Text
Global Awareness Initiative: Substance Abuse in Latin America
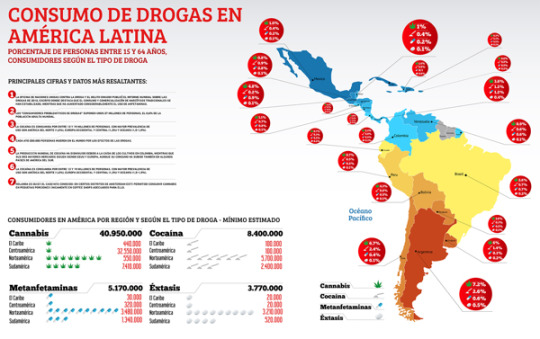
Focusing on Latin America in efforts to address the substance abuse epidemic is crucial due to several factors that make the region particularly vulnerable. Firstly, Latin America serves as a major transit route for illegal drugs destined for global markets, exposing its populations to high levels of drug trafficking and availability. Additionally, socioeconomic disparities, political instability, and historical patterns of violence have contributed to social divide and lack of access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, exacerbating the risk factors associated with substance abuse. Furthermore, cultural norms and attitudes towards drug use, combined with limited resources for prevention and treatment, create a challenging environment for addressing the problem effectively. Therefore, prioritizing Latin America in global awareness initiatives is essential to addressing the root causes of substance abuse and promoting sustainable solutions that benefit the region and beyond.
Creating a multi-faceted global awareness initiative to address the substance abuse epidemic in Latin America requires a holistic approach including online campaigns, community engagement, and educational outreach, and cross-border collaboration.

Online Campaigns:
Social Media Awareness: Develop content for platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok to raise awareness about substance abuse in Latin America. Utilize visually appealing graphics and videos to engage a wide audience to teach about the dangers of substance abuse, including statistics, personal stories of recovery, and resources for help.
Influencer Partnerships: Collaborate with social media influencers and celebrities with a significant following in Latin America to amplify the reach of the campaign.
Online Forums and Q&A Sessions: Organize virtual forums and live Q&A sessions on platforms like Reddit or Discord, featuring experts in addiction treatment, mental health, and public policy. Encourage participants to ask questions and share their experiences.
Digital Resources: Create a website or mobile app where people can access information, find treatment facilities, and connect with support groups and helplines

Community Engagement:
Support Groups: Establish support groups and recovery communities in towns across Latin America. This will provide a safe space for individuals struggling with substance abuse to share their experiences and receive encouragement.
Community Workshops: Organize workshops and training sessions for community leaders, educators, and healthcare professionals on topics such as addiction awareness, stigma reduction, and harm reduction strategies.
Street Outreach Programs: Conduct outreach activities in urban areas, public parks, and even homeless shelters to reach vulnerable populations affected by substance abuse. Distribute educational materials, hygiene kits, and information about support services.
Neighborhood Events: Host events such as sports tournaments and cultural festivals that promote healthy living and provide opportunities for community members to learn about substance abuse prevention and treatment options.

Educational Outreach:
Schools: Work with schools to integrate drug education into curriculums. Provide teachers with training and resources to effectively teach students about the risks associated with drug abuse and the importance of making healthy choices.
Parent Education Workshops: Organize workshops for parents to increase their awareness of substance abuse issues, recognize warning signs, and learn effective communication strategies with their children. Provide resources for seeking help and support.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch public service announcements (PSAs) on television, radio, and billboards to communicate key messages about the dangers of drug abuse and where to seek help. These campaigns should be culturally sensitive and tailored to the diverse populations within Latin America.

Cross-Border Collaboration:
Regional Partnerships: Encourage collaboration among governments, NGOs, and international organizations working on substance abuse prevention and treatment in Latin America. Share best practices, resources, and data to strengthen regional efforts.
Information Sharing: Establish a database or online platform where organizations can access up-to-date information on substance abuse trends, treatment practices, and available resources across Latin America
By implementing this multi-faceted global awareness initiative, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of substance abuse in Latin America and promoting healthier, drug-free communities.
0 notes
Text
youtube
Nelson Mandela is a figure in a social justice movement that I admire. I wanted to represent Nelson Mandela's accomplishments through movements to convey themes of resilience, unity, and liberation. My dance began with movements symbolizing oppression and struggle, depicting the harsh realities of apartheid. As the dance progressed, the movements evolved to reflect Mandela's resilience and determination, with powerful and uplifting gestures symbolizing his unwavering commitment to justice and equality.
Nelson Mandela played a pivotal role in dismantling apartheid in South Africa. As a leader of the African National Congress (ANC), he fiercely opposed the oppressive policies of racial segregation enforced by the apartheid government. Mandela's unwavering commitment to equality and justice led to his imprisonment for 27 years. Upon his release in 1990, he continued his efforts, negotiating with the government to end apartheid and advocating for peaceful reconciliation between the country's diverse racial groups. In 1994, Mandela became South Africa's first black president in the nation's first democratic elections, symbolizing the triumph of democracy over apartheid's legacy of discrimination and division.
0 notes
Text
Once again I want to say that I am not a dancer but this was still fun!
I found that I had a little more creative liberty with this dance, as dismantling, undoing, disassembling is more of an open ended theme in comparison to the other dances in the past. In this dance, I tried to gradually soften my movements and become more fluid, symbolizing the process of undoing or disassembling. I also tried to show emotional turmoil, like a sort of mental unraveling, which can be seen when I break down and when I cover my face.
0 notes
Text
Issue Exploration and Analysis
Throughout human history, poverty has been an unrelenting issue, and both its causes and effects have changed throughout time. Recognizing the historical background of poverty can help reveal the multifaceted components that have contributed to its existence. Furthermore, analyzing how it currently affects society sheds light on ongoing issues as well as potential solutions. Poverty has been a problem spanning from the first agrarian societies all the way up to post World War II and modern-day society; poverty has affected populations in various ways, from health disparities to crime and social unrest.
When looking at pre-industrial societies, poverty was often linked to agricultural economies. Widespread poverty could result from a lack of access to fertile land, natural disasters, and discrepancies in crop yields. The shift from agrarian to industrial societies brought about economic changes . Although it brought about more economic expansion, it also brought about unfavorable working conditions and exploitation, which aided in the rise of urban poverty. Through resource exploitation, forced labor, and the establishment of unfair economic systems, the colonization of many regions by European powers exacerbated poverty. Jumping all the way to the 1930's, a worldwide economic crisis caused high rates of unemployment and poverty. This crisis was the Great Depression, and it devastated the U.S. economy. During this time, the necessity of government intervention and social safety nets to combat poverty was brought to light for the first time. After WWII, the mid-20th century saw the establishment of welfare states in many developed countries, aiming to offer social protection and combat poverty through programs like healthcare and unemployment benefits.
Looking at more modern-day causes of poverty, there are much more complex and perhaps even more detrimental foundations of poverty. For example, although globalization, which is the stretching of economic, political, and social relationships across the world, has brought economic growth, it has also widened income inequality. Economic integration helps certain areas while making it difficult for others to compete, which causes disparities in wealth and poverty. Another issue is populations who lack access to technology, which results in fewer options for education, employment, and civic engagement. This has led to the rise of a "digital divide," restricting opportunities for social mobility in the lower class. Poverty is also frequently made worse in areas where there is political unrest or conflict. Persistent poverty is worsened by displacement, infrastructural destruction, and other disruptions to economic activity. There are also environmental factors that contribute to poverty; climate change and environmental degradation disproportionately affect vulnerable communities, leading to losses of livelihoods and therefore income. One of the most prevalent causes of poverty however is structural inequality. Persistent poverty is most often a result of systemic problems like discrimination based on race, gender, or ethnicity. Social mobility, work opportunities, and education are constantly restricted for marginalized groups. All these combined factors are what unfortunately contribute to poverty in modern-day society.
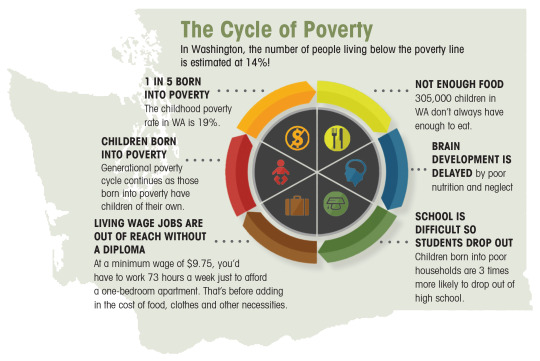
There are various impacts of poverty upon impoverished communities that are in effect everyday. Firstly, because poverty impedes access to sanitary living conditions, healthcare, and nutrition, it is associated with negative health consequences. Additionally, poverty prevents children from receiving a high-quality education, which limits their prospects for the future and keeps families in poverty for generations to come. Poverty also greatly contributes to crime; impoverished people often turn to criminal activity as a means of obtaining money or basic needs, which lead to increased crime rates and social unrest. Nations with high rates of poverty may also face political unrest as a result of disregarded citizens' demands for reform aimed at achieving social and economic justice/equality. This can lead to movements, protests, and general political unrest. Lastly, the brutal cycle of poverty leads to generational impoverishment that is difficult to break. There is often an intergenerational transmission of poverty, where children born into impoverished families face systemic challenges that make it difficult to break free from poverty.
Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach, including economic policies, social programs, education initiatives, and efforts to promote equality and justice. The ongoing challenge is to create sustainable solutions that address the root causes of poverty and empower individuals and communities to improve their economic circumstances.

1 note
·
View note