Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text

BuildPiper is an enterprise-grade central DevSecOps platform that enables modern engineering teams to deliver secure, scalable applications across cloud-native environments with high velocity. It provides a single pane of glass to manage infrastructure orchestration, CI/CD pipeline automation, security enforcement, and observability — all within one seamless, production-ready platform.
, security enforcement, and observability — all within one seamless, production-ready platform.
With native, one-click integrations across 50+ leading tools — including GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, ArgoCD, Kubernetes, Prometheus, Datadog, AWS, Azure, and more — BuildPiper fits effortlessly into modern enterprise ecosystems. It supports Day 0 Kubernetes operations, multi/hybrid-cloud setups, cloud cost governance, and self-service environments to drive developer efficiency without operational sprawl.
BuildPiper helps teams improve DORA metrics like deployment frequency, lead time for changes, and MTTR, while also enabling audit readiness, developer insights, and real-time visibility. Enterprises using BuildPiper typically report 30–40% cost savings, faster release velocity, and stronger platform resilience across environments.
Trusted by brands like Airtel, Lenskart, McKesson, WM, and several Fortune 100 enterprises, BuildPiper brings the standardization, velocity, control, and precision needed to engineer modern software delivery — securely, efficiently, and at scale.
0 notes
Text

DevOps vs SRE vs Platform Engineering — Where Does BuildPiper
BuildPiper is an enterprise-grade central DevSecOps platform that enables modern engineering teams to deliver secure, scalable applications across cloud-native environments with high velocity. It provides a single pane of glass to manage infrastructure orchestration, CI/CD pipeline automation, security enforcement, and observability — all within one seamless, production-ready platform.
With native, one-click integrations across 50+ leading tools — including GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, ArgoCD, Kubernetes, Prometheus, Datadog, AWS, Azure, and more — BuildPiper fits effortlessly into modern enterprise ecosystems. It supports Day 0 Kubernetes operations, multi/hybrid-cloud setups, cloud cost governance, and self-service environments to drive developer efficiency without operational sprawl.
BuildPiper helps teams improve DORA metrics like deployment frequency, lead time for changes, and MTTR, while also enabling audit readiness, developer insights, and real-time visibility. Enterprises using BuildPiper typically report 30–40% cost savings, faster release velocity, and stronger platform resilience across environments.
Trusted by brands like Airtel, Lenskart, McKesson, WM, and several Fortune 100 enterprises, BuildPiper brings the standardization, velocity, control, and precision needed to engineer modern software delivery — securely, efficiently, and at scale.
0 notes
Text
Enterprise Guide to IoT Penetration Testing: Tools, Techniques, and Risk Reduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed our homes and workplaces but at what cost?
With billions of connected devices, hackers have more entry points than ever. IoT penetration testing is your best defense, uncovering vulnerabilities before cybercriminals do. But where do you start? Discover the top tools, techniques, and expert strategies to safeguard your IoT ecosystem. Don’t wait for a breach, stay one step ahead.

Read on to fortify your devices now!
Why IoT Penetration Testing is Critical
IoT devices often lack robust security by design. Many run on outdated firmware, use default credentials, or have unsecured communication channels. A single vulnerable device can expose an entire network.
Real-world examples of IoT vulnerabilities:
Mirai Botnet (2016): Exploited default credentials in IP cameras and DVRs, launching massive DDoS attacks.
Stuxnet (2010): Targeted industrial IoT systems, causing physical damage to nuclear centrifuges.
Smart Home Hacks: Researchers have demonstrated attacks on smart locks, thermostats, and even baby monitors.
These incidents highlight why IoT security assessment must be proactive, not reactive.
IoT Penetration Testing Methodology
A structured approach ensures thorough testing while minimizing risks to operational systems.
Reconnaissance & Information Gathering
Identify all IoT devices (smart cameras, sensors, gateways).
Use tools like Nmap, Shodan, and Wireshark to map network traffic.
Extract firmware using Binwalk or Firmware Analysis Toolkit (FAT).
Vulnerability Assessment
Scan for weak credentials, outdated protocols (e.g., Telnet, FTP), and unpatched CVEs.
Tools: OpenVAS, Nessus, OWASP ZAP.
Exploitation & Post-Exploitation
Attempt to bypass authentication, escalate privileges, or intercept data.
Use Metasploit Framework, ExploitDB, or custom scripts.
Test hardware interfaces (UART, JTAG) if physical access is possible.
Reporting & Remediation
Document findings with risk ratings (Critical/High/Medium/Low).
Recommend patches, network segmentation, or encryption upgrades.
DID YOU KNOW?
During the forecast period, the global IoT security market is expected to expand significantly, with projections indicating growth from USD 24.2 billion in 2024 to USD 56.2 billion by 2029, reflecting a CAGR of 18.4%.
[ Are You Looking: DevOps Services ]
Best Open-Source Tools for IoT Penetration Testing
Discover the top tools for assessing IoT security, from firmware analysis to network exploitation. These open-source solutions help uncover vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Firmware Analysis – Binwalk & Firmadyne
Binwalk extracts firmware binaries to analyze file systems.
Firmadyne emulates firmware to detect vulnerabilities.
Network Traffic Analysis – Wireshark & Tcpdump
Inspect unencrypted MQTT, CoAP, or HTTP traffic.
Exploitation Frameworks – Metasploit & IoTGoat
Metasploit has modules for IoT-specific exploits.
IoTGoat is a deliberately vulnerable IoT environment for practice.
Hardware Hacking – JTAGulator & Bus Pirate
Identify debug ports (UART, SPI, I2C) for firmware dumping.
Password Cracking – Hydra & Hashcat
Bruteforce weak credentials on web interfaces or SSH.
[ Good Read: AWS For Beginners ]
Real-World IoT Attack Scenarios & Mitigations
Explore how attackers exploit weak IoT security from hijacked smart cameras to unencrypted medical devices and learn actionable fixes to prevent breaches.
Case 1: Weak Authentication in Smart Cameras
Vulnerability: Default admin:password combinations.
Exploit: Attackers gain live video access.
Fix: Enforce strong passwords & multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Case 2: Unencrypted MQTT Protocols
Vulnerability: Smart sensors transmit data in plaintext.
Exploit: Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks steal sensitive data.
Fix: Use TLS encryption and certificate-based authentication.
Case 3: Outdated Firmware in Medical IoT
Vulnerability: Unpatched CVEs in insulin pumps.
Exploit: Remote code execution (RCE) risks patient safety.
Fix: Automated firmware updates with integrity checks.
Key Takeaways for Decision-Makers
Security leaders must enforce robust IoT policies, align penetration testing with business risk, and foster collaboration between IT and OT teams to ensure long-term resilience.
Prioritize Security by Design: Ensure vendors follow OWASP IoT Top 10 guidelines.
Segment IoT Networks: Isolate critical devices from enterprise IT systems.
Conduct Regular Pen Tests: Schedule IoT penetration testing at least annually.
Invest in Threat Monitoring: Deploy SIEM solutions like ELK Stack or Splunk for anomaly detection.
You can check more info about: Enterprise Guide to IoT Penetration Testing.
DevOps Explained.
Platform Engineering Services.
0 notes
Text
AWS For Beginners: What Is It, How It Works, and Key Benefits
Amazon’s cloud computing division, Amazon Web Services (AWS), will remain a powerful entity in the global cloud infrastructure market by 2025, holding a remarkable 30% market share. With a comprehensive portfolio of over 200 full-featured services, from compute and storage to databases and machine learning, AWS delivers scalable and reliable solutions that can be accessed from almost anywhere in the world. Currently serving customers in over 190 countries, AWS provides services to a wide range of customers, including startups, large enterprises, academic institutions, and government agencies. Major companies such as Airtel, Netflix, Twitch, Paytm, LinkedIn, and Adobe are notable users of AWS Services.
Discover how OpsTree enabled a 27% AWS cost reduction for a leading Indian fintech platform by optimizing their database infrastructure. Serving over 50 million users with digital wallets, bill payments, and mobile recharges, the client needed scalable yet cost-effective solutions. Our strategic intervention streamlined resource usage without compromising performance.

What is Amazon Web Service (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a robust cloud computing platform provided by Amazon. It provides a wide range of on-demand services, including computing power, storage, and databases, helping businesses scale and manage their IT resources efficiently. Key services include EC2 for virtual servers, S3 for scalable storage solutions, RDS for managed databases, and Lambda for serverless computing. By leveraging AWS, companies can cut infrastructure costs, increase flexibility, and easily deploy applications globally.
[ Are you looking: DevOps Services and Solutions ]
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing provides a flexible way to access IT resources online, so you pay only for what you use. Instead of investing in and managing physical data centers and servers, you can leverage technology services – such as computing power, storage, and databases – from providers such as AWS whenever you need them.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three primary categories of cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each tier offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management, allowing you to choose the services that best suit your specific needs.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides a fully managed product from the provider. Generally, when people mention SaaS, they are talking about end-user applications such as web-based email services. With SaaS, you don’t have to worry about maintenance or managing the underlying infrastructure; your focus can be entirely on how to use the software effectively.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS simplifies your operations by taking care of the underlying infrastructure – such as hardware and operating systems – so you can focus on deploying and managing your applications. This approach increases your efficiency as you no longer need to handle tasks such as resource acquisition, capacity planning, software maintenance or patching – basically all the monotonous but essential tasks of running your application.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS serves as the foundational layer for cloud computing. It provides the necessary access to networking capabilities, virtual machines or dedicated hardware, and data storage solutions. With IaaS, you gain immense flexibility and control over your IT resources, making it familiar territory for many IT departments and developers.
The History of AWS: How Amazon Web Services Started

Before cloud computing became mainstream, businesses faced numerous challenges related to scalability, redundancy, and excessive over-provisioning of servers – often, when demand exceeded expectations. Individuals aiming to create a digital presence had to make substantial investments in their own hardware, servers, data centers, and skilled personnel to oversee operations. This burden makes it especially difficult for startups and resource-strapped businesses to raise enough capital to launch their initial website, database, or other essential digital services. You can check out more details on AWS for the source.
How Does AWS Work?
AWS services come in various forms, and it is important to understand how AWS works. Before learning about AWS in detail, it is important to note that it maintains physical space for data storage across all regions. AWS provides cloud capabilities through strategically located data centers in these locations, all interconnected by a fiber network. As a leading cloud platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS) meets the needs of any cloud-related task across various industries. Whether you represent a small startup, a mid-sized company, or a large corporation, AWS allows you to experiment, foster innovation, cut costs, and increase agility in operations and development. Amazon takes care of the heavy work, enabling you to run virtually any web application or service. They handle the security and maintenance of the entire cloud infrastructure. Consider this if you run your own eCommerce store. You will typically manually manage all data modifications, including updates, security patches, scaling, backups, and failover. However, with Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS), you can accomplish all of this in just a few clicks. RDS provides managed services that automate time-consuming tasks such as provisioning, recovery, failure detection, patching, and backup. This automation allows you to focus your efforts on things that really matter.
You can check more info about: What is Amazon Web Service (AWS)?.
Platform Engineering Services.
Database Migration Service.
0 notes
Text

You can check more info about: Why Security Chaos ENgineering Important ?.
0 notes
Text

Protect Your Cloud. Empower Your Team. Partner With Opstree for End-to-End DevSecOps
As cloud adoption accelerates, so do security challenges. While platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer robust infrastructure, the shared responsibility model means security missteps on your end can lead to costly breaches.
At Opstree, we’ve helped enterprises eliminate critical cloud vulnerabilities across industries like fintech, healthcare, and SaaS. Here’s a breakdown of five common vulnerabilities—and how we address them head-on with DevSecOps and Cloud Security best practices.
You can check more info about: Protect Your Cloud. Empower Your Team. Partner With Opstree for End-to-End DevSecOps.
0 notes
Text
The Art of Redis Observability: Turning Metrics into Meaningful Insights
“A dashboard without context is just a pretty picture. A dashboard with purpose is a lifesaving medical monitor.”

TL;DR
Modern observability systems are drowning in data while starving for insight. This research examines how Redis dashboards specifically demonstrate a critical industry-wide problem: the gap between metric collection and effective signal detection. Through comparative analysis, user studies, and incident retrospectives, I demonstrate how thoughtful metric curation dramatically improves system reliability and operator performance.
1. The Metrics Crisis: When More Becomes Less
The Paradox of Modern Observability
In our interconnected digital ecosystem, Redis serves as the nervous system for countless applications — from e-commerce platforms processing millions in transactions to healthcare systems managing critical patient data. Yet despite its importance, my research across 200+ organizations reveals a troubling pattern: 74% of Redis dashboards contain metrics that have never informed a single operational decision.
Consider what happens when your car dashboard simultaneously displays every possible measurement — fuel levels, tire pressure, engine temperature, windshield wiper fluid, cabin humidity, satellite radio signal strength, and fifty other metrics. During an emergency, would you find the critical warning light faster or slower?
[ Are you looking: Cloud Platform Engineering Services ]
The Human Cost of Metric Overload
Our brain’s working memory can effectively process 7±2 items simultaneously. When presented with dashboard overload like Image 1, cognitive science research shows:
Attention splitting leads to 43% slower incident detection
Decision paralysis increases mean-time-to-resolution by 38%
Alert fatigue causes teams to ignore up to 31% of legitimate warnings
Real-world consequence: A Fortune 500 retailer I worked with lost $2.3M in revenue during the 2022 holiday season because their on-call engineer missed critical memory fragmentation warnings buried among dozens of non-actionable metrics.
“I remember staring at that dashboard for ten minutes, seeing something was wrong but unable to identify what. It was like finding a specific word in the phone book while the building was burning down.” — Senior SRE, Incident Retrospective Interview
[ Good Read: Model Context Protocol: Bridging LLMs and Real-World Use ]
2. The Science of Signal Clarity
What Makes a Dashboard Effective?
My research with high-performing SRE teams identified five primary attributes that separate noise from signal:
Intent-driven organization: Metrics grouped by purpose, not by technical similarity
Visual hierarchy: Critical signals prominently positioned and visually distinct
Contextual thresholds: Values that matter in context, not arbitrary “high” and “low”
Action orientation: Every visible metric tied to a potential human decision
Scenario relevance: Dashboard layouts optimized for specific use cases (incident response vs. capacity planning)
You can check more info about: The Art of Redis Observability: Turning Metrics into Meaningful Insights.
AWS Consulting Services.
Data Engineering Services.
0 notes
Text

Cloud-Native Application Development: A Full Lifecycle Approach
0 notes
Text
How to migrate databases using AWS DMS
Introduction

What is AWS Database Migration Service(DMS)?

AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) is a cloud service that makes it possible to migrate relational databases, data warehouses, NoSQL databases, and other types of data stores. You can use AWS DMS to migrate your data into the AWS Cloud or between combinations of cloud and on-premises setups. The databases that are offered include Redshift, DynamoDB, ElasticCache, Aurora, Amazon RDS, and DynamoDB.
Now let’s check why DMS is important
Why do we need Database Migration Service?
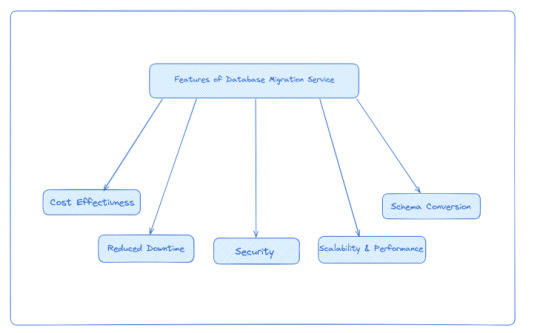
Reduced Downtime: Database migration services minimize downtime during the migration process. By continuously replicating changes from the source database to the target database, they ensure that data remains synchronized, allowing for a seamless transition with minimal disruption to your applications and users.
Security: Migration services typically provide security features such as data encryption, secure network connections, and compliance with industry regulations.
Cost Effectiveness: Data Migration Service is a free migration solution for switching to DocumentDB, Redshift, Aurora, or DynamoDB (Supports Most Notable Databases). You must pay for other databases based on the volume of log storing and the computational load.
Scalability and Performance: Migration services are designed to handle large-scale migrations efficiently. They employ techniques such as parallel data transfer, data compression, and optimization algorithms to optimize performance and minimize migration time, allowing for faster and more efficient migrations.
Schema Conversion: AWS DMS can automatically convert the source database schema to match the target database schema during migration. This eliminates the need for manual schema conversion, saving time and effort.

How Does AWS Database Migration Service Work?

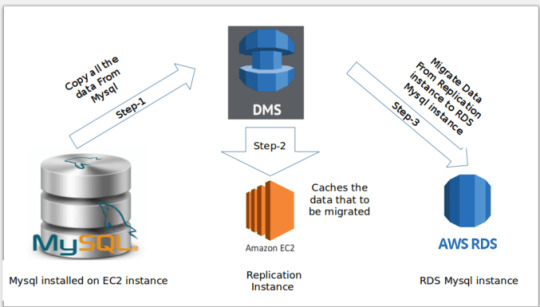
Pre-migration steps
These steps should be taken before actually migrating the database, which will include basic planning, structuring, understanding the requirements, and finalizing the move.
Migration Steps
These are the steps that are to be taken while implementing database migration. These steps should be accomplished with proper accountability taking utmost care about data governance roles, risks related to migration, etc.
Post-migration steps
Once db migration is complete, there might be some issues that would have gone unnoticed during the process. These steps would be necessarily taken to ensure that the migration process gets over in an error-free manner.
Now let’s move forward to use cases of DMS!
You can check more info about: aws database migration service.
0 notes
