Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
How to Reset Your Browser Settings: A Comprehensive Guide
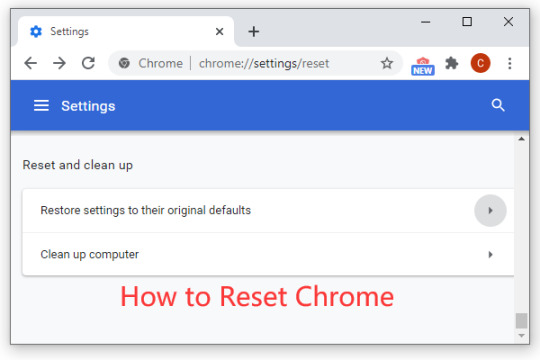
Modern web browsers are essential tools for accessing the internet, but over time they can become cluttered with extensions, cached data, and customized settings that can impact performance and functionality. Resetting your browser settings can resolve various issues, enhance performance, and provide a fresh start. This guide covers how to reset settings for the most popular browsers: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Safari.
Why Reset Your Browser Settings?
Performance Improvement: Over time, browsers accumulate cache, cookies, and extensions that can slow down performance.
Security: Removing unwanted or malicious extensions and resetting settings can enhance security.
Troubleshooting: Fixing issues like browser crashes, slow loading times, or unwanted pop-ups often requires a reset.
Starting Fresh: Sometimes, it's just easier to start from a clean slate rather than manually adjusting settings.
Resetting Google Chrome
Open Settings: Click on the three dots in the upper right corner and select "Settings."
Advanced Settings: Scroll down and click on "Advanced" to expand more options.
Reset and Clean Up: Under the "Reset and clean up" section, select "Restore settings to their original defaults."
Confirm: A pop-up window will appear; click "Reset settings" to confirm.
This process will disable extensions, clear temporary data, and reset the default search engine, homepage, and pinned tabs without deleting bookmarks, history, or saved passwords.
Resetting Mozilla Firefox
Open Help Menu: Click on the three horizontal lines in the upper right corner and select "Help."
Troubleshooting Information: Choose "More troubleshooting information."
Refresh Firefox: Click the "Refresh Firefox" button on the top right.
Confirm: A confirmation window will appear; click "Refresh Firefox" again to proceed.
Firefox will save your essential information (bookmarks, history, passwords, and open tabs) but will remove extensions, themes, and other custom settings.
Resetting Microsoft Edge
Open Settings: Click on the three dots in the upper right corner and select "Settings."
Reset Settings: Go to the "Reset settings" section in the left-hand menu.
Restore Settings: Click on "Restore settings to their default values."
Confirm: A confirmation dialog will appear; click "Reset" to confirm.
This will reset Edge’s settings, clear temporary data, and disable extensions without affecting your favorites, history, or saved passwords.
Resetting Safari
For Safari, a more manual approach is necessary:
Clear History: Click on "Safari" in the top menu and select "Clear History."
Remove Extensions: Go to "Preferences" from the Safari menu, select the "Extensions" tab, and uninstall any unwanted extensions.
Reset Homepage: In the "Preferences" window, go to the "General" tab and reset the homepage.
Clear Cache: In the "Develop" menu (enable it from "Preferences" > "Advanced" > "Show Develop menu in menu bar"), select "Empty Caches."
Safari does not have a single reset button, so these steps must be done manually to achieve a similar result.
Conclusion
Resetting your browser can significantly improve performance, enhance security, and resolve persistent issues. While each browser has its own specific steps, the general process involves accessing settings, choosing the reset option, and confirming the action. Regularly resetting your browser settings can keep your browsing experience smooth and trouble-free.
0 notes
Text
Samsung Galaxy Watch: A Comprehensive Overview

The Samsung Galaxy Watch series has been a significant player in the smartwatch market since its inception. Known for its blend of style, functionality, and innovative features, the Galaxy Watch has continually evolved to meet the needs of both tech enthusiasts and casual users. This article provides an in-depth look at the Samsung Galaxy Watch, its key features, and what sets it apart from other smartwatches.
Design and Build Quality
One of the most striking aspects of the Samsung Galaxy Watch is its design. Samsung has managed to create a device that looks and feels like a traditional watch, appealing to those who prefer a classic aesthetic. The Galaxy Watch series features a circular AMOLED display, which is vibrant and easy to read even in bright sunlight. The rotating bezel, a hallmark of the Galaxy Watch design, offers a tactile and intuitive way to navigate through the watch's interface.
The build quality of the Galaxy Watch is top-notch. It typically comes in two sizes, catering to different wrist sizes and style preferences. The materials used, such as stainless steel or aluminum for the body and high-quality silicone or leather for the straps, ensure durability and comfort. Moreover, the Galaxy Watch is water-resistant, making it suitable for swimming and other water activities.
Performance and Software
Under the hood, the Samsung Galaxy Watch is powered by Samsung's own Exynos processor, ensuring smooth performance and efficient power management. The watch runs on Samsung's Tizen OS, which is known for its user-friendly interface and robust performance. Tizen OS offers a variety of customizable watch faces and supports a wide range of third-party apps, enhancing the overall user experience.
The Galaxy Watch integrates seamlessly with Samsung's ecosystem, including Galaxy smartphones, tablets, and earbuds. Features like Samsung Pay, Bixby voice assistant, and SmartThings integration make the Galaxy Watch a versatile companion for managing various aspects of daily life.
Health and Fitness Tracking
Samsung has placed a strong emphasis on health and fitness tracking in the Galaxy Watch series. The watch is equipped with a comprehensive set of sensors, including an accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, heart rate monitor, and ECG sensor. These sensors enable the Galaxy Watch to track a wide range of activities and health metrics, such as steps taken, calories burned, distance traveled, and sleep quality.
One of the standout features is the automatic workout detection, which can recognize and track different types of exercises without manual input. The Galaxy Watch also supports advanced health monitoring features like blood oxygen level measurement, stress tracking, and even fall detection. Additionally, the ECG and blood pressure monitoring features, though region-dependent, provide valuable health insights and are approved by various health authorities.
Battery Life
Battery life is a critical factor for smartwatches, and the Samsung Galaxy Watch generally performs well in this area. Depending on the model and usage patterns, the Galaxy Watch can last anywhere from 2 to 4 days on a single charge. The watch also supports wireless charging, making it convenient to recharge using compatible charging pads.
Connectivity and Smart Features
The Galaxy Watch offers robust connectivity options, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and optional LTE models for standalone functionality. With LTE, users can make and receive calls, send messages, and stream music directly from their watch without needing to be near their smartphone. This feature is particularly useful for those who want to stay connected while on the go.
In terms of smart features, the Galaxy Watch supports notifications from a wide range of apps, allowing users to stay informed without constantly checking their phone. It also features music storage and playback capabilities, Samsung Pay for contactless payments, and integration with smart home devices through SmartThings.
Conclusion
The Samsung Galaxy Watch is a versatile and stylish smartwatch that offers a comprehensive suite of features for both casual users and fitness enthusiasts. Its blend of classic watch design, robust performance, extensive health tracking capabilities, and seamless integration with the Samsung ecosystem make it a compelling choice in the crowded smartwatch market. Whether you're looking to stay connected, monitor your health, or simply enjoy a beautifully crafted timepiece, the Samsung Galaxy Watch is well worth considering.
0 notes
Text
Samsung Galaxy Watch: A Comprehensive Overview

The Samsung Galaxy Watch series has been a significant player in the smartwatch market since its inception. Known for its blend of style, functionality, and innovative features, the Galaxy Watch has continually evolved to meet the needs of both tech enthusiasts and casual users. This article provides an in-depth look at the Samsung Galaxy Watch, its key features, and what sets it apart from other smartwatches.
Design and Build Quality
One of the most striking aspects of the Samsung Galaxy Watch is its design. Samsung has managed to create a device that looks and feels like a traditional watch, appealing to those who prefer a classic aesthetic. The Galaxy Watch series features a circular AMOLED display, which is vibrant and easy to read even in bright sunlight. The rotating bezel, a hallmark of the Galaxy Watch design, offers a tactile and intuitive way to navigate through the watch's interface.
The build quality of the Galaxy Watch is top-notch. It typically comes in two sizes, catering to different wrist sizes and style preferences. The materials used, such as stainless steel or aluminum for the body and high-quality silicone or leather for the straps, ensure durability and comfort. Moreover, the Galaxy Watch is water-resistant, making it suitable for swimming and other water activities.
Performance and Software
Under the hood, the Samsung Galaxy Watch is powered by Samsung's own Exynos processor, ensuring smooth performance and efficient power management. The watch runs on Samsung's Tizen OS, which is known for its user-friendly interface and robust performance. Tizen OS offers a variety of customizable watch faces and supports a wide range of third-party apps, enhancing the overall user experience.
The Galaxy Watch integrates seamlessly with Samsung's ecosystem, including Galaxy smartphones, tablets, and earbuds. Features like Samsung Pay, Bixby voice assistant, and SmartThings integration make the Galaxy Watch a versatile companion for managing various aspects of daily life.
Health and Fitness Tracking
Samsung has placed a strong emphasis on health and fitness tracking in the Galaxy Watch series. The watch is equipped with a comprehensive set of sensors, including an accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, heart rate monitor, and ECG sensor. These sensors enable the Galaxy Watch to track a wide range of activities and health metrics, such as steps taken, calories burned, distance traveled, and sleep quality.
One of the standout features is the automatic workout detection, which can recognize and track different types of exercises without manual input. The Galaxy Watch also supports advanced health monitoring features like blood oxygen level measurement, stress tracking, and even fall detection. Additionally, the ECG and blood pressure monitoring features, though region-dependent, provide valuable health insights and are approved by various health authorities.
Battery Life
Battery life is a critical factor for smartwatches, and the Samsung Galaxy Watch generally performs well in this area. Depending on the model and usage patterns, the Galaxy Watch can last anywhere from 2 to 4 days on a single charge. The watch also supports wireless charging, making it convenient to recharge using compatible charging pads.
Connectivity and Smart Features
The Galaxy Watch offers robust connectivity options, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and optional LTE models for standalone functionality. With LTE, users can make and receive calls, send messages, and stream music directly from their watch without needing to be near their smartphone. This feature is particularly useful for those who want to stay connected while on the go.
In terms of smart features, the Galaxy Watch supports notifications from a wide range of apps, allowing users to stay informed without constantly checking their phone. It also features music storage and playback capabilities, Samsung Pay for contactless payments, and integration with smart home devices through SmartThings.
Conclusion
The Samsung Galaxy Watch is a versatile and stylish smartwatch that offers a comprehensive suite of features for both casual users and fitness enthusiasts. Its blend of classic watch design, robust performance, extensive health tracking capabilities, and seamless integration with the Samsung ecosystem make it a compelling choice in the crowded smartwatch market. Whether you're looking to stay connected, monitor your health, or simply enjoy a beautifully crafted timepiece, the Samsung Galaxy Watch is well worth considering.
0 notes
Text
The Essential Guide to Cleaners: Choosing the Right Solutions for Every Job

Cleanliness is fundamental to health, safety, and comfort, whether at home, in the workplace, or in public spaces. To maintain this essential standard, a wide array of cleaners are available, each designed to tackle specific tasks and surfaces. This article delves into the different types of cleaners, their applications, and tips for choosing the right one for your needs.
Types of Cleaners
All-Purpose Cleaners: As the name suggests, all-purpose cleaners are versatile and can be used on a variety of surfaces, including countertops, floors, and appliances. They typically contain a mix of detergents and solvents to remove dirt and grease.
Disinfectants: These cleaners contain antimicrobial agents that kill bacteria, viruses, and fungi. They are essential for maintaining hygiene in kitchens, bathrooms, and medical facilities. Common disinfectants include bleach solutions, alcohol-based cleaners, and hydrogen peroxide.
Glass Cleaners: Formulated to clean glass surfaces without leaving streaks, glass cleaners often contain ammonia or vinegar. They are ideal for windows, mirrors, and glass furniture.
Bathroom Cleaners: Designed to tackle soap scum, mildew, and hard water stains, bathroom cleaners typically contain strong acids or bases to dissolve grime. They are suitable for sinks, tubs, tiles, and toilets.
Floor Cleaners: These products vary depending on the type of flooring—wood, tile, laminate, or carpet. Each type is formulated to clean without damaging the specific material. For example, wood floor cleaners often include conditioners to protect the finish, while carpet cleaners may have stain removers and deodorizers.
Kitchen Cleaners: Specially formulated to handle grease and food residues, kitchen cleaners are effective on stovetops, countertops, and kitchen appliances. They often contain degreasers and surfactants to break down tough residues.
Specialty Cleaners: These include products for specific tasks such as stainless steel cleaners, upholstery cleaners, and automotive cleaners. Each is designed with a particular surface or material in mind to ensure optimal cleaning without damage.
Choosing the Right Cleaner
Selecting the appropriate cleaner for a task involves considering several factors:
Surface Type: Ensure the cleaner is suitable for the surface you intend to clean. Using the wrong cleaner can cause damage or leave residues.
Cleaning Power: Depending on the level of dirt or grime, you may need a stronger or more specialized cleaner. For heavy-duty cleaning, industrial-strength products might be necessary.
Ingredients: Be mindful of the ingredients, especially if you have allergies or sensitivities. Eco-friendly and non-toxic cleaners are available for those looking to reduce their environmental impact.
Purpose: Determine whether you need a general cleaner or a product for a specific task, like disinfecting or stain removal. This will help narrow down your options.
Ease of Use: Consider how the cleaner is applied and whether it requires rinsing or other follow-up actions. Convenient spray bottles and wipes can make quick cleaning tasks easier.
Tips for Effective Cleaning
Read Labels: Always read the product label for instructions and safety information. This ensures proper usage and maximum effectiveness.
Test First: When using a new cleaner, test it on a small, inconspicuous area first to ensure it doesn’t damage the surface.
Ventilation: Use cleaners in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhaling fumes, especially with strong chemicals like bleach or ammonia.
Protective Gear: Wear gloves, masks, or goggles if necessary to protect yourself from harsh chemicals.
Regular Maintenance: Regular cleaning can prevent the buildup of dirt and grime, making each cleaning session easier and more effective.
Conclusion
The right cleaner can make a significant difference in maintaining a clean and healthy environment. With a wide variety of cleaners available, understanding their specific uses and choosing the appropriate one for each task is crucial. By following the tips provided and considering the type, purpose, and ingredients of cleaners, you can ensure that your cleaning efforts are both effective and safe. Invest in quality cleaners tailored to your needs, and enjoy the benefits of a spotless and hygienic space.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution and Impact of Headphones

Headphones have become an indispensable part of modern life, serving as companions for commuters, gamers, fitness enthusiasts, and music lovers alike. Their evolution from bulky, wired devices to sleek, wireless marvels underscores significant technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences. This article explores the history, technological progression, types, and societal impact of headphones.
A Brief History
The journey of headphones began in the late 19th century with the invention of the first pair by Nathaniel Baldwin in 1910. Initially, these devices were used primarily by telephone operators and the military. It wasn't until the 1950s that headphones became more accessible to the general public, largely due to the burgeoning popularity of portable radios.
The 1970s saw a significant leap with the introduction of the Sony Walkman, revolutionizing personal audio consumption. This era marked the beginning of headphones as a fashion statement and a personal accessory. The 1990s and early 2000s introduced in-ear headphones, offering greater portability and convenience, further cementing their role in everyday life.
Technological Advancements
The evolution of headphones has been driven by several technological advancements:
Wireless Technology: The shift from wired to wireless headphones, facilitated by Bluetooth technology, has provided users with unprecedented freedom of movement. This development has been crucial for fitness enthusiasts and those seeking convenience.
Noise Cancellation: Introduced by Bose in the early 2000s, active noise cancellation (ANC) technology uses microphones and speakers to reduce unwanted ambient sounds. This feature has become essential for travelers and those working in noisy environments.
Sound Quality Enhancements: Advances in driver technology, high-resolution audio codecs, and the integration of digital signal processing (DSP) have significantly improved the sound quality of headphones. Audiophiles now have access to studio-quality audio on the go.
Smart Features: Modern headphones often come equipped with smart features like voice assistants, touch controls, and fitness tracking. These integrations have transformed headphones from simple audio devices to multifunctional gadgets.
Types of Headphones
Headphones come in various forms, each catering to different needs and preferences:
Over-Ear Headphones: Known for their superior sound quality and comfort, over-ear headphones are popular among audiophiles and gamers. They provide excellent noise isolation and are ideal for extended listening sessions.
On-Ear Headphones: These are more compact than over-ear models and rest on the ears rather than enclosing them. They offer a balance between sound quality and portability.
In-Ear Headphones: Also known as earbuds, these are highly portable and often come with features like sweat resistance, making them ideal for sports and daily commuting.
True Wireless Earbuds: The latest trend in headphone technology, true wireless earbuds, such as Apple's AirPods and Samsung's Galaxy Buds, offer complete freedom from wires and often come with smart features and ANC.
Societal Impact
Headphones have had a profound impact on society, influencing how we consume media, communicate, and interact with our environment. They have:
Enhanced Mobility: Wireless headphones have enabled users to enjoy music and podcasts while engaging in various activities, from working out to commuting, enhancing productivity and entertainment on the go.
Created Personal Soundscapes: With the advent of noise-canceling technology, individuals can create personal soundscapes, allowing them to focus in noisy environments or find solitude in public spaces.
Influenced Fashion and Culture: Headphones have become a fashion accessory, with brands like Beats by Dre and Apple's AirPods shaping trends and cultural identity. Celebrity endorsements and collaborations with designers have further cemented their status as style statements.
Changed Communication Norms: The integration of microphones and smart features has made headphones a primary tool for communication, particularly in the era of remote work and virtual meetings.
Conclusion
From their inception as utilitarian devices to their current status as multifaceted gadgets, headphones have come a long way. They have not only revolutionized how we experience audio but also influenced our lifestyle and culture. As technology continues to advance, the future of headphones promises even more exciting innovations, further enhancing their role in our daily lives.
0 notes
Text
The Essential Guide to Power Banks: Staying Charged on the Go

In our increasingly connected world, maintaining battery life on our devices is crucial. This is where power banks come in handy. Whether you are traveling, at a conference, or just out and about, a power bank ensures your smartphone, tablet, or other electronic devices stay charged. This article delves into what power banks are, how they work, the different types available, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Power Bank?
A power bank, also known as a portable charger or external battery, is a device that stores electrical energy for later use. It typically consists of a battery encased in a housing with one or more USB ports for charging other devices. The power bank itself is charged through an input port, usually via a USB cable.
How Do Power Banks Work?
Power banks operate by storing electrical energy in their internal battery when connected to a power source. Once charged, the stored energy can be transferred to other devices through a USB output port. The process involves the following steps:
Charging the Power Bank: Connect the power bank to a power source using the input port and appropriate cable. An LED indicator often shows the charging status.
Storing Energy: The internal battery stores the energy until needed.
Discharging: When your device's battery is low, connect it to the power bank using a USB cable. The power bank transfers the stored energy to your device.
Types of Power Banks
Power banks come in various shapes, sizes, and capacities, catering to different needs. Here are the common types:
Standard Power Banks: These are the most common and come in a variety of capacities. They are suitable for charging smartphones and other small devices.
High-Capacity Power Banks: Designed for extended use or charging larger devices like tablets and laptops, these power banks offer higher mAh (milliampere-hour) ratings.
Solar Power Banks: Equipped with solar panels, these power banks can be recharged using sunlight, making them ideal for outdoor activities.
Wireless Power Banks: These power banks provide wireless charging capabilities, eliminating the need for cables.
Ultra-Portable Power Banks: Small and lightweight, these are designed for maximum portability, often fitting in a pocket or small bag.
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a power bank, several factors should be considered:
Capacity (mAh): This determines how much charge the power bank can hold. Higher capacity means more charges for your devices.
Portability: Size and weight are crucial, especially if you need to carry it around frequently.
Output Ports: The number and type of output ports determine how many devices can be charged simultaneously and at what speed.
Input Charging Speed: A higher input rating means the power bank itself charges faster.
Durability: Look for power banks with robust build quality, especially if you plan to use them outdoors.
Additional Features: Some power banks offer extras like built-in flashlights, digital displays showing charge levels, or waterproof and shockproof designs.
How to Choose the Right Power Bank
Choosing the right power bank depends on your specific needs and usage patterns. Here are some tips:
For Daily Use: A standard power bank with 10,000 to 20,000 mAh capacity is usually sufficient for smartphones and small devices.
For Travel: Consider a high-capacity power bank (20,000 mAh or more) to ensure multiple charges and compatibility with various devices.
For Outdoor Activities: A durable, solar-powered option can be invaluable, providing extra charge in remote locations.
For Convenience: Wireless power banks and those with multiple ports can add convenience by reducing the number of cables needed.
Conclusion
Power banks are indispensable tools for anyone relying on electronic devices throughout the day. With a wide variety of options available, it's essential to choose one that fits your lifestyle and needs. Whether you need a compact charger for your phone or a high-capacity one for multiple devices, there's a power bank out there to keep you powered up and connected.
0 notes
Text
The Joystick: A Key to Interactive Control

The joystick is a pivotal device in the realm of interactive control, playing a crucial role in various fields ranging from gaming to aviation. This article delves into the history, types, applications, and future trends of the joystick, highlighting its enduring importance and versatility.
Historical Overview
The concept of the joystick can be traced back to the early 20th century. Its earliest known use was in aviation, where it was employed to control aircraft. The first joystick, or "control stick," was introduced in 1908 by French aviator Louis Blériot, providing pilots with a more intuitive way to maneuver their planes.
The transition of the joystick into the realm of entertainment began in the 1960s and 1970s with the advent of video games. The Atari 2600, released in 1977, popularized the joystick as a game controller, setting a standard for future gaming systems.
Types of Joysticks
Joysticks come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications:
Analog Joystick: Features a stick that pivots on two axes, allowing for a wide range of motion. It provides precise control and is commonly used in aviation and complex simulations.
Digital Joystick: Utilizes switches to register directional input, offering less precision than analog joysticks but often used in simpler gaming setups.
Flight Stick: A specialized analog joystick used in flight simulators and aircraft, designed to mimic the controls of an actual plane. It often includes multiple buttons and throttle controls.
Thumbstick (Gamepad Joystick): Smaller joysticks integrated into game controllers, such as those on the PlayStation or Xbox controllers. They offer precise control in a compact form factor.
Force Feedback Joystick: Provides haptic feedback to the user, simulating the feel of real-world interactions by resisting movements or vibrating, enhancing the immersive experience in games and simulations.
Applications
The joystick's versatility is evident in its wide range of applications:
Gaming: Joysticks are integral to gaming, from arcade machines to modern consoles and PC gaming setups. They offer intuitive control for flight simulators, racing games, and first-person shooters.
Aviation: In both real and simulated flight, joysticks (or control sticks) provide pilots with precise control over aircraft. They are essential in training simulators, helping pilots develop their skills in a safe environment.
Industrial Control: Used in machinery and equipment control, joysticks allow operators to manage cranes, robots, and other heavy machinery with precision and ease.
Accessibility Devices: Joysticks are incorporated into devices designed for individuals with mobility impairments, enabling them to control computers, wheelchairs, and other assistive technology.
Military and Defense: Joysticks are used in controlling drones, military vehicles, and weaponry, providing precise and responsive control necessary for defense operations.
Modern Innovations
Modern joysticks have evolved significantly, integrating advanced technology to enhance user experience:
Wireless Connectivity: Many contemporary joysticks are wireless, offering greater freedom of movement and reducing clutter.
Enhanced Ergonomics: Modern designs prioritize user comfort, with features like adjustable grips, customizable button layouts, and contoured shapes to reduce strain during extended use.
Advanced Sensors: Incorporation of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and other sensors has improved the precision and responsiveness of joysticks.
Virtual Reality (VR): Joysticks are being adapted for use in VR environments, providing intuitive and immersive control mechanisms that enhance the virtual experience.
Future Trends
The future of joysticks lies in further integration with emerging technologies. Augmented reality (AR) and VR will likely drive the development of more sophisticated control devices, blending physical and digital interactions seamlessly. Additionally, advancements in haptic feedback technology will provide even more realistic and immersive experiences.
Moreover, as artificial intelligence and machine learning continue to evolve, joysticks may incorporate these technologies to adapt to user behavior, providing customized control experiences and improving efficiency in various applications.
Conclusion
The joystick has come a long way from its origins in early aviation to its widespread use in gaming, industry, and beyond. Its ability to provide intuitive and precise control has made it an indispensable tool in numerous fields. As technology advances, the joystick will continue to evolve, maintaining its relevance and expanding its applications in exciting new directions.
0 notes
Text
Running qBittorrent as an Administrator

qBittorrent is a popular open-source BitTorrent client that offers a range of features including a user-friendly interface, integrated search engine, and support for sequential downloading. While qBittorrent typically runs with standard user permissions, there are scenarios where running it as an administrator may be necessary. This article will guide you through the steps to run qBittorrent with administrative privileges on a Windows system, explain why you might need to do this, and discuss the potential risks involved.
Why Run qBittorrent as Administrator?
Running qBittorrent as an administrator can be beneficial in certain situations:
Access to Restricted Folders: If you need to download files to or from directories that require elevated permissions, running qBittorrent as an administrator can grant the necessary access.
Network Configuration: Administrative privileges might be required to modify network settings or to open specific ports in the firewall for improved connectivity.
Plugin and Script Execution: Some plugins or scripts that qBittorrent might use could require higher permissions to function correctly.
Steps to Run qBittorrent as Administrator
Here’s a step-by-step guide to run qBittorrent with administrative privileges on Windows:
Method 1: Run as Administrator Temporarily
Locate the qBittorrent Shortcut:
Find the qBittorrent shortcut on your desktop or in the Start menu.
Right-Click the Shortcut:
Right-click on the qBittorrent icon.
Select 'Run as Administrator':
From the context menu, select 'Run as administrator'.
Method 2: Always Run as Administrator
If you frequently need to run qBittorrent with administrative privileges, you can configure it to always run as an administrator:
Locate the qBittorrent Shortcut:
Find the qBittorrent shortcut on your desktop or in the Start menu.
Open Properties:
Right-click on the qBittorrent icon and select 'Properties'.
Navigate to Compatibility Tab:
In the Properties window, go to the 'Compatibility' tab.
Enable Administrator Mode:
Under the 'Settings' section, check the box that says 'Run this program as an administrator'.
Apply Changes:
Click 'Apply' and then 'OK' to save the changes.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While running qBittorrent as an administrator can solve specific issues, it also comes with risks:
Security Risks: Running any application with elevated privileges increases the risk of malicious attacks. If qBittorrent or one of its plugins is compromised, it could potentially lead to a security breach.
System Stability: Granting administrative rights to applications unnecessarily can lead to system instability. It can affect system files or settings unintentionally.
Accidental Changes: With higher privileges, there’s a greater chance of making accidental changes that could affect your system’s configuration or performance.
Best Practices
To mitigate risks while still benefiting from the necessary administrative privileges, follow these best practices:
Use Administrative Rights Sparingly: Only run qBittorrent as an administrator when absolutely necessary.
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update qBittorrent and any plugins or scripts to ensure you have the latest security patches.
Use a Firewall: Configure your firewall to monitor and control qBittorrent’s network access.
Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of your important data to prevent loss in case of an incident.
Conclusion
Running qBittorrent as an administrator can be useful for accessing restricted folders, configuring network settings, and ensuring that plugins work correctly. However, it’s essential to balance these needs against the potential risks. By following the steps outlined above and adhering to best practices, you can use qBittorrent effectively and safely with administrative privileges when needed.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying Megapixels: Understanding Their Role in Digital Photography

In the realm of digital photography, the term "megapixels" is often bandied about, but what does it really mean? Are more megapixels always better? Let's delve into the world of image resolution and uncover the significance of megapixels in capturing that perfect shot.
What are Megapixels?
Simply put, a megapixel is equal to one million pixels. Pixels are the smallest individual elements that comprise a digital image, and megapixels denote the total number of these pixels that make up an image. When you hear that a camera has, say, a 20-megapixel sensor, it means that the sensor is capable of capturing images composed of 20 million pixels.
Megapixels and Image Resolution
Clarity and Detail: Generally, higher megapixel counts result in images with greater clarity and detail, especially when viewed at larger sizes or cropped extensively. More megapixels mean more information is captured, allowing for finer details to be preserved.
Print Size: The number of megapixels in an image also determines how large it can be printed while maintaining high quality. Higher megapixel counts enable larger prints without sacrificing sharpness or clarity.
Post-Processing Flexibility: Images with higher megapixel counts offer greater flexibility in post-processing. They can withstand more aggressive cropping and resizing without losing too much detail, making them ideal for editing and manipulation.
Considerations Beyond Megapixels
Sensor Size: While megapixels are important, they're not the only factor influencing image quality. The size and quality of the camera's sensor also play a crucial role. A larger sensor can capture more light and detail, contributing to better overall image quality.
Lens Quality: The quality of the lens used with a camera can significantly impact image sharpness and clarity. A high-resolution sensor paired with a subpar lens may not deliver the best results.
Usage Scenario: Consider how you plan to use your photos. For casual snapshots or social media sharing, a moderate megapixel count may suffice. However, if you're a professional photographer or require images for large-format printing, higher megapixels are desirable.
The Megapixel Myth
It's important to note that the pursuit of higher megapixels isn't always the answer. In some cases, cramming more megapixels onto a small sensor can lead to diminishing returns. Excessive megapixels on a tiny sensor may result in increased image noise, reduced low-light performance, and larger file sizes without a significant improvement in image quality.
Conclusion
Megapixels are a crucial aspect of digital photography, influencing image resolution, clarity, and print size. However, they're just one piece of the puzzle. When evaluating cameras, consider factors like sensor size, lens quality, and your intended usage scenario alongside megapixel count. By understanding the role of megapixels and their relationship with other elements of camera technology, you can make informed decisions to capture stunning photos that exceed expectations.
0 notes
Text
Understanding MicroSD Cards: Everything You Need to Know

In today's digital age, where smartphones, cameras, and other gadgets have become ubiquitous companions, the importance of storage cannot be overstated. MicroSD cards have emerged as a ubiquitous solution, offering a compact yet powerful means of expanding storage capacities for various devices. Let's delve into the world of MicroSD cards and explore everything you need to know about these tiny but mighty storage solutions.
What is a MicroSD Card?
A MicroSD card is a small, removable flash memory card designed to provide additional storage space for devices such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and handheld gaming consoles. Despite their diminutive size, MicroSD cards offer impressive storage capacities ranging from a few gigabytes to multiple terabytes, making them ideal for storing photos, videos, music, and other digital content.
Types of MicroSD Cards
MicroSD cards come in different types and formats, each tailored to specific device requirements and performance needs:
Standard Capacity (SDSC): These cards, also known as MicroSD, have a capacity of up to 2GB. While they are less common now due to their limited storage capacity, they still find utility in some older devices.
High Capacity (SDHC): SDHC cards have a capacity ranging from 2GB to 32GB. They are commonly used in devices that require moderate storage, such as older smartphones and digital cameras.
Extended Capacity (SDXC): SDXC cards offer storage capacities beyond 32GB, reaching up to 2TB (although as of writing, 1TB is the largest readily available size). They are ideal for devices that demand high storage capacity, such as 4K video cameras and professional DSLRs.
Ultra High-Speed (UHS): UHS-I and UHS-II are speed classifications that denote the maximum transfer rates of MicroSD cards. UHS-I cards offer speeds up to 104 MB/s, while UHS-II cards can reach up to 312 MB/s, making them suitable for high-performance applications like 4K video recording and rapid file transfers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a MicroSD Card
When selecting a MicroSD card for your device, several factors should be taken into account:
Storage Capacity: Choose a card with sufficient capacity to accommodate your data storage needs, keeping in mind the size of your files and how much space they require.
Speed Class: Consider the speed class of the MicroSD card, especially if you plan to record high-definition video or capture burst-mode photos. Higher speed classes ensure smoother data transfer and better performance.
Compatibility: Ensure that the MicroSD card is compatible with your device by checking its specifications and supported formats. Using an incompatible card may result in errors or reduced performance.
Brand and Reliability: Opt for reputable brands known for producing high-quality MicroSD cards with reliable performance and durability. Cheap, generic cards may be prone to data corruption and failure.
Care and Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your MicroSD card, follow these maintenance tips:
Handle with Care: Avoid bending, dropping, or exposing the card to extreme temperatures, moisture, or magnetic fields, as these can damage the card and result in data loss.
Format Properly: Format the MicroSD card periodically to prevent file system errors and optimize storage space. However, ensure to back up any important data before formatting.
Eject Safely: Always eject the MicroSD card from your device using the proper procedure to prevent data corruption. Most devices have an option to safely eject or unmount the card before removal.
Conclusion
MicroSD cards have revolutionized the way we store and manage digital content, offering convenient and expandable storage solutions for a wide range of devices. By understanding the different types, factors to consider, and maintenance tips, you can make informed decisions when choosing and using MicroSD cards, ensuring seamless storage expansion and reliable performance for your devices.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Advantages of Electronic Insurance

In today’s rapidly advancing digital age, electronic insurance, also known as e-insurance or digital insurance, has emerged as a game-changer in the insurance industry. Leveraging technology to streamline processes and enhance customer experiences, electronic insurance offers a myriad of advantages over traditional insurance methods. Let’s delve into some of the key benefits:
Convenience: One of the most significant advantages of electronic insurance is the unparalleled convenience it offers. Gone are the days of lengthy paperwork and physical visits to insurance offices. With e-insurance, policyholders can conveniently purchase, renew, and manage their insurance policies online, anytime and anywhere, using their computers or mobile devices. This convenience not only saves time but also provides a hassle-free experience for customers.
Cost-Effectiveness: Electronic insurance eliminates many of the overhead costs associated with traditional insurance methods, such as printing and distributing paper documents. This cost-saving is often passed on to customers in the form of lower premiums or reduced fees. Additionally, the automation of processes in e-insurance reduces the need for manual intervention, further driving down operational costs for insurance providers.
Accessibility: Electronic insurance enhances accessibility for both insurance providers and policyholders. Insurance companies can reach a wider audience by offering their services online, breaking geographical barriers and expanding their market reach. Similarly, policyholders have easy access to their insurance information, policy documents, and customer support services through digital platforms, enhancing transparency and communication.
Efficiency and Speed: Digitalization streamlines the entire insurance process, from policy issuance to claims settlement. With electronic insurance, policy applications can be processed and approved much faster than traditional methods, reducing the waiting time for customers. Moreover, claims can be submitted online, accompanied by digital documentation, leading to quicker claim processing and settlement, thereby improving overall customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Security: Electronic insurance platforms employ robust security measures to safeguard sensitive customer data and transactions. Encryption technologies, multi-factor authentication, and secure payment gateways are implemented to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. By ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of customer information, e-insurance instills trust and confidence among policyholders.
Personalization and Flexibility: Digital platforms allow insurance companies to offer personalized products and services tailored to the unique needs of individual customers. Through data analytics and customer insights, insurers can better understand customer preferences and behaviors, leading to customized insurance solutions. Furthermore, electronic insurance enables policyholders to make changes to their policies, such as coverage adjustments or beneficiary updates, with ease and flexibility.
Environmental Sustainability: By reducing the consumption of paper and minimizing the carbon footprint associated with traditional insurance practices, electronic insurance contributes to environmental sustainability. The shift towards digital processes aligns with global efforts towards eco-friendly initiatives and promotes a greener, more environmentally responsible insurance industry.
In conclusion, electronic insurance presents a host of advantages that revolutionize the way insurance products and services are delivered and consumed. From convenience and cost-effectiveness to enhanced security and sustainability, e-insurance embodies the future of the insurance industry, offering unparalleled benefits for both insurers and policyholders alike.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying Electronic Insurance: Understanding How It Works

Electronic insurance, also known as e-insurance or digital insurance, revolutionizes the traditional insurance industry by leveraging technology to streamline processes, enhance accessibility, and improve customer experience. At its core, electronic insurance operates on digital platforms, offering policy management, claims processing, and customer support through online portals or mobile applications. Here's a closer look at how electronic insurance works:
Online Enrollment and Policy Management: Instead of filling out paper forms or visiting brick-and-mortar offices, consumers can browse insurance products, compare quotes, and enroll in policies entirely online. Through user-friendly interfaces, individuals input personal information, select coverage options, and customize policy details according to their needs and preferences. Once enrolled, policyholders can access their insurance documents, update information, and make payments through secure digital platforms.
Automated Underwriting and Risk Assessment: Electronic insurance streamlines the underwriting process through automation and data analytics. Algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, including demographic information, health records, and credit scores, to assess risk profiles and determine premium rates. By eliminating manual assessments and paperwork, insurers can expedite policy issuance and offer competitive pricing tailored to individual risk factors.
Digital Documentation and Communication: Gone are the days of cumbersome paper trails and snail mail correspondence. Electronic insurance provides policyholders with digital copies of insurance contracts, certificates, and endorsements, accessible anytime, anywhere. Communication with insurers, agents, and claims adjusters occurs through email, instant messaging, or online chat features, enabling swift resolution of inquiries and concerns.
Claims Submission and Processing: In the event of covered losses or damages, policyholders can initiate claims through online claim submission forms or mobile apps. Digital documentation, such as photos or videos of the incident, can be uploaded for review, expediting the claims process. Insurers leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to assess claim validity, estimate damages, and authorize payments efficiently. Electronic payments directly deposited into policyholders' bank accounts further streamline the settlement process, eliminating the need for paper checks.
Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: Electronic insurance embraces IoT technology to enhance risk management and preventive measures. Connected devices, such as smart home sensors, telematics devices in vehicles, or wearable health trackers, provide real-time data insights that enable insurers to offer personalized discounts, incentivize proactive behaviors, and mitigate risks. For example, safe driving habits recorded by telematics devices can lead to lower auto insurance premiums, promoting safer roads and reducing accident rates.
Data Security and Privacy Measures: With the digitization of sensitive personal and financial information, data security is paramount in electronic insurance. Insurers invest in robust encryption protocols, secure cloud storage, and multi-factor authentication to safeguard customer data against cyber threats and unauthorized access. Compliance with regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR or HIPAA, ensures adherence to strict standards for data protection and privacy rights.
Continuous Innovation and Adaptation: Electronic insurance is a dynamic landscape driven by innovation and technological advancements. Insurers continually invest in research and development to enhance digital capabilities, such as predictive analytics, chatbots for customer service, or blockchain for secure transactions and fraud prevention. By staying at the forefront of technological innovation, insurers can deliver seamless digital experiences and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
In conclusion, electronic insurance represents a paradigm shift in the insurance industry, harnessing the power of technology to simplify processes, improve efficiency, and empower consumers with greater transparency and control over their insurance needs. As digitalization continues to reshape the landscape of financial services, electronic insurance stands poised to redefine the future of risk management and protection in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Coverage of Electronic Insurance Policies

Electronic devices have become an integral part of our daily lives, serving as essential tools for communication, productivity, entertainment, and more. However, these devices are also susceptible to various risks, including accidental damage, theft, and malfunctions. To mitigate these risks, many individuals opt for electronic insurance, which provides coverage for a wide range of electronic devices. Understanding what is covered under electronic insurance can help consumers make informed decisions about protecting their valuable gadgets.
Here's a closer look at what electronic insurance typically covers:
Accidental Damage: One of the most common types of coverage offered by electronic insurance is protection against accidental damage. This can include scenarios such as dropping a smartphone, spilling liquid on a laptop, or cracking the screen of a tablet. Policies often cover the cost of repairs or provide a replacement device in such cases.
Theft: Electronic insurance policies typically provide coverage in the event of theft. If a covered device is stolen, the policyholder can file a claim to receive compensation for the value of the device. Some policies may also cover theft from various locations, such as home, office, or even while traveling.
Malfunctions and Mechanical Breakdowns: In addition to accidental damage and theft, electronic insurance may cover malfunctions or mechanical breakdowns that occur outside of the manufacturer's warranty period. This can include issues such as power failures, software glitches, or hardware defects.
Loss: Some electronic insurance policies offer coverage for loss, which extends beyond theft. If a covered device is lost or misplaced, the policyholder may be eligible to receive compensation for its value. However, it's important to note that not all policies include coverage for loss, and those that do may have specific requirements or limitations.
Extended Warranty: Electronic insurance policies often function as extended warranties, providing coverage beyond the standard manufacturer warranty period. This means that even after the manufacturer warranty expires, the device remains protected against certain risks, subject to the terms and conditions of the policy.
Accessories and Peripherals: In addition to the main electronic device, many insurance policies also cover accessories and peripherals that are essential for its operation. This can include items such as chargers, cables, cases, and external storage devices.
Worldwide Coverage: Depending on the policy, electronic insurance may offer worldwide coverage, allowing policyholders to receive protection for their devices wherever they are located. This can be particularly beneficial for travelers or individuals who frequently move between locations.
It's important to carefully review the terms and conditions of any electronic insurance policy to understand the specific coverage provided, as well as any exclusions or limitations. Factors such as deductibles, coverage limits, and premium costs should also be considered when selecting a policy.
In conclusion, electronic insurance offers valuable protection for a wide range of electronic devices, safeguarding against risks such as accidental damage, theft, malfunctions, and loss. By understanding what is covered under electronic insurance policies, consumers can make informed decisions to protect their investments and maintain peace of mind in an increasingly digital world.
0 notes
Text
Why Insurance is essential for your electronics

In today's digital age, electronics play an indispensable role in our lives, from smartphones and laptops to smart home devices and gaming consoles. However, alongside their convenience and utility comes the risk of damage, theft, or malfunction. This is where insurance steps in, offering a crucial safety net to protect your valuable electronic devices. Let's explore why insurance is essential for safeguarding your electronics.
Protection Against Accidents and Damage
Accidents happen, and when they involve expensive electronic devices, the financial implications can be significant. Whether it's dropping your smartphone, spilling liquid on your laptop, or experiencing a power surge damaging your TV, insurance provides coverage for repairs or replacements, sparing you from bearing the full cost out of pocket. With the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing fragility of modern electronics, insurance offers peace of mind, knowing that you're financially protected against unforeseen mishaps.
Coverage for Theft and Loss
Electronics are prime targets for theft due to their portability and high resale value. Additionally, the risk of losing a device, whether through misplacement or theft, is ever-present in our daily lives. Insurance policies tailored for electronics typically offer coverage against theft and loss, ensuring that you're not left empty-handed in the event of a stolen or misplaced device. This coverage extends beyond the confines of your home, providing reassurance whether you're traveling, commuting, or simply going about your daily routine.
Financial Security Against Malfunctions and Breakdowns
Even the most meticulously maintained electronic devices are susceptible to malfunctions and breakdowns, often occurring outside the manufacturer's warranty period. Repairing or replacing a malfunctioning device can be costly, especially for high-end electronics. Insurance policies that cover mechanical and electrical breakdowns ensure that you're protected against unexpected failures, ensuring that you can swiftly repair or replace your device without incurring exorbitant expenses.
Comprehensive Coverage for All Your Electronics
Whether it's your smartphone, laptop, tablet, gaming console, or smart home devices, insurance offers comprehensive coverage for all your electronic gadgets under a single policy. This consolidated approach simplifies the insurance process, eliminating the need for separate policies for each device and streamlining claims management.
Peace of Mind and Financial Preparedness
Beyond the tangible benefits of coverage, insurance provides peace of mind, knowing that your electronic devices are safeguarded against a wide range of risks. In an increasingly connected world where digital devices are integral to both work and leisure, the financial repercussions of not having insurance can be severe, potentially disrupting your daily life and draining your savings in the event of an unforeseen incident.
Conclusion
In an era where electronic devices are omnipresent, insurance serves as a vital tool for protecting your investments and ensuring uninterrupted access to technology. By providing coverage against accidents, damage, theft, loss, and malfunctions, insurance offers peace of mind and financial security, allowing you to embrace the benefits of technology without fear of the accompanying risks. Whether you're a casual user or a tech enthusiast, investing in insurance for your electronics is a prudent decision that safeguards your devices and your financial well-being in the long run.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of Insurance for Your Electronics: Safeguarding Your Investments

In today's digital age, electronics have become indispensable assets in both personal and professional spheres. From smartphones and laptops to smart home devices and appliances, our reliance on electronic gadgets is ever-growing. However, along with the convenience they offer, electronic devices also come with the risk of damage, theft, or malfunction. This is where insurance plays a crucial role in protecting your valuable investments.
Financial Protection: Electronics can be expensive to repair or replace, especially high-end devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Insurance provides financial coverage against unexpected events such as accidental damage, water damage, fire, theft, or vandalism. With the right insurance policy in place, you can avoid significant out-of-pocket expenses and ensure that your electronics are promptly repaired or replaced.
Comprehensive Coverage: While manufacturers often provide limited warranties for electronic devices, these warranties may not cover all types of damages or accidents. Insurance offers more comprehensive coverage, filling the gaps left by warranties. It can protect your devices against a wide range of risks, including accidental drops, spills, screen damage, electrical failures, and even loss or theft, depending on the policy.
Peace of Mind: Knowing that your electronic devices are insured provides peace of mind, allowing you to use them with confidence without constantly worrying about potential mishaps. Whether you're traveling, working remotely, or simply using your devices at home, insurance offers reassurance that you'll be financially protected in case of any unforeseen incidents.
Replacement Value: In the event that your electronic device is damaged beyond repair or stolen, insurance policies often provide coverage for the full replacement value of the item. This means you can receive a new, equivalent device without having to bear the entire cost yourself, minimizing the impact on your finances.
Customized Policies: Insurance providers offer a variety of policies tailored to suit different needs and budgets. Whether you own a single device or a collection of electronics, you can find insurance plans that meet your specific requirements. Additionally, some policies offer flexible options such as deductible amounts and coverage limits, allowing you to customize your coverage according to your preferences.
Risk Mitigation: With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, insurance for electronics can also include coverage for identity theft, cyber extortion, and data recovery. This additional layer of protection helps mitigate the risks associated with storing sensitive information on your devices and using them for online activities.
In conclusion, insurance for electronics is essential for safeguarding your valuable investments and ensuring peace of mind in an increasingly digital world. By investing in the right insurance policy, you can protect yourself financially against unexpected events and enjoy using your electronic devices without worrying about potential risks. Whether it's your smartphone, laptop, tablet, or any other electronic gadget, insuring your devices is a wise decision that can save you from costly expenses and headaches down the line.
1 note
·
View note