Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
What is a thermowell?
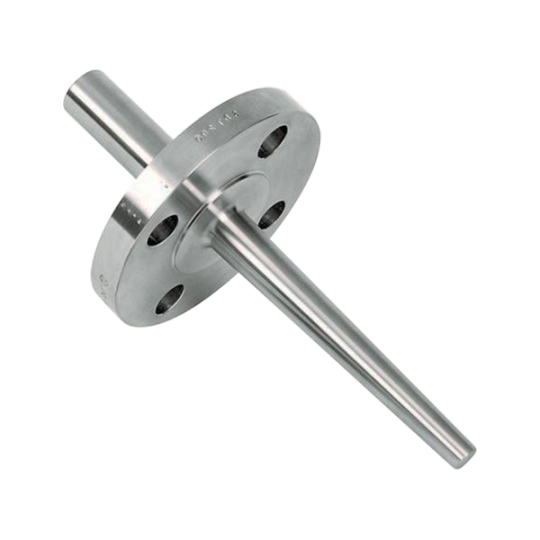

A thermowell is a cylindrical fitting used to protect temperature sensors installed when measuring liquid such as in the production of beer, the thermowell protects the thermometer when measuring the temperature as well as protects the liquid from contamination. The thermowell acts as a barrier between the device measuring temperature and the liquid as well as the liquid from the outside air.
Thermowells are recommended whenever a temperature element is to be inserted into a process where corrosion, pressure, abrasion, or shear forces may threaten the life of the element. In addition, thermowells allow for a defective instrument to be removed without shutting down or draining the process.
They fit into three broad categories: screwed, flanged, or weld-in, and can be designed to accept thermocouples, RTDs, temperature gauges or filled systems.
Thermowells can be machined from solid bar stock, or fabricated from a pipe. Fabricated thermowells offer a lower-cost alternative where high pressure is not a design consideration. Standard thread forms are BSP and NPT (others available to order), and flange size and rating can be supplied to suit any requirements.
If you are confused about buying thermowell, then Contact Us now you can mail also at
Address:
Precision Mass Products Pvt. Ltd.
Plot No. 2306, G.I.D.C. Chhatral,
Ta. Kalol, Dist. Gandhinagar,
Chhatral 382729, Gujarat, India.
Tell : +91-2764-233681/2/3
0 notes
Text
Thermowell Manufacturer in India

TWT Screwed Thermowell
Description
TWT Screwed Thermowell
Connection
1/2” to 2″ BSP / NPT, M20x1.5, and more
Material
CS, SS304, SS316, SS316L, SS316Ti, SS321, Monel, Hastelloy-C, Hastelloy-B, Duplex, Inconel
Accessories
Thermometers, RTD, thermocouples
Application:
Power plants, chemical & petrochemical industry, machine & apparatus construction,onshore & offshore installations, pulp & paper industry, food & beverage industry, waste water treatment, etc.
Features:
Wide selection of materials
Material Certificates 3.1
Solid bore construction, barstock
Materials according NACE MR 0175 / ISO 15156
Standard and customer specified testing available
ISO 228-1 and ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 connections
Optional WFC Wake Frequency Calculation ASME PTC 19.3 Contact Us for Thermowell https://www.precisionmass.com/products/thermowell/rth-resistant-temperature-detector/
0 notes
Text
What is Pressure Switch, How Do They Work?

A pressure switch is a device made to respond to a specific level of pressure by producing an output.
Electrical feedback is produced by the switch in response to changes in pressure. The switch's automated response is based on pressure. Its use is widespread, from businesses to homes and workplaces.
For instance, it is frequently used in commercial sliding door pressure panels, electronic gas compressors, well pump systems, and security alarms.
A regular pressure switch and a differential pressure switch are very similar. But in this instance, the switch is turned on when it detects a pressure difference between two points. Mechanical pressure switch and electronic pressure switch are the two main types of pressure switches. Their structures and the pressure sensing component they use are slightly different, but their operating principles are the same. Bellows, diaphragms, and pistons are the most frequently utilised sensing components
How does it function?

Let's take a closer look at a primary pressure switch's structure before analyzing its operating system.
Following are the components of a pressure switch include:
(A) Micro-switch
(B) Operating pin
(C) Range spring
(D) Operating piston
(E) Insulated trip button
(F) Switch case
(G) Trip setting nut
(H) Inlet pressure
A pressure sensor and a switch contact are the two main components of a modern pressure switch. The switch contact starts or stops the electric circuit whenever the pressure level is reached.
A piston serves as the pressing sensing element in a mechanical pressure switch that also includes the essential parts. However, this operates on the same principles as devices that use bellows or diaphragms for sensing.
As seen, the components remain inside the switch case (F); the inlet pressure (H) moves against the operating piston (D); the resulting pressure moves the spring (C). The range of the spring can be adjusted to a set pressure that activates the switch. The operating pin (B) that is activated by the motion of the spring and piston, in turn, triggers the micro-switch (A). The micro-switch has two components — usually close contact (NC) and normally open contact (NO); when the pressure switch is triggered, the micro-switch enables the electric circuit, making the switch work. In the absence of pressure, the micro-switch’s electric contact remains NO; when the set pressure is reached, the micro-switch activates the NO electric connection, closing the circuit.
The difference in the Working of a Mechanical and Electronic Pressure Switch:
A mechanical pressure switch's physical mechanism is triggered by fluid pressure, as in hydraulic or water pumps, whereas electronic pressure switches function via electronic pressure sensors and an electronic circuit. Some switches do not allow for pressure point adjustment because it is pre-set.
Mechanical switches are known to be better at handling higher voltages and can operate without any additional power. Electronic switches, on the other hand, can be changed in order to alter the delay time, output signal, deadband adjustability, turndown ratio, etc.
Selecting the Right Pressure Switch:
The user must consider the type of the process media, working pressure, temperature range, deadband or differential (the interval between the switch set and reset point), enclosure based on type of environment, and type of pressure switch based on application when choosing the best pressure switch. For instance, a piston design should be used for high-pressure applications, while a diaphragm-operated switch should be used for low-pressure applications. Get in Touch with Us!
0 notes
Text
Advantages & Types of Diaphragm Seal

What is Diaphragm Seal?
The diaphragm seal system consists of Pressure Instruments, Fill fluid, and Diaphragm seal direct mounting type or capillary type.
In the process a flexible diaphragm and filling fluid separate the pressure instruments from process media, temperature, or service.
When process pressure acts on the diaphragm, diaphragm displacement transfers the measured pressure through the filling system. This transferred pressure displaces the pressure sensing element of Pressure Instruments.
A diaphragm seal is used to seal and safeguard instruments from the process medium. The flexibility of the seal is as such that, the diaphragm, seals the contents safely at same time permeating the instrument to measure the pressure accurately.
Diaphragm seals are in general use with other devices and instruments including pressure gauges, transmitters and switches. This combination can be used in extreme and harsh environmental conditions. The fact that they can isolate instruments from any kind of toxic and reactive chemical makes them an especially useful device.
Application of Diaphragm Seals
The application range of diaphragm seals is wide. The use of diaphragm seals in pressure gauges is to protect the sensing element from toxic and hazardous chemicals. Diaphragm seals are manufactured for use in extreme conditions, suitable for different industrial processes.
For instance, they are used with pressure gauges that are generally subjected to difficult process environments. They are used to protect the instrument from dangerous and corrosive media. In a way, diaphragm seals are used to enhance the lifetime of any instrument by protecting them against harmful media which can be at high temperature, highly corrosive in nature, vicious, and with highly toxic chemical combinations.
Types of Diaphragm Seals
Diaphragm seals are available for a variety of applications. Based on application, diaphragm seals can be categorized into:
1. Inline Diaphragm Seal
These diaphragm seals are used to permit fluid flow and are inserted inside various connector types. The arrangement of the seals prevents process clogging or the gradual growth of any bacteria in the diaphragm.
2. Threaded Diaphragm Seals
Designed to mount directly on threaded process connections, and threaded diaphragm seals. To work with gauges in switches and transmitters, these seals are connected via flexible and threaded capillaries. They are very small in size and are made to fit in tiny spaces.
3. Diaphragm Seals with Flanges
Flanged diaphragm seals can be clamped between the process and covering flanges or are designed for direct mounting on the process counter flange. These seals are made to be mounted on gauges and transmitters and are offered in all international flange standards, including ASME EN, BS, API, ISO, or JIS. There are flanged diaphragm seals with flushing connections available.
4. Sanitary Diaphragm Seals
Sanitary diaphragm seals are created especially for the food and pharmaceutical industries, where it is important to stop the growth of bacteria. Through the use of threaded or quick clamp couplings, these seals allow for simple cleaning. These seals comply with FDA regulations and prevent the growth of any bacteria.
Advantages of Diaphragm Seals:
Diaphragm seals guarantee that the results produced by the instrument are extremely accurate in addition to providing protection. To extend the life of instruments, diaphragm seals are installed, which over time saves both time and money.
The ability to adapt the mounting of these seals to the application is another key benefit. They are dependable tools that can be used in a variety of applications because they are built to meet industry standards.
Diaphragm seals have developed a reputation as tools that increase device longevity and reduce the cost of replacing a broken device.
Conclusion:
If you're looking for a diaphragm seal, Precision Mass, a reputable diaphragm seal manufacturer, can help. We have a variety of diaphragm seals for every type of application. You can get in touch to get answers to your questions about the diaphragm seal. Get the best diaphragm seal by getting in touch with us right away.
0 notes
Text
All About Oxygen Pressure Gauge

These gauges are used in a wide range of industrial and medical applications to control the use of oxygen within a usable range. In fact, the installation and use of oxygen pressure gauges have the corresponding skills.
Oxygen pressure gauge installation and use
1、Before installation, carefully inspect the parts to ensure that they are fastened, that there are no visible signs of damage or destruction, and that all loose parts are still in place.
2、Don't let any nuts slip as you connect the oxygen filler, oxygen pressure-reducing valve, and oxygen filling conduit.
3, In order for the output oxygen pressure table to show 2.8-3.0MPa, the oxygen cylinder valve must be opened, and the pressure reducing valve must be adjusted. At this point, the entire gas circuit should be leak-free; if not, it should be checked until normal.
4, The oxygenator on the pressure gauge should be consistent with the output table pressure on the pressure reducing valve at this point in the oxygen experiment test. It should also operate freely and without leaks.
5, Test oxygen experiment: at this time, the oxygenator on the pressure gauge should be consistent with the output table pressure on the pressure reducing valve. It should also operate freely and without leaks.
The difference between an oxygen pressure gauge and a general pressure gauge
The main distinction between an oxygen pressure gauge and a general pressure gauge is that an oxygen pressure gauge forbids oil, meaning that during the final calibration of the assembly, the pressure gauge calibrates the instrument's pressure using gas or water, whereas a general pressure gauge calibrates using oil because oxygen can't cause spontaneous combustion but can aid in it, thus forbidding oil.
Structure
A general pressure gauge and an oxygen pressure gauge basically have the same structure.
Function
The oxygen gauge measures oxygen, and the amount in the air is represented numerically.
The pressure, atmospheric pressure, and pipeline (liquid gas) pressure should all be measured with a general pressure gauge.
The difference: the oxygen meter above the O2 logo, and the pressure gauge only numbers!!!!
Switching direction
The difference between the clockwise and counterclockwise rotations of the pressure switches on the oxygen pressure gauge and the general pressure gauge is primarily intended to prevent malfunction.
Simply put, understanding the oxygen pressure gauge is an auxiliary skill; once the subject is abandoned, the value of the gauge will be completely lost and will be of little further use. Similar to this, the pressure gauge's accuracy will still have a sizable influence on our actual work.
Contact Us for Inquiry about Oxegen Pressure Gauge
0 notes
Text
sanitary pressure transmitter manufacturer
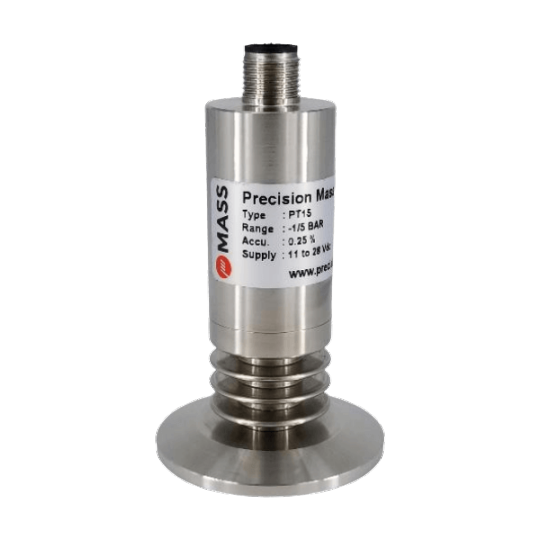

Description
PT15 Sanitary Pressure Transmitter
Accuracy
≤ 0.5 % FS, optional ≤ 0.25 % FS
Pressure Range
0 to 1 bar up to 40 bar
Gauge, Compound, Vacuum & Absolute pressure ranges.
Material
Stainless Steel 316L
Application:
Dosing Systems, Pharmaceuticals, Food Processing, Biotechnology and filtration industries, Breweries, distilleries
Features:
1.5” Tri-clamp Flush Diaphragm
High vibration stability
Rugged stainless steel construction
Reverse polarity and limited protection
High accuracy, stability, and reliability
Protection IP67
Contact Us now for the Sanitary Pressure Transmitter
0 notes
Text
What Are The Types of Pressure Gauges?

Pressure gauges are the tools used to measure atmospheric pressure. In other words, pressure is the amount of perpendicular force applied to a surface per unit area. There are numerous methods for measuring pressure that researchers have developed. It is essential to think about the reference point being used when measuring pressure in order to do it correctly. It is categorised as "absolute," "gauge," or "differential" pressure as a result. A pressure gauge can be mechanical or hydrostatic.
Liquid column or piston type gauges work by comparing the pressure to the hydrostatic force per unit area at the base of the column of fluid. Other pressure gauge types, such as those that employ bellows, diaphragms, or Bourdon tubes, measure pressure through mechanical motions.
The three different types of pressure can all be measured accurately with pressure gauges.
1. Absolute Pressure Instruments
2. Gauge Pressure Measuring Devices
3. Differential Pressure Gauges
If you are looking to buy pressure gauge precision mass is one of the leading pressure gauge manufacturer in India, Contact us now - https://www.precisionmass.com/contact-us/
0 notes
Text
What Are The Types of Pressure Gauges?

Pressure gauges are the tools used to measure atmospheric pressure. In other words, pressure is the amount of perpendicular force applied to a surface per unit area. There are numerous methods for measuring pressure that researchers have developed. It is essential to think about the reference point being used when measuring pressure in order to do it correctly. It is categorised as "absolute," "gauge," or "differential" pressure as a result. A pressure gauge can be mechanical or hydrostatic.
Liquid column or piston type gauges work by comparing the pressure to the hydrostatic force per unit area at the base of the column of fluid. Other pressure gauge types, such as those that employ bellows, diaphragms, or Bourdon tubes, measure pressure through mechanical motions.
The three different types of pressure can all be measured accurately with pressure gauges.
1. Absolute Pressure Instruments
A. Absolute Pressure Measurement – The pressure in a complete vacuum is used as the standard for measuring absolute pressure. At a complete vacuum, there is no pressure. As a result, it is referred to as "absolute" pressure.
B. Measuring Instruments Description - A measuring cell and a diaphragm are the basic components of a mechanical absolute pressure gauge. The vacuum-filled reference chamber is one part of the instrument. The hydrostatic gauge known as a barometer can also be used to measure absolute pressure.
C. Applications - Absolute pressure gauges can be used to measure the vapour pressure of liquids, vacuum reactors, to check for leaks in tanks and circuits, and to measure the drop in pressure of distillation vacuum columns. They can also be used to perform distillation operations in the oil refining industry. The food packaging industry and vacuum pumps both use absolute pressure gauges. For measuring atmospheric pressure, we use barometers.
2. Gauge Pressure Measuring Devices
A. Gauge pressure is measured in relation to the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level in item A of the list (approximately 1013.25 mbar). When gauge pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure, it is positive; when it falls below atmospheric pressure, it is negative.
B. Measuring Instruments Description - A Bourdon tube pressure gauge is the instrument that is most frequently used to measure gauge pressure. It is a mechanical device made of a tube that has been bent into a C shape and has one end sealed. According to the pressure that is applied inside the tube, entering through the open end, the sealed end is free to move a pointer over a scale. Diaphragms and bellows are two additional mechanical tools that can measure pressure gauge. The u-tube manometer is a useful hydrostatic one.
C. Applications - Gauge pressure measuring devices are the most frequently used pressure measuring tools in industry, especially in the power, refinery, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food, refrigeration, air-conditioning, and sanitation industries.
3. Differential Pressure Gauges
A. Differential pressure measurement - Differential pressure only quantifies the variation in pressure between two readings. It provides no details regarding the pressure differentials between the two points it compares.
B. Measuring Instruments Description - Differential pressure gauge are typically mechanical in design. Piston-style, diaphragm-style, and bellows differential pressure gauges are the three main types of gauges used to measure differential pressure. Each has a specific use in various industrial processes.
C. Applications - Differential pressure gauges are used in a variety of industries to monitor liquid flow, level, and filtration. These can be used in clean rooms, petrochemical and chemical plants, refineries, and power plants.
Different Pressure Gauges and Their Uses
1. Pressure gauges for industry and commerce - Commercial gauges are all-purpose pressure measuring devices frequently used in refrigeration and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). The use of an industrial pressure gauge is appropriate for manufacturing procedures that won't obstruct the pressure system. Industrial gauges are used in the manufacturing, OEM, hydraulic, water treatment, and RO sectors of the economy.
2. Process Pressure Gauges - A process pressure gauge can be used safely in industries where the production process operates under harsh conditions, subjected to vibrations, pressure spikes, and a corrosive environment (like in some areas of the petrochemical and other chemical industries).
3. Low pressure gauges - As long as they don't interfere with their operation, these can be used to measure liquid and gaseous pressure. Low pressure gauges are frequently required in pneumatic systems, cleanrooms, and plant construction processes.
4. Seal Gauges – These gauges are used in a variety of industrial applications to meet material compatibility requirements, viscous applications, corrosive chemicals, vibrations, sanitary and pharmaceutical requirements. They are designed to seal potential leak paths.
5. High Precision Test Gauges - These gauges are ideal for procedures requiring exact calibration, such as those carried out in testing labs.
6. Duplex pressure gauges - These differential pressure gauges, which measure the difference between two applied pressures, can operate in harsh environments. In the refrigeration, fuel, chemical, and air-handling industries, this is occasionally necessary.
The Best Pressure Gauge to Use
What kind of gauge you should use depends on a number of factors, including the level of accuracy needed, the required dial size for readability, the durability of the material to withstand environmental and process conditions, the mounting options available, the range of pressure that it can measure, and the pressure type to be measured. Choosing the right gauge will not be difficult if you go with a manufacturer that offers a wide range of options.
0 notes
Text
Precision Mass Will Exhibit in Boiler India 2022

A unique networking and progress-driven platform, BOILER INDIA EXPO combines a trade show and seminars to bring together the Indian and international boilers and related industries under one roof. Manufacturers of boilers and related products, services, engineering solution providers, steam solution providers, pharmaceutical, food & beverage, chemical, power generation, rice, sugar, textile, cement, steel, paper & pulp, rubber, distilleries, refineries, marine, cosmetics, paint & dye, etc. are among the industries that collaborate.
BOILER INDIA 2022 which will be held from 14 - 16 September 2022 at CIDCO Exhibition and Convention Centre, Mumbai, India.
Hurry up And get a chance to connect with Precision Mass in the exhibition.
0 notes
Text
How does Differential Pressure Gauge work?
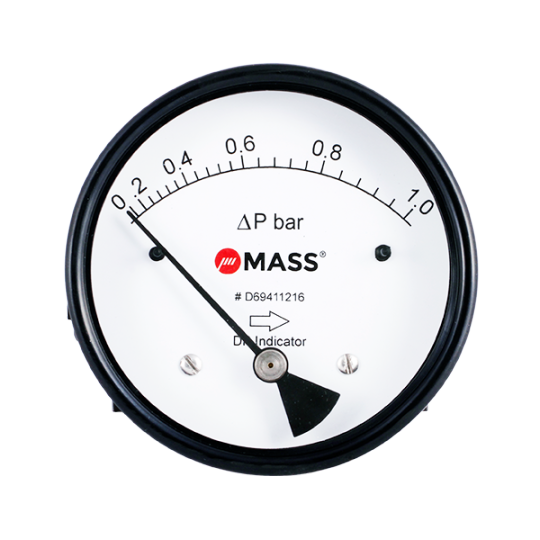

The differential pressure gauge works by measuring how much pressure difference exists between the two. The differential pressure, as the name implies, is a measurement of two pressures that then indicates the difference in pressure.
Differential pressure gauges are ideal for determining the following values.
Contamination control in filters
Bag clogging monitoring in the bag dust collector
Measurements of overpressure in clean rooms
Flow measurement in liquids and gases
What is the function of a pressure gauge with a differential function?
The differential pressure gauge is made up of two medium-sealed chambers. Using measuring components, the chambers can be separated. If the pressure is the same in both chambers, the measuring elements will not feel pressure, and the DP gauge will not show any deflection.
Read more about Differential Pressure Gauge
0 notes
Text
Pressure Transmitter – Types & Accuracy

What is a Pressure Transmitter?
Pressure transmitters, also known as pressure transducers, are used to measure the pressure of liquids, fluids, and gases in various working equipment in industrial and process applications. These transmitters are essential in process industries, particularly the oil and gas industry, which deals with a wide range of fluids and gases.
They are commonly used to make a liquid interface detector, which monitors the level of liquid in a system's various connected pipelines. The measurement and maintenance of pressure levels in various components in these industries is critical for their smooth operation because any variation above or below the prescribed pressure can cause disasters.
Pressure transmitters are frequently used in conjunction with other devices to ensure that any system operates properly. These transmitters are built to withstand harsh environments, making them useful in a variety of industries. Pressure and differential pressure transmitters are primarily used in level measurement, flow measurement, and monitoring of filtration systems.
Because of their wide range of applications, pressure transmitters and sensors have become an essential component in the industrial sector. These transmitters are used to measure the pressure of various fluids as well as to detect any type of leakage. Pressure transmitters are increasingly being used in various types of research and development activities in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
They are used to measure the pressure of fuel, water, air, and other manufactured products in this location. The food and beverage industry has emerged as a new arena of application, with pressure transmitters used to measure bottling points in brewing and dairy applications. New types of sensors are entering the market. Pressure transmitters are also being used to meet new requirements in a variety of new fields and domains.
Pressure Transmitter Types
Pressure transmitters are classified into four types:
1. Transmitter for Gauge Pressure
They measure gauge pressure in relation to atmospheric pressure, as the name implies. Because they involve the use of liquids and gases, these types of transmitters are widely used in process industries. Because gauge pressure transmitters are required to keep their pressure under control, they are an essential component of the industry.
2. Transmitters that are absolute
These transmitters are used to measure pressure in relation to a complete vacuum. To create a reference to absolute vacuum, the media under measurement is placed in a sealed chamber. These absolute pressure transmitters are typically used in applications that require a high level of accuracy.
3. Transmitter of Differential Pressure
These transmitters are commonly used to compare various types of pressure. Their applicability includes both level applications and flow applications. Because of their advantages over other alternatives, these transmitters have been used to measure flow rates.
4. Pressure Transmitters with Multiple Variables
These transmitters are used when more than one variable is present. Temperature and volumetric flow are examples of these variables. These types of transmitters are commonly used in industries that measure gas and steam flow.
Pressure Transmitter Accuracy
Pressure transmitter accuracy has improved significantly over time. Accuracy is comprised of various device parameters such as linearity, hysteresis, and repeatability. These are three of the most important characteristics of any pressure transmitter, regardless of the type of instrumentation or application. Manufacturers frequently combine all of these parameters and present them as a single value.
Conclusion: Precision Mass carries a wide range of pressure transmitters. We are a leading manufacturer of pressure transmitters known for producing high-quality products. We can assist you in customising and integrating the pressure transmitter with other devices. Contact us today to find the best industrial pressure transmitter for your needs.
0 notes
Text
What is a Compound Pressure Gauge and When to Use One?

A compound gauge is a gadget that can show both positive and negative (vacuum) pressures (vacuum and pressure gauge). You want to utilize a compound Pressure Gauge when you are measuring a framework that is exerting both positive and negative pressure on the gauge.
A sensor equipped for compound pressure measurement can quantify both positive and negative (vacuum) pressures. The no references of the sensor are set at encompassing pressure. The sensor isn't fixed however has a vent opening that permits inherent pay for barometrical pressure changes.
When To Use
It's hard to suggest one sort over the other as the two of them achieve a similar undertaking - a method for measuring both positive and vacuum pressure. Be that as it may, as the vast majority are more acquainted with compound pressure gauges, you will probably need to keep to a standard.
In any case, on the off chance that you're in a shut framework with siphons, using outright pressure gauges is smart - in some measure on the pull and release of the siphons. It's likewise smart to utilize outright pressure gauge valve when you're in especially wet or filthy conditions because the sensing components and gadgets are completely fixed.
So think about it! Next time you buy pressure gauges or transmitters for vacuum measurements, rethink your suppositions and inquire as to whether outright pressure is a superior decision for you.
Inform us if you have any inquiries regarding pressure gauges, transmitters, or the different reference points. Our measurement experts are eager to assist! Reach us at [email protected] or call us at 912764233681 to purchase pressure and temperature measurement instruments in India.
0 notes
Text
Different Types Of Thermocouples | Precision Mass

A thermocouple is a temperature measuring sensor. Two different types of metal wires are connected at a junction which is called the thermal junction.
To measure temperature at any point, this thermal junction is subjected to that point which develops a thermal gradient or change in temperature at this junction.
The change in temperature at the junction creates a voltage used to calculate the temperature of the reference point using the reference tables.
Thermocouples are used widely across the different industrial and scientific applications.
Some of the most common application areas of thermocouples are;
Read More
0 notes
Text
What is Thermowell and Why It is Required?

Many industrial processes require harsh environments and extreme temperatures for their operation. Temperature measurement is a challenge in such circumstances.
Besides heat, there can be other conditions such as high pressure and powerful chemical substances, radioactivity etc. A regular temperature sensor may fail to stand in such an aggressive environment.
Therefore, some device is required to guarantee the mechanical protection of this equipment.
Thermowell acts as the medium of mounting these temperature sensors in industrial processes and protecting them.
What is Thermowell?
Thermowell is used to guard the temperature sensors against extreme working conditions. It is in the form of a hollow tube with one open and one closed end.
A Thermocouple, RTD or a Temperature Gauge is mounted in it through the open end. A thermowell facilitates many other functions besides safeguarding the instruments.
The sensor is easily replaced when mounted in a thermowell, and the chances of any contamination are also significantly reduced.
Thermowells are designed to maintain the integrity and accuracy of measuring instruments in high-pressure and demanding industrial processes
Ways a Thermowell Can Help:
Thermowell has evolved as an essential component of any industrial process. Owing to its benefits, both small, as well as large thermowells are manufactured.
The former is used in operations with high pressure conditions and the latter for measurements in tanks and vessels.
Power plants, Chemical industries, Petrochemicals, Refineries, Fertilizers, Oil & Gas, Cement, Steel, Glass and various other process industries require different types of Thermowells according to their applications.
This blog is originally published on Precision Mass
0 notes
Text
Precision-mass manufacturer gas pressure transmitter
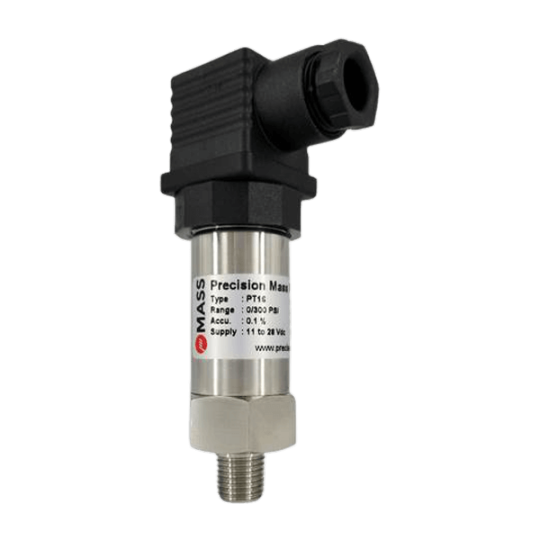

Precision-mass manufacturer gas pressure transmitter (gts) designed for the requirements of the process industry with temperature compensated. inquiry now about different types of temperature guage.
Application:
Equipment testing, Research & Development, Emissions monitoring, Automation
Features:
Rugged stainless-steel construction
Temperature compensated
Reverse polarity and limit protection
High accuracy, stability, and reliability
Protection IP67 / IP65
Contact Us for pressure transmitter
0 notes
Text
Pressure Gauges What Are The Types of Pressure Gauges?

The instruments utilized to measure pressure are referred to as pressure gauges. Simply stated, pressure is the force perpendicular to the surface applied to the surface of an area. Researchers have devised a myriad of techniques to measure pressure. To accurately measure pressure it is crucial to think about the reference point used to measure it. This is why it is categorised in 'absolute "gauge or 'differential' pressure. A pressure gauge could be a hydrostatic gauge or mechanical.
Columns of liquid as well as piston gauges gauge the pressure by comparing it to the area of hydrostatic force that is at the base of a column. Different types of pressure gauges, such as diaphragms, bellows or Bourdon tubes gauge pressure using mechanical motions.
The pressure gauge is designed to measure three kinds of pressure.
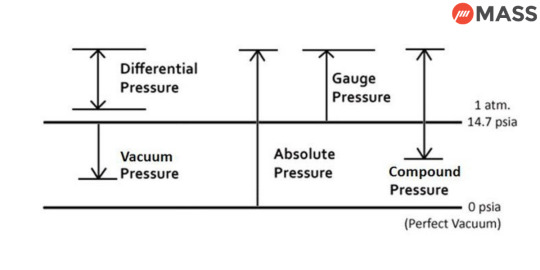
1. Absolute Pressure Gauges
A. Absolute Pressure Measurement Pressure is measured using reference to the pressure which exists in a complete vacuum. The pressure at a full vacuum will be zero. This is why it is referred to as "absolute" pressure.
B. Description of measuring Instruments The typical absolute mechanical pressure gauge is made up of a measuring unit and diaphragm. The instrument's one component refers to the chamber, and is the vacuum. Barometers, which are an hydrostatic gauge, can be used to determine absolute pressure.
Read More about the types of Pressure Gauges
1 note
·
View note