This blog will share a lot of solutions about optical fiber networking.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
10 Gigabit Ethernet SFP + Kabel Definition, Typen & Deployment Guide
Die Netzwerkverkabelung hat im Laufe der Jahre tief greifende Änderungen durchlaufen und macht einen großen Sprung nach vorn zu hoch Geschwindigkeits Faserkabeln. Aber in einigen Fällen, Kupfer Twinax Kabel, zB SFP+ Kabel oder SFP + DAC Twinax Kabel noch als eine optimierte Lösung für 10-GbE-Anwendungen über kurze Strecken. Dieser Beitrag stellt einige grundlegende Informationen über SFP + DAC-Kabel und Überlegungen für die Bereitstellung von 10 Gigabit-Ethernet-SFP +-Kabel.
SFP + Cable Basics: Definition & Typen
Das SFP + DAC Twinax-Kabel ist eine Kupferverbindung mit einer Twinax-Kabelkonfektion, die direkt in das SFP +-Gehäuse integriert wird. Durch die direkte Verbindung von zwei SFP + Slots eliminiert es effektiv den kostengünstigen optischen Transceiver, der in der Ausrüstung benötigt wird, und reduziert den Stromverbrauch, die Latenz und die Installationszeit erheblich. Daher hat sich das SFP + DAC-Kabel zu einer optimalen Wahl für moderne Kurzstrecken-Hochgeschwindigkeits-10-Gigabit-Ethernet-Anwendungen. Obwohl es eine Entfernungsbegrenzung von 10M hat, wird 10G SFP + DAC-Kabel häufig in Intra-Rack-und Inter-Rack-Verbindungen verwendet: einschließlich der Verbindung von Top-of-Rack-Switches mit Servern und Speichergeräten innerhalb eines Racks oder in benachbarten Racks.
10-Gigabit-SFP + Direct-Attach-Kabel können in direkt anbringen Kupfer-Kabel (DAC) und direktes aktives optisches Kabel (AOC) klassifiziert werden. Das DAC-Kabel kann entweder passiv oder aktiv sein. Direktes aktives optisches Kabel AOC Bonds die Faserverbindung innerhalb des Transceivers endet, so dass eine komplette Faserkabel Montage ähnlich wie ein direktes Kupferkabel, aber mit einem 3-200 Meter erreichen Fähigkeit. Die obige Abbildung zeigt die führenden Typen von passiven und aktiven Direct-Attach-Kabeln für das Rechenzentrum Tor-Zusammenschaltung.
Passives DAC-Kabel und aktives DAC-Kabel
Passive DAC-Kabel enthält keine elektrischen Komponenten, so hat es minimalen Stromverbrauch von < 0.15 w, aber die Verknüpfung Abstand ist auf 5M begrenzt. Während aktive Kupferkabel enthält elektrische Komponenten in den Anschlüssen, die Signalpegel erhöhen können, so dass größere Entfernungen (5M oder mehr) über Kupfer-Medien und eine bessere Übertragungsqualität zu gewährleisten. Dies macht die aktiven Kupferkabel etwas teurer und verbraucht mehr Leistung als direkte Anbringen von passiven Kupferkabeln. Die Details sind in der folgenden Tabelle zu sehen.
SFP + Kabel Kauf Überlegungen
Marken-oder kompatibles SFP + DAC-Kabel
Als OEM oder Vendor Branded SFP + Twinax Kabel sind eher Kosten-unerschwinglich, sind die Nutzer eher geneigt zu wählen kompatiblen SFP + DAC-Kabel mit dem gleichen Industrie-Standard, aber nur einen Bruchteil der Kosten. FS.com SFP + zu SFP + Kabel ist getestet und mit Geräten von namhaften Herstellern kompatibel. Wir entwerfen auch speziell SFP + DAC Twinax Kabelkonfektionen mit unterschiedlichen Marken kompatiblen Gehäuse an zwei Seiten, und Sie können nach Ihren Bedürfnissen anpassen. Auf diese Weise ist das Anschließen von Switches von mehreren Anbietern kein Hindernis mehr.
Produkt Details des SFP + DAC Twinax-Kabels lesen
Um die Kauf Besprechung mit ihren spezifischen Anforderungen zu treffen, sollten sich die Käufer der RoHS-Konformität, der Speichertemperatur und der MSA-Konformitäts Funktionen hinsichtlich der SFP + DAC Twinax-Kabel voll bewusst sein. Dies ist wichtig für die ordnungsgemäße Ausführung Ihres Netzwerksystems.
AWG ist auch ein wichtiger Faktor
Ein weiterer wichtiger Faktor im Zusammenhang mit SFP + DAC Kupferkabel ist die AWG. Es gibt verschiedene Optionen von SFP + DAC Twinax Kabellänge und Draht Lehren, wie 24AWG, 28AWG und 30AWG. Beachten Sie bei der Wahl des AWG immer eine Regel: je länger der Abstand, desto niedriger ist die AWG-Bewertung. Gesehen in der unteren Bild, das Messgerät von SFP + Kabel 2M ist 30AWG, während SFP + Kabel 5M ist 24AWG.
SFP + Kabel Bereitstellungstipps
Hier bieten wir Antworten auf einige häufig gestellte Fragen über SFP + DAC Twinax Kabel, in der Hoffnung, es würde helfen, mit allen Verwirrungen in Bezug auf SFP + DAC Kupfer-Kabel befassen.
Soll ich passives oder aktives SFP + DAC-Kabel wählen?
Passive SFP + DAC Twinax Kabel enthält keine elektrischen Komponenten, daher erfordert wenig oder gar keine Macht zu bedienen. SFP + Active Copper-Kabel, im Gegenteil, benötigt DC-Strom, um Signalverarbeitung Schaltung in seine eingebauten Anschlüsse integriert, so dass es teurer. Es wird empfohlen, passive SFP + DAC zu verwenden, wenn der Abstand nicht mehr als 7M beträgt. Wie für die Verbindung Abstand größer als 7 m (wie Tor zu EOR), aktive DACs erforderlich wäre.
Kann ich ein kompatibles SFP + DAC-Kabel für Cisco-Switches verwenden?
Ja, genau wie optische Transceiver werden kompatible SFP + DAC Twinax-Kabel mit dem gleichen Industriestandard wie die Cisco-Kabel hergestellt. Ein qualifiziertes 10-GbE-SFP +-Kabel sollte getestet und von Cisco-Geräten vollständig erkannt werden, um eine einwandfreie Funktion zu gewährleisten. Holen Sie sich einen zuverlässigen Direct-Attach-Kabelhersteller, um SFP + DAC Twinax-Kabel zu kaufen, damit Ihr kompatibles SFP + DAC-Kabel genauso groß wie die Branded One-mit deutlich recuded Kosten-leisten kann.
Kann ich SFP + DAC-Kabel in SFP-Ports verwenden?
Ja, SFP +-Kabel sind abwärtskompatibel zu SFP-Ports und funktionieren einwandfrei. SFP-Kabel sind jedoch nicht kompatibel zu SFP +-Ports. SFP-Kabel können an SFP +-Ports angeschlossen werden, Sie sind jedoch nicht für 10Gb/s-Datenraten ausgelegt.
Quellartikel:
https://www.fs.com/de/10-gigabit-ethernet-sfp-kabel-definition-typen-deployment-guide-aid-692.html
0 notes
Text
Funktioniert Cat6 auf Cat5e Patchpanel oder Cat5e auf Cat6 Patchpanel?
Auf dem Markt gibt es sowohl Cat5e Patchpanel als auch Cat6 Patchpanel. Wir wissen, dass Cat5e-Patch-Panels für die Verwendung mit Cat5e-Kabeln vorgesehen sind und Cat6-Patchpanels für die Verwendung mit Cat6-Kabeln, aber was ist der Unterschied zwischen Cat5e- und Cat6-Patch-Panels? Kann ich ein Cat6-Kabel an Cat5e-Schalttafeln verwenden oder kann ich Cat5e-Kabel an Cat6-Schalttafeln verwenden? Antworten werden in diesem Blog zur Verfügung gestellt.
Kann ich Cat6 auf Cat5e Patchpanel verwenden?
Es gibt nicht viel praktischen Unterschied in den Schalttafeln selbst. Es gibt einen Unterschied in der Drahtstärke zwischen Cat5e und Cat6. Der Cat6-Draht ist dicker. Cat6 hat normalerweise 23 AWG Kupferleiter, verglichen mit nur 24 AWG in Cat5e Kabel. Ein weiterer Faktor, der Cat6 zu einem größeren Draht als Cat5e macht, ist die Tatsache, dass zwischen jedem der vier Paare in einem Cat6-Kabel ein Spline vorhanden ist, der jedes Paar voneinander trennt. Das Trennen der Paare hilft, das Übersprechen zwischen den Paaren zu reduzieren und gibt Ihnen ein besseres Signal. Dieser Spline erhöht jedoch auch den Durchmesser des Kabels. Unabhängig vom Größenunterschied zwischen Cat5e und Cat6 war das Cat6-Kabel abwärtskompatibel zu Cat5e. Ja, Cat6 ist oft ein größeres Kabel, aber das ändert nichts an der Verwendung mit Cat5e Patchpanels. Fühlen Sie sich frei, Cat5e Patch-Panels zu verwenden, wenn Sie sie bereits haben. Sie können sie später jederzeit aktualisieren.
Kann ich Cat5e auf Cat6 Patchpanel verwenden?
Zusätzlich zur Verwendung von Cat6 auf dem Cat5e-Patchpanel können wir auch in einigen Situationen, in denen wir Cat5e auf einem Cat6-Patchpanel verwenden möchten, vorgehen. Laut dem obigen Abschnitt wissen wir, dass Cat6-Kabel dicker als Cat5e sind. Wenn ich Cat5e auf einem Cat6-Patchpanel verwende, ist es dann zu locker? Obwohl die einzelnen Twisted-Pair-Isolierungen von Cat6 normalerweise dicker sind als Cat5e, ist dies normalerweise nie ein Problem mit der Terminierung, sondern nur mit der Anzahl der Kabel, die Sie durch ein Stück Conduit stopfen können. Also, wird ein Cat5e-Kabel "looser" terminiert an einer Cat6-Buchse, ein wenig ja, aber elektrisch wird es immer noch Kontakt und funktioniert gut. Sie sollten jedoch beachten, dass Ihr Kabelkanal standardmäßig auf die niedrigste Catx-Komponente eingestellt wird. Auch wenn auf dem Patch-Panel Cat6 steht, sollten Sie bei Cat5e-Kabeln nur Cat5e-Performance an diesen Buchsen erwarten.
Fazit
Wenn Cat5e-Draht auf einem Cat6 niedergeschlagen wird, ist der Cat5e-Draht so klein, dass es möglich ist, etwas zu bekommen, was wie ein guter Schlag aussieht, aber die Isolation auf dem Draht wird nicht durchdrungen oder nur teilweise von der Vampirklaue des Stempels durchdrungen Block. Wenn Cat6-Kabel auf ein Cat5e-Panel gestanzt werden, kann das größere Kabel dazu führen, dass die Vampirbacken auf dem Stanzblock gebogen oder sogar gebrochen werden. In beiden Fällen können Sie in der Regel dafür sorgen, dass jede Verbindung ordnungsgemäß funktioniert und getestet wird. Wenn Sie nur ein Panel zu Hause machen, sind Sie wahrscheinlich in Ordnung. Obwohl es beides gut funktioniert, empfehlen wir nicht, dies zu tun. Verwenden Sie das Cat5e auf Cat5e Patchpanel und Cat6 auf Cat6 Patchpanel wird die beste Leistung erhalten. FS.COM bietet sowohl Cat5e-Patch-Panels mit hoher Dichte für Fast-Ethernet-Anwendungen als auch Cat6-Patchpanels für 1-Gigabit-Ethernet-Anwendungen. Einfach zu verwalten und spart Platz im Rechenzentrum.
0 notes
Text
ABC of GPON SFP: Understanding GPON OLT / ONU / ONT SFP Module
Since the advances in Ethernet technology, “last mile” connectivity is expected to realize between the network backbone and local area networks (end users). Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a cost-effective point-to-multipoint access network, which brings great improvement in data transmission distance (up to 20km) and bandwidth (an downstream capacity of 2.5Gbit/s and an upstream capacity of 1.25Gbit/s ). However, GPON's higher bandwidth and split ratios are only achievable by using GPON-capable optical transceivers. It is well positioned to help meet the needs for higher bandwidth in FTTx applications, and continues to fuel growth in demand for GPON SFP modules. So this article will introduce the basics of GPON SFP, including GPON OLT, GPON ONU and GPON ONT SFP module.
What Is GPON SFP Module?
GPON SFP is a new higher-speed bi-directional optical transceiver, which can deliver 2.5 Gbits/sec of bandwidth. And it is a kind of single fiber transceiver which comes with SC connector and can transmit data up to 20km. In addition, it features a 28-dB optical loss budget to enable 1:64 split ratios and provides adequate optical loop lengths. Most EPON and some BPON systems deployed today use 25-dB optics, which limit the split ratio and loop length. For this reason, GPON transceiver enjoys the added advantage of industrial demand. The key performance advantage is to reduce the upstream split loss arising from utilizing the mode-coupled-receivers (MCR) in a PON application. Moreover, this innovative module dose not outweigh the costs over a standard module. For these two reasons, the GPON SFP modules are very attractive to the network operators to improve the utilization of GPON network. On top of that, GPON SFP transceiver is an essential part of GPON system which is necessary both for optical network unit (ONU) installed at the subscriber’s premises and for the optical line terminal (OLT) at the central office (CO). The following part will respectively introduce the GPON OLT, GPON ONU and GPON ONT SFP module.
GPON OLT SFP Module
GPON OLT SFP is designed for OLT side in GPON network. OLT is a equipment integrating L2/L3 switch function, which is located in central office (CO). The main function is to control the information float in both directions: upstream and downstream. The GPON OLT module plays an inevitable role in the upstream and downstream transmission. In order to put across the transmission process, the downstream transmission is taken as an example. A single mode optical fiber coming from OLT (at the central office) PON port, runs to the passive optical splitter (POS) located near end users. And then the optical splitter will divide signals into separate paths which can provide service up to 64 end users. In this basic GPON topology, a GPON OLT module is used to connect a single-mode fiber patch cable to a passive optical splitter. Therefore, GPON OLT transceiver works to get the data, voice and video traffic from metro network or from a long-haul network.
GPON ONU/ONT SFP Module
Since the ONU and ONT are deployed at customer’s premises, they are connected to the OLT by means of optical fiber and no active elements are present in the link. In GPON network, the ONU/ONT transceiver is the physical connection between the customer premises and the central office OLT. This type of modules gets the signals from OLT, so they have the opposite characteristic of GPON OLT transceiver, incorporating a high performance 1310nm burst mode DFB transmitter and 1490nm CW mode APD receiver. By being plugged into advanced “triple play” (data, voice & video) ONT or ONU equipment (with SFP ports), such as Ethernet switches, routers, DSLAMs or home gateway, ONU/ONT SFP module fits seamlessly into existing communications equipment and provides end users with a smooth upgrade to GPON. Therefore, GPON ONU/ONT SFP module plays an important role in the applications for point-to-multipoint (P2MP) ONT / ONU equipment in GPON network.
Conclusion
GPON SFP transceiver meets the the requirements of FTTx network to accelerate the speed or capacity. GPON OLT, ONU and ONT SFP module have their respective roles to play in the GPON networks. Many people may worry the high attenuation losses from optical splitter in the GPON networks, as above mentioned, the GPON optical module is just used to solve this problem in that it utilizes the MCR technology that protects large numbers of signals. In a word, this new module is a compelling network alternative to save cost and increase bandwidth and security.
Related Article: ABC of PON: Understanding OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN
0 notes
Text
Good Forecasts for Global Optical Fiber Cable Market
An optical fiber cable uses light wave for voice and data transmission, its data transmission capacity is 4.5 times more than conventional copper cables. So in the past several decades, we have seen that fiber optic cables are superior to traditional copper twisted-pair cable or coaxial cable because of its unique physical characteristics, allowing information to travel at speeds increasingly approaching the speed of light without interference between adjacent wavelengths. In leading market, the global drive to implement FTTx into more new venues is good news for the market of optical fiber cables. Another good trend is that the price erosion of optical fiber cables had been 10 to 15 percent annually, in result that the demand of optical fiber cable is expected to continue growing in the foreseeable future. And the growing data transmission workloads placed by high-performance computers, servers and network storage systems is helping spur growth in the market. Consequently, fiber optic cables are now the indispensable backbone of today’s communication network. This article will analyse the global optical fiber cable market in three main applications, including long-distance communication, submarine cable and FTTx network.
Global Optical Fiber Cable Market to Grow at 9.8% till 2021
According to the report "Fiber Optics Market by Cable - Global Forecast to 2021”, the optical fiber cable market is anticipate to grow at a CAGR of over 9.8% during 2016-2021. The growing importance of cloud computing, data transfer & storage, and IoT is driving the use of Internet, which is driving the fiber optic cable market, as it acts as the backbone for data transmission. Moreover, growing technological advancements increase in number of connected devices and data centers are expected to positively influence global optical fiber cable market. In addition, next generation technologies such as LTE and FTTx, which require last mile connectivity, is expected to propel the demand for optical fiber cables in the coming years. All these factors have led to an increase in Internet users, which in turn has led to the higher usage of optical fiber cable to transfer information over the Internet, thus driving the fiber optics market.
Global Optical Fiber Cable Demand from 2012 to 2018 (Source: Statista)
Optical Fiber Cable Market in Long-distance Communication
Currently, the growing adoption of optical technology in the telecommunications appears to be promising. Optical fiber has virtually unlimited capacity and low signal attenuation allowing long distances without amplifier or repeater, no exposure to parasite signals or crosstalk, and no electromagnetic interference (EMI). So fiber optic cable is especially advantageous for high-speed data transfer services in long-distance communications over electrical cabling. Furthermore, the increasing cloud-based applications, audio-video services, and Video-on-Demand (VoD) services further stimulate the demand for optical fiber cable installations.
Growing Need for Capacity (Source: Goldmedia)
Submarine Optical Fiber Cable Market
Submarine optical fiber cables are undersea cables used for carrying data across interconnected networks between continents. With the advancements of technology, most of the submarine optical fiber cables that currently form the backbone of the Internet connect the U.S. to Europe and Asia by crossing the Atlantic or Pacific oceans. Instead, there is a proposal for deployment of Trans-polar submarine cable system in Arctic Ocean. Laying an undersea fiber optic cable is meant to connect Asia and Europe by crossing the Arctic Circle - the shortest practical distance yet for Internet signals traveling between the two continents. According to the report by Global Industry Analysts (GIA), cumulative installations of submarine optical fiber cables globally are projected to reach 2 million kilometers by 2020, driven by the growing demand for fiber broadband and the ensuing deployment of fiber optic cables in the Internet backbone. Presently, submarine optical fiber cables transmit 100% of the international Internet traffic, and more than 95% of the world’s combined data and voice traffic.
Submarine Optical Fiber Cable Market (Source: Technavio)
Optical Fiber Cable Market in FTTx Networks
In recent years, the market for optical fiber cable has shifted dramatically to local deployments, away from long haul and regional. This is the impact of FTTx, which calls for far more dense applications in neighborhoods, cities and other highly focused areas. Optical fiber cable is being caught up in the global move to broadband in the near future. The next generation of high bandwidth applications, along with the proliferation of connected devices, is expected to require faster and higher bandwidth networks which will require the use of multimode fiber cable for data transfer. This growth in the FTTx networks in turn is expected to drive the fiber optics market. Future Market Insights (FMI) forecasts the global fiber to the home (FTTH) market's value will grow from $9.5 billion in 2017 to more than $37 billion by the end of 2027, a 14.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). In the leading Asian economies, more than 44% of all homes and buildings are already directly connected to the fiber optic cable network; in North America penetration is 8.4%, in Europe 5.6%.
Final Thought
Fiber optic cable is widely used for data transmission and is increasingly being used in place of metal wires because of its efficiency and high transmission capacity. Since the use and demand for great bandwidth and fast speed, there is no doubt that fiber optic transmission will bring more opportunities and be continuously researched and expanded to cater for future demands. However, although fiber optic cable in itself is considered a long-term stable investment, it also faces huge challenge. The major restraint in the fiber optics market is the growing use of wireless communications systems in remote areas.
Related Article:?The Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Transmission
0 notes
Text
A Brief Introduction of Cisco BiDi SFP Transceiver
In the early stage of optical fiber communication, one optical fiber can only transmit signals of one wavelength. This is known as conventional two-fiber Bi-Directional communication - at least two fibers are needed to accomplish the full-duplex communication with TX and RX optical signals. With the development of WDM technology, transmitting and receiving of optical signals on separate wavelength can be achieved through only one single fiber. This single fiber BiDi transmission gradually becomes a popular and cost-effective solution for today’s data center and IT infrastructure, because it helps to maximize the capacity and usage of optical fibers. Consequently, BiDi optical transceiver as the basic component plays an irreplaceable role in the WDM BiDi transmission application. This article will generally introduce Cisco BiDi SFP transceivers, including GLC-BX-U, GLC-BX-D, GLC-BX-20U, GLC-BX-20D, GLC-BX40-D-I, GLC-BX40-U-I, GLC-BX80-D-I, GLC-BX80-U-I, GLC-BX120-U, GLC-BX120-D, etc.
What Is a BiDi SFP?
BiDi SFP transceiver can be defined as a compact, hot swappable, input/output optical module that can transmit and receive data to/from interconnected equipment through a single optical fiber. Unlike traditional optical transceivers, BiDi optical transceivers are fitted with wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) diplexers, which combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. To simplify it, conventional optical module has two ports - the TX for the transmit port and the RX for receive port; but BiDi transceiver has only one port to complete the 1310nm optical signal transmitting and 1550nm optical signal receiving, or vice versa. Therefore, BiDi transceivers must be deployed in matched pairs with their diplexers tuned to match the expected wavelength of the transmitter and receiver. These BiDi optical transceivers can offer bi-directional data links over single-mode fiber up to 120 km. BiDi SFP transceiver is applicable to many access networks: passive optical networks (PON) and point-to-point, digital video and closed circuit television (CCTV) applications, inter-system communication between servers, switches, routers, optical add drop multiplexer (OADM), WDM fast Ethernet links, SDH/STM-1, SONET/OC3, metropolitan area networks and other optic link.
Common Types of Cisco BiDi SFP
1G BiDi SFP is also known as 1000BASE-BX SFP, which use two different wavelengths (1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX, 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX, 1490nm-TX/1550nm-RX and 1510nm-TX/1570nm-RX) for transmission in different distance. The following will list some main Cisco BiDi SFP modules in 10km, 20km, 40km, 80km and 120km.
10km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX-D and GLC-BX-U is a pair of 10km BiDi SFP transceiver with LC duplex connectors, operating on a single strand of standard SMF. The GLC-BX-U transceiver operates at 1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX wavelength with upstream bidirectional single fiber, while the GLC-BX-D transceiver operates at 1490nm-TX/1310nm-RX wavelength with downstream bidirectional single fiber. These two BiDi optical modules, compliant to 1000Base-BX standard, are rated for distances up to 10 km over SMF and a maximum bandwidth of 1Gbps. A 1000BASE-BX-D device is always connected to a 1000BASE-BX-U device with a single strand of standard SMF. In addition, the GLC-BX-D and GLC-BX-U BiDi SFPs also support digital optical monitoring (DOM) functions according to the industry-standard SFF-8472 multisource agreement (MSA). This feature gives the end user the ability to monitor real-time parameters of the SFP, such as optical output power, optical input power, temperature and transceiver supply voltage.
(GLC-2BX-U and GLC-2BX-D are 2-channel 1000BASE-BX SFP modules, also known as compact SFPs that integrate two IEEE 802.3ah 1000BASE-BX10 interfaces in one SFP module. They are designed to connect to any standard-based Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) in FTTx links.)
20km Cisco BiDi SFP
GLC-BX-20U and GLC-BX-20D are Cisco 20km BiDi SFP transceivers that work with single mode fiber. The GLC-BX-20U operates at 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX wavelength, and GLC-BX-20D operates at 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX. So these two BiDi SFPs always work in pairs. Their max data rate is 1000Mbps. FS.COM compatible Cisco BiDi transceivers are high performance, cost effective modules supporting data-rate of 1000Mbps and 20km transmission distance with SMF. Among the Cisco 20km BiDi SFPs, Cisco Linksys MFEBX1D provides up to 155Mbps bi-directional data transfer rate at distances up to 20km on a single fiber core. These bidirectional SFP transceivers allow data transfer in either direction through a single optical fiber by employing separate wavelengths travelling in either direction.
40km Cisco BiDi SFP
Cisco GLC-BX40-D-I and GLC-BX40-U-I is a pair of 40km BiDi SFP modules for Gigabit Ethernet 1000BASE-BX and Fiber Channel communications. They support link length of up to 40km point to point on single mode fiber at 1Gbps bidirectional and use an LC connector. The GLC-BX40-D-I is 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX 40km BiDi WDM SFP simplex transceiver module, GLC-BX40-U-I is 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX BiDi WDM SFP module. They are specified for duplex optical data communications such as 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet per IEEE802.3z and 1G Fiber Channel extended reach application.
80km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX80-D-I and GLC-BX80-U-I SFPs are 1G BiDi SFP modules that provide 80km transmission distance over single strand of single-mode fiber. GLC-BX80-D-I operates at 1570nm-TX/1490nm-RX wavelength, whereas GLC-BX80-U-I operates at 1490nm-TX/1570nm-RX. These bidirectional SFP transceivers are intended mainly for connecting high-speed hubs, Ethernet switches, and routers together in different wiring closets or buildings using long cabling runs, and developed to support longer-length on fiber backbones. Compared with commonly used dual fiber SFP transceiver modules, the BiDi SFP transceiver allows end users to reduce the total cost on fiber cabling infrastructure by requiring half of fiber cables, providing increased transmission capacity very convenient without installing new fibers.
120km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX120-U and GLC-BX120-D are 1490nm and 1550nm bidirectional SFP transceivers that are used with single mode optical fiber. They also use two wavelength 1490nm-TX/1550nm-RX(1550nm-TX/1490nm-RX) simultaneously. These BiDi SFP modules can support transmission distance up to 120 km, which are connected through pluggable LC connector type optical interface. They have a DFB (Distributed Feedback) type transmitter, an APD (Avalanche Photo-Diode) type receiver, an LD (Laser Driver), a limiting amplifier and digital diagnostic monitor. Those BiDi SFP transceivers are Class 1 laser safety product which complies with US FDA regulations, SFP MSA, SFF-8472 and RoHS standards. More importantly, 120km SFP modules have the same or even lower transmit power as compared to 80km SFP. It is the reason that 120km modules extend the range thanks to receiver not transmitter. 120km modules have much better receiving sensitivity than 80km modules.
Conclusion
BiDi SFP transceiver serves as an ideal and feasible solution in situations where only limited fibers or limited conduit space is available. And the deployment of BiDi optical transceivers efficiently enhances the bandwidth capacity of the existing optical fiber infrastructure and help to achieve economical and reliable performance of the optical network. Although BiDi transceivers may be more expensive than common transceiver modules, they can save you the cost on fiber cables from the long run.
0 notes
Text
SFP-GE-S-2 VS. GLC-SX-MM: What’s the Difference?
SFP-GE-S-2 and GLC-SX-MM are Cisco 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode fiber transceivers. Since there are similar specifications for these two multimode modules, many end users may be confused when choosing a multimode fiber SFP LC connector SX transceiver for their Cisco switches. So, are they the same one? This post intends to give a simple explanation of SFP-GE-S-2 vs. GLC-SX-MM.
SFP-GE-S-2 Module
Cisco SFP-GE-S-2 is a 1 GbE SFP SX fiber transceiver that supports the maximum data rate of 1Gbps. It’s compatible with the IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX standard, and can operate on standard multimode fiber optic link spans of up to 2 km.
Module/Specs Cisco SFP-GE-S-2 Interface LC duplex Wavelength 1310nm Tx power -9.5 ~ -3dBm Receiver Sensitivity < -17dBm DOM Support Yes Temperature Range 32℉to 158℉ (0℃ to 70℃) Data Rat 1G Fiber Mode MMF
GLC-SX-MM Module
GLC-SX-MM transceiver is also a Cisco 1000BASE-SX fiber transceiver that designed for Gigabit Ethernet applications. This SX module is compatible with the IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX standard, and can operate on standard multimode fiber optic link spans of up to 550m.
Module/Specs Cisco GLC-SX-MM Interface LC duplex Wavelength 850nm Tx power -9.5 ~ -3dBm Receiver Sensitivity < -17dBm DOM Support No Temperature Range 32℉to 158℉ (0℃ to 70℃) Data Rat 1G Fiber Mode MMF
SFP-GE-S-2 VS. GLC-SX-MM
From the above specs comparison, we can learn that these two SX multimode modules support same data rate and operating temperature range. They all can operate on the multimode fiber optic cables. The main differences include:
Wavelength
SFP-GE-S-2 can support a wavelength of 1310nm, whereas GLC-SX-MM works in 850nm.
Transmission Distance
SFP-GE-S-2 can support up to 2km over laser-optimized 50 μm multimode fiber cable, while GLC-SX-MM can operate on legacy 50 μm multimode fiber links up to 550m.
DOM Support
SFP-GE-S-2 can support DOM, but GLC-SX-MM does not have DOM function. DOM (Digital Optical Monitoring) is an important function available on fiber optic transceiver. It allows users to monitor parameters of modules, such as optical output power, optical input power, temperature, laser bias current and transceiver supply voltage. In real time, it offers users more convenience when using optical modules.
Price
GLC-SX-MM is a legacy model, it doesn’t feature DOM function. It comes with the lowest price compared with other SX modules . Take FS.COM compatible transceivers as example, SFP-GE-S-2 costs $ 11.00, while GLC-SX-MM is only $ 6.00.
Conclusion
From the contents above - SFP-GE-S-2 vs. GLC-SX-MM, we can draw a conclusion that these two SX multimode fiber transceivers nearly can be used as the same one type module sometimes, but their existing differences still differ them from some applications. Most of the Cisco switches and routers support all two models, but please note, some of the switches require different models, you may visit Cisco SFP Compatibility Matrix for more detailed information.
0 notes
Text
SFP 40 km VS. DWDM SFP: Which to Choose?
Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) is a compact, hot-pluggable transceiver used for both telecommunication and data communications applications. It is also called mini-GBIC for its smaller size, which is the upgraded version of GBIC transceiver. These 1Gb SFP modules are capable of supporting speeds up to 4.25 Gbps. And they are most often used for Fast Ethernet of Gigabit Ethernet applications. It interfaces a network device motherboard (for a switch, router, media converter or similar device) to a fiber optic or copper networking cable. SFP modules are commonly available in several different categories: 1000BASE-T SFP, 1000BASE-EX SFP, 1000BASE-SX SFP, 1000BASE-LX/LH SFP, 1000BASE-BX SFP, 1000BASE-ZX SFP, CWDM SFP and DWDM SFP. These modules support different distance according to the different Gigabit Ethernet standard. Today’s main subject will discuss SFP 40 km vs. DWDM SFP.

SFP 40 km
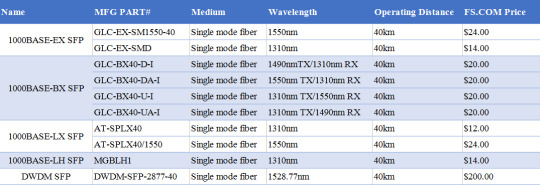
SFP 40 km transceiver is designed for highly reliable fiber optic network links up to 40 km. It is a cost effective transceiver designed to enable 1Gb for data center and core network applications. 1000BASE-EX SFP is the most popular SFP 40 km transceiver which runs on 1310nm wavelength lasers and achieves 40km link length. Except that, 1000BASE-BX BiDi SFP, 1000BASE-LH SFP and 1000BASE-LX SFP can also realize the transmission distance up to 40 km. The following will introduce these 1GbE SFP 40 km transceivers respectively.
1000BASE-EX SFP 40 km
1000BASE-EX SFP transceiver module is designed to connect a Gigabit Ethernet port to a network and has dual LC/PC single mode connectors. It operates on standard single-mode fiber-optic link spans of up to 40 km in length. The SFP Ethernet module provides a dependable and cost-effective way to add, replace or upgrade the ports on switches, routers and other networking equipment. Cisco GLC-EX-SM1550-40 and Cisco GLC-EX-SMD are 1G single mode fiber SFP 40 km modules for 1000BASE-EX Gigabit Ethernet transmission. GLC-EX-SM1550-40 supports a 1550nm wavelength signaling, while GLC-EX-SMD supports a 1310nm wavelength signaling.

1000BASE-BX SFP 40 km
1000BASE-BX SFP is a kind of BiDi transceiver, which can be divided into 1000BASE-BX-D SFP and 1000BASE-BX-U SFP. These two SFP transceivers must be used in pairs to permit a bidirectional Gigabit Ethernet connection using a single strand of single mode fiber (SMF) cable. The 1000BASE-BX-D SFP operates at wavelengths of 1490nm TX/1310nm RX, and the 1000BASE-BX-U SFP operates at wavelengths of 1310nm TX/1490nm RX.
1000BASE-BX-D BiDi SFP 40 km
Cisco GLC-BX40-D-I and GLC-BX40-DA-I are pluggable fiber optical transceivers for Gigabit Ethernet 1000BASE-BX and Fiber Channel communications. They support link length of up to 40 km point to point on single mode fiber at 1Gbps bidirectional and use an LC connector. The GLC-BX40-D-I transceiver transmits a 1490nm channel and receives a 1310nm signal, whereas GLC-BX40-DA-I transmits at a 1550nm wavelength and receives a 1310nm signal.
1000BASE-BX-U BiDi SFP 40 km
Similar to 1000BASE-BX-D 40 km SFP , Cisco GLC-BX40-U-I and GLC-BX40-UA-I also support link length of up to 40 km point to point on single mode fiber at 1Gbps bidirectional and use an LC connector. The main difference is the wavelength: GLC-BX40-U-I transmits a 1310nm channel and receives a 1550nm signal, whereas GLC-BX40- UA-I transmits at a 1310nm wavelength and receives a 1490nm signal. A GLC-BX40-D-I or GLC-BX40-DA-I device connects to a GLC-BX40-U-I or GLC-BX40-UA-I device with a single strand of standard SMF with an operating transmission range up to 40 km.
1000BASE-LX SFP 40 km
1000BASE-LX is a standard specified in IEEE 802.3 Clause 38 which uses a long wavelength laser. The “LX” in 1000BASE-LX stands for long wavelength, indicating that this version of Gigabit Ethernet is intended for use with long-wavelength transmissions (1270 - 1355nm) over long cable runs of fiber optic cabling. Allied Telesis AT-SPLX40 and Allied Telesis AT-SPLX40/1550 are 1000BASE-LX SFP single-mode modules supports Gigabit Ethernet over single-mode cables at distances up to 40 km. AT-SPLX40 operates over a wavelength of 1310nm for 40 km, whereas AT-SPLX40/1550 operates over a wavelength of 1550nm.
1000BASE-LH SFP 40 km
Unlike 1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-LH is just a term widely used by many vendors. Long Haul (LH) denotes longer distances, so 1000BASE-LH SFP modules operate at a distance up to 70 km over single mode fiber. Cisco Linksys MGBLH1 is a easy-to-install modules that provide a simple way to add fiber connectivity or to add an extra Gigabit Ethernet port to switches. The MGE transceiver can support distances up to 40 km over single-mode fiber at a 1310nm wavelength.
DWDM SFP
DWDM SFP transceivers are used as part of a DWDM optical network to provide high-capacity bandwidth across an optical fiber network, which is a high performance, cost effective module for serial optical data communication applications up to 4.25Gb/s. DWDM transceiver uses different wavelengths to multiplex several optical signal onto a single fiber, without requiring any power to operate. There are 32 fixed-wavelength DWDM SFPs that support the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) 100-GHz wavelength grid. The DWDM SFP can be also used in DWDM SONET/SDH (with or without FEC), but for longer transmission distance like 200 km links and Ethernet/Fibre Channel protocol traffic for 80 km links. Cisco C61 DWDM-SFP-2877-40 is a 1000BASE-DWDM SFP 40km transceiver, which is designed to support distance up to 40 km over single-mode fiber and operate at a 1528.77nm DWDM wavelength (Channel 61) as specified by the ITU-T.
SFP 40 km VS. DWDM SFP
Transmission Medium
Generally, the standard SFP 40 km transceivers transmit through the single mode fiber, while DWDM SFP carries signals onto a single optical fiber to achieve maximum distances by using different wavelengths of laser light. So the DWDM SFP transceivers do not require any power to operate.
Wavelength
The standard SFP 40 km transceivers support distances up to 40 km over single-mode fiber at a 1310nm/1550nm wavelength. (the BiDi SFP has 1490nm/1550nm TX & 1310nm RX or 1310nm TX & 1490nm/1550nm RX ). However, DWDM SFP operates at a nominal DWDM wavelength from 1528.38 to 1563.86nm onto a single- mode fiber. Among them, 40 km DWDM SFP operates at a 1528.77nm DWDM wavelength (Channel 61).
Application
DWDM SFP is used in DWDM SONET/SDH, Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel applications. These modules support operation at 100Ghz channel. The actual SFP transceiver offers a transparent optical data transmission of different protocols via single mode fiber. And for back-to-back connectivity, a 5-dB inline optical attenuator should be inserted between the fiber optic cable and the receiving port on the SFP at each end of the link.
Price
DWDM provides ultimate scalability and reach for fiber networks. Boosted by Erbium Doped-Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) - a sort of performance enhancer for high-speed communications, DWDM systems can work over thousands of kilometers. Most commonly, DWDM SFP is much more expensive than the standard SFP. You can see the price more clearly in the following cable.
Conclusion
1000BASE SFP transceiver is the most commonly used component for Gigabit Ethernet application. With so many types available in the market, careful notice should be given to the range of differences, both in distance and price of multimode and single-mode fiber optics. Through SFP 40 km vs. DWDM SFP, if you are looking for SFP modules over long distance and with better scalability, DWDM SFP module is the ideal choice.
Related Article: SFP Transceiver: To Be or Not To Be?
0 notes
Text
EPON SFP VS. GPON SFP: Cost-effective Solution for Access Network
With the increasing demands for higher capacity, more diversity and more personalization of services, the capacity and versatility of access networks needs to be expanded. Passive optical network (PON), as a major technology of FTTH, offers point-to-multipoint (P2MP) network access with lower installation and maintenance costs. EPON (Ethernet PON) and GPON (Gigabit PON) are popular versions of PONs at present. The related technologies keep developing and meanwhile the market of PON components keep growing. PON transceiver (EPON SFP or GPON SFP) is an essential part of PON system, in which a single fiber from a central office optical network unit (ONU) is connected to optical network terminals (ONTs) or optical network units (ONUs) at costomer premises. EPON SFP vs. GPON SFP is today’s main subject matter of this paper.
Passive Optical Network (PON)
Passive optical network (PON) is a form of fiber-optic access network. As the leading technology being used in FTTx (FTTH) deployments, so it is also called FTTH (fiber to the home) network. The typical PON arrangement is a point to multi-point (P2MP) network where a central optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider’s facility distributes TV or Internet service to as many as 16 to 128 customers per fiber line. A PON reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures. PON only uses fiber and passive components, thus it costs significantly less than those using active components. However, a PON has a shorter range of coverage limited by signal strength, which is typically limited to fiber cable runs of up to 20 km (12 miles). There are two different solutions developed by the IEEE and ITU-T - EPON and GPON. The main differences between them lie in the protocols used for upstream and downstream communications. The following table shows the detailed information about EPON vs. GPON.
Table 1: EPON vs. GPON
What Is PON Transceiver?
PON transceiver is a bi-directional optical transceiver that uses different wavelengths to transmit and receive signals between the OLT at the CO and the ONUs at the end users’ premises over a single fiber. According to the pluged-in device, PON transceiver can be divided into OLT transceiver module and ONU transceiver module with SFF, SFP/SFP+ or XFP package. Here mainly introduce two common OLT transceivers used in GPON or EPON network: GPON SFP and EPON SFP.
GPON SFP
GPON SFP OLT transceiver is designed for OLT side in GPON network. GPON SFP uses 1490nm continuous-mode transmitter and 1310nm burst-mode receiver. The transmitter section uses a 1490nm DFB (Distributed Feed Back) LD with automatic power control (APC) function and temperature compensation circuitry to ensure stable extinction ratio overall operating temperature range. And it is Class I laser compliant IEC825 and CDRH standards. The receiver has a hermetically packaged burst-mode APD-TIA (trans-impedance amplifier) pre-amplifier and a burst-mode limiting amplifier with LVPECL compatible differential outputs. The GPON OLT SFP transceiver is a high performance and cost-effective module for serial optical data communication applications to 2.5Gpbs. For GPON transceivers, there are 2 Class available - Class B+ and Class C+. The table below shows the key differences between GPON SFP class B+ and class C+:
Table 2: GPON SFP class B+ vs. GPON SFP class C+
EPON SFP
EPON SFP transceiver is the family of high performance optical modules providing a symmetric 1.25 Gb/s downstream and 1.25 Gb/s upstream data link over a single fiber using a 1490 nm continuous-mode transmitter and 1310 nm burst-mode receiver. The transmitter section uses a 1490nm DFB laser for superior performance and is Class 1 laser compliant. The receiver section uses a 1310nm APD, pre-amplifier, and limiting post-amplifier. The receiver does not require a reset pulse between incoming optical packets of varying signal strength. EPON SFP OLT transceivers support 1000BASE-PX20-D for 20 km applications.
EPON SFP VS. GPON SFP
In terms of OLT module, there are many similarities through EPON SFP?vs. GPON SFP, such as type of laser, transmission distance and communication model. The key difference among them is the sending power and receiver sensitivity. The sending power of GPON SFP Class B+ is 1.5~5dBm, and its receiver sensitivity is -28dBm while the sending power of Class C+ is 3~7dBm and receiver sensitivity is -32dBm. The sending power of EPON SFP is 2~7dBm and its receiver sensitivity is -28dBm. For GPON SFP, the upstream bandwidth is scalable from 155Mbps to 2.5Gbps while the downstream is designed to deliver 1.25Gbps or 2.5Gbps. It is the most widely used consumer broadband service in FTTH networks of present times. On the other hand, EPON SFP supports symmetric bandwidth of 1.25Gbps in both the upstream and downstream directions.
Table 3: EPON SFP vs. GPON SFP
Conclusion
Through EPON SFP VS. GPON SFP, we can see that they are the same in architecture but for different data rate and applications. In terms of cost, The GPON SFP optical module is more expensive than EPON SFP. Because the GPON chipsets available in the market are mostly based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), which is more expensive than the EPON MAC (Media Access Control) layer ASIC. When GPON reaches deployment stage, the estimated cost of a GPON OLT is 1.5 to 2 times higher than an EPON OLT. For the users who have demands of multi-service, high QoS and security, as well as ATM backbone network, GPON SFP seems to be an ideal. And for the one who is much care about the cost and has less security requirements, EPON SFP may be better.
Related Article: Passive Optical Network Tutorial
0 notes
Text
Where to Buy Reliable Low Cost 1000BASE-T SFP Modules?
Gigabit Ethernet, as a part of the Ethernet family of computer networking and communication standards, has been in the market for more than 15 years. 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet is the most successful networking technology in the history. Delivering Gigabit performance over up to 100 meters of twisted pair cabling (Cat5 UTP), it is ideal solution to upgrade network smoothly without change its original architecture and decrease the cost of upgrading for a wide range of enterprise and embedded networking applications. When investing in 1000BASE-T SFP modules to keep the highest working quality for business, everyone wants to find the best deals when they come to their network hardware, but also with the same compliance certification and quality. So where to buy reliable low cost 1000BASE-T SFP modules? This article will tell you answer.
1000BASE-T SFP for Copper Networks
1000BASE-T SFP copper transceiver is based on the SFP Multi Source Agreement. It is compatible with the Gigabit Ethernet and 1000BASE-T standards as specified in IEEE 802.3z and 802.3ab. This Gigabit RJ45 copper SFP transceiver module supports 1000Mbps over Cat5 cables with RJ45 connector interface, which operates on standard Cat5 unshielded twisted-pair copper cabling of link lengths up to 100 m (328 ft). So those 1G copper SFPs can plug into any standard SFP interface allowing for 1000BASE-T Gigabit transmission. When referring to the types of 1000BASE-T copper SFP modules, there are generally three types provided by Cisco: Cisco GLC-T, Cisco GLC-TE, Cisco SFP-GE-T.
Cisco GLC-T
GLC-T is the Cisco 1G copper SFP, which is compliant to IEEE 802.3, and operates over Cat5 copper wire for a distance of 100m. It provides 1Gbps data transfer and full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet connectivity to high-end workstations and between wiring closets over existing copper network infrastructure.
Cisco GLC-TE
Similar to GLC-T SFP modules, GLC-TE provides a link length of 100m over Cat5 copper wires. The only difference between these two SFP modules lies in the operating temperature range. GLC-T SFP is commercial temperature range (COM) from 0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F), while GLC-TE is Extended temperature range (EXT) from -5 to 85°C (23 to 185°F).
Cisco SFP-GE-T
SFP-GE-T is Cisco copper SFP transceiver that works with 1000BASE-T. This 1Gb SFP RJ45 module is with spring latch for high density applications. The most difference is that SFP-GE-T has the function of NEBS 3 ESD. (NEBS is short for Network Equipment Building System and is a set of standards for building networking equipment which can withstand a variety of environmental stresses.) Therefore, SFP-GE-T supports extended working temperature.
Where to Look for Compatible Cisco 1000BASE-T SFP?
There are all sorts of resources to get the most out of technology budget, especially when it comes to find the Cisco 1000BASE-T SFP modules either for brand new, refurbished, or gently used. What are the best ways to find them for a much more inexpensive price?
Online Retailers
Online retailers with warehouses not only provide consumer-side purchasing with modules and networking hardware, they can also be a valuable asset to all sorts of companies looking to spend less money on equipment. There are online retailers that give almost as high as 90% discounts and price reductions. You need to be careful when it comes to certain warehouses as they might have huge savings but the parts might be used or not of the highest quality.
Certified Sellers
Certified sellers, or re-sellers, can offer brand new or refurbished modules with great prices. Besides, they have professionals who can help you with all of your technology questions and make sure that you get the best deal.
Third-Party Companies
In fact, there are many third party vendors to manufacture compatible SFP modules, such as FS.COM, 10GTek, Finisar, Fluxlight etc. Many people are confused about whether I should use 3rd party SFP modules. Most "third party” transceivers are made and assembled in exactly the same plants assembling officially-branded transceivers. There is almost no big difference between an official Cisco transceiver and a third-party plug, aside from the branding and about two hundred to a few thousand bucks. And now, using 3rd party SFP modules seems to more and more popular, as many 3rd party SFP module vendors are providing high quality and reliable 3rd party SFP modules with low prices. Besides, third-party SFPs can be as reliable as official OEM products.
Copper SFP Models Description Operating Temperature Range FS.COM Price Fluxlight Price Cisco GLC-T 1000BASE-T SFP Copper RJ-45 100m Transceiver COM $ 21.00 $ 44.00 Cisco GLC-TE 1000BASE-T SFP Copper RJ-45 100m Transceiver EXT $ 21.00 $49.00 Cisco SFP-GE-T 1000BASE-T SFP Copper RJ-45 100m Transceiver NEBS 3 ESD EXT $ 21.00 $44.00
Conclusion
The 1000BASE-T SFP copper transceiver offers a flexible and simple method to be installed into SFP MSA compliant ports at any time with no interruption of the host equipment operation. It enables for seamless integration of fiber with copper LAN connections wherever SFP interface slots can be found. Such system is economical, it saves time, offers flexibility and eliminates the necessity for replacing entire devices once the customers have to change or upgrade fiber connections and you will benefit so much from it.
Related Article: GLC-T vs GLC-TE vs SFP-GE-T: Which One to Choose?
0 notes
Text
FS S1400-24T4F 24-Port PoE Switch for High-density PoE Installations
Due to the increased requirements for IP surveillance networks, the appearance of PoE switches give you an easy way to add PoE devices to the network. They are ideal for small business networks that need to inexpensively use PoE to deploy wireless access points, VoIP phones and IP cameras. The PoE switch models are available with 4, 8, 16, 24 or 48 ports, although other variants are also available. 24 port PoE switch is the most prevalent variant on the market. So why your network needs a 24-port PoE switch and how can network benefit from deploying it? This article explains it in detail.
Why Your Network Needs A 24-Port PoE Switch?
When choosing an Ethernet switch, the most important is to check whether the numbers of ports on the switch are enough to connect all your devices. The same is true when choosing PoE switch. PoE ports are flexible to connect with Cat5e cable without additional settings. Generally, the PoE switch has the uplink ports, which allow long distance data transmission between switches. Switches without uplink ports can still be linked together but you may experience bandwidth issues with switch to switch data flow. A 24-port PoE switch fully complies to the the IEEE 802.3af standard for PoE up to 15.4W per port and the latest IEEE 802.3at standard for PoE+ up to 30W per port. On the whole, the 24-port PoE switch can greatly reduce the associated cost with smaller PoE installations in a home or small business environment. At the same time, it will allow you to expand your network to areas with no power lines. Essentially, the plug-and-play PoE switch will automatically detect whether connected devices are PoE and send power accordingly. For a 24-Port Gigabit PoE managed switch with a power budget of 360W, you need a total power per port of 30W to power an IP camera network. And you can continue to add IP cameras until you reach your budget. If you have 2 SFP ports, you can also connect to multiple switches. Keep in mind, if you exceed the power threshold and the devices aren’t getting sufficient power, they may not boot up properly. Finally, please ensure you check the power requirement for your PoE enabled device, the standard it complies to and the overall PoE budget of your installation before purchasing a 24-Port PoE switch.
FS S1400-24T4F 24-Port Gigabit PoE Managed Switch - 4 SFP, 400W
FS S1400-24T4F managed PoE switch comes with 24 10/100/1000Base-T RJ45 Ethernet ports, 1 console port, 2 combo port and 2 dedicated SFP ports for fiber uplinks. It offers network managers the advantage of connecting up to 24 power-hungry wireless access points, IP security cameras, LED lighting or VoIP endpoints to the network with a single wire for power and connectivity. With its robust PoE power budget of 400W, the S1400-24T4F switch supports denser deployment of PoE devices. This switch has 52Gbps switching capacity with 8K MAC address table, 9KB Jumbo Frame and 4MB Buffer Memory. Power supply is supportive as well, which is about 100-240V. This is a solidly built excellent switch from the firm with a data transfer rate of 1,000 Mb/s. What’s more, it offers configurable Layer 2+ network switching features like VLANs and fast Ring Protection Protocol(RSTP), which achieved real ring loop redundancy protection. It represents an ideal switching solution for even advanced SMBs or entry-level enterprise which demands industrial, surveillance, IP Phone, IP Camera or Wireless applications. All in all, the PoE switch provides security, performance, quality of services, central managed and other network control capabilities.
Features:
- 400W PoE budget available across 24 Gigabit PoE ports
- 4 Gigabit SFP fiber ports for aggregation to the network core
- Support various advanced management, such as WEB, CLI, TELNET, SNMP
- Support Port-based VLAN, IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and GVRP, simplify the network planning
- Support PoE intelligent management system, timing of PoE power supply, power online configuration, voltage and current online monitoring etc.
- Switching capacity with 52Gbps line rate fabric for maximum throughput across all 24 ports of Gigabit Ethernet
Conclusion
PoE switch is a cost-effective solution to increase the reliability and security of networks by providing centralized backup power to all connected IP surveillance devices. Before purchasing PoE switches, try to know as more details about the switch specifications as possible and also your own needs. FS S1400-24T4F managed PoE switch is an affordable switch to support SMB switching needs for wireless converged networks and IP surveillance. If you prepare for growth and buy infrastructure for the long-term, you will find this 400W PoE power budget provides headroom for future expansion.
0 notes
Text
10G DWDM Tunable XFP - Up to 80 km Reach
With the spread of cloud computing and mobile broadband service, the volume of communications traffic has rapidly increased. In order to enable high-capacity optical networks, using a single optical fiber for optical signals of several different wavelengths in DWDM system is widely used. For this reason, tunable transceiver that enables ROADM functionality in next-generation networks is becoming more and more popular. In today’s market, there are mainly two kinds of tunable DWDM transceivers: tunable XFP and tunable SFP+. This article will take you to explore the DWDM C-band tunable XFP transceiver with 40 / 80 km transmission distance options.

Tunable XFP Transceiver
Tunable XFP transceiver is an integrated fiber optic transceiver that provides a high-speed serial link at signaling rates from 9.95 Gbps to 11.35 Gbps. It complies with the ITU-T G.698.1 S-D100S1-2D standard with 50GHz channel spacing for SONET/SDH, IEEE DWDM 10GBASE-ZR for 40 or 80 km reach (Ethernet), and DWDM 10G FC (Fibre Channel) for 40 or 80 km reach applications. Tunable XFP can be tuned from channel C17 (1563.86nm) to C61 (1528.38nm). The maximum distance of this transceiver on a single mode fiber is up to 80 km. As mentioned above, tunable XFP optical transceiver is a full-duplex serial electric, serial optical device with both transmit and receive functions contained in a single module. On the transmit side, the 10 Gbps serial data stream is recovered, retimed, and passed to a modulator driver. The modulator driver biases and modulates a C-band-tunable integrated laser Mach-Zehnder (ILMZ), enabling data transmission over singlemode fiber through an industry-standard LC connector. On the receive side, the 10 Gbps optical data stream is recovered from an APD/transimpedance amplifier, retimed, and passed to an output driver. This module features a hot-pluggable XFI-compliant electrical interface. Here is a simple picture showing its working process.
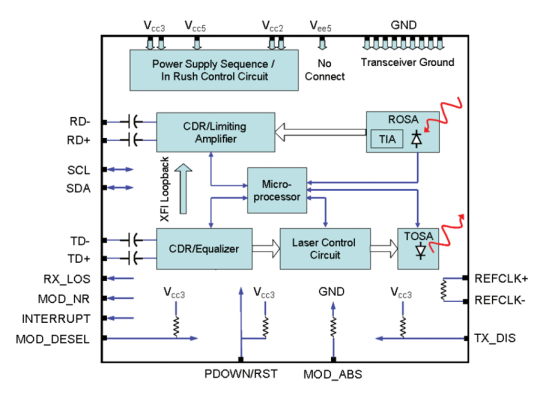
Tunable XFP Optics Specifications:
50 GHz ITU channel spacing with intergrated wavelength locker
Available in all C-Band Wavelengths on the DWDM ITU grid
Available distances 40 or 80 km
Supports 9.95Gb/s to 11.35Gb/s
Built-in Digital Diagnostic Functions
Tempereature Range: -5°C to 70°C
Two Transmission Distance Options: 40 km or 80 km
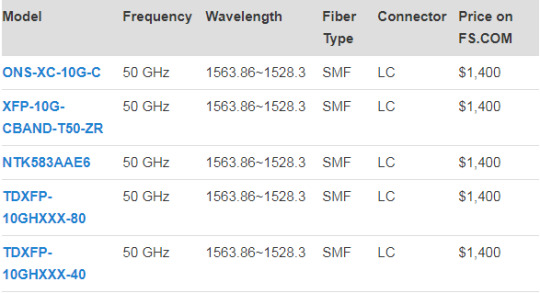
There are two transmission distance options for tunable XFP transceiver: 40 km or 80 km. Tunable XFP DWDM 80 km transceiver is designed for long distance optical communications up to 80 km with signaling rates up to 10Gbps. Obviously, the main difference is transmission distance. On account that 10G tunable DWDM XFP optical transceiver provides digital diagnostic functions via a 2-wire serial interface, which allows real-time access to the following operating parameters: transmitted optical power, received optical power, transceiver temperature, laser bias current and transceiver supply voltage. Therefore, the differences between 40 km tunable XFP and 80 km tunable XFP mainly lie on theses parameters. One thing to note is that 40 km tunable XFP optics is designed with high performance PIN receiver, while the 80 km tunable XFP transceiver is APD receiver. The APD (avalanche photodiode) receiver employed in these extended-reach optical transceivers has an enhanced sensitivity to allow for these extended distance fiber runs. However, it is to be noted that the input power is typically between -7 and -24 dBm. Therefore, the receiver sensitivity between these two distance has a big difference. Generally, the max receive dBm of 40 km tunable XFP transceiver is -15, while the 80 km tunable XFP transceiver is -24. And for power budget, 40 km tunable XFP is 14dB while a distance up to 80 km is up to 22dB power budget. The following table lists the main differences.
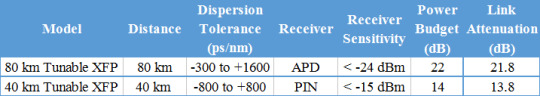
Conclusion
In general, the channel switching of tunable switches can enable the service operators to turn up circuits faster and reduce their sparing costs dramatically in today’s DWDM systems. On the other hand, tunable transceiver is usually two or four times more expensive than the regular static DWDM optical module, because a special tunable laser is applied in it. Tunable XFP transceiver provides a full C-band window covering 1528nm to 1566nm for DWDM optical networks, which meets the need of rapid increase in the volume of communications traffic from telecom carrier and operator. The tunable DWDM XFP module can replace the fixed DWDM channel XFP transceivers that are currently used, while reduce the large stock since all wavelengths can now be covered with one transceiver module.
0 notes
Text
Unveil 10G DWDM Tunable SFP+
Optical transceivers play a key role in handling all storage, data, voice and video traffic whether linking rack to rack, bottom to top of rack, data center to data center or enterprise networks to network. A range of flexible fiber optic transceiver modules cover all of network needs, such as SFP, SFP+, QSFP, QSFP28, CFP, etc. But for 10G DWDM tunable SFP+, many people might find themselves in the mire. When I first heard about this tunable transceiver, I thought that it would definitely bring revolutionary change to future metro Ethernet and optical transport networks with its important practical value for flexibly selecting working wavelength. So this article will unveil all of the things about tunable SFP+ optical transceiver.
About 10G DWDM Tunable SFP+
As the demand for great traffic capacity keeps growing, more optical transceivers of different wavelengths are needed. So tunable transceivers are recent innovations in DWDM transport systems. DWDM tunable transceivers are within the scope of DWDM transceivers, through which different DWDM wavelengths can be configured and output in the same optical module. But compare with conventional fixed-wavelength DWDM SFP+, the tunable SFP+ uses tunable laser as light sources in DWDM systems, which is tunable across the entire C-band with 96 channels on the ITU-T 50-GHz grid.
The tunable laser technology is firstly introduced by Oclaro, a leading supplier and and innovator of tunable laser and transceiver solutions. In 2013, it announced a standards-compliant, multi-rate tunable SFP+, which supports rates between 9.95 and 11.3 Gbps. But the first-generation tunable SFP+ optical transceivers were not widely adopted, because they did not meet the critical requirement of less than 1.5 W of power consumption at high operating temperatures. So in 2014, Oclaro demonstrated a new tunable SFP+ module based on a new Oclaro InP tunable laser platform. With the innovative new chip design and the use of next generation materials, the new module is fully compliant to the SFP MSA form factor and can operate at 1.5W at 70 degrees C with excellent OSNR tolerance. With the breakthrough of technology, the 10G tunable SFP+ transceivers become an important component for next generation data center, metro and regional optical network equipment. They meet the world’s growing bandwidth demands while reducing the size and power consumption for 10G connections.
Key Highlights of Tunable SFP+ Module:
(1) Fully compliant with MSA standard size based on SFF-8432 specification for Improved Pluggable Form Factor, rev. 5.1
(2) Tunable across the full C-band with 96 channels on the ITU-T 50GHz grid
(3) Multi-rate operation: 9.95 Gbit/s to 11.3 Gbit/s
(4) Operates at 1.5W at 70 degrees C with excellent OSNR tolerance
Advantages of Tunable SFP+
The tunable SFP+ transceivers are high-performance optics which can be tuned to the appropriate wavelength. The ability to operate on various wavelengths has set these optics apart from fixed-wavelength DWDM SFP+. Besides, These tunable optics will become popular among DWDM systems due to the several advantages.
Flexible network management
A tunable SFP+ transceiver will be remotely configured for a specific wavelength to support bandwidth changes as needed in Enterprise or Metro networks.
Reduced network inventory
One tunable SFP+ transceiver will support more than 80 different wavelengths. It will allow network operators to hold one tunable device code as opposed to 80+ fixed wavelength transceivers.
Reduced power consumption
It will provide a significant reduction in electrical power dissipation compared to other tunable solutions.
Compact and high-density form factor
The new tunable SFP+ transceiver will be about the size of a pack of gum, saving valuable real estate in data centers.
Increased network capacity
The tunable SFP+ will double the number of channels supported in this compact transceiver form factor. Upgrading to 50GHz channel spacing doubles the capacity potential in Enterprise and Metro networks.
Conclusion
The advent of 10G DWDM tunable SFP+ transceivers in the market will accelerate the trend for pace-, power-, and cost-efficient network solutions. Because tunability is critical for minimizing inventory and enabling flexible rapid service provisioning. Although now the market share for DWDM tunable SFP+ transceiver is not big enough, the huge potential will be demonstrated in the near future.
0 notes
Text
Optics Solutions for Netgear ProSAFE XS712T (XS712T-100NES)
With the growth of virtualization, cloud-based services and applications like VoIP, video streaming and IP surveillance, SMB networks need to extend beyond simple reliability to higher speed and performance. As a leading provider of networking equipment for SMBs, Netgear had launched a variety of cost-effective 10GBASE-T switches including Netgear ProSAFE XS708Ev2, XS716E, XS708T, XS712T, XS716T, XS728T, XS748T and XSM7224. When looking for a lower cost and high capacity 10GBASE-T switch in SMB home/office lab environments, the Netgear ProSAFE XS712T is one of the best options. It comes in at around $1,100 at Amazon which is more budget friendly than the larger data center switches. This article will review the Netgear ProSAFE XS712T (XS712T-100NES) 10GBASE-T switch.
Netgear ProSAFE XS712T (XS712T-100NES): 12-Port 10GBASE-T Switch
Netgear ProSAFE XS712T is a powerful smart managed switch that comes with 10 dedicated 10GBASE-T RJ-45 copper ports supporting 100M/1G/10G speeds and 2 combo copper/SFP+ fiber 10G ports. The 2 combo SFP+ ports can be used as 10GASE-T ports or as SFP+ 10Gb Ethernet ports. This is an awesome feature as it allows an inexpensive SPF+ link via DAC to a 24 or 48 port 1Gb Ethernet switch for non-10Gb networking needs. All ports can automatically negotiate to the highest speed, which makes the switch ideal for environments that have a mix of Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or 10-Gigabit Ethernet devices. Cat 5e/Cat 6/Cat 6a/Cat 7 can be used to make 10G connections. Cat 6a/Cat 7 cables are recommended if the cable distance is greater than 45 meters. Besides, the smart switch can be freestanding or rack mounted in a wiring closet or equipment room. This 10G smart managed switch is purposely designed as a cost-effective way to provide 10G connections to 10G-capable servers and NAS (Network Attached Storage) systems. It also can be used at the center of a small business network or as an aggregation/access switch in a larger organization.
Figure 1: Netgear ProSAFE XS712T (Source: www.netgear.com )
Highlights of Netgear ProSAFE XS712T
In order to meet the current and future needs on virtualization, converged network and mobility, the XS712T provides comprehensive L2+/Layer 3 Lite features, such as VLAN, QoS, IGMP and MLD snooping, Static Routing, Link Aggregation, ACL binding. Besides, it has an easy-to-use Web-based management GUI which makes setup and management simple. Some of main features include:
10GBASE-T Connection
The RJ-45 copper ports of XS712T comply with IEEE 10GBASE-T standards. They support low-latency, line-rate 10G copper “Base-T” technology with backward compatibility to Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. So it allows for a cost effective and simpler upgrade path to 10-Gigabit Ethernet. The existing Cat5/Cat5e is supported for Gigabit speeds up to 100 meters, Cat6 for 10-Gigabit speeds up to 45 meters and Cat6a/Cat7 for 10GBASE-T connection up to 100 meter.
Designed as Core Switch for SMB Network
The powerful L2+/Layer 3 Lite features make XS712T the most cost-effective core switches for SMB and virtualization environment. This switch is also a future-proofing choice with 10G bandwidth, advanced traffic management and comprehensive IPv6 support.
Figure 2: Netgear ProSAFE XS712T in SMB Network (Source: www.netgear.com )
Act as Aggregation Switch for Medium Sized Networks
The XS712T used as a aggregation switch has many useful purposes. It can help to resolve the congestion issue between network edge and core, which is caused by the broader adoption of Gigabit-to-the-desktop. Unlike multiple Gigabit Ethernet links, it provides greater scalability resulting in a simplified and highly efficient network infrastructure. What’s more, it can reduce cabling complexity because it can use existing cabling efficiently.
Optics Solutions for Netgear ProSAFE XS712T (XS712T-100NES)
As mentioned above, The Netgear ProSAFE XS712T smart switch provides 12 twisted-pair ports that support nonstop 100M/1000M/10G networks. The switch also has two built-in SFP+ GBIC combo slots that support 1000M and 10G optical modules. Using these Gigabit slots, 100M/1000M/10G copper and 1000M/10G fiber connectivity can create high-speed connections to a server or network backbone. So 1000BASE-T SFP copper transceiver, 1000BASE SFP and 10G SFP+ transceivers are suitable for this switch. The following table lists the compatible transceivers and optic cables from FS.COM.
MFG PART# Description AGM734 NETGEAR AGM734 Compatible 1000BASE-T SFP Copper 100m Transceiver, RJ-45 Interface AGM731F NETGEAR Compatible 1000BASE-SX SFP 850nm 550m DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AGM732F NETGEAR Compatible 1000BASE-LX SFP 1310nm 10km DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AXM761 NETGEAR Compatible 10GBASE-SR SFP+ 850nm 300m DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AXM762 NETGEAR Compatible 10GBASE-LR SFP+ 1310nm 10km DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AXM763 NETGEAR Compatible 10GBASE-LRM SFP+ 1310nm 220m DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AXM764 NETGEAR Compatible 10GBASE-LR Lite SFP+ 1310nm 2km DOM Transceiver, LC Interface AXC761 1m NETGEAR Compatible 10G SFP+ Passive DAC AXC763 3m NETGEAR Compatible 10G SFP+ Passive DAC
Conclusion
The Netgear XS712T (XS712T-100NES) provides a solid cost-effective solution especially for those with SMB home/ office lab environments. If you are seeking for afforable 10GBASE-T switch for your home lab, the XS712T can be taken into consideration. What’s more, the compatible fiber transceivers and cables can be found in many third party vendors with reasonable prices, such as cablestogo, fluxlight, smartoptics, FS.COM, and etc. You have a lot of choices to save money.
0 notes
Text
Layer 3 Switch VS. Router
In the OSI model, we know that traditional network switches operate at Layer 2 while network routers operate at Layer 3. Besides, switches are understood to be forward traffic based on MAC address, while routers perform the forwarding based on IP address. Layer 3 switches have a lot in common with traditional routers: they can also support the same routing protocols, inspect incoming packets and make dynamic routing decisions based on the source and destination addresses inside. For this reason, many networking beginners are puzzled over the definition and purpose of a Layer 3 switch. So what is on earth Layer 3 switch and how is it different from router?
Layer 3 Switch
Layer 3 switch is also called multilayer switch. It is a specialized hardware device used in network routing, which is conceived as a technology to improve network routing performance on large local area networks (LANs) like corporate intranets. A Layer 3 switch is both a switch and a router. So Layer 3 switch is a switch that can route traffic, and a router with multiple Ethernet ports has a switching functionality. It can switch packets by checking both IP addresses and MAC addresses. On this account, Layer 3 switches separates ports into VLANs and perform the routing between them, in addition to supporting routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF and EIGRP.
Layer 3 Switch VS. Router
From the basics of Layer 3 switch, it may seem to perform the same functionality with the router. In fact, they have some key distinction facts. The key differences between Layer 3 switches and routers lay in the hardware technology used to build the unit. The hardware inside a Layer 3 switch merges that of traditional switches and routers, replacing some of a router’s software logic with hardware to offer better performance in some situations. The table below illustrates the differences between Layer 3 switch and router.
Main Differences:
Cost - Layer 3 switch is much more cost effective than router for delivering high-speed inter-VLAN routing. High performance router is typically much more expensive than Layer 3 switch.
Port density - Layer 3 switch has much higher port count while router has a lower port density than Layer 3 switch.
Flexibility - Layer 3 switch allows you to mix and match Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching. It means that you can configure a Layer 3 switch to operate as a normal Layer 2 switch.
WAN technologies support - Layer 3 switch is limited to usage over LAN environment where Inter VLAN routing can be performed. However, when it comes to working on WAN and edge technologies, Layer 3 switch lags behind. Router is the front runner in such scenario where WAN technologies such as Frame Relay or ATM need to be fostered.
Hardware/Software decision making - The key difference between Layer 3 switch and router lies in the hardware technology used to making forwarding decision. Layer 3 switch uses ASICs for forwarding decisions. Conversely, the router makes forwarding decisions based on hierarchical Layer-3 addresses.
Layer 3 Switch with VLANs
As here is mentioned the VLAN, so let’s talk about it firstly. A VLAN (virtual LAN) is a logical subnetwork that can group together a collection of devices from different physical LANs. VLANs can improve the overall performance of busy networks. So they are often set up for improved traffic management by larger business computer networks. With a VLAN, traffic can be handled more efficiently by network switches.
Each virtual LAN must be entered and port-mapped on the switch. Routing parameters for each VLAN interface must also be specified. Some Layer 3 switches implement DHCP support that can be used to automatically assign IP addresses to devices within a VLAN. Alternatively, an outside DHCP server can be used, or static IP addresses configured separately. The diagram below shows an example of a layer 3 switching routing between VLANs through its two VLAN interfaces.
These switches are most commonly used to support routing between virtual LANs (VLANs). Benefits of Layer 3 switches for VLANs include:
Reduction in the amount of broadcast traffic
Simplified security management
Improved fault isolation
Conclusion
From what we have discusses, Layer 3 switch may be more preferable in result of its capability of routing and switching. Besides, it can perform as a top of rack device and a distributed core switching layer at the same time. This reduces the L2 complexity of the client access layer, which makes the network more reliable and easier to manage. FS.COM can provide a comprehensive, scalable and secure portfolio of switches for enterprise and service provider networks. There are also a huge stock of compatible fiber optic transceivers and cables.
0 notes
Text
FS S2800-24T4F Fanless Switch - Energy-saving Ethernet Access Switch
As we all know, network switches are always a little bit noisy. Many people are bewildered by this problem. In fact, the noise mainly comes from the multiple fans that operate from within the network switch, in order to cool the various components of the switch from within. Considering the certain situation when some SMB might prefer having a fanless network switch, FS now has introduced a brand new S2800-24T4F fanless switch to meet the silent and cost-effective requirement for SMB customers. Let’s take a closer look at this energy-saving S2800-24T4F fanless switch.
What Is Fanless Switch?
In some scenarios, operating fans within the network switches is inevitable. It is the reason that the switches emanate so much heat, especially when multiple network switches are locked up into a rack along with many other active devices. At this time, fans play a important role to help cool various components within the network switch. However, the constant noise coming from the fans within the switch might be disturbing to everyone around the switch. In such situation, people might prefer to the fanless switches. Apart from being quiet, these switches are more reliable and utilize less power than their fan-cooled counterparts. Fanless design might be purposefully incorporated into the switches to increase their reliability. These switches are come with solid-state cooling apparatus instead of fans that help cool the various parts inside the switch and hence provide a higher degree of reliability.
FS S2800-24T4F Fanless Switch
FS S2800-24T4F is a kind of fanless and energy-saving Ethernet access switch, which is designed to meet the demand of cost-effective Gigabit access or aggregation for enterprise networks. For the advantage of silent and cost-saving design, it is perfect to use in SMBs, labs, schools and Internet cafes. In addition, it offers flexible port combination form to facilitate user operations as the result of the equipped 24x100/1000Base-T ports and 4x1GE Combo SFP ports. So you can directly connect to a high-performance storage server or deploy a long-distance uplink to another switch. Moreover, S2800-24T4F supports multiple configuration modes to make it easy for network management and maintenance. Also, high performance processor is adopted to provide full speed forwarding and line-dormant capacity to offer customs multitudinous service features.
Highlights & Benefits
Layer 2 Full Wire Speed Gigabit Forwarding Capability.
FS S2800-24T4F has up to 48Gbps backplane bandwidth and 42Mpps packet forwarding rate. And its performance will be not impacted by ACL / binding / attack protection and other functions.
Function Optimization for WEB Configuration of Internet Bar.
Customers can configure the port automatically or manually, and secure their network through using its IP+VLAN+MAC+Port binding functions.
Perfect Management and Maintenance.
The Web management interface of S2800-24T4F has been optimized for enterprise users, supporting SNMP, Telnet, and cluster. Looback port loopback detection and LLDP neighbor detection functionalities have also been provided.
Supported Optical Transceivers for S2800-24T4F
As being mentioned, the FS S2800-24T4F has 24 24x100/1000Base-T ports to achieve network connectivity. For these ports, you can use 100BASE SFP, 1000BASE SFP, BIDI SFP, CWDM SFP, DWDM SFP optical transceiver or 1000BASE-T SFP copper RJ-45 transceiver to achieve the link. FS provides many high-quality compatible SFP modules for S2800-24T4F fanless switch.
Conclusion
Ethernet switches have become an integral part of networking because of the speed and efficiency with which they handle data traffic. At FS, we know very well how much our small and medium-sized clients need a reliable and affordable Ethernet switches. So we come with this S2800-24T4F fanless switch for you, which is assured with high-quality and a one-year limited warranty, including any quality problems during the free maintenance. Besides, all of FS.COM’s transceivers are tested for 100% functionality and guaranteed compatible for outstanding network performance. So does the above SFP transceivers, they are completely applicable to this S2800-24T4F switch. Compared to the other vendors’ optical modules, they are much cheaper.
0 notes
Text
Compatible SFP Transceivers for HP 1810-48G Switch (J9660A)
Today, small and midsize businesses are embracing mobile and cloud technologies to improve employee productivity and engage with customers. More business needs an affordable, high-performance and secure wired and wireless infrastructure that can support the growing number of mobile devices and cloud-based applications. When asking for a recommendation for SMB switches, many people always recommend the HP because it has most of the same capabilities such as full management capability, rock solid operation and great support (as the Cisco), but at half the price. And HP 1810-48G switch is one of such SMB switches. This article intends to give a simple introduction to HP 1810-48G switch and provide compatible SFP transceiver solutions for it.
HP 1810-48G Switch (J9660A)
The HP 1810-48G switch is a basic smart managed Gigabit Ethernet Layer 2 switch that is designed for small businesses. This HP ProCurve 48 port gigabit switch has four additional true Gigabit Ethernet SFP ports (52 total active ports) for fiber connectivity, which supports Gigabit-SX, -LX, or 100-FX and SFP 1G RJ-45 copper connections. Besides, it supports flexible deployment options, including mounting on walls or ceilings, under tables, or desktop operation. More than anything, it comes with an anti-theft protection Kensington Lock slot, which allows switches to be secured in open-space deployments. A HP 1810-48G switch also has some customizable features, including VLANs, Spanning Tree and link aggregation trunking.
Key Features or Benefits:
Customized operation using intuitive Web interface
Flexible connection and deployment options
Layer 2 operation at wire speeds
VLANs and link aggregation support
HP ProCurve Mini-GBICs and SFPs
HP ProCurve transceivers as the part of the networking accessories that are applied to their corresponding switches or routers. Thus, it is also important to get some knowledge of the HP ProCurve Mini-GBICs and SFPs. HP ProCurve Mini-GBICs and SFPs have three version: revision A, revision B and revision C. Though there is no big difference between these three version, some improvement will be added in the newest version. The “revision C” Mini-GBICs (eg. J4858C, J4859C, J4860C) are supported in all ProCurve products that support Mini-GBICs. In addition, “revision B” and “revision C” mini-GBICs can be used together in any ProCurve switch that supports mini-GBICs. FS.COM can support the 100% compatible HP ProCurve Mini-GBICs and SFPs at version A, B and C, such as J4858A/B/C, J4859A/B/C, J4860A/B/C.
HP Compatible SFP Transceivers for HP 1810-48G Switch (J9660A)
According to HP ProCurve Networking Mini-GBIC Support Matrix, we can easily find out which Mini-GBICs and SFPs are supported for HP 1810-48G Switch (J9660A).
HP X111 100M SFP LC FX Transceiver (J9054C)
The HP J9054C compatible SFP transceiver provides 100Base-FX throughput up to 2km over multi-mode fibre (MMF) at a wavelength of 1310nm using a LC connector. FS is guaranteed to be 100% compatible with the equivalent HP transceiver. This hot swappable transceiver has been programmed, uniquely serialized and data-traffic and application tested to ensure that it will initialize and perform identically. It is built to comply with multi-source agreement (MSA) standards to ensure seamless network integration.
HP X121 1G SFP LC SX Transceiver (J4858C)
This SFP (mini-GBIC) transceiver module is designed for use with HP network equipment and is equivalent to HP part number J4858C. It provides 100Base-FX throughput up to 550m over multi-mode fibre (MMF) at a wavelength of 850nm using a LC connector. The transceiver is hot-swappable input/output device which allows a Gigabit Ethernet port to link with a fibre optic network. And this transceiver may be mixed and deployed with other OEM or third party transceivers and will deliver seamless network performance.
HP X121 1G SFP LC LX Transceiver (J4859C)
HP ProCurve J4859C 1000BASE-LX-LC Mini-GBIC is a small form factor pluggable (SFP) gigabit LX transceiver that provides a full-duplex gigabit solution up to 10 km (singlemode) or 550 m (multimode). It is an SFP format gigabit transceiver with LC connectors using LX technology.
HP X121 1G SFP RJ45 T Transceiver (J8177C)
J8177C is a small form-factor pluggable (SFP) Gigabit copper transceiver with RJ45 connectors using 1000BaseT technology, that provides a full-duplex Gigabit solution up to 100m on Category 5 or better cable. It is guaranteed compatible for all HP switch and router product lines. This transceiver can be mixed and deployed with HP OEM transceivers for seamless network performance and interoperability.
Precautions:
To remove the J8177C from a Mini-GBIC slot on the switch, follow this procedure:
1. Remove the attached cable from the Mini-GBIC.
2. Without forcing the latch, swivel the latch 90 degrees to the unlocked position.
CAUTION: Do not force the latch! If the latch does not easily swivel 90 degrees, move the latch back to the locked position, re-seat the Mini-GBIC by pressing it into the switch, then repeat step 2.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose a Suitable Network Switch?
A network switch is a small hardware device that centralizes communications among multiple connected devices within one local area network (LAN). Network switches come in different sizes, features and functions, so choosing a switch to match a particular network sometimes constitutes a daunting task. This blog will give you a few useful things to consider when choosing the appropriate switch for a layer in a particular network.
Network Switch Technology
While switching capabilities exist for several kinds of networks, including Ethernet, Fibre Channel, RapidIO, ATM, ITU-T G.hn and 802.11, network switch can operate at one or more layers of the OSI model. Switches provide multiple advantages in network designs. All switches provide the basic traffic filtering functions, which improves network bandwidth. Besides, the internal switching circuits allow traffic flows to simultaneously occur between multiple ports. Currently, mainstream network switches support Gigabit Ethernet speeds per switch port, but high-performance switches in data centers generally support 10 Gbps per link. Different models of network switches support varying numbers of connected devices. Home network switches provide 4/8 connection for Ethernet devices, while SMB switches typically support between 32 and 128 connections.
Considerations for Choosing the Suitable Network Switch
Careful planning before purchasing a switch will save you money. At the same time, it can help you ensure the equipment has the functionality that you organization is needed, or the switches can expand their capabilities as your requirements change and grow. Here are some suggestions you can use to help guide your switch purchase.
Connection Requirements
Connection requirements are a good place to start, since they usually dictate what types of switches will be needed, and they can affect pricing dramatically. Here are something you need to consider in advance:
1. Consider the number of users that your network will have to support
2. Consider your basic network infrastructure
3. Determine the network needs of the users (Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet)
4. Choose the role of the switch (core switch, distribution switch, access switch)
5. Pick a vendor and/or company (for example: Cisco, Juniper, HP, Dell, Arista, Brocade, FS.COM)
Number of ports
The number of users and the basic network infrastructure determine the number of ports. Common numbers of ports on network switches are 5, 8, 10, 24, and 48 ports. If you only have 5 or 6 users, then a small 8 port switch will probably be enough for your needs. Number of ports is one of the biggest factors in the cost of a switch, so if you buy a switch that only supports the number of users that you will have, you will likely save a fair amount of money.
Port Speeds and Types
Fixed switches come in Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. Fast Ethernet allows up to 100 Mb/s of traffic per switch port while Gigabit Ethernet allows up to 1000 Mb/s of traffic per switch port. These ports may be a combination of SFP/SFP+ slots for fiber connectivity, but more commonly they are copper ports with RJ-45 connectors on the front, allowing for distances up to 100 meters. With Fiber SFP modules, you can go distances up to 40 kilometers. Currently, Gigabit Ethernet is the most popular interface speed though Fast Ethernet is still widely used, especially in price-sensitive environments.
Link Aggregation
If you have a 24-port switch, with all its ports capable of running at gigabit speeds, you could generate up to 24 Gb/s of network traffic. If the switch is connected to the rest of the network by a single network cable, it can only forward 1 Gb/s of the data to the rest of that network. Due to the contention for bandwidth, the data would forward more slowly. That results in 1 out of 24 wire speed available to each of the 24 devices connected to the switch. Therefore, the more ports you have on a switch to support bandwidth aggregation, the more speed you have on your network traffic.
Performance
Core Layer Switches: These types of switches are routed at the core layer of a topology, which is the high-speed backbone of the network and requires switches that can handle very high forwarding rates. The switch that operates in this area also needs to support link aggregation to ensure adequate bandwidth coming into the core from the distribution layer switches. Because of the high workload carried by core layer switches, they tend to operate hotter than access or distribution layer switches. Virtually, core layer switches have the ability to swap cooling fans without having to turn the switch off.
Distribution Layer Switches: Distribution layer switches plays a very important role on the network. They collect the data from all the access layer switches and forward it to the core layer switches. Distribution layer switches provides advanced security policies that can be applied to network traffic using Access Control Lists (ACL). This type of security allows the switch to prevent certain types of traffic and permit others.
Access Layer Switches: Access layer switches facilitate the connection of end node devices to the network. For this reason, they need to support features such as port security, VLANs, Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet, Power over Internet, and link aggregation. Port security allows the switch to decide how many or what type of devices are permitted to connect to the switch.
Power requirements
At any layer, a modern switch may implement power over Ethernet (PoE), which avoids the need for attached devices, such as a VoIP phone or wireless access point, to have a separate power supply. Since switches can have redundant power circuits connected to uninterruptible power supplies, the connected device can continue operating even when regular office power fails. Another characteristic you consider when choosing a switch is PoE. This is the ability of the switch to deliver power to a device over the existing Ethernet cabling. To find the switch that is right for you, all you need to do is choose a switch according to your power needs. When connecting to desktops which do not require PoE switches, the non-PoE switches are a more cost-effective option.
Future Growth: Stackable VS. Standalone
As the network grows, you will need more switches to provide network connectivity to the growing number of devices in the network. When using standalone switches, each switch is managed, troubleshot, and configured as an individual entity. In contrast, stackable switches provide a way to simplify and increase the availability of the network. With a true stackable switch, you can connect the stack members in a ring. If a port or cable fails, the stack will automatically route around that failure, many times at microsecond speeds. You can also add or subtract stack members and have it automatically recognized and added into the stack.
Conclusion
As you can see, there is a multitude of switch options to choose from. So, have a close look at your current deployment and future needs to determine the right switch for your network.
0 notes