Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
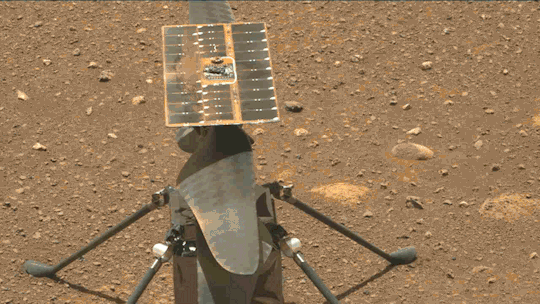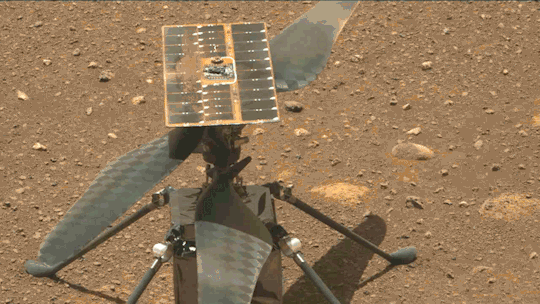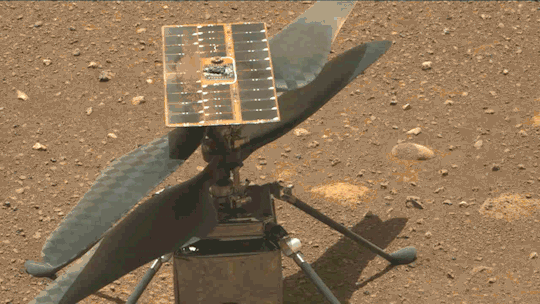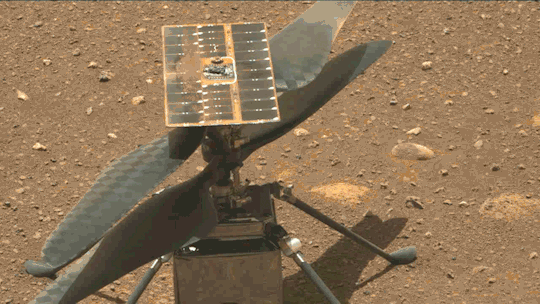
What We Learned from Flying a Helicopter on Mars

The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter made history – not only as the first aircraft to perform powered, controlled flight on another world – but also for exceeding expectations, pushing the limits, and setting the stage for future NASA aerial exploration of other worlds.
Built as a technology demonstration designed to perform up to five experimental test flights over 30 days, Ingenuity performed flight operations from the Martian surface for almost three years. The helicopter ended its mission on Jan. 25, 2024, after sustaining damage to its rotor blades during its 72nd flight.
So, what did we learn from this small but mighty helicopter?
We can fly rotorcraft in the thin atmosphere of other planets.
Ingenuity proved that powered, controlled flight is possible on other worlds when it took to the Martian skies for the first time on April 19, 2021.
Flying on planets like Mars is no easy feat: The Red Planet has a significantly lower gravity – one-third that of Earth’s – and an extremely thin atmosphere, with only 1% the pressure at the surface compared to our planet. This means there are relatively few air molecules with which Ingenuity’s two 4-foot-wide (1.2-meter-wide) rotor blades can interact to achieve flight.
Ingenuity performed several flights dedicated to understanding key aerodynamic effects and how they interact with the structure and control system of the helicopter, providing us with a treasure-trove of data on how aircraft fly in the Martian atmosphere.
Now, we can use this knowledge to directly improve performance and reduce risk on future planetary aerial vehicles.

Creative solutions and “ingenuity” kept the helicopter flying longer than expected.
Over an extended mission that lasted for almost 1,000 Martian days (more than 33 times longer than originally planned), Ingenuity was upgraded with the ability to autonomously choose landing sites in treacherous terrain, dealt with a dead sensor, dusted itself off after dust storms, operated from 48 different airfields, performed three emergency landings, and survived a frigid Martian winter.
Fun fact: To keep costs low, the helicopter contained many off-the-shelf-commercial parts from the smartphone industry - parts that had never been tested in deep space. Those parts also surpassed expectations, proving durable throughout Ingenuity’s extended mission, and can inform future budget-conscious hardware solutions.

There is value in adding an aerial dimension to interplanetary surface missions.
Ingenuity traveled to Mars on the belly of the Perseverance rover, which served as the communications relay for Ingenuity and, therefore, was its constant companion. The helicopter also proved itself a helpful scout to the rover.
After its initial five flights in 2021, Ingenuity transitioned to an “operations demonstration,” serving as Perseverance’s eyes in the sky as it scouted science targets, potential rover routes, and inaccessible features, while also capturing stereo images for digital elevation maps.
Airborne assets like Ingenuity unlock a new dimension of exploration on Mars that we did not yet have – providing more pixels per meter of resolution for imaging than an orbiter and exploring locations a rover cannot reach.

Tech demos can pay off big time.
Ingenuity was flown as a technology demonstration payload on the Mars 2020 mission, and was a high risk, high reward, low-cost endeavor that paid off big. The data collected by the helicopter will be analyzed for years to come and will benefit future Mars and other planetary missions.
Just as the Sojourner rover led to the MER-class (Spirit and Opportunity) rovers, and the MSL-class (Curiosity and Perseverance) rovers, the team believes Ingenuity’s success will lead to future fleets of aircraft at Mars.
In general, NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions test and advance new technologies, and then transition those capabilities to NASA missions, industry, and other government agencies. Chosen technologies are thoroughly ground- and flight-tested in relevant operating environments — reducing risks to future flight missions, gaining operational heritage and continuing NASA’s long history as a technological leader.
youtube
You can fall in love with robots on another planet.
Following in the tracks of beloved Martian rovers, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter built up a worldwide fanbase. The Ingenuity team and public awaited every single flight with anticipation, awe, humor, and hope.
Check out #ThanksIngenuity on social media to see what’s been said about the helicopter’s accomplishments.
youtube
Learn more about Ingenuity’s accomplishments here. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
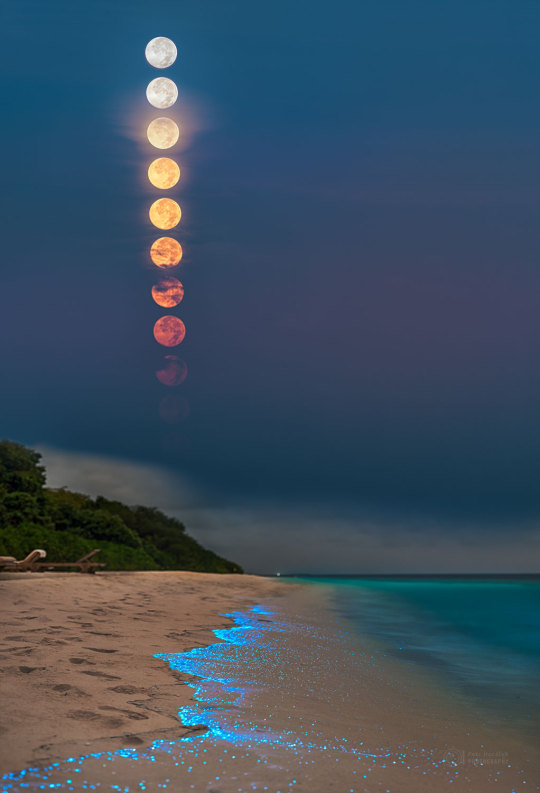

Full Plankton Moon over Maldives l Petr Horálek via NASA APOD
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sakura to Supernova
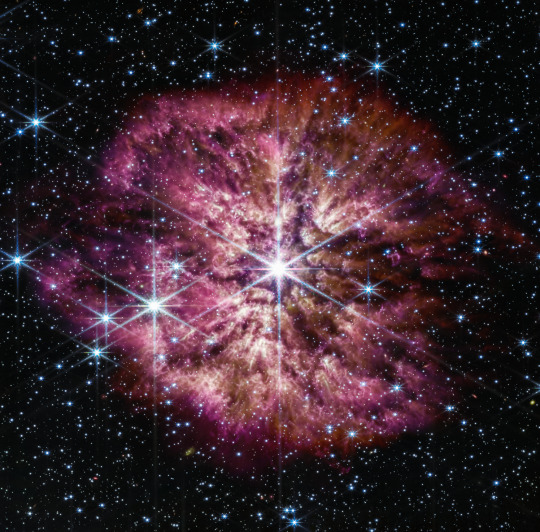

This rare sight is a super-bright, massive Wolf-Rayet star. Calling forth the ephemeral nature of cherry blossoms, the Wolf-Rayet phase is a fleeting stage that only some stars go through soon before they explode.
The star, WR 124, is 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. It is 30 times the mass of the Sun and has shed 10 Suns worth of material – so far. As the ejected gas moves away from the star and cools, cosmic dust forms and glows in the infrared light detectable by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope.
The origin of cosmic dust that can survive a supernova blast is of great interest to astronomers for multiple reasons. Dust shelters forming stars, gathers together to help form planets, and serves as a platform for molecules to form and clump together, including the building blocks of life on Earth.
Stars like WR 124 also help astronomers understand the early history of the universe. Similar dying stars first seeded the young universe with heavy elements forged in their cores – elements that are now common in the current era, including on Earth.
The James Webb Space Telescope opens up new possibilities for studying details in cosmic dust, which is best observed in infrared wavelengths of light. Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera balances the brightness of WR 124’s stellar core and the knotty details in the fainter surrounding gas. The telescope’s Mid-Infrared Instrument reveals the clumpy structure of the gas and dust nebula of the ejected material now surrounding the star.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
5K notes
·
View notes
Text


State schools should be free. Community College should be free.
Student debt should not be public policy.
[Private schools will always have billions in endowments and charge $50,000 per year. ]
21K notes
·
View notes














