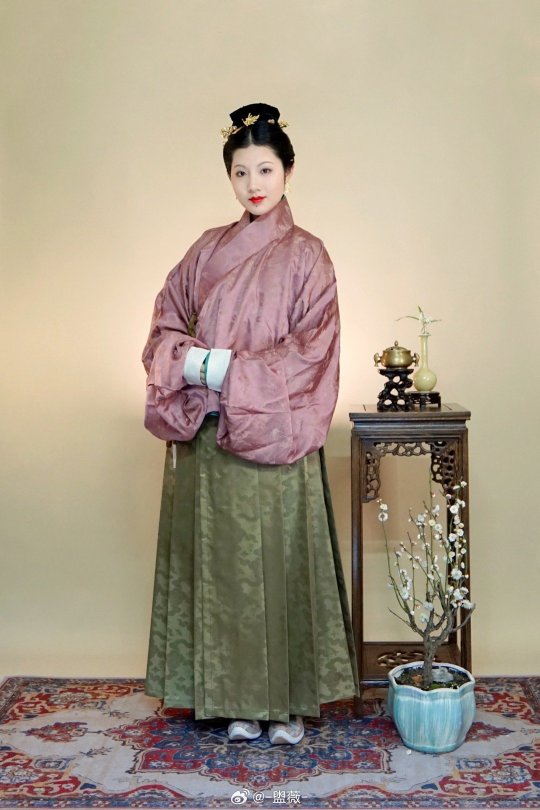
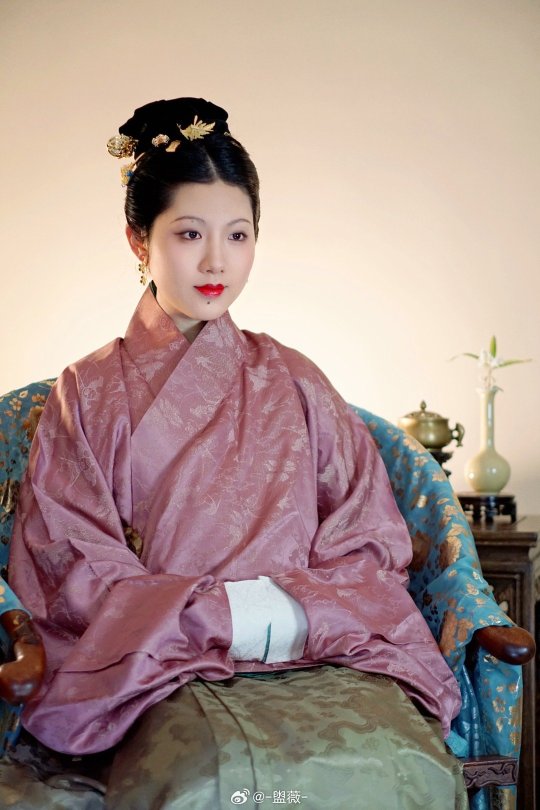
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Ming Dynasty(1368-1644 AD) Hanfu Based On Ming Dynasty Portrait
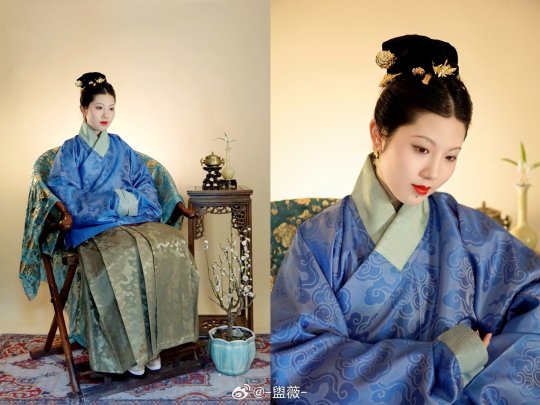













【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
China Ming Dynasty Portrait of Chen Gongniang/陈恭娘容像Collection of Anhui Museum

China Ming Dynasty Portrait of Zhu Yinzhen/朱隐贞容像Collection of Anhui Museum

————————
📸Recreation Work &🧚🏻 Model :@-盥薇-
🔗 Weibo:https://weibo.com/3942003133/O0o77n2WN
————————
112 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty(618–907AD)Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
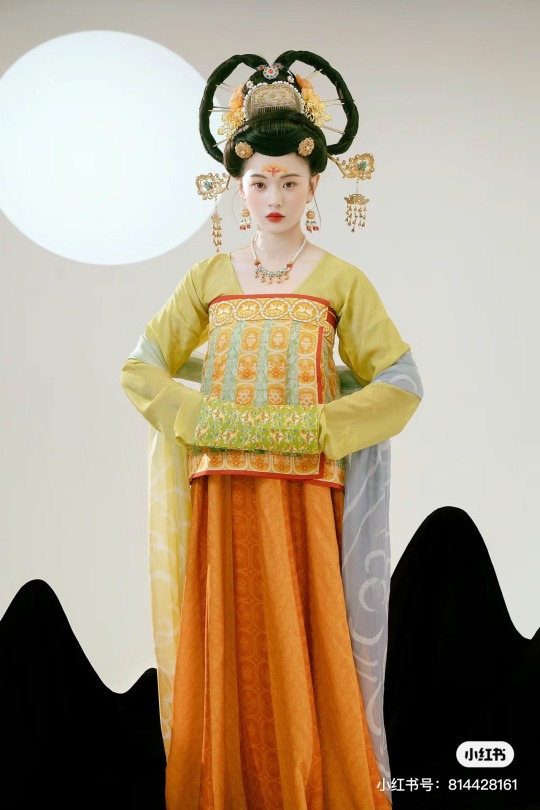
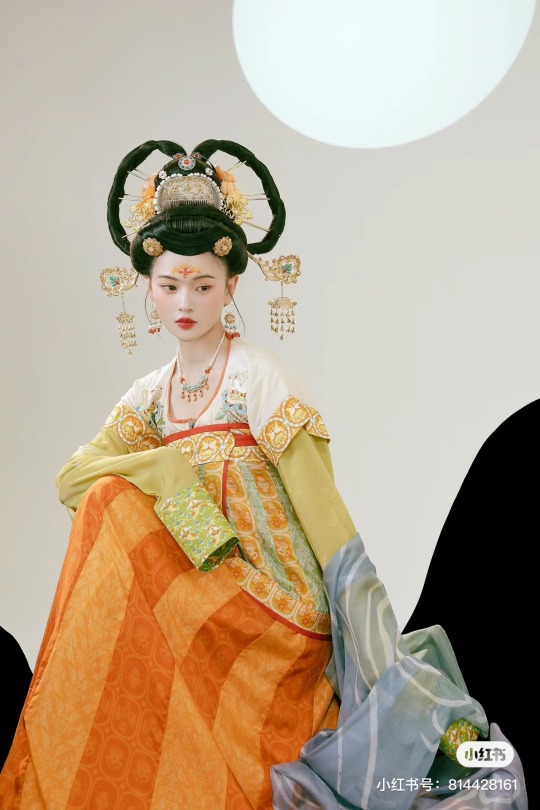
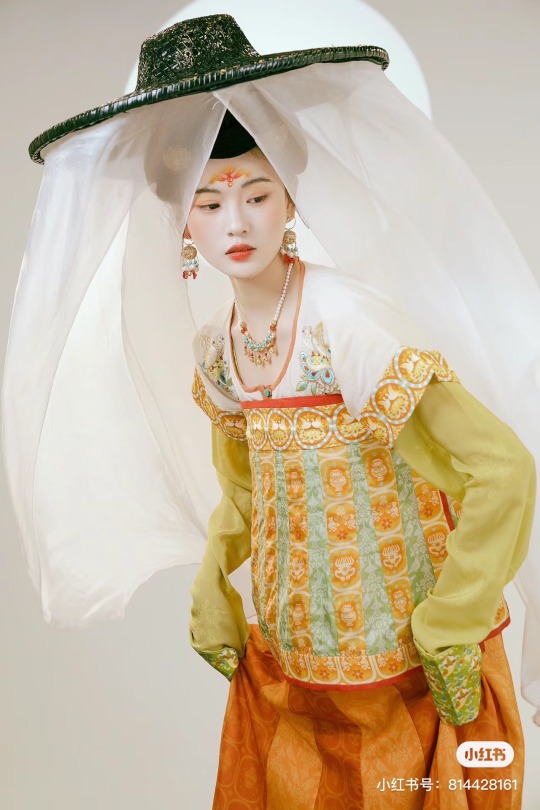
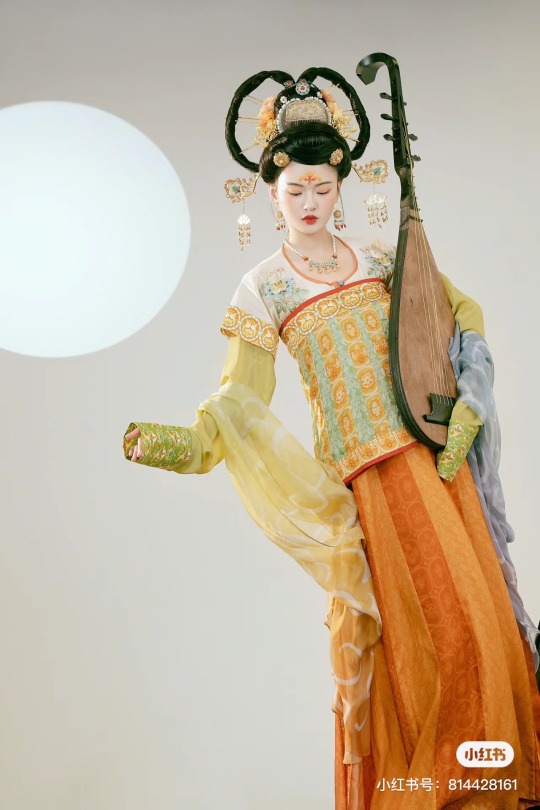
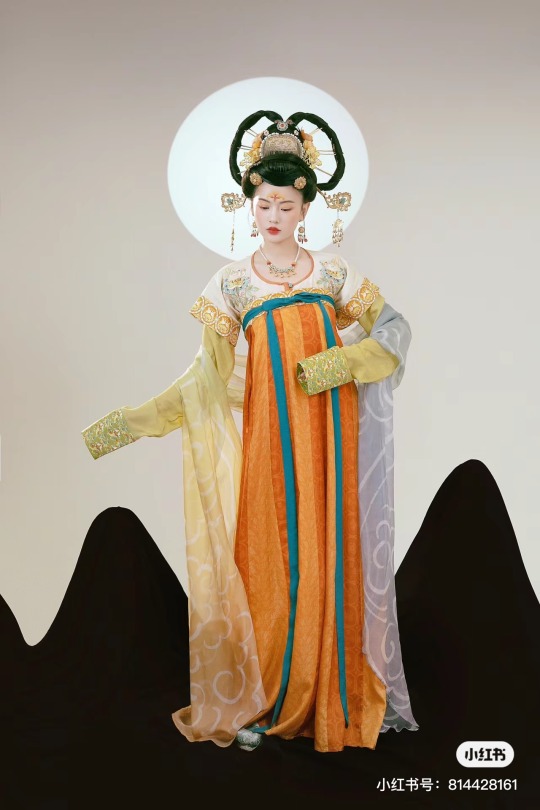
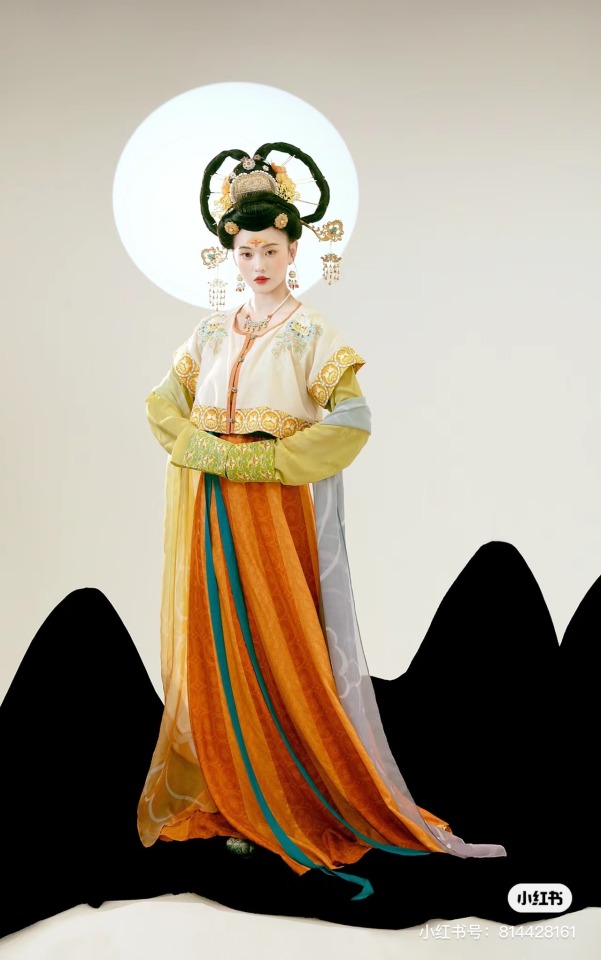
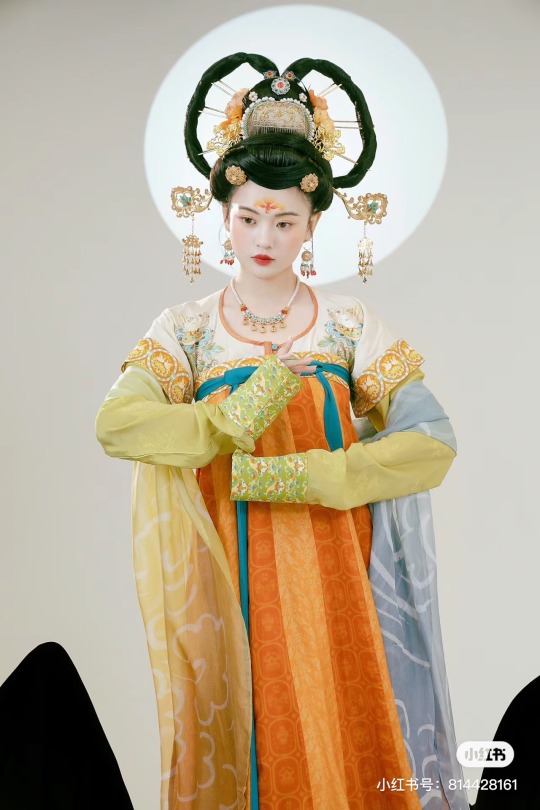
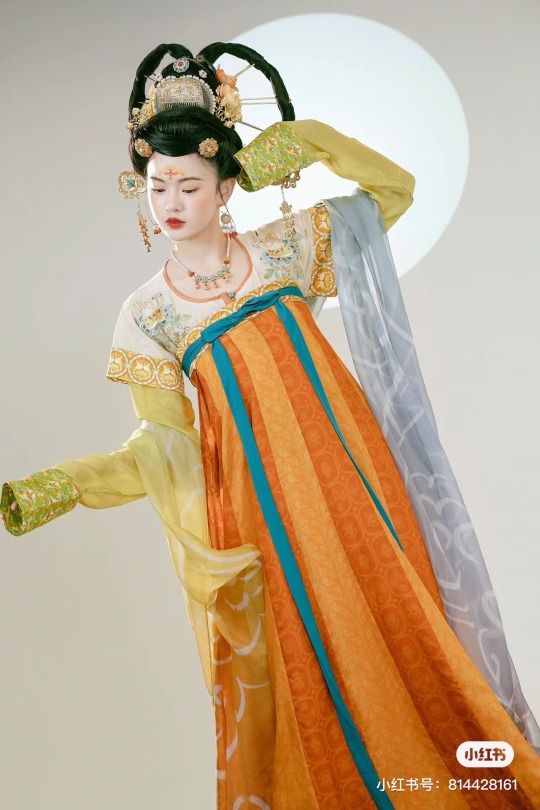
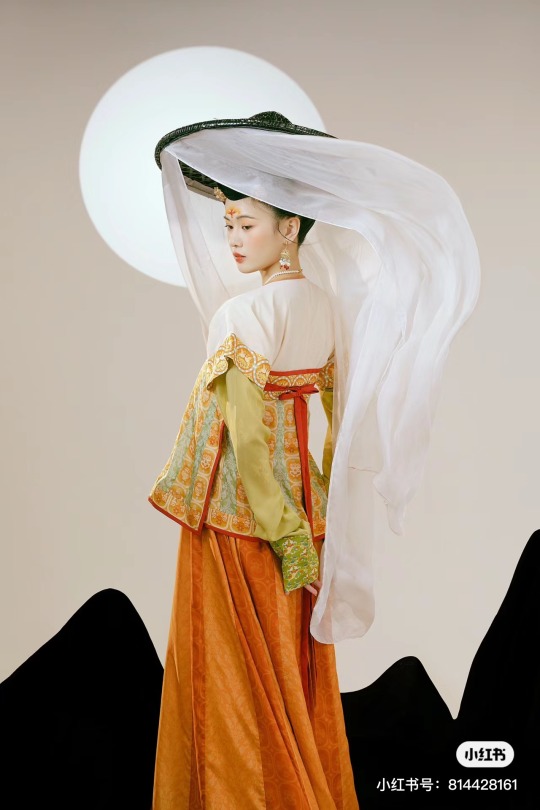
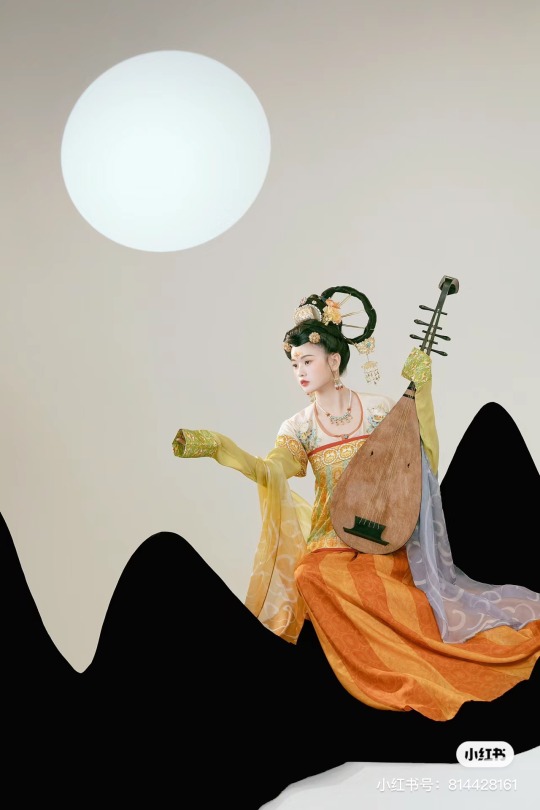
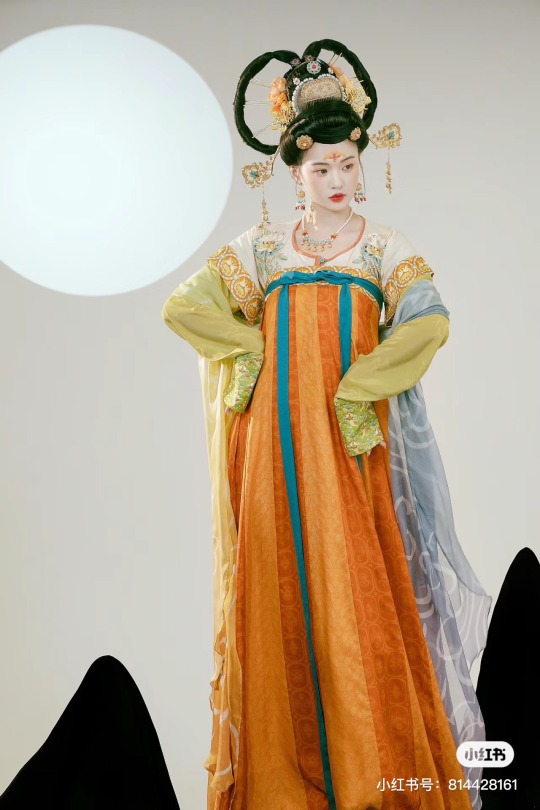













【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
Mural from Princess Xincheng新城公主 of the Tang Dynasty (634-663)
Princess Xincheng新城公主 was the youngest daughter of Emperor Taizong of the Tang Dynasty in China and was born to the eldest Zhangsun Empress.

————————
📸Photo:@成都临溪摄影
🧚🏻 Model :@钟钟
👗Hanfu: @墨名堂真丝汉服 & 墨名堂的箱掌柜
🔗Xiaohongshu:http://xhslink.com/lrGnEB
————————
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
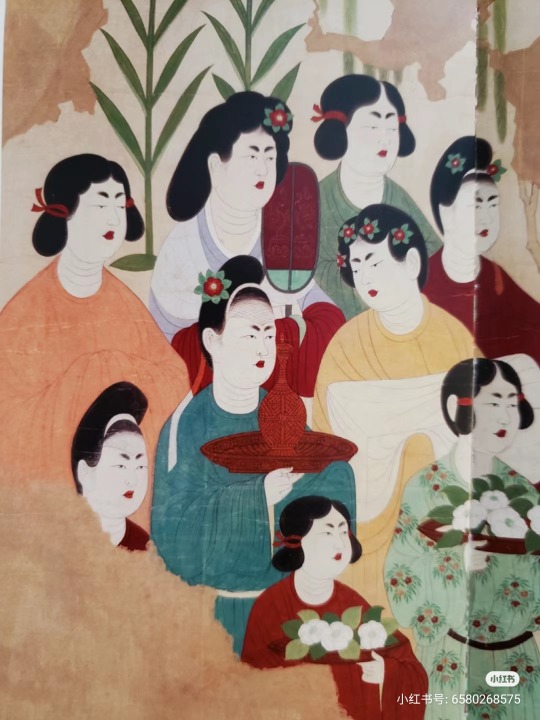
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty(618–907AD)Traditional Clothing Hanfu Based On Dunhuang Mural
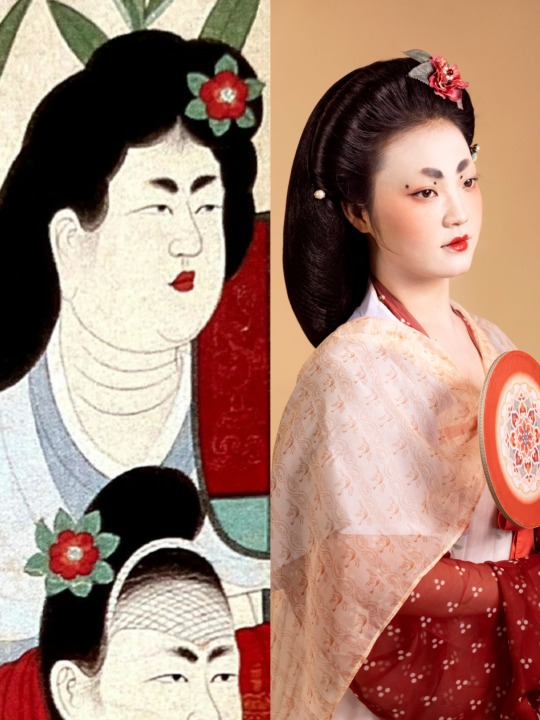
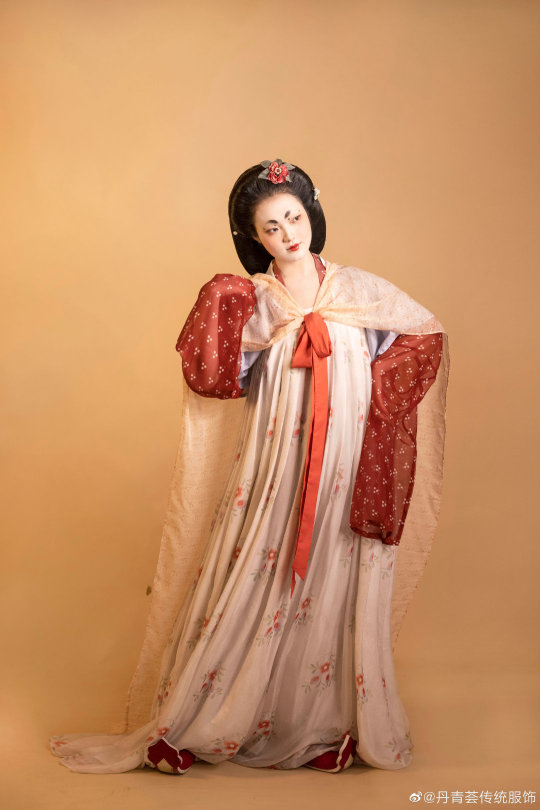
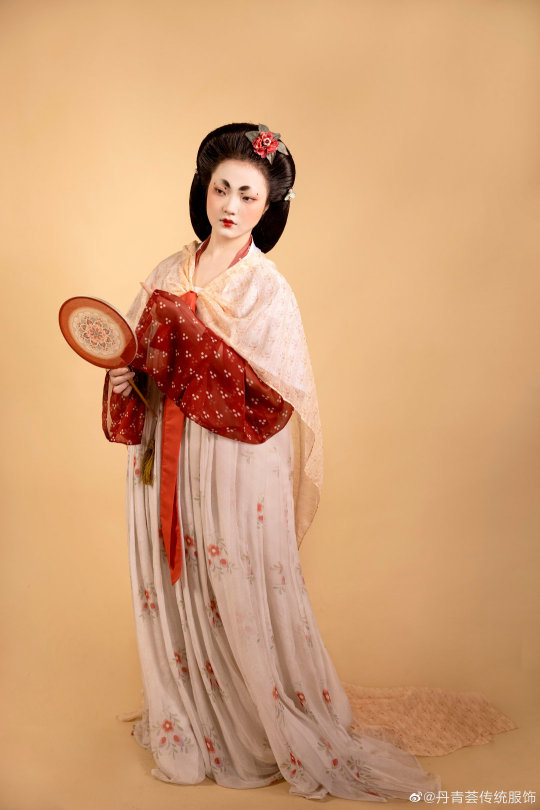
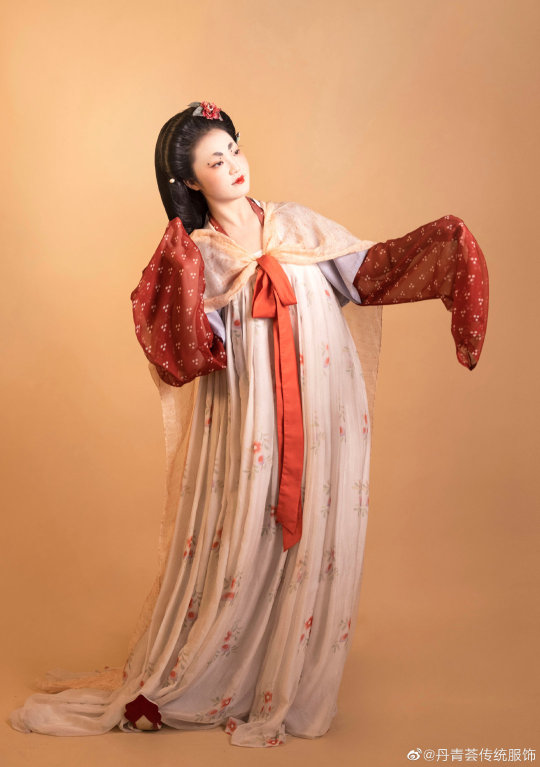
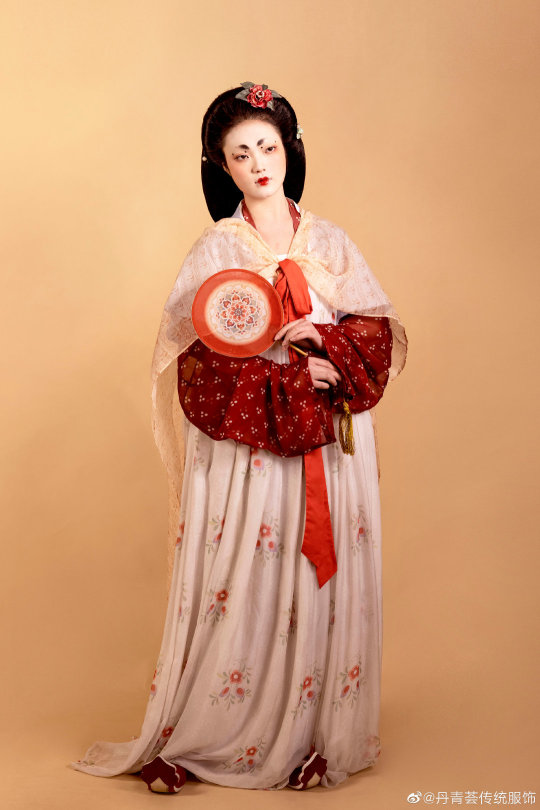







【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
China Tang Dynasty Dunhuang Mural:
《都督夫人太原王氏礼佛图/Governor Wife Mrs.Wang and her daughters and servants in Cave 130 of Mogao Grottoes in Dunhuang》


_________________
Recreation Work:@丹青荟传统服饰
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/6311444174/MCBp7hAbo
_________________
213 notes
·
View notes
Text
🐲WISH EVEYONE HAVE A HAPPY LONG(龍)YEAR

Wish everyone good luck in the year of the dragon and happy holiday!!
This is my first time to draw such big dragon, I kinda worried but surprisingly it's okay(ˊᗜˋ*)
2024 is the year of the Green Dragon(青龍) and also the year of the Wood Dragon.
※青 originally meant blue in ancient times, but in painting colors, if blue is mixed with a small amount of green, it is called cyan (one of the three subtractive primary colors), and it has multiple levels.So the dragon I drew is closer to blue><
【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
Princess Xincheng新城公主 of the Tang Dynasty (634-663)
Princess Xincheng新城公主 was the youngest daughter of Emperor Taizong of the Tang Dynasty in China and was born to the eldest Zhangsun Empress.

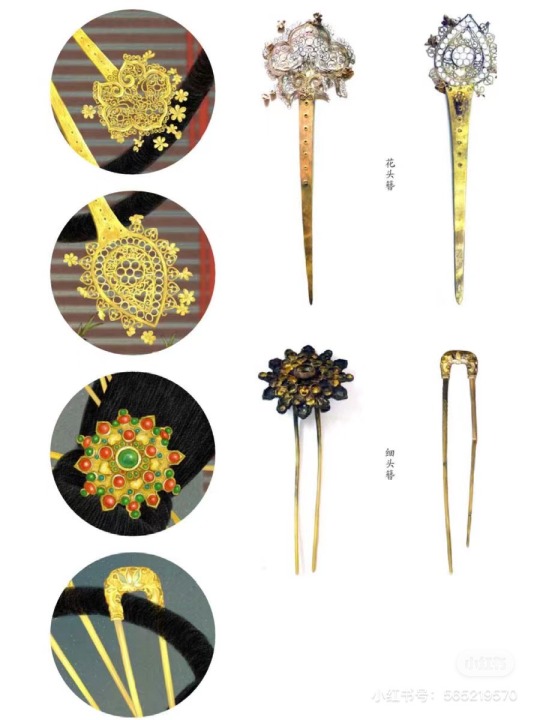
Various Hairpin were Unearthed from the Tang Dynasty Tomb of Princess Yang of Wu

270 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty (618–907AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
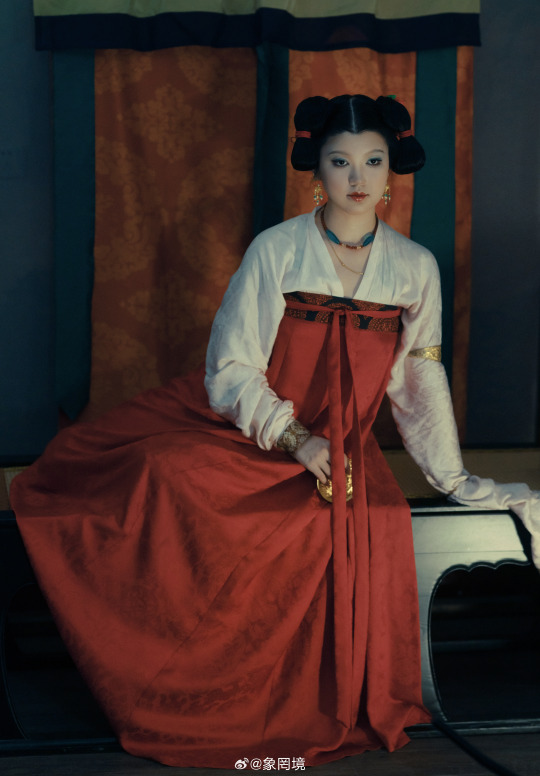
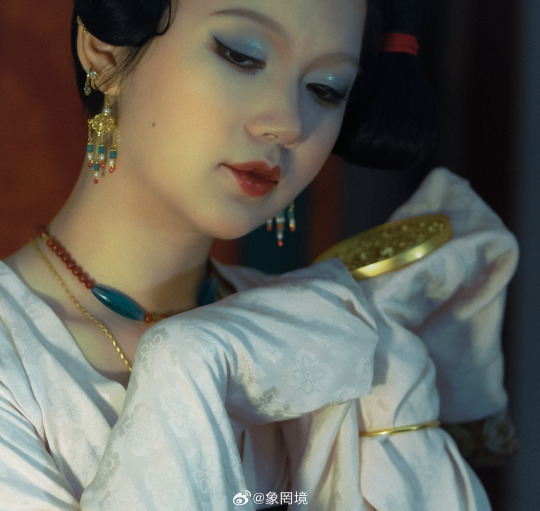
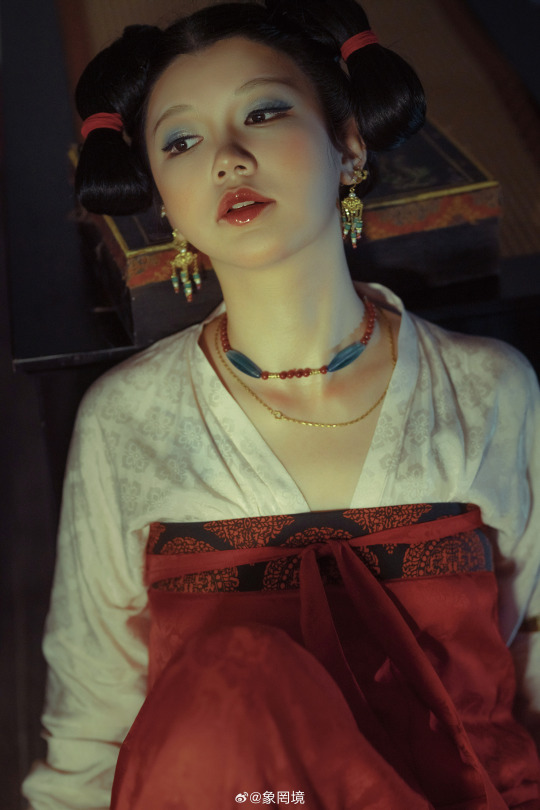
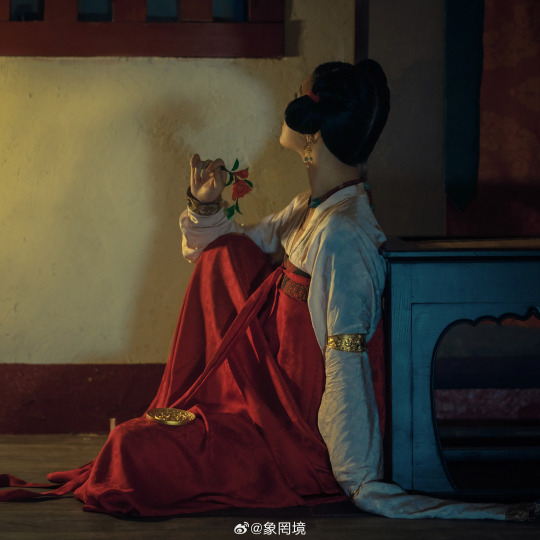
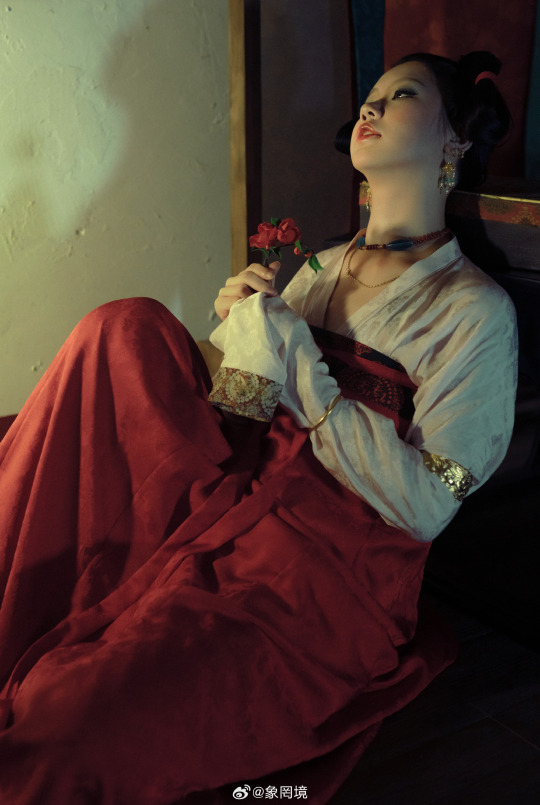
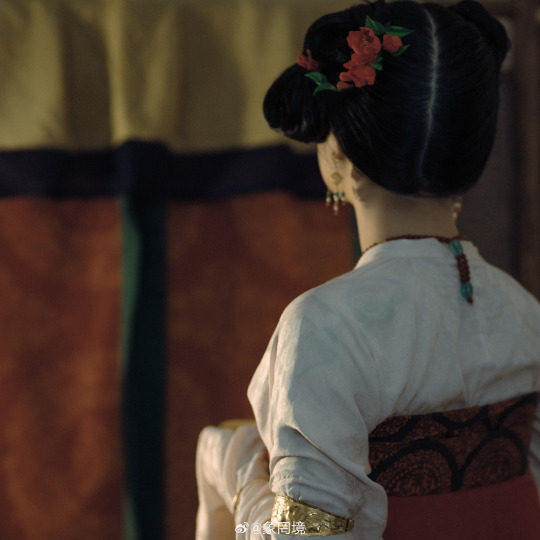
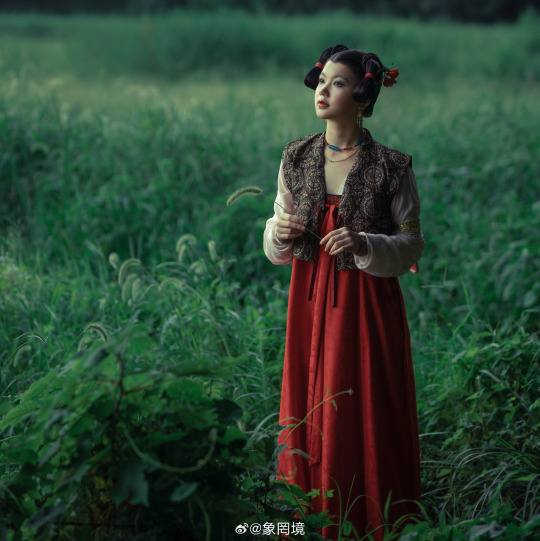
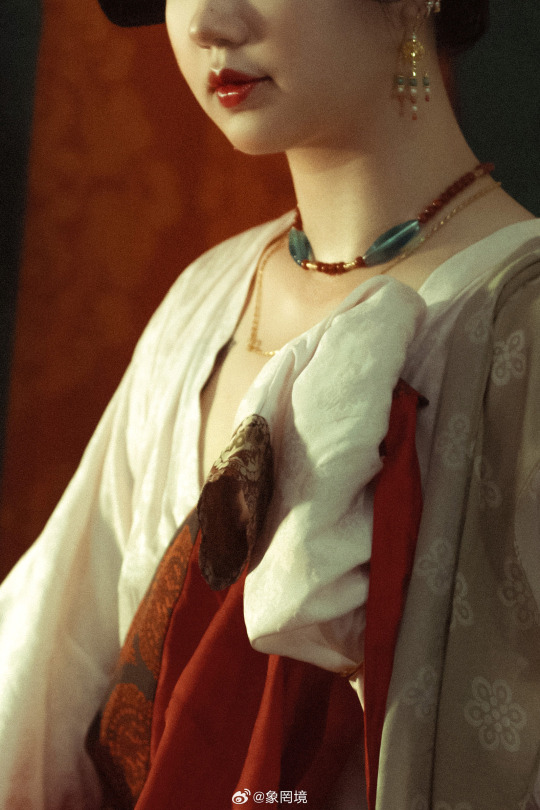










————————
📸Photo:@象罔境
🧚🏻 Model :@仑百百客
💄Stylist:@象罔境
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/2825602213/NBwrgBPeo
————————
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
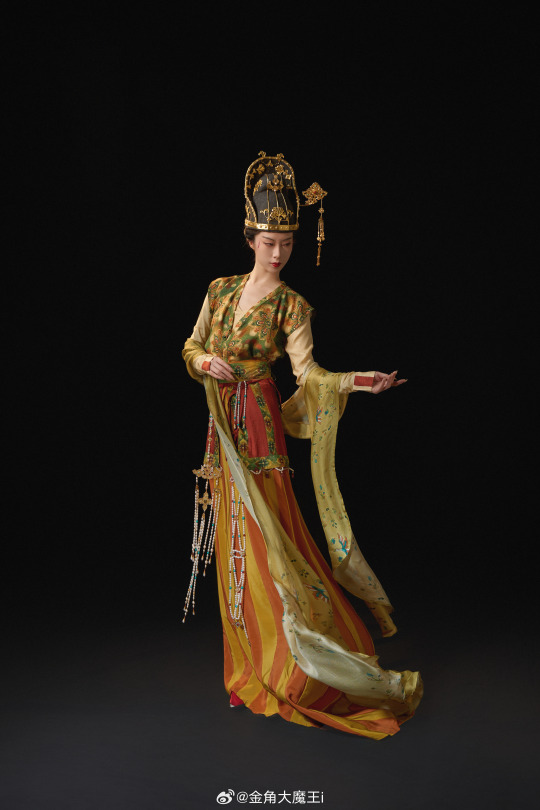
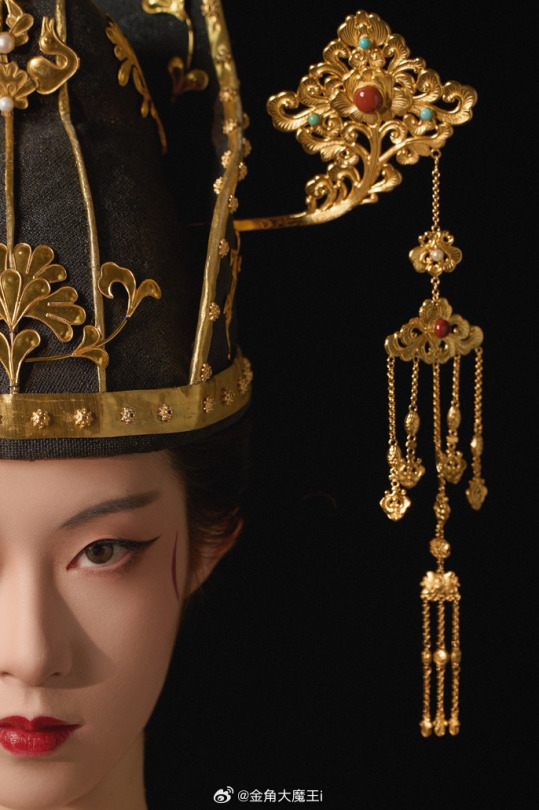
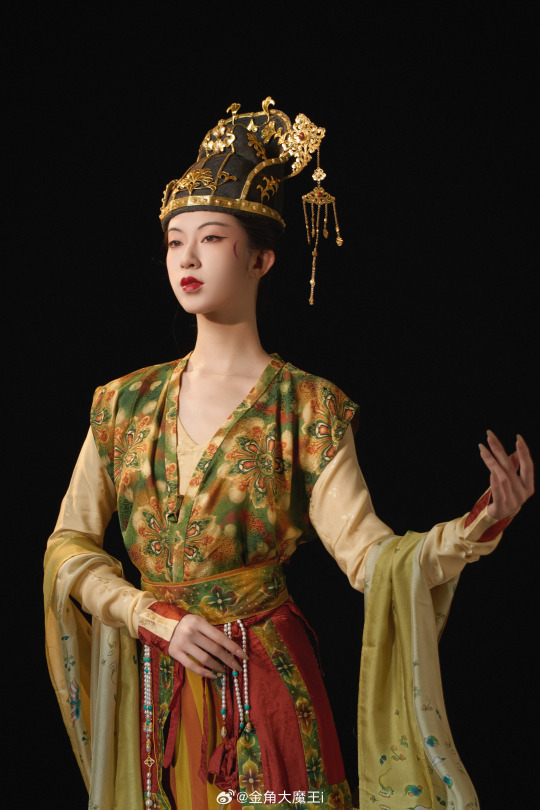
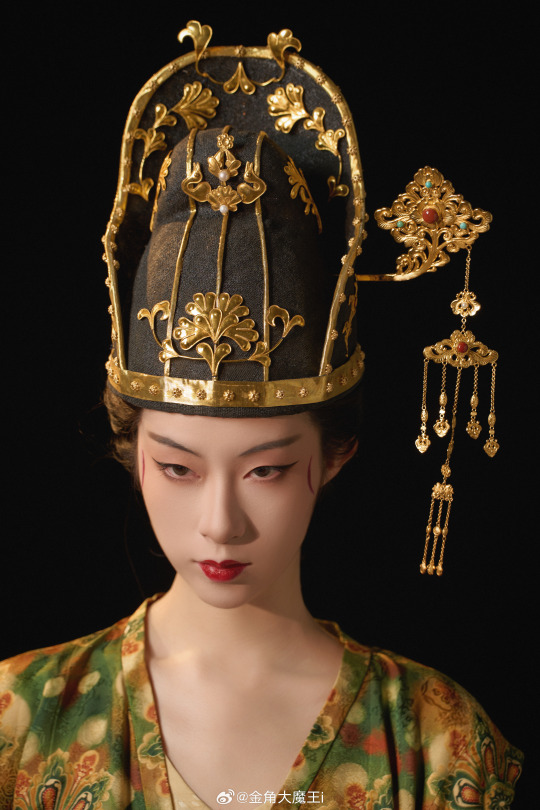
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty(618-907A.D)Woman Officer Hanfu Refer to Tang Dynasty Stone Coffin Line Carving
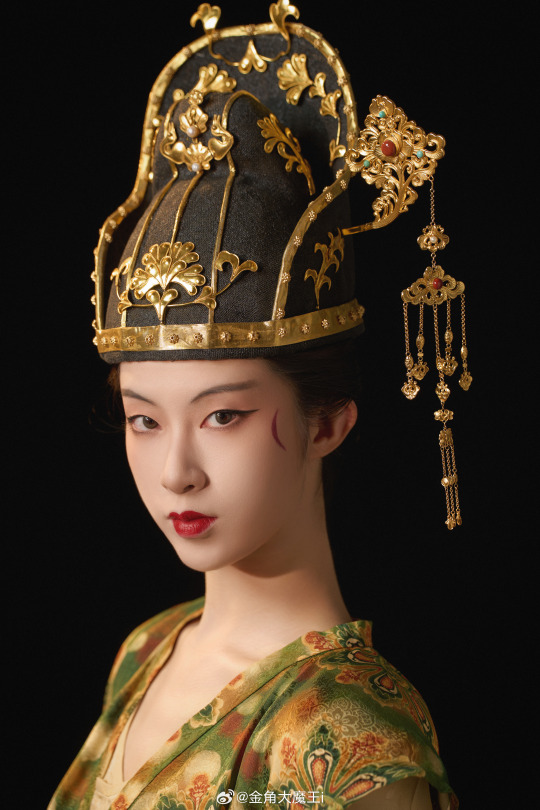
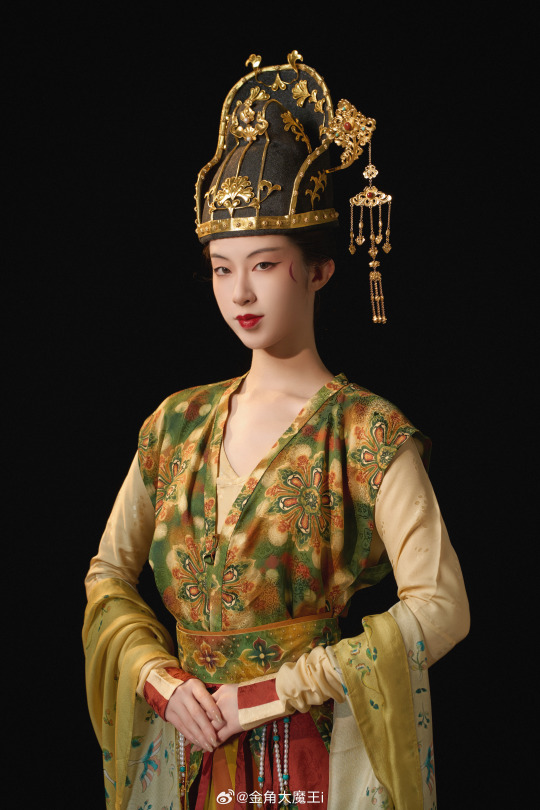









【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
China Tang Dynasty Tomb of Wei Shiqiniang's Stone Coffin Line Carving/韦十七娘石椁线刻
Showing Tang Dynasty Woman Officer In WuZetian (690–705)period
武周女官
————————
📸Recreation Work: @金角大魔王i
👗Hanfu: @山涧服饰
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/NDuAoFtZz
————————
312 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese immortal Hanfu Based On Ming Dynasty Zhengtong ear (1439AD)Fahai Temple Murals
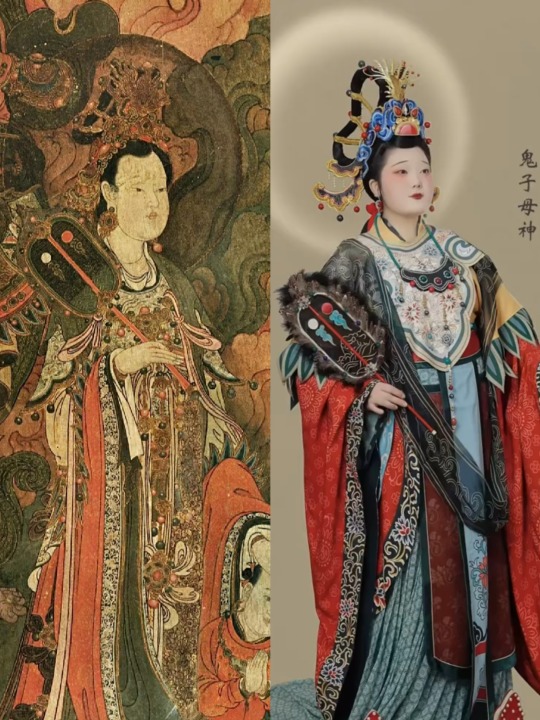
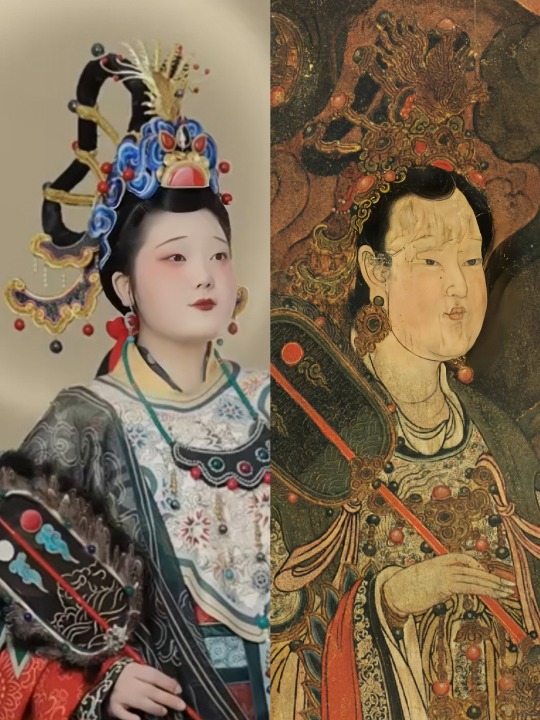







【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
Ming Dynasty "鬼子母神" in the mural of Fahai Temple in Beijing,China.


【About the "鬼子母神" 】
鬼子母神,also known as Hārītī (Sanskrit),is both a revered goddess and demon, depending on the Buddhist tradition. She is one of the Twenty-Four Protective Deities of Mahayana Buddhism.
In her positive aspects, she is regarded for the protection of children, easy delivery and happy child rearing, while her negative aspects include the belief of her terror towards irresponsible parents and unruly children.
In both Chinese and Japanese Buddhism, she is venerated as a protector deity, but in many folk traditions is often recognized as a female demon of misery and unhappiness towards children and parents.
In Chinese Buddhism, Hārītī is also known as Hēlìdì (訶利帝) or Hēlìdìmǔ (訶梨帝母). In Chinese tradition, she is one of the Twenty-Four Protective Devas (二十四諸天 Èrshísì zhūtiān), a group of Dharmapalas who are venerated as protectors of Buddhists and the Dharma.Statues of this group (and Hārītī) are often enshrined within the Mahavira Hall in Chinese temples and monasteries.
————————
📸Recreation Work:@粉墨长安古典妆造
🔗 Xiaohongshu:http://xhslink.com/cNP1Hz
————————
374 notes
·
View notes
Text
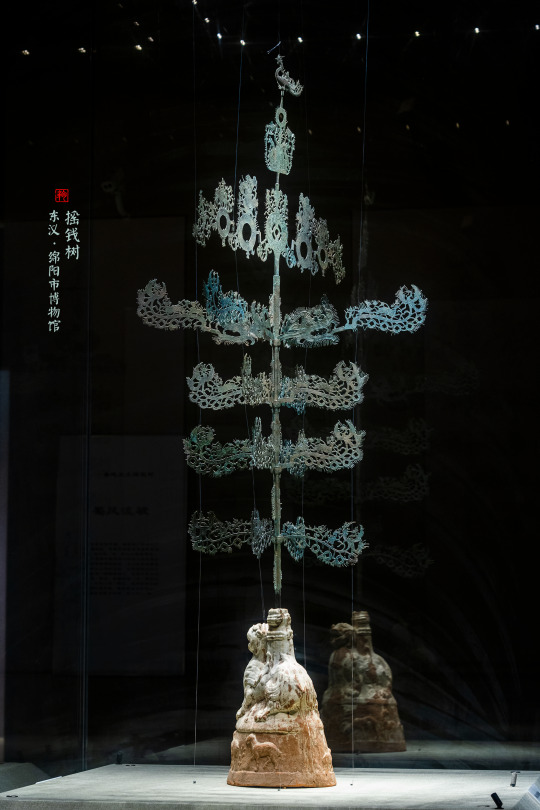
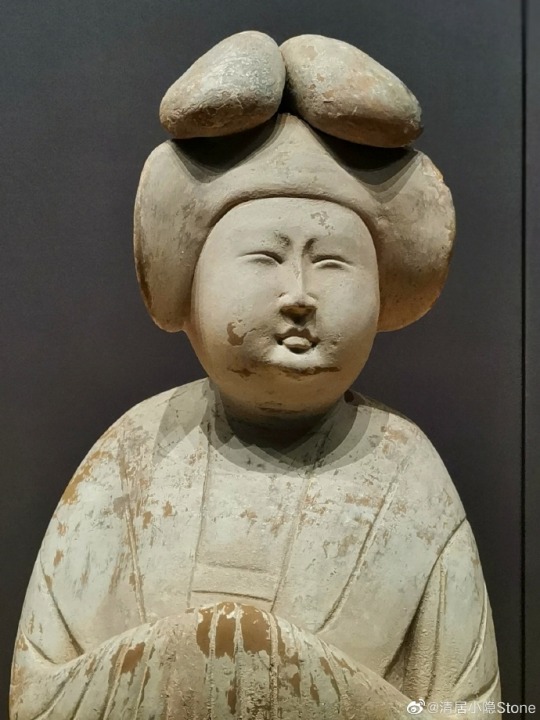
[Hanfu · 漢服]China's national Important Cultural Relics Impression Series By Artist @陆曼陀
China Neolithic Period:The Hongshan culture(4700-2900 BC)Relics<玉猪龙/Pig dragon>

China Shang dynasty / Western Zhou dynasty(1200–800 BC) · Shu state Relics < 太阳神鸟金饰/Golden Sun Bird>


China Western Han Dynasty (202 BC – 9 AD)Artifact Relics<长信宫灯/oil lamp in the shape of a kneeling female servant>


After the lamp is lit, the soot enters the base of the palace lantern through the sleeve to achieve the purpose of cleaning the air.

China Eastern Han Dynasty(25–220 AD)Artifact Relics<铜奔马 or the Galloping Horse Treading on a Flying Swallow (馬踏飛燕)>


China Eastern Han Dynasty(25–220 AD) Artifact Relics<摇钱树/Money tree (myth)>


China Tang Dynasty(618–907CE) Artifact Relics<女立俑/Female standing figurine >


China Song Dynasty (960–1279) Artifact Relics<汝窑天蓝釉刻花鹅颈瓶/Ru kiln sky blue glaze carved gooseneck bottle>


China Song Dynasty (960–1279) Painting<千里江山图/A Thousand Li of Rivers and Mountains>by 王希孟(Wang Ximeng)



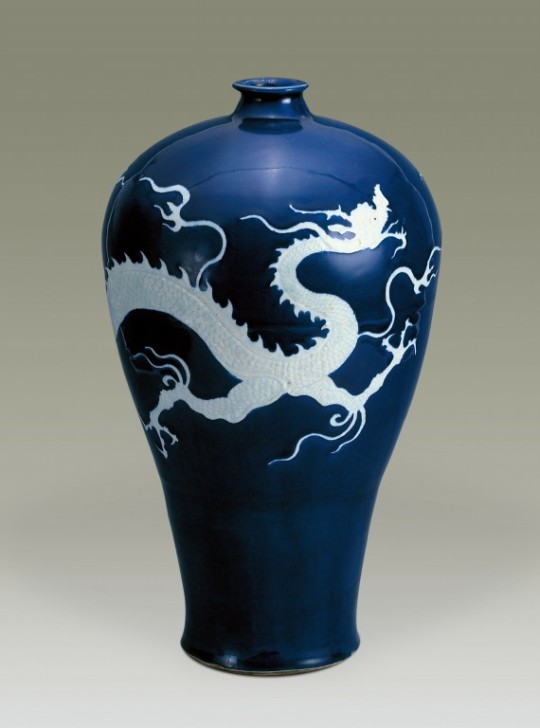
China Yuan dynasty (1279–1368) Artifact Relics<霁蓝釉白龙纹梅瓶/Ji blue-glazed plum vase with white dragon pattern>


【Artist:陆曼陀 Social Media】
————————
Twitter:https://twitter.com/LuDanling
Weibo:https://weibo.com/u/2846691957
Post Source:https://weibo.com/2846691957/NzQ9IyzKL
————————
427 notes
·
View notes
Text
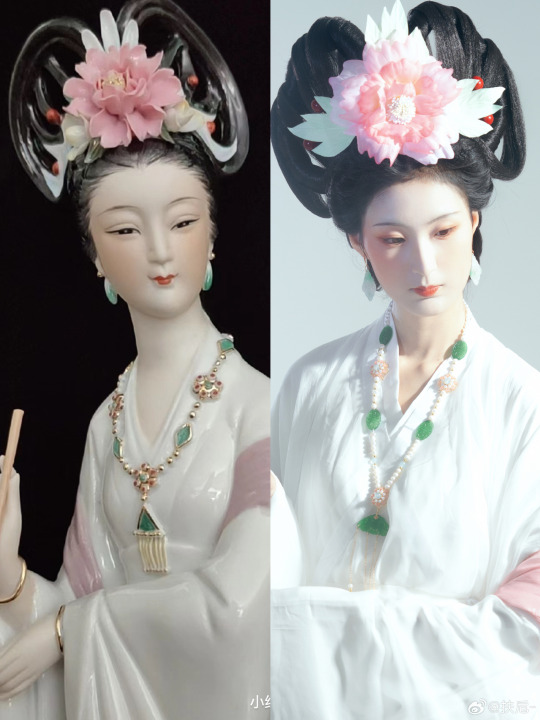
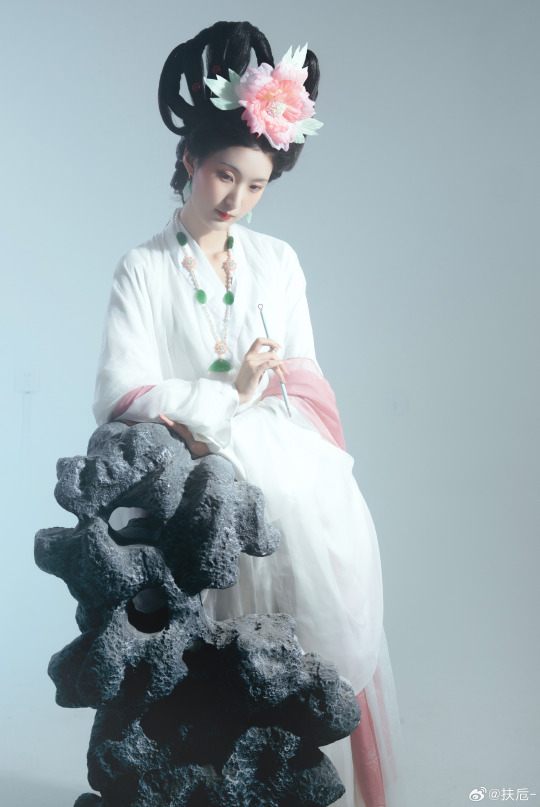
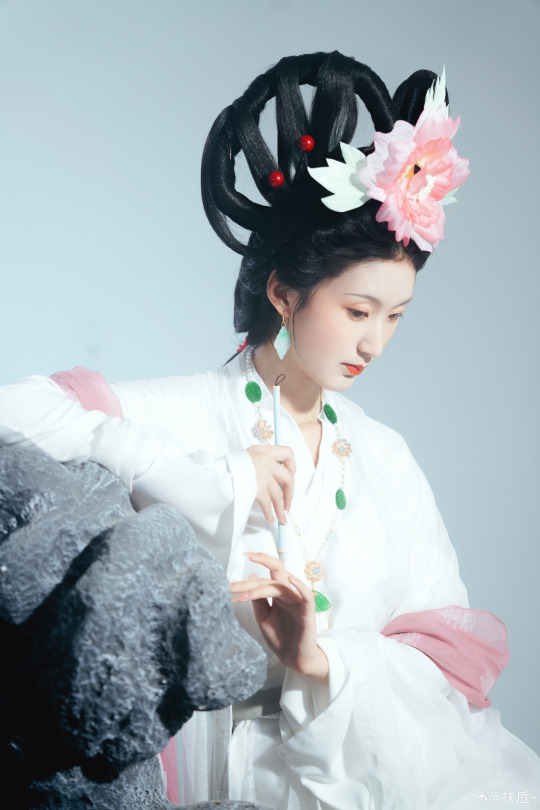
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Hanfu Photoshoot Inspired by porcelain figures ·瓷人仿妆·【思凡】
“一具瓷人,却生了凡人心。”
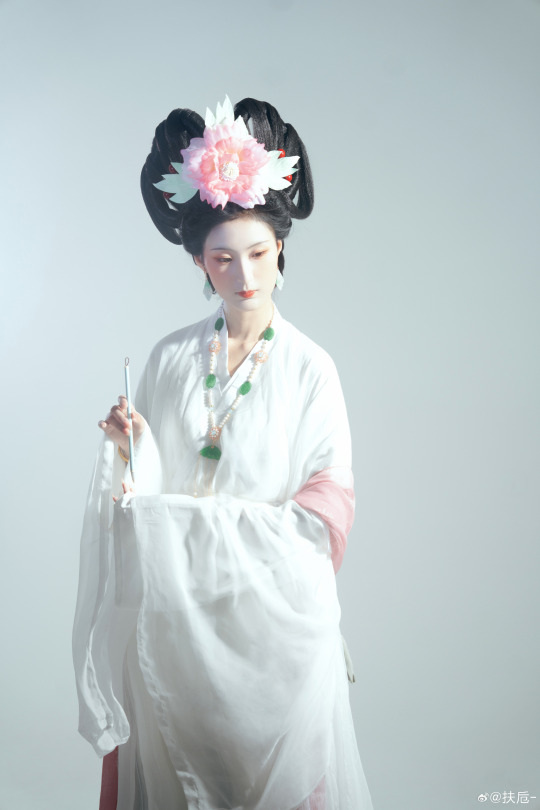
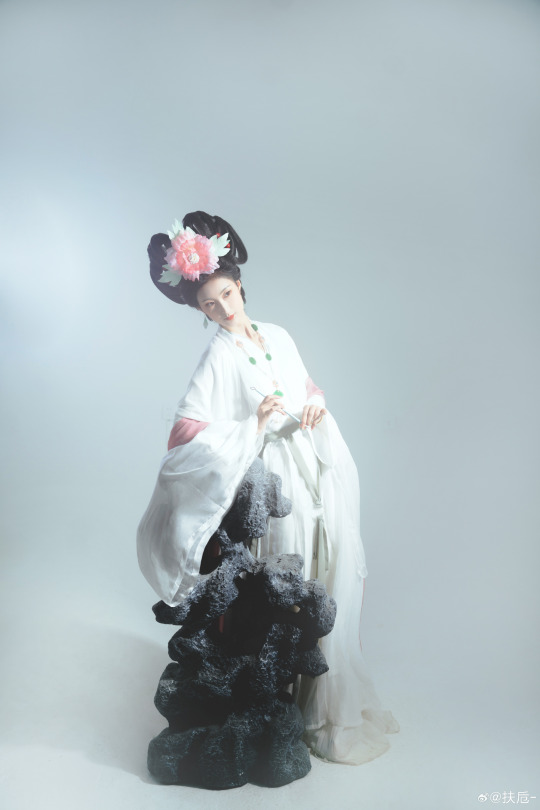
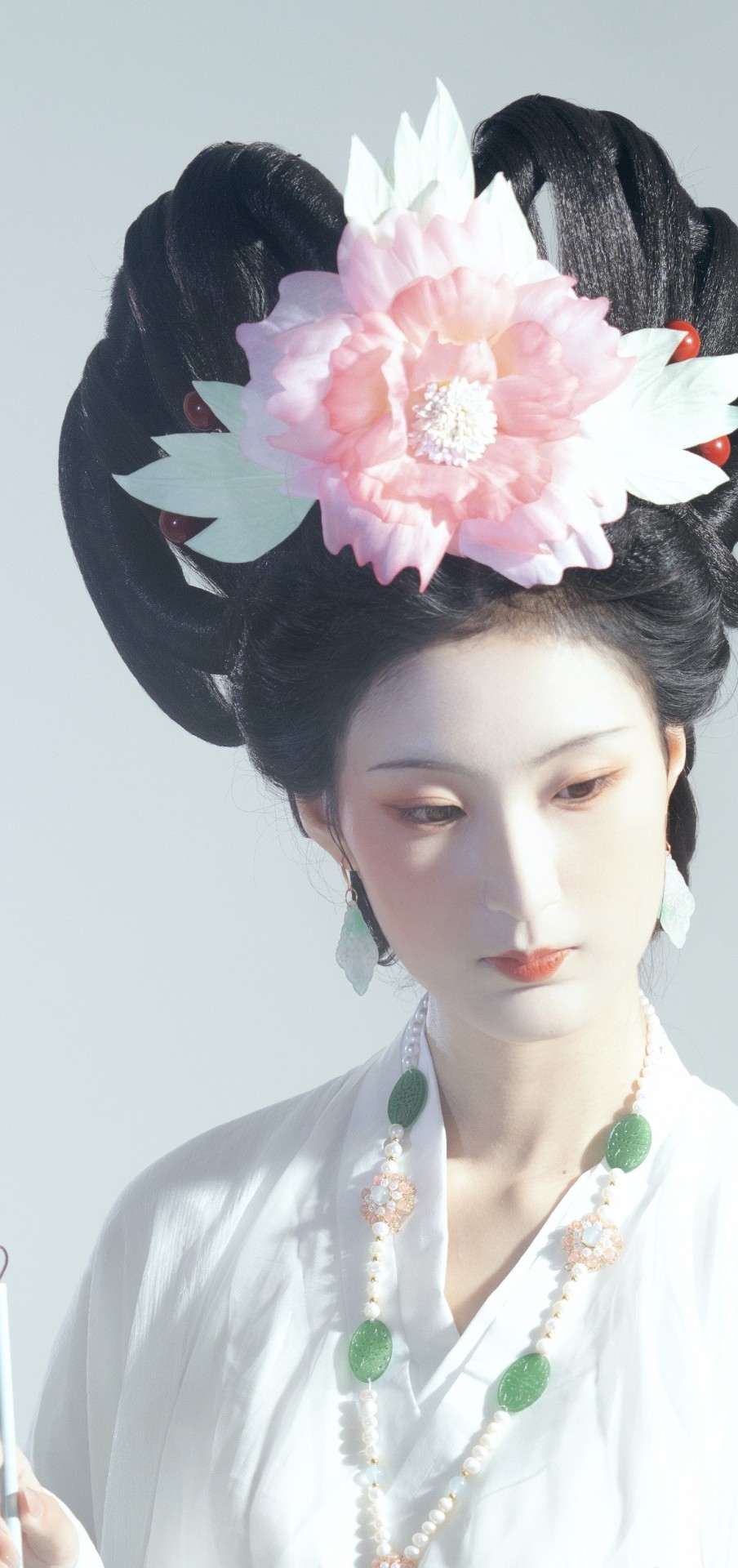
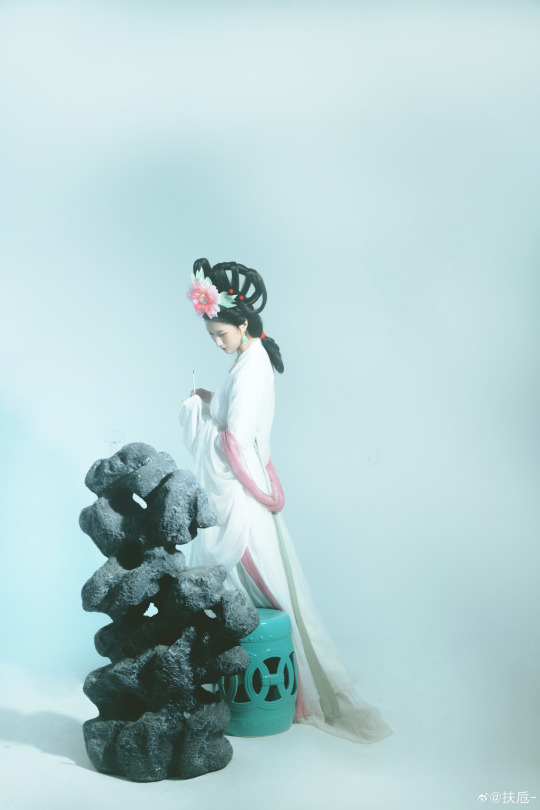
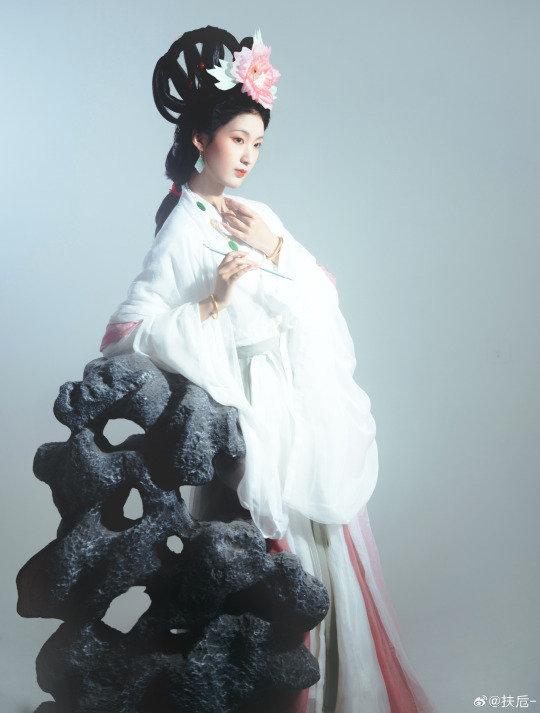
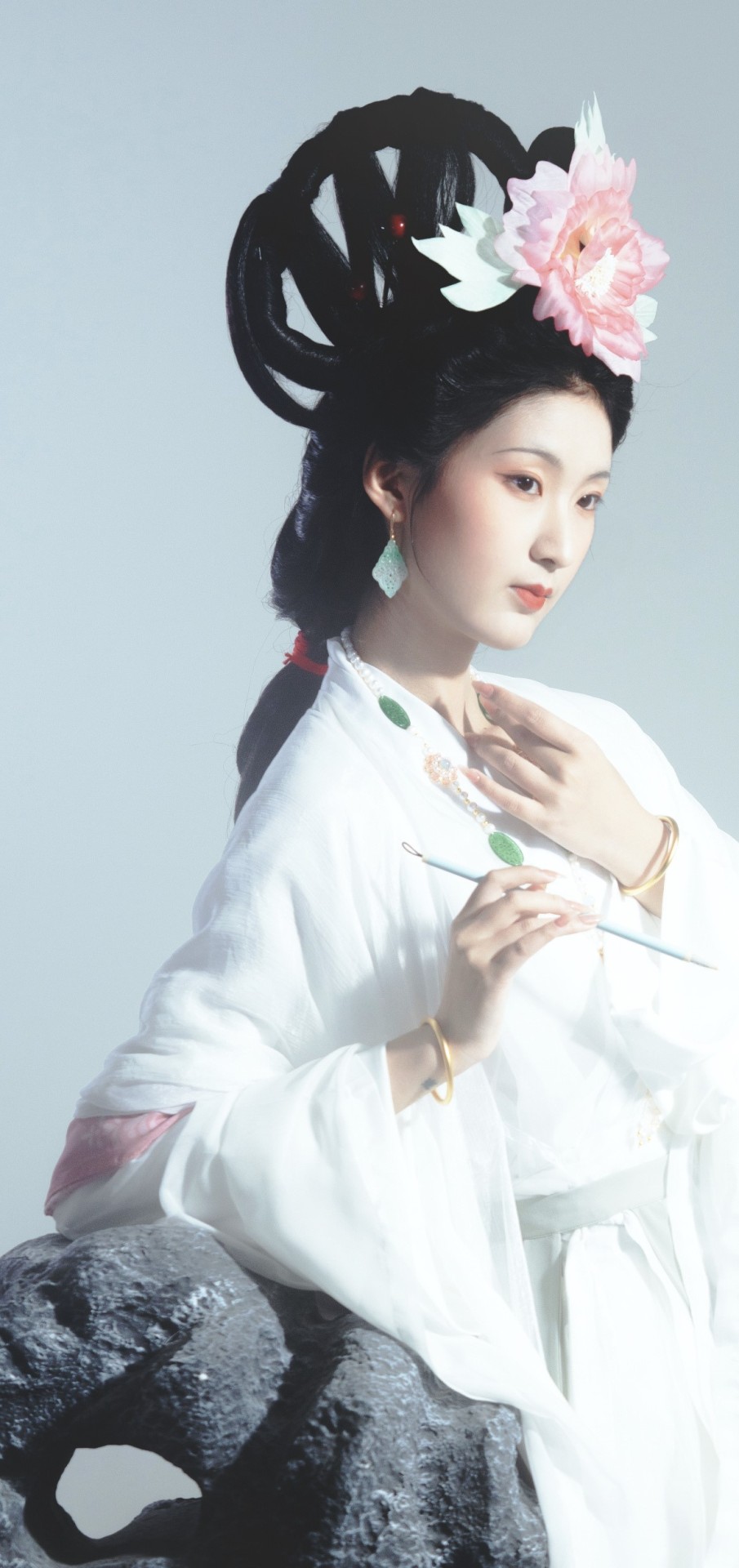
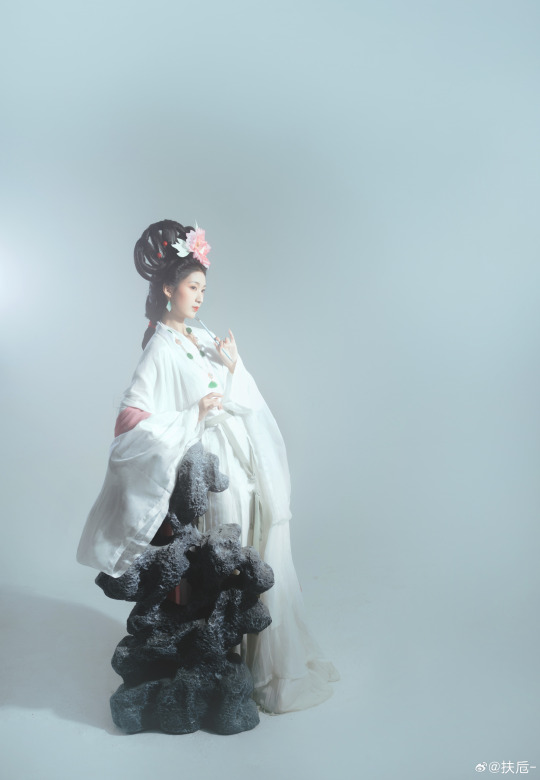












————————
📸Photo:@扶卮-
🧚🏻 Model :@荷里寒
💄Stylist:@山有木兮_Ivy
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1741209390/NB3aQn1fa
————————
799 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty(618–907AD)Winter Hanfu Based On Tang Dynasty Mural and figurines
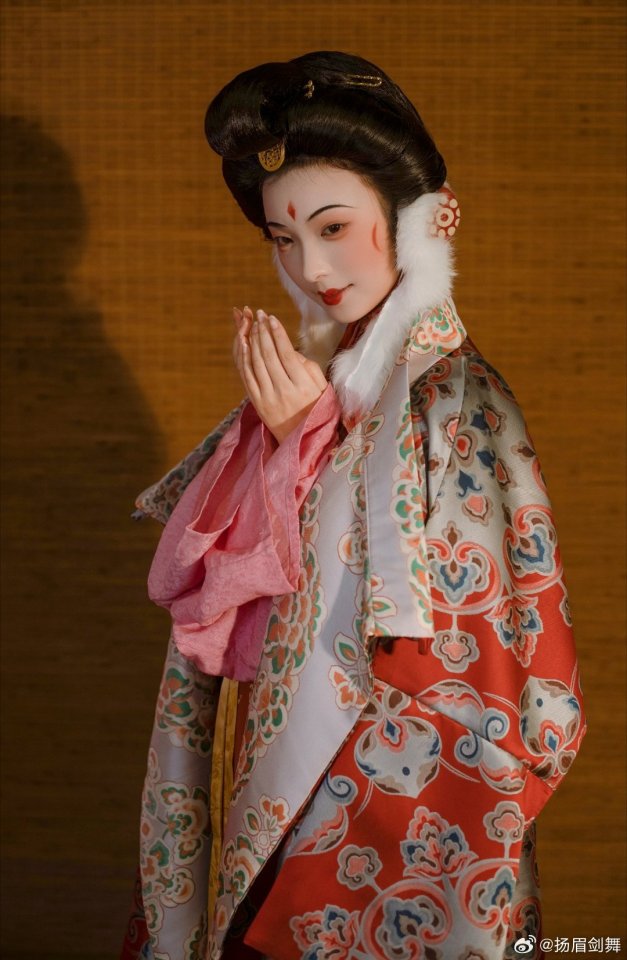
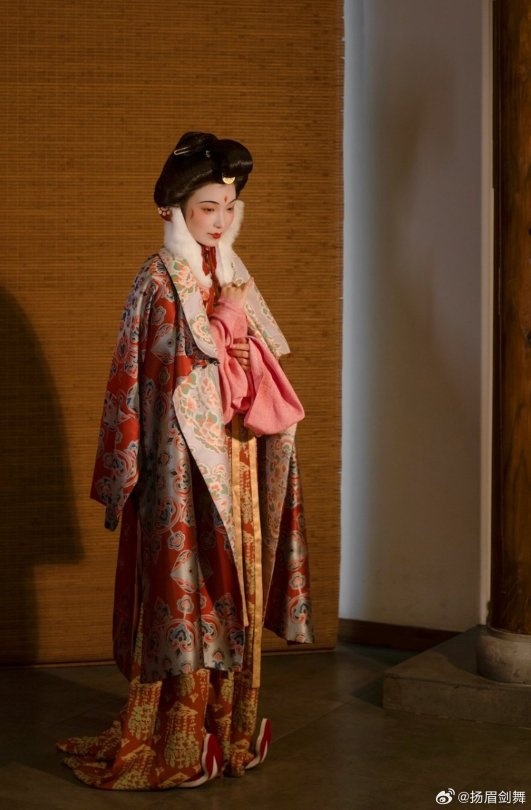
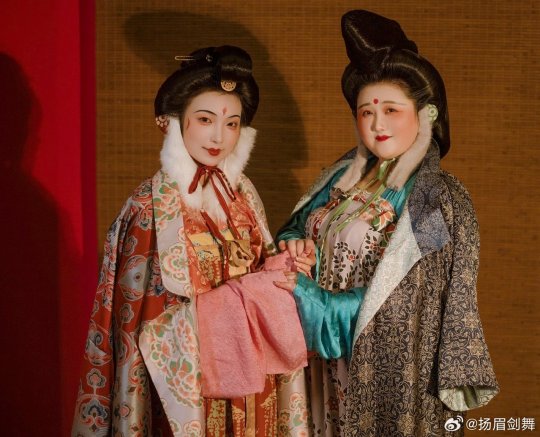
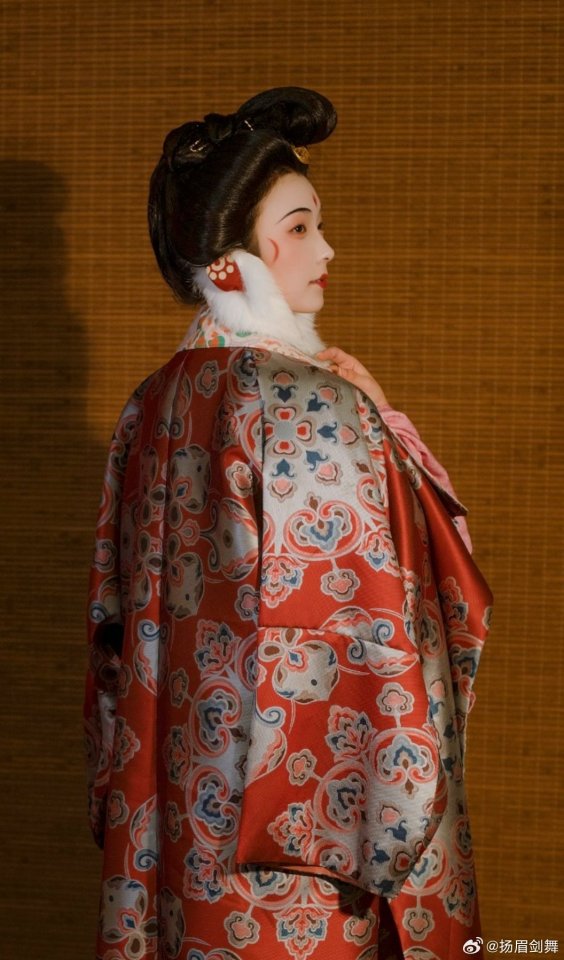
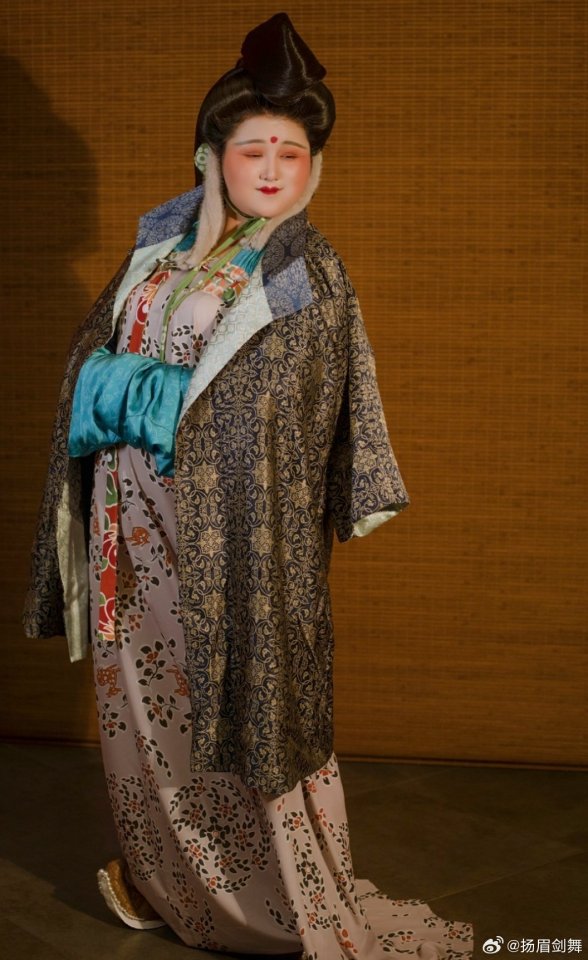
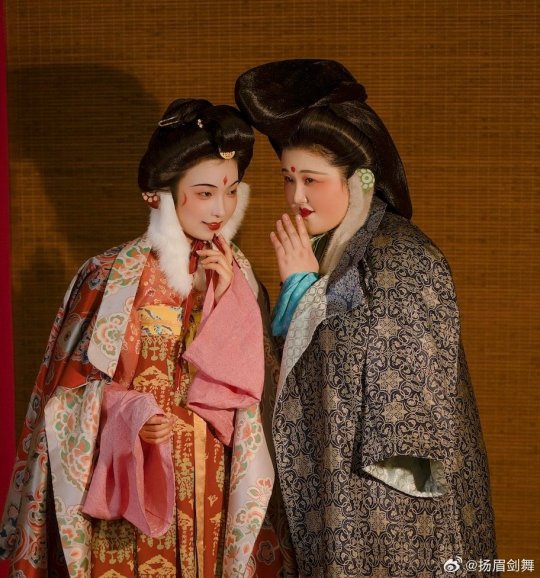
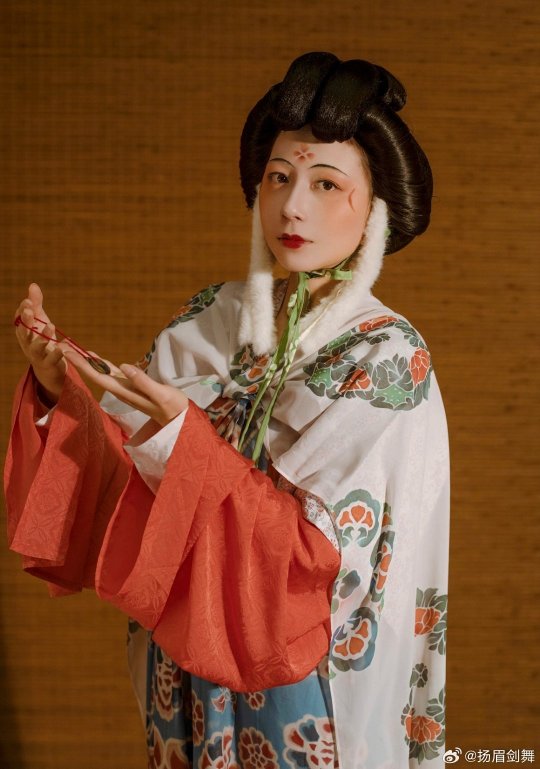







【Historical Artifacts Reference 】:
China Tang Dynasty female figurine:
showing woman wearing“披袄/ Pī ǎo",“披袄/ Pī ǎo" is kind of formal wear. It is said began in the period of Cao Wei(曹魏)period, and was derived from Yiyi(祎衣). Mostly used in winter.
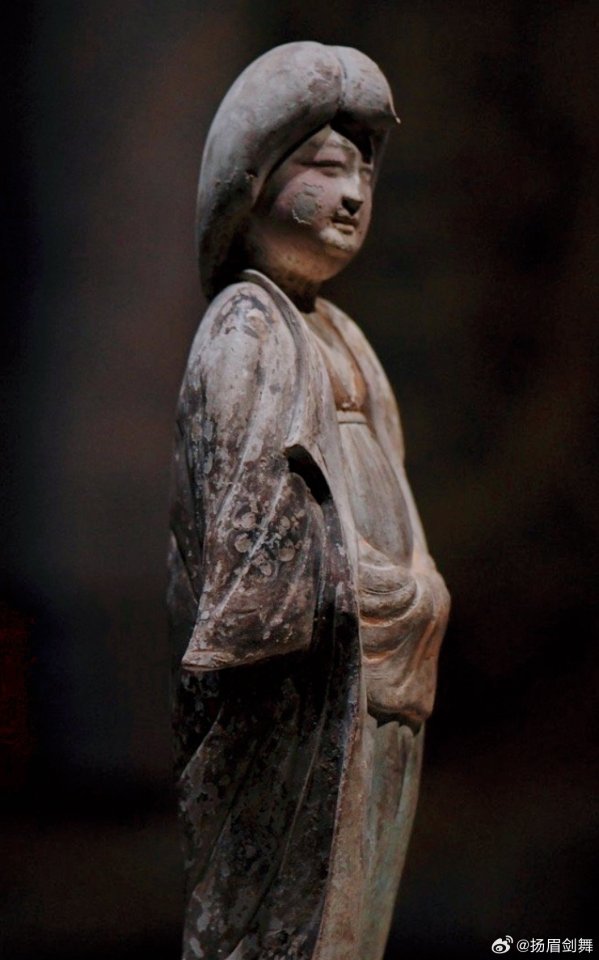


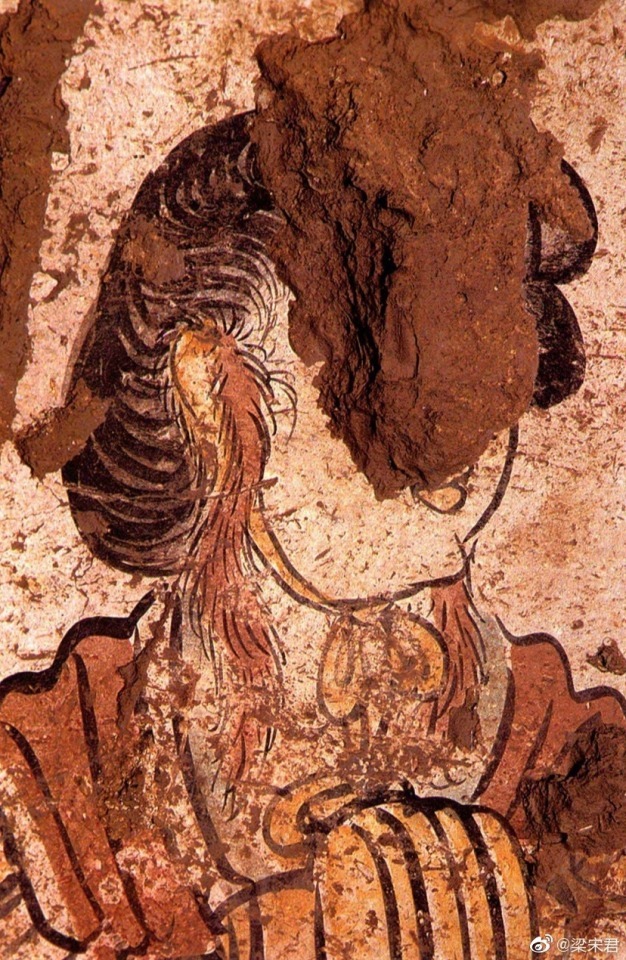
Among the pottery figurines and line carvings of the Tang Dynasty, wearing 披袄/ Pī ǎo" is a very common combination, as well as winter clothing such as double-layered thick Pī bó(披帛)and Earmuffs(暖耳/Nuǎn ěr)
Tang Dynasty”Earmuffs”:暖耳(Nuǎn ěr):
The mural of Li Yong(李邕)'s tomb in Fuping, Shaanxi (the fifteenth year of Tang Kaiyuan, 727 AD),showing a woman wears 暖耳(Nuǎn ěr).
It is presumed to be made of animal fur and a cloth belt, and the cloth belt is tied under the chin.

————————
📸Recreation Work:@扬眉剑舞
🧚🏻 Model :@陈喜悦耶 @长歌要努力吖
🔗 Weibo:https://weibo.com/1879589532/NyTNDD1Eb
————————
203 notes
·
View notes



