Text
CRITERIA IN EVALUATING MEDIA CONTENT
Leyte Normal University
College of Arts and Sciences
LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE UNIT
Submitted by:
JELEANNA IMECILLE BATICA
MAVEL ANGELA GOMBA
KEMUEL RABI
Submitted to:
MR. ROGELIO TICOY, JR.
Introduction
Language is one of the most important aspects of human life. Its role is crucial in the process of communication. Language is acquired by individuals which is used every micro second. It shapes our thoughts, ideas, and reflects our own culture and society. It introduces us to reality because we use it in all aspects of our lives, be it verbally or through physical or nonverbal communication. Language is considered as an avenue for which people communicate and interact with the world; therefore, it is highly important for us to use the correct language in the different types of media that people in the contemporary world uses for education, advertising, disseminating news around the globe, entertainment, etc. The evolution of the different types of media creates for us a room full of excitement, knowledge, and exploration because through the print and visual media, we gain information that makes us more logical, be educated, and see the world and the people through pictures or photography and texts that we read and hear from the television, newspaper, etc.; electronic broadcasting media which is very convenient for people who suffers from blindness, but many people are still listening to radio broadcasts because it is where local news is being disseminated and it also a room for entertainment and relaxation by listening to old and new songs being played; outdoor and transit media which is an important content used for businesses to advertise a product, place (e.g., tourist spots, hotels), food, etc., through the use of billboards or other strategies that would catch the attention of the target market; and, digital media which is so broad and very useful especially in the modern world where most people make use of it in terms of getting different kinds of information through the use of mobile phones, laptop, and other devices—may it be educational, for entertainment purposes, finding a job, running a business, etc. Therefore, media without language is nothing, as well as language without media will not be recognized its importance and worse, there will be no unity from one country to the other because people will not be able to learn other languages without the existence of media.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
REGISTERS- Linguistically, Registers is defined as the way a speaker uses a language differently in different circumstance. Registers are marked by a variety of specialized vocabulary and turns of phrases, colloquialisms and the use of jargon, and a difference in intonation and pace.
STYLISTICS- is the study of the devices in languages (such as rhetorical figures and syntactical patterns) that are considered to produce expressive or literary style.
GRAMMAR- is the whole system and structure of a language or of languages in general, usually taken as consisting of syntax and morphology (including inflictions) and sometimes also phonology and semantics.
SEMIOTICS- is an investigation into how meaning is created and how meaning is communicated. Its origins lie in the academic study of how signs and symbols (visual and linguistic) create meaning.
PRAGMATICS- is a branch of linguistics concerned with the use of language in social contexts and the ways people produce and comprehend meanings through language.
CRITERIA IN EVALUATING MEDIA CONTENT
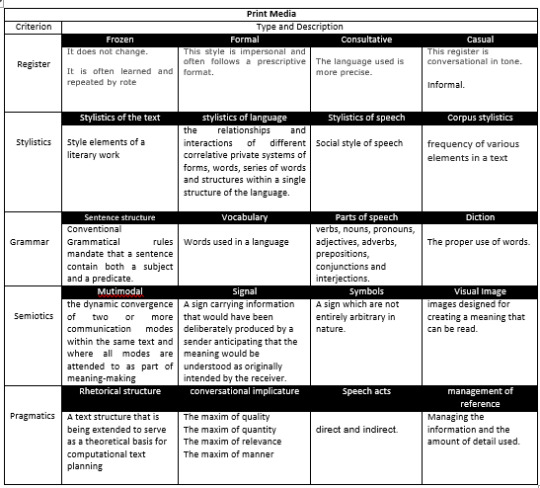
Print Media
Electronic Broadcasting Media

Visual Media

Outdoor Media

Digital Media

Transit Media

References
Akpan, Idorenyin & Akpan, Emilienne & Obukoadata, Presly. (2019). A Semiotic Deconstruction of Symbols in Print Advertising Contents: Implications for Consumers Purchase Decisions in Nigeria. 13-26.
E. A. Plekhanova, I. Y. Moiseeva. 2014. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science.
http://www.ijhssnet.com/journals/Vol_4_No_9_July_2014/26.pdf
PARSA, A. VISUAL SEMIOTICS: HOW STILL IMAGES MEAN? INTERPRETING STILL IMAGES BY USING SEMIOTIC APPROACHES.
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/781d/6950129265acd1b7646f77153a6be29b28d4.pdf
Nordquist, R. (2019). Stylistics and Elements of Style in Literature.
https://www.thoughtco.com/stylistics-language-studies-1692000#:~:text=Stylistics%20is%20a%20branch%20of,a%20distinctness%20to%20someone's%20writing.
Hickey, Raymond. Pragmatics. https://www.uni-due.de/ELE/Pragmatics.pdf
Nazar, M. 2014. Pragmatics Presentation. https://www.slideshare.net/mehwishnazar77/pragmatics-presentation-36657885
Tehseen, Iqra. 2015. Stylistics. https://www.slideshare.net/iqratehseen14/stylistics-45277719
https://creatingmultimodaltexts.com/modes-and-meaning-systems/
0 notes
Text
LANGUAGE AND MEDIA: EVALUATION ON THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF MEDIA THROUGH ITS LANGUAGE USE
Leyte Normal University
College of Arts and Sciences
Language and Literature Unit
EVALUATING THE LANGUAGE USE IN DIFFERENT TYPES OF MEDIA
A Concept Paper
Submitted by:
JELEANNA IMECILLE N. BATICA
MAVEL ANGELA GOMBA
KEMUEL RABI
Submitted to:
MR. ROGELIO TICOY, JR.
Instructor, Language and Media
INTRODUCTION
Language is one of the most important aspects of human life. Its role is crucial in the process of communication. Language is acquired by individuals which is used every micro second. It shapes our thoughts, ideas, and reflects our own culture and society. It introduces us to reality because we use it in all aspects of our lives, be it verbally or through physical or nonverbal communication. Language is considered as an avenue for which people communicate and interact with the world; therefore, it is highly important for us to use the correct language in the different types of media that people in the contemporary world uses for education, advertising, disseminating news around the globe, entertainment, etc. The evolution of the different types of media creates for us a room full of excitement, knowledge, and exploration because through the print and visual media, we gain information that makes us more logical, be educated, and see the world and the people through pictures or photography and texts that we read and hear from the television, newspaper, etc.; electronic broadcasting media which is very convenient for people who suffers from blindness, but many people are still listening to radio broadcasts because it is where local news is being disseminated and it also a room for entertainment and relaxation by listening to old and new songs being played; outdoor and transit media which is an important content used for businesses to advertise a product, place (e.g., tourist spots, hotels), food, etc., through the use of billboards or other strategies that would catch the attention of the target market; and, digital media which is so broad and very useful especially in the modern world where most people make use of it in terms of getting different kinds of information through the use of mobile phones, laptop, and other devices—may it be educational, for entertainment purposes, finding a job, running a business, etc. Therefore, media without language is nothing, as well as language without media will not be recognized its importance and worse, there will be no unity from one country to the other because people will not be able to learn other languages without the existence of media.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
REGISTERS- Linguistically, Registers is defined as the way a speaker uses a language differently in different circumstance. Registers are marked by a variety of specialized vocabulary and turns of phrases, colloquialisms and the use of jargon, and a difference in intonation and pace.
STYLISTICS- is the study of the devices in languages (such as rhetorical figures and syntactical patterns) that are considered to produce expressive or literary style.
GRAMMAR- is the whole system and structure of a language or of languages in general, usually taken as consisting of syntax and morphology (including inflictions) and sometimes also phonology and semantics.
SEMIOTICS- is an investigation into how meaning is created and how meaning is communicated. Its origins lie in the academic study of how signs and symbols (visual and linguistic) create meaning.
PRAGMATICS- is a branch of linguistics concerned with the use of language in social contexts and the ways people produce and comprehend meanings through language.
EVALUATING THE LANGUAGE USE IN THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF MEDIA
I. PRINT MEDIA
Print Media is the oldest medium of communication. Its purpose is to spread information by printing texts and images on paper with the use of printing press; selling it in cheaper value for it to be affordable among masses. Print media is composed of newspapers, magazines, books, banners, brochure, flyers, and other publications.
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Print Media:
Registers: The language used in writing news for newspapers, controversial issues for magazines, literary books and textbooks, and other publications uses a formal language that is comprehensible for any readers. In marketing also, the language used in creating an eye-catching advertisement with the use of banners, brochure, and flyers are formal in a way that people will easily get interested with the product.
Stylistics: In printed materials, it is necessary to use a formal language when writing outputs to present the facts and data thoroughly. For example, in newspapers, journalists should always include accurate facts and evidences when writing a story of a particular issue to gain the trust of their readers; therefore, for it to be understood, the language used should be in a formal style.
Grammar: Correct grammar structure and spelling is a major requirement that should be evident in all printed mediums. Books, newspapers, magazines are where people get knowledgeable information applied in their daily lives and even used for their education. Products that are being advertised using brochures and other advertising mediums should use a powerful tagline that will speak to the target market and it will only be effective if the catchphrase is grammatically correct because it will be fully apprehended.
Semiotics: Using signs, symbols, images in printed materials is important because it helps grab the attention of people to a particular product, to give readers an idea about the story or genre of a particular literary book that they would like to read, even in newspapers and magazines to let the readers know who, where, what are they reading is about.
Pragmatics: Correct use and construction of symbols, words, phrases, and sentences should always be considered especially when applied to these kinds of printed materials (as mentioned above) to avoid misinterpretations because not all people, if not mistaken, are grammatically intellect to really understand what the advertisement, the story, the news is trying to relay.
II. ELECTRONIC BROADCASTING MEDIA
Electronic Broadcasting Media is a channel through which every message is communicated usually through the use of radio and television, but as technology evolves, people can now broadcast through online streaming, and with the use of internet media-like websites also. Electronic broadcasting media is where people carefully listen to local news and at the same time, being entertained and relaxed by listening to old songs. One’s business can also be advertised through commercials which is cued in short news breaks.
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Electronic Broadcasting Media:
Registers: A formal type of register is frequently used in news broadcasting, relaying facts and information about life events, announcements and certain issues circulating in local areas. In entertainments, however, uses informal register to give entertainment to the listeners but not to the point that will ruin the image of their channel.
Stylistics: In broadcasting, we will notice that the style used by news anchors or DJs when speaking to their audience has a good impact or effect which makes them sit, listen and respond positively.
Grammar: Like readers notice grammatical imperfections on what they’re reading, so does listeners sensitively hear grammatical errors when they carefully listen to news anchors reporting of recent events, that is why newscasters must always make sure that what they will be reading are grammatically correct and the information that will be heard by the people are reliable and will not be misinterpreted.
Semiotics: In broadcasting, signs and cues from the production director is important, hence, it should not be ignored. While in television, the use of signs, symbols, and images is applied for advertisements to catch the attention of the viewers.
Pragmatics: Electronic broadcasting media uses a language that is only applicable in the news field which is also comprehensible for the listeners.
III. VISUAL MEDIA
Visual media can be used in any subject matter especially in presenting texts through visuals such as data presented through graphs, tables, and illustrations like pie chart and projects through power point presentations. It is also used to designate things like TV movies, photography, paintings, etc. It is very important because it also caters visual learners’ needs especially to the young generations who will eventually be introduced to the world of new technology.
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Visual Media:
Registers: There are different registers used in Visual Media depending on the content presented. For example, business or marketing presentations uses a formal register in presenting the data during a board meeting. On the contrary, TV movies uses different kinds of language register depending on its genre. It may be casual, intimate, or consultative.
Stylistics: Visual Media is more attracting and interesting than the other types of media because of its vividness. It lets us interpret things deeper more than what we see and perceive its true meaning.
Grammar: This type of media uses informal grammar specifically in American movies or series wherein the characters uses slang words in their conversation depending on the situation they’re in or the story itself. However, in photography and paintings, it speaks different languages with different grammar structure. It depends on how one will perceive it and communicate with it.
Semiotics: Visual Media uses different kinds of signs and symbols depending on the content. Signage and other road signs are made to instruct people on what they should do and should not do on that particular place or in the streets; where this particular place is, etc., these leads us with just a glance because images, too, can be heard even by just looking at it. Furthermore, in paintings, people are able to interpret it because of the variety of color which has different symbolizations and emotions when applied.
Pragmatics: In movies, there are ways on how the characters deliver the message of the story effectively: they use a body language which is very important and effective to let the viewers understand the actor’s character; the use of gestures depending on his or her line to let the viewers be moved by the emotion implied by the character; and, using the correct intonation when speaking their lines to make it sound more interesting and real.
IV. OUTDOOR MEDIA
Outdoor media is typically consisting of any advertising seen outside and is primarily grouped into categories such as billboards, posters, etc. outdoor advertisements are the best medium to inform the moving population.
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Outdoor Media:
Registers: In advertising, the goal is to grab the attention of the people walking alongside the streets, people driving on high ways and waiting for the traffic to move; so, the language register they use to promote their product is casual to make it more attractive and effective.
Grammar: This type of media uses informal grammar because in advertising, the words used in promoting a product need not be lengthy to make sure that the target market will be able to read the words written on the billboard or posters while walking down the streets. Therefore, business marketing professionals come up with new morphemes that they think will attract everyone who belongs to different social classes.
Semiotics: Outdoor Media uses signs that lets people see straight through its meaning without having a hard time analyzing it. It uses images to make it more engaging.
Pragmatics: Using limited words in advertising, with the use of Outdoor Media, is necessary to make it more noticeable and legible. Different strategies are deeply thought to come up with new combination of words that will positively attract the target market.
V. DIGITAL MEDIA
The Digital Media is now a frontline of all types of media. A weather app on a smartphone, a racing game on a video game console, and an ultrasound imaging device in a hospital are all digital media products. They are successful because they are engaging, easy to use, and deliver results. The world we live today is populated by digital media products, and these products enable and deliver experiences in many industries, including industries that aren’t typically associated with digital media—such as health, government, and education (What is Digital Media, 2007).
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Digital Media:
Registers: Digital Media uses different kinds if language registers: casual, consultative, intimate, and formal register; but it still depends on the context. For example, in social media accounts (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram), it uses casual register and even intimate. In email, delivered and received messages are more formal and sometimes consultative depending on the message being delivered to and received from.
Stylistics: In Digital Media, the style of writing depends on what the person wants to convey based on his or her content. For example, in social medias, people are more comfortable in conveying their message because it is not that necessary to be technical. They decide to use punctuation marks freely and not minding its correct use at all; some even construct new words just to express their feelings or what comes out from their mind.
Grammar: In Digital Media, specifically social medias, people are given the freedom to express their thoughts without attending to its correct use of grammar. Although, other social media users make sure that their grammar structure is correct before posting their thoughts online because they avoid criticisms; but some posts are for professional or academic purposes that’s why it is really necessary for the content to be grammatically correct.
Semiotics: Digital Media uses icons and graphic designs that would attract the users. They use these symbols to let the users know what the application is about or what it is exactly. The usage of images and encoding texts based on the image are also important in Digital Media for it to be more understood.
Pragmatics: Since Digital Media is virtual and it is widely used for communication nowadays, can a person really know if the person that he or she is talking to from the other line is feeling the exact same emotion as he encodes his message? This is the problem with this type of media, the language used is not as we expect it to be, that’s why it is important for the users to be more sensible and logical in communicating.
VI. TRANSIT MEDIA
Target marketing accurately knows product and brand market, and because your target market is not recluse nor retires in their twilight years, they move a travel within their community, city, province or region. In other words, it is imperative for them to travel anywhere they like. Because of this fundamental need, Transit Media innovatively popularize the use of these as tools of advertising-buses, taxis, jeepneys, tricycles, and school buses. With Transit Media, advertising and communicating to your target market need not be expensive. Transit Media is the welcome alternative to traditional advertising in hard times like these and more so in prosperous times.
The following are the evaluation of the language used in Transit Media:
Registers: Transit Media uses different kinds of language registers depending its content: formal, consultative, static, or casual.
Stylistics: Transit Media uses formal and informal style of writing depending on the message that it wants to convey.
Grammar: Transit Media uses informal grammar because of its rule to only use limited words to easily catch the attention of the target market and for it to be immediately read since it is posted on jeepneys and other advertising-buses.
Semiotics: Since advertising in this type of media is not steadily displayed on the streets, rather on buses or jeepneys, they do not use symbols or other signs that would make the advertising complicated to understand.
Pragmatics: Transit Media is more comprehensible than the other types of media because it should be direct to the point, but still depends on what is being advertised.
CONCLUSION
Media Language is the way in which the meaning of a media text is conveyed to the audience (Orlebar, 2009). Media, as a part of communication, need a language to convey its meaning; therefore, we need words and language code, verbal and nonverbal communication to reach the audience, text and writing in a specific language for making newspapers, news on magazine, TV and online media. Media and language are indeed inseparable despite its unique differences, for we will not be able to construct any interpretation if language is not used in media as well as media in language.
REFERENCE(S):
Orlebar, J. (2009). Understanding media language. Retrieved from http://media.edusites.co.uk/article/understanding:media-language/
No Author (2007). What is digital media? Retrieved from https://thecdm.ca/prgram/digital-media
Jeremy Orlebar (2009) Understanding Media Language retrieved at 25/11/2015 from: http://media.edusites.co.uk/article/understanding-media-language/
Matthews, J. (2000). The Role of Print Media in Education. Retrieved from http://pmg-assets.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/docs/2000/appendices/000912PrintMedia.htm
Bote, K. (2013). Evolution of Print Media. Retrieved from https://prezi.com/rlp7jssriw-t/chapter-12-evaluation-of-print-media/?fallback=1
Burke, M. (2014). The Routledge Handbook of Stylistics. Retrieved from https://www.routledge.com/The-Routledge-Handbook-of-Stylistics-1st-Edition/Burke/p/book/9781138297838
Miriam B. (2019). The Influence of Modern Electronic Media on the Usage of the English Language. Retrieved from https://m.grin.com/document/468191
Maillat, D. (2008). "Broadcast Yourself!" The Future of Broadcast English in an IT Age. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/26430877https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/register
Nordquist, R. (2019) Stylistics and Elements of Style in Literature. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/stylistics-language-studies-1692000
Veszelszki Á. (2017). Digilect. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110499117
1 note
·
View note