Kidney C.O.P.® was developed and optimized by individuals with a wealth of experience in the pharmaceutical industry and scientific medical field. Calcium Oxalate Lab mission is committed to researching options for inhibiting the growth of calcium oxalate crystals, the most common type of crystal, and to provide a single source resource for all things calcium oxalate crystal related. Order Kidney C.O.P.® Supplement on Online Now : https://kidneycop.com/
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
What's Causing Your Recurring Kidney Stones?

Kidney stones are a common, painful disorder affecting many people worldwide. However, knowing what causes recurrent kidney stones may be critical for protecting and treating kidney stones and general health. This article discusses a wide range of causes of recurring kidney stones. It also explains the importance of a diet for kidney stones, which might allow people to manage and prevent this distressing issue in life.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt aggregates in the kidneys. They can range in size from the size of sand to that of a golf ball. They are quite painful and miserable when passing through the urinary tract. These often happen for various reasons, such as diet, hydration level, and genetic predisposition.
Causes of Kidney Stones
The causes of kidney stones can be multifaceted, but usually, they combine dietary choices, dehydration, and probably genetic factors. What triggers the most variety of those stones is dehydration as it produces more concentrated urine, carrying more minerals and salts concentrated to facilitate the development of kidney stones. Some dietary factors also increase the chances of stone formation- such as high sodium intake or excessive consumption of oxalate-rich foods.
Diet's Role on the Formation of Kidney Stones
Diet plays a key role in forming kidney stones, especially with foods with higher risks than others. Foods that are high in animal proteins increase uric acid levels, which might lead to the production of uric acid stones. Large quantities of sodium lead to more calcium excretion in urine, increasing the possibility of causing calcium stone development. Therefore, knowing the connection between kidney stone diet forms an essential framework for prevention.
Also Read: 9 Foods That Increase the Risk of Oxalate Stones
Genetic Factors and Kidney Stone Formation
Diet and hydration are major factors in developing a kidney stone, but hereditary factors should not be ignored. Some have a family tendency to develop kidneys, which means that the frequency of their kidney stones will always be high, regardless of diet or hydration. That understanding is important in preventive measures, such as regular check-ups and urine composition monitoring.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Recurring Kidney Stones
Some lifestyle changes can also prevent the formation of kidney stones. Maintaining a fit body and ideal weight through regular physical activity could help maintain health and reduce the risk of such kidney stones. Further, avoiding excessive intake of caffeine and alcohol stimulates healthy kidneys. A person can highly avoid kidney stones just by adopting a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of recurring kidney stones is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Focusing on a kidney stone diet, keeping yourself hydrated, and doing what must be done to change lifestyles significantly reduce the risk so people do not experience this painful condition. Therefore, taking active steps to improve kidney health can guarantee a better quality of life.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Manage Kidney Stones: How Diet and Nutrition Can Help

Kidney stones are a fairly common medical condition in the population of any part of the world and are usually quite a painful experience too. Those are the hard mineral deposits that develop in the kidneys, and if not treated, they may cause severe pain and discomfort and lead to complications.
The following article will examine the various types of kidney stone diet, the types of dietary habits recommended against, and the best everyday eating plans.
Classification of Kidney Stones
Different types of kidney stones and each has its features and causes which are distinct :
Stones Made of Calcium: Almost 80% of all cases with kidney stones and by far the most common are calcium stones. These can also occur due to high calcium or other mineral levels in the urine in the metabolic processing and excretion of such materials from the body.
Stones made of Uric Acid: Uric acid stones come next; they are approximately 10-15% of kidney stones. These emerge as a result of excessive uric acid concentration in the urine which most often relates to dietary, genetic, or other ailments that cause an increase in uric acid levels.
Cystinuria Spheres or Stone: The cases of cystine stones are quite unusual, covering only 1% of kidney stone ailments.
Managing and Treating Kidney Stones Through Controlled Diet
If one wishes to treat and/or avoid kidney stone recurrence, knowing what foods and drinks can favor their development is essential. The following are some of the kidney stone diet categories of food.
Soaked Foods High in Oxalate: It is common knowledge that food items with increased oxalate levels such as spinach, beets, rhubarb, and almonds contribute to the risk of developing more calcium oxalate stones which are the most common type of kidney stones.
High Salt Foods: A diet with excess sodium shows high levels of calcium in urine which may promote the formation of calcium stones.
Soda and Other Sugar-laden Beverages: Ingesting excessive amounts of sugar-containing beverages like soda, fruit juices, and the like tends to create conditions that favor the formation of kidney stones by distorting the mineral and pH balance in the body.
Dietary Strategies for Kidney Stone Prevention
There are minor changes to the meal planning and to the specification of the subsequent aspects, which foods to avoid with kidney stones management:
Enhance Fluid Consumption: One should take at least 2-3 liters of water per day. It aids in reducing the concentration of their urine thereby allowing for the removal of any excess minerals or other matter that could lead to the formation of stones in the body.
Eat More Calcium-Rich Foods: It is a common myth that consuming calcium-rich food-dairy products, for example- increases the chances of developing kidney stones.
Incorporate Magnesium-Rich Foods: Some foods with high magnesium content such as whole grain cereals, nuts, and green enough vegetables can inhibit kidney stones from forming by regulating the calcium and oxalate concentration in the urine.
Also Read: Dietary Changes That May Help Prevent the Recurrence of Kidney Stones
Conclusion
No doubt that kidney stones can be quite both disturbing and distressing. But you can easily cope with and even prevent their occurrence thanks to the right dietary and nutritional modifications. You can take charge of your urinary health management by knowing the different forms of kidney stones, avoiding the foods and drinks that are known to cause their formation, and eating a well-rounded, kidney-friendly diet to lower the risks of such painful stones.
0 notes
Text
The 4 Top Vitamins for Kidney Health

Our kidneys work hard daily, filtering waste from our blood to keep our whole body healthy. Taking care of our kidney health is important for overall wellness. Certain vitamins can help support kidney function when obtained through a balanced diet or supplements. This article will discuss four key Kidney stone vitamins - Vitamin D, Vitamin B9, Vitamin B12, and Iron.
Vitamins for Kidney Health
By including these kidney health vitamins in your regular diet, you may be able to preserve the health of your kidneys and prevent the development of consequences from chronic renal disease.
Also Read: What to Know About Taking Kidney Supplements
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in absorbing calcium from food and keeping bones and teeth strong and healthy. It is also crucial for kidney health as the kidneys activate Vitamin D. Not getting enough Vitamin D can cause calcium levels to become irregular, which has been linked to an increased risk of developing kidney stones. Good sources of Vitamin D include fatty fish like salmon and tuna, cheese, egg yolks, and mushrooms.
Vitamin B9
Also known as folate or folic acid, Vitamin B9 is important for forming new cells and genetic material. It works closely with Vitamin B12 for these vital functions in the body. In some studies, low levels of Vitamin B9 have been associated with a higher risk of kidney disease. Good food sources include spinach, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, legumes, and fortified grains.
Vitamin B12
This important B vitamin helps produce red blood cells, aids in fatty acid synthesis and is crucial for energy production in cells. Anaemia from Vitamin B12 deficiency puts extra strain on the kidneys to cleanse the blood and maintain fluid balance. Quality sources are various seafood, meat, eggs, and dairy.
Iron
As a key component of hemoglobin in red blood cells, iron carries oxygen throughout the body and removes waste. Too little iron can lead to anemia, overworking the kidneys' filtration processes to maintain blood health and volume. Good dietary iron sources are red meat, poultry, fish, spinach, and beans. Menstruating women, especially, may benefit from an 18mg supplemental iron dose per day along with kidney-supportive nutrients.
Types of Kidney Stones
The four primary types of kidney stones are calcium oxalate, struvite, urate, and cystine. Calcium oxalate accounts for about 80 percent of cases and forms when oxalate and calcium levels in urine become too concentrated. Struvite stones signal a urinary tract infection. Uric acid stones form in those prone to high uric acid in the urine, like gout sufferers. Rare cystine stones form if a genetic disorder causes high cystine levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin D, B9, B12, and Iron through diet and supplementation can help in kidney stone treatment by aiding blood filtration, fluid regulation, and waste removal. Individual nutrient requirements vary, so consulting a physician can help determine what levels are most appropriate for each person's needs and risk factors to promote kidney health. Small lifestyle changes with nutritional support make a difference.
0 notes
Text
Are Kidney Stones Common in Teenagers?

Kidney stones, which refer to hard mineral deposits that form inside kidneys, are becoming more prevalent in teenagers even though they were traditionally considered an ailment majorly affecting adults. This article aims to explore if teenagers are indeed at a higher risk of developing kidney stones and the various causes and types of stones seen among this age group.
Types of Kidney Stones
The two most common types of kidney stones seen in teenagers are calcium oxalate stones and struvite stones. Calcium oxalate stones form when the urine contains higher amounts of calcium and oxalate. They constitute approximately 80% of total kidney stones. Struvite stones occur due to urinary tract infections caused by urea-splitting bacteria. These bacteria convert urea to struvite crystals in the kidneys.
Causes of Kidney Stones Among Teenagers
Some of the main reasons for the rising prevalence of stones in teenagers include dehydration, nutritional deficiencies, overweight or obese body mass index, certain medical conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, and frequent consumption of foods high in oxalates, sodium, and animal protein without sufficient water intake daily leading to highly concentrated urine.
Calcium Oxalate Stones
Calcium oxalate stones are the most prevalent type seen in teenagers and adults. These stones form when the urine contains higher levels of calcium and oxalate allowing their mutual precipitation. Major causes contributing to their formation include low fluid intake resulting in highly concentrated urine, high dietary intake of oxalate-rich foods like spinach, and rhubarb without sufficient calcium intake, and medical conditions causing calcium malabsorption. Obesity is another emerging risk factor for calcium oxalate stone formation.
Prevention of Kidney Stones in Teenagers
Some effective kidney stone prevention tips teenagers can adopt to lower their risk of kidney stone formation include adequate hydration by drinking enough water and fluids every day, maintaining a healthy weight by regular exercise and a balanced diet, limiting consumption of high oxalate foods, choosing low oxalate vegetables, having dairy products as a good source of calcium and monitoring salt, animal protein, and supplement intake under medical guidance.
Are Kidney Stones Becoming Prevalent in Teenagers?
According to various recent epidemiological studies, the incidence of kidney stone formation has been steadily rising among teenagers over the past few decades parallel to increasing rates of childhood obesity.
Although the exact reasons are not fully understood, lifestyle changes including low physical activity levels, increased screen time, frequent consumption of processed foods high in refined carbohydrates and salt coupled with lower water and calcium intakes attributed to the obesity epidemic are considered major contributors towards the higher prevalence seen now compared to past generations.
Also Read: Kidney Stones in Children and Teens: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Conclusion
Though previously considered a disease of adults, kidney stones are no longer uncommon in teenagers owing to changing dietary patterns and lifestyles. Adopting simple everyday preventive measures particularly adequate hydration through water can go a long way in lowering the rising risk. Seeking medical attention promptly for early diagnosis and management of stones is also important.
0 notes
Text
Natural Supplements For Kidney Stones

Kidney stones are a painful condition that affects millions worldwide. While prescription medication is often used to treat and prevent stones, natural supplements can also provide relief. This article will explore some of the best herbal and dietary supplements for different types of kidney stones like calcium oxalate stones. Read on to learn natural ways to keep your kidneys stone-free and pain-free.
Best Supplements for Calcium Oxalate Stones
Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type, forming when too much calcium and oxalate collect in the urine. Best supplements for calcium oxalate stones for preventing and treating stones:
Citrus Fruits and Juices
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are good sources of citrate, which attaches to calcium in the urine to help prevent stones from forming. Drink fresh citrus juices as part of a well-hydrated diet. The citrate can help dissolve small calcium oxalate crystals before they get bigger. Citrus fruits make for a tasty supplement.
Water is key for flushing out stones
Most experts recommend drinking at least ten 8-ounce glasses daily to steadily dilute and wash out the urine. For those with a history of stones, an even higher fluid intake of 12–14 glasses may be advisable. Being well hydrated promotes urinary output of around 2 litres each day which reduces the likelihood of crystal/stone formation. Even increasing water by just 1–2 glasses extra can slash risk significantly.
Magnesium is an unsung hero
Taking a magnesium supplement may help reduce the risk of recurrent calcium oxalate stones by competing with calcium absorption in the gut and increasing citrate levels in the urine. Magnesium is also needed to metabolize and flush out oxalate from the body. Opt for a chelated form like magnesium glycinate for maximum absorption.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, assists the liver in producing citrate to bind with calcium in the urine and reduce stone risks. A daily 25–50 mg supplement provides the recommended amount. B6 is non-toxic even at higher doses. Combined with citrus and magnesium, B6 supports urinary properties that hinder stone growth.
Also Read: Are Carrots and Cilantro Good for Your Kidneys?
Kidney Stone Treatment and Prevention
Natural kidney stone treatment focuses on dissolving any existing stones while long-term prevention maintains a stone-free state. Here are some top supplements:
Dandelion Leaf
Studies show dandelion leaf extract helps treat and prevent calcium kidney stones. The bitters stimulate bile flow and liver function to promote healthy digestion and metabolism. The potassium content balances sodium levels while diuretic properties flush out minerals through urine. It’s a gentle yet effective herbal remedy.
Plant Silica
Colloidal plant silica from horsetail and bamboo contains beneficial silicic acid to strengthen connective tissues in the kidneys and throughout the body. Some research indicates silica may also inhibit stone formation by binding excess minerals in urine before crystal buildup. It supports overall kidney and urinary tract health.
Oxalate-Blocking Probiotics
Certain probiotic strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum help break down and eliminate oxalate in the gut before it’s absorbed. This reduces urinary oxalate levels linked to stone risk. Look for broad-spectrum probiotic supplements, or dietary sources of active cultures like yogurt, kimchi, and kefir.
Conclusion
Approaches towards kidney stone prevention and treatment have been shown to be very effective because they include dietary modifications along with enough amounts of water intake and the use of natural supplements based on the type of kidney stones. Compounds such as water, magnesium, lemon balm, citrus fruits, probiotics, and vitamin B6 are able to adjust the concentration of minerals that promote the formation of stones in the body.
Are recurring kidney stones stressing your body and budget? Kidney COP tailors organic supplement packs to your individual biochemistry, giving your kidneys the daily backup they deserve. Our dedicated advisors make kidney health attainable — inquire now to rid yourself of stones safely and for good.
0 notes
Text
Surprising Facts About Kidney Stones
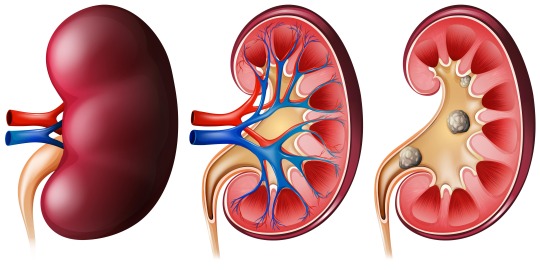
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form inside the kidneys. These tiny crystals can be very painful when they move through the urinary tract. There are many facts about kidney stones that may come as a surprise to people who have never suffered from this painful condition. Here are some of the more intriguing and unexpected truths about kidney stones.
Types of Kidney Stones and Their Causes
The two most common types of kidney stones are calcium oxalate stones and struvite stones. Calcium oxalate stones account for approximately 75% of all kidney stones and form when the urine contains too much calcium and oxalate.
Struvite stones compose about 10-15% of kidney stones and are usually caused by a urinary tract infection. They develop due to high levels of magnesium, phosphate, and ammonium in the urine. Rarer types include cystine stones from a genetic disorder and uric acid stones from high urate levels.
Kidney Stone Treatment Options
Kidney stones were once managed simply by providing pain relief and trying to pass them naturally. However, multiple kidney stone treatment alternatives are now available. Small stones under 5mm have a good chance of passing on their own with medication assistance. Larger stones may require lithotripsy, which uses shock wave therapy to break up the stone into smaller fragments for easier passage.
Surprising Facts about Calcium Oxalate Stones
There is more than one type of stone: Calcium oxalate stone is the most common, but others include uric acid, struvite, and cystine, which have different compositions and causes.
Kidney stones can be almost any color: Depending on their mineral composition and the presence of molecules like magnesium, they may appear brown, tan, white, grey, or even bright orange.
Kidney stones can be many different sizes: They range from as small as a grain of sand to larger sizes over 1cm. Most pass on their own if under 5mm, but larger ones require external procedures.
Certain foods can cause stones but not calcium: High animal protein, sodium, vitamin C, coffee, and cola foods may promote stone formation by acidifying urine, albeit calcium intake alone does not cause them.
Water can stave off stones: Drinking fluids helps dilute substances in the urine to prevent supersaturation and reduce risk as dehydration increases concentrations.
Kidney stones are more common in summer and hotter climates: Higher fluid losses through sweating in heat stress the kidneys more, requiring increased fluid intake to compensate and avoid concentrated urine.
Once you have one stone, you’re more likely to have another: Existing stones may suggest an underlying issue increasing long-term risk, like gut absorption problems, that medical management aims to address for recurrence prevention.
Also Read: Calcium Oxalate Stones: Major Symptoms and Signs
Conclusion
Calcium oxalate stones are an extremely common condition affecting up to 1 in 11 people at some point in their lives. While they can cause severe pain, most cases are not life-threatening and many stones can be treated non-invasively. Small modifications to diet and fluid intake along with medication in selected cases can help prevent recurrences.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Whole Diet Approach To Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stone Prevention

Calcium oxalate kidney stones affect many people around the world and can cause chronic pain. While medication and other medical treatments can help dissolve stones once formed, preventing new ones from forming in the first place is ideal. Lifestyle and Calcium oxalate stone diet changes play a major role in stone prevention. This article discusses a whole diet approach focusing on balancing calcium and oxalate intake to help reduce the risk of calcium oxalate kidney stones.
Knowledge About Calcium Oxalate Stones
Kidney stones that contain calcium oxalate are among the most typical types. Researching the factors that contribute to their creation in the urinary system will help us better understand their development and prevention of kidney stones and treatment.
Calcium oxalate stones form when levels of calcium and oxalate in urine become supersaturated. Both oxalate and calcium are normal constituents in urine, but excreting too much of either one can cause them to bind together and crystallize as stones.
Calcium Oxalate Diet for Kidney Stones
The goal of a Calcium oxalate diet for kidney stones is to lower oxalate, sodium, and calcium intake while keeping yourself hydrated and consuming foods that stop stone formation from happening. For example, it is advisable to avoid excessive diets in order to effect long-lasting changes. Some modifications can be made such as:
Reducing oxalate-rich foods like spinach, rhubarb, and beetroot in amounts exceeding 1/2 cup per day.
Choosing calcium sources wisely by prioritizing dairy alternative calcium sources like salmon on most days.
Limiting processed foods to no more than 2300 mg of sodium each day.
Consuming 10–12 glasses of water a day to help urine rid itself of substances that can cause stones.
Kidney Stones Prevention Using Appropriate Substitutions
Making simple food swaps with oxalate-rich alternatives can help manage calcium oxalate levels.
For example, substituting 1–2 servings of rice, millet, or quinoa per week instead of pasta reduces excessive oxalates. Replacing spinach in salads with greens like mixed lettuce lowers oxalate intake sufficiently.
Including 1–2 servings of calcium alternative foods like sardines and broccoli per day prevents calcium overload. Balancing urine pH with citrus fruits also encourages stone prevention.
Also Read: 5 Foods to Help Reduce Kidney Stones
Role of Fluid Intake in Calcium Oxalate Stone Prevention
Drinking adequate fluids is crucial for calcium oxalate stone prevention. Urine dilution helps keep stone-forming components like calcium and oxalate in solution rather than precipitating as crystals. Recent research recommends a higher daily fluid intake of closer to 2–2.5 liters for stone formers.
Addressing Nutrient Deficiencies in Calcium Oxalate Diet
Balanced nutrition addressing deficiencies in stone-inhibiting nutrients supports an oxalate diet. Food sources of magnesium like nuts and seeds consumed 2–3 times weekly reduce recurrence. Similarly, eating citrus fruits supplying vitamin C twice a week prevents the crystallization of calcium oxalate. Ensuring adequate fluid intake with Calcium oxalate stones diet plan boosts the efficacy of stone-preventing nutrients in urine.
Conclusion
Preventing calcium oxalate kidney stones can be achieved by a sustainable lifestyle that emphasizes moderation of oxalate, calcium, and sodium while increasing food and fluid consumption. This can be achieved by using a smart oxalate diet strategy. Regularly sticking to this well-rounded, holistic schedule can reduce the chance of recurrence with little disturbance to lifestyle. A long-term, healthy kidney stone prevention and treatment regimen is reinforced by proper compliance and routine monitoring.
0 notes
Text
What To Know About Kidney Stones In Women?

In today’s generation, one of the most common medical conditions increasing among humans is kidney stones. However, women are more likely to experience these kidney stones than men, especially during the time of childbearing. In this blog, we are going to explore how to manage these kidney stones in women effectively. Let’s begin!
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are tiny, solid mineral deposits in the kidneys caused by an excess of certain types of minerals in the urine. These minerals may also include oxalate, calcium, and uric acid. However, when they accumulate they may lead to the formation of a stone which can result in intense pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The kidney stones symptoms in women are completely dependent on the location and size of the stone. To get a better understanding of common symptoms, here are a few mentioned below:-
Intense pain in the side or lower back, just below the ribs
Nausea and vomiting
Frequent urination
Burning sensation while urinating
Blood in the urine
Also Read: What Foods Should You Avoid Eating If You Have Kidney Stones?
Causes of Kidney Stones
There are many reasons why a woman can face kidney stones in their body. these reasons may include:-
Genetics: Women, who have kidney stone issues and family history are most likely to develop stones.
Diet: Consuming high animal protein, sodium, and sugar can have a great negative impact on the kidneys, leading to stone formation.
Dehydration: Water plays a crucial role in flushing toxic materials from the urine. Not drinking enough water may cause the formation of kidney stones.
Medical conditions: Many medical conditions, such as kidney disease or gout, can increase the risks of kidney stone development.
Also Read: Why Are Men More Predisposed to Kidney Stones?
Preventing Kidney Stones in Women
Depending on the size of kidney stones, there are a few ways in which women can get kidney stone treatment without surgery.
Drinking plenty of water: Keeping a daily goal of 8–10 glasses of water can help in diluting the concentration of minerals in your urine.
Eating a healthy diet: Avoiding consumption of highly risked foods and consuming a balanced diet can significantly prevent kidney stones.
Considering supplements: Intake of a few supplements such as potassium citrate and calcium citrate can be the best way to pass a kidney stone. Some reliable formulas can be helpful for the prevention of calcium oxalate stone formation.
Conclusion
Kidney stones are a common and painful medical condition that can affect women. Regardless of gender and age, these issues can affect any person and could cause long-term concerns. By understanding the kidney stones symptoms in women, their causes, and treatment options it can be easily treated among women.
0 notes
Text
4 Types of Kidney Stones and Their Treatment

As per recent research, it has been proved that males are more at risk of facing kidney stones than women. 11% of males face kidney stones, on the other hand, only 9% of females go through this issue. It’s crucial to understand the different types of kidney stones that could badly affect your body condition. These kidney stones can cause severe pain and discomfort. When you can recognize them, you can easily find effective ways to manage and prevent them. In this blog, we are going to cover all 4 types and the best way to get rid of kidney stones.
4 Types of Kidney Stones
1. Calcium Stones
The most common type of kidney stones that are faced is calcium stones. Almost 70–80% of kidney stones are calcium stones, which may also include calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate stones. High levels of calcium in the urine could be caused due to many dietary factors and metabolic disorders that lead to these calcium stones. Maintain the intake of dietary calcium and avoid foods such as spinach, nuts, and tea that contain high-oxalate content.
Treatment
Increasing fluid intake can eventually dislodge the stone. It is also crucial to take medications to prevent any kind of stone from forming. Utilizing shock wave lithotripsy could be highly beneficial for breaking down stones into smaller pieces. If you are thinking of how to prevent kidney stones or calcium stones, then you might limit yourself to sodium and animal protein.
Read More: Calcium Oxalate Stones: Major Symptoms and Signs
2. Uric Acid Stones
When your urine becomes too acidic, your kidney starts to form uric acid stones. Almost 5%-10% of kidney stones are uric acid stones. It may occur due to excessive intake of a high-protein diet, dehydration, or medical conditions. Kidney stones treatment is possible if you are ready to follow a few measures.
Treatment
Prevent kidney stones of these types by keeping yourself well-hydrated and limited to high-protein foods. To stop uric acidic stones, it’s crucial to increase the intake of fluids. Allopurinol may also be helpful to reduce the uric acid level effectively. Ensure you are monitoring your urine PH, to keep yourself updated about your body hydration level.
3. Struvite Stones
Struvite stones are not much common kidney stones. They occur due to urinary tract infection (UTI). Around 10–15% of kidney stones are formed due to this infection. When there are bacteria present in the urinary system, it ends up producing ammonia, which leads to these stones formation.
Treatment
The best way to get rid of kidney stones like struvite stones lies in antibiotics. If required percutaneous nephrolithotomy is used to remove large stones. To prevent issues related to your urinary tract, it is really important to manage it. Try to keep yourself hygienic and hydrated to avoid risks of infection.
4. Cystine Stones
One of the rarest kidney stones that are formed are cystine stones. Only 1–2% of kidney stones are cystine stones. However, these can be the result of a genetic disorder also known as cystinuria. When amino acid has been leaked into the urine, it starts the formation of these types of stones.
Treatment
Every kidney stone treatment lies in fluids, especially water. It helps in diluting the urine and reducing the cysteine concentration. It is crucial to consult with the right doctors who provide the medication to improve the urinary tract. Reducing salt and protein intake also makes a great impact on your stones prevention and treatment efforts.
Read More: Dietary Changes That May Help Prevent the Recurrence of Kidney Stones
Conclusion
By understanding different types of kidney stones, you can find the best way to treat them. Consulting with a reputable health care center could eventually help in reducing the risk of developing kidney stones. Remember, kidney stones prevention and treatment is completely in your hands, manage your kidney health by taking the right advice.
0 notes