Text
𝗢𝗘𝗧 𝗘𝘅𝗮𝗺𝗶𝗻𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗛𝗲𝗮𝗹𝘁𝗵 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗳𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻𝗮𝗹𝘀
The OET (Occupational English Test) is an international English language test designed specifically for healthcare professionals. It assesses the language communication skills of healthcare workers who wish to register and practice in an English-speaking environment.
𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗱𝗲𝘁𝗮𝗶𝗹𝘀 𝗼𝗳 𝗢𝗘𝗧:
Full Form: Occupational English Test
Purpose: To assess English proficiency of healthcare professionals
For Whom: Doctors, Nurses, Dentists, Pharmacists, Physiotherapists, and 12 other healthcare professions
Accepted: In UK, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, Dubai, Singapore, and more
𝗧𝗲𝘀𝘁 𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗮𝘁
4 sub-tests: Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking
Test Duration: Approximately 3 hours
Scoring Each sub-test graded A (highest) to E (lowest)
Passing Grade: Most institutions require at least B (350-450 score) in each sub-test
Test Delivery: On paper, computer at test centers, or at home (OET@Home)
𝗧𝗲𝘀𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗿𝘂𝗰𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲:
1.Listening (approx. 45 minutes):
Part A: Consultation extracts
Part B: Workplace extracts
Part C: Presentations or interviews
2.Reading (60 minutes):
Part A: Expeditious reading (skim and scan)
Part B & C: Careful reading (understanding gist, purpose, detail)
3.Writing (45 minutes):
One task: Typically a referral, discharge, or transfer letter based on case notes
Profession-specific
4. Speaking (20 minutes):
Profession-specific role plays
2 role plays where you interact as a healthcare professional with a patient or relative
𝗧𝗲𝘀𝘁 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘀
Available multiple times per month
Can be booked through the official OET website
𝗣𝗿𝗲𝗽𝗮𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗧𝗶𝗽𝘀:
Understand the real-life workplace context used in the OET.
Practice profession-specific vocabulary.
Use official OET Practice Books and Sample Tests.
Get familiar with the letter-writing format for your profession.
Work on fluency and empathy in speaking role plays.

0 notes
Text
𝗣𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗰𝘁 𝗟𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿 𝘁𝗼 𝗟𝗶𝘃𝗲 தமிழில்
They are excreted by the kidneys only after two hours of drinking alcohol, but alcohol mixes with our blood within the next 4/5 seconds. The liver's struggle to separate the alcohol from the blood and provide a smooth flow of blood to the heart is what makes a person intoxicated, and the nerves of the brain are stimulated. If the liver does not do its job properly, the person will die shortly after drinking alcohol...
It is working tirelessly to save him and separate the alcohol mixed in his blood! It is a struggle, and the organ that fights like that is called the liver!
It produces more than a thousand enzymes.
Even if there is a small injury in our body and blood leaks, the brain immediately sends a message to the liver.
The frightened liver will immediately send a chemical called 'prothrombin' to the place where the blood is leaking.
That chemical will form a spider web-like structure at the place where the blood is leaking and cause the blood to clot.
This prevents the bleeding.
If the liver is not doing its job, a small injury is enough to kill us.
Today, whether it is a mild headache, weight loss, or nutritional deficiency, we take pills.
All these pills are full of toxins.
The liver protects our body by preventing that toxicity from entering the body.
Alcohol also contains a lot of toxins. The liver fights all night to remove that toxicity.
Only until the liver fights against the poison can alcoholics speak without stopping, no matter how much they drink.
If the liver is damaged, they cannot even breathe steadily. Then where can they speak?
If a person's liver is not working properly, no matter what food they eat, it will not digest. Like sour dough in the stomach, it is in the stomach and intestines...
This is such an important digestive organ. Therefore, we should not give it a hard time by saying, 'No matter how much you beat it, it will be fine.' When you drink excessively, you cannot prevent liver inflammation.
The liver is compared to a donkey. No matter how much weight is placed on it, it will carry it without hesitation. If the same donkey lies down, it will never get up again.
The liver also keeps fighting the poison of alcohol without stopping!
To protect such a liver,
~ Alcohol and smoking should be avoided. ~
~ Milk tea, coffee and artificial soft drinks should be avoided. ~ Instead, you can drink blackcurrant coffee, sukku coffee, unsweetened inju tea and lemon tea, natural fruit juices, sugarcane juice, bitter gourd, buttermilk etc.
We should chew and swallow food slowly.
When we are feeling unwell, we should prioritize rest.
~ We should avoid taking English medicines as much as possible. ~
Let's protect the liver and live well!!!!
மது அருந்தி இரண்டு மணி நேரத்திற்கு பிறகுதான் அவை சிறுநீரக வெளியேற்றப்படுகிறது, ஆனால் ஆல்கஹால் அடுத்த 4/5 நொடியிலேயே நம் இரத்தத்தில் கலந்துவிடுகிறது, இரத்தத்தின் ஆல்கஹலை பிரித்து இதயத்தில் சீரான இரத்த ஓட்டத்தை கொடுக்க கல்லீரலின் போராட்டமே மனிதனுக்கு அது போதையாக மூலையின் நரம்புகள் தூண்டப்படுகிறடது, கல்லீரல் அதனுடைய வேலையை சரியாக செய்யவில்லை என்றால் மது அருந்திய சிறிது நேரத்திலேயே மனிதன் இறந்து போய்விடுவான்...
அவனைக் காப்பாற்றவும், அவனது ரத்தத்தில் கலந்த ஆல்கஹாலை பிரிக்கவும் ஒரு நொடிகூட ஓயாமல் உழைத்துக் கொண்டிருக்கும் ! அது ஒரு போராட்டம், அப்படி போராடும் உறுப்பின் பெயர் கல்லீரல் !
இது ஆயிரத்திற்கும் மேலான என்சைம்களை உருவாக்குகிறது.
நமது உடலில் சிறிய காயம் ஏற்பட்டு ரத்தம் வெளியேறினால் கூட உடனே மூளை கல்லீரலுக்கு தான் தகவல் அனுப்பும்.
பதறிப்போன கல்லீரல் நொடிப் பொழுதில் ரத்தம் வெளியேறும் இடத்திற்கு 'ப்ரோத்ரோம்பின்' என்ற ரசாயனத்தை அனுப்பி வைக்கும்.
அந்த ரசாயனம் ரத்தம் வெளியேறிக் கொண்டிருக்கும் இடத்தில் ஒரு சிலந்தி வலைப் போன்ற ஒரு அமைப்பை ஏற்படுத்தி ரத்தத்தை உறைய செய்துவிடும்.
இதனால் ரத்த வெளியேற்றம் தடுக்கப்படுகிறது.
கல்லீரல் மட்டும் இந்த வேலையை செய்ய வில்லை என்றால் ஒரு சின்ன காயம் போதும் நம்மைக் கொல்வதற்கு.
இன்றைக்கு லேசான தலைவலி என்றாலும், உடல் மெலிவதற்கு என்றாலும், சத்துப் பற்றாக்குறை என்றாலும் மாத்திரைகளாக உள்ளே தள்ளுகிறோம்.
இந்த மாத்திரைகள் எல்லாவற்றிலும் நச்சுத் தன்மை நிறைந்திருக்கிறது.
அந்த நச்சுத்தன்மையை உடலில் சேராமல் தடுத்து நம் உடலை பாதுகாப்பது கல்லீரல்தான்.
மதுவிலும் ஏராளமான விஷத்தன்மை உள்ளது. அந்த விஷத்தன்மையை போக்குவதற்காக இரவு முழுவதும் கல்லீரல் போராடுகிறது.
கல்லீரல் விஷத்திற்கு எதிர���க போராடும் வரைதான் குடிகாரர்கள் எவ்வளவு குடித்தாலும் அசராமல் நிற்பேன் என்று வசனம் பேசமுடியும்.
கல்லீரல் கெட்டு விட்டது என்றால் அவரால் ஸ்டெடியாக மூச்சுக் கூட விடமுடியாது. அப்புறம் எங்கு வசனம் பேசுவது.
கல்லீரல் ஒருவருக்கு சரியாக இல்லையெனில், சாப்பிடும் எந்த உணவும் செரிக்காது. வயிறு உப்பி புளித்த மாவு போல அது வயிற்றிலும் குடலிலும் இருக்கிறது...
அத்தகைய முக்கியமானதொரு ஜீரண உறுப்பு இது. அதற்காக ‘எவ்ளோ அடிச்சாலும் தாங்குதே; ரொம்ப நல்லது போல’ என்று தாறுமாறாக அதற்குக் கஷ்டம் கொடுக்கக் கூடாது. கண்மூடித்தனமாக அளவு கடந்து குடிக்கிறபோது கல்லீரல் வீக்கத்தைத் தடுக்க இயலாது.
கல்லீரலை கழுதையோடு ஒப்பிடுவார்கள். கழுதை எவ்வளவு பாரத்தை அதன் மீது தொடர்ந்து ஏற்றிக் கொண்டே இருந்தாலும் அசராமல் சுமக்கும். அதே கழுதை படுத்துவிட்டால் திரும்பவும் எழுந்திருக்கவே எழுந்திருக்காது.
கல்லீரலும் அப்படிதான் தொடர்ந்து குடிக்க குடிக்க மது என்னும் விஷத்தோடு ஓயாமல் தொடர்ந்து போராடிக்கொண்டே இருக்கும் !
இத்தகைய கல்லீரலை காப்பாற்ற
~மதுவையும் புகையும் தவிர்க்க வேண்டும்.~
~பால் கலந்த டீ, காப்பி மற்றும் செயற்கை குளிர்பானங்கள் போன்றவற்றை தவிர்க்க வேண்டும்.~ அதற்கு பதிலாக கருப்பட்டி காப்பி, சுக்கு காப்பி, பால் கலக்காத இஞ்சு டீ மற்றும் எலுமிச்சை டீ, இயற்கையான பழச்சாறுகள், கரும்புச்சாறு, பதநீர், மோர் போன்றவற்றை பருகலாம்.
உணவை நிதானமாக மென்று விழுங்க வேண்டும்.
நமக்கு அசதியாக இருக்கும்போது ஓய்வுக்கு முன்னுரிமை அளிக்க வேண்டும்.
~முடிந்தவரை தொட்டதிற்கெல்லாம் ஆங்கில மருந்துக்கள் உட்கொள்வதை தவிர்க்க வேண்டும்.~
கல்லீரல் காத்து நலமாய் வாழ்வோம்!!!!

0 notes
Text
Did you know you don’t have to wash off your baby’s skin immediately after birth?
That creamy white stuff some babies are born with? It’s called vernix caseosa—and no, it’s not “dirt” or “mess.”
It’s actually your baby’s first protection.
How long did you wait before your baby's first bath? 24 hrs

0 notes
Text
Bronchial Asthma
🔘Nursing Science Focus:
Asthma is a reversible obstructive airway disease. Nurses are key in patient education, monitoring respiratory status, administering medications, and preventing attacks.
🔘Health Care Highlight:
Asthma control relies on identifying triggers, medication compliance, and emergency preparedness. Primary care nurses often lead asthma management programs.
🔘Disease Overview – Bronchial Asthma:
A chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways causing episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing, especially at night or early morning.
🔘Diagnostic Tools:
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio <70%)
Allergy Testing
Chest X-ray (to rule out other conditions)
🔘Treatment Options:
¹Rescue Medications: Short-acting beta-agonists (e.g., albuterol)
²Controller Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta-agonists
³Allergy management: Antihistamines, immunotherapy
🔘Side Effects of Treatment:
¹Inhaled corticosteroids: Oral thrush, hoarseness
²Beta-agonists: Tremors, palpitations
³Systemic steroids (if needed): Weight gain, mood swings
🔘Nursing Advice:
¹Teach proper inhaler/spacer technique
²Identify and help eliminate environmental triggers
³Monitor respiratory rate, O2 saturation, and PEFR
⁴Develop an asthma action plan with the patient
⁵Encourage yearly influenza and pneumococcal vaccines

0 notes
Text
Digital Addiction: How Screens Are Rewiring Your Brain
We live in a world surrounded by glowing screens. From the moment we wake up to the second we fall asleep, we’re plugged in—scrolling, watching, liking, swiping. But have you ever paused to ask: What is this doing to my brain?
The answer is startling: we're not just using technology—we're being shaped by it.
🔘The Hijack of Human Attention
Our attention is one of the most powerful and limited resources we have. Big tech companies know this. That’s why apps are designed not to inform or connect—but to hook.
▪️Endless scrolling ensures you never reach the end.
▪️Auto-play videos remove pause points.
▪️Likes, hearts, and shares give you quick dopamine bursts.
▪️Push notifications train your brain to crave interruptions.
The result? We’re constantly distracted, unable to focus, and mentally exhausted.
This isn’t just a bad habit—it’s neurochemical warfare.
🔘The Cost of Constant Connection
1.Reduced Deep Work Ability
When constantly switching tasks, the brain struggles to engage in deep, focused thought. This means fewer breakthroughs, less creativity, and declining productivity.
2.Increased Stress and Anxiety
Constant alerts and notifications trigger the fight-or-flight response, keeping your body in a mild state of panic throughout the day.
3.Sleep Disturbances
Blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production, harming your natural sleep cycle and reducing the quality of rest.
4.Lowered Emotional Intelligence
Real human interactions are being replaced by emojis and messages. The result? We’re losing the ability to read emotions, empathize, and communicate deeply.
🔘How to Break Free: A Digital Detox Strategy
1.Screen-Free Mornings
Avoid your phone for the first 60 minutes of the day. Start with sunlight, stretching, or journaling instead.
2.Turn Off Push Notifications
Reclaim your focus by muting unnecessary alerts. Your attention is sacred—guard it.
3.Establish "No-Screen Zones"
Keep phones out of the bedroom, dining table, and bathroom. These boundaries protect your mental space.
4.Set App Time Limits
Use tools like Focus Mode or Screen Time to control usage. Reward yourself with breaks after completing real tasks.
5.Practice Boredom
Boredom isn’t the enemy—it’s the gateway to creativity and clarity. Allow yourself time to do nothing. Let your mind wander.
🔘Rewiring Begins with Awareness
You’re not weak—you’re wired to crave stimulation. But the same brain that got hijacked can be rewired.
Every step away from digital addiction brings you closer to:
▪️Better sleep
▪️Deeper focus
▪️Genuine relationships
▪️Inner peace
🔘Final Message
Technology should serve you, not control you.
Take back your attention.
Rebuild your focus.
Live with intention—not addiction.

0 notes
Text
Some women receive the Tetanus injection during pregnancy without even knowing what Tetanus is or why the injection is important.
To some, it feels like just another routine jab given during ANC. But let me educate you...
Tetanus is a very dangerous infection caused by a bacterium called Clostridium tetani, usually found in soil, dust, and unclean instruments. It enters the body through cuts, wounds, or the umbilical cord — especially during unclean deliveries.
That’s why the Tetanus Toxoid (TT) vaccine is a vital part of antenatal care. It helps the mother develop strong immunity that also protects her baby.
Now, the reason it’s given during pregnancy is simple:
✅ It protects both mother and baby from tetanus.
✅ With 2 doses, you get 3 years of protection.
✅ With 5 doses, you get lifelong protection.
Tetanus is deadly. Please protect yourself and your baby.

0 notes
Text
Digital Addiction: How Screens Are Rewiring Your Brain
We live in a world surrounded by glowing screens. From the moment we wake up to the second we fall asleep, we’re plugged in—scrolling, watching, liking, swiping. But have you ever paused to ask: What is this doing to my brain?
The answer is startling: we're not just using technology—we're being shaped by it.
🔘The Hijack of Human Attention
Our attention is one of the most powerful and limited resources we have. Big tech companies know this. That’s why apps are designed not to inform or connect—but to hook.
▪️Endless scrolling ensures you never reach the end.
▪️Auto-play videos remove pause points.
▪️Likes, hearts, and shares give you quick dopamine bursts.
▪️Push notifications train your brain to crave interruptions.
The result? We’re constantly distracted, unable to focus, and mentally exhausted.
This isn’t just a bad habit—it’s neurochemical warfare.
🔘The Cost of Constant Connection
1.Reduced Deep Work Ability
When constantly switching tasks, the brain struggles to engage in deep, focused thought. This means fewer breakthroughs, less creativity, and declining productivity.
2.Increased Stress and Anxiety
Constant alerts and notifications trigger the fight-or-flight response, keeping your body in a mild state of panic throughout the day.
3.Sleep Disturbances
Blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production, harming your natural sleep cycle and reducing the quality of rest.
4.Lowered Emotional Intelligence
Real human interactions are being replaced by emojis and messages. The result? We’re losing the ability to read emotions, empathize, and communicate deeply.
🔘How to Break Free: A Digital Detox Strategy
1.Screen-Free Mornings
Avoid your phone for the first 60 minutes of the day. Start with sunlight, stretching, or journaling instead.
2.Turn Off Push Notifications
Reclaim your focus by muting unnecessary alerts. Your attention is sacred—guard it.
3.Establish "No-Screen Zones"
Keep phones out of the bedroom, dining table, and bathroom. These boundaries protect your mental space.
4.Set App Time Limits
Use tools like Focus Mode or Screen Time to control usage. Reward yourself with breaks after completing real tasks.
5.Practice Boredom
Boredom isn’t the enemy—it’s the gateway to creativity and clarity. Allow yourself time to do nothing. Let your mind wander.
🔘Rewiring Begins with Awareness
You’re not weak—you’re wired to crave stimulation. But the same brain that got hijacked can be rewired.
Every step away from digital addiction brings you closer to:
▪️Better sleep
▪️Deeper focus
▪️Genuine relationships
▪️Inner peace
🔘Final Message
Technology should serve you, not control you.
Take back your attention.
Rebuild your focus.
Live with intention—not addiction.

0 notes
Text
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2:
▪️Nursing Science Focus:
Type 2 Diabetes is a major public health issue. Nurses are vital in patient education, monitoring blood glucose, managing complications, and promoting lifestyle changes.
▪️Health Care Highlight:
Preventive care and routine screening for adults at risk (especially obese individuals over 45) can drastically reduce long-term complications like neuropathy or kidney disease.
▪️Disease Overview – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
A chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Insulin resistance is the key underlying issue.
▪️Diagnostic Tools:
¹Fasting Blood Glucose ≥126 mg/dL
²HbA1c ≥6.5% (average glucose over 3 months)
³Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
⁴Random Blood Sugar Test ≥200 mg/dL with symptoms
▪️Treatment Options:
1.Lifestyle: Diet (low glycemic index), exercise, weight control
2.Medications: Metformin (first-line), sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, insulin (if needed)
▪️Side Effects of Treatment:
1.Metformin: GI upset, lactic acidosis (rare)
2.Sulfonylureas: Risk of hypoglycemia
3.SGLT2 inhibitors: Urinary tract infections, dehydration
▪️Nursing Advice:
¹Teach blood glucose self-monitoring techniques
²Promote dietary planning with a nutritionist
³Recognize and manage signs of hypoglycemia
⁴Encourage regular foot care and eye checkups
⁵Educate on medication timing and compliance

0 notes
Text
❇️ Types of Foot Deformities (Talipes):
✔️ Talipes cavus
→ High arch of the foot (exaggerated plantar flexion of forefoot).
✔️ Talipes equinus
→ Plantarflexed foot; patient walks on toes (cannot dorsiflex).
✔️ Talipes calcaneus
→ Dorsiflexed foot; patient walks on heel (cannot plantarflex).
✔️ Talipes valgus
→ Foot everted (turned outward at heel).
✔️ Talipes equinovalgus
→ Combination of plantarflexion + eversion.
✔️ Talipes calcaneovalgus
→ Combination of dorsiflexion + eversion.
✔️ Talipes varus
→ Foot inverted (turned inward at heel).
✔️ Talipes cavovarus
→ High arch + inversion of the foot.
✔️ Talipes equinovarus
→ Plantarflexion + inversion (classic clubfoot deformity).
✔️ Talipes calcaneocavus
→ Dorsiflexion + high arch.

0 notes
Text
Why Can’t You Focus? Understanding the Dopamine Dilemma
Do you constantly check your phone?
Feel restless, anxious, or easily distracted?
Struggle to control your habits and choices?
These are signs of a deeper neurological pattern rooted in one powerful chemical—dopamine. This molecule holds the key to our drive, curiosity, and focus. But in the modern world, it’s also the cause of widespread distraction, anxiety, and dissatisfaction.
🔘Dopamine: The Engine of Human Progress
Dopamine is not just a “pleasure chemical.” It’s a motivation molecule—the reason we strive, explore, and learn. Our ancestors relied on dopamine to survive. Finding food, discovering fire, or inventing tools—all these achievements were rewarded with a dopamine release.
The brain learned: “This action worked—do it again.”
This feedback loop drove human evolution—encouraging risk, discovery, and progress.
🔘Dopamine in the Modern Era
In today’s world, dopamine continues to reward meaningful achievements:
Mastering a skill
Completing a project
Achieving fitness goals
Helping others succeed
These are examples of Slow Dopamine—a deep, fulfilling kind of pleasure that follows effort, patience, and discipline.
🔘The Trap of Instant Gratification
Unfortunately, modern technology has weaponized dopamine against us. Social media, endless scrolling, instant entertainment—all provide quick dopamine hits.
The cycle is simple:
Scroll → Spike → Crash → Repeat
These artificial spikes disrupt our brain’s reward system, reducing our ability to focus, work hard, or find joy in real accomplishments.
🔘The Consequences
Shortened attention spans
Weakened motivation
Dependence on external stimuli
Increased anxiety and dissatisfaction
We’re stuck chasing digital highs, while neglecting real-life progress.
🔘The Dopamine Crisis Explained
1.Pleasure-Pain Balance
The brain seeks balance.
Hard work (e.g., reading, exercising, creating) leads to delayed but lasting pleasure.
Instant gratification (e.g., phone, junk food) gives quick pleasure followed by emptiness.
Choose long-term satisfaction over temporary highs to restore balance.
2.Willpower as a Mental Muscle
The Anterior Mid-Cingulate Cortex controls self-discipline.
Each time you resist a distraction—whether it's a notification or a sugar craving—you strengthen this region.
Willpower grows through repetition.
3.ADHD and the Gift of Hyperfocus
ADHD is linked to lower dopamine levels, causing boredom and impulsivity.
But in areas of passion—music, sports, or creativity—individuals with ADHD experience hyperfocus: a state of intense concentration and productivity.
4.Symptoms of Low Dopamine
Chronic fatigue
Irritability
Low motivation
Poor sleep
Difficulty starting or finishing tasks
Treatment isn’t pharmaceutical alone—you can rebuild dopamine naturally through behavior and lifestyle.
🔘How to Cultivate Slow Dopamine
1.Limit Phone Use:
No screens upon waking or before sleep
Turn off non-essential notifications
2.Exercise Regularly:
Walk, run, cycle, or play sports daily
3.Read and Learn:
Replace scrolling with deep, focused reading
4.Set Daily Goals:
Break big tasks into smaller wins
5.Engage with Nature:
Morning sunlight, bird sounds, or a walk in the park refresh the mind
6.Follow Your Passion:
Create space for hobbies and skills that bring true joy
🔘Final Insight: Reclaim Your Mind
Every choice matters.
Choose discipline over distraction.
Choose books over screens.
Choose real joy over cheap thrills.
Your brain is not broken—it’s hijacked. But with awareness and effort, you can rewire it.
Master your mind, and you master your life.
Start now.
(Author: JAVAD AHMAD HURA, UN Educationist, Chief Editor of Srinagar Samachar)

0 notes
Text
Nursing Science
Topic: Wound Care Management
▪️Definition:
Wound care involves assessment and interventions to promote healing and prevent infection in damaged skin or tissue.
▪️Types of Wounds:
1.Acute Wounds – Surgical incisions, abrasions
2.Chronic Wounds – Pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers
3.Open/Closed Wounds – Depending on skin integrity
▪️Nursing Responsibilities:
Perform thorough wound assessment (location, size, color, drainage, odor).
Maintain sterile technique during dressing changes.
Choose appropriate dressing type (gauze, hydrocolloid, foam, etc.).
Monitor for signs of infection: redness, swelling, pus, fever.
▪️Steps in Wound Dressing:
1.Hand hygiene and PPE
2.Remove old dressing gently
3.Clean wound from clean to dirty area
4.Apply new sterile dressing
5.Document findings
▪️Clinical Tips:
Encourage adequate nutrition for wound healing (protein, Vitamin C, zinc).
Turn and reposition immobile patients to prevent pressure ulcers.
Collaborate with wound care specialists for complex wounds.
▪️Outcome:
Promotes faster healing, reduces complications, and enhances patient comfort and safety.
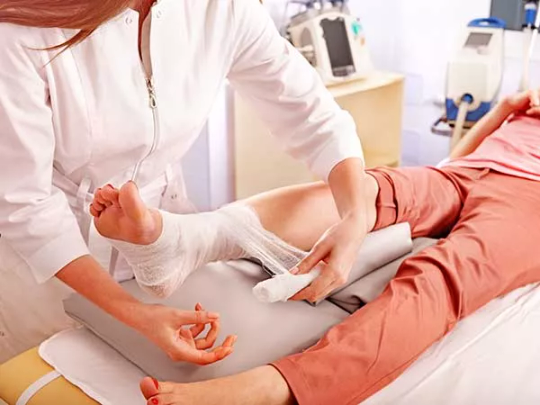
0 notes
Text
Rubin’s maneuver is a technique used when a baby’s shoulder gets stuck during childbirth called shoulder dystocia.
In this case, the midwife presses just above the mother’s pubic bone (this is called suprapubic pressure). The goal is to gently push the baby’s front shoulder toward its chest. This slight rotation helps the shoulder slip through more easily.
Sometimes, if that doesn’t work, the midwife may gently reach inside the vagi!na to help rotate the baby’s shoulder known as Rubin II.
Rubin’s maneuver is often combined with the McRoberts maneuver, where the mother’s legs are pulled up to her chest to open the pelvis more.
This method is very different from fundal pressure, and when it's done correctly, it can help deliver the baby safely without causing harm to the mother or child.
~ Student Nurses & Midwives - Health Care Champions
Courtesy:

0 notes
Text
Nursing Science
Topic: Wound Care Management
▪️Definition:
Wound care involves assessment and interventions to promote healing and prevent infection in damaged skin or tissue.
▪️Types of Wounds:
1.Acute Wounds – Surgical incisions, abrasions
2.Chronic Wounds – Pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers
3.Open/Closed Wounds – Depending on skin integrity
▪️Nursing Responsibilities:
Perform thorough wound assessment (location, size, color, drainage, odor).
Maintain sterile technique during dressing changes.
Choose appropriate dressing type (gauze, hydrocolloid, foam, etc.).
Monitor for signs of infection: redness, swelling, pus, fever.
▪️Steps in Wound Dressing:
1.Hand hygiene and PPE
2.Remove old dressing gently
3.Clean wound from clean to dirty area
4.Apply new sterile dressing
5.Document findings
▪️Clinical Tips:
Encourage adequate nutrition for wound healing (protein, Vitamin C, zinc).
Turn and reposition immobile patients to prevent pressure ulcers.
Collaborate with wound care specialists for complex wounds.
▪️Outcome:
Promotes faster healing, reduces complications, and enhances patient comfort and safety.
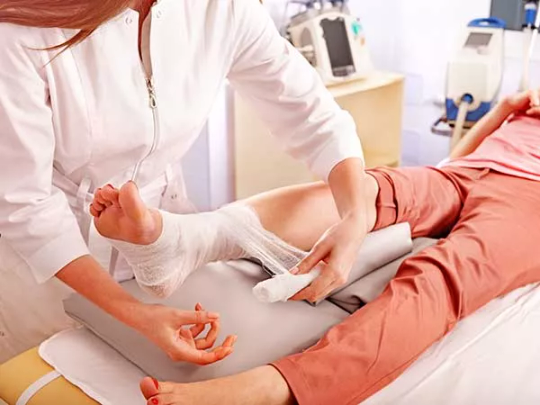
0 notes
Text
Nursing Science
Topic: Vital Signs Monitoring
Definition:
Vital signs are clinical measurements that indicate the state of a patient's essential body functions.
Key Parameters:
1.Temperature – Normal: 36.5°C to 37.5°C
2.Pulse Rate – Normal: 60 to 100 bpm
3.Respiratory Rate – Normal: 12 to 20 breaths per minute
4.Blood Pressure – Normal: 120/80 mmHg
5.Oxygen Saturation (SpO₂) – Normal: 95–100%
Nursing Responsibilities:
1.Ensure accurate use of equipment (thermometer, sphygmomanometer, pulse oximeter).
2.Record findings clearly and immediately.
3.Monitor for abnormal values and report promptly.
4.Reassess frequently in critical patients.
Clinical Tips:
¹Always check vital signs before and after administering medications.
²Use the same arm for BP monitoring unless contraindicated.
³Note any signs of distress (e.g., sweating, pallor, altered breathing patterns).
Outcome:
Early detection of complications, better management of patient condition, and informed clinical decisions.

0 notes
Text
Functions of the spleen:
1.Filtration of Blood:
The spleen filters old, damaged, or abnormal red blood cells and removes them from circulation. It also filters out pathogens and debris.
2.Immune Response:
The spleen plays a key role in the immune system. It produces lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and helps mount an immune response to bacteria, viruses, and other invaders.
3.Storage of Blood:
It stores blood, especially platelets and white blood cells. In case of sudden blood loss (like injury), it can release stored blood into circulation.
4.Recycling of Iron:
When red blood cells are broken down, the spleen helps recycle iron and other useful components for reuse in the body.
5.Support in Fetal Life:
In the fetus, the spleen helps in producing red blood cells (a function taken over by the bone marrow after birth).
CLINICAL NOTE:
An enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) can be due to infections, liver disease, or blood cancers.
A damaged or removed spleen increases infection risk, so vaccines and antibiotics may be needed for protection.

0 notes
Text
ANTI ALLERGIC MEDICATIONS
This list includes anti-allergic medications and drugs used to treat anaphylaxis, which is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. Here's a breakdown of the medications mentioned:
1.DEXAMETHASONE
Form: Injection, 4 mg/mL (as disodium phosphate).
Use: A potent corticosteroid that reduces inflammation and suppresses immune response.
Role in anaphylaxis: Used as a secondary treatment to help control inflammation after initial stabilization (not first-line in acute phase).
2.EPINEPHRINE (Adrenaline)
Form: Injection, 1 mg/mL.
Use: The first-line treatment for anaphylaxis.
How it works: 1. Opens airways (bronchodilation), 2. Raises blood pressure (vasoconstriction), 3. Reduces swelling and hives.
Dosage route: Usually given intramuscularly for rapid action.
3.HYDROCORTISONE
Form: Powder for injection, 100 mg vial.
Use: A corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation.
Role in anaphylaxis: Given after epinephrine to prevent prolonged or biphasic reactions.
4.LORATADINE
Form: Oral liquid: 1 mg/mL,
Tablet: 10 mg.
Type: Non-sedating antihistamine.
Alternatives: Cetirizine, Fexofenadine.
Use: Treats milder allergic reactions (e.g., hay fever, urticaria), not first-line for anaphylaxis.
Note: Sedating antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine) may still have roles in limited settings such as acute care.
5.PREDNISOLONE
Use: Corticosteroid used to manage allergic inflammation.
Form: Oral (usually),
Alternative: Prednisone (similar action and used interchangeably).
Role: Given after initial emergency treatment to prevent recurrence of symptoms.

1 note
·
View note
Text
GALLBLADDER - Structure and Functions
The bladder, a crucial organ in your urinary system, is essentially a hollow, muscular sac that stores urine. Think of it like a balloon that can expand and contract.
🔰STRUCTURE OF THE BLADDER:
The bladder's wall is composed of several layers, each with a specific role:
MUCOSA (Inner Lining): This layer is made of transitional epithelium, a unique type of tissue that can stretch significantly without being damaged. When the bladder is empty, this lining appears folded (rugae), allowing for expansion as it fills with urine.
SUBMUCOSA: A layer of connective tissue that supports the mucosa and contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
MUSCULARIS (Detrusor Muscle): This is the thickest layer, consisting of smooth muscle fibers that run in various directions. The coordinated contraction of this muscle is essential for expelling urine.
SEROSA (Outer Layer): A layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of the bladder.
🔰The bladder has a few key anatomical features:
TRIGONE: A triangular region at the base of the bladder formed by the openings of the two ureters (tubes that carry urine from the kidneys) and the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body). This area is less distensible than the rest of the bladder wall.
INTERNAL URETHRAL SPHINCTER: A thickening of the detrusor muscle around the opening of the urethra. This sphincter is under involuntary control and helps to keep the urethra closed to prevent leakage.
NECK OF THE BLADDER: The region where the bladder narrows and connects to the urethra.
🔰Function of the Bladder:
The primary function of the bladder is the storage and expulsion of urine, a waste product produced by the kidneys. Here's a breakdown of this process:
STORAGE: Urine continuously flows from the kidneys down the ureters and into the bladder. As the bladder fills, its walls stretch, and the rugae in the mucosa flatten out. The capacity of the bladder varies but can typically hold around 400-600 milliliters (about 1.7 to 2.5 cups) of urine. During filling, the detrusor muscle remains relaxed, and the internal urethral sphincter remains contracted to prevent leakage.
SENSING FULLNESS: Specialized stretch receptors in the bladder wall send signals to the brain as the bladder fills. The urge to urinate typically begins to be felt when the bladder contains around 150-200 milliliters of urine.
MICTURITION (Urination): The process of emptying the bladder is a complex reflex controlled by the nervous system.
When you decide to urinate (voluntary control), the following happens:
▪️Signals from the brain cause the detrusor muscle to contract.
▪️Simultaneously, the internal urethral sphincter relaxes (involuntary control).
▪️The external urethral sphincter, which is under voluntary control, also relaxes.
▪️The coordinated contraction of the detrusor muscle and relaxation of both sphincters forces urine out of the bladder and through the urethra.
EMPTYING: After urination, the detrusor muscle relaxes, the bladder returns to its smaller size, and the sphincters contract again to prevent further urine flow.
In essence, the bladder acts as a temporary reservoir, allowing us to control when we eliminate waste from our bodies. Its ability to stretch and contract, along with the coordinated action of its muscular wall and sphincters, ensures efficient and controlled urination.

0 notes