Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Title: Understanding the Holistic Health of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples”
The well-being of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia is detailed, complex, and woven from the interconnected threads of culture, spirituality, community, and physical health (Australian Institute of Health and Wellbeing, 2022). Not just the absence of illness, but a holistic concept that includes social, psychological, physical, spiritual, and cultural aspects, understanding and addressing the well-being of these communities requires a sensitive approach.
A Holistic View of Health
From an Indigenous perspective, well-being is not about the body being healthy but is found in the interaction between the social, psychological, physical, spiritual, and cultural realms. It is put within notions of belonging, land, spirituality, and culture; the cohesion and practice of a cultural life among community members nurture the well-being of an individual.
Physical Well-being:
First Nation people are nurtured in their physiological health concerning their body through nourishing diets, physical activity, and avoidance of harmful substances. This definition of physical well-being in First Nations people has been articulated to be determined by factors like the environment, access to nutrient foods, and disease prevalence (Lemke & Delormier, 2017); it should address inequality and exist within systems.
Psychological Well-being:
Psychological well-being emanates from feelings of belonging, strong cultural identity, good interpersonal relationships, and lifestyles with a perceived sense of purpose (Morales-Rodríguez, 2020). However, unresolved trauma, cultural separation, discrimination, and socio-economic disadvantage significantly challenge psychological well-being and will require culturally safe interventions and support systems. Factors Affecting Well-being Health determinants for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples relate to historical trauma, dislocation from culture, discrimination, socio-economic detriment, and adverse environmental conditions (Dossetor et al., 2023). These require a comprehensive strategy to improve health and social determinants in their interrelatedness.

Fig-1: Components of health and wellbeing of Aboriginal and Torress Strait Islanders
(Source: Menzies, 2022)
Determinants of Well-being
The health of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people is interdependently related to factors such as historical trauma, cultural dislocation, discrimination, socio-economic disadvantage, and poor environmental conditions (Hatton et al., 2024). Addressing key determinants calls for all-inclusive approaches that also recognize health as interrelated with social determinants.
Practices
A range of programs has been implemented by Australian Government, recognizing the different challenges involved in seeking to achieve well-being among the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander community. These include programs in mental health, cultural healing practices, community-led initiatives, and initiatives focusing on sport/physical activities (Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care, 2024). All of them are focused on cultural appropriateness and community engagement with an emphasis on.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite efforts, a lot remains to be desired in the well-being of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Very little has been researched on how to holistically address their well-being, current disparities in socio-economic status, and cultural barriers to healthcare (Carmel, 2019). These efforts need to be focused on cultural safety, increased investments into community-led solutions (Lemke & Delormier, 2017), and the breaking down of systemic inequalities to make meaningful gains and improvements in well-being.
References
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. (2023, December 18). Our work related to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health. https://www.health.gov.au/topics/aboriginal-and-torres-strait-islander-health/related-work
Australian Institute of Health and Wellbeing. (2022). Indigenous health and wellbeing. https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-health/indigenous-health-and-wellbeing
Carmel, S. (2019). Health and well-being in late life: Gender differences worldwide. Frontiers in medicine, 6, 218. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2019.00218
Dossetor, P. J., Freeman, J. M., Thorburn, K., Oscar, J., Carter, M., Jeffery, H. E., Harley, D., Elliott, E. J., & Martiniuk, A. L. C. (2023). Health services for aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children in remote Australia: A scoping review. PLOS global public health, 3(2), e0001140. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0001140
Hatton, C. R., Kale, R., Pollack Porter, K. M., & Mui, Y. (2024). Inclusive and intersectoral: community health improvement planning opportunities to advance the social determinants of health and health equity. BMC public health, 24(1), 170. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12889-023-17496-5
Lemke, S., & Delormier, T. (2017). Indigenous Peoples' food systems, nutrition, and gender: Conceptual and methodological considerations. Maternal & child nutrition, 13 Suppl 3(Suppl 3), e12499. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12499
Menzies. (2022). Aimhi nt - Aboriginal and Islander Mental Health initiative. https://www.menzies.edu.au/page/Research/Projects/Mental_Health_and_wellbeing/AIMhi_NT_-_Australian_Integrated_Mental_Health_Initiative/
Morales-Rodríguez, F. M., Espigares-López, I., Brown, T., & Pérez-Mármol, J. M. (2020). The Relationship between Psychological Well-Being and Psychosocial Factors in University Students. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(13), 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134778
0 notes
Text
Positive Education
Title: "Fostering Flourishing: The Power of Positive Education for Wellbeing"
In a transformational approach to education, positive education prioritises the overall development of students' well-being and resilience over traditional academic accomplishment (Hasanuddin & Mappaompo, 2024). Positive education, which has its roots in positive psychology, seeks to develop a pleasant school climate and provide students with the abilities and perspective necessary to succeed in all facets of life.

Fig-5: Positive Education
(Source: Millacci, 2024)
Understanding Positive Education
Stressing the development of students' strengths, resilience, and overall well-being, positive education incorporates the science of positive psychology into classroom instruction (Ellis & Robson-Kelly, 2018). Positive education acknowledges the value of developing students' emotional intelligence, character traits, and social skills in addition to emphasising academic achievement (Cabanas & González-Lamas, 2022). Utilising Martin Seligman's PERMA model and the Values in Action (VIA) categorization, positive education integrates traditional educational concepts with the study of happiness and well-being (Millacci, 2024). One of the pioneers of positive psychology, Seligman, has integrated positive psychology into educational models to improve the well-being and happiness of younger people and reduce depression (Alam, 2022). The purpose of educators and practitioners utilising his PERMA model (or its extension, the PERMAH framework) in schools is to support instructors and students in having positive mental health.

Fig-6: Positive Education through the PERMAH Model
(Source: Millacci, 2024)
Evidence-based Practices of Positive Education
To improve and enhance students' resilience and overall well-being, positive education makes effective and appropriate use of a variety of research-backed strategies. These particular practices cover a broad spectrum of activities, exercises, and tactics intended to strengthen character traits, encourage a very growth mindset, and encourage pleasant emotions.
Positive emotions are essential for improving learning, encouraging creativity, and reducing stress (Diener et al., 2020). It has been demonstrated and illustrated that activities including blogging about gratitude, doing random acts of kindness (Ellis & Robson-Kelly, 2018), and practicing mindfulness may foster and enhance happy feelings and enhance general well-being.
Characteristics like compassion, persistence, and resilience are very crucial for overcoming obstacles and issues in life and reaching one's greatest potential (Lavy, 2020). To help and assist students feel much more purposeful and accomplished, positive education programmes very frequently include activities and interventions that target recognising, and strengthening these qualities in their pupils.
Resilience and academic achievement are based on a growth mindset, which is defined as the conviction that skills can be acquired with practice and effort (Anderson et al., 2020). Through techniques including rephrasing obstacles as chances and opportunities for development, accepting failure as a normal part of learning, and offering much more constructive criticism that emphasizes effort and advancement, positive education promotes the development of a growth mindset.
Overall, by very significantly putting students' resilience and well-being first, positive education has the potential to drastically change the educational system. Schools may provide and offer supportive environments that enable children to flourish and foster academically, socially, and emotionally by using evidence-based strategies with an effective foundation in positive psychology.
References
Alam, A. (2022). Positive psychology goes to school: conceptualizing students’ happiness in 21st century schools while ‘minding the mind!’are we there yet? evidence-backed, school-based positive psychology interventions. ECS Transactions, 107(1), 11199. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/10701.11199ecst/meta
Anderson, R. C., Beach, P. T., Jacovidis, M. J. N., & Chadwick, K. L. (2020). Academic buoyancy and resilience for diverse students around the world. Inflexion, August. https://www.ibo.org/globalassets/new-structure/research/pdfs/academic-resilience-policy-paper-en.pdf
Cabanas, E., & González-Lamas, J. (2022). A critical review of positive education: challenges and limitations. Social Psychology of Education, 25(5), 1249-1272. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11218-022-09721-7
Diener, E., Thapa, S., & Tay, L. (2020). Positive emotions at work. Annual review of organizational psychology and organizational behavior, 7, 451-477. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-012119-044908
Ellis, K. & Robson-Kelly, L. (2018). Enhancing learning through positive education, well-being, and resilience. https://my.chartered.college/impact_article/enhancing-learning-through-positive-education-wellbeing-and-resilience/
Hasanuddin, M. I., & Mappaompo, M. A. (2024). OPTIMIZING PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH ACHIEVEMENT: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SOCIETY REVIEWS, 2(1), 193-208. https://injoser.joln.org/index.php/123/article/view/54
Lavy, S. (2020). A review of character strengths interventions in twenty-first-century schools: Their importance and how they can be fostered. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 15(2), 573-596. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11482-018-9700-6
Millacci, T. S. (2024, March 13). What is positive education, and how can we apply it? (+PDF). PositivePsychology.com. https://positivepsychology.com/what-is-positive-education/
0 notes
Text
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Title: “Exploring Holistic Healing: The Role of Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Wellbeing”
Welcome to our blog post on Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM)! We will dive into the fascinating realm of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) in this post, looking at its many forms, advantages, and practical uses.
What is CAM?
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is the phrase typically used to characterise a medical technique or product that falls beyond the purview of conventional, mainstream, or traditional medicine (Healthify, 2024). Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) encompasses a wide range of healthcare and medical practices, methods, and products that are not part of traditional medicine (Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023). CAM therapies are frequently employed in conjunction with conventional treatments or as a substitute to enhance health and overall wellness.
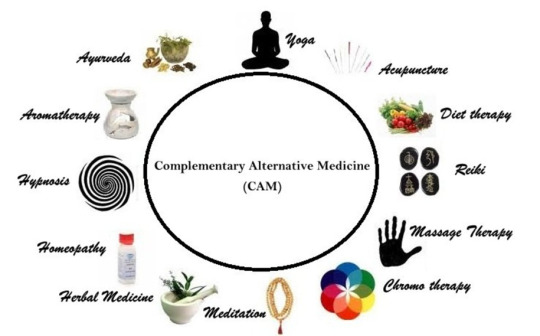
Fig-4: Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM)
(Source: Jain, 2017)
Types of CAM
According to Johns Hopkins (2024), CAM encompasses five main categories:
Mind-body therapies: Yoga, tai chi, meditation, and hypnosis are a few examples. Biologically based practices: This group includes natural goods, dietary supplements, and herbal medicines.
Energy healing procedures: The manipulation of the body's energy fields is the main goal of methods such as qigong, reiki, and acupuncture.
Manipulative and body-based practices: This includes massage treatment, acupuncture, and chiropractic adjustments.
Whole medical systems: Whole medical systems include conventional therapeutic modalities including homoeopathy, Ayurveda, and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM).
Benefits of CAM
CAM treatments appear to have a wide range of positive effects on one's emotional, mental, and physical health, according to research (Mora et al., 2022). For instance, studies on CAM have demonstrated its ability to lower stress, ease pain, promote better sleep, and improve the general quality of life (Tidy, 2022). Furthermore, complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) can aid in the management of symptoms related (Trkulja & Barić, 2020), and linked to long-term illnesses.
Practices Of CAM
Mindful breathing is an easy-to-try yet powerful complementary and alternative medicine technique. Close your eyes, find a comfortable posture, and concentrate on your breathing. Breathe in deeply with your nose, feeling your lungs expand, and then slowly release any tension by exhaling through your mouth. For a few minutes, keep doing this, allowing yourself to let go of any tension and worry and to become totally present in the here and now.
According to research by Wemrell et al., (2020), patients very frequently choose and select complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) over traditional treatments in Swedish mental hospitals. Similarly, Thomson-Casey et al., (2023) observed that the appropriate use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is growing and developing in mental healthcare settings just because of its capacity to reduce pharmaceutical dependency, enhance treatment results, and relieve symptoms.
With a very broad range of treatments and procedures, complementary and alternative medicine provides and offers a comprehensive approach to health and wellness (Tangkiatkumjai et al., 2021). CAM could be much more helpful if you are hoping to improve and enhance your general well-being, manage stress and anxiety, or get relief from physical illnesses.
References
Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/survivors/patients/complementary-alternative-medicine.htm#:~:text=Complementary%20and%20alternative%20medicine%20are,used%20instead%20of%20standard%20treatments.
Jain, A. S. (2017). Top 10 complementary and alternative medicine therapies that work - hubpages. https://discover.hubpages.com/education/Complementary-Alternative-Medicine-Therapies-cam-meaning-difference
Johns Hopkins (2024). Types of Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/types-of-complementary-and-alternative-medicine
Thomson-Casey, C., Adams, J., & McIntyre, E. (2023). The engagement of psychology with complementary medicine: A critical integrative review. Heliyon, 9(10). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844023084098
Tidy, C. (2022). Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://patient.info/treatment-medication/complementary-and-alternative-medicine-cam
Wemrell, M., Olsson, A., & Landgren, K. (2020). The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) in psychiatric units in Sweden. Issues in mental health nursing, 41(10), 946-957. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/01612840.2020.1744203#:~:text=CAM%20was%20here%20described%20as,somatic%20sensations%20and%20well%2Dbeing.
Mora, D. C., Kristoffersen, A. E., Overvåg, G., Jong, M. C., Mentink, M., Liu, J., & Stub, T. (2022). Safety of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) treatment among children and young adults who suffer from adverse effects of conventional cancer treatment: A systematic review. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 21, 15347354221105563. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/15347354221105563
Tangkiatkumjai, M., Boardman, H., & Walker, D. M. (2020). Potential factors that influence usage of complementary and alternative medicine worldwide: a systematic review. BMC complementary medicine and therapies, 20, 1-15. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12906-020-03157-2
Trkulja, V., & Barić, H. (2020). Current research on complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) in the treatment of anxiety disorders: an evidence-based review. Anxiety Disorders: rethinking and understanding recent discoveries, 415-449. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_22 Healthify. (2024, March 19). Complementary and Alternative Medicine | Healthify. Healthify. https://healthify.nz/medicines-a-z/c/complementary-and-alternative-medicine/#:~:text=The%20term%20complementary%20and%20alternative%20medicine%20%28CAM%29%20is,used%20together%20with%20conventional%20medicine%2C%20it%27s%20considered%20%E2%80%98complementary%E2%80%99
0 notes
Text
Mindfulness
Title: “Cultivating Presence: The Power of Mindfulness for Wellbeing”
It is very simple to become engaged in everyday life in today's fast-paced world, frequently at the price of our ability and capacity to stay in the present. One method to rebuild that connection is through the practice of mindfulness, which has its roots in old meditation traditions (Oman, 2023). It significantly entails embracing the current moment without passing judgment on it and deliberately focusing one's attention on it. Let's look at some useful mindfulness exercises and examine the advantages of mindfulness that are supported by scientific data.
Benefits of Mindfulness
An abundance of research has demonstrated and illustrated the numerous advantages of integrating mindfulness into one's everyday practice. Mindfulness has earned attention in the medical and psychiatric fields for its ability to reduce stress and anxiety (Lomas et al., 2019), as well as improve general well-being.

Fig-3: Benefits of Mindfulness
(Source: Smith, 2023)
Harvard Health research has demonstrated that mindfulness meditation improves and enhances both physical and emotional health, as well as lowering symptoms of chronic pain, anxiety, and despair. Further benefits of mindfulness include reduced blood pressure (HelpGuide, 2024), better sleep, and enhanced coping strategies for stress management.
How Mindfulness Works
According to German-Ponciano et al., (2023), mindfulness encourages people to embrace their experiences, including difficult emotions, rather than reacting with aversion or avoidance. People can become more self-aware and emotionally resilient by just monitoring their thoughts (HelpGuide, 2024), and feelings without passing judgment.
Mindfulness Practices
People can develop present-moment awareness by engaging in a variety of mindfulness practices (Levit-Binnun et al., 2021). Basic mindfulness meditation is a popular method in which practitioners let their thoughts come and go without attachment while focusing on their breath or a mantra that they repeat (Chow, 2021). During body scan meditation, one methodically examines each region of the body, noting any pain or sensations without passing judgment.
By removing labels and preconceived ideas, sensory awareness enables people to pay attention to the sights, sounds, tastes, smells, and touches in their surroundings (Kakoschke et al., 2021). To observe emotions with compassion and avoid becoming overwhelmed by them (HelpGuide, 2024), people who practise emotion-focused mindfulness must name and acknowledge their feelings as they emerge.
One effective strategy to improve present-moment awareness is to include mindfulness in routine tasks (Hoshaw, 2022). By focusing entirely on their sensations without interruption, people can practise mindfulness while eating, walking, or engaging with others. People may strengthen their bonds with themselves and their environment by taking their time (News in Health, 2021), and appreciating each moment.
Overall, living in the present moment more fully and acceptingly can be achieved via the transforming practice of mindfulness. Scientific research has demonstrated that mindfulness activities can improve mental, emotional, and physical well-being. People may develop a stronger feeling of calm, resilience, and connectedness to both themselves and the outside world by incorporating mindfulness into their everyday lives through easy-to-do yet profound exercises.
References
Chow, S. (2021). Meditation spirituality and religion. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Meditation-Spirituality-and-Religion.aspx
German-Ponciano, L. J., Zapata-de la Rosa, M. F., Molina-Cadena, B. I., Velasco-Gómez, Y. S., & Puig-Lagunes, Á. A. (2023). Effectiveness evaluation of online Mindfulness in mental health and alcohol consumption in medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Salud mental, 46(2), 45-54. https://www.medigraphic.com/cgi-bin/new/resumen.cgi?IDARTICULO=111333
HelpGuide. (2024). Benefits of Mindfulness. https://www.helpguide.org/harvard/benefits-of-mindfulness.htm#:~:text=If%20greater%20well%2Dbeing%20isn,sleep%2C%20and%20alleviate%20gastrointestinal%20difficulties.
Hoshaw, C. (2022, March 29). What is Mindfulness? A Simple Practice for Greater Well-being. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/mind-body/what-is-mindfulness#:~:text=Mindfulness%20is%20the%20practice%20of%20gently%20focusing%20your,during%20everyday%20activities%2C%20like%20cooking%2C%20cleaning%2C%20or%20walking.
Kakoschke, N., Hassed, C., Chambers, R., & Lee, K. (2021). The importance of formal versus informal mindfulness practice for enhancing psychological wellbeing and study engagement in a medical student cohort with a 5-week mindfulness-based lifestyle program. PLoS One, 16(10), e0258999. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0258999
Levit-Binnun, N., Arbel, K., & Dorjee, D. (2021). The mindfulness map: A practical classification framework of mindfulness practices, associated intentions, and experiential understandings. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 727857. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.727857
Lomas, T., Medina, J. C., Ivtzan, I., Rupprecht, S., & Eiroa-Orosa, F. J. (2019). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on the well-being of healthcare professionals. Mindfulness, 10, 1193-1216. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12671-018-1062-5
News in Health. (2021). Mindfulness for your health. https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2021/06/mindfulness-your-health#:~:text=Studies%20suggest%20that%20focusing%20on,help%20people%20cope%20with%20pain.
Oman, D. (2023). Mindfulness for global public health: Critical analysis and agenda. Mindfulness, 1-40. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12671-023-02089-5
Smith, L. (2023, September 18). 32 Health-Boosting Benefits of Mindfulness. The Good Body. https://www.thegoodbody.com/mindfulness-benefits/
0 notes
Text
Nutrition and Wellbeing
Title: “Fuel Your Wellbeing: The Impact of Nutrition on Mental and Physical Health”
Welcome to our blog content on nutrition and well-being! We will explore the intriguing relationship between diet and general health today, with an emphasis on both physical and mental well-being.

Fig-1: Human Nutrients
(Source: Mey, 2023)
According to Kiani et al., (2022), nutrition is essential for preserving normal bodily functions while preventing malfunction brought on by a variety of internal or external influences. Maintaining well-being and excellent health depends on proper nutrition (Nithiyanantham et al., 2019). A varied, well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients, including water, vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats, and carbs, is necessary for human consumption (GGI Insights, 2024). Did you know that eating a healthy diet has a significant influence on your mental and physical health as well? Let's explore how.
The Relationship Between Nutrition and Mental Health
Research significantly highlights and indicates that supporting brain health and cognitive performance requires a very well-balanced diet high in nutrients (Puri, Shaheen, & Grover, 2023). For the maintenance of brain health and cognitive function, very essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals are very essential (Fekete et al., 2023). Similar to how our bodies need fuel to operate at their best, our brains too need a consistent supply of nutrients to support the creation of neurotransmitters and cognitive functions.

Fig-2: Link Between Nutrition and Mental Health
(Source: Grajek et al., 2022)
Effect on Emotions and Mood
There is significant evidence that certain meals and dietary habits impactfully affect mood and mental health. According to analysis, eating more fruits and vegetables and omega-3 fatty acids is associated with reduced anxiety (Aucoin et al., 2021). For instance, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, nutritious grains, and lean meats are very closely linked to a decreased risk of depression, stress, and anxiety (Headlight, 2021). However, consuming an excessive amount of much more processed meals that are very heavy in sugar and refined carbs can exacerbate mental health issues (Sutter Health, 2024), and result in addictive eating behaviours.
Preventive Strategies Using Nutrition
Maintaining and obeying a nutritious diet lowers the likelihood of developing chronic illnesses including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain malignancies in addition to enhancing and increasing mental health (Headlight, 2021). Nutrient density was evaluated using the Nutrient-Rich Food Index and the Nutrient-Rich Diet Index, accounting for around 11% (n = 16) of the health outcomes (Harrison et al., 2023). People may safeguard and preserve their general health and quality of life by giving much more priority to nutrient-rich meals and minimising the consumption of harmful choices.
Practice on Nutritional Health
Expand The Variety on Your Plate: To significantly make sure you are receiving a wide range of very appropriate nutrients, including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats in your meals.
Mindful Eating: Eat slowly, focus-free, and take note of your body's signals of hunger and fullness. Savour each meal.
Stay Hydrated: To stay much more hydrated and support body processes, take lots of water throughout the day.
Reduce Your Intake of Processed Foods: Reduce and minimise the appropriate amount of packaged and processed foods that are rich in salt, bad fats, and added sugars.
References
Aucoin, M., LaChance, L., Naidoo, U., Remy, D., Shekdar, T., Sayar, N., ... & Cooley, K. (2021). Diet and anxiety: A scoping review. Nutrients, 13(12), 4418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124418
Fekete, M., Lehoczki, A., Tarantini, S., Fazekas-Pongor, V., Csípő, T., Csizmadia, Z., & Varga, J. T. (2023). Improving Cognitive Function with Nutritional Supplements in Aging: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Clinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Vitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants, and Other Dietary Supplements. Nutrients, 15(24), 5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245116
GGI Insights. (2024, April 3). Nutrition and Health: The Key to Well-Being and Longevity. Grey Group International. https://www.graygroupintl.com/blog/nutrition-and-health
Grajek, M., Krupa‐Kotara, K., Białek-Dratwa, A., Sobczyk, K., Grot, M., Kowalski, O., & Staśkiewicz, W. (2022). Nutrition and mental health: A review of current knowledge about the impact of diet on mental health. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.943998
Harrison, M., Palma, G., Buendia, T., Bueno-Tarodo, M., Quell, D., & Hachem, F. (2022). A scoping review of Indicators for Sustainable Healthy Diets. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2021.822263
Headlight. (2021). The importance of Good Nutrition for Mental and Physical health. Retrieved from https://headlight.health/the-importance-of-good-nutrition-for-mental-and-physical-health/
Kiani, A. K., Dhuli, K., Donato, K., Aquilanti, B., Velluti, V., Matera, G., ... & Bertelli, M. (2022). Main nutritional deficiencies. Journal of preventive medicine and hygiene, 63(2 Suppl 3), E93. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9710417/
Mey, J. T., Kirwan, J. P., & Axelrod, C. L. (2023). The Role of Nutrition in Mitigating the Effects of COVID-19 from Infection through PASC. Nutrients, 15(4), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040866
Nithiyanantham, S., Kalaiselvi, P., Mahomoodally, M. F., Zengin, G., Abirami, A., & Srinivasan, G. (2019). Nutritional and functional roles of millets—A review. Journal of food biochemistry, 43(7), e12859. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12859
Puri, S., Shaheen, M., & Grover, B. (2023). Nutrition and cognitive health: A life course approach. Frontiers in public health, 11, 1023907. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1023907
1 note
·
View note