Text
Test Post from NTA UGC NET PAPER 1
Test Post from NTA UGC NET PAPER 1 https://ugcnetpaper1.com
0 notes
Text
UGC NET Admit Card : 2022 Exam Date, Hall Ticket Out, Exam Schedule
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/ugc-net-admit-card-2022-exam-date-hall-ticket-out-exam-schedule/
UGC NET Admit Card : 2022 Exam Date, Hall Ticket Out, Exam Schedule
Latest Update :
UGC NET 2022 Exam Dates have been released for the Phase III exam.
Admit Card has been released on 17th September 2022 for Phase II exam to be held on 20th To 22nd Sep 2022. Examination City Slip was released on 13th September 2022.
University Grants Commission National Eligibility Test (UGC NET) is a national-level eligibility test conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) twice a year.
The test will be conducted for determining the eligibility of candidates for the post of ‘Assistant Professor’ and ‘Junior Research Fellowship and Assistant Professor in Indian universities and colleges. Through this article, we will provide complete information along with authentic updates on the UGC NET 2022.
UGC NET Admit Card 2022 out Direct Links
UGC Net Admit card has been released
UGC Net Admit card 2022 has been released by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for every successfully registered candidate individually through online mode. Candidates can download their UGC Net 2022 Admit Card from 16th September 2022 for the Phase II exam.
Advance Intimation for Allotment of Examination City of UGC NET December 2021 & June 2022 (merged Cycles)-Phase II for the exam to be held on 23 September 2022
Download
Subject-wise Schedule of UGC NET December 2021 and June 2022 (merged cycles) Phase-III and release of Admit Card for the exam to be held on 20, 21 & 22 September 2022
Download
0 notes
Text
UGC NET PAPER 1 Question 2021 With Solutions
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/ugc-net-paper-1-question-2021-with-solutions/
UGC NET PAPER 1 Question 2021 With Solutions
UGC-NET is an exam directed by the National Testing Agency, twice a year, However, due to an unsolicited pandemic, it was accomplished once a year for two consecutive years i.e 2020 and 2021. The students, as well as teachers, glimpsed a significant hike in the level of questions asked by UGC-NET. They are undoubtedly in demand of students who comprehend every concept and can manage pressure within a restricted time frame. My friends, trust me gone are the days when you can clear the UGC net exam just by stuffing a few concepts. Now UGC-NET wants you to understand each idea so that only the well-deserved can qualify.
Question#1- What is the name of the score the student would get if the measurements were completely accurate and error‐free?
I‐score
Neutral score
True score
Z‐score
Correct Answer: ‐ I‐score Explanation- This question is taken from the teaching and the aptitude chapter. The teacher evaluated the performance of the students by different means and different criteria. The name of the score the student would get if the measurements were completely accurate and error‐free is I‐score
Question#2- “Contagious” spreading of behaviours through imitation, is known as
Random effect
Ripple effect
Scripted effect
Norm effect
Correct Answer: ‐ Random effect Behavioural contagious is a form of social contagion which spreads through the group. More prevalent in the young age group. In this, a person tries to imitate another person either his ideal or some socially famous personality like a hero or cricketer. It results in losing their own identity.
Question#3 – Given below are two statements
Statement I: In all interactions, a message is sent and a message is received. Sometimes teachers believe they are sending one message, but their voices, body language, choice of words, and gestures may communicate a different message.
Statement II: To deal with cyberbullying, parents should be encouraged to keep computers in a public room in the house.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Question #4 – Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ IV, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
2. A ‐ I, B ‐ II, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
3. A ‐ II, B ‐ III, C ‐ IV, D ‐ I
4. A ‐ III, B ‐ IV, C ‐ I, D ‐ II
Correct Answer:‐ A-IV, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
Question#5- Which among the following are components of decision traps to illustrate what needs to be a possible evaluatory framework to monitor the learning process?
A. Overconfidence
B. Coaching
C. Frame blindness
D. Taking shortcuts
E. Persistent misconception
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, C and D only
2. A, D and E only
3. B, D and E only
4. B, C and D only
Correct Answer:‐ A, C and D only Explanation- As we all know learning is not a one-night process. It takes time to learn and it has its own speed. It also varies from person to person. Some students perceive in a very short term and other students will take a longer time in understanding and comprehend the same question
Question#6 – The rationalistic mode of knowledge accepts the rules of
1. Legality
2. Manipulation
3. Logic
4. Authority
Correct Answer:‐ Legality Rationalistic mode means that depends on the reasons ratchet then on the subjective views of a particular person.
Question#7- Which of the following reliability techniques are used in qualitative research?
A. Diachronic reliability
B. Quixotic reliability
C. Synchronic reliability
D. Holsti’s constant
E. Chronbach’s alpha
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and D only
3. C, D and E only
4. A, C and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only Explanation- Quantitative studies- is a kind of research strategy in which we usually focus on the data and numbers rather than on theory as we do in qualitative studies.It is an objective approach and gives more emphasis on clear-cut precision and disseminated facts. The deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals and links premises with conclusions.
Question#8- Which of the following are the essential characteristics of the case study method?
A. Negatively oriented
B. Appreciation oriented
C. Particularistic
D. Descriptive
E. Inductive
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and D only
3. C, D and E only
4. A, B and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only
Explanation- The case study method is a form of qualitative analysis which means you have to do a very careful study and a deep observation to find out a theory, but here one thing is to remember that though we try to get a theory out of qualitative study it is not the only motive of a qualitative study. It is more than this.. It is a method of study in depth rather than breadth. It is a method in which a deep study of the same structure is organized to apply the outcome of the problem to get a solution.
Question#9- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Qualitative research is impressionistic and subjective.
Statement II: Quantitative research has a higher level of possibility of generalising the findings.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Explanation- The important aim of the research is not the development of a theory. It can be if it was qualitative research, in that we develop a theory however the research is not solely for the purpose of deriving a theory. Both facts and theory are important for doing the research. Type 1 error and type 2 error – are two types of errors that occurred while we do our research Type 1- A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is false in the population.
Question#10- Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ I, B ‐ II, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
2. A ‐ IV, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
3. A ‐ III, B ‐ IV, C ‐ I, D ‐ II
4. A ‐ II, B ‐ III, C ‐ IV, D ‐ I
Correct Answer:‐ A ‐ I, B ‐ II, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
Question#11- A competent communicator is
A. Culturally neutral
B. Culturally sensitive
C. Totally ethical
D. Situationally ethical
E. An effective listener
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and D only
3. B, C and E only
4. C, D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only
Explanation- Competent communicators are beware of their own beliefs and ethical values, and are always conscious of their behaviours while communicating. They self-monitor their behaviour and always work in terms of improving it.
Question#12- Information provided before sending the primary message is known as
Question- Information provided before sending the primary message is known as
1. Intro
2. Indicator
3. Pre‐message
4. Feed forward
Correct Answer:‐ Intro
Question#13 – Given below are two statements
Statement I: People use non‐verbal cues more than verbal cues.
Statement II: Non‐verbal cues have better believability than spoken words.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Explanation- In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand if both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion. There is not any formula or magic trick which you can apply to solve these types of questions. With a deep understanding of concepts and by applying common sense and a little bit of presence of mind you can easily solve these types of questions.
Question#14- What number should replace the question mark – 48, 67, 78, ?, 789
1. 126
2. 89
3. 98
4. 146
Correct Answer:‐ 126
Question#15- A man weighs 75% of his own weight plus 39 lbs. How much does he weigh?
1. 165 lbs
2. 160 lbs
3. 156 lbs
4. 166 lbs
Correct Answer:‐ 165 lbs
Explanation (Try Solving Your self!)- Here is one example for your reference(A man weight 75% of his own + 19 Kg ). Assuming his weight = x So, x=0.75x+19 //His total weight being 75% of x + 19kg … lets solve the equation
x-0.75x=19 Then 0.25x=19 hence x=19/0.25 finally x=76 – And there you have it. His weight is 76 kg.
Question#16 – Ravi’s salary is increased by 20%. On the increased salary, the tax rate is 10% higher. The percentage increase in tax liability is
1. 20 %
2. 22 %
3. 23 %
4. 24 %
Question#17 – Given below are two statements
Statement I: A 60 m long train passes a 90 m platform in 10 seconds. The speed of the train is 45 km/hour.
Statement II: If the ratio of the speeds of A and B is a:b, then the ratio of the time taken by them to cover the same distance is a:b.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Question#18 – Answer the following statements
A. At a 5% rate of simple interest, a certain sum will be doubled in 15 years.
B. A sum becomes double in 10 years. The annual rate of simple interest is 12%.
C. ₹1000 will become ₹1331 in 3 years at a compound interest rate of 10% per annum.
Which of the above statements is/are CORRECT?
1. C only
2. A and C only
3. B and C only
4. A and B only
Correct Answer:‐ C only
Question#19- Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ I, B ‐ II, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
2. A ‐ II, B ‐ III, C ‐ IV, D ‐ I
3. A ‐ III, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ IV
4. A ‐ IV, B ‐ I, C ‐ III, D ‐ II
Correct Answer:‐ A ‐ I, B ‐ II, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
Question#20- Name the fallacy committed in the argument
All dogs are mammals.
No cats are dogs. Therefore, no cats are mammals.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Illicit Major
2. Illicit Minorfallacy
3. Undistributed Middle
4. Existential Fallacy
Correct Answer:‐ Illicit Major
Explanation- Fallacies are errors in arguments that deceive our minds. It is a defect in an argument that consists of something other than merely false premises. As we see, fallacies can be committed in many ways, but usually, they involve either a mistake in reasoning or the creation of some illusion that makes a bad argument appear good or bad (either). An argument is valid when the truth of the premises guarantees the truth of the conclusion. The process that gives no rational grounds for accepting the conclusion is a defective form of an argument known as a fallacy. Fallacies can be used positively, to avoid or expose error or they can be used for negative means, to deceive.
Question #21- From the options given below, pick the CORRECT sequence in the context of constituent parts of inference
1. Hetu, Udāharaṇa, Nigamana, Upanaya, Pratijña
2. Nigamana, Hetu, Udāharaṇa, Upanaya, Pratijña
3. Pratijña, Hetu, Upanaya, Udāharaṇa, Nigamana
4. Pratijña, Hetu, Udāharaṇa, Upanaya, Nigamana
Correct Answer :‐ Hetu, Udāharaṇa, Nigamana, Upanaya, Pratijña
Question#22- The example ‘sound is eternal because it is caused’ represents which of the following Hetvabhasa ‘
1. Ashrayāsiddha
2. Svarūpāsiddha
3. Viruddha
4. Kālātita
Correct Answer:‐ Ashrayāsiddha
Question#23 – Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: A good computer networking solution can be very much beneficial for your business.
Reason R: With computer networking, you can cut back on costs and allow for efficient use of resources.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
2. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
3. A is true but R is false
4. A is false but R is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question#24 – Arrange the following optical storage devices in increasing order of their storage capacity.
A. DVD
B. CD‐ROM
C. Blu‐Ray
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B, C
2. B, A, C
3. A, C, B
4. B, C, A
Correct Answer:‐ A, B, C Explanation- DVD has the minimum storage capacity in the above-given options.
Question#25 – Given below are two statements
Statement I: Tablet computers have touch screens.
Statement II: A tablet computer has a keyboard.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Explanation- As explained earlier, in some questions you only have to apply common sense and your 2 marks are in your hands.
Question#26- Which of the following statements about desktop and laptop computers are TRUE?
A. Most modern laptop computers have built‐in webcams
B. Desktop computers are not very portable
C. All desktop computers have a built‐in touchpad
D. Laptop computers are rarely supplied with a mouse
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. A, B and D only
3. B, C and D only
4. A, B, C and D
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and D only Explanation- these three statements – Most modern laptop computers have built‐in webcams, Desktop computers are not very portable, and All desktop computers have built‐in touchpads is false.
Question#27 – Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ I, B ‐ IV, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
2. A ‐ II, B ‐ IV, C ‐ I, D ‐ III
3. A ‐ II, B ‐ IV, C ‐ III, D ‐ I
4. A ‐ III, B ‐ II, C ‐ I, D ‐ IV
Correct Answer:‐ A ‐ I, B ‐ IV, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
Question#28- If the wind speeds increase from 4.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s, the power output from an ideal windmill will increase by a factor of about
1. 2
2. 3
3. 4
4. 5
Correct Answer:‐ 2
Explanation- Power output is calculated as follows: power = [(air density) times (swept area of blades) times (wind speed cubed)] divided by 2. The area is in meters squared, air density is in kilograms per meter cubed and wind speed is in meters per second.
Question# 29 – In which year did the first commitment period of the Kyoto Protocol come to an end?
1. 2011
2. 2012
3. 2014
4. 2008
Correct Answer:‐ 2011
Question #30 – Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ II, B ‐ III, C ‐ IV, D ‐ I
2. A ‐ III, B ‐ I, C ‐ IV, D ‐ II
3. A ‐ III, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ IV
4. A ‐ I, B ‐ III, C ‐ II, D ‐ IV
Correct Answer:‐ A ‐ II, B ‐ III, C ‐ IV, D ‐ I
Question# 31- Which one of the following Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is related to sustainable consumption and production patterns?
1. SDG 9
2. SDG 10
3. SDG 11
4. SDG 12
Correct Answer:‐ SDG 9
Explanation- The energy which is obtained from natural resources like wind, tides, solar, biomass, etc are called non-conventional sources of energy. These are pollution-free and hence we can use these to produce a clean form of energy. Therefore greater use of the non-conventional source of energy should be promoted.
Question#32 – What fraction (%) of the total primary energy used in India is derived from biomass?
1. ~ 32%
2. ~ 42%
3. ~ 56%
4. ~ 22%
Correct Answer:‐ ~ 32%
Explanation- Biomass energy – When plants and animal material is used as fuel to produce electricity or heat is called biomass energy. bio means living being and mass means material so energy is obtained by using the mass of living beings (plants and animals) is called biomass. example – wood, corn, soybean, crop residues, and organic waste. We can burn biomass directly to produce heat and electricity and can be easily converted to liquid fuel and gas through the process of fermentation and anaerobic digestion. Biomass Is an important source of renewable energy that is gaining importance in developed countries for electricity and transportation. Biomass such as municipal waste and cattle manure is used to produce methane through anaerobic digestion.
Question#33 – What does NIRF stand for?
1. National Institute of Ranking Federation
2. National Institute of Ranking Framework/
3. National Institutional Ranking Framework
4. National Institutional Ranking Federation
Correct Answer:‐ National Institute of Ranking Federation
Question#34 – The term ‘open learning’ represent approaches that focus on
A. Opening access to education and training provision
B. Freeing learners from the constraints of time and place
C. Learning and evaluation without a specified curriculum
D. Offering flexible learning opportunities to individuals and groups of learners
E. Making students free from any educational loads Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. A, B and D only
3. A, B and E only
4. B, C and D only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only
Explanation- Opening access to education and training provision, Freeing learners from the constraints of time and place, Learning and evaluation without a specified curriculum.
Question# 35- In CBCS, Ability Enhancement Courses are of two kinds. They are:
A. Ability Enhancement Compulsory Courses
B. Skill Enhancement Compulsory Courses
C. Ability Enhancement Elective Courses
D. Skill Enhancement Elective Courses
E. Skill Enhancement Courses
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A and B only
2. A and C only
3. A and D only
4. A and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A and B only
Question#36 – Which of the following is a private university?
1. Anna University
2. BITS Pilani
3. Burdwan University
4. IIIT Correct
Answer:‐ Anna University
Question#37- India has been attracting only a fraction of international students because of
A. Lack of residential accommodation for foreign students
B. Difficulties in recognition of international qualification
C. Rigid admission process
D. Lack of enthusiasm among teachers
E. Lack of enthusiasm among students
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. A and B only
2. B and C only
3. C and D only
4. D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A and B only
Question#38 – Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow. A global light pollution map developed by a group of researchers has ranked New Delhi, Kolkata and Bengaluru as the three cities with the highest light pollution in India. It should serve to alert us to the looming problem of light pollution about which we are not only doing so little to prevent but are also unaware about. Light pollution refers to the harmful impact of artificial outdoor lighting. While artificial outdoor lighting is needed in the form of street lights it increases safety on roads and enables us to study and work in the dark, its use for floodlighting, illumination, advertising, etc has grown manifold in recent decades, resulting in the problem of light pollution. Studies show that the brightness from outdoor lights has risen steadily across India over a 20 year period, with New Delhi, Telangana, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh showing a “very high light intensity pollution” rise between 1993 and 2013. The use of excessive artificial outdoor lighting has several harmful implications not just for human health but for the wellbeing of animals, birds, insects and our environment. Use of artificial lights at night gives us more working and studying hours but it results in the problem of ‘loss of night.’ We find it difficult to fall asleep when the glow of streets enters our homes. It impacts our sleep‐wake rhythm, which could have serious implications for our moods and health. Illumination of gardens impacts animals and insects too. It is nocturnal insects and birds that suffer the most due to light pollution. It makes them disoriented, impacts their reproduction and thus their populations.
Read More – Tricks To Solve Paper 1 Reading Comprehension UGC NET Exam (ugcnetpaper1.com)
Question#39 – The light pollution map is related to the adverse effects of
1. Sunlight
2. Outdoor artificial light
3. Urban electricity projects
4. Rural electricity projects
Correct Answer:‐ Sunlight
Question# 40- One of the major pollutants is in the form of
1. Indoor lights
2. Street lights
3. Home lights
4. Illuminated advertising
Correct Answer :‐ Indoor lights
Question#41 – Light pollution intensity refers to
1. Increased outdoor brightness during nighttime
2. Manifold hike in the use of electricity in rural areas
3. Use of artificial light for road safety
4. More and more use of electricity in urban areas
Correct Answer:‐ Increased outdoor brightness during nighttime
Question#42 – Excessive hours of artificial light adversely impact our
A. Work schedule
B. Sleep cycle
C. Study hours
D. Moods and health
Question- Choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. A and B only
2. B and C only
3. B and D only
4. C and D only
Correct Answer:‐ A and B only
Question#43 – The loss of the night, as mentioned in the passage, will lead to
1. More human productivity
2. Increase in education
3. The altered activities of nocturnal creatures
4. The well‐being of the human population
Correct Answer:‐ More human productivity
Question-Based on Data Interpretation
Based on the data in the table, answer the questions that follow The following table presents the percentage breakup of employees and the ratio of male to female employees working in five different organisations (A to E). There is a total number of 35,000 employees working in all five organisations.
Read – Solving Tricks | Data Interpretation NET EXAM | Updated 2021 (ugcnetpaper1.com)
Question#46- The total number of employees in Organisation C is approximately what percent of the total number of employees in Organisation D?
1. 147 %
2. 312 %
3. 207 %
4. 183 %
Correct Answer:‐ 147 %
Question#47 – What is the total number of males in all the five organisations together?
1. 13350
2. 14700
3. 15960
4. 16280
Correct Answer:‐ 13350
Question #48 – What is the ratio of the number of males in Organisation A to the number of males in Organisation C?
1. 18:31
2. 9:31
3. 7:27
4. 9:19
Correct Answer:‐ 18:31
Question#49- What is the difference between the number of females in Organisation E and the number of females in Organisation B?
1. 210
2. 350
3. 170
4. 300
Correct Answer:‐ 210
Question#50- What is the sum total of the number of females in Organisation D and the number of males in Organisation E?
1. 4375
2. 4475
3. 4500
4. 4875
Correct Answer:‐ 4375
0 notes
Text
NTA UGC NET PAPER1 DECEMBER 2021 | Solved With Explanation
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/nta-ugc-net-paper1-december-2021-solved-with-explanation/
NTA UGC NET PAPER1 DECEMBER 2021 | Solved With Explanation

This extract of Paper1 Question is the OFFICIAL Question Paper asked in Commerce Subject (Shared by Students During Answer Key Review) & Answer Key for the UGC NET December 2021 Paper taken from www.ugcnet.nta.nic.in.
UGC-NET is an exam directed by the National Testing Agency, twice a year, However, due to an unsolicited pandemic, it was accomplished once a year for two consecutive years i.e 2020 and 2021. The students, as well as teachers, glimpsed a significant hike in the level of questions asked by UGC-NET.
They are undoubtedly in demand of students who comprehend every concept and can manage pressure within a restricted time frame. My friends, trust me gone are the days when you can clear the UGC net exam just by stuffing a few concepts. Now UGC-NET wants you to understand each idea so that only the well-deserved can qualify.
Question #1 – Which region of the brain is involved in our ability to learn new information, particularly if it is verbal?
Cerebrum
Hippocampus
Pons
Thalamus
Correct Answer:‐ Cerebrum Explanation– See, Many questions asked by ugc-net are very irrelevant. You can not answer each and every question irrespective of how much you study. So, don’t pay attention to these questions. Always focus on what you know and just make sure you don’t mark them incorrectly. Cerebrum– The largest part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, or halves called the cerebral hemispheres. Areas within the cerebrum control muscle functions and also control speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning. Question #2- mooKIT platform uses _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, an open-source content management system.
DRUPAL
JOOMLA
SAKAI
Moodle
Correct Answer:‐ DRUPAL
Question #3- INFLIBNET Centre, which is an autonomous Inter‐University Centre of the University Grants Commission, maintains
Swayam Prabha
e‐Pathshala
e‐Gyankosh
Shodhganga
Correct Answer:‐ Swayam Prabha Explanation- Information and Library Network Centre is an organisation that promotes and facilitates libraries and information resources for Indian further education. Its premises are in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. The Centre started in March 1991 as a project under the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics. This is an autonomous Inter‐University Centre of the University Grants Commission, maintained by Swayam Prabha which is an initiative of the Ministry of Human Resources Development to provide 32 High-Quality Educational Channels through DTH (Direct to home).
Question #4- Given below are two statements
Statement I: According to Piaget, the ability to solve conservation problems depends on having an understanding of three basic aspects of reasoning: identity, compensation, and reversibility.
Statement II: The stage of classification does not depend on a student’s ability to focus on a single characteristic of objects in a set and group the objects according to that characteristic.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct Explanation- In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand if both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion. There is not any formula or magic trick which you can apply to solve these types of questions. With a deep understanding of concepts and by applying common sense and a little bit of presence of mind you can easily solve these types of questions. Jean William Fritz Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget’s theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called “genetic epistemology”. Piaget placed great importance on the education of children
Question #5- According to Urie Bronfenbrenner’s biological model of human development, the microsystem constitutes ________________.
A. Immediate family
B. School
C. Beliefs
D. Customs
E. Neighbourhood
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. A, C and E only
3. A, B and E only
4. C, D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only Explanation- According to Urie Bronfenbrenner’s biological model of human development, the microsystem constitutes Immediate family, School, and Beliefs
Question #6- Which one of the following is an important characteristic of the researchers involved in a qualitative study?
Non‐partisan
Reflexivity
Transparency
Enthusiasm
Correct Answer:‐ Non‐partisan Explanation- Quantitative studies– is a kind of research strategy in which we usually focus on the data and numbers rather than on theory as we do in qualitative studies. It is an objective approach and gives more emphasis on clear-cut precision and disseminated facts. The deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals and links premises with conclusions.
Question #76 – Some of the types of hypothesis are as follows:
A. Descriptive
B. Null
C. Confounding
D. Intervening
E. Explanatory (Causal)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and D only
3. A, B and D only
4. A, B and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only Explanation- The important aim of the research is not the development of a theory. It can be if it was qualitative research, in that we develop a theory however the research is not solely for the purpose of deriving a theory. Both facts and theory are important for doing the research. Type 1 error and type 2 error – are two types of errors that occurred while we do our research. Type 1- A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is false in the population.
Question #8- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Exploration is particularly useful when researchers lack a clear idea of the problems they will meet during the study.
Statement II: Through exploration, researchers develop concepts more clearly, establish priorities, develop operational definitions, and improve the final research design.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true Explanation- In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand if both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion. There is not any formula or magic trick which you can apply to solve these types of questions. With a deep understanding of concepts and by applying common sense and a little bit of presence of mind you can easily solve these types of questions.
Question #9- Survey research is based on one of the following?
1. Constructivism
2. Interpretivism
3. Positivism
4. Hermeneutics
Correct Answer:‐ Constructivism Explanation- The important aim of the research is not the development of a theory. It can be if it was qualitative research, in that we develop a theory however the research is not solely for the purpose of deriving a theory. Both facts and theory are important for doing the research. Type 1 error and type 2 error – are two types of errors that occurred while we do our research
Positivism– it was the era in which science started advancing and people started believing in science and logic behind everything and they accepted that everything is because of science and everything can be proved on the basics of facts. Only objectivity mattered to them. Human beings were the centre for them.
Post positivist- We can say post-positivists were a mixture of both. They believed in science with the acceptance that everything is not in the hands of human beings. there are some higher powers. Everything cannot be proved with objectivity. So they were both subjective and objective with their approach. They were realistic and accepted their own limitations. Hence, post-positivists were realistic in their approach.
Question #10- Which among the following are non‐parametric statistics?
A. t‐test
B. F‐test
C. Spearman’s rank-order correlation
D. Mann‐Whitney‐Wilcoxon test
E. Kendall coefficient of concordance
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and D only
3. B, D and E only
4. C, D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only Explanation- Nonparametric statistics is the branch of statistics that is not based solely on parametrized families of probability distributions. Nonparametric statistics are based on either being distribution-free or having a specified distribution but with the distribution’s parameters unspecified.
Question #11 – ________ messages have more or less the same meaning for the audience.
1. Denotative
2. Complex
3. Connotative
4. Abstract
Correct Answer:‐ Denotative Explanation- In linguistics and philosophy, the denotation of an expression is its literal meaning. For instance, the English word “warm” denotes the property of being warm. Denotation is contrasted with other aspects of meaning including connotation
Question #12- Which one of the following is an example of a technological barrier in communication?
1. Physical locations of communicators
2. Low bandwidth of internet
3. Personal attitude towards technology
4. Complexity of ideas
Correct Answer:‐ Physical locations of communicators
Explanation- See, in many questions asked by UGC net, you can’t do it by applying formulas, especially in paper 1. In many questions, you only have to use your common sense,
Let’s say in the above question you can solve this answer by using your common sense and all you need to have is a little information about what topic they are asking. In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand if both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion. There is not any formula or magic trick which you can apply to solve these types of questions. With a deep understanding of concepts and by applying common sense and a little bit of presence of mind you can easily solve these types of questions.
Question #13- The communication among persons working at different levels who have no direct reporting relationship is called: 1. Intrapersonal communication
2. Upward communication
3. Horizontal communication
4. Diagonal communication
Correct Answer:‐ Intrapersonal communication
Explanation– communication is the process through which we can express our feelings and emotions. Barriers are those things that act as hurdles in communication and are called barriers to communication. There are many different types of barriers. As we can see in the above-given options these culture, power and time are not any physical traits. Intrapersonal Communication- the communication which we do with ourselves is called intrapersonal communication. There is no involvement of any other person. Like- diary writing, stream of consciousness, spirits talks and most important even once asked by ugc net is Dreams. Dreams are also part of intrapersonal communication.
Intrapersonal communication is the process by which an individual communicates within themselves, acting as both sender and receiver of messages, and encompasses the use of unspoken words to consciously engage in self-talk and inner speech.
Question #14- Marshall Mcluhan’s name is associated with the assertion:
1. The message is the medium
2. The medium is the message
3. The message determines the medium accurately
4. A message is a message
Correct Answer:‐ The message is the medium Explanation- Herbert Marshall McLuhan CC was a Canadian philosopher whose work is among the cornerstones of the study of media theory. He studied at the University of Manitoba and the University of Cambridge.
Question #15- Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: In classroom communication, teachers should acknowledge and take into account students’ views.
Reason R: In a classroom, the probability of message reception can be enhanced by establishing a viewpoint.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
2. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
3. A is true but R is false
4. A is false but R is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A Explanation- In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand if both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion. There is not any formula or magic trick which you can apply to solve these types of questions. With a deep understanding of concepts and by applying common sense and a little bit of presence of mind you can easily solve these types of questions.
Question #16- How many terms are there in the series 168, 175, 182,_ _ _ _, 266?
1. 13
2. 14
3. 15
4. 16
Correct Answer:‐ 13 Explanation- First of all you should try to take the differences. If the first difference does not give anything significant, you can go for the second difference i.e. the difference of the differences.
Question #17- Given below are two statements
Statement I: The compound interest on ₹280 for 18 months at 10 % per annum is ₹44.3.
Statement II: At a 5.6 % rate of simple interest, a certain sum will be doubled in 15 years In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Question #18- The average of ten numbers is 7. If each number is multiplied by 11, then the average of the new set of numbers is:
1. 82
2. 72
3. 78
4. 77
Correct Answer:‐ 82 Explanation- For your reference, The mean of 10 numbers is 7 If each number is multiplied by 12 then the mean of the new set of numbers is a Total of 10 numbers =10×7=70… If each number is multiplied by 12… New Total =70×12 divide by 10= 84
Question #19 – Which of the following fractions is the smallest?
1. 65/80
2. 11/16
3. 5/8
4. 29/40
Correct Answer:‐ 65/80 Explanation– To compare the fractions, first of all, we go with the denominator. If the denominator is the same as all the fractions then we will compare only the numerator. The fraction that has the smallest numerator will be the smallest fraction.
Question #20- A total of 324 coins of 20 paise and 25 paise make a sum of ₹71. The number of 20 paise coins is 20
1. 144
2. 124
3. 200
4. 125
Correct Answer:‐ 124 For your reference, see this example and then try to solve this question. A total of 324 coins of 20 paise and 25 paise make a sum of Rs. 71. The number of 25-paise coins is? Let there are n 25 paise coins. So n×25+(324-n)20=7100, or 25n-20n=7100-6480=620, or 5n=620, n=620÷5=124. So there are 124 numbers of 25 paise coins.
Question #21- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Truth and Falsehood are predicates of Arguments
Statement II: Validity and Invalidity are predicates of Statements In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct Explanation– An argument is valid when the truth of the premises guarantees the truth of the conclusion. The process that gives no rational grounds for accepting the conclusion is a defective form of an argument known as a fallacy. Fallacies can be used positively, to avoid or expose error or they can be used for negative means, to deceive.
Question #22- Identify the fallacy committed in the argument: Some birds are not beautiful creatures. All dogs are beautiful creatures. Therefore, no dogs are birds.
1. Fallacy of the Undistributed Middle Term
2. Fallacy of the Illicit Process of Major Term
3. Fallacy of the Illicit Process of Minor Term
4. Fallacy of Exclusive Premises
Correct Answer:‐ Fallacy of the Undistributed Middle Term Explanation– Fallacies are errors in arguments that deceive our minds. It is a defect in an argument that consists of something other than merely false premises. As we see, fallacies can be committed in many ways, but usually, they involve either a mistake in reasoning or the creation of some illusion that makes a bad argument appear good or bad (either). An argument is valid when the truth of the premises guarantees the truth of the conclusion. The process that gives no rational grounds for accepting the conclusion is a defective form of an argument known as a fallacy. Fallacies can be used positively, to avoid or expose error or they can be used for negative means, to deceive. Ethos- Ethos is an argument that appeals to ethical authority or credibility.[ ] Pathos- pathos is an argument that appeals to emotions. Fallacies are usually divided into two groups: Formal and Informal Groups.
Question #23– If ‘All men are mortal’ is given as True, then which of the following options can be validly inferred from it?
A. ‘No men is mortal’ is False
B. ‘Some men are mortal’ is True
C. ‘Some men are not mortal’ is True
D. ‘Some men are not mortal’ is False
E. ‘Some men are mortal’ is False
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. A, B and D only
3. A, B, C and D only
4. B, C, D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only
Question #24- Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: According to Naiyāyikas, the fallacy of Savyabhicāra occurs when the middle term leads to different opposite conclusions.
Reason R: When the middle term is irregular, it is distributively not related to the major term.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
2. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
3. A is true but R is false
4. A is false but R is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question #25- Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A ‐ III, B ‐ II, C ‐ I, D ‐ IV
2. A ‐ III, B ‐ IV, C ‐ II, D ‐ I
3. A ‐ II, B ‐ I, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
4. A ‐ III, B ‐ I, C ‐ II, D ‐ IV
Correct Answer:‐ A-III, B ‐ II, C ‐ I, D ‐ IV
Question #26- The number of characters in 8-bit ASCII code (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
1. 64
2. 128
3. 256
4. 512
Correct Answer:‐ 64
Question #27- The Post Office protocol is
1. Protocol used for transfer of files from one computer to another computer
2. Protocol used to handle email attachments
3. Protocol used when receiving emails from the email server
4. Protocol used for sending emails
Correct Answer:‐ Protocol used for transfer of files from one computer to another computer Explanation- The post office protocol (POP) is the most commonly used message request protocol in the Internet world for transferring messages from an e-mail server to an e-mail client. With POP3, the e-mail client requests new messages from the e-mail server, and the server “pops” all new messages out to the client.
Question #28- Given below are two statements regarding the Router
Statement I: It enables data packets to be routed between different networks.
Statement II: It works in the Data Link Layer.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false
3. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
4. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are true Explanation– A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet.
Question #29- Following are some statements regarding File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Choose the correct statements
A. It is used to access the world wide web (www)
B. It is used to download data from file servers
C. It is used for very small files
D. Files are transferred from one device to another
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A and B only
2. A and C only
3. B and D only
4. B and C only
Correct Answer:‐ A and B only Explanation- The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard Communication Protocol used for the transfer of Computer Files from a server to a client on a Computer Network. FTP is built on a client-server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a clear-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content,
Question #30- The number of Sustainable Development Goals is
1. 13
2. 15
3. 17
4. 19
Correct Answer:‐ 13 Explanation- The Sustainable Development Goals or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked global goals designed to be a “blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all”. The SDGs were set up in 2015 by the United Nations General Assembly and are intended to be achieved by 2030.
Question #31- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Small amount of atmospheric Nitrogen dioxide NO is produced from polluting sources
Statement II: Most of the atmospheric NO is produced due to photochemical reactions in the atmosphere
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Question #32- Which of the following water-borne diseases may be caused by viruses, bacteria and protozoa?
1. Cholera
2. Hepatitis
3. Typhoid
4. Diarrhea
Correct Answer:‐ Cholera Explanation- Cholera is a bacterial disease usually spread through contaminated water. Cholera causes severe diarrhoea and dehydration. Left untreated, cholera can be fatal within hours, even in previously healthy people. Modern sewage and water treatment have virtually eliminated cholera in industrialized countries.
Question #33- United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP) was the result of deliberations held during
1. Human Environmental Conference at Stockholm in 1972
2. Earth Summit at Rio de Janeiro in 1992
3. Montreal Protocol 1987
4. Kyoto Protocol 1997
Correct Answer:‐ Human Environmental Conference at Stockholm in 1972 Explanation– The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is the leading environmental authority in the United Nations system. UNEP uses its expertise to strengthen environmental standards and practices while helping implement environmental obligations at the country, regional and global levels. UNEP’s mission is to provide leadership and encourage partnership in caring for the environment by inspiring, informing, and enabling nations and peoples to improve their quality of life without compromising that of future generations. UNEP re-organised its work programme into six strategic areas as part of its move to results-based management. The selection of six areas of concentration was guided by scientific evidence, the UNEP mandate and priorities emerging from global and regional forums.
Question #34- Which of the following states has maximum installed wind power as per MNRE’s latest report?
1. Andhra Pradesh
2. Karnataka
3. Tamil Nadu
4. Maharashtra
Correct Answer:‐ Andhra Pradesh
Question- #35 Global Citizenship Education promotes
1. Common international laws for global citizenship
2. Issues pertaining to citizenship across countries involving VISA
3. International public relations
4. More peaceful, tolerant, inclusive, secure and sustainable societies
Correct Answer:‐ Common international laws for global citizenship Explanation- Global Citizenship Education inspires and empowers individuals to Reflect on their biases and assumptions. Value diversity and inclusion. Develop a greater understanding of countries, communities, and cultures around the world; events shaping our world.
Question- #36 CBCS is
1. Criteria-Based Choice System
2. Choice-Based Credit System
3. Criteria-Based Creditable Scores
4. Credit-Based Choice Scores
Correct Answer:‐ CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (CBCS): Explanation- The CBCS provides an opportunity for the students to choose courses from the prescribed courses comprising core, elective/minor or skill-based courses. The courses can be evaluated following the grading system, which is considered to be better than the conventional marks system.
Question #37- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Policy action and implementation plans require sound database systems at the regional level only.
Statement II: The statistical system should ensure its impeccability with data architecture, security, quality, cleaning and integration.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
3. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
4. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Correct Answer:‐ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Question #38- Education, the NEP proposes to set up HECI (Higher Education Commission of India). Which of the following are verticals of HECI?
A. NHERC
B. NAS
C. HEGC
D. NCIVE
E. NAC
Question- Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B and C only
2. B, C and E only
3. A, C and E only
4. C, D and E only
Correct Answer:‐ A, B and C only
Question #39- Match List I with List II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A ‐ II, B ‐ I, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
2. A ‐ III, B ‐ IV, C ‐ II, D ‐ I
3. A ‐ IV, B ‐ III, C ‐ II, D ‐ I
4. A ‐ I, B ‐ IV, C ‐ II, D ‐ III
Correct Answer:‐ A-II, B ‐ I, C ‐ III, D ‐ IV
Question 40 – Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow
Leadership studies are an emergent discipline, and the concept of leadership will continue to change. Leadership lore is defined as an influence relationship among leaders and followers who want real change and outcomes that reflect their shared purpose. Leadership involves influence. It occurs among people; those people who intentionally desire significant changes, and the changes reflect purpose shared by the leaders and their followers. Influence means that the relationship among people is not passive; however, also part of this definition is that influence is multidirectional. It does not use orders or threats to make somebody do something. The basic cultural values in America make it easiest to think of leadership as something a leader does to a follower. However, leadership has an effect in both directions. In most organizations, superiors influence subordinates, but subordinates also influence superiors. The people involved in the relationship want real and important changes‐ leadership involves creating change, not maintaining what normally happens. In addition, the changes sought are not dictated by leaders, but reflect purposes that leaders and followers share. Moreover, change is toward an outcome that the leaders and followers both want; a desired future or shared purpose that motivates them toward this more preferable outcome. An important aspect of leadership is influencing others to come together around a common vision. Thus, leadership involves the influence of people to bring about change toward a desirable future
Explanation- Tip- Albeit, there is no hard and fast rule to solve comprehension. You can solve comprehension by doing more and more practice. Students usually take these types of questions for granted but you need to understand that this is a very complex topic and this deserves as much attention as you give to other topics. There are some rules which you can follow,
1st Rule- Do not read the full paragraph. Yes, you read it right. Do not spend a lot of time reading the whole paragraph. Just by having a look try to understand the gist of the paragraph. A quick read.
2nd- Read all the questions very carefully, yes very very carefully, and then again look at the paragraph. All I can guarantee you is that with this rule you will be able to solve 2 or 3 questions.
3rd – Now one thing that I observed is that usually, questions are chronological as per the paragraph. So, let’s say you solved the first 2 or 3 questions by applying the above tricks. You don’t need to read the whole paragraph again. Just read the last few lines and you are ready to rock.
4th – The most important question of any comprehension is the title – so the title is like the Bollywood song’s title line. They will repeat the line or title just as bole chudiyan repeats in bole chudiyan song. So try to pick that title. (thanks to me later)
5th – By applying overhead rules I can assure you, that you can easily solve 3 -4 questions, and because of the lack of availability of time that is more than enough.
Question #40 – Leadership studies are an emerging discipline”, means: ‘
1. Leadership studies are an established field
2. Leadership studies are a valid field of research
3. Leadership studies is an evolving domain of scholarship
4. Leadership studies is an elaborate field
Correct Answer:‐ Leadership studies are an established field
Question #41- What variables are used for defining leadership?
1. Power to affect relationships and desire for change in the true sense of the team
2. Power to get things done quickly by the influence
3. Power to change and control
4. Power to effect and desire for mandated change
Correct Answer:‐ Power to affect relationships and desire for change in the true sense of the team
Question #42 – What is the main theme of this passage?
1. Explanation of leadership construct
2. Argument about leadership
3. Models of leadership
4. Pros and cons of leadership
Correct Answer:‐ Explanation of leadership construct
Question #43- What should be the outcome of leadership actions?
1. Movement towards the vision of the leader
2. Movement towards a common vision of the leader and the followers
3. Movement towards the vision of the majority
4. Strengthening of the authority of leaders
Correct Answer:‐ Movement towards the vision of the leader
Question-#44 The concept of leadership discussed in this passage is
1. Vertical‐top down
2. Horizontal
3. Individualistic
4. Exceptional
Correct Answer:‐ Vertical‐top down
Question #45- Study the table carefully and answer the questions that follow In the following table, the total Exports and Imports of 5 countries over 4 years (in Rs Crore) is given. Study the table carefully and answer the given questions. (I‐import, E‐export)
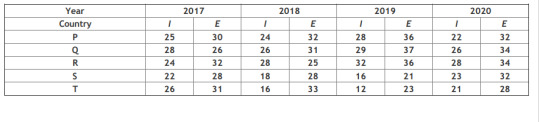
Explanation– Let’s understand how we can solve these Data integration problems. If you are a humanities student like me, Data interpretation is a big ghost for us. When I was preparing for this exam initially I used to ignore data interpretation. However, you can’t deny that this is very crucial and you can’t crack this exam without data interpretation. Here are a few tips which I used during my preparation days, which I hope will help you as well.
Try to solve simple problems like addition, subtraction, dividing and multiplying. You might be thinking that you are good with this but with this I mean you should be able to solve this without paper and pen.
Try to solve percentages and average questions. These two topics are the base of Data integration. You can’t even think of solving Data integration problems without these two topics. Solve as much as you can.
Then last but not least, timings matter the most while solving these questions. Questions are easy but lengthy. You can solve all these questions but the game is of time. You have to solve these 5 questions in only 10 minutes otherwise you won’t be able to solve other questions which are of equal weightage.
Practise as much as you can.
Question#46- Find out the difference between the average export and average import for the country P.
1. 8.25
2. 7.75
3. 8.50
4. 7.25
Correct Answer:‐ 8.25
Question#47- Which country has the maximum percentage of profit increase from 2019 to 2020? (Profit = Export-Import)
1. P
2. Q
3. R
4. S
Correct Answer:‐ P
Question #48- Which year has the maximum export?
1. 2017
2. 2018
3. 2019
4. 2020
Correct Answer:‐ 2017
Question#49 – Which year has the minimum average import?
1. 2017
2. 2018
3. 2019
4. 2020
Correct Answer:‐ 2017
Question #50 – Find out the ratio of export done by countries S and T during 2017‐2020

0 notes
Text
UGC NET December 2020 and June 2021 examination 
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/ugc-net-december-2020-and-june-2021-exam/
UGC NET December 2020 and June 2021 examination 
**As you are aware from Dec 2018 onwards NTA conducts the exam online and no Question papers were given to students, However, we have collected this question from our students and the answer given is also based on Keys provided by NTA Agency Answer Key.
You can access ugc net 2021 paper 1 question papers with answer key below.
Question#1 -Which of the following is a physical/environmental barrier to communication?
Culture
Personality
Power/authority
Time
Answer- 2nd
Explanation-The barrier of communication- communication is the process through which we can express our feelings and emotions. Barriers are those things that act as hurdles in communication are called barriers of communication. There are many different types of barriers. As we can see in the above-given options these culture, power and time are not any physical traits. All these are abstract qualities, only personality is the physical trait. So this is the correct option.
Question#2 – Disaster Management Act came into existence in
1985
1992
2000
2005
Answer-(4.) 2005
Explanation– The Disaster Management Act received the assent of The President of India on 23 December 2005. The Disaster Management Act, 2005 has 11 chapters and 79 sections. The Act extends to the whole of India.
Question#3– When an unperceived fact is supposed to resolve an apparent contradiction in the presented phenomenon, which one of the following pramaṇas is employed according to Advaitins?
Arthap̅atti
Pratyakṣa
Anumar̅a
Anupalabdhi
Answer – 1
Explanation– Arthapatti is a Sanskrit term that means “presumption” or “implication.” It is said to be the six pramanas in the yogic philosophy of the Advaita Vedanta system and the Bhatta school of Purva-Mimamsa. When knowledge is derived from a particular set of circumstances, it is called Arthapatti. When an unperceived fact is supposed to resolve an apparent contradiction in the presented phenomenon, it is called Arthapatti.
Question#4 -Identify the correct sequence for successful communication.
Options:-
Sender → Encode message → Channel → Decode message → Audience → Feedback
Sender → Encode message → Decode message → Channel → Audience → Feedback
Sender → Encode message → Audience → Channel → Decode the message → Feedback
Sender → Encode message → Channel → Decode message → Feedback → Audience
Answer– 1st
Explanation: Successful communication- Communication is the process through which we can express our feelings and emotions. The process of transmission of messages from one person to another person is called communication. These are emotions, cultural situations, and even our location. There is a fixed pattern in which we should initiate communication and this should be in a fixed chronology.
Sender– one who starts the conversation, who wants to transfer some feelings
Encode message– before sending any message we encode(made) that message or we can say structure that message is called encoding message. This can be explained with the help of an example. If I want to ask permission from my manager for 2 days’ leave, first I will structure a message in my mind or draft that message in my mail in a proper way that is called encoding that message.
Channel– the medium through which we send our encoded message is called a channel. It could be anything like WhatsApp, social media, or letters.
Decode message- so after receiving that message, the person whom we send that message tries to understand that message, that understanding of the message is called decoding. One should keep in mind that the message should be structured in a way it could be easily decoded.
Audience– it is our target audience to whom we want to send our message.
Feedback- it is the last processor in layman’s language we can say when we receive a reply it is called feedback.
Question #5
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Option 1: A – I, B – III, C – II, D-IV
Option 2: A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – II,
Option 3: A-IV, B – I, C – II, D – III
Option 4: A-II, B – I, C – III, D – IV,
Answer-2nd
Explanation: So here in the above question as you can see we were asked to match list 1 wish list 2 like
1. A joystick is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling.
2. Direct data entry is on radio frequency identification readers.
3. Output devices- An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment that converts information into a human-perceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, or video.
4. Data backup-. Backup is the process of creating a copy of the data on your system that you use for recovery in case your original data is lost or corrupted. You can also use the backup to recover copies of older files if you have deleted them from your system.
Question#6 – A Network Interface Card (NIC) contains
Options:-
Domain address
IP address
MAC address.
Port address
Answer – 3rd
Explanations: MAC address is called media access control address. It is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Question#7 – Arrange the following components of municipal solid waste in order of their increasing abundance.
A. Paper and Cardboard
B. Food
C.Tin Cans
D. Dirt and Ash
E.Textiles
C, E, D, B, A
E, C, A, D, B
E, C, D, A, B
E, C, D, B, A
So the correct answer is 4th
Here in the above question, we were asked to arrange the given items in the manner they are increasing in the environment.
Question#8
A – I, B – III, C – IV, D – II
A – II, B – I, C – IV, D – III
A – III, B – IV, C – I, D – II
A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – III
Answer– 2nd
There are four types of statements in a syllogism. 1. Contradictory 2. Contrary 3. Sub-contraries 4. Sub- Altern or sub-alteration. This is the chart with the help of which we will discuss this topic further.
Tips to draw this diagram step by step
First,draw a huge X from English alphabets.
2nd- Make a square on the X as given in the diagram.
3rd- Write a, e, i, o on the four corners of X.
4th- Write “contrary” on A to E
5th- Write sub- contrary on I to O
6th- Write “sub -alteration” from A to I and E to O.
7th- Write “ contradictory” vertically from A to O and E to I
Tip to remember what to write – remember the vowels a, e, I, o .write in this manner only.•
A is universal positive. Example- All apples are good.
E Is universal negative. Example- No apple is good
I is a particular positive Example- some apples are good.
O is particular negative. Example- Apples are not good.
Contrary- “A and B” is a pair of the contrary. Now, what is the contrary? The contrary is those statements that cannot be true together but can be false together. If one is true, the other will be definitely false. And if one is false, the other will be doubtful. We will try to understand this perplexing statement with the help of an example.
For example –“ If all apples are good” is true then automatically “No apples are good” will be false but on the other hand if “no apples are good” is false then “all apples are good” will be doubtful.
Sub- contraries – The Sub-contraries pair is “ I and O”, which means these both can be true together but cannot be false together. For example- if somebody says “ some apples are good, that automatically means that “some apples are not good” so in these statements if one is true, the other will be definitely true but these statements cannot be false together. We cannot say that “some apples are good” is also right And “ some apples are not good” is also right. Contradictory- This combination has two pairs: “A and O”, and “E and I”.
In these types of statements “ if one is true, the other will be definitely false. Or If one is false, the other will definitely be true. For example- A “ all apples are good” is proved then O statements “-some Apple are not good” is totally opposite with each other and if “No Apple is good” is true then the exact opposite(contradictory)of this treatment will be “some apples are good” so these “A and 0” or “ E and I” will always be exact opposite(contradictory)to each other.
Sub-alteration- The pair “A and I” and “E and O” are sub-alteration pairs. Now, what is a sub- alteration? In this, ‘ truth downwards, but falsity upwards ‘ I.e.- if A statement is true, then I statement will also be true If A statement is false, then nothing can be said about I.
On the other hand, if I statement is false, then A statement will also be false. For example- if “ all apples are good” is true, then “ some Apples are good” will also be true. If “ some Apples are good” is false, then “ All Apple are good” will also be false…
Question#9- A lady is reflecting on the causes of the environmental crisis. She is considering and attempting to link varied variables to make sense of the issue. This scenario is an example of
Didactic communication
Interpersonal communication
Intrapersonal communication
Mass communication
Answer– 3rd
Explanation – Communication is the process through which we can express our feelings and emotions. The process of transmission of messages from one person to another person is called communication. These are emotions, cultural situations, and even our location.
Intrapersonal communication is the process by which an individual communicates within themselves, acting as both sender and receiver of messages, and encompasses the use of unspoken words to consciously engage in self-talk and inner speech.
Question#10– Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: The aim of education in ancient India was not just the acquisition of knowledge but preparation for life in this world beyond schooling.
Reason R: Ancient Indian education emphasized complete realization and liberation of self.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given
A is correct but R is not correct
A is not correct but R is correct
Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are correct but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Answer– 3rd
Explanations: In these above types of questions what we have to do is we have to understand the meaning of each statement and then try to understand both statements can make any sense and then here is a trick which can really help you is while solving this type of question just put “Because” after reading the first given assertion.
Like- The aim of education in ancient India was not just the acquisition of knowledge but preparation for life in this world beyond schooling because Ancient Indian education laid emphasis on complete realization and liberation of self.
Now, we can ourselves realize that both these statements are making sense in themselves but not in each other’s relation. So the answer is 3rd Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question#11- The main reason for low enrollment in vocational education courses in India is
Options:-
High fee structure
Lack of adequate infrastructure to impart Vocational education
Unavailability of a large number of vocational courses
Wrong perception of vocational education among students and parents
Answer– 4th Wrong perception of vocational education among students and parents
Vocational courses are an educational discipline that enables individuals to acquire skills that are required for a particular trade. Vocational courses are traditionally non-academic and are completely related to a specific trade, occupation, or vocation.
See, in many questions asked by UGC net, you can’t do it by applying the formula, especially in paper 1. In many questions, you only have to use your common sense,
Let’s say in the above question you can solve this answer by using your common sense and all you need to have is a little information about what topic they are asking. The main reason for low enrollment in vocational education courses in India can’t be high fees because the fees are very low, it can’t be infrastructure as well, and availability is out of the question because there are more vocational courses available in India than fish in the Arabian sea.
So by applying common sense, you can easily answer this question- The wrong perception of vocational education among students and parents is the main reason.
Question#12– Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a key indicator of the process performance of wastewater treatment plants. The plant is said to be efficient when BOD:
Decreases
Increases for the first 36 hours
Increases
Remains unchanged
Answer– 1st
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) represents the amount of oxygen consumed by bacteria and other microorganisms while they decompose organic matter under aerobic (oxygen is present) conditions at a specified temperature. The decay of organic matter in water is measured as biochemical or chemical oxygen demand.
Question#13 -Ethnography refers to –
A measure that is employed to refer to a concept when no direct measure is available
A research design that rules out alternative causal explanations of findings deriving
A research method where the researcher immerses himself/herself in a social setting for an extended period for providing an account of a particular culture, society, or community
An attribute in terms of which cases do not differ.
Answer – 3rd
Explanation– The meaning of ethnography is the study and systematic recording of human cultures.A research method where the researcher immerses himself/herself in a social setting for an extended period to provide an account of a particular culture, society, or community.
Question#14- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Value development requires conscious, planned, and deliberate attempts by the school and the teachers.
Statement II: Values needed for sustainable development cannot be taught in a school setting.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given
Options-
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
The answer is clear just by applying common sense that the 3rd option is correct. Again See, in many questions asked by UGC net, you can’t do it by applying the formula, especially in NTA UGC NET Paper 1.
Question#15- The main concept behind solar ponds to store the solar energy is
Options:-
Fixed salt gradient from surface to bottom in the pond/
Presence of sand in the pond
Presence of solar cells in the pond
Uniform salinity of the pond
Answer– 1st
Explanation– A solar pond is a pool of saltwater that collects and stores solar energy in the form of heat. The saltwater naturally forms a vertical salinity gradient also known as “halocline”, where low-salinity water flows above high-salinity water. In other words, it contains water with a definite gradient of salt concentration.
Question#16 – Which one of the following is an example of the ‘Pull Technology’ form of communication?
Options:-
Social media sites
Websites delivered to browser on search
Websites that are advertised
Websites that are not alive
Answer 2nd
Explanation-Pull coding or client pull is a style of network communication where the initial request for data originates from the client and then is responded to by the server. The reverse is known as push technology, where the server pushes data to clients.
Question#17- Which among the following are statistical packages?
A. SPSS
B. SAS
C. ANOVA
D. STATA
E. R
1. A, B, C, and D only
2. A, B, C, and E only
3. A, B, D, and E only
4. B, C, D, and E only
Answer– 3rd
Statistical packages are collections of software designed to aid in statistical analysis and data exploration. Second, statistical packages can provide a unified operating framework and common interface for data manipulation, visualization, and statistical analysis.
Question#18- Identify the fallacy committed in the argument.
All household pets are domestic animals. No unicorns are domestic animals. Therefore, some unicorns are not household pets
Existential fallacy
The fallacy of Four terms
The fallacy of Illicit Major
The fallacy of Illicit Minor
Answer– 1st
Existential fallacy– as the name indicates, it has crises even in the possibility that it even exists. That means it is not necessary whether the statement is true or not but if it is true then it must be like that. Too confusing let me help you with the help of an example-
One example would be: “Every unicorn has a horn on its forehead“. It does not imply that there are any unicorns at all in the world, and thus it cannot be assumed that, if the statement were true, somewhere there is a unicorn in the world (with a horn on its forehead). The statement, if assumed true, implies only that if there were any unicorns, each would have a horn on its forehead.
In simplest terms- it is not the question of whether there are unicorns in the world or the statement that but if that is true if there is any Unicron there in the world then it must have a horn on the head.
Question#19- The number of bits in IPv6 addresses is:
Options:-
128 bits
256 bits
32 bit
64 bits
Answer– 128 bits
Question#20- Over the past 100 years, the estimated rise of global sea level is by 10 to 25 cms or more. This is attributed to which of the following?
A. Thermal contraction of ocean water
B. melting of glaciers and small ice caps
C. Thinning of the Greenland ice sheet
D. Changes in terrestrial water storage
Options:-
A, B, and C only
A, C, and D onyx
B and C only
B, C, and D only
Answer– 4th
Explanation– the main reason for the rise in sea level is global warming. Man-made activities like the burning of coal and oil and cutting of forests to meet ever-growing human needs are the main reasons for global warming and the Melting of glaciers and small ice caps. Thinning of the Greenland ice sheet Changes in terrestrial water storage ultimately result in the rising of the sea level.
Question#21- Identify the correct sequence to join a Google Meet session
A. Enter code and click continue
B. Click ASK to join
C. Click use a meeting code
D. Go to meet.google.com
E. When someone in the meeting gives you access you will join it.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B, D, C, E,
2. D, A, E, B, C
3. D, C, A, B, E
4. E, A, B, C, D,
Answer– 3rd
This was again a free question. Who had not used google meet in this pandemic? So simply follow the correct answers steps and you are ready to go and join any google meet.
Question#22- Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: Generalisation of a finding is possible only in quantitative studies.
Reason R: Quantitative studies make use of deductive reasoning.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:-
A is false but R is true.
A is true but R is false
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Answer- 2nd
This was a very tricky question asked by us net and you must be aware of everything in detail like what is quantitative studies, what is deductive reasoning.
Quantitative studies- it is a kind of research strategy in which we usually focus on the data and numbers rather than on theory as we do in qualitative studies.
It is an objective approach and gives more emphasis on clear-cut precision and disseminated facts.
The deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals and links premises with conclusions.
Question#23-Given below are two statements
Statement I Type I Error refers to the decision to reject the null hypothesis when it is incorrect.
Statement II: Sampling error occurs due to the violation of the principle of random sampling.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Options:-
Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Answer– 1st
Explanation– sampling- sampling is the most important part of the research. It is the selection of the population on whom we want to conduct our research. In simpler terms, to do any research we need a population, but we can��t research the whole of India so as an alternative we will select a small portion of India, which is called sampling. There are many different types of sampling.
Type 1 error and type 2 error – they are two types of errors that occurred while we do our research
Type 1- A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is false in the population.
Question#24 -Given below are two statements
Statement I: The aim of Naiyāyikas in formulating the anumāna theory is to obtain pramā (right knowledge).
Statement II: The aim of Naiyāyikas in formulating the anumāna theory is to verify only and only formal validity.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Answer 4th
Question#25- The average of the first 100 positive integers is
49
50
50.5
51.5
Answer– 3rd
Explanation– first 100 positive integers are1 to 100= 100 * (1 +100)/2 = 50 * 101. Required Average = (50 *101)/100 = 50.5. For the above given series average, = ( 1 +100)/2 = 50.5)
Question#26- Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: Quality questions promote deep learning.
Reason R: The quality of questions asked determines a teacher’s level of success with a lesson.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:-
A is false but R is true/(A)
A is true but R is false/(A)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Answer– 4th
Question#27- Which among the following is a MOOC platform?
Options:-
Coursera
Google Mee
Jitsi Meet
Urkund
Answer– 1st
Explanation– MOOC stands for massive open online courses. These are the online, digital platforms that help you to learn online and even get a degree by registering online in these courses with the flexibility of time and place and duration and of course individual pace. 014 In July 2014, The first Indian MOOC on edX developed and targeted learners across the world. It witnessed massive success in attracting over 35,000 learners. 2015 IIT Bombay, Birla Institute of Technology and SciencePilani, IIM Bangalore, and Indian School of Business launched MOOCs on edX and Coursera.
Question#28- Post-positivism is related to which one of the following philosophies?
Options:-
Critical Realism
Empiricism
Objectivism
Subjectivism
Answer-1st
Post positivist in the simplest term, is a philosophy that comes after positivism. There are three types of philosophies
1. Theology- those who believe that only divine power or God is responsible for everything. God was at the centre for them. It was considered the darkest era of human history like the medieval era.
2. Positivism- it was the era in which science started advancing and people started believing in science and logic behind everything and they accepted that everything is because of science and everything can be proved on the basics of facts. Only objectivity mattered to them. Human beings were the centre for them.
3. Post positivist- we can say post-positivists were a mixture of both. They believed in science with the acceptance that everything is not in the hands of human beings. there are some higher powers. Everything cannot be proved with objectivity. So they were both subjective and objective with their approach. They were realistic and accepted their own limitations. hence, post positivists were realistic in their approach.
Question#29- Given below are two statements
Statement I: Operant conditioning was discovered by Thorndike.
Statement II: Classical conditioning was discovered by Ivan Pavlov.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Options:
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Answer -4th
Question#30-Which one of the following sections of the UGC Act is concerned with the promotion and coordination of university education for the maintenance of standards of teaching examination and research?
Options:-
Section 12
Section 14/धारा – 14
Section 25/धारा – 25
Section 28/धारा – 28
Answer– 1st
Question#31
Options:-
A – I, B – III, C – IV, D – II
A – III, B – IV, C – II, D – I
A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – III
A-II, B – I, C – III, D-IV
Answer – 4th
Question#32- Following are the statements regarding a Repeater
A. It distributes the data packets
B. It is added to transmission systems to boost the signal
C. It sends the data to a specific computer
D. It can also be used on wireless systems Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:-
A and D only
A, B, and C only
B and D only.
C and D only
Answer– 3rd
Explanations– Repeaters are network devices operating at the physical layer of the OSI model that amplifies or regenerate an incoming signal before retransmitting it. They are incorporated in networks to expand their coverage area. They are also known as signal boosters.
Question#33 -Which of the following statements are correct concerning argument by analogy?
A. It is a deductive type of argument
B. It is an inductive type of argument
C. It is not intended to be mathematically certain
D. It is to be classified as either valid or invalid
E. Its conclusion does not follow from the premises with logical necessity
Options:-
1. A, C, and D only
2. A, D, and E only
3. B, C, and E only
4. B, D, and E only
Answer– 3rd
Explanation– Deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals and links premises with conclusions.
Question#34- Given below are two statements regarding Wireless Access Points (WAPs).
Statement I: WAPs are connected to the wired network at fixed locations.
Statement II: The WAP receives and transmits data between the two wired LANs.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:-
1 . Both Statement I and Statement II are false
2. Both Statement I and Statement II are true
3. Statement I is false but Statement II is true
4. Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Answer– 4
Explanation-Wireless access points (APs or WAPs) are networking devices that allow Wi-Fi devices to connect to a wired network. They form wireless local-area networks (WLANs). An access point acts as a central transmitter and receiver of wireless radio signals.
Question#35- What per cent of the children’s brain development occurs prior to 6 years?
Options:-
1 .25 % ,
2. 45 %,
3. 65 %,
4. 85 %
Answer– D
(Again a very irrelevant question asked by UGC-NET. See, you can’t prepare for these types of questions. Nobody can’t, but you have to act smartly in these types of questions.)
Question#36- What comes next in the following sequence?
5, 16, 51, 158,
Option 1- 387
Option 2- 481
Option 3 -482
Option 4- 487
Answer– 2nd
The next number is 481. The series is followed as: Step1- 5*3+1=16 Step2- 16*3+3=51 Step3- 51*3+5=158 Step4- 158*3+7=481 Number is multiplied by 3 in all steps .
Question: Read the given passage and answer the question that follows:
Let us try to explain social life as the pursuit of pleasure and the avoidance of pain. You will soon be saying that the hedonist begs the question, for even supposing that man does pursue these ends, the crucial problem of why he thinks one course rather than another likely to produce pleasure, is untouched. Does the guidance of man’s conscience explain? How then does he happen to have the particular conscience that he has? The theory of economic self-interest? But how do men come to conceive their interest in one way rather than another? The desire for security or prestige or domination or what is vaguely called self-realization? How do men conceive of their security, what do they consider prestige, how do they figure out the means of domination, or what is the notion of self which they wish to realize? Pleasure, pain, conscience, acquisition, protection, enhancement mastery are undoubtedly names for some of the ways people act. There may be instinctive dispositions that work toward such ends. But no statement of the end or any description of the tendencies to seek it can explain the behaviour which results. The very fact that men theorize at all is proof that their pseudo-environments, their interior representations of the world, are a determining element in thought, feeling, and action. For, if the connection between reality and human response were direct and immediate, rather than indirect and interred indecision and failure would be unknown and (if each of us fitted as snugly into the world, as the child in a womb), Mr Bernard Shaw would not have been able to say that except, for the first nine months of its existence, no human being manages its affairs as well as a plant.
Question#38- The thoughts of men are decided by
Options:-
Societal tendencies
Their behaviour
Their environment
Their inner perception of the world
Answer– 4th
Question#39- If the connection between reality and human response is direct, it will result in
Acquistion of prestige
Self-realisation
Successful actions
Useful theorization
Answer-3rd
Question#40- A man’s course of action is guided by –
Collective action
Critical evaluation of choices
Pursuit of self-interest
The thought of social welfare
Answer– 3rd
Question#41- The gist of the passage is that human behaviour is dictated by
Choices for pleasure
Emotional vagueness
Seeking smugness in a false world
The harsh realities of the world
Answer-3rd
Albeit, there is no hard and fast rule to solve comprehension. You can solve comprehension by doing more and more practice. Students usually take these types of questions for granted but you need to understand that this is a very complex topic and this deserves as much attention as you give to other topics.
There are some rules which you can follow,
1st- Do not read the full paragraph. Yes, you read it right. Do not spend a lot of time reading the whole paragraph. Just by having a look try to understand the gist of the paragraph. A quick read.
2- Read all the questions very carefully, yes very very carefully, and then again look at the paragraph. All I can guarantee you is that with this rule you will be able to solve 2 or 3 questions.
3- now one thing that I observed is that usually, questions are chronological as per the paragraph. So, let’s say you solved the first 2 or 3 questions by applying the above tricks. You don’t need to read the whole paragraph again. Just read the last few lines and you are ready to rock.
4- The most important question of any comprehension is the title – so the title is like the Bollywood song’s title line. They will repeat the line or title just as “bole chudiyan repeats in bole chudiyan song”. So try to pick that title. (thanks to me later)
5- By applying overhead rules I can assure you, you can easily solve 3 -4 questions, and because of lack of availability of time that is more than enough.
Study the table carefully to answer the question that follows :
The given table has the number of boys and girls (in hundreds) in 5 different years in 4 different schools (A, B, C, D) (M-Boys, F-Girls).
Question– Which school has the lowest number of girl students enrolled during 2016-2020?
Options:-
1 .A ,
2. B,
3. C,
4. D,
Question- Find out the difference between the number of boys in School A and School B during 2016-2020.
1. 440
2.445
3. 460
4. 450
Question- Which school has the minimum percentage increase in total student enrollment (both boys and girls) from 2019 to 2020?
A
B
C
D
Question- Which year has the minimum number of girls enrolled during 2016-2019?
A
B
C
D
Question- Which school has the maximum number of boys enrolled during 2016-2020?
A
B
C
D
Question– Identify the correct phases of activity for the Advance Organiser Model.
A. Presentation of curriculum embedding
B. Presentation of advance organizer
C. Presentation of study groups
D. Presentation of learning task or material
E. Strengthening cognitive organization Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
1. A, B, and C only
2. B, C, and D
3. B, D, and E only
4. C, D, and E only
Answer– 3rd
Explanation– An advance organizer is a cognitive instructional strategy used to promote the learning and retention of new information
Question– Given below are two statements
Statement I: The length and breadth of a rectangle are increased by 10% and 20% respectively, then its area increases by 23%.
Statement II: In 12 hours, the hour hand and the minute hand coincide 11 times.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:-
Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Question- What per cent decrease in salaries would exactly cancel out the 20% increase?
Question– Which of the following statements are correct?
A. The product of two integers is 500 and their difference is 5. Then, one of the numbers is 25.
B. The HCF of 108, 288, and 360 is 18.
C. The least number which is exactly divisible by each one of the given numbers is called their LCM.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Options:-
A and B only
A and C only
B and C only
Answer-2nd
0 notes
Text
Types of definitions in logic | Logical Reasoning Study Notes UGC NET
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/types-of-definitions-in-logic/
Types of definitions in logic | Logical Reasoning Study Notes UGC NET
A question from this topic features in the exam paper every time. A definition or a concept is given and candidate has to choose the definition name to which it belongs. This topic is sub topic of Locical Reasoning Syllabus and most of the time it has been skipped by Students !
Topics Based on UGC NET Syllabus of Logical Reasoning
Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, the structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition.
Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning.
Analogies.
Venn diagram: Simple and multiple uses for establishing the validity of arguments.
Indian Logic: Means of knowledge.
Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana(Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension).
Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference).
Types of definitions
What is a definition?
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term.
When writers are trying to explain an unfamiliar idea, they rely on definitions.
All definitions attempt to explain or clarify a term.
In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition that unambiguously qualifies what a mathematical term is and is not.
Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed.
What is axiom ?
a statement or proposition which is regarded as being established, accepted, or self-evidently true .
So, A definition is made up of two parts :
DEFINIENDUM- term which is to be defined.
A word, phrase, or symbol which is the subject of a definition, especially in a dictionary entry, or which is introduced into a logical system by being defined .
DEFINIEN– words used to define a term.
The different types of definitions are given below –
Different Types of definition
#1. Formal definition-
It is the definition which we generally see in the dictionary for a book, describing some particular characteristics of a concept things, or phenomenon. Such characteristics are used to familiarise reader with unknown terms.
A formal definition is based upon a concise, logical pattern that includes as much information as it can within a minimum amount of space .
Formal sentences components are the term being defined, the class it belongs to, and its distinguishing characteristics.
#2. Informal definition –
sometime a known word in the form of antonyms and synonyms can be used for explaining something unknown.
Such definitions are introduced by “ like “ “also known as” or “in other words” extra these are used to familiarise a lesson on term with any other well-known related term.
Having a relaxed, friendly, or unofficial style, manner, or nature.
Informal language is more casual and spontaneous. It is used when communicating with friends or family either in writing or in conversation.
#3. Extended definition –
An extended definition is a one or more paragraphs that attempt to explain a complex term. Some terms may be so important in your report, there may be so much confusion about them, or they may be so difficult to understand that an extended discussion is vital for the success of your report.
The extended definition can be formal or informal. As the name suggest these are used for explanation by including examples of listing familiar points, explaining concepts, historical references etc .
When you write reports, you may often discover that you need to explain certain basics before you can discuss the main subject matter.
For example:
In a report on new treatments for sickle cell anemia, you’d need a section defining the disease.
In a report on the benefits of drip irrigation, you’d need to write an extended definition of drip irrigation, explaining how it works and what equipment is used.
In a report showing small businesses how to weather economic recessions, an extended definition of the term economic recession would be needed first.
One of the first things to do when you write an extended definition is to compose the formal sentence definition of the term you are writing about. Place it toward the beginning of the extended definition.
It establishes the focus for the rest of the discussion. It is “formal” because it uses a certain form .
#4. Lexical definition –
Its relating to the words or vocabulary of a language.
The lexical definition also known as the dictionary definition, is the closely matching the meaning of the term in common usage.
It is also known as reporting definition.
According to Oxford English dictionary, lexical means relating to the words or vocabulary of a language. Does the lexical definition related to a words dictionary meaning of the meaning in the common vocabulary of language. It shows how the term is used in a language. It is difficult to change.
Lexical meanings are denotative meanings .
Lexical meanings can’t be changed.
It is used to avoid ambiguity.
It should be universal, never supporting any positive or negative aspects.
As its other name implies, this is the sort of definition , one is likely to find in the dictionary. A lexical definition is usually the type expected from a request for definition, and it is generally expected that such a definition will be stated as simply as possible in order to convey information to the widest audience .
The definition which reports the meaning of a word or a phrase as it is actually used by people is called a lexical definition. Meanings of words given in a dictionary are lexical definitions. As a word may have more than one meaning, it may also have more than one lexical definition.
Lexical definitions are either true or false. If the definition is the same as the actual use of the word then it is true, otherwise it is false .
#5 Stipulative definition –
A stipulative definition is a type of definition in which a new or currently existing term is given a new specific meaning for the purposes of argument or discussion in a given context .
When the term already exists, this definition may, but does not necessarily, contradict the dictionary definition of the term.
It is the new meaning giving to an already existing term on meaning assigned to a new term.
It is arbitrary in nature .
A term can have different stipulative meaning at different places or among different people.
For example some people use “LOL” for “lots of love” and some use it for “laughing out loud”.
Idioms and slangs have stipulative meanings .
The terms to prove stipulative definition is sometimes used to make a deliberately misleading definition.
It is easy to change as it has a meaning in local language.
When the stability of definition of a term that popular former y my get included in the dictionary and becomes a lexical definition.
For example:
Suppose we say that to love someone is to be willing to die for that person.
Take “human” to mean any member of the species Homo sapiens.
For the purposes of argument, we will define a “student” to be “a person under 18 enrolled in a local school”
#6 Persuasive definition –
Such definitions favour a particular view or an favour any view, but are presented in a neutral form. In such definitions , emotional, positive or derogatory meaning is attached to the term.
The term “persuasive definition” was introduced by philosopher Charles Stevenson as part of his emotive theory of meaning .
It is usually used in discussions, debates , etc to favour or unfavour particular views. For example – there can be different views on death penalty , those who are in favour will define it as Harsh punishment which will help in preventing heinous crimes and those who are not in its favour will define it as “legalized murder”.
A persuasive definition is a form of stipulativedefinition which supports to describe the true or commonly accepted meaning of a term, while in reality stipulating an uncommon or altered use, usually to support an argument for some view, or to create or alter rights, duties or crimes.
Examples of persuasive definitions (definist fallacies) include:
Democrat – “a leftist who desires to overtax the corporations and abolish freedom in the economic sphere”.
Persuasive definitions commonly appear in controversial topics such as politics, sex, and religion, as participants in emotionally charged exchanges will sometimes become more concerned about swaying people to one side or another than expressing the unbiased facts.
#7 Parenthetical definition –
Sometimes, for the sake of explanation we write the meanings of some words in parentheses in a sentence. Meaning of a difficult word mentioned in a few words in parentheses ( brackets) is known as parenthetical definition.
Some times to understand better difficult words we write easy words or meaning in brackets are called parenthetical meaning.
For example – to understand meanings of arbitrariness we write in brackets to choose randomly or by chance . what ever we write in bracket for own understanding are called parenthetical definition.
Parenthetical phrase is an explanatory or qualifying word, clause, or sentence inserted into a passage. The parenthesis could be left out and still form grammatically correct text.
Parentheses are usually marked off by round or square brackets, dashes, or commas.
Billy-bob, a great singer, was not a good dancer. The phrase a great singer, set off by commas, is both an appositive and a parenthesis.
A dog (not a cat) is an animal that barks. The phrase not a cat is a parenthesis.
My umbrella (which is somewhat broken) can still shield the two of us from the rain. The phrase which is somewhat broken is a parenthesis.
The following are examples of types of parenthetical phrases:
Introductory phrase: Once upon a time, my father ate a muffin.
Interjection: My father ate the muffin, gosh damn it!
Aside: My father, if you don’t mind me telling you this, ate the muffin.
Appositive: My father, a jaded and bitter man, ate the muffin.
Absolute phrase: My father, his eyes flashing with rage, ate the muffin.
Free modifier: My father, chewing with unbridled fury, ate the muffin.
Resumptive modifier: My father ate the muffin, a muffin which no man had yet chewed.
Summative modifier: My father ate the muffin, a feat which no man had attempted.
While a parenthesis need not be written enclosed by the curved brackets called parentheses, their use, principally around rhetorical parentheses, has made the punctuation marks the only common use for the term in most contexts.
#8. Sentence definition-
such definitions are given in sentence forms , like ‘ computer is an electronic machine used to store , process and retrieve data.
Here is the first part of definition is ‘ computer the term itself , the next part- electronic machine , shows what it is , and the last part depicts the function of computer.
Sentence is a set of words that is complete in itself, typically containing a subject and predicate, conveying a statement, question, exclamation, or command, and consisting of a main clause and sometimes one or more subordinate clauses.
The sentence is generally defined as a word or a group of words that expresses a thorough idea by giving a sentence or order.
#9. Intention definition –
Such definitions specifiy the properties, features, meanings , and the necessary and sufficient conditions of a term.
For example – even numbers are the numbers divisible by two.
#10. Ostensive definition –
literal meaning of ostensive is denoting a way of defining by direct demonstration, e.g. pointing .
In this type of definition, a term is described by showing the real objects; for example, showing banana, tulips, mangos, etc, to describe the yellow colour .
An ostensive definition conveys the meaning of a term by pointing out examples.
This type of definition is often used where the term is difficult to define verbally, either because the words will not be understood (as with children and new speakers of a language) or because of the nature of the term (such as colors or sensations).
It is usually accompanied with a gesture pointing to the object serving as an example, and for this reason is also often referred to as “definition by pointing”.
An ostensive definition assumes the questioner has sufficient understanding to recognize the type of information being given .
SOLVED MCQ Question for practice
Question 1 – Determine the nature of the following definition “abortion” means the ruthless murdering of innocent beings.
Lexical
Persuasive
Stipulative
Theoretical
Answer- Persuasive
Solution – A persuasive definition is a form of stipulative definition which supports to describe the true or commonly accepted meaning of a term, while in reality stipulating an uncommon or altered use, usually to support an argument for some view, or to create or alter rights, duties or crimes.
Question 2 – when the conclusion of an argument follows from its premise conclusively, the argument is called
Circular argument
Inductive argument
Deductive argument
Analogical argument
Answer- Deductive argument
Solution– Deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals, and links premises with conclusions.
Question 3- A stipulative definition may be said to be
Always true
Always false
Sometime true, Sometime false
Neither true Neither false.
Answer-Sometime true, Sometime false
Solution- Stipulative definition is a type of definition in which a new or currently existing term is given a new specific meaning for the purposes of argument or discussion in a given context . When the term already exists, this definition may, but does not necessarily, contradict the dictionary definition of the term.
Question 4. A definition put forward to resolve a dispute by influencing attitudes or stirring emotions is called
Lexical
Persuasive
Stipulative
Precision
Answer– Persuasive [See Above Notes]
Question 5 – A definition that has a meaning that is deliberately assigned to some symbol is called :
Lexical
Pressing
Stipulative
Persuasive
Answer– Stipulative [See Above Notes]
Solution already given in one of the above question.
0 notes
Text
Types of definitions in logic | Logical Reasoning Study Notes UGC NET
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/types-of-definitions-in-logic/
Types of definitions in logic | Logical Reasoning Study Notes UGC NET

A question from this topic features in the exam paper every time. A definition or a concept is given and candidate has to choose the definition name to which it belongs. This topic is sub topic of Locical Reasoning Syllabus and most of the time it has been skipped by Students !
Topics Based on UGC NET Syllabus of Logical Reasoning
Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, the structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition.
Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning.
Analogies.
Venn diagram: Simple and multiple uses for establishing the validity of arguments.
Indian Logic: Means of knowledge.
Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana(Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension).
Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference).
Types of definitions
What is a definition?
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term.
When writers are trying to explain an unfamiliar idea, they rely on definitions.
All definitions attempt to explain or clarify a term.
In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition that unambiguously qualifies what a mathematical term is and is not.
Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed.
What is axiom ?
a statement or proposition which is regarded as being established, accepted, or self-evidently true .
So, A definition is made up of two parts :
DEFINIENDUM- term which is to be defined.
A word, phrase, or symbol which is the subject of a definition, especially in a dictionary entry, or which is introduced into a logical system by being defined .
DEFINIEN– words used to define a term.
The different types of definitions are given below –
Different Types of definition
#1. Formal definition-
It is the definition which we generally see in the dictionary for a book, describing some particular characteristics of a concept things, or phenomenon. Such characteristics are used to familiarise reader with unknown terms.
A formal definition is based upon a concise, logical pattern that includes as much information as it can within a minimum amount of space .
Formal sentences components are the term being defined, the class it belongs to, and its distinguishing characteristics.
#2. Informal definition –
sometime a known word in the form of antonyms and synonyms can be used for explaining something unknown.
Such definitions are introduced by “ like “ “also known as” or “in other words” extra these are used to familiarise a lesson on term with any other well-known related term.
Having a relaxed, friendly, or unofficial style, manner, or nature.
Informal language is more casual and spontaneous. It is used when communicating with friends or family either in writing or in conversation.
#3. Extended definition –
An extended definition is a one or more paragraphs that attempt to explain a complex term. Some terms may be so important in your report, there may be so much confusion about them, or they may be so difficult to understand that an extended discussion is vital for the success of your report.
The extended definition can be formal or informal. As the name suggest these are used for explanation by including examples of listing familiar points, explaining concepts, historical references etc .
When you write reports, you may often discover that you need to explain certain basics before you can discuss the main subject matter.
For example:
In a report on new treatments for sickle cell anemia, you’d need a section defining the disease.
In a report on the benefits of drip irrigation, you’d need to write an extended definition of drip irrigation, explaining how it works and what equipment is used.
In a report showing small businesses how to weather economic recessions, an extended definition of the term economic recession would be needed first.
One of the first things to do when you write an extended definition is to compose the formal sentence definition of the term you are writing about. Place it toward the beginning of the extended definition.
It establishes the focus for the rest of the discussion. It is “formal” because it uses a certain form .
#4. Lexical definition –
Its relating to the words or vocabulary of a language.
The lexical definition also known as the dictionary definition, is the closely matching the meaning of the term in common usage.
It is also known as reporting definition.
According to Oxford English dictionary, lexical means relating to the words or vocabulary of a language. Does the lexical definition related to a words dictionary meaning of the meaning in the common vocabulary of language. It shows how the term is used in a language. It is difficult to change.
Lexical meanings are denotative meanings .
Lexical meanings can’t be changed.
It is used to avoid ambiguity.
It should be universal, never supporting any positive or negative aspects.
As its other name implies, this is the sort of definition , one is likely to find in the dictionary. A lexical definition is usually the type expected from a request for definition, and it is generally expected that such a definition will be stated as simply as possible in order to convey information to the widest audience .
The definition which reports the meaning of a word or a phrase as it is actually used by people is called a lexical definition. Meanings of words given in a dictionary are lexical definitions. As a word may have more than one meaning, it may also have more than one lexical definition.
Lexical definitions are either true or false. If the definition is the same as the actual use of the word then it is true, otherwise it is false .
#5 Stipulative definition –
A stipulative definition is a type of definition in which a new or currently existing term is given a new specific meaning for the purposes of argument or discussion in a given context .
When the term already exists, this definition may, but does not necessarily, contradict the dictionary definition of the term.
It is the new meaning giving to an already existing term on meaning assigned to a new term.
It is arbitrary in nature .
A term can have different stipulative meaning at different places or among different people.
For example some people use “LOL” for “lots of love” and some use it for “laughing out loud”.
Idioms and slangs have stipulative meanings .
The terms to prove stipulative definition is sometimes used to make a deliberately misleading definition.
It is easy to change as it has a meaning in local language.
When the stability of definition of a term that popular former y my get included in the dictionary and becomes a lexical definition.
For example:
Suppose we say that to love someone is to be willing to die for that person.
Take “human” to mean any member of the species Homo sapiens.
For the purposes of argument, we will define a “student” to be “a person under 18 enrolled in a local school”
#6 Persuasive definition –
Such definitions favour a particular view or an favour any view, but are presented in a neutral form. In such definitions , emotional, positive or derogatory meaning is attached to the term.
The term “persuasive definition” was introduced by philosopher Charles Stevenson as part of his emotive theory of meaning .
It is usually used in discussions, debates , etc to favour or unfavour particular views. For example – there can be different views on death penalty , those who are in favour will define it as Harsh punishment which will help in preventing heinous crimes and those who are not in its favour will define it as “legalized murder”.
A persuasive definition is a form of stipulativedefinition which supports to describe the true or commonly accepted meaning of a term, while in reality stipulating an uncommon or altered use, usually to support an argument for some view, or to create or alter rights, duties or crimes.
Examples of persuasive definitions (definist fallacies) include:
Democrat – “a leftist who desires to overtax the corporations and abolish freedom in the economic sphere”.
Persuasive definitions commonly appear in controversial topics such as politics, sex, and religion, as participants in emotionally charged exchanges will sometimes become more concerned about swaying people to one side or another than expressing the unbiased facts.
#7 Parenthetical definition –
Sometimes, for the sake of explanation we write the meanings of some words in parentheses in a sentence. Meaning of a difficult word mentioned in a few words in parentheses ( brackets) is known as parenthetical definition.
Some times to understand better difficult words we write easy words or meaning in brackets are called parenthetical meaning.
For example – to understand meanings of arbitrariness we write in brackets to choose randomly or by chance . what ever we write in bracket for own understanding are called parenthetical definition.
Parenthetical phrase is an explanatory or qualifying word, clause, or sentence inserted into a passage. The parenthesis could be left out and still form grammatically correct text.
Parentheses are usually marked off by round or square brackets, dashes, or commas.
Billy-bob, a great singer, was not a good dancer. The phrase a great singer, set off by commas, is both an appositive and a parenthesis.
A dog (not a cat) is an animal that barks. The phrase not a cat is a parenthesis.
My umbrella (which is somewhat broken) can still shield the two of us from the rain. The phrase which is somewhat broken is a parenthesis.
The following are examples of types of parenthetical phrases:
Introductory phrase: Once upon a time, my father ate a muffin.
Interjection: My father ate the muffin, gosh damn it!
Aside: My father, if you don’t mind me telling you this, ate the muffin.
Appositive: My father, a jaded and bitter man, ate the muffin.
Absolute phrase: My father, his eyes flashing with rage, ate the muffin.
Free modifier: My father, chewing with unbridled fury, ate the muffin.
Resumptive modifier: My father ate the muffin, a muffin which no man had yet chewed.
Summative modifier: My father ate the muffin, a feat which no man had attempted.
While a parenthesis need not be written enclosed by the curved brackets called parentheses, their use, principally around rhetorical parentheses, has made the punctuation marks the only common use for the term in most contexts.
#8. Sentence definition-
such definitions are given in sentence forms , like ‘ computer is an electronic machine used to store , process and retrieve data.
Here is the first part of definition is ‘ computer the term itself , the next part- electronic machine , shows what it is , and the last part depicts the function of computer.
Sentence is a set of words that is complete in itself, typically containing a subject and predicate, conveying a statement, question, exclamation, or command, and consisting of a main clause and sometimes one or more subordinate clauses.
The sentence is generally defined as a word or a group of words that expresses a thorough idea by giving a sentence or order.
#9. Intention definition –
Such definitions specifiy the properties, features, meanings , and the necessary and sufficient conditions of a term.
For example – even numbers are the numbers divisible by two.
#10. Ostensive definition –
literal meaning of ostensive is denoting a way of defining by direct demonstration, e.g. pointing .
In this type of definition, a term is described by showing the real objects; for example, showing banana, tulips, mangos, etc, to describe the yellow colour .
An ostensive definition conveys the meaning of a term by pointing out examples.
This type of definition is often used where the term is difficult to define verbally, either because the words will not be understood (as with children and new speakers of a language) or because of the nature of the term (such as colors or sensations).
It is usually accompanied with a gesture pointing to the object serving as an example, and for this reason is also often referred to as “definition by pointing”.
An ostensive definition assumes the questioner has sufficient understanding to recognize the type of information being given .
SOLVED MCQ Question for practice
Question 1 – Determine the nature of the following definition “abortion” means the ruthless murdering of innocent beings.
Lexical
Persuasive
Stipulative
Theoretical
Answer- Persuasive
Solution – A persuasive definition is a form of stipulative definition which supports to describe the true or commonly accepted meaning of a term, while in reality stipulating an uncommon or altered use, usually to support an argument for some view, or to create or alter rights, duties or crimes.
Question 2 – when the conclusion of an argument follows from its premise conclusively, the argument is called
Circular argument
Inductive argument
Deductive argument
Analogical argument
Answer- Deductive argument
Solution– Deductive argument, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. Deductive reasoning goes in the same direction as that of the conditionals, and links premises with conclusions.
Question 3- A stipulative definition may be said to be
Always true
Always false
Sometime true, Sometime false
Neither true Neither false.
Answer-Sometime true, Sometime false
Solution- Stipulative definition is a type of definition in which a new or currently existing term is given a new specific meaning for the purposes of argument or discussion in a given context . When the term already exists, this definition may, but does not necessarily, contradict the dictionary definition of the term.
Question 4. A definition put forward to resolve a dispute by influencing attitudes or stirring emotions is called
Lexical
Persuasive
Stipulative
Precision
Answer– Persuasive [See Above Notes]
Question 5 – A definition that has a meaning that is deliberately assigned to some symbol is called :
Lexical
Pressing
Stipulative
Persuasive
Answer– Stipulative [See Above Notes]
Solution already given in one of the above question.
0 notes
Text
Career After NET JRF Exam: Salary Structure, Options & Road Ahead
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/career-options-after-ugc-net-exam/
Career After NET JRF Exam: Salary Structure, Options & Road Ahead
NTA UGC NET Job Profile 2021: Career Options After JRF & Assistant Professor
Career Scope After Qualifying UGC NET Exam
One may wonder what’s next once they qualify after sitting for the UGC NET Exam. The most commonly asked question regarding qualifying for the exams is the career scope going forward.
That’s only normal because most people learn to get jobs or advance their careers if they already have one. It is no secret that the UGC NET mainly revolves around research and lecturing.
It allows you to join the Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) or become an assistant lecturer.
What’s next after passing the JRF Exam?
This article is all about the career scope after qualifying for the UGC NET exam. So, without further ado, let’s get started and see what your future looks like upon qualifying.
Career Opportunities after Qualifying for the UGC NET JRF Exam
It is no secret that the JRF is all about research. Upon qualifying for the JRF exam, you are at liberty to embark on the research and discover various future things.
You get to choose a university or college among the many NET coordinating learning institutions to pursue the research.
Below is a summary of career options to choose from.
Select the college or university of choice among the NET coordinating Institutes
Identify an experienced senior faculty and utilize it to get the knowledge necessary for your career.
Choose research projects that will significantly impact your career, whether short-term or long-term, because it would make a huge difference in the end as far as your career advancement is concerned.
Look for fields that often attract research funding and start researching, preferably those with over two funding sources.
After qualifying following the JRF exam, you can look for a renowned organization with a research department and start your career right there.
You can work in government labs such as SERB, ICMR, DRDO, ISRO and ICAR.
Alternatively, establish a laboratory, hire research experts and work together to discover new things.
Last but not least, start research training which is perfect for boosting your knowledge in your area of specialty.
UGC NET Job Opportunities and Promotions after Qualifying for the JRF Exam
The Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) scheme of the University Grants Commission (UGC) is open to candidates who qualify in the National Eligibility Testing (NET) of the UGC and the UGC-Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) joint test.
The objective of the JRF scheme is to provide opportunities to NET-qualified candidates to undertake advanced studies and research leading to M.Phil/Ph.D.
for JRF Eligibility are Candidates who have qualified in NET or the UGC-CSIR joint test. However, the selection for the JRF is made by the universities/institutions/colleges.
Upon choosing a college or university for further studies in research, that marks the beginning of a promising career path.
For instance, if working as a Junior Research Fellow (JRF), you can get promoted to Senior Research Fellow (SRF). Other promotions include Project Fellow (PF) to Senior Project Fellow (SPF), Project Assistant or Associate (PA) to Senior Project Assistant or Associate (SPA), Author to Senior Author, and Project Manager to Project Head.
PostAfter PromotionJunior Research Fellow (JRF)Senior Research Fellow (SRF)Project Fellow (PF)Senior Project Fellow (SPF)Project Assistant (PA)Senior Project Assistant (SPA)AuthorSenior AuthorProject ManagerProject Head
There is a lot to achieve after passing the JRF Exam and qualifying for the fellowship.
Heads up!
The tenure of fellowship is initially for two years under the JRF scheme. Upon expiry of this period, the work of the Fellow will be evaluated by experts.
If the research work is found satisfactory, his/her tenure will be extended for a further period of three years under the enhanced emoluments of the Senior Research Fellowship (SRF).
In case the work for the first two years is not found satisfactory, an additional year will be given to him/her for improvement.
However, during this period he/she will bedesignated as a Junior Research Fellow. In such cases work will be evaluated again after three years, and if improvement is found, the Fellow will get two more years under the SRF.
Thus, the total period of fellowship (JRF and SRF) is five years, will no further provision of extension.
Benefits of Pursuing Research in the Relevant Postgraduate Subject after the UGC NET Exam
Upon passing the JRF Exam, qualifying for the fellowship, and enrolling in a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree, there is a lot to expect.
A 5-year fellowship
The first two years on this fellowship will see the JRF pocket up to Rs. 31000 monthly and an additional House Rent Allowance (HRA) every month.
The HRA differs from one individual to the other depending on the institutions they are working for.
The last three years mean more money for the JRF fellows since they earn up to Rs. 35000. The HRA is also offered, but again, it is different depending on the institution you chose.
Additionally, various grants are offered to the JRF. The amount is not constant since multiple universities have different policies when it comes to this matter. Each IIM and private university also has a different program policy. Therefore, research on what the various institutions provide when selecting the one to enroll in.
After the JRF Exam, qualifiers end up killing two birds with the same stone. By the end of the fellowship, they get to earn a doctorate, not forgetting to earn a stipend all along the way.
Upon completion, you have a high chance of getting a job in a corporate firm to work as a researcher. After all, they usually prefer JRF qualifiers over other researchers.
House Rent Allowance –
Suitable single-seated hostel accommodation may be provided to the JRF candidate in the institutions. In case of non-availability, HRA as per rules of the university/institution will be paid, to the fellow subject to the submission of the HRA Certificate through the Registrar/Principal.
If the fellow makes his/her own arrangements of accommodation, he/she may be entitled to draw HRA as per categorization of cities by the Government of India.
The fellow need to submit a certificate for the purpose to the UGC for claiming HRA through the concerned university/institution/colleges.
Medical–
No separate/fixed medical assistance is provided. However, the fellow may avail of the medical facilities available in the institution/university/college.
Leave-
JRFs are entitled to a maximum period of 30 days of leave in a year in addition to public holidays. They are not entitled to any other vacations.
Women candidates are eligible for maternity leave of 180 days at full rates of fellowship once during the tenure of their award.
In special cases, Junior Research Fellows may be allowed leave without fellowship by the Commission up to one academic year during the entire tenure
Career Opportunities after Qualifying for the UGC NET Exam as an Assistant Professor or Lecturer
The main reason why people sit for the UGC NET exams is to qualify for the lecturer or assistant professor position. Upon qualifying, this is what to expect:
Select any top university in India and apply for an assistant professor post
You can teach professional students, undergraduates, or post-doctoral fellows. It all depends on the position you get and the skills you possess.
Carry out problem-solving sessions to help the students learn
UGC NET Job Opportunities and Promotions after Qualifying as an Assistant Professor
Becoming an assistant professor is an excellent opportunity to pursuing even better careers in the future. You stand a chance to serve in other job posts and even earn yourself promotions in the future. Let’s dive into the jobs and their respective promotions.
As a junior Assistant Professor, you can get a promotion to an Assistant Professor. Others include Assistant Professor to Senior Assistant Professor, Senior Assistant Professor to Assistant Professor (Selection Grade), Assistant Professor (Selection Grade) to Associate Professor, Associate Professor to Professor, and Professor to General Head or Manager.
S. No.Offered PositionsPosition after Promotion1.Junior Assistant ProfessorAssistant Professor2.Assistant ProfessorSenior Assistant Professor3.Senior Assistant ProfessorAssistant Professor (Selection Grade)4.Assistant Professor (Selection Grade)Associate Professor5.Associate ProfessorProfessor6.ProfessorHead of Department (HOD)
UGC NET Exam qualifiers opportunities in Public Sector Undertakings
Upon passing your JRF exam or the assistant professor, you no longer have to pursue a lectureship. After all, some Public Sector Undertakings (PSU’s) are willing to hire candidates who have qualified for the UGC NET Exam.
They employ executives in corporate communications, management, finance, human resource, and Research & Development.
Some of the PSU’s one can work with include: (Open Link )
Department of Space, Indian Space Research Organisation
Oil and Natural gas corporation (ONGC)
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
Naval Materials Research Laboratory
Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL)
Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL)
Oil India Limited (OIL)
University Grants Commission (UGC) – Also provides opprtunity as consulatnt puerly on contract basis.
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited
UGC NET Career Options in Various Academic Departments
You can also consider these job profiles upon passing your JRF exam or qualifying for the assistant professor:
Program Executive
Author
IP Lead
Guest Faculty
Coaching Tutor both Online and Offline
Transmission Executive
Center Manager
Lab Trainer
Consultant
UGC NET Job Portal
Let’s Look at some data based on UGC NET JOB Portal to see how competitive for you to get the JRF and opportunity for an Assitant lectureship.
[Please note – Below graphs are based on data shown on UGC NET Job Portal, i.e considered only those who has registered on the portal.]
#1. Top 20 Subject Wise Subject wise list for NET Qualified Candidates – You can see here that commerce and management subjects are most popular and contain higher no of qualified students followed by computer science and education.
#2. Top 20 Subject wise list for NET-JRF Qualified Candidates – You can see that JFR counts are in line with the NET qualified students shown above. Commerce and management subject is most popular for NET Exam.
How to Apply for a Job Opportunity for UGC NET Exam Qualifiers
Things are now plentiful, thanks to the official UGC NET Job Portal. It is a place to find all the jobs discussed above. If you want to recruit, you get to post the job over there, not forgetting to check out the academic profiles and resumes of the relevant and interested parties. On the other hand, students search for the jobs that suit them best. Follow these steps to use the portal for jobs.
Visit the official page of the UGC NET Job Portal.
On the left side of that page, choose to register if it is your first time or log in if you already have an account.
Fill in the necessary details, including category, password, user name or email ID, and verification code.
Finally, browse the jobs and apply for the ones you deem fit, not forgetting to consider your skills and qualifications while at it.
FAQs on Career Scope after Qualifying for UGC NET Exam
Is it easy to get a job after qualifying for UGC NET Assistant Professor or JRF Exams?
As long as you qualified for the UGC NET Exam, you can rest assured that the future of your career is bright. For instance, presenting that certificate is enough to earn you a job in renowned learning institutions and organizations.
Does qualifying after the JRF exam offer you a scholarship or a job?
It is important to note that JRF is a scholarship program. It allows you to pursue a PhD in the relevant subject, but you also get to pocket a monthly stipend while at it. Equally important, it gives you a great opportunity to get other jobs related to research.
Will NTA ensure that you get a job after qualifying for the UGC NET Exam?
After you qualify for the JRF exam, a job isn’t a guarantee. However, qualifiers can rest assured that they will get a 2-year research scholarship. Alternatively, they can enrol in a PhD program which increases their chances of getting great jobs in the future.
What salary should I expect after qualifying for the UGC NET Exam?
Upon qualifying after the JRF exam, you can expect a monthly stipend of Rs. 31000 for at least two years. On the other hand, assistant professors receive Rs. 41000 every month. The salary increases as you get various promotions which is easy and possible with the UGC NET certificate.
Final Words
Passing the JRF exam and qualifying for the program offers you many job opportunities, especially in years to come. The same case applies to the assistant professor posts. Therefore, consider doing the UGC NET exam even if you are yet to do so.
0 notes
Text
Structure of Categorical propositions | Mood and Figure
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/structure-of-categorical-propositions-mood-and-figure/
Structure of Categorical propositions | Mood and Figure

UGC NET Exam Study Notes on “Structure of Categorical propositions” and “Mood and Figure”
Topics Based on UGC NET Syllabus of Logical Reasoning
Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, the structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition. ( This is Big Section, Categorical Propositions & Mood and Figure Part is covered in this article,)
Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning.
Analogies.
Venn diagram: Simple and multiple uses for establishing the validity of arguments.
Indian Logic: Means of knowledge.
Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana(Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension).
Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference).
Whats is the Categorical Propositions?
A “Subject” of a sentence is the thing that has some property or class is being attributed to, the “Predicate” is the property or class that is being attributed to the subject, and the “Copula” is the word that links the two together.
For Example – All dogs are mammals
Here, “dogs” is the subject, “mammals” is the predicate, and “are” is the copula. This particular statement about bunnies has a certain form, the form of a categorical proposition.
So in simple words, “A proposition that relates two classes or categories” is known as a Categorical Proposition.
If you look at the above example in addition to subject, predicate and coupla it also has “quantifiers” that tells you HOW MANY of the subjects are being referred into the statement.
Categorical propositions tell us one of four things: (1) ALL members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (2) NONE of the members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (3) SOME of the members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (4) SOME of the members of the subject class are NOT included in the predicate class.
Here are some examples of each of these 4 kinds of the categorical proposition: (1) All dogs are mammals. (2) No dogs are reptiles. (3) Some dogs are cute. (4) Some dogs are not potty-trained.
Here is the FORM of each of these 4 kinds of categorical proposition: (1) All S are P. (2) No S are P. (3) Some S are P. (4) Some S are not P
Now, let’s go over some definitional terms: Categorical statements each have a quantity and a quality.
Quantity: Refers to HOW MUCH of the subject class is included in the predicate class.
Quantity is either: (a) Universal – Tells us something about how ALL of the subjects are related to the predicate. (b) Particular – Tells us how SOME of the subjects are related to the predicate.
Quality: Refers to whether the proposition is AFFIRMING something or DENYING something of a subject.
Quality is either: (a) Affirmative – Members of the subject ARE included in the predicate. (b) Negative – Members of the subject are NOT included in the predicate.
For instance, of the 4 kinds of the categorical proposition we discussed above:
PropositionQuantityQualityLetterAll S are P.universalaffirmativeANo S are P.universalnegativeESome S are P.particularaffirmativeISome S are not P.particularnegativeO
For shorthand, it is common to refer to each of these types of the proposition by a letter; Those letters are A, E, I, and O.
Now, you must be wondering what are these “A, E, I, O”, Let’s understand with more examples.
A is universal positive.
All apples are good.
All milk is white .
E Is universal negative.
No bread is butter.
No egg is white.
I is particular positive
Some apples are good.
Some bread is butter.
Some eggs are white.
O is particular negative
No apple are good.
No bread is butter.
NO eggs are white.
Categorical Syllogisms
Syllogism: An argument consisting of three statements: TWO premises and ONE conclusion.
Categorical syllogism: A syllogism consisting of three categorical propositions, and containing THREE DISTINCT TERMS, each of which appears in exactly two of the three propositions.
So, what are these 3 terms mentioned? Consider the following syllogism:
All mammals are creatures that have hair.
All dogs are mammals.
Therefore, all dogs are creatures that have hair.
There are THREE different terms in this argument (besides the quantifiers and the copulas). The three different terms are called the “major term”, the “minor term”, and the “middle term.”
Notice that the conclusion only contains TWO of the three terms but one of the terms is found only on the premises.
Here are some definitions: Major Term: The predicate term of the conclusion (above, “creatures that have hair”) Minor Term: The subject term of the conclusion (above, “dogs”) Middle Term: The term that does NOT appear in the conclusion (above, “mammals”)
Finally, note that premise 1 contains the major term, while premise 2 contains the minor term. Premise 1 is therefore called the major premise, while premise 2 is called the minor premise. The standard form demands that the major premise (i.e., the one containing the major term) ALWAYS be listed first.
Easy to grasp right? We will cover a very simple trick to remember these “there terms” and this question is the favourite of a UGC NET examiner from the last few years.
Warning! Tricks to remember “MAJOR”, “MINOR” and “MIDDLE” terms. Let’s take another example.
Statement 1 – All A are B .
Statement 2 – All B are C .
Conclusion – All A are C .
Here –
Statement first is also known as premises 1 and Statement second is also known as premises 2.
In the above statement “B” is the middle term which is also known as cancelling term and in Indian logic known as “Hetu”.
In the above statement “A” is minor term and “C” is major term.
Now, how to find out which one is major term, minor term and middle term?
MAJOR TERM – the term in a syllogism that is the predicate of the conclusion is known as major term .
You should always check “conclusion” for major term. For example is above statement, the conclusion is All A are C . So, the last term in the conclusion that is C is your major term.
Example 1– If the conclusion is “ All parrots are green”
So, in the above statement “green” is major term.
Example 2– No apple is good .
So, in the above statement “good” is your major term .
Tip– second word of your conclusion is always your major term.
MINOR TERM- the term in a syllogism that is the subject of the conclusion is known as Minor term. It is also known as subject.
You always should look into conclusion to find out Minor term. Remember- major term was the last term of conclusion but Minor term is the first term in the conclusion .
This Minor term is known as “paksha” .
Remember it as – it is in the increasing order that is it goes from small to big. In the above given statement our conclusion is “All A are C” so, in this statement “a” is minor term because A is the first term in the conclusion.
For more clarity have a look on the given examples :
1st example – No blackboard is green
Minor term – blackboard
Major term – green
2nd example – some bread is butter
Minor term- bread
Major term – butter
MIDDLE TERM- In syllogism, a middle term is a term that appears in both premises but not in the conclusion of a categorical syllogism. This is also known as cancelling term and Indian logic this is known as “Hetu” or “Reason”.
To find out which one is middle term, you always should look into premises. Middle term never appears in the conclusion.
The term which is present in both premises- premises 1 and premises 2 is called middle term.
The mutual term present in both statements are called middle term.
Example 1
Statement1 – some breads are milk .
Statement2- some milk is butter .
Conclusion – some butter are bread .
In this given statement “ milk” is the mutual word available in both statements. So, milk is our middle term . Observe carefully “ Milk is not present in conclusion”.
Mood and Figure
Now that we know the correct FORM of categorical syllogisms, we can learn some tools that will help us to determine when such syllogisms are valid or invalid.
All categorical syllogisms have what is called a “mood” and a “figure.”
What are mood and Figures?
Mood: The mood of a categorical syllogism is a series of three letters corresponding to the type of proposition the major premise, the minor premise, and the conclusion is (A, E, I, or O).
Mediaeval logicians invented a simple method of labelling the various forms in which a categorical syllogism may occur by simply stating its mood and figure.
Mood – It usually depends upon the type of propositions (A, E, I, O).
Figure – It depends on the arrangement of the middle term in the proposition.
The figure of the syllogism is based on the arrangement of Subject and predicate and middle term or the common term.
The different types of figures in syllogism are:
First figureSecond figureThird figureFourth figureM-PP-MM-PP-MS-MS-MM-SM-PS-PS-PS-PS-P
In this above table: M stands for “middle term”, S stands for “subject”, P stands for “predicate”
Tips to remember this above table-
In first figure – M makes a sort of vertical right hand like this “ \”.
In second figure- M makes a straight hand in right direction like this “|” in right hand side.
In Third figure- M makes a right hand is left direction like this “|” in left hand side.
In Fourth figure- M makes a sort of vertical left hand like this “/” .
There is 256 combination of the different forms of mood and figure. Out of these 256 combinations, only 15 were found to be valid by Aristotle. There are 9 conditionally valid argument forms for categorical syllogisms in addition to the 15 unconditionally valid argument forms: The valid combinations are given below in the table.
Unconditionally Valid Forms: There are 15 combinations of mood and figure that are valid from the Boolean standpoint (we call these “unconditionally valid” argument forms).
The below chart depicts ALL of 15 the unconditionally valid argument forms
First figureAAA,EAE,AII,EIOSecond figureEAE,AEE,EIO,AOOThird figureIAI, AII, OAO, EIOFourth figureAEE,IAI,EIO
Recall this argument from earlier:
All mammals are creatures that have hair.
All dogs are mammals.
Therefore, all dogs are creatures that have hair.
Its mood is “AAA” since all three propositions are “A” propositions (i.e., they are all of the forms “All S are P”). Its figure is “figure 1”
Points to keep in mind( only for the first figure)
If both the premises are positive (A or I), then the conclusion will also be positive (A Or I)
If one of the premises is negative (E or O), then the conclusion will also be negative (E or O).
If one of the premises is particular (I or O), then the conclusion will also be particular (I or O)
If one of the premises is particular negative (O) , then the conclusion will aslo be particular negative .
If one of the premises is particular and the second one is negative, then also the conclusion will be particular negative (0).
Some of the mood and figure examples
Examples of the First figure
AAA
Major premises : All B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : All A are C.
EAE
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : No A are C.
AII
Major premises : All B are C.
Minor premises : Some A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
EIO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : some A are B.
Conclusion : some A are not C.
Special cases
AAI
Major premises :All B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
EAO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Examples of the second figure
EAE
Major premises : No C are B.
IMinor premises : All A are B
Conclusion : No A are C.
AEE
Major premises : All C are B
Minor premises : No A are B.
Conclusion :No A are C.
EIO
Major premises: No C are B.
Minor premises : Some A are B
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
AOO
Major premises : All C are B .
Minor premises : Some A are not B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Special cases
AEO
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : No A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C
EAO
Major premises : No C are B.
Minor premises : All A Are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Examples of the Third figure
IAI
Major premises : Some B are C.
Minor premises : All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
AII
Major premises: All A are C.
Minor premises :Some B are A.
Conclusion: Some A are C.
OAO
Major premises : Some B are not C.
Minor premises: All B are A.
Conclusion: Some A are not C.
EIO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : some B are A.
Conclusion : some A are not C
Special cases
AAI
Major premises : All A are C.
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
EAO
Major premises :No B are C.
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : some A are not C.
Examples of the Fourth figure
AEE
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : No B are A.
Conclusion : No A are C
IAI
Major premises : Some C are B.
Minor premises : All B are A .
Conclusion : Some A are C .
EIO
Major premises : No C are B .
Minor premises : Some B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Special cases
AEO
Major premises :All C are B.
Minor premises :No B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
EAO
Major premises : No C are B
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
AAI
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : All B are A.
Conclusion :Some A are C.
Solved MCQ Based on Mood and Figure
Identify the mood and figure of the following syllogism:
Question 1 –
some B are A
All B are C
Some A are C
Options :
IAI – 3 [Answer]
IAI – 2
IAI – 1
IAI – 4
Question 2 –
No A are B
ALL c are B
NO A are C
Options :
EAE -3
EAE – 2 [Answer]
EAE – 1
EAE – 4
Question- 3
All C are A
Some B are A
Some C are A
Options :
First [Answer]
Second
Third
Fourth
References –
Study Notes from – https://rintintin.colorado.edu/~vancecd/phil1440/notes.html
0 notes
Text
Structure of Categorical propositions | Mood and Figure
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/structure-of-categorical-propositions-mood-and-figure/
Structure of Categorical propositions | Mood and Figure

UGC NET Exam Study Notes on “Structure of Categorical propositions” and “Mood and Figure”
Topics Based on UGC NET Syllabus of Logical Reasoning
Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, the structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition. ( This is Big Section, Categorical Propositions & Mood and Figure Part is covered in this article,)
Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning.
Analogies.
Venn diagram: Simple and multiple uses for establishing the validity of arguments.
Indian Logic: Means of knowledge.
Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana(Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension).
Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference).
Whats is the Categorical Propositions?
A “Subject” of a sentence is the thing that has some property or class is being attributed to, the “Predicate” is the property or class that is being attributed to the subject, and the “Copula” is the word that links the two together.
For Example – All dogs are mammals
Here, “dogs” is the subject, “mammals” is the predicate, and “are” is the copula. This particular statement about bunnies has a certain form, the form of a categorical proposition.
So in simple words, “A proposition that relates two classes or categories” is known as a Categorical Proposition.
If you look at the above example in addition to subject, predicate and coupla it also has “quantifiers” that tells you HOW MANY of the subjects are being referred into the statement.
Categorical propositions tell us one of four things: (1) ALL members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (2) NONE of the members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (3) SOME of the members of the subject class are included in the predicate class. (4) SOME of the members of the subject class are NOT included in the predicate class.
Here are some examples of each of these 4 kinds of the categorical proposition: (1) All dogs are mammals. (2) No dogs are reptiles. (3) Some dogs are cute. (4) Some dogs are not potty-trained.
Here is the FORM of each of these 4 kinds of categorical proposition: (1) All S are P. (2) No S are P. (3) Some S are P. (4) Some S are not P
Now, let’s go over some definitional terms: Categorical statements each have a quantity and a quality.
Quantity: Refers to HOW MUCH of the subject class is included in the predicate class.
Quantity is either: (a) Universal – Tells us something about how ALL of the subjects are related to the predicate. (b) Particular – Tells us how SOME of the subjects are related to the predicate.
Quality: Refers to whether the proposition is AFFIRMING something or DENYING something of a subject.
Quality is either: (a) Affirmative – Members of the subject ARE included in the predicate. (b) Negative – Members of the subject are NOT included in the predicate.
For instance, of the 4 kinds of the categorical proposition we discussed above:
PropositionQuantityQualityLetterAll S are P.universalaffirmativeANo S are P.universalnegativeESome S are P.particularaffirmativeISome S are not P.particularnegativeO
For shorthand, it is common to refer to each of these types of the proposition by a letter; Those letters are A, E, I, and O.
Now, you must be wondering what are these “A, E, I, O”, Let’s understand with more examples.
A is universal positive.
All apples are good.
All milk is white .
E Is universal negative.
No bread is butter.
No egg is white.
I is particular positive
Some apples are good.
Some bread is butter.
Some eggs are white.
O is particular negative
No apple are good.
No bread is butter.
NO eggs are white.
Categorical Syllogisms
Syllogism: An argument consisting of three statements: TWO premises and ONE conclusion.
Categorical syllogism: A syllogism consisting of three categorical propositions, and containing THREE DISTINCT TERMS, each of which appears in exactly two of the three propositions.
So, what are these 3 terms mentioned? Consider the following syllogism:
All mammals are creatures that have hair.
All dogs are mammals.
Therefore, all dogs are creatures that have hair.
There are THREE different terms in this argument (besides the quantifiers and the copulas). The three different terms are called the “major term”, the “minor term”, and the “middle term.”
Notice that the conclusion only contains TWO of the three terms but one of the terms is found only on the premises.
Here are some definitions: Major Term: The predicate term of the conclusion (above, “creatures that have hair”) Minor Term: The subject term of the conclusion (above, “dogs”) Middle Term: The term that does NOT appear in the conclusion (above, “mammals”)
Finally, note that premise 1 contains the major term, while premise 2 contains the minor term. Premise 1 is therefore called the major premise, while premise 2 is called the minor premise. The standard form demands that the major premise (i.e., the one containing the major term) ALWAYS be listed first.
Easy to grasp right? We will cover a very simple trick to remember these “there terms” and this question is the favourite of a UGC NET examiner from the last few years.
Warning! Tricks to remember “MAJOR”, “MINOR” and “MIDDLE” terms. Let’s take another example.
Statement 1 – All A are B .
Statement 2 – All B are C .
Conclusion – All A are C .
Here –
Statement first is also known as premises 1 and Statement second is also known as premises 2.
In the above statement “B” is the middle term which is also known as cancelling term and in Indian logic known as “Hetu”.
In the above statement “A” is minor term and “C” is major term.
Now, how to find out which one is major term, minor term and middle term?
MAJOR TERM – the term in a syllogism that is the predicate of the conclusion is known as major term .
You should always check “conclusion” for major term. For example is above statement, the conclusion is All A are C . So, the last term in the conclusion that is C is your major term.
Example 1– If the conclusion is “ All parrots are green”
So, in the above statement “green” is major term.
Example 2– No apple is good .
So, in the above statement “good” is your major term .
Tip– second word of your conclusion is always your major term.
MINOR TERM- the term in a syllogism that is the subject of the conclusion is known as Minor term. It is also known as subject.
You always should look into conclusion to find out Minor term. Remember- major term was the last term of conclusion but Minor term is the first term in the conclusion .
This Minor term is known as “paksha” .
Remember it as – it is in the increasing order that is it goes from small to big. In the above given statement our conclusion is “All A are C” so, in this statement “a” is minor term because A is the first term in the conclusion.
For more clarity have a look on the given examples :
1st example – No blackboard is green
Minor term – blackboard
Major term – green
2nd example – some bread is butter
Minor term- bread
Major term – butter
MIDDLE TERM- In syllogism, a middle term is a term that appears in both premises but not in the conclusion of a categorical syllogism. This is also known as cancelling term and Indian logic this is known as “Hetu” or “Reason”.
To find out which one is middle term, you always should look into premises. Middle term never appears in the conclusion.
The term which is present in both premises- premises 1 and premises 2 is called middle term.
The mutual term present in both statements are called middle term.
Example 1
Statement1 – some breads are milk .
Statement2- some milk is butter .
Conclusion – some butter are bread .
In this given statement “ milk” is the mutual word available in both statements. So, milk is our middle term . Observe carefully “ Milk is not present in conclusion”.
Mood and Figure
Now that we know the correct FORM of categorical syllogisms, we can learn some tools that will help us to determine when such syllogisms are valid or invalid.
All categorical syllogisms have what is called a “mood” and a “figure.”
What are mood and Figures?
Mood: The mood of a categorical syllogism is a series of three letters corresponding to the type of proposition the major premise, the minor premise, and the conclusion is (A, E, I, or O).
Mediaeval logicians invented a simple method of labelling the various forms in which a categorical syllogism may occur by simply stating its mood and figure.
Mood – It usually depends upon the type of propositions (A, E, I, O).
Figure – It depends on the arrangement of the middle term in the proposition.
The figure of the syllogism is based on the arrangement of Subject and predicate and middle term or the common term.
The different types of figures in syllogism are:
First figureSecond figureThird figureFourth figureM-PP-MM-PP-MS-MS-MM-SM-PS-PS-PS-PS-P
In this above table: M stands for “middle term”, S stands for “subject”, P stands for “predicate”
Tips to remember this above table-
In first figure – M makes a sort of vertical right hand like this “ \”.
In second figure- M makes a straight hand in right direction like this “|” in right hand side.
In Third figure- M makes a right hand is left direction like this “|” in left hand side.
In Fourth figure- M makes a sort of vertical left hand like this “/” .
There is 256 combination of the different forms of mood and figure. Out of these 256 combinations, only 15 were found to be valid by Aristotle. There are 9 conditionally valid argument forms for categorical syllogisms in addition to the 15 unconditionally valid argument forms: The valid combinations are given below in the table.
Unconditionally Valid Forms: There are 15 combinations of mood and figure that are valid from the Boolean standpoint (we call these “unconditionally valid” argument forms).
The below chart depicts ALL of 15 the unconditionally valid argument forms
First figureAAA,EAE,AII,EIOSecond figureEAE,AEE,EIO,AOOThird figureIAI, AII, OAO, EIOFourth figureAEE,IAI,EIO
Recall this argument from earlier:
All mammals are creatures that have hair.
All dogs are mammals.
Therefore, all dogs are creatures that have hair.
Its mood is “AAA” since all three propositions are “A” propositions (i.e., they are all of the forms “All S are P”). Its figure is “figure 1”
Points to keep in mind( only for the first figure)
If both the premises are positive (A or I), then the conclusion will also be positive (A Or I)
If one of the premises is negative (E or O), then the conclusion will also be negative (E or O).
If one of the premises is particular (I or O), then the conclusion will also be particular (I or O)
If one of the premises is particular negative (O) , then the conclusion will aslo be particular negative .
If one of the premises is particular and the second one is negative, then also the conclusion will be particular negative (0).
Some of the mood and figure examples
Examples of the First figure
AAA
Major premises : All B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : All A are C.
EAE
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : No A are C.
AII
Major premises : All B are C.
Minor premises : Some A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
EIO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : some A are B.
Conclusion : some A are not C.
Special cases
AAI
Major premises :All B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
EAO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : All A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Examples of the second figure
EAE
Major premises : No C are B.
IMinor premises : All A are B
Conclusion : No A are C.
AEE
Major premises : All C are B
Minor premises : No A are B.
Conclusion :No A are C.
EIO
Major premises: No C are B.
Minor premises : Some A are B
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
AOO
Major premises : All C are B .
Minor premises : Some A are not B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Special cases
AEO
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : No A are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C
EAO
Major premises : No C are B.
Minor premises : All A Are B.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Examples of the Third figure
IAI
Major premises : Some B are C.
Minor premises : All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
AII
Major premises: All A are C.
Minor premises :Some B are A.
Conclusion: Some A are C.
OAO
Major premises : Some B are not C.
Minor premises: All B are A.
Conclusion: Some A are not C.
EIO
Major premises : No B are C.
Minor premises : some B are A.
Conclusion : some A are not C
Special cases
AAI
Major premises : All A are C.
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are C.
EAO
Major premises :No B are C.
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : some A are not C.
Examples of the Fourth figure
AEE
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : No B are A.
Conclusion : No A are C
IAI
Major premises : Some C are B.
Minor premises : All B are A .
Conclusion : Some A are C .
EIO
Major premises : No C are B .
Minor premises : Some B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
Special cases
AEO
Major premises :All C are B.
Minor premises :No B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
EAO
Major premises : No C are B
Minor premises :All B are A.
Conclusion : Some A are not C.
AAI
Major premises : All C are B.
Minor premises : All B are A.
Conclusion :Some A are C.
Solved MCQ Based on Mood and Figure
Identify the mood and figure of the following syllogism:
Question 1 –
some B are A
All B are C
Some A are C
Options :
IAI – 3 [Answer]
IAI – 2
IAI – 1
IAI – 4
Question 2 –
No A are B
ALL c are B
NO A are C
Options :
EAE -3
EAE – 2 [Answer]
EAE – 1
EAE – 4
Question- 3
All C are A
Some B are A
Some C are A
Options :
First [Answer]
Second
Third
Fourth
References –
Study Notes from – https://rintintin.colorado.edu/~vancecd/phil1440/notes.html
0 notes
Text
Logical Fallacies - Study Notes based on Fallacies
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/logical-fallacies-study-notes-based-on-fallacies/
Logical Fallacies - Study Notes based on Fallacies

Study Notes on Formal & Informal Fallacies
UGC NET Syllabus of Logical Reasoning
Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, the structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition. (Some part are covered in this article)
Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning.
Analogies.
Venn diagram: Simple and multiple uses for establishing the validity of arguments.
Indian Logic: Means of knowledge.
Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana(Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension).
Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference).
What are fallacies?
Fallacies are errors in arguments that deceive our minds. It is a defect in an argument that consists of something other than merely false premises.
As we see, fallacies can be committed in many ways, but usually, they involve either a mistake in reasoning or the creation of some illusion that makes a bad argument appear good or bad (either).
An argument is valid when the truth of the premises guarantees the truth of the conclusion. The process that gives no rational grounds for accepting the conclusion is defective forms of an argument known as a fallacy.
Fallacies can be used positively, to avoid or expose error or they can be used for negative means, to deceive.
[ ] Ethos- ethos is in an argument that appeals to ethics authority or credibility.
[ ] Pathos- pathos is an argument that appeals to emotions.
Fallacies are usually divided into two groups.
Formal and Informal Fallacies
A formal group– It may be identified through mere inspection of the form of structure of an argument.
[ ] In the case of formal fallacies, the conclusion does not follow from the given premises or proposition. The relation depicted in such an argument is not valid and supported by the given premises.
[ ] Formal fallacies can be the result of poor logic.
[ ] Informal fallacy’s error is in structure.
Informal fallacy-. Informal fallacies are the result of wrong information, assumptions, misuse of language, lack of evidence, or wrong analogy.
Informal fallacies are a form of incorrect argument in natural language. In this, unlike formal fallacies, the source of error is not just due to their form but can also lie in their content and context.
[ ] It will give an appearance of being correct despite being incorrect and thereby seduces into committing and accepting that this is true.
[ ] It is a fallacy in meaning. You’ll think that premises follow the conclusion but there will be an error.
Let’s first discuss what is the difference between formal and informal fallacy –
[ ] In the formal fallacy -premises will not follow the conclusion and you will easily find that there is an error in the statement.
[ ] In the informal fallacy -it will usually give an appearance of being correct and thereby it will persuade us into committing and accepting them.
Types of informal fallacies
#Ad ignorantiam
It is an appeal to ignorance. This fallacy is usually committed by us because of ignorance of the truth. We tend to commit this fallacy because it is not proven by anyone till now.
For example- Shyam said to Mohan that he does not believe in God.
When Mohan asked him the reason he said ” Because science failed to give any valid proof of the existence of God.”
Here we can simply say that Mohan has committed the fallacy of ad ignorantiam. We are ignorant of something does not mean it is not possible. Maybe in the coming future science will prove the existence of God.
#Ad populam
It is a proposition which we accept just because everyone else is accepting the same thing. If everyone is doing one thing, it does not guarantee the rightness of that thing.
For example- If everybody is driving the car at a 200 km per hour speed that does not mean it is legal to drive a car at this speed. It will still be considered wrong.
# Ad verecundlam
This is also called “appeal to authority”. Accepting something because it is coming from some authority.
For example- if Deepika Padukone says the secret of my beauty is Lux, that does not ensure at all that using Lux will surely give the same beauty to everyone.
In this type of fallacy, we do not apply any kind of logic. We blindly follow some authority without giving any logic.
#Hasty generalization fallacy
also called ” converse accident “. Coming to a conclusion without any evidence. or Drawing conclusions from incomplete information.
Hasty generalization is a policy that affects inductive generalizations. The fallacy occurs when there is a reasonable likelihood that the sample is not representative of the group. Such a likelihood May arise if the sample is either too small or not when only selected.
#Strawman fallacy
When you know the other person is right and you don’t have any logical counterargument to fight but to make sure that you always have an upper hand you create a whole new scenario just to win an argument is called the strawman fallacy.
The strawman fallacy is committed when an arguer distorts an opponent’s argument for more easily attacking it, demolishes the distorted argument, and then concludes that the opponent’s real argument has been demolished.
By doing so the argument is said to have set up a strawman and knocked it down, only to conclude that the real man( opposing argument) has been knocked down as well.
For example, Mr. Goldberg has argued against prayer in Public School. Mr. Goldberg advocates atheism but atheism is what they used to have in Russia. Atheism leads to the suppression of all religions and the replacement of God by an omnipotent state. Is that what we want for this country?
As this example illustrates, the kind of distortion the second arguer resorts to is often an attempt to exaggerate the first person’s argument or make it look more extreme than it is.
#Red herring fallacy– (deliberate diversion)
This fallacy is closely associated with missing the point. The arguer diverts the attention of The Reader or Listener by changing the subject to a different but subtly related one. To use the Red Herring fallacy effectively, the arguer must change the original subject of the argument without The Reader or listener noticing it.
For example- Boy- Mom, I want that toy.
Mother- Hey, let’s go home, yummy food is waiting for you.
Here you can see that mother has changed the entire topic deliberately.
# Argument against the person(argumentum ad Hominem)
This fallacy always involves two arguments. One of them advances either directly or implicitly a certain argument, and the other than a response by directing his or her attention, not to the first person’s argument but the first person himself.
For example- If a politician is speaking well and giving a brilliant speech with logical reason another politician who does not have anything to say in opposition says “you can’t control the nation. Your daughter eloped with someone else.
This is clearly attacking personally.
2nd example- You cannot come first in class because you are ugly.
Here we can see that coming first or last in class has nothing to do with being ugly or beautiful but the opponent has nothing to say against his intelligence, so he attacks him personally.
# Missing the point– (ignoratio elenchi)
The arguer is ignorant of the logical implication of his or her premises and, as a result, draws a Conclusion that misses the point entirely.
This fallacy occurs when the premises of an argument support one particular conclusion but then a different conclusion often vaguely related to the correct conclusion is drawn.
For example- Crimes of theft and robbery have been increasing at an alarming rate lately. The conclusion obvious: we must reinstate the death plenty immediately “
In the above statement at least two correct conclusions are implied by the premises of the first argument 1. Either we should provide increased police protection in vulnerable neighborhoods or 2.we should initiate programs to eliminate the causes of the crimes.
Reinstating the death penalty is not a logical conclusion at all. Among other things, theft and robbery are not capital crimes.
#Complex Question–
When someone invites 2 or 3 questions in one single question.
The fallacy of complex questions is committed when in a single question, more questions are asked and a single answer is then applied to both questions.
When the respondent answers are added to the complex question, an argument emerges that establishes the presumed condition.
This argument is usually intended to trap the respondent into acknowledging something that he or she might otherwise not want to acknowledge.
For example- Have you stopped cheating on exams?
Now let us suppose the respondent answers “yes” to the question.
Therefore, it follows that you have cheated in the past.
0 notes
Text
Natural and Energy Resources|Study Notes UGC NET Exam
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/natural-and-energy-resources/
Natural and Energy Resources|Study Notes UGC NET Exam
Natural and Energy Resources: Solar, Wind, Soil, Hydro, Geothermal, Biomass, Nuclear, and Forests.
The term natural resources mean anything that we use from our environment to achieve our objective. For example, we require sugar, baking powder, flour, milk, and eggs to bake a cake. so these all are the resources used to bake a cake.
Resources can be anything artificial or natural, energy or organism which human beings consume to achieve the desired goal.
First, we need to know what is artificial and natural resources ?
Natural resources– All those resources which are provided by nature are called natural resources. example, soil, air, water, sunshine, plants, coals, and minerals.
Artificial resources- The resources which human being developed during the growth of civilization to fulfill the requirement is called artificial resources. ex. biogas, thermal electricity, plastic, etc.
we generally get these artificial resources from other natural resources.
Similar to other topics based on the latest UGC NET EXAM Syllabus…we have covered the people and environment syllabus topics in 8 parts as below along with the last 16 Years solved Question paper at the end of the tutorial.
You are advised to go through them in sequence and attempt the MCQ Question only after completion of all topic listed below.
Not only this there is some additional note has been provided specifically for this section as it was seen that some question was asked from recent affairs based on people and environment.
Unit-IX People, Development and Environment
Development and environment: Millennium development and Sustainable development goals.
Human and environment interaction: Anthropogenic activities and their impacts on the environment.
Environmental issues: Local, Regional and Global; Air pollution, Water pollution, Soil pollution, Noise pollution, Waste (solid, liquid, biomedical, hazardous, electronic), Climate change and its Socio-Economic and Political Dimensions. [This Post]
Impacts of pollutants on human health.
Natural and energy resources: Solar, Wind, Soil, Hydro, Geothermal, Biomass, Nuclear and Forests. ((This article))
Natural hazards and disasters: Mitigation strategies.
Environmental Protection Act (1986), National Action Plan on Climate Change, International agreements/efforts -Montreal Protocol, Rio Summit, Convention on Biodiversity, Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement, International Solar Alliance.
MCQ Based on People, Development and Environment(Coming Soon)
Additional Notes –
Must Read – 40 Major International/Indian Environmental Organizations Fighting Issues
Classification of Natural and Energy Resources
The air we breathe and the sunlight that we enjoy for free are available to us in unlimited quantity but have you ever think about coal, forests, and petroleum. yes, we do not have these fossil fuels in unlimited amounts. the stock of these is very limited and depleting day by day.
Exhaustible
Inexhaustible
Renewable
Non-renewable
Inexhaustible resources: The resources which we have in unlimited amounts are called inexhaustible resources. These resources will never get exhausted. We have been enjoying these resources for ages and our coming generations will continue to use these resources. Solar radiation, wind power, water power, tidal power, and substances like sand, clay, and water in oceans are some examples of inexhaustible resources.
Exhaustible resources: This is the exact opposite of inexhaustible resources. These resources are available to us in a very limited amount and we are using them for ages but now these resources are depleting day by day because of continuous use. For example, the coal available to us is in a very limited amount and one day we will be deprived of coal.
According to U.S coal production in 2019- the recoverable reserves at producing mines would last about just 20 years though this depends on the change in production and reserve estimates.
Renewable resources: There are some resources which regenerate naturally after consumption are called renewable resources like plants and trees grow again if we cut them but if we destroy a forest completely because of the growing population it will not regenerate again.
Non-renewable resources: This is the opposite of renewable resources. These are the resources that we can not regenerate again after consumption. examples are minerals, wildlife species, etc.
As the population of the world is increasing continuously at an alarming rate, and because of urbanization and industrialization, the consumption of these resources is also increasing. These resources are very important to maintain the ecological balance and to save them for our children and grandchildren.
You must be pondering why the conservation of these natural resources is so important for us. so, here is your answer
For ages, nature has provided us with everything that we need but we exploit nature by taking more than our requirement for profits. If we go on exploiting nature, there will be no more resources available to us in the future and we can’t even imagine our lives without these resources. Can you imagine a day without forest i.e no more oxygen no more wood and medicines? This will eventually lead to the destruction of mankind.
If we want to preserve the species of different kinds of flora and fauna, conservation of these natural resources is very important.
Ecological balance is important for supporting life
To ensure even the survival of mankind, the conservation of natural resources is important.
We have different types of energy available to us which we obtain from different resources for our daily activities like cooking, heating, transportation, and lighting, etc.
Types of Energy Resources
There are two types of energy resource
Conventional energy
Non-conventional energy
Conventional source of energy
The energy which is available to us for ages and very easily cable is called conventional energy. like fossil fuels. these are present in limited quantity, not abundant in nature. conventional sources of energy are also called the non-renewable source of energy conventional source of energy if further divided into two parts
Conventional non-renewable energy
Conventional renewable energy
Fossil fuels: These are made from decomposing plants and animals. these are the products of a series of biological, chemical, and physical transformations of plants and animals that remain over millions of years. coal is the most abundant fossil fuel widely used for combustion in cooking and industrial activities.
Properties of coal: coal mainly consists of carbon and a small amount of sulfur and nitrogen and ash. coal can be extracted through mining.
Petroleum: Also called rock oil. it is in the liquid form present in the upper crust of the earth. like coal, petroleum is derived from the biological and chemical transformation of plants and animals’ debris over millions of years. it is the combination of hydrocarbons.
Natural gas: it occurs in the underground reservoir of porous rock. it emits co2.
natural gas consists of methane in large amounts with a small amount of ethane, propane, butane, and other paraffin. it is easy to transport natural gas in special tankers. The united state is considered the largest producer as well as consumer of natural gar followed by Russia, Iran, and Canada.
Biomass energy
When plants and animal material is used as fuel to produce electricity or heat is called biomass energy. bio means living being and mass means material so energy obtained by using the mass of living beings (plants and animals) is called biomass.
Example – wood, corn, soybean, crop residues, and organic waste. we can burn biomass directly to produce heat and electricity and can be easily converted to liquid fuel and gas through the process of fermentation and anaerobic digestion.
Biomass as an important source of renewable energy is gaining importance in developed countries for electricity and transportation. biomass such as municipal east and cattle manure is used to produce methane through anaerobic digestion.
Non-conventional source of energy
The energy which is obtained from natural resources like wind, tides, solar, biomass, etc are called non-conventional souse of energy. These are pollution-free and hence we can use these to produce a clean form of energy. Therefore greater use of the non-conventional source of energy should be promoted.
Types of non-conventional souse of energy • Solar energy • Hydel energy • Wind energy • Nuclear energy • Hydrogen energy • Geothermal energy • Biogas • Tidal energy • Biofuels
Point to remember- Students usually get confused when NTA asks about biogas or biofuel. So keep in mind both these are a non-conventional source of energy as these are obtained through natural resources
Solar energy: As the name implies, it is the energy that we get from the sun. it is created by harnessing the power produced by the sun. it is the ultimate souse of energy on earth. we are blessed with sunlight and this sunlight can provide us an abundant amount of energy known as solar energy. photovoltaic cells convert the energy captured from the sun into electricity. recent advances in efficiency have resulted in staggering improvements and growths in its use. it is available almost everywhere and free from the political barrier. this can solve the problem of no electricity in remote areas and poor countries which are otherwise deprived of electricity. china (205 GW)is the biggest producer of solar energy, followed by the united states(76GW) and Japan (63.22 GW).
Hydro energy: it is power obtained through the movement of water typically gravitational. this is also known as water energy or hydel energy. the use of fast running water to produce electricity or to power use is called hydro energy. it is obtained by converting the kinetic form of energy into the mechanical form of energy. the generation of hydroelectricity dies does not produce any climate-changing emission the construction of dams does cause significant environmental and social problems like the temperature change has caused fish kills.
Wind energy: as the name implies the energy that we get through wind is called wind energy. it is generated through the force of the wind, which spins rotor blades attached to a turbine. the clean and efficient nature of wind energy has seen a rapid expansion in the development of wind farms. China is the world leader in wind energy, with over a third of the world’s capacity. It boasts the world’s largest onshore wind farm in Gansu Province, which has a capacity of 7,965MW, five times larger than its nearest rival.14-Mar-2019.
Tidal energy: it refers to generating electricity from the flow of the tides. it is produced y making the use of water movement from a huge tide to low tide. ocean waves and tides can be made to turn a turbine and generate electricity
Now, one thing to remember is what is the difference between hydro energy and tide energy though both use water as the primary souse to produce energy.
The difference is – what is causing the water to move. in hydro energy is achieved by damming a river, or running a pipe from a high lake to a lower lake, river o the sea. whereas io the tidal energy ocean waves and tides can be made to turn a turbine and generate electricity.
Areas where rivers flow the sea experiences waves and tides and electricity can be generated there. inside have a large coastline and major river system so producing electricity is very convenient in India.
With a total installed tidal power capacity of 511MW, South Korea is leading the way globally, according to the information provided by the National Energy Board of Canada. South Korea is followed by France with 246MW, and the United Kingdom with 139MW.
• Nuclear energy: radioactive elements like uranium and thorium disintegrates spontaneously releasing a large quantity of an entry. The US continues to generate by far the most nuclear energy in the world. According to BP, the annual balance was 852.0 terawatt-hours.
That was almost two and a half times as much as in China and ten times as much as Ukraine in seventh place. Almost a third (30.5 per cent) of the world’s nuclear energy came from the US in 2019. • Although the storage of radioactive waste makes the adoption of nuclear energy in many parts of the world problematic. some of the nuclear power platys in India are in tarapura, kalpakkam, narora and kota.
Hydrogen energy: hydrogen is the most common element in the universe and is found in the waster and all living beings. Hydrogen Energy Hydrogen energy involves the use of hydrogen and/or hydrogen-containing compounds to generate energy to be supplied to all practical uses needed with high energy efficiency, overwhelming environmental and social benefits, as well as economic competitiveness. From: Science and Engineering of Hydrogen-Based Energy Technologies, 2019
Geothermal energy– Also called hot rock energy, generate electricity by the infection of water into a borehole in rocks with a temperature of a least 200 degrees C.
• The water is heated upon contact with the rock and is returned to the surface via a second borehole in the form of steam, which is then used to turn turbines that generate electricity.
• The cooled stream is then reinjected back into the first borehole where the process begins again
• The use of this form in energy is highest in the Philippines, with geothermal energy providing approximately 27 per cent of power needs.
• There are 46 hydrothermal areas in India where the water temperature normally exceeds 150 degrees.
Biogas- is a renewable fuel produced by the breakdown of organic matter such as food scraps and animal waste from living organisms like plants and animals. The gas which we get can be used in a variety of ways including as vehicle fuel and for heating and electricity generation. It is produced by the microbial activities on cattle dung a specially designed tank called a digester.
A mixture of water and cattle dung is poured into this digester where anaerobic decomposition takes place and biogas is generated. This gs contains 55-70 per cent methane. China is the biggest producer of biogas followed by the U.S and Thailand.
Status of renewable energy in India
Keeping in look our dedication to a healthy planet and our nationally determined supplements as per the Paris accord on climate change, India pledged that by 2030, 40% of installed power generation capacity shall be based on clean sources.
It was decided that 175 G.W of renewable energy capacity will be installed by 202.
This includes 100 GW from bio-power and 5 GW from small hydropower.
India has 5th global positions for overall established renewable energy capacity, 4th position for wind power, and 5th position for solar power.
The substantial higher capacity target will ensure greater energy security, improved energy access, and enhanced employment opportunities.
A total of around 73.35 GW of renewable energy capacity has been installed in the county as of October 2018 from all renewable energy resources.
This capacity includes around 34.98 GW fro, wind, 24.33 GW from solar,4.5 GW from small hydropower, and 9.54 GW from biopower.
UGC NET Paper1 study notes have combined all the topics from latest syllabus and explained in an easier way. You should be also able to print them in PDF for your offline reading.
Please see the topic wise link below-
Unit-I Teaching Aptitude Based Question
Unit-II Research Aptitude Based Question
Unit-III Comprehension Based Question
Unit-IV Communication Based Question
Unit-V Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude Based Question
Unit-VI Logical Reasoning Based Question
Unit-VII Data Interpretation Based Question
Unit-VIII Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Based Question
Unit-IX People, Development and Environment Based Question
Unit-X Higher Education System Based Question
References
1.ENVIRONMENTAL ORGANISATIONS IN INDIA | ONLYIAS – Nothing else | UPSC IAS EXAM PREPARATION
2. Core Environmental NGOs List (wwfenvis.nic.in)
3. THE DIRECTORY OF ENVIRONMENTAL ORGANIZATIONS AND ENVIRONMENTAL GOVERNMENT AGENCIES IN INDIA (earthdirectory.net)
We hope you have liked our Natural and Energy Resources topic notes, Make sure you study each and every topic in-depth and understand it carefully to answer questions correctly.
0 notes
Text
Tricks to Solve Blood Relations Problems in Reasoning
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/tricks-to-solve-blood-relations-problems-reasoning/
Tricks to Solve Blood Relations Problems in Reasoning
TRICKS TO SOLVE FAMILY OR BLOOD RELATIONS BASED QUESTION
Introduction :
Blood Relations Based Question are very common in all type of examination where you have been given relationship among few members of the family and based on given details you need to find out the ‘Unknown’ relation that exists satisfying the given criteria.
Questions depict relationships among the various members of a family in a roundabout chain.
The candidate is expected to find the relation of two particular persons mentioned in the question.
Generally, the question deals with a hierarchical structure which is based on seven generation three above & three below like this:
Generation Male Female Three generations above↑↑↑Great-grandfather Maternal great-grandfather Great grandfather-in-lawGreat-grandmother Maternal great grandmother Great grandmother-in-lawTwo generations above ↑↑Grandfather Maternal grandfather Grandfather-in-lawGrandmother Maternal grandmother Grandmother-in-law One generation above ↑Father, Uncle, Maternal uncle, Father-in-lawMother, Aunt Maternal aunt, Mother-in-lawThe current generation(Self) →Husband, Brother Cousin, Brother-in-lawWife, Sister Cousin, Sister-in-lawOne generation below ↓Son Nephew Son-in-lawDaughter Niece Daughter-in-lawTwo generations below ↓↓Grandson Grandson-in-lawGranddaughter Granddaughter-in-lawThree generations below ↓↓↓Great-grandson Great grandson-in-lawGreat-granddaughter Great grand daughter-in-law
(Source –bankexamstoday )
(This is the key to solve all type of Blood relation Problems )
Also, You need to understand the common terms used while describing the family & blood relations.
Family/Blood Relations Described
DescriptionRelationSister of fatherAuntWife of uncleAuntSon of father or motherBrotherBrother of husband or wifeBrother-in-lawHusband of sister/sister-in-lawBrother-in-lawSon/daughter of uncle/auntCousinGranddaughter of father/motherDaughter or NieceWife of sonDaughter-in-lawFather’s father/mother onlyFatherHusband of motherFatherSon of grandfather/grandmotherFather/UncleFather of wife/husbandFather-in-lawDaughter of son/DaughterGranddaughterFather of father or motherGrandfatherHusband of grandmotherGrandfatherFather-in-law of father/motherGrandfatherMother of father or motherGrandmotherWife of grandfatherGrandmotherMother-in-law of father/motherGrandmotherSon of son/DaughterGrandsonSon’s/Daughter’s granddaughterGreat granddaughterFather of grandfather or grandmotherGreat grandfatherMother of grandfather or grandmotherGreat grandmotherSon’s/Daughter’s grandsonGreat GrandsonSister of motherMaternal AuntBrother of motherMaternal UncleOnly daughter-in-law of father’s father/father’s motherMotherWife of fatherMotherDaughter of father-in-law/mother-in-law of fatherMother/AuntMother of wife/husbandMother-in-lawSon of brother or sisterNephewDaughter of brother/sisterNieceFather’s/Mother’s only son/daughterOneselfSon of fatherOneself/BrotherFather of daughter/sonOneself/husbandMother of son/daughterOneself/WifeChildren of same parentsSiblingsDaughter of father or motherSisterSister of husband or wifeSister-in-lawWife of brother/brother-in-lawSister-in-lawGrandson of father/motherSon/NephewHusband of daughterSon-in-lawSon of second wife of fatherStep brotherSecond wife of fatherStep motherDaughter of second wife of fatherStep sisterBrother of fatherUncleHusband of auntUncle
Important tips!
First of all choose the two persons, between whom the relationship is to be established.
Next, pinpoint the intermediate relationship i.e., such relationship through which long drawn relationship can be established between the required persons.
Finally, conclude the relationship directly between the two persons as per the requirement of the question.
From a particular name, we cannot ascertain the sex (gender) of that person. The name does not always show the gender beyond the reasonable doubt.
Never make an assumption about the sex of given relation based on the name provided
Always draw a pictorial diagram or Diagram based on Symbols to ascertain Family Tree Structure
Representation of family tree structure is important as if you are able to draw valid pictorial you will be able to solve any kind of problem(We will see how to draw diagram step by step later in this blog post)
Something not to do while solving the Blood relation problems
Few Teachers suggest ” to relate the question to yourself e.g if a person’s name is given in the question and other relationships are related to him, try to put yourself on his place and relate yourself to him and this will help you in understanding the problem easily “.
The above method only works if the problem is in simple nature and only involve few levels of Relationship
How to Draw Family Tree Diagram
You can draw tree diagrams in the following fashion.
Use vertical lines to represent parent-child relationships.
Horizontal lines like <-> to denote marriages and dashed lines to represent sibling relationships. Apart from that, a sibling relationship can easily be established if they share the same root.
You can also add gender differentiation to it by using a + sign for male and – sign for female.
You can use (?) for the information that has not been provided to you.
For Example
⊕ │ ⊕Father-Son⊕ │ ϴFather-Daughterϴ │ ⊕Mother-Sonϴ │ ϴMother-Daughter
As we have now understood the method to draw the diagram let’s move forth and practice some questions
Before that let’s see what type of Blood Relationship Questions are asked in various formats.
They are different in representation but substantially there is no difference between them.
Mainly Questions on Blood Relations are of the following types:
Mixed-Up Relationship Descriptions
Coded Relations/Symbolically Coded
Puzzle-Based Question
(NET Exam Syllabus of Reasoning don’t provide exact information on what type of question can be asked but most of the time it has seen that Question asked are of a mixed nature )
Important Note- Pattern of UGC NET EXAM is not as tough as Bank PO & CAT Exam so you should avoid solving tough and puzzle based question. Also, Only one question come from this topic .
However, if we consider the pattern of the question we should practise them separately-
Let’s Solve a few Examples!
Type I – Mixed-Up Relationship Descriptions/Statements
The questions in this category are generally a dialogue/ conversation between two people and followed up with a question on the basis of the information provided in the conversation.
Given below are some examples.
D is the brother of B, M is the brother of B, K is the father of M and T is the wife of K. How is B related to T?
Pointing to a man in a photograph, a man said to a woman, “His mother is the only daughter of your father”.How is the woman related to the man in the photograph?
Above type of problem can be easily solved using pen and paper and start plotting the family tree diagram and the question will just fall into place.
Example –
Abbas said to Chand, “Your mother’s husband’s sister is my aunt.” How is the lady related to Abbas? (1) Brother (2) Daughter (3) Sister (4) Aunt (5) None of these
Solution:
Lady’s father’s sister is Lady’s aunt. But this sister is also Abbas’s aunt. Therefore Lady (Chand) is Abbas’s sister.
Hence, the answer is (3) Sister.
Give a Try for Below Question
Read the information carefully and answer the question given below it.
A family consists of 6 members P, Q , R, X, Y, Z. 2. Q is the son of R but R is not mother of Q. 3. P and R are married couple. 4. Y is the brother of R, X is the daughter of P. 5. Z is the brother of P.
Questions :
Who is the brother in law of R?
How many female members are there in the family?
How is Q related to X?
How is Y related to P?
Type II- Coded Relations/Symbolically Coded
In this type, relationships represented by codes and symbols like + , – , / , *. You have to analyze the required relation based on the given code. In this also you may need diagrammatic representation of problem to solve it. Use the same representation used in mixed blood relations.
In the coding equation better to solve the code from the last letter.
If P+Q means P is the husband of Q, P/Q means P is the sister of Q, P*Q means P is the son of Q. how is D related to A in D*B+C/A?
Solution :
C/A – C is the sister of Q.
B+C/A – B is brother in law of A (sister’s husband – brother in law.
D*B+C/A – D is the nephew of A (sister’s husband’s son means sister’s son i.e. nephew).
So, the answer is Nephew.
Type III- Puzzle Based Question on Blood Relations
This type of Question is the mixture of other reasoning concepts like seating arrangement, direction problem, statement & conclusion and others.
So far, It has been not seen much questions were asked in the NET exam on these types but as NTA NET exam is online now and would be chances to have these types.
the most important aspect of this is there will be multiple questions based on the same set of instruction provided in one question; SO if you draw the incorrect family tree or pictorial Diagram chances are very high that you end of making mistake for all question.
The key aspect of solving these type of problem is “Practise as Much as you can ”
Directions (6 – 10): Study the following information and answer the questions given below. Eight persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table facing the centre, but not necessarily in the same order.
A’s the only son sits second to the left of F’s daughter, who is not E. B’s daughter G is an immediate neighbour of F’s daughter.
D’s mother sits opposite to G and sits is third to the left of C’s son. D’s sister and D’s mother are immediate neighbours of B’s sister, who is not sitting opposite any female.
G’s father is B, who is the son of C. D’s sister F, sits opposite E’s grandfather C, who is the father of D.
C is an immediate neighbour of D’s nephew, who is not the son of F.
6. Who among the following sits opposite to H? a) C b) E c) A d) D e) G
7. Who among the following is D’s mother? a) B b) G c) A d) H e) C
8. If B’s daughter and D’s mother interchange their positions then who among the following sits third to the left F’s sister? a) B b) A c) H d) F e) None of these
9. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way find the one who does not belong to the group? a) HB b) FG c) EB d) CA e) DH
10. Who among the following sit third to the right of E? a) B b) F c) D d) G e) B
Answer : –
(Try Your Self – Below will Pictorial Diagram of Solution…. Check Answer from Diagram ….)
REFERENCES STUDY NOTES
Read More here –
passbankexam sample course pdf
0 notes
Text
A detailed guide on Number System in Mathematics
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/number-system-in-mathematics/
A detailed guide on Number System in Mathematics
Important topic based on the recent pattern of MCQ based on Number System
The number system or the numeral system is the system of identifying and expressing numbers. The number system presents a unique representation of each number and signifies the arithmetic and algebraic structure of the figures. It enables us to perform different arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and division.
The different kinds of number systems in mathematics are:-
Binary
Octal
Decimal
Hexadecimal
This article includes the whole concept of the number system with its kinds, conversions, and examples.
The number of radix or base ten is known as decimals. It’s the first number system in mathematics, where all the modern and ancient calculations are done. Other number systems based on this number is also derived from it. It’s generated using the combined use of digits ranging from zero to nine.
The number system uses digits like 0 and 1, which are the very common digits in the system, and thus it is used to express binary numbers. Whereas on the other side, 0 to 9 digits are used for different types of number systems. Let us discuss the different kinds of number systems.
Decimal Number System (having Base 10)
The decimal number system includes a base of 10 since it practices ten digits from 0 to 9. The positions succeeding to the left of the decimal point express units, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc. The place value is described from right to left. The units have the position value as 100, tens have the position value as 101, hundreds as 102, thousands as 103, and carry on.
For example, the decimal number system 1747 comprises of the digit 7 in the units place, 4 in the tens place, 7 in the hundreds place, and 1 in the thousands position whose value can be addressed as
1747
Explanation:- The unit digit 7 with base 10 is multiplied by 10 with power 0.
The tens place digit 4 with base 10 is multiplied by 10 with power 1.
The hundredth place digit 7 with base 10 is multiplied by 10 with power 2.
The thousand place digit 1 with base 10 is multiplied by 10 with power 3.
Here is a description of it:
(1×103) + (7×102) + (4×101) + (7×100)
=> (1×1000) + (7×100) + (4×10) + (7×1)
=> 1000 + 700 + 40 + 7
=> 1747
10675 has place values as
(1 × 104) + (0 × 103) + (6 × 102) + (7× 101) + (5 × 100)
=> 1 × 10000 + 0 × 1000 + 6 × 100 + 7 × 10 + 5 × 1
=> 10000 + 0 + 600 + 70 + 5
=> 10675
Binary Number System (having Base 2)
The Binary number system has a base of 2. The number of digits existing here is two, i.e., 0 and 1. Mostly, the common base-2 is a radix of 2. The figures represented in this system are called binary numbers, which are 0 and 1.
For example, 100101 is binary. The binary number system is beneficial in electronic devices and computer systems since it can be quickly implemented using just two states, ON and OFF, i.e., 0 and 1.
Using the concept of 8421, he Decimal Numbers 0-9 are expressed in binary as:
0= 8421
[0000]
1= 8421
[0001]
2 = 8421
[0010]
3 = 8421
[0011]
4 = 8421
[0100]
5 = 8421
[0101]
6 = 8421
[0110]
7 = 8421
[0111]
8 = 8421
[1000]
9 = 8421
[1001]
We can describe 0 in binary representation as 0000 because the sum of 8,4,2,1 none can form a 0. Similarly, for 9, the representation is 1001 because one 8 and one 1 can sum up to forming 9 from the given sequence of 8421. You can transform any system into binary and vice versa.
Octal Number System (the ones having base 8)
The octal Number System has a base value of 8. It uses the number of digits from 0-7 for the conception of Octal Numbers. We can convert octal numbers to Decimal value by multiplying every digit with the place value and then summing the result. The octal numbers are beneficial for the description of UTF8 Numbers. The octal numbers are usually used in computer applications.
Example: Convert 217 (octal number representation) into decimal.
Solution:
217 = (2 × 82) + (1 × 81) + (7 × 81)
=> (2 × 64) + (1 × 8) + (7 × 1)
=> 128 + 8 + 7
=> (143)10
Explanation: The unit digit 7 with base 8 is multiplied by 8 with power 0.
The digit 1 with base 8 is multiplied by 8 with power 1.
The digit 2 with base 8 is multiplied by 8 with power 2.
Hexadecimal Number System (having base 16)
The Hexadecimal Number System has a base value of 16. It uses the number of 16 digits i.e. from 0 to 15, to produce its numbers. The digits from 0 to 9 are taken just the same as the digits in the decimal number system except for the integers from 10 to 15 are represented as A to F i.e.
10 is expressed as A
11 = B
12 = C
13 = D
14 = E
15 = F
The hexadecimal Numbers are beneficial for managing memory address locations.
Number System Conversion
The number system conversion is a pretty simple task. Any of the number from any number system can be transformed into different number systems with the use of some techniques that are mentioned below:
Conversion of Decimal Number System to Other:
The change of a number system means the transition from one base to different.
A. Decimal to Binary number system Conversion:
For decimal to binary, the two steps needed to perform the conversion are mentioned below:-
Do the division process on the integer and the progressive quotient with the base of binary(2).
Later, do the multiplication on the integer and the progressive quotient with the binary(base 2).
Example: Convert 19 with base 10 to binary:
Division by 2QuotientRemainder19/2919/2414/2202/210
And, the result goes from bottom to up, including the quotient of the last division. So, the result is (10011)2.
B. Decimal to Octal number system Conversion
For converting decimal to octal, the two steps needed to perform are mentioned below:
Do the division process on the integer and the next quotient with the octal base (base 8).
After this, do the multiplication process on the integer and the next quotient with the octal base (base 8).
Example 1: (160.25)10
Step 1:
Divide 160 and its consecutive quotients with base 8.
OperationQuotientRemainder160/820020/884
OperationAnswerCarry0.25*802
As a result goes from bottom to up, including the quotient, at last, the answer will be (240.2)8
C. Decimal to hexadecimal conversion
For converting decimal to hexadecimal, the two steps needed to perform are mentioned below:
Do the division process on the integer and the next quotient with the base of hexadecimal (16).
Later, do the multiplication process on the integer and the continuous quotient with the hexadecimal base (16).
Example 1: (152)10
Step 1:
Divide 152 and its continuous quotients with base 8.
OperationQuotientRemainder152/16989/1609
As a result goes from bottom to up, including the last quotient value, the answer will be (98)16.
Conversion of Binary to other Number Systems:
The three conversions feasible for binary numbers are binary to decimal, binary to octal, and binary to hexadecimal.
A. Binary to Decimal Conversion
The method of converting binary number systems to decimals is quite easy. The method begins by multiplying every bit of binary number with its identical positional weights. Finally, add all the products.
Example 1: (11110.001)2
Multiply every bit of (10110.001)2 with its corresponding positional weight, and in the last, add all the products of each bit with its weight.
(11110.001)2 = (1×24) + (1×23) + (1×22) + (1×21) + (0×20) + (0×2-1) + (0×2-2) + (1×2-3)
=> (1×16) + (1×8) + (1×4) + (1×2) + (0×1) + (0×1⁄2) + (0×1⁄4) + (1×1⁄8)
=> 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0.125
=> (30.125 )10
B. Binary to Octal Conversion
The binary and octal base numbers are 2 and 8, respectively. In a binary number, the combination of three bits is similar to one octal digit. The two steps to convert a binary number into an octal number are mentioned below:
You need to secure the pairs of three bits on both sides of the binary point. If anyone or two bits are left in a set of three bits pairs, we attach the demanded number of zeros on the last sides.
Then, write the octal digits resembling every pair.
Example 1: (111111101011)2
1. We create pairs of three bits on the binary point, as follows:
111 111 101 011
Next, write the octal digits which resemble every pair.
(111110101011)2 = (7753)8
C. Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
The binary and hexadecimal bases are 2 and 16, respectively. In a binary number system, the combination of four bits is similar to one hexadecimal digit. The two steps to change a binary number system into a hexadecimal number are mentioned below:
Make the pairs of four-four bits on each side of the binary point. If anyone, two, or three bits are still left in a combination of four bits, append the demanded number of zeros on needed sides.
Write the hexadecimal digits resembling every pair.
Example 1: (11110101111.0011)2
1. Create pairs of four-four bits on each side of the binary point. Like,
111 1010 1111.0011
On the left side, the first pair only holds three bits. Present a total set of four bits, attach one zero on the left side.
0111 1010 1111.0011
2. Write the hexadecimal digits that resemble every pair.
(011110101111.0011)2 = (7AF.3)16
Octal number system to other Number System
The octal number can be converted into different number systems. The method of changing octal to decimal differs from the other process.
A. Conversion of Octal to Decimal number system
The method of changing octal to decimal is just like binary to decimal. The method begins by multiplying the numbers of octal with their identical positional weights. Then, add all products.
Example 1: (149.25)8
Step 1:
Multiply every digit of 149.25 with its corresponding positional weight, and then add products of each bit with its weight.
(149.25)8 = (1×82) + (4×81) + (9×80) + (2×8-1) + (5×8-2)
(149.25)8 = 64 + 32 + 9 + (2×1⁄8) + (5×1⁄64)
(149.25)8 = 64 + 32 + 9 + 0.25 + 0.078125
(149.25)8 = 105.328125
The conversion of a decimal number of the octal 149.25 is 105.328125
B. Octal to Binary Conversion
The method of changing octal to binary is just the opposite method of binary to octal. Write the three-three bits of binary code for each octal number digit.
Example 1: (105.25)8
Write the three-bit binary code for 1, 0,5 2, and 5.
(108.25)8 = (001 000 101.010 101)2
The binary conversion of the octal number 105.25 is (001000101.010101)2
C. Conversion of Octal to hexadecimal number system
To convert octal to hexadecimal, the two steps needed to do, are mentioned below:-
Find the binary equivalent of 25.
Create the sets of four bits on each side of the binary point. If any one, two, or three bits are still left in a set of four bits combinations, Add the demanded number of zeros on the utmost sides. Write hexadecimal digits resembling every pair.
Example 1: (142.25)8
Step 1:
Write the three-bit binary code.
(142.25)8 = (001100010.010101)2
The binary number of the octal number is (001100010.010101)2
Step 2:
1. Create sets of four bits on each side of the binary point.
0 0110 0010.0101 01
On the left side, the first set has one digit only, and on the right side, the end set contains two-digit only. Create perfect pairs of four bits, append zeros on needed sides.
0000 0110 0010.0101 0100
2. Write the hexadecimal code, which resembles every pair.
(0000 0110 0010.0101 0100)2 = (62.54)16
Conversion of Hexa-decimal to other Number System:
Hexadecimal numbers can easily be transformed into different number systems. The method of changing hexadecimal to decimal differs from others.
A. Conversion of Hexa-decimal to Decimal
The method of changing hexadecimal to decimal is just like binary to decimal. The method begins by multiplying the numbers of hexadecimal digits with their similar positional weights. Then, add all products.
Example 1: (142A.25)16
Step 1:
Multiply every number of 142A.25 with its corresponding positional weight, then add the products of every bit with its weight.
(142A.25)16 = (1×163) + (4×162) + (2×161) + (A×160) + (2×16-1) + (5×16-2)
(142A.25)16 = (1×4096 )+ (4×256) +(2×16) + (10×1) + (2×16-1) + (5×16-2)
(142A.25)16 = 4096 + 1024 + 32 + 10 + (2×1⁄16) + (5×1⁄256)
(142A.25)16 = 5162 + 0.125 + 0.125
(142A.25)16 = 5162.14453125
The decimal number of the hexadecimal number is 5162.14453125
B. Conversion of Hexadecimal to Binary
The method of changing hexadecimal to binary is the opposite method of binary to hexadecimal. Write the four-four bits binary code of every hexadecimal number.
Example 1: (142A.25)16
Write the four-bit binary code.
(142A.25)16 = (0001 0100 0010 1010.0010 0101)2
The binary number of the hexadecimal number is (1010000101010.00100101)2.
C. Conversion of Hexadecimal to Octal
To convert hexadecimal to octal, the two steps needed to do, are mentioned below
Find the binary equivalent of the hexadecimal digit.
Then, create the sets of three-three bits on each side. If one or two bits are still left in a combination of three bits pairs. Add the expected amount of zeros on needed sides. Compose the octal digits resembling every pair.
Example 1: (AF.2B)16
Step 1:
Use binary as a mediator.
Write the four-bit binary code.
The binary code of (AF.2B)16 is (10101111.00101011).
Step 2:
Create sets of three-three bits on each side of the binary point.
010 101 111.001 010 110
Write the octal code, which resembles every pair.
The octal number of the hexadecimal AF.2B is (257.126)8.
0 notes
Text
MCQ NTA UGC NET PAPER 1 June 2020
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/mcq-nta-ugc-net-paper-1-june-2020/
MCQ NTA UGC NET PAPER 1 June 2020

UGC NET PAPER 1 JUNE 2020
(Based on Question asked in UGC NET PAPER 1 JUNE 2020)
Unit-I Teaching Aptitude Based Question
Identify those teaching strategies which are learner-centered A. Cooperative learning B. Team teaching C. Laboratory based projects D. Pair-share discussions E. Lecturing with PowerPoint presentations
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A, B and C only 2. B, C and D only 3. A, C and D only 4. C, D and E only Answer: 3
From the following, identify those features which are associated with “Indirect Instructional Strategies”
A. Guided student practice B. Focus on concept acquisition through question-answer sessions C. Presenting the stimulus material in small, easy to take steps D. Problem based presentation E. Participatory and collaborative moves stressed
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. B, D and E only 2. A, B and C only 3. B, C and D only 4. C, D and E only Answer: 1
Which one of the following assessment procedures is conducted during an in-progress teaching-learning session? 1. Summative 2. Formative 3. Norm-referenced 4. Criterion-referenced Answer: 2
Reflective level teaching is different from memory level teaching because the pattern of communication that is involved reflective level teaching is basically 1. Linear 2. Bottom-up 3. Interactional 4. Transactional Answer: 4
Unit-II Research Aptitude Based Question
Identify sampling procedures in which units are chosen giving an equal and independent chance A. Quota sampling procedure B. Stratified sampling procedure C. Dimensional sampling procedure D. Random sampling procedure E. Systematic sampling procedure
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A, B and C only 2. B, C and D only 3. C, D and E only 4. B, D and E only Answer: 4
Given below are two statements Statement I: Qualitive research paradigm emphasizes participant perspectives and uses an empirico-inductive approach Statement II: In the same research project, it is neither possible nor desirable to use both Qualitative and Quantitative research paradigms In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct 2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect 3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect 4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct Answer: 3
What is the usual sequence of steps in the scientific method? A. Hypothesis making by identifying the variables B. Felt need which is creating the problem C. Identifying the difficulty and problem statement formulation D. Data analysis and interpretation E. Collection of data using appropriate research tools
Choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. A, C, B, D, E 2. B, C, A, E, D 3. C, D, E, B, A 4. B, A, C, E, D Answer: 2
What are the characteristic features of the Quantitative Research paradigm? A. It is hypothetico-deductive B. It is focused on natural settings C. It lays stress on generalizations to the population characteristics D. It emphasizes numeric data from a large number of people E. It says that the literature review plays a minor role but justify the problem
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A, C and D only 2. A, B and C only 3. B, C and D only 4. C, D and E only Answer: – 1
The research method which focuses on establishing causal relationships with control among variables – independent, moderator and dependent, is called 1. Ex post facto method 2. Survey method 3. Case study method 4. Experimental method Answer: 4
Unit-III Comprehension Based Question
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow
In Skinner’s system, reinforcement is automatic, almost by definition. Perhaps the most convincing demonstration of the automatic effect of a reinforcer is what Skinner (1948) has called “superstitious behaviour”. In this situation, an event known to be reinforcing is presented intermittently without respect to what the subject is doing. But if it is doing anything (and this can be made likely through deprivation, etc.), the response just prior to the delivery of the reinforcer is strengthened, as evidenced by an increase in its rate of emission. The subject comes to “act as if” the response that has been fortuitously strengthened somehow produces the reinforcement. This occurs even though the reinforcer is actually delivered by a mechanical device that is in no way responsive to the subject’s behaviour.
The automatic effect of reinforcement is also illustrated in Skinner’s effective techniques of shaping behaviour. These procedures could hardly have sprung from a point of view that regarded all behaviour as elicited. But with the organism viewed as “emitting” the varied responses already in his repertoire, it was an easy step to conceive of shaping. If the observer simply controlled the quick presentation of a reinforcer, then he could strengthen any behaviour the organism happened to emit. Responses not in the subject’s repertoire could then be built into it by appropriate arrangements of environmental conditions and the successive approximation technique.
#1. The procedure of shaping a subject’s behavior is related to his
A. Susceptibility B. Desire for reinforcement C. Responses already in his repertoire D. Responses reinforced by approximation techniques
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A and B only 2. B and C only 3. C and D only 4. A and D only Answer: 3
#2. According to Skinner, the superstitious behaviour of individual is the outcome of
1. Constant exposure to an event 2. Exposure to an event without regularity 3. Occasional exposure to an event 4. Natural exposure to an event Answer: 2
#3. The delivery of the reinforcer gets strengthened due to
1. The subject involved in the event 2. Increase in the rate of reinforcement 3. Factors such as deprivation 4. The use of a mechanical device Answer: 3
#4. The responses that are not in the emission list of a subject, can be observed by
1. Coercive measures 2. Creating suitable environmental conditions 3. Inhibiting his natural emission behavior 4. Using mechanical devices for reinforcement Answer: 2
#5. The example of a mechanical device reinforcing the subject’s behaviour demonstrates
1. The automatic effect of reinforcement 2. The illusion of reinforcement 3. The discrepancy in the subject’s behavior 4. The belief that every reaction is an act of reinforcement Answer: 1
Unit-IV Communication Based Question
In communication, interpretation of the message depends upon 1. The context 2. Transmission speed 3. Associated noise 4. Channel efficiency Answer: 1
Which of the following factors are important in communication? A. Slang B. Cynical attitude C. Framing D. Priming E. Immediacy
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. A, B and C only 2. B, C and D only 3. A, D and E only 4. C, D and E only Answer: 4
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R Assertion A: Giving orders to students in the classroom is a specific form of communication Reason R: The manner of orders depends upon the cultural background of the students involved
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A 2. Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A 3. A is true but R is false 4. A is false but R is true Answer: 1
The sequence of cultural institutions is communication is A. Family B. School C. Religion D. Mass media
Choose the correct answer from the options below 1. A, B, C, D 2. B, C, D, A 3. C, D, A, B 4. D, A, B, C Answer: 1
Unit-V Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude Based Question
If 30% of A=0.25 of B=1/5 of C, then which of the following is true about A: B: C? 1. 10:11:12 2. 10:15:12 3. 10:12:15 4. 10:11:15 Answer: 3
A man is facing south-west. If he turns 90 in the anticlockwise direction and then 135 in the clockwise direction, which direction is he facing now? 1. West 2. North- West 3. North- East 4. East Answer: 1
The product of the ages of Sagun and Srishti is 240. If twice the age of Srishti is more than Sagun’s age by 4 years, then what is Srishti’s age? 1. 15 2. 12 3. 10 4. 20 Answer: 2
Consider the following three sets of numbers
A. 2, 5, 9 B. 1, 6, 10 C. 3, 4, 8
Which of the following represents correct ascending order of the averages of three sets A, B, and C? Choose the correct answer from the options given below
1. C < A < B 2. B < C < A 3. B < A < C 4. C < B < A Answer: 1
Given below are two statements
Statement I: Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 Statement II: The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true 2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false 3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is false 4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is false Answer: 1
Complete the following series 9,11,15,23,39, ______? 1. 71 2. 65 3. 44 4. 68 Answer: 1
Unit-VI Logical Reasoning Based Question
Asidha is a fallacy when the middle term is 1. Unproved 2. Too wide 3. Too narrow 4. Non-exclusive Answer: 1
All things which have smoke have fire; This hill has smoke; Therefore, the hill has smoke; and No non-fiery things have smoke; This hill has smoke; Therefore, this hill is not non-fiery
The above is an example of which type of inference in Indian logic? 1. Purvavat 2. Anvayavyatireki 3. Kevalanayi 4. Kevalavyatireki Answer: 2
A, B, C, D, E and F are standing in a circle and looking at the centre. Only D is between A and B. Only F is between A and C. E is just left of B. Who is the only one standing between E and F? 1. A 2. B 3. D 4. C Answer: 4
Unit-VII Data Interpretation Based Question
Study the data in the given table and answer the questions that follow The table below embodies data on the number of students who appeared (A) and passed (P) in a competitive examination from four different zones (K, L, M and N) during the year 2014 to 2019.
#1.From the which of the following zones, the percentage of students who passed out to the total of those who appeared in the examination is minimum in the year 2019? 1. K 2. L 3. M 4. N Answer: 2
#.2 What is the difference between the total number of students who appeared in the exam and the total number of students who passed in the exam from Zone-K in all six years taken together? 1. 2060 2. 2070 3. 2080 4. 2090 Answer: 4
#3. What is the ratio of the number of students who passed from Zone-K in the year 2017 compared to that in 2018? 1. 7:5 2. 3:5 3. 5:7 4. 5:3 Answer: 3
#4. The total number of students who passed from Zone-M in all the six years taken together is approximately what percentage of the total number of students who appeared from Zone-M in all the six years taken together? 1. 56% 2. 58% 3. 60% 4. 64% Answer: 1
#5 What is the average number of students who passed in the exam from all the four zones in the year 2015? 1. 528 2. 529 3. 530 4. 531 Answer: 2
Unit-VIII Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Based Question
#1. RAM is placed on
Hard Disk
Extension board
Motherboard
USB Answer: 3
Given below are two statements Statement I: Cache memory is faster than random access memory Statement II: Random access memory is closer to the processor than cache memory
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below 1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct 2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect 3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect 4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct Answer: 3
Which one of the following is NOT a web browser? 1. Firefox 2. Facebook 3. Chrome 4. Safari Answer: 2
URL stands for 1. Universal Resource Location 2. Universal Response Locator 3. Unified Response Location 4. Uniform Resource Locator Answer: 4
Given below are two statements Statement I: The use of ICT in organizing teaching-learning programmes in the universities has the potential to optimise the learning outcomes Statement II: Formative assessment provides support to enhancing the quality of teaching-learning sessions
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below 1. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct 2. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect 3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect 4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct Answer: 1
Which of the following statements are correct?
A. N.K.N stands for New Knowledge Network B. MOOCs are offline courses C. National Supercomputing Mission is a Government of India initiative D. Clock rate of CPU is measured in Gigabytes E. Param Shivay is a super computer
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: 1. C and E only 2. B and C only 3. C and D only 4. A and E only Answer: 1
Unit-IX People, Development and Environment Based Question
Identify the correct sequence of sectoral global CO2 emissions in increasing order as per IPCC (2014) report A. Electricity and heat production B. Buildings C. Transportation D. Industry
Choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. B, C, D, A 2. B, C, A, D 3. B, D, C, A 4. B, D, A, C Answer: 1
When did the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) and the International Program in Environmental Education (IEEP) come into existence? 1. 1972 2. 1975 3. 1982 4. 1992 Answer: None
Identify correct sequence of the following State Union of India in terms of increasing wind energy potential A. Gujarat B. Rajasthan C. Madhya Pradesh D. Tamil Nadu
Choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. D, C, B, A 2. B, D, C, A 3. B, C, A, D 4. B, C, D, A Answer: None
Among the following elements which is typically the most abundant in dried sewage sludge? 1. Total nitrogen 2. Total Sulphur 3. Calcium 4. Total phosphorous Answer: 3
Dissolved oxygen (DO), an important parameter of water quality, is essential for survival of 1. Humans 2. Animals 3. Fish 4. Crops and vegetables Answer: 3
Under Goal 2 of Millennium Development Goals, UN member countries were to ensure that by 2015, children everywhere, boys and girls would be able to complete a full course of 1. Primary education 2. Secondary education 3. Tertiary education 4. Skill based education Answer: 1
Unit-X Higher Education System Based Question
#1. Given below are two statements
Statement I: A deemed to be university is a non-affiliating university Statement II: The teacher-student ratio in a deemed to be university must not be less than 1:10
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below 1. Both Statement I and Statement II are true 2. Both Statement I and Statement II are false 3. Statement I is correct but Statement II is false 4. Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true Answer: 3
The full form of ‘NEAT’, a recently launched schemed of MHRD, Government of India, is 1. National Engineering Aptitude Test 2. National Educational Alliance for Technology 3. National Education Alliance for Testing 4. National English Aptitude Test Answer: 2
An Inter-University Center for Yogic sciences has been set up by University Grants Commission in the state of 1. Karnataka 2. Madhya Pradesh 3. Uttarakhand 4. Himachal Pradesh Answer: 1
According to the census of 2011, which state/union territory had the minimum number of graduates in relation to its population? 1. Uttar Pradesh 2. Kerala 3. Daman and Diu 4. Chandigarh Answer: 4
0 notes
Text
40 Major International/Indian Environmental Organizations Fighting Issues
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/environmental-organizations/
40 Major International/Indian Environmental Organizations Fighting Issues
Important Environmental Organizations related to environment conservation
Are you planning to take the UGC NET exam? That’s a smart move since it will determine whether you are eligible for Assistant Professor and Junior Research Fellowship (JRF). For you to become eligible for Assistant professor, you need to pass it with flying colors, though. You have no choice but to pass both Papers I and II. As far as Paper I is concerned, you need to be prepared for all ten categories. One of them is People and Environment. This article discusses essential organizations for the environment, and knowing about them could make all the difference. Check them out!
The organizations are subdivided into two groups, international and Indian organizations.
International Environmental Organisation
World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF)
It is an international NGO that came into existence in 1961 on 29th April. Formerly known as World Wide Fund, the organization advocates for wilderness preservation. It also aims to reduce the impact of humans on the environment. Its headquarters are in Rue Mauverney 28 Gland, Vaud, Switzerland
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
Formerly known as the World Conversational Union and International Union for the Protection of Nature, this international organization revolves around nature conservation. It also works on how natural resources should be used sustainably. It was founded in 1948, whereas its headquarters are in Gland, Switzerland.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
This intergovernmental body is part of the United Nations. Its focus is on the contribution of humans toward climate change. Additionally, it oversees how it impacts the economic, political, and natural aspects of the world. It also touches on risks and reasonable cause of action for human-induced climate change. It was formed in 1988, and its headquarters are Geneva, Switzerland.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
It focuses on how to respond to environmental issues with excellent coordination. From leadership to science delivery to solutions development, the organization targets several issues. They include green economic development, terrestrial ecosystems, marine management, and climate change. It was founded in 1972, and its headquarters are in Nairobi, Kenya.
World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
It is a United Nations specialized agency obliged to promote international cooperation as far as geophysics, hydrology, atmospheric science, and climatology. Initially, it was a weather data and research forum that was formed in 1873. At that time, the non-governmental organization’s name was the International Meteorological Organization. WMO was founded in 1950, and its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland.
International Whaling Commission (IWC)
As the name suggests, this international body focuses on whales. It is based on the terms of the International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) held in 1946. It was formed that same year. To develop the whaling industry in an orderly manner, the involved parties saw the need to facilitate proper conversation of the whale stocks. With about 88 member nations, its headquarters are in Impington, United Kingdom.
BirdLife International
It is a non-governmental organization founded in 1922 and focuses on birds. Besides fighting against their extinction, they also focus on their habitats. They identify and safeguard essential sites for birds, maintain and restore their main habitats and empower conservationists globally. Its headquarter is Cambridge, United Kingdom.
TRAFFIC (Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network)
It is a non-governmental organization working across the world on sustainable development and biodiversity. Its focus is the trade of wild animals as well as plants. The organization doesn’t want a scenario where that trade would threaten the conservation of nature. It came about after a strategic collaboration between WWF and IUCN. It was founded in 1976, whereas its headquarters are Cambridge, UK.
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
It is a multilateral treaty focused on the protection of endangered animals and plants. It ensures that trading wild animals and plants isn’t a danger to their survival. The resolution that led to its drafting was during the IUCN meeting held in 1963. It became official through signing in 1973 but started its operation in 1975. Its headquarters are Geneva, Switzerland.
South Asia Wildlife Enforcement Network (SAWEN)
It is a regional inter-governmental body advocating for the conservation of flora and fauna. To achieve that, eight countries in South Asia came up with collective goals and strategies to combat illegal trade within their boundaries. They include Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Maldives, India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan. Its secretariat is Kathmandu, Nepal.
Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR)
It is an International Science Council (ISC) interdisciplinary body, and its focus is the Antarctica region, Southern Asian area included. It contributes towards the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings by offering independent advice. It also provides information to various international bodies, including the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the IPCC. Its responsibility is to initiate, develop and coordinate international science research efforts in the region. It has Science Groups in charge of its scientific work. It was founded in 1958.
World Nature Organization (WNO)
This inter-governmental organization focuses on promoting global environmental protection and was founded in 2010. Its member states came together due to threats emanating from the rising sea levels. Its treaty became official in 2014 on 1st May, and it is essential to note that India is not its member.
Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA)
It is a platform that’s part of Climate-smart Agriculture (CSA). Its focus is no different from CSA since its focus is improving food security and nutrition despite climate change. It works on improving agricultural productivity and what farmers pocket without overlooking sustainability. It aims to reduce agricultural greenhouse gas emissions and make farmers resilient to climate change and extreme weather conditions.
Arctic Council
It is an intergovernmental forum that focuses on issues that the people and the governments of the Arctic region face. The member states include the United States, Sweden, Russia, Norway, Iceland, Finland, Denmark, and Canada. All the 8 have sovereignty of land within the Arctic Circle. It was founded in 1996, whereas its headquarters are Tromso, Norway.
Global Environment Facility (GEF)
It is an organization striving to achieve sustainable development programs and address environmental issues cutting across the globe. It was founded in 1992 during the Rio Earth Summit. Ever since then, it has funded a long list of projects in up to 170 countries. It has 184 member states, and it is located in Washington, District of Columbia, US.
Global Climate Change Alliance (GCCA)
It was formed by European Union (EU) in efforts of reaching out to developing countries, precisely the Small Island Developing States (SIDs) and the Least Developed States (LDCs). Its focus includes reducing poverty, mainstreaming climate change. Furthermore, it aims to strategize the mitigation and adaptation to climate change. There is also increasing resilience when shocks and stresses related to climate emerge. It was founded in 2007.
Climate Action Network (CAN)
It is an international network comprising more than 1300 non-governmental organizations working on the environment in more than 130 countries. It focuses on promoting individual and government actions in ensuring that human-induced climate change stays at ecologically sustainable levels. It was founded in 1989, and its headquarter is Bonn, Germany.
Forest Carbon Partnership Facility (FCPF)
It is a global partnership including governments, civil society, businesses, and indigenous people. Its focus is REDD+, which involves reducing emissions, managing forests sustainably, conserving and enhancing forest carbon stocks. It has 47 REDD countries participating so far. 18, 18, and 11 are in Africa, Latin America, and Asia-Pacific, respectively.
Global Tiger Forum (GTF)
It is an international inter-governmental body focusing on the protection of tigers. It was established in 1994 following its recommendation during the 1993 International Symposium on Tiger Conservation held in New Delphi. Coincidentally, its headquarters are in New Delhi.
Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI)
It is an international organization based on a treaty to promote green growth. That’s to be achieved by balancing economic growth and environmental sustainability. It was formed in 2010, and its headquarters are in Seoul, South Korea. So far, its members are not less than 30 states.
Indian Environmental Organization
Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
It is a ministry in the government of India. It plans, promotes, coordinates, and oversees the implementation of programs related to forestry and the environment at large. It is in charge of conserving wild animals, plants, wilderness areas, and forests. Besides, it mitigates land degradation, deforestation, and pollution while also controlling afforestation. Its headquarters are in Indira Paryavaran Bhavan, Jorbagh Road, New Delhi
Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI)
It is a statutory advisory body that advises the Ministry of Animal Husbandry, Dairying, and Fisheries of the Government of India. Its headquarters are Ballabhgarh, Haryana.
Central Zoo Authority (CZA)
It is a body of India’s government and an affiliate member of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA). As the name suggests, it is in charge of overseeing the zoos and bringing them to international standards. It was founded in 1992.
National Biodiversity Authority (NBA)
This statutory autonomous body was formed in 2003. It is under the Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change. Its establishment resulted from the signing of the Convectional of Biological Diversity by India back in 1992. Consequently, the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 came along. That’s when the body was formed for the implementation of the provisions of the act. Its headquarters are in Chennai, India.
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
It is a statutory body founded in 2006 to fight against organized wildlife crime. It is under the Government of India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. It is important to note that its operations commenced in 2008. Its headquarters are in Trikoot-1 Building, 2nd Floor, Bhikaji Cama Place, New Delhi-110066.
National Green Tribunal (NGT)
The name says it all. It solves human-wildlife conflicts and settles cases related to the same. It advocates for the compensation of people or properties destroyed by wildlife. Additionally, it handles cases concerning the protection and conservation of the environment, including forests and natural resources. It was formed in 2010 following the National Green Tribunal Act 2010.
National Board of Wildlife (NBWL)
The statutory advisory body advises the government on matters concerning wildlife conservation in India. It also promotes wildlife and forest development and conservation. It is in charge of the wildlife sanctuaries and national park boundaries; hence can’t be altered without its permission. It also reviews and approves projects around these areas. It is constituted under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
It is a statutory body that regulates biotechnology in India. It focuses on genetically engineered cells and organisms or hazardous microorganisms in India. The organization regulates how they are used, manufactured, stored, imported, and exported. Initially, its name was Genetic Engineering Approval Committee until 2010, when it got its name. It is under the Government of India’s Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change.
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
It is a statutory organization under India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change. It was formed in 1974, and its functions are governed by several acts, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, and the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. It offers the ministry technical services. It also offers State Pollution Control Boards technical assistance, guides them, coordinates their activities, and resolves disputes whenever a need arises.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
It came as a result of a recommendation of a Tiger Task Force to reorganize the management of 1973 Project Tiger and other Tiger Reserves in the country, which are about 51. India’s Prime Minister was in charge of its constitution, and its establishment took place in December 2005.
National Afforestation and Eco-Development Board (NAEB)
The organization was formed in August 1992. Its focus is mainly on protected areas such as sanctuaries, national areas, degraded lands, and forest areas adjacent to forests. Its primary role is to promote eco-development, ecological restoration, afforestation, and tree planting through related activities. It also pays attention to Western Ghats, Aravallis, and Western Himalayas, among other ecologically fragile geographical areas
Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
It is an independent institution providing natural resource service. Its wildlife research is on Climate Change, Habitat Ecology, Ecotoxicology, Ecodevelopment, Spatial Modeling, Wildlife Forensics, Wildlife Policy, Endangered Species, Wildlife Management, and Biodiversity. It is under the Government of India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. Its establishment took place in 1982.
Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)
It is a national advisory council responsible for monitoring, providing technical help, and evaluating compensatory activities. It aims to provide transparency regarding forest land diversion to create room for private or governmental projects.
Zoological Survey of India (ZSI)
It was formed in 1916 as the first organization in India about zoological studies and research. Its founder was the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change of India. It focuses on promoting research, surveying, and exploring the country’s fauna, whereas its headquarters are in Kolkata.
Botanical Survey of India (BSI)
It was formed in 1890 to promote research, survey, and conservation of the country’s flora. Besides flora, it also focuses on the country’s plant wealth and endangered species. It collects and maintains the gene bank and germplasm of plant species that are either vulnerable, patent, or endangered. Its founder was the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change of India. Its headquarters are in Kolkata.
Forest Survey of India (FSI)
It was formed in 1981, and its founder was the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of India. It focuses on promoting research, survey, and studies of the country’s forests. The findings help in the consistent monitoring of changes in forest resources and land. Equally important, the data helps the government plan, conserve and manage sustainable environmental protection. It is also in charge of implementing social forestry programs. Its headquarters are in at Dehradun in Uttarakhand.
National Ganga Council
Formed in 2016, the central role of this organization is to clean up the River Ganga. As a matter of fact, its full name is the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management of River Ganga. It was constituted under the River Ganga (Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management) Authorities Order, 2016. Its chair is the Prime Minister of India. Its member states are those within the River Ganga Basin or along its major tributaries. They include Delhi-NCR, Jharkhand, Haryana, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Himachal. Pradesh
Wildlife Trust of India (WTI)
This nature conservation organization has lived up to its name ever since its formation in 1998. It focuses on conserving wildlife and habitat without overlooking the welfare of each world life as an individual. Its headquarters are in Noida, Uttar Pradesh.
Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS)
It is among India’s largest non-governmental organizations working on research in biodiversity and conservation. It funds various researches through grants and collaborates with famous naturalists, including S. Dillon Ripley and Salim Ali. It was formed in 1883, and its headquarters are in Hornbill House, Mumbai (Bombay), India.
Environmentalist Foundation of India
This environmental conservation group has two significant areas of focus, habitat restoration and wildlife conservation. It is famous for promoting biodiversity, especially in India’s lakes, by cleaning and restoring them scientifically. Despite starting in 2007, its registration occurred in 2011. It covers Chennai, Coimbatore, Kolkata, Delhi, Mumbai, Trivandrum, Bangalore, Puducherry, and Hyderabad.
Conclusion
Understanding all the above international and Indian environmental organizations is a step closer to passing your UGC NET exam. As you prepare for it, do it thoroughly to ensure that you pass with flying colors. Add more knowledge on this category, people, and Environment, and don’t forget the other nine and Paper-II.
0 notes
Text
Various Environmental Protection Act and Conventions | 2021
New Post has been published on https://ugcnetpaper1.com/environmental-protection-act/
Various Environmental Protection Act and Conventions | 2021
Important Environmental Protection Act
Important Study Notes Based on Unit-IX People, Development, and Environment, As there will be always surprised question-based on this Unit, So you need to have depth knowledge of Environmental Topics. All topics of UGC NET PAPER 1 Sylalbus have been covered step by step.
Unit-IX People, Development and Environment Study Notes Topic Wise
Development and environment: Millennium development and Sustainable development goals
Human and environment interaction: Anthropogenic activities and their impacts on the environment.
Environmental issues: Local, Regional and Global; Air pollution, Water pollution, Soil pollution, Noise pollution, Waste (solid, liquid, biomedical, hazardous, electronic), Climate change and its Socio-Economic and Political Dimensions.
Impacts of pollutants on human health.
Natural and energy resources: Solar, Wind, Soil, Hydro, Geothermal, Biomass, Nuclear, and Forests.
Natural hazards and disasters: Mitigation strategies.
Environmental Protection Act (1986), National Action Plan on Climate Change, International agreements/efforts -Montreal Protocol, Rio Summit, Convention on Biodiversity, Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement, International Solar Alliance. [THIS POST]
MCQ Based on People, Development and Environment(Check MCQ Section)
Environmental Protection Act of 1986
19th November 1986, Environment Protection Act came into force in the Parliament of India in the wake of the Bhopal Tragedy. It is under Article 253 of the Indian Constitution. The Environment Protection Act is mainly for the protection and development of the environment from the danger of human beings, other living beings, plants, and property.
It mainly focuses on the prevention and development of pollution in the environment and the causes of human health if any accident happens.
National Action Plan on Climate Change
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) an initiative formulated by the Government of India on 30th June 2008 to deal with future policies and programs for climatic improvement and adjustment. It put together the national plan on water, renewable energy, energy efficiency agriculture, etc.
The executions of the Action plan are constituted under 8 missions that are responsible to achieve the goals of adaptation and improvement. They are as follows:
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) an initiative formulated by the Government of India on 30th June 2008 to deal with the future policies and programs for climatic improvement and adjustment. It put together the national plan on water, renewable energy, energy efficiency agriculture, etc. The executions of the Action plan are constituted under 8 missions that are responsible to achieve the goals of adaptation and improvement. They are as follows:
National Solar Mission – The main objective is to use solar energy for power generation and other uses. To promote the use of solar power, this initiative was started in 2010.
National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency – The main objective is to save and promote maximum energy by developing new policies and measures. In 2009, the Prime Minister’s Council approved it on Climate Change.
National Mission on Sustainable Habitat – It emphasized Energy conservation on urban waste, management recycling which includes the production of power from waste, development of energy efficiency in buildings, and use of public transport. Prime Minister approved this mission in 2011.
National Water Mission – To improve water efficiency through pricing and other measures. The main objective of the mission is to help to preserve water, minimize wastage, and to make sure that the distributions of water are done on an equitable basis across and within the states. Ministry of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation are the members who supported this mission.
National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem – It aims to preserve the biodiversity, forest conservation, and other ecological problems that are causing problems in the Himalayan region.
National Mission for a “Green India” – Its main goal is to expand the forest and promote “Green India” by protecting, refurbishing, and enhancing the forests in India which are diminishing. It’s taking various measures in responding to climate change by adopting and taking different steps towards it. In 2014, the Ministry of Environment and Forests got the go-ahead to work on this from the Cabinet.
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture – The main objective is how climatic change affects crops and their development through various mechanisms. For example, in areas where there are more rains, it focuses on integrated farming, use of water efficiently, soil health management, etc. It got approval from the government in 2010.
National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change – It aims for the climatic changes and its impact. The mission tries to improve through research and international collaboration. The mission is run by the Department of Science and Technology.
International Agreements/efforts
Environmental Conventions and Protocols Short Notes
[1971] Ramsar Convention
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands (Convention on Wetlands)
The Convention on Wetlands is the intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
The Convention was adopted in the Iranian city of Ramsar in 1971 and came into force in 1975. Since then, almost 90% of UN member states, from all the world’s geographic regions, have acceded to become “Contracting Parties”.
The Convention was signed on the 2nd of February, 1971.
The 2nd of February each year is World Wetlands Day.
The number of parties to the convention (COP) is 171.
The Ramsar Convention Secretariat has its headquarters in Gland, Switzerland
Montreux Record under the Ramsar Convention is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance.
Currently, two wetlands of India are in Montreux record: Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) and Loktak Lake (Manipur).
Chilika Lake (Odisha) was placed in the record but was later removed from it.
The United Kingdom has the world’s largest number of Ramsar sites i.e 175.
As of now, 27 sites of India are listed as Ramsar Sites.
Read here for more details – https://www.ramsar.org/wetland/india
[1972] Stockholm Declaration
The Stockholm Convention was held in Sweden from June 5-16, 1972. The object behind this convention was to “create a basis for comprehensive consideration within the United Nations of the problems of the human environment,” and to “focus the attention of Governments and public opinion in various countries on the importance of the problem.”
The Stockholm convention paved the way for other international conventions on the preservation of the environment such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna, 1973.
This convention led UNEP to coordinate global action for the protection and preservation of the environment in December 1972.
In the same line, the Parliament of India passed the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and the Forest Conservation Act, 1980 to give effect to the Stockholm convention.
[1973] CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora)
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) is an international treaty to prevent species from becoming endangered or extinct because of international trade. Under this treaty, countries work together to regulate the international trade of animal and plant species and ensure that this trade is not detrimental to the survival of wild populations.
In 1963, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) called for an international convention on the trade in animal species and their products. A first draft of the Convention was produced in 1964, and in 1973, CITES was signed by 21 nations in Washington, DC.
India is a CITES Party since 1976.
Also known as Washington Convention
It is administered by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
It was signed on March 3, 1973 (World Wildlife Day is celebrated on March 3).
Out of 34 global biodiversity hotspots in the world, India has 4 of them: Western Ghats, Sundaland, Himalayas, and Indo-Burma region.
As an active CITES Party, India prohibits the international trade of endangered wild species.
[1979] Convention on Migratory Species (CMS)
CMS is also known as the Bonn Convention. It is the only convention that deals with taking or harvesting of species from the wild. It currently protects 173 migratory species from across the globe. Enforcement Year: The Convention came into force on November 1, 1983.
Signed: 6 November 1979
Migratory species threatened with extinction are listed on Appendix I of the Convention. CMS Parties strive towards strictly protecting these animals, conserving or restoring the places where they live, mitigating obstacles to migration and controlling other factors that might endanger them. Besides establishing obligations for each State joining the Convention, CMS promotes concerted action among the Range States of many of these species.
Migratory species that need or would significantly benefit from international cooperation are listed in Appendix II of the Convention. For this reason, the Convention encourages the Range States to conclude global or regional agreements.
India has been a party to the Convention since 1983.
India has signed a non-legally binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with CMS on conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008), and Raptors (2016).
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is an international treaty with three main objectives:-
Conservation of biodiversity
Sustainable use of biodiversity
Fair and equitable sharing of the benefits which occur from the genetic recourses.
It is a legally binding treaty to conserve biodiversity that has been in force since 1993
The CBD Secretariat is based in Montreal, Biodiversity Authority (NBA). Canada and operates under the United Nations Environment Programme.
This treaty was signed on 5th June 1992 and was effective from 29th December 1993. Over 196 countries participated in Rio de Janeiro.
The COP-10 also adopted a ten-year framework known as “Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011- 2020”, which provides a set of 20 ambitious yet achievable targets, collectively known as the Aichi Targets for biodiversity.
Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol on Substance is a global agreement to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of various substances that are responsible for ozone reduction. The main objective of the Montreal Protocol was to protect the ozone layer by taking different steps to manage the production and consumption of depleting substances (ODS) and to remove it completely.
It was agreed on 26 August 1987, and entered into force on 16 September 1989, following the first meeting in Helsinki, May 1989.
The parties to the Protocol meet once a year to make decisions aimed at ensuring the successful implementation of the agreement. These include adjusting or amending the Protocol, which has been done six times since its creation. The most recent amendment, the Kigali Amendment, called for the phase-down of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) in 2016. These HFCs were used as replacements for a batch of ozone-depleting substances eliminated by the original Montreal Protocol. Although they do not deplete the ozone layer, they are known to be powerful greenhouse gases and, thus, contributors to climate change.
Kigali Agreement happened during the 28th Meeting of Parties (2016) when the 197 member countries signed the agreement to amend the Montreal Protocol.
Given all of these factors and more, the Montreal Protocol is considered to be one of the most successful environmental agreements of all time. What the parties to the Protocol have managed to accomplish since 1987 is unprecedented, and it continues to provide an inspiring example of what international cooperation at its best can achieve.
Vienna Convention for Protection of the Ozone Layer
It is a multilateral environmental agreement agreed upon at the 1985 Vienna Conference and entered into force in 1988.
It acts as a framework for international efforts to protect the ozone layer. These are laid out in the accompanying Montreal Protocol. It does not include legally binding reduction goals for the use of CFCs, the main chemical agents causing ozone depletion.
[1992]United Nations Conference on Environment and Development, 1992 (Earth Summit/Rio Summit)
Rio Summit or The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit was the major United Nations conference which was held in Rio from 3rd to 14th June 1992.
The main objective of the summit was to stop the destruction of various natural resources and to handle pollution which is affecting the planet. And the condition of the global environment and its association between economics, science, and the environment in a political context. 105 countries participated in the Earth Summit, for this development.
UNFCCC – United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change
The UNFCCC secretariat (UN Climate Change) was established in 1992 when countries adopted the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
The UNFCCC entered into force on 21 March 1994. Today, it has near-universal membership. The 197 countries that have ratified the Convention are called Parties to the Convention.
The convention is legally non-binding but makes provisions for the meeting called ‘protocols’ where negotiating countries can set legally binding limits
REDD+ is a mechanism developed by Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
It creates a financial value for the carbon stored in forests by offering incentives for developing countries to reduce emissions from forested lands and invest in sustainable development
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement which was extended on the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change like to reduce the greenhouse gas emission based on scientific agreement.
It is an international treaty to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Kyoto Protocol applies to 6 greenhouse gases; carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride. It is an extension to the 1992 UNFCCC.
This Protocol was signed on 11th December 1997 and was effective from 16th February 2005 in Kyoto. Over 192 countries participated in this.
India has ratified the second commitment period of the Kyoto Protocol known as the Doha Amendment to the protocol
Read More – Kyoto Protocol
Paris Agreement
Paris Agreement is an international agreement to fight against climate change. The main objective of this agreement was to stop global warming and the threat of dangerous climatic changes. Over 195 countries participated in the Paris Agreement from 30th November to 11th December 2015.
The Paris Agreement opened for signature on 22 April 2016 – Earth Day – at UN Headquarters in New York. It entered into force on 4 November 2016.
Holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels
World Charter of Nature
It was adopted by United Nations member nation-states on October 28, 1982.
It proclaims five principles of conservation by which all human conduct affecting nature is to be guided and judged.
All areas of the earth, both land, and sea, shall be subject to these principles of conservation; special protection shall be given to unique areas, to representative samples of all the different types of ecosystems and the habitats of rare or endangered species.
Nature shall be secured against degradation caused by warfare or other hostile activities.
International Solar Alliance
In International Solar Alliance over 122 countries participated and the same was initiated by India and founded in the year 2015.
The main objective of this alliance is to increase the use of solar energy among the International Solar Alliance member countries in a convenient, safe, affordable and sustainable manner.
The vision and mission of the International Solar Alliance are to provide a dedicated platform for cooperation among solar resource-rich countries where the global community, including bilateral and multilateral organizations, corporate, industry, and other stakeholders, can make a positive contribution to assist and help achieve the common goals of increasing the use of solar energy in meeting energy needs of prospective ISA member countries in a safe, convenient, affordable, equitable and sustainable manner.
Its major objectives include global deployment of over 1,000GW of solar generation capacity and mobilization of investment of over US $1000 billion into solar energy by 2030.
Study Notes Related to the NTA UGC NET EXAM Paper 1 Other Units.
Unit-I Teaching Aptitude
Unit-II Research Aptitude
Unit-III Comprehension
Unit-IV Communication
Unit-V Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude
Unit-VI Logical Reasoning
Unit-VII Data Interpretation
Unit-VIII Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Unit-IX People, Development and Environment
Unit-X Higher Education System
0 notes