Text


Illustrations by Gekko Hayashi (Gōjin Ishihara) x, x
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
[“Coming out was very lonely. I had very few friends. Most of the adult lesbians I knew were alcoholics, chronically unemployed, prone to violence, self-hating, apolitical, closeted, cliquish. Lesbians hated each other. If you found a lover you stopped going to the bar because you could not trust other lesbians; they would try to break up your relationship. My first woman lover went into the military, where she turned in other lesbians so she would not be exposed. One of my dyke friends got a job as a supervisor in a cabinet-making company and refused to hire lesbians because, she said, they were unreliable employees who were disliked by the other workers. The only thing that seemed worse to me than the apolitical lesbian community I came out in was the strangulation of pretending to be straight. I came out only because I could not go back; there was no place for me to stand in the het world. I was driven out.
Moving to San Francisco improved things somewhat. There was more public lesbian space there—six bars instead of one. But it did not alleviate the loathing with which my family viewed me. Nor was San Francisco in the early seventies any sort of gay utopia. We had no gay-rights law, queer bashing was a frequent event, and everyone had lost at least one job or been denied a place to live. It was a relief to be surrounded by other lesbian feminists, but only to a point. Bar dykes and feminists still had contempt for one another. Feminism rapidly became a way to reconstitute sexual prudery, to the point that it seemed to me that bar dykes were actually more accepting of and knowledgeable about the range of behavior that constituted lesbianism. In the bars or in the women’s movement, separatism was pretty much mandatory, if you didn’t want to get your ass kicked or be shunned. Separatism deteriorated into a rationalization for witch hunts in the lesbian community rather than a way for women to bond with one another and become more powerful activists. The lesbian community of that decade did terrible things to bi women, transgender people, butch/femme lesbians, bar dykes, dykes who were not antiporn, bisexual and lesbian sex workers, fag hags, and dykes who were perceived as being perverts rather than über-feminists. We were so guilty about being queer that only a rigid adherence to a puritanical party line could redeem us from the hateful stereotypes of mental illness and sexual debauchery.
What did I gain? I came a little closer to making my insides match my outsides, and that was no small blessing. The first time I met other dykes I recognized a part of myself in them, and knew I would have to let it out so I could see who I was. For a time, being a lesbian quieted my gender dysphoria because it made it possible for me to be a different kind of woman. That was an enormous relief.
For a long time, I hoped that by being strong, sexually adventurous, and sharpening my feminist consciousness, I could achieve a better fit between my body and the rest of me. Lesbianism was a platform from which I could develop a different sort of feminism, one that included a demand for sexual freedom and had room for women of all different erotic proclivities. I had a little good sex and discovered that I was not a cold person, I could love other people. It was as a lesbian that I began to find my voice as a writer, because in the early days of the women’s movement, we valued every woman’s experience. There was a powerful ethic around making it possible for every woman to speak out, to testify, to have her say. But there were always these other big pieces of my internal reality that lesbianism left no room for.
The first big piece of cognitive dissonance I had to deal with, in my second coming out, was S/M. I date my coming out as a leather dyke from two different decisions. One was a decision to write down one of my sexual fantasies, the short story that eventually became “Jessie.” At the time I wrote the rough draft of that story, I had never tied anybody up or done anything else kinky. I was terribly blocked as a writer. I kept beginning stories and poems that I would destroy. I have no idea if they were any good or not. My self-loathing was so intense, my inner critic so strong, that I could not evaluate my own work.
So I decided to write this one piece, under the condition that I never had to publish it or show it to another person. I just wanted to tell the truth about one thing. And I was badly in need of connecting with my own sexuality since I was in the middle of what would be a five-year relationship with a woman who insisted we be monogamous, but refused to have sex with me. So I wrote about dominance and submission, the things I fantasized about when I masturbated that upset me so much I became nauseated. Lightning did not strike. As I read and reread my own words, I thought some of them were beautiful. I dared show this story to a few other people. Some of them hated it. Some of them were titillated. Nobody had ever seen anything like it before. The story began to circulate in Xerox form, lesbian samizdat. I found the strength to defend my story when I was told it was unspeakable or wildly improbable.
In October of 1976, I attended a lesbian health conference in Los Angeles and went to a workshop there about S/M. In order to go to a workshop, you had to sign a registration sheet. I was harassed by dykes who were monitoring this space to see who dared sign up for that filthy workshop. On my way, I had to walk through a gauntlet of women who were booing and hissing, calling names, demanding that the workshop be canceled, threatening to storm the room and kick us all out of the conference. The body language and self-calming techniques I had learned when I had to deal with antigay harassment on the street came in very handy, but how odd it was to be using those defenses against the antagonism of other dykes. Their hatred felt like my mother’s hatred. I am so glad I did not let it stop me.
When I got home from that workshop, I knew that I was not the only one. Not only were there other lesbians who fantasized about sadomasochism, there were women who had done these things with each other. I decided to come out again. If there were other leather dykes in San Francisco, they had to be able to find me, so I had to make myself visible. This meant that I often did not get service at lesbian bars, or I was asked to leave women-only clubs and restaurants. I was called names, threatened, spit at. I got hate mail and crank calls. But I also found my tribe. And because I had already experienced my first coming out, I knew we were not going to be an ideal, happy family. I could be more patient with our dysfunctions, and see them as the result of being scared, marginalized, kicked around. Being a leather dyke took me another step closer to dealing with my gender issues. I could experiment with extreme femme and extreme butch drag; take on a male persona during sex play. I gave up separatism because I needed to take support from any place where it was available. Gay men already had a thriving leather culture, and I wanted to learn from them. I also wanted to have sex with them. It still wasn’t okay as far as lesbian feminism was concerned to be bisexual, to be transgendered, but I could bring those folks into my life and make alliances with them. I could defend them in print. There was even more good sex, and people who loved me and received my love despite the fact that it was dangerous for us to show ourselves to one another. I faced my sexual shadow, and she bowed to me and then danced beautifully in profile against the white walls of my consciousness. My writer’s voice was unlocked.”]
pat califa, from layers of the onion, spokes of the wheel, from a woman like that: lesbian and bisexual writers tell their coming out stories, 2000
772 notes
·
View notes
Text





Please keep work place safety in mind at all times
THESE ARE DRAWINGS. I DREW THESE.
111K notes
·
View notes
Text





'Bordered Lives: Transgender Portraits from Mexico' (2014) photos by Kike Arnal (x/x)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm reading a book named "A Guide to The Correction of Young Gentlemen Or, The Successful Administration Of Physical Discipline To Males, By Females" - essentially, a fantasy femdom BDSM book, written in 1924 by Alice Kerr-Sutherland but first published in 1991.
It has some genuinely fascinating stuff to say about gender, and I feel like it's worth looking at/thinking about in the context of Historical Gender Stuff. This 100 year old book has the following to say:
"The truth is that some young gentlemen would rather they had been born young ladies: they cannot admit this openly, because in the male world to confess as much would lead to instant ostracism if not worse; but they cannot conceal it either, and by preferring the company of girls, and soft, feminine clothing, and by flinching during the rough pursuits to which all boys, willing or no, are occasionally heirs, they attract opprobrium."
"Such boys weep too readily for their fellows' tastes - weeping is a great crime among boys unless it is generally admitted that circumstances left little choice - and are hounded for that reason."
"Just as there are girls who had rather been boys - we all know examples of the type - there are boys who, in a kinder world, would have been born into the gender more suited to their dispositions."
"Many young people of this sort are riven with a guilt they do not deserve but have been forced, by the conventions of society, to adopt; they are confused, ashamed and thoroughly unhappy."
"The ideal thing to do would be to treat these cases on their merits, send them to girls' schools, and so on. (The same thing should happen with those girls who would rather be young gentlemen.) Boys of this sort are girls in any case-in all respects save one."
"Most subjects of this sort have a secret name - a girl's name."
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
Vintage Homoerotic Photographs from issue 93 of kink and leather magazine Drummer by photographer George Dureau depicting different bodied men




6K notes
·
View notes
Text
[“In Magnus Hirschfeld’s The Transvestites, “Case 13” consists of letters, written in 1909, from a person known variously as Jenny, Johanna, and John, who was born in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and who later moved to the United States. Hirschfeld considered this person to be “a typical representative of the group we are concerned with.” These reminiscences are abridged from the original.
I was born in 1862. I did not want any trousers and put up such a fuss, and since my sister was one year older I could wear her clothes until Mother died in 1868. My aunts then forced me to wear boys clothing. I clearly remember that I always only wanted to be a girl, and my relatives and acquaintances would tease me.
I wanted to go to the teachers’ seminary because later, I thought, when I finished, I could go around as a governess or a children’s teacher. Even at the time I had firm plans to become a woman. When I saw that they were not going to allow me to study to be a teacher, at the first opportunity I stole from a girl who was my size. I put on her things and took her certificate of domicile and burned my boy’s things that night. Everything boyish I left behind and went to Switzerland where my relatives would not know where I was.
I first went to work as a nanny and did general housework. At the same time, I learned embroidery. I grew strong and not ugly, so that boys would lie in wait for me. At that time I felt fully a young woman, except when the fellows got fresh with me, and it would occur to me that, unfortunately, I was not one. At 16½ a man tried to rape me. I protected myself, but he gave me a bad name as being a hermaphrodite, so I had to move away and went to France. I had a friendship with a girl, who, like me, was in opposition to her sex, namely manly, and when she went to St. Quentin to the embroidery factory there, I followed her. There I had the opportunity for the first time to come together with women who with other women lived like married people.”]
susan stryker, transgender history
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
In contrast with professional drag queens, who were only playing at being women onstage, [Esther] Newton learned that the very bottom of the gay social hierarchy was the province of street queens. In almost total contrast to professional queens, street queens were "the underclass of the gay world." Although they embraced effeminacy, too, they did so in the wrong place and for the wrong reason: in public and outside of professional work. As a result, Newton explained, the street queens "are never off stage. Their way of life is collective, illegal, and immediate." Because they didn't get paid to be feminine and were locked out of even the most menial of nightlife jobs, Newton observed that their lives were perceived to revolve around "confrontation, prostitution, and drug 'highs'." Even in a gay underworld where everyone was marked as deviant, it was the sincere street queens who tried to live as women who were punished most for what was celebrated-and paid-as an act onstage. When stage queens lost their jobs, they were often socially excluded like trans women. Newton explained that when she returned to Kansas City one night during her fieldwork, she learned that two poor queens she had met had recently lost their jobs as impersonators. Since then, they had become "indistinguishable from street fairies," growing out their hair long and wearing makeup in public-even "passing" as girls in certain situations," in addition to earning a reputation for taking pills. They were now treated harshly by everyone in the local scene. Most people wouldn't even speak to them in public. Professional drag queens who didn't live as women still had to avoid being seen as too "transy" in their style and demeanor. One professional queen that Newton interviewed explained why: it was dangerous to be transy because it reinforced the stigma of effeminacy without the safety of being onstage. "I think what you do in your bed is your business," he told Newton, echoing a middle-class understanding of gay privacy, "[but] what you do on the street is everybody's business."
The first street queen who appears in Mother Camp is named Lola, a young Black trans girl who is "becoming a woman,' as they say'." Newton met Lola at her dingy Kansas City apartment, where she lived with Tiger, a young gay man, and Godiva, a somewhat more respectable queen. What made Godiva more respectable than Lola wasn't just a lack of hormonal transition. It was that Godiva could work as a female impersonator because she wasn't trying to sincerely live as a woman. Lola, on the other hand, was permanently out of work because being Black and trans made her unhireable, including in female impersonation. When Newton entered their apartment, which had virtually no furniture, she found Lola lying on "a rumpled-up mattress on the floor" and entertaining three "very rough-looking young men." These kinds of apartments, wrote Newton, "are not 'homes.' They are places to come in off the street." The extremely poor trans women who lived as street queens, like Lola, "literally live outside the law," Newton explained. Violence and assault were their everyday experiences, drugs were omnipresent, and sex work was about the only work they could do. Even if they didn't have "homes," street queens "do live in the police system."
As a result of being policed and ostracized by their own gay peers, Newton felt that street queens were "dedicated to "staying out of it" as a way of life. "From their perspective, all of respectable society seems square, distant, and hypocritical. From their 'place' at the very bottom of the moral and status structure, they are in a strategic position to experience the numerous discrepancies between the ideals of American culture and the realities." Yet, however withdrawn or strung out they were perceived to be, the street queens were hardly afraid to act. On the contrary, they were regarded by many as the bravest and most combative in the gay world. In the summer of 1966, street queens in San Francisco fought back at Compton's Cafeteria, an all-night venue popular with sex workers and other poor gay people. After management had called the police on a table that was hanging out for hours ordering nothing but coffee, an officer grabbed the arm of one street queen. As the historian Susan Stryker recounts, that queen threw her coffee in the police officer's face, "and a melee erupted." As the queens led the patrons in throwing everything on their tables at the cops-who called for backup-a full-blown riot erupted onto the street. The queens beat the police with their purses "and kicked them with their high-heeled shoes." A similar incident was documented in 1959, when drag queens fought back against the police at Cooper's Donuts in Los Angeles by throwing donuts-and punches. How many more, unrecorded, times street queens fought back is anyone's guess. The most famous event came in 1969, when street queens led the Stonewall rebellion in New York City. Newton shares in Mother Camp that she wasn't surprised to learn it was the street queens who carried Stonewall. "Street fairies," she wrote, "have nothing to lose."
Jules Gill-Peterson, A Short History of Trans Misogyny
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

Photography by Arthur Tress & David Warner in Honcho, October 1981
4K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Daniel Uzdowski by Michal Polak for Schön! Magazine
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
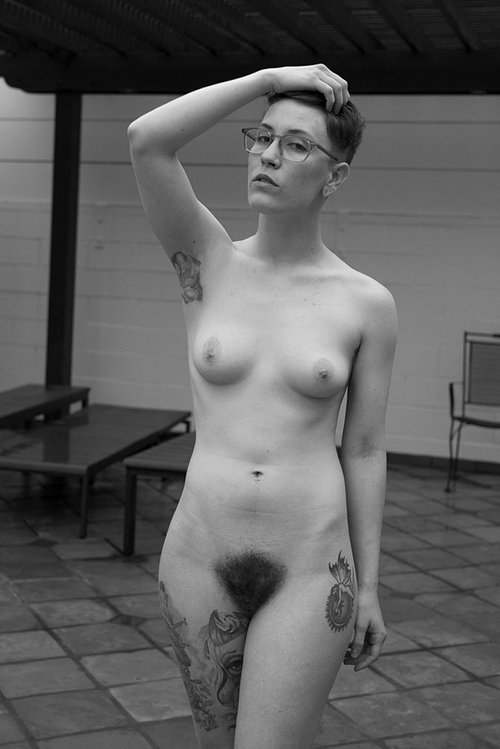
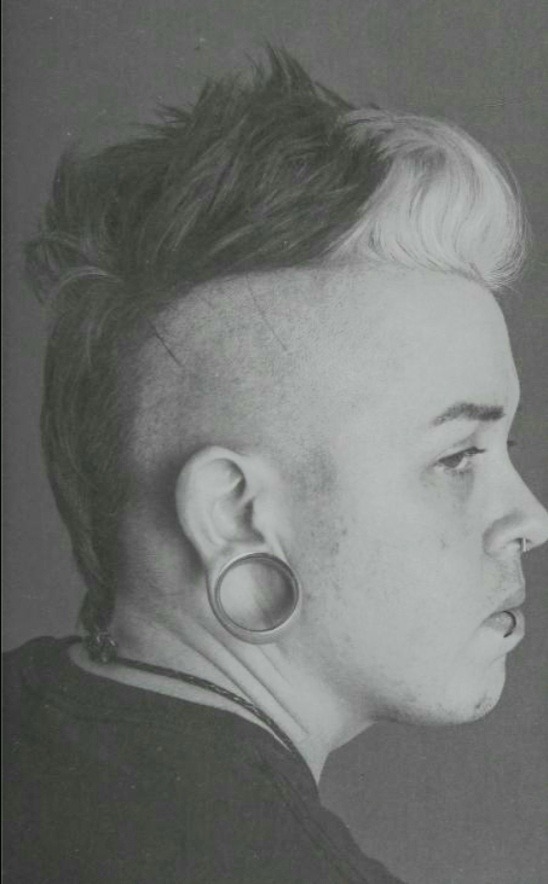
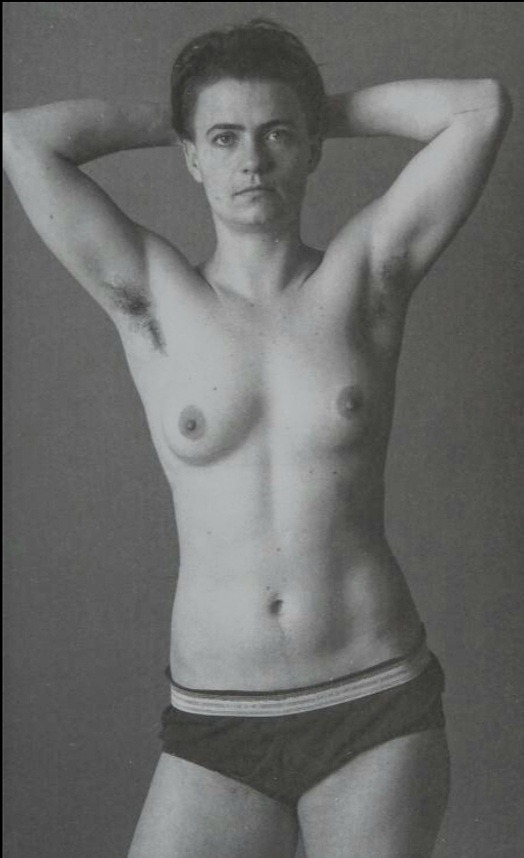
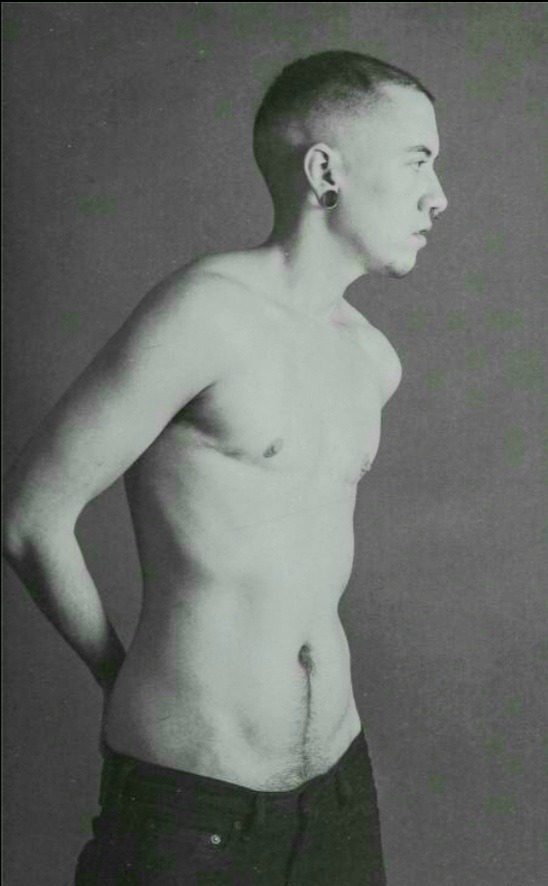










portraits from Identity: in and beyond the gender binary by Naz Dave
7K notes
·
View notes
Text





Gender Troublemakers Jeanne B/ Mirha-Soleil Ross and Xanthra Phillipa, 1993, Canada
What happens when two Transdykes get sick of non-transsexual's uninformed representation of their sexualities and their lives? They grab their 8 millimeter home video camera, their last 200 bucks, and come up with an uncompromising in-your-face flick about their shitty relationships with gay men and their unabashed attraction to other transsexual women. (watch here 18+)
468 notes
·
View notes
Photo
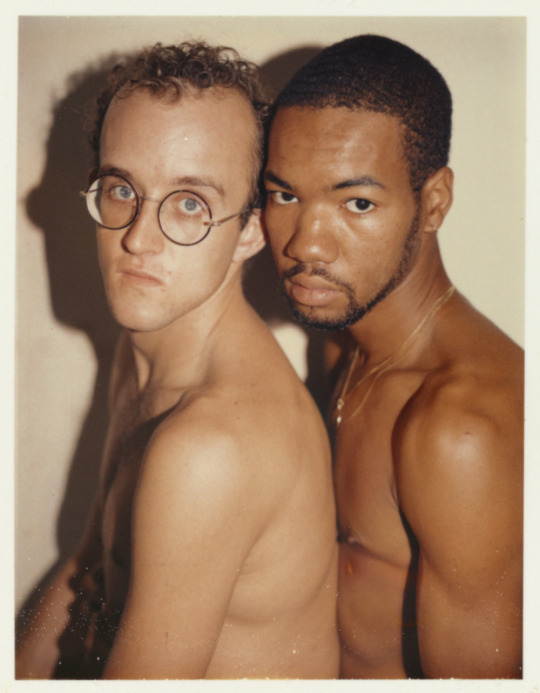
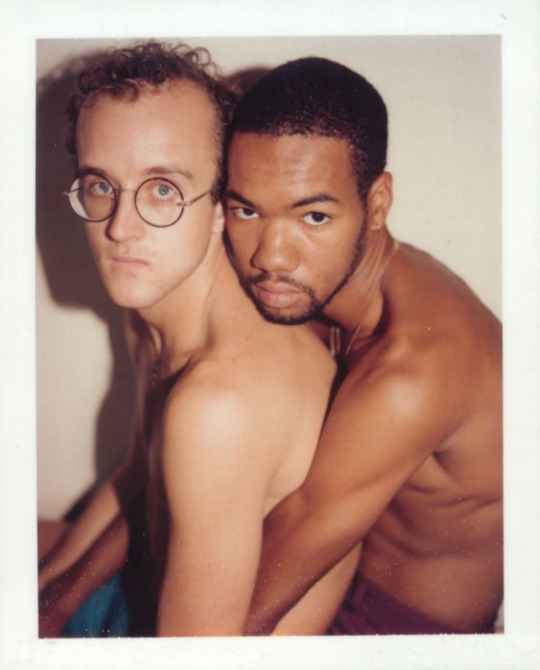
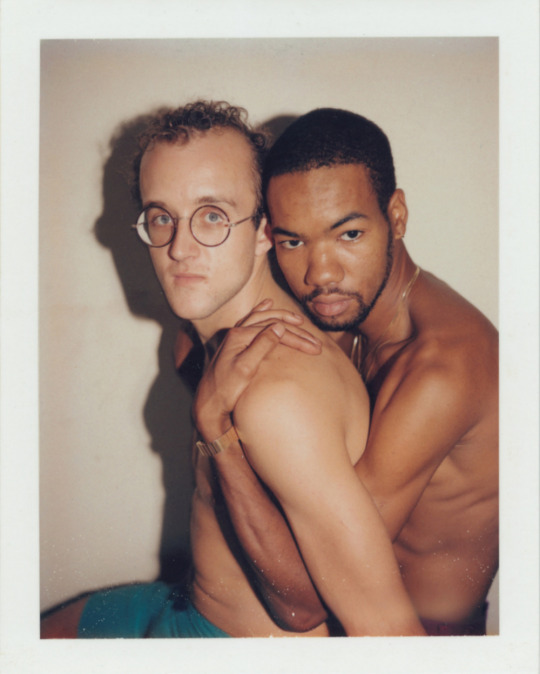
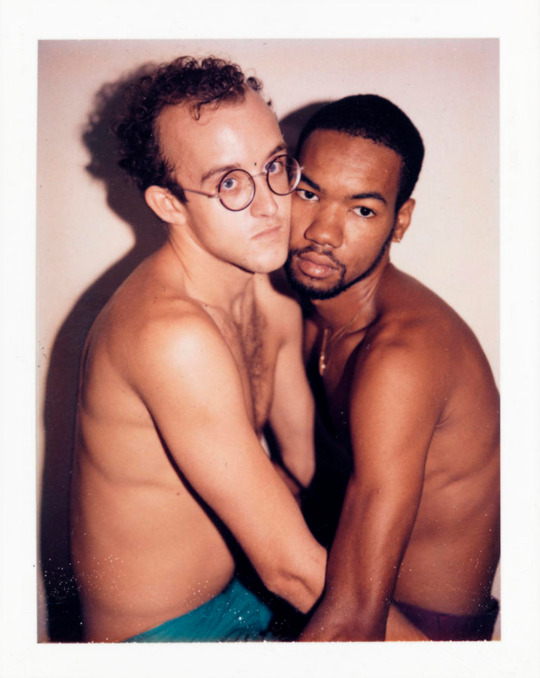
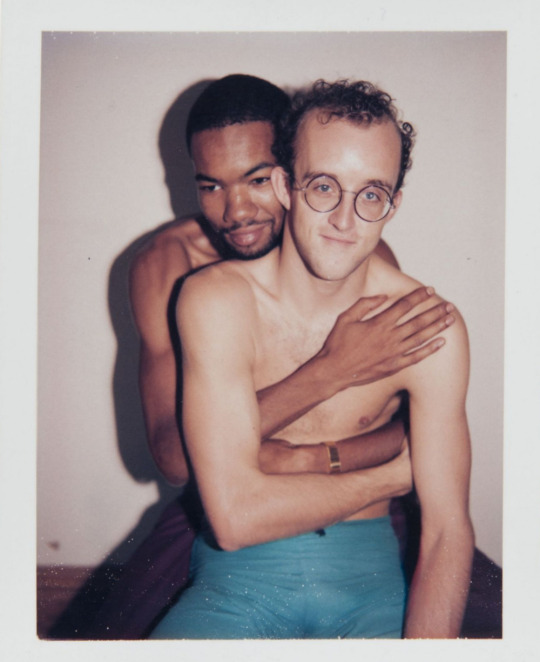
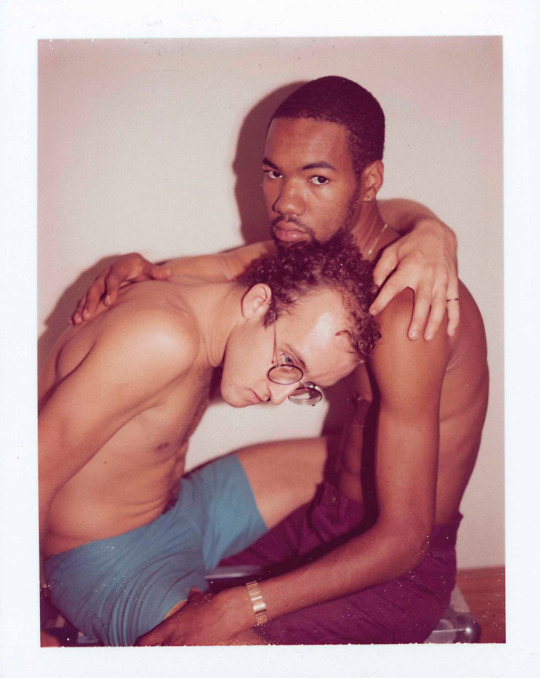






Polaroid portraits of Keith Haring and Juan Dubose taken by Andy Warhol, 1983.
1K notes
·
View notes









