Heali AI is a nutrition tech company that uses AI to analyze the compatibility of foods with personalized nutrition requirements. It should be easy to adhere to any nutrition plan. We’re creating the tools to support it.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Photo

Aloe Vera, a member of the Asphodelaceae family, is a perennial plant that grows in hot, dry climates. In ancient cultures of Greece, Egypt, Mexico, Japan, China, and India, aloe vera was used in traditional medicine as a skin treatment. Today, aloe vera is used both topically and orally to treat skin disorders, digestive issues, lower blood sugar, and more. Aloe Vera contains compounds that provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and wound-healing properties. It is high in vitamins A and C, minerals, antioxidants, enzymes, and amino acids. Aloe vera is most commonly known for its ability to relive sunburns through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms from the compounds aloesin, aloin, and emodin.* It can be found in the form of a gel, juice, or extract. Learn more about the uses of aloe vera in your @healiapp! *Sánchez, M., González-Burgos, E., Iglesias, I., & Gómez-Serranillos, M. P. (2020). Pharmacological Update Properties of Aloe Vera and its Major Active Constituents. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 25(6), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061324
0 notes
Photo

Marion Nestle is one of the most prominent writers in health and science. Nestle is a Paulette Goddard Professor of nutrition, food studies, and public health, and has a Ph.D. in molecular biology and an M.P.H. in public health nutrition. She uses her vast experience investigating scientific and socioeconomic influences on food choice, obesity, and food safety, with an emphasis on the role of the food industry influence on processed foods. While it is necessary to have a balanced dietary regime, it is also very important to ensure that there is diversity in the types of foods that we consume. Nestle advocates for the intake of natural, unprocessed foods and a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
0 notes
Photo

Tracey Grant, RDN, CWHC started school in 2010 as a chemical engineer with no intent to study nutrition. After overcoming many autoimmune and digestive issues, she spent several years researching ways to help others through a journey similar to her own. She currently does virtual work as a registered dietitian and certified wellness health coach, where she specializes in autoimmunity, digestive concerns, and weight management. Tracey is passionate about helping clients find a whole-foods based nutrient-dense diet that does not nourish the body and soul.
0 notes
Photo



Roses are not only a beautiful addition to a garden, but also an edible plant. Belonging to the family Rosaceae, some of the rose’s relatives are cherries and almonds. Historically, roses were used as herbal remedies to treat menstrual, digestive, and blood circulation disorders. While roses have been cultivated for thousands of years, ancient Romans are credited as the first to introduce them as an edible flower. Roses have high levels of phenolic compounds, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and carotenoids, which possess strong antioxidant activity. A recent study found that rose has the second highest antioxidant level among 30 medicinal plants.** The consumption of edible roses can help hydrate skin, reduce inflammation, boost immune system, enhance mood, aid digestion, and ease symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Edible roses can be found in a variety of preparations, such as teas and beverages, salads, wraps, and breads. Discover ways to incorporate roses in your @healiapp. *Vijayanchali, S. S. (2019, March 26). Nutrient, phytonutrient and antioxidant activity of the dried rose petals. **Yang, H., & Shin, Y. (2017, March 3). Antioxidant compounds and activities of edible roses (Rosa Hybrida spp.) from different cultivars grown in Korea - applied biological chemistry. SpringerOpen.
0 notes
Photo




Saffron, derived from the Crocus sativus flower, is a spice used to flavor foods, add color, and as medicine. Believed to be native to the Mediterranean, saffron was traditionally used for its medicinal properties, including boosting mood and improving memory. The production of saffron is very labor-intensive, making it the most expensive spice in the world. Saffron has an abundant variety of plant compounds, acting as a powerful antioxidant. The antioxidants in saffron have been shown to have beneficial effects on neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer and Parkinson's disease, as well as treating mild to moderate depression.** Saffron may also decrease inflammation, suppress growth of cancer cells, ease symptoms of premenstrual syndrone (PMS), AND reduce appetite. Saffron is slightly sweet and fragrant, often used in rice-based dishes, soups, and stews. Find recipes using saffron in your @healiapp. *Abedimanesh, N., Bathaie, S. Z., Abedimanesh, S., Motlagh, B., Separham, A., & Ostadrahimi, A. (2017). Saffron and crocin improved appetite, dietary intake and body composition in patients with coronary artery disease. Journal of cardiovascular and thoracic research, 9(4), 200–208. https://doi.org/10.15171/jcvtr.2017.35 **Khazdair, M. R., Boskabady, M. H., Hosseini, M., Rezaee, R., & M Tsatsakis, A. (2015). The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review. Avicenna journal of phytomedicine, 5(5), 376–391.
0 notes
Photo




Chamomile is one of the most ancient and most widely used herbs in the world. As a member of the daisy family, Asteraceae, Chamomile is known for its medicinal purposes. Chamomile was traditionally used in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome as an important medicinal herb to treat conditions such as hay fever, muscle spasms, menstrual disorders, ulcers, wounds, rheumatic pain, and more. Today, chamomile is most often used as an herbal tea to help with sleep, anxiety, and to ease gastrointestinal symptoms. Chamomile is rich in terpenoids and flavonoids, which play a significant role in its many beneficial effects. Beyond its ability to ease a variety of symptoms, studies* have shown chamomile has anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties, can improve cardiac health, and treat many gastrointestinal conditions. Chamomile tea is most well-known for its sedative effects to help improve sleep. In fact, a recent study** showed individuals who consumed chamomile extract had significant improvements in sleep quality compared to individuals not using chamomile. *Srivastava, J. K., Shankar, E., & Gupta, S. (2010). Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Molecular medicine reports, 3(6), 895–901. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2010.377 **Abdullahzadeh, M., Matourypour, P., & Naji, S. A. (2017). Investigation effect of oral chamomilla on sleep quality in elderly people in Isfahan: A randomized control trial. Journal of education and health promotion, 6, 53. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_109_15
0 notes
Photo

The use of edible flowers has rapidly evolved following the growing evidence of the health benefits of flowers used as both food and medicine. The first records of the use of edible flowers were in Ancient Greece, Rome and Egypt in 140 B.C. They were believed to be cleansing for the body and used for both medicinal and culinary purposes. Now, edible flowers are added to food to provide fragrance, flavor, and decoration. The many health benefits of flowers are derived from their rich phytochemicals. To the same degree as fruits and vegetables, phytochemicals in flowers are also responsible for their visible color and antioxidant activity. The antioxidant activity of flowers have been observed in floral tissues both before ingestion and after the digestive process, suggesting they have prolonged bioactive effects.* The wide range of phytochemicals offer many benefits to human health, especially protecting against specific pathologies. These include hypoglycemic, antimicrobial, analgesic, anti-obesity, visual health, neuroprotective, anti-bacterial, and diuretic properties.* *Benvenuti, S., & Mazzoncini, M. (1AD, January 1). The biodiversity of edible flowers: Discovering new tastes and new health benefits. Frontiers. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2020.569499/full
0 notes
Photo

Artichokes, a member of the Asteraceae or aster family, are believed to be native to the western and central Mediterranean. As a relative of lettuce and sunflower seeds, artichokes were historically used to treat treating hepatic and renal dysfunctions, as a diuretic, and for the treatment of arteriosclerosis. Although artichokes were originally used for their young leaves, they are now eaten as an immature flower head. California is responsible for nearly all artichoke production in the United States due to its Mediterranean-like climate. Artichokes are one of the richest antioxidant foods and are high in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, phosphorus, and magnesium. Artichokes are known to help regulate blood pressure through their ability to fight free radicals and influence nitric oxide production from their high antioxidant content.* Recent studies also suggest artichoke extract can help ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) due to inulin, which helps feed gut microbes. *** Artichoke is commonly used in a variety of dishes and can be steamed, boiled, grilled roasted, or sauteed. Find delicious recipes that use artichoke in your @healiapp today! *Moradi, M., Sohrabi, G., Golbidi, M., Yarmohammadi, S., Hemati, N., & Campbell, M. et al. (2021). Effects of artichoke on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies In Medicine, 57, 102668. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2021.102668 **Holtmann G, Adam B, Haag S, Collet W, Grünewald E, Windeck T. Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: a six-week placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Dec;18(11-12):1099-105. ***Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Marakis G, Booth JC. Artichoke leaf extract reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and improves the quality of life in otherwise healthy volunteers suffering from concomitant dyspepsia: a subset analysis. J Altern Complement Med. 2004 Aug;10(4):667-9.
0 notes
Photo



Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds found in plants. There are over 8,000 types of polyphenols, which are abundant in many fruits, vegetables, spices, and teas. Polyphenols can contribute to the bitterness, astringency, color, flavor, and odor found in foods. Polyphenols act as antioxidants, helping protect against damage to cells and decreasing risk of disease. Studies* have shown diets rich in polyphenols have the potential of protecting against the development of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis and neurodegenerative diseases. Foods with the highest concentration of polyphenols include berries, spices, coffee and tea, cocoa, nuts, flaxseeds, vegetables, and olives. Find many ways to boost your consumption of polyphenols through these foods in the @healiapp.
*Pandey, K. B., & Rizvi, S. I. (2009). Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2835915/
0 notes
Photo




Allicin is an organosulfur compound, which is one of the bioactive components of garlic. Allicin is responsible for the strong smell and taste of garlic, but also the many health benefits garlic provides. Allicin is often used to help ease inflammation and act as an antioxidant by blocking free radicals that cause the body harm. The allicin in garlic can help protect against diseases like cancer, cardiovascular disease, and more. Allicin remains stable for a short period of time once fresh garlic is chopped or minced, but can also be taken in powder, oil, or extract form. Find many delicious ways to use garlic in your @healiapp. * Zare E., Alirezaei A., Bakhtiyari M., Mansouri A. Evaluating the effect of garlic extract on serum inflammatory markers of peritoneal dialysis patients: A randomized double-blind clinical trial study. BMC Nephrol. 2019;20:26. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1204-6. **Lee G.Y., Lee J.J., Lee S.M. Antioxidant and anticoagulant status were improved by personalized dietary intervention based on biochemical and clinical parameters in cancer patients. Nutr. Cancer. 2015;67:1083–1092. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2015.1073754 ***Ried K. Garlic lowers blood pressure in hypertensive individuals, regulates serum cholesterol, and stimulates immunity: an updated meta-analysis and review. J Nutr. 2016;146(2):389S-396S. doi:10.3945/jn.114.202192
0 notes
Photo




Anthocyanins are a type of water-soluble pigment found in plants. Anthocyanins are responsible for the vibrant red, purple, and blue colors of fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables with high anthocyanin content include berries, currants, grapes, tropical fruits, leafy vegetables, grains, roots, and tubers. The colors provided by anthocyanins are dependent on pH, light, and temperature of their environment. They have traditionally been used as a natural food colorant, but these pigments also have many benefits. Anthocyanins belong to a class of compounds, flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties. Anthocyanins have been shown to be beneficial for the prevention of many chronic diseases including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, obesity, and more.*** *Li D, Zhang Y, Liu Y, et al. Purified anthocyanin supplementation reduces dyslipidemia, enhances antioxidant capacity, and prevents insulin resistance in diabetic patients. J Nutr. 2015;145(4):742–748 **Belwal, T., Nabavi, S. F., Nabavi, S. M., & Habtemariam, S. (2017). Dietary Anthocyanins and Insulin Resistance: When Food Becomes a Medicine. Nutrients, 9(10), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101111 ***Khoo, H. E., Azlan, A., Tang, S. T., & Lim, S. M. (2017). Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food & nutrition research, 61(1), 1361779. https://doi.org/10.1080/16546628.2017.1361779 ****Côté J, Caillet S, Doyon G, et al. Antimicrobial effect of cranberry juice and extracts. Food Cont. 2011;22(8):1413–1418
0 notes
Photo

Phytochemicals are chemical compounds produced by plants. They are found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, beans, herbs, spices, nuts, and seeds. There are many types of phytochemicals, which are categorized based on their unique chemical structures and functional properties. The action of phytochemicals is different depending on the color and type of food. For example, carotenoids, found mainly in yellow and orange fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamin A and are known to prevent growth of cancerous cells. Phytochemicals provide many health benefits including boosting immune function, reducing inflammation, regulating hormones, and protecting against disease through their antioxidant properties. They also aid in maintaining a balanced gut microbiota, which is associated with reduced risk of many chronic diseases.* Recent studies**suggest the antioxidant capacity of fruits and vegetables is related to color. The foods with stronger pigmentation were associated with higher antioxidant power. Therefore, it is recommended to consume a variety colorful fruits and vegetables to obtain an abundance of vitamins and minerals. *Zhang, Y. J., Gan, R. Y., Li, S., Zhou, Y., Li, A. N., Xu, D. P., & Li, H. B. (2015). Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 20(12), 21138–21156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219753 **Cömert, E., Mogol, B., & Gökmen, V. (2020). Relationship between color and antioxidant capacity of fruits and vegetables. Current Research In Food Science, 2, 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2019.11.001
0 notes
Photo

Ellie Krieger is a leading registered dietitian in the media today who is a strong believer that healthy and delicious can be used in the same sentence. She earned a bachelor's in clinical nutrition from Cornell University and a master's in nutrition education from Teacher’s College Columbia University. Ellie has published seven award-winning cookbooks and has since launched the television series Ellie's Real Good Food, of which she's both the host and producer.
0 notes
Photo

As a member of the pea family, Fabaceae, edamame is a soybean that is harvested when it's immature and tender green. Edamame is believed to be cultivated in central China, thriving in warm, fertile, well-drained, sandy soil. Soy products have been an important source of protein in the United States since the 1960s when they were first incorporated into cereals. Edamame is high in vitamin K and folate and is a complete protein source. Soybeans, including edamame, are rich in isoflavones, which are known to lead to a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Research has found these non-protein soy components of edamame to have beneficial effects on hypertension, hyperglycemia, inflammation, and obesity.** Edamame is most commonly steamed or boiled and eaten directly from the pod. Find different ways to use edamame in your @healiapp! * FDA Talk Paper. FDA Approves New Health Claim for Soy Protein and Coronary Heart Disease. Available at: http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~lrd/tpsoypr2.html.
**Ramdath, D. D., Padhi, E. M. T., Sarfaraz, S., Renwick, S., & Duncan, A. M. (2017, March 24). Beyond the cholesterol-lowering effect of soy protein: A review of the effects of dietary soy and its constituents on risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Nutrients.
0 notes
Photo

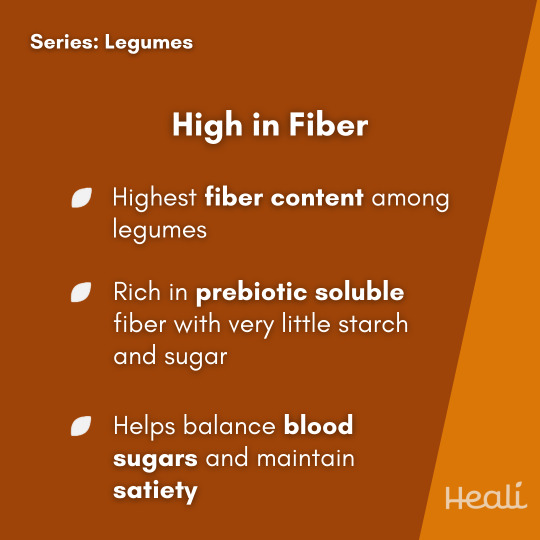


Lupin beans, also known as lupinis, are the yellow legume seeds of the Lupinus plant. Coming from the same family as chickpeas and lentils, lupins are traditionally a staple food of the Mediterranean region. Lupin beans are highly nutritious and an excellent source of plant-based protein and fiber. Compared to other legumes, lupins have the highest amounts of vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and B vitamins. Consumption of lupins have been linked to a reduced risk of many chronic diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, some cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and osteoporosis. Lupins are very versatile and can be incorporated into a variety of meals and snacks as a plant-based protein alternative. They are often found in a pickled state due to their naturally bitter taste. Find delicious ways to use lupins in your @healiapp.
0 notes
Photo



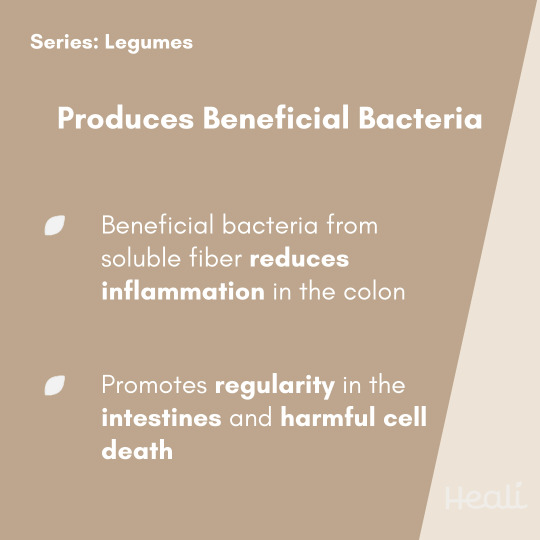
Chickpeas, commonly known as garbanzo beans, are part of the legume family. Chickpeas are a staple of many diets, with their earliest records dating back to 3500 BCE in Turkey and 6790 BCE in France. There are two main varieties of chickpeas. One is a large, round, light-colored Kabuli-type and the other is a small, dark, irregularly shaped Desi-type. Chickpeas are rich in protein, fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. The high nutritional value of chickpeas may aid in the prevention of many chronic diseases and improve overall health. Chickpeas are widely accessible in both canned and dried forms used in a variety of dishes. They have a nutty and buttery flavor often used in salads, soups, and stews or to make a hummus spread. Many unique ways to use chickpeas can be found on your @healiapp!
0 notes
Photo

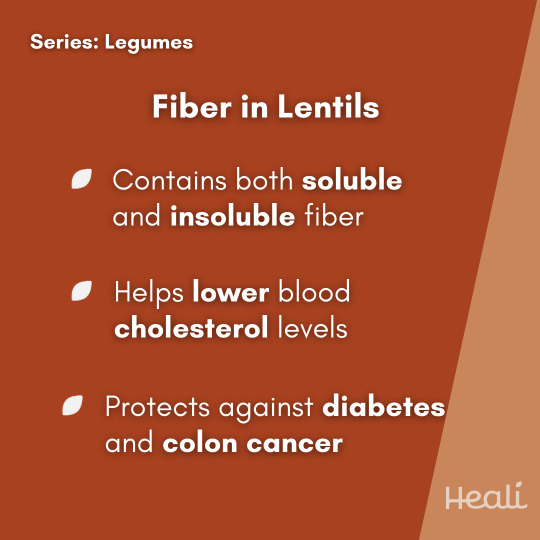


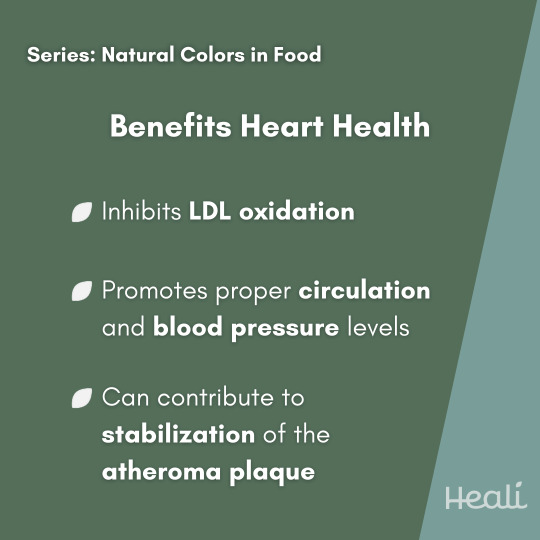
Lentils are a type of legume found in brown, green, black, and red varieties. Native to Western Asia and North America, lentils are one of the earliest domesticated crops. Along with being a plant-based source of protein, their low cost and accessibility make them a staple around the world. Lentils are an excellent source of fiber, protein, folate, iron, and potassium. These nutrients support heart health and reduce the risk of many other chronic diseases. Lentils also have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties from plant chemicals, known as polyphenols. Lentils have an earthy and nutty flavor and hearty texture that works well in a variety of recipes. Find delicious recipes with lentils in your @healiapp!
0 notes