Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Reasons Behind Low Haemoglobin in Non-Anaemic People
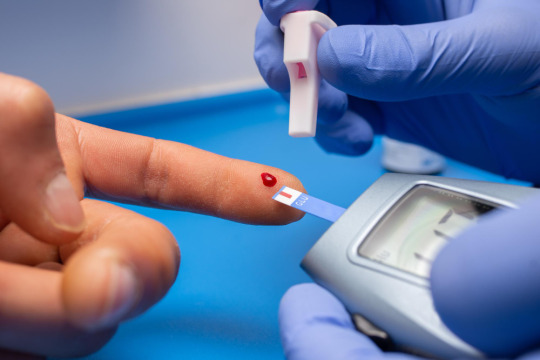
When people think of low haemoglobin, they often assume it's always linked with anaemia. But that’s not always true. You can have a slightly low haemoglobin count even if your red blood cell count and iron levels are still in the normal range.
So, what does it mean when non-anaemic people have low haemoglobin? Should you worry? Let’s explore the reasons behind low haemoglobin in non-anaemic people and what you can do about it.
What Is Haemoglobin?
Haemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. The average normal levels are:
Men: 13.5 – 17.5 g/dL
Women: 12.0 – 15.5 g/dL
Levels just below the normal range may not be classified as anaemia—but they can still indicate something going on.
Common Reasons for Low Haemoglobin in Non-Anaemic People
1. Mild Nutrient Deficiencies
Even if you’re eating regularly, you could still lack key nutrients needed to build haemoglobin—such as:
Vitamin B12
Folate (Vitamin B9)
Vitamin C (helps absorb iron)
Low levels of these don’t always lead to full-blown anaemia but can reduce haemoglobin production.
2. Chronic Inflammation or Infections
Your body may produce less haemoglobin during periods of chronic inflammation—such as:
Thyroid disorders
IBS or gut issues
Low-grade infections
These may not show symptoms right away but can slightly lower your haemoglobin over time.
3. Dilution from Overhydration
If you drink too much water before a blood test, your blood plasma volume may increase and dilute your haemoglobin, giving a lower reading.
This is temporary and often not harmful, but it can confuse test results.
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Conditions like hypothyroidism can subtly affect red blood cell and haemoglobin production.
In women, heavy menstrual bleeding can cause periodic dips in haemoglobin levels—especially if not supported with iron-rich nutrition.
5. Athletic Training (Pseudo-Anaemia)
In endurance athletes or those who do high levels of cardio, the body increases plasma (fluid) volume to improve circulation. This can lower the haemoglobin concentration without reducing red cell count—this is called athlete’s pseudo-anaemia.
What Tests to Consider
If you have low haemoglobin but no signs of anaemia, your doctor may recommend:
Serum Ferritin (iron storage)
Vitamin B12 and Folate tests
Thyroid profile
CRP or ESR (for inflammation)
You can get these tests easily with home sample collection from trusted platforms like SecondMedic.com, powered by Thyrocare.
Should You Be Concerned?
If your haemoglobin is:
Slightly below normal (e.g., 11.8–12.2 g/dL)
You have no symptoms (fatigue, paleness, breathlessness)
…then it may not be an emergency. However, monitoring and lifestyle changes are still important.
If it drops further or if symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
What You Can Do Naturally
Improve Your Diet
Eat leafy greens, legumes, citrus fruits
Add iron-rich foods like beetroot, dates, and jaggery
Pair iron with vitamin C (e.g., lemon + spinach)
Reduce Inflammation
Avoid excessive sugar, fried foods, and processed meals
Include turmeric, ginger, and antioxidants in your diet
Stay Active but Balanced
Don’t overtrain
Rest and hydrate well, especially before blood tests
Conclusion
Low haemoglobin without anaemia is more common than you might think. The causes are often mild and reversible, but keeping an eye on your numbers and adjusting your diet or lifestyle can make a big difference.
If you’ve been wondering about the reasons behind low haemoglobin in non-anaemic people, now you know how to understand and manage it better—naturally and confidently.
0 notes
Text
Why Do You Wake Up Tired Even After 8 Hours Sleep?

Getting 8 hours of sleep is often seen as the gold standard for good health. But what if you’re still waking up feeling groggy, exhausted, and low on energy—despite clocking in those 8 hours? If that sounds like you, you’re not alone.
In this blog, we’ll explore why you wake up tired even after 8 hours sleep, the possible reasons behind it, and simple ways to fix the issue so you can start your day refreshed and energized.
Sleep Quantity vs. Sleep Quality
It’s important to understand that sleep is not just about how long you sleep, but how well you sleep.
There are different stages of sleep your body goes through:
Light Sleep (Stage 1 & 2)
Deep Sleep (Stage 3)
REM Sleep (Stage 4) – where dreams and memory processing happen
If your sleep is constantly interrupted, or if you don’t get enough deep or REM sleep, your body and brain won’t be fully rested—even after 8 hours in bed.
7 Common Reasons You Wake Up Tired After a Full Night’s Sleep
1. Poor Sleep Quality
You may be lying in bed for 8 hours, but if your sleep is light or frequently interrupted, it won’t be refreshing. Common reasons include:
Noisy environment
Uncomfortable mattress or pillow
Room too hot or too cold
Lights or electronics nearby
Fix: Try blackout curtains, keep the room cool and dark, and follow a fixed bedtime routine.
2. Undiagnosed Sleep Disorders
Conditions like sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or insomnia can reduce sleep quality without you even realizing it.
Sleep apnea, for example, causes you to stop breathing for short periods during sleep. You may not wake up fully, but your body doesn’t get enough oxygen—leading to morning tiredness and brain fog.
Fix: If your partner says you snore heavily or you often wake up gasping for air, consult a doctor for a sleep study.
3. Too Much Screen Time at Night
Smartphones, laptops, and TVs emit blue light, which blocks melatonin—a hormone that helps you fall asleep.
If you scroll Instagram or binge-watch shows late at night, your brain might stay active even after you fall asleep.
Fix: Stop using screens 1 hour before bedtime. Use night mode or blue light filters if necessary.
4. Eating or Drinking Close to Bedtime
Heavy meals or caffeine before bed can disturb your sleep by causing indigestion, bloating, or increased alertness.
Fix: Avoid caffeine after 5 PM, and try to have your dinner at least 2 hours before sleeping.
5. Mental Health Issues
Conditions like stress, anxiety, or depression can impact sleep quality. You may sleep for hours but still wake up tired due to mental fatigue.
Fix: Practice stress management through:
Journaling
Breathing exercises
Meditation
Seeking therapy if needed
6. Vitamin or Hormonal Imbalance
Low levels of Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, iron, or thyroid dysfunction can cause constant fatigue—even with good sleep.
Fix: A simple blood test can help detect deficiencies. You can book these tests via SecondMedic.com, powered by Thyrocare, with home sample collection.
Recommended tests:
Vitamin D Test
Vitamin B12
Thyroid Profile
CBC (Complete Blood Count)
7. Lack of Physical Activity
Not moving your body enough during the day can lead to low-quality sleep at night. Exercise helps burn excess energy and improves deep sleep.
Fix: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity, like walking, yoga, or cycling daily.
Signs That You’re Not Getting Good Sleep
You hit the snooze button multiple times
You feel sleepy by mid-morning
You wake up with a heavy head or sore body
You need coffee immediately to function
You feel irritated, anxious, or unmotivated
These are signs your body is not truly rested.
Simple Tips for Better Sleep & Morning Energy
Stick to a sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day—even on weekends.
Create a sleep-friendly space: Keep your bedroom cool, quiet, and dark.
Limit naps: Daytime naps should be less than 30 minutes and before 3 PM.
Stay hydrated—but not too close to bedtime: Drinking too much water late may wake you up to pee.
Practice relaxation before bed: Try reading, light stretching, or herbal tea.
Conclusion
Feeling tired despite getting enough sleep can be frustrating. But remember, quality beats quantity when it comes to sleep. By making small changes in your routine, checking for hidden health issues, and improving your lifestyle, you can wake up feeling refreshed and ready to take on the day.
If you’ve been wondering why do you wake up tired even after 8 hours sleep, now you know where to start fixing it. Begin today with a better sleep routine��and better mornings will follow.
0 notes
Text
How to Prevent Food Poisoning in Monsoon

Monsoon brings relief from the heat—but along with cool breezes and rains come increased chances of infections, especially food poisoning. The high moisture in the air creates a perfect breeding ground for bacteria, making food more likely to spoil and cause illness.
In this article, we’ll help you understand how to stay safe with easy, practical tips on how to prevent food poisoning in monsoon.
Why Is Food Poisoning So Common in Monsoon?
The damp and humid conditions during the rainy season promote bacterial and fungal growth. This contamination can easily affect the food we eat and the water we drink.
Common causes of food poisoning in monsoon include:
Eating contaminated street food
Drinking unfiltered or untreated water
Improper storage or refrigeration
Eating undercooked or reheated leftovers
Symptoms can range from mild stomach pain to vomiting, diarrhea, and fever—and can become serious if not treated on time.
How to Prevent Food Poisoning in Monsoon: Easy Tips
Let’s go step by step into what you should do (and not do) during this season to avoid foodborne illness:
1. Avoid Street Food and Raw Salads
Street vendors often use unclean water and keep food exposed to dust, flies, and pollution. In monsoon, this risk becomes even higher.
What to avoid:
Chaat, golgappas, sandwiches from carts
Cut fruits or raw vegetables sold outside
Juices from roadside stalls
Instead, eat home-cooked meals where you can control the hygiene.
2. Drink Only Boiled or Purified Water
Unfiltered water is a major cause of stomach infections during monsoon. Make sure your drinking water is:
Boiled for 10 minutes, or
Filtered using a RO/UV purifier, or
Packaged from a trusted brand
Avoid consuming water-based drinks like sherbets or ice made with unclean water.
3. Eat Fresh and Hot Food
In monsoon, bacteria multiply quickly. Avoid eating food that has been left out for hours.
Tips:
Eat freshly cooked meals while still warm
Avoid reheating food multiple times
Don't leave cooked food at room temperature for more than 2 hours
4. Refrigerate Perishables Quickly
Your fridge is your best friend in this season—but only if you use it right.
Refrigeration tips:
Store cooked food in airtight containers
Don't keep raw meat and vegetables together
Use leftovers within 24 hours
Check for expired or spoiled food regularly
5. Clean Fruits and Vegetables Properly
Rainwater often brings mud and germs to fresh produce. Even greens from the market can carry bacteria and insect eggs.
Cleaning tips:
Wash produce thoroughly with clean water
Use salt water or vinegar soak for 10–15 minutes to disinfect
Peel fruits like mangoes and bananas before eating
Avoid leafy vegetables that are difficult to clean, like spinach and lettuce
6. Practice Good Kitchen Hygiene
Contamination often starts in your kitchen.
Hygiene habits to follow:
Wash hands before and after handling food
Keep utensils and chopping boards dry and clean
Don't let water collect on kitchen surfaces
Wash dish cloths and sponges regularly
Related Health Checkups to Consider
If you're experiencing stomach problems or want to monitor your digestive health during monsoon, these lab tests (available via SecondMedic powered by Thyrocare) may help:
🔹 Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Checks for infections or inflammation.
🔹 Stool Routine & Culture Test
Detects bacterial infections, parasites, or digestive disorders.
🔹 CRP Test (C-Reactive Protein)
Shows whether your body is fighting an infection.
🔹 Food Intolerance Test
For people with recurring food-related digestive issues.
All tests come with home sample collection and online report access at www.secondmedic.com.
Foods You Can Eat During Monsoon
Here are some healthy, safe food choices during the rainy season:
Warm soups and khichdi – light and easy to digest
Steamed vegetables – safer than raw
Ginger tea – helps digestion
Turmeric milk – natural immunity booster
Boiled eggs or well-cooked lean meat
Avoid oily, uncooked, or refrigerated food that’s more than a day old.
Conclusion
Monsoon brings beauty, but also bacteria. Staying safe is all about being smart with your food and water. By following simple hygiene rules and eating fresh, clean food, you can enjoy the season without worrying about stomach issues.
Be alert, eat smart, and protect your family by following these tips on how to prevent food poisoning in monsoon.
0 notes
Text
Teen Mental Health – Signs Parents Must Never Ignore

Teenage years are a time of transformation—emotionally, physically, and mentally. While moodiness and rebellion may seem like part of the package, sometimes these behaviors can hide serious mental health issues.
Today, more teenagers are struggling with anxiety, depression, stress, and even thoughts of self-harm—but many go unnoticed because the signs are subtle.
As a parent or guardian, it’s crucial to know the early signs of mental health problems in teens. Let’s explore the red flags you should never ignore and how you can help your child feel supported and heard.
Why Teen Mental Health Matters More Than Ever
In India and around the world, teen mental health issues are on the rise due to:
Academic pressure
Social media stress
Body image concerns
Bullying or peer pressure
Family conflicts
Hormonal changes
Ignoring early signs can lead to worsening conditions or even risky behavior. Early action is the key to prevention and healing.
5 Warning Signs of Teen Mental Health Issues
1. Withdrawal from Family and Friends
If your once-social teen starts avoiding friends, skipping family dinners, or isolating in their room more than usual—it could be a sign of depression or anxiety.
What to watch for:
Saying "I’m fine" but acting distant
Losing interest in favorite activities
Avoiding calls or texts from friends
2. Sudden Drop in Academic Performance
Stress, low motivation, or emotional exhaustion often lead to a dip in school performance. If your child suddenly starts failing or avoids school altogether, take it seriously.
What to watch for:
Skipping homework or classes
Teachers reporting attention issues
Saying "What’s the point?" or "I don’t care anymore"
3. Changes in Eating or Sleeping Habits
Teen depression often changes daily habits. Some teens may sleep or eat too much, while others may lose their appetite and suffer insomnia.
What to watch for:
Skipping meals or binge eating
Staying up all night
Always feeling tired
4. Talk of Hopelessness or Self-Harm
If your teen talks about feeling worthless, says things like “No one cares” or shows an interest in self-harm—it’s a serious red flag.
What to watch for:
Negative self-talk
Writing or drawing about death
Wearing long sleeves to hide cuts
Tip: If you hear even a hint of suicidal thoughts, seek professional help immediately.
5. Unexplained Aches and Pains
Sometimes mental health problems appear as physical complaints, especially in teens who struggle to express emotions.
What to watch for:
Frequent stomach aches, headaches, or nausea
No clear medical cause
Always feeling “sick” before school or social events
How to Support Your Teen
As a parent, your role is not to fix everything but to listen and support. Here’s how:
Create a safe space: Let your teen know they can talk without judgment
Ask open-ended questions like: “How have you been feeling lately?” “Do you want to talk or just need someone to listen?”
Avoid dismissing their emotions with phrases like: “You’ll get over it” or “It’s just a phase”
Encourage healthy routines: Regular sleep, a balanced diet, physical activity, and tech breaks
When to Seek Professional Help
Call a psychologist, counselor, or pediatrician if you notice:
Signs persist for more than 2–3 weeks
Risky behavior like substance use, aggression, or self-harm
Extreme withdrawal or refusal to attend school
Talk of suicide or self-hatred
Useful Health Checks for Teens (Available at SecondMedic.com)
Mental health issues can also be connected to physical imbalances. Consider these lab tests (via Thyrocare):
Thyroid Profile
Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can affect mood and energy.
Vitamin D Test
Low vitamin D is linked to fatigue, depression, and anxiety.
CBC (Complete Blood Count)
To rule out anemia or infections that might affect mood or focus.
CRP Test (C-Reactive Protein)
Detects inflammation, which can also impact mental well-being.
These tests are easily bookable online with home sample collection and fast results.
Conclusion
As a parent, you play a key role in recognizing early warning signs and guiding your teen to emotional well-being. What may look like rebellion, laziness, or "drama" could actually be a silent cry for help.
Stay present. Stay open. And most importantly—act early.
If you're unsure about what’s normal and what’s not, just remember this: Teen mental health – signs parents must never ignore could be the first step to saving a life.
0 notes
Text
Lack of Sunlight and Mental Health Link: What You Should Know

Do you ever feel gloomy, tired, or anxious during the rainy season or in winter when sunlight is low? You're not alone. There’s a growing body of research that shows a strong link between lack of sunlight and mental health problems—including depression, anxiety, and fatigue.
In this blog, we’ll break down this connection in simple terms and help you understand why stepping outside for just 20 minutes of sunshine could boost your mood naturally.
Why Is Sunlight So Important?
Sunlight does more than just brighten our days. It plays a critical role in our physical and mental well-being by:
Regulating sleep through the circadian rhythm
Boosting serotonin, the “feel-good” hormone
Helping the body produce vitamin D, which supports mood and immunity
Improving alertness and reducing fatigue
When we don’t get enough sunlight—whether due to indoor lifestyles, long winters, or pollution—our mental health may suffer.
The Science Behind the Mood-Sunlight Connection
Sunlight impacts the brain's chemistry, especially serotonin and melatonin levels.
Serotonin improves mood, helps you feel calm, and supports focus.
Melatonin controls sleep and is produced when it's dark.
When you lack sunlight, serotonin production drops, while melatonin levels rise earlier in the day. This imbalance can cause:
Low energy
Sadness or depression
Irritability
Oversleeping
Poor concentration
What Is Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)?
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs at certain times of the year—usually in winter when sunlight is limited.
Common SAD symptoms:
Feeling hopeless or down most of the day
Sleeping more than usual
Craving carbs and gaining weight
Losing interest in activities you usually enjoy
Low motivation and energy
SAD is real, and it affects millions worldwide—especially in places with long winters or low sunlight.
The Role of Vitamin D
Sunlight helps your skin make vitamin D, which is essential for your mood and immune function. Low levels of vitamin D are linked to:
Depression
Fatigue
Brain fog
Weak immunity
How do I know if I have low vitamin D?
You can take a Vitamin D blood test—available through platforms like SecondMedic.com with Thyrocare home collection.
Signs You May Be Affected by Low Sunlight
You feel sad or “off” during cloudy or winter days
You avoid going outdoors
You feel sleepy all day
You lose interest in daily tasks
You are deficient in vitamin D
If you check more than 2 of these, it’s time to focus on getting more light.
Simple Ways to Get More Sunlight and Boost Mental Health
1. Get Morning Sunlight
Spend 15–30 minutes in direct morning sunlight every day. This resets your internal clock and boosts serotonin.
2. Open Curtains and Use Natural Light Indoors
Let natural light into your home or workspace whenever possible.
3. Take a Walk Outside
Even a short daily walk can improve your mood.
4. Consider a Vitamin D Supplement
If your doctor confirms deficiency, a supplement may help restore mood balance.
5. Use Light Therapy
In areas with very little sunlight, light therapy lamps mimic natural light and can reduce SAD symptoms.
Related Lab Tests (Available on SecondMedic)
To understand how sunlight impacts your health, consider these lab tests:
Vitamin D Test
Check your vitamin D levels and confirm if sunlight deficiency is affecting your mood.
Thyroid Profile
Low sunlight can affect thyroid function, which is closely tied to mental health.
CRP Test (C-Reactive Protein)
To check if inflammation is contributing to fatigue or mood issues.
All of these are available for home sample collection through SecondMedic.com.
Conclusion
It’s easy to overlook how much sunlight affects our mind. But science clearly shows that regular exposure to natural light improves mood, energy, and mental clarity.
Whether you're feeling low or want to prevent future problems, just a few minutes of daily sunlight can make a big difference.
If you’re concerned about the lack of sunlight and mental health link, start by stepping outside—your brain will thank you.
0 notes
Text
Let’s simplify the medical jargon and walk you through the CRP test meaning and when to do it, especially in the Indian healthcare context.
What Is a CRP Test?
CRP stands for C-reactive protein. It is a substance produced by your liver in response to inflammation in the body.
The CRP test is a blood test that measures the amount of C-reactive protein in your blood. High levels of CRP usually mean there’s inflammation in your body, which could be due to an infection, injury, or a chronic disease like arthritis.
High CRP = Inflammation Alert
This test doesn’t tell you what’s causing the inflammation—it simply tells you that something is wrong, and further testing might be needed.
What Does the CRP Test Detect?
While CRP is a general marker, it is helpful in detecting:
Bacterial or viral infections
Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
Inflammatory bowel diseases
COVID-19 severity
Heart disease risk (especially with high-sensitivity CRP or hs-CRP)
When Should You Do a CRP Test?
You should get a CRP test done when:
You have fever or chills that won’t go away
You’re showing signs of infection like cough, swelling, or pain
Your doctor is monitoring an autoimmune disease
You’re recovering from surgery or injury
Your doctor is checking inflammation due to chronic disease
You are showing COVID-like symptoms (to assess severity)
Normal CRP Levels:
CRP Level
Interpretation
Below 1 mg/L
Low risk of inflammation
1–3 mg/L
Moderate risk
Above 3 mg/L
High inflammation or infection present
Above 10 mg/L
May indicate serious infection or disease
Note: For heart disease risk, a high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) test is used.
Is Fasting Required for the CRP Test?
No, fasting is not required. You can take the CRP test at any time of day, unless it is being done with other tests that require fasting (like blood sugar or cholesterol).
Lab Tests Packages Including CRP
You can book a CRP test alone or as part of a health package via SecondMedic.com, powered by Thyrocare:
Basic CRP Test
Detects inflammation/infection
Simple blood draw
Home sample collection
COVID Monitoring Panel
CRP, D-Dimer, Ferritin, CBC
Recommended if you have COVID symptoms or are recovering
Inflammation Panel
CRP + ESR + CBC + Liver Profile
For those with chronic fatigue, joint pain, or autoimmune diseases
Lifestyle Tips If Your CRP is High
A high CRP may indicate ongoing inflammation. Along with medical treatment, here are some tips:
Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Cut down on sugar and processed food
Include omega-3 rich foods like flaxseed and fish
Exercise regularly
Manage stress and sleep better
Quit smoking and limit alcohol
5 Most Asked Questions About the CRP Test
1. What is the CRP test used for?
CRP tests are used to check for inflammation due to infections, autoimmune diseases, and to monitor treatment effectiveness.
2. What causes a high CRP level?
Infections, chronic inflammation, surgery, injuries, and lifestyle diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
3. Is a CRP test painful?
No. It’s a simple blood test and usually takes just a few minutes.
4. How long does it take to get CRP test results?
Most labs deliver CRP results within 24 to 48 hours.
5. Can CRP levels return to normal?
Yes, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, CRP levels can go back to the normal range.
Booking a CRP Test Online (Thyrocare via SecondMedic)
Here’s how you can book it:
Go to www.secondmedic.com
Search for "CRP Test – Thyrocare"
Select home sample collection
Enter your location and schedule pickup
Get digital results within 1–2 days
Conclusion
The CRP test is a simple, affordable, and powerful tool to detect inflammation early. Whether you’re dealing with an infection, monitoring a chronic condition, or recovering from illness, this test gives your doctor a clearer picture of what’s happening inside your body.
Don’t ignore signs like unexplained fever, fatigue, or body pain. Get tested.
If you’re wondering about CRP test meaning and when to do it — the answer is simple: whenever inflammation or infection is suspected, this test is your body's alert system.
0 notes
Text

Sleep is essential for growing teens, yet many struggle to get enough of it. From school stress to social media scrolling, teenagers today face multiple challenges that affect their sleep. One of the most common sleep disorders among adolescents is insomnia—the inability to fall asleep, stay asleep, or wake up feeling rested.
In this blog, we’ll break down the causes, effects, and simple strategies to handle insomnia in teens and how to manage it naturally.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it hard to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get quality rest. Teens with insomnia often feel tired during the day, even if they’ve spent enough time in bed.
There are two main types:
Short-term insomnia: Lasts for a few days or weeks, often triggered by stress or changes in routine.
Chronic insomnia: Occurs at least three times a week for over three months.
Why Is Insomnia Common in Teens?
Teenagers go through many physical, emotional, and social changes. All these factors can disturb their sleep:
1. Hormonal Shifts
During puberty, the sleep hormone melatonin is released later at night. This shifts the body clock, making teens naturally want to sleep and wake up later.
2. Screen Time
Excessive use of phones, tablets, or laptops before bedtime exposes the brain to blue light, which delays melatonin release and interferes with sleep.
3. Academic Stress
Homework, exams, and performance pressure can cause anxiety and overthinking at night, preventing restful sleep.
4. Caffeine Intake
Energy drinks, tea, coffee, and cola consumed in the evening can make it difficult to fall asleep due to their stimulating effects.
5. Mental Health Issues
Anxiety, depression, and emotional distress are often linked with poor sleep in teens.
Signs of Insomnia in Teenagers
Difficulty falling asleep at night
Waking up multiple times during the night
Feeling tired or sleepy during the day
Irritability or mood swings
Trouble focusing in school
Frequent headaches or stomach issues
Increased use of stimulants (coffee, energy drinks)
How Insomnia Affects Teens
Sleep deprivation can harm a teen's physical and mental health. Here are a few ways it affects their well-being:
Poor concentration in school
Weakened immunity
Increased risk of depression and anxiety
Weight gain due to hormonal imbalance
Risky behaviors due to impaired judgment
Teens who consistently sleep less than 7–8 hours are more likely to face emotional and academic challenges.
Natural Ways to Manage Insomnia in Teens
Thankfully, insomnia doesn’t always need medication. Many teens can improve their sleep with simple lifestyle changes.
1. Set a Regular Sleep Schedule
Encourage going to bed and waking up at the same time every day—even on weekends. This helps reset the body’s internal clock.
2. Limit Screen Time Before Bed
Avoid phones, TVs, and tablets at least 1 hour before bedtime. Use “night mode” or blue light filters if screen use is necessary.
3. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Deep breathing, meditation, gentle yoga, or reading a book before bed can calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
4. Watch Food and Drink
Avoid heavy meals, sugar, or caffeine in the evening. A light snack like warm milk, bananas, or almonds can promote better sleep.
5. Get Daily Exercise
Physical activity during the day can improve sleep quality—but avoid intense workouts right before bedtime.
6. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Keep the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains, soft bedding, and remove distractions like phones or bright lights.
When to See a Doctor
If your teen’s insomnia lasts longer than 3 weeks or affects their daily life, school, or mood, it’s important to consult a doctor or sleep specialist. Underlying conditions like anxiety, ADHD, or depression might need professional care.
Lab Tests That May Help
If your teen complains of constant fatigue or disrupted sleep, you might consider lab tests to rule out medical reasons such as:
Thyroid Function Test (for hormonal imbalance)
Vitamin D & B12 Tests (deficiency can affect sleep)
Stress Hormone Panel (Cortisol)
Iron Levels (especially in girls)
These tests are available through diagnostic providers like Thyrocare on platforms like SecondMedic.
Helping Teens Build Healthy Sleep Habits
As a parent, here’s how you can support better sleep:
Encourage open conversations about school pressure or emotional issues.
Set boundaries for screen use, especially at night.
Make the home environment calm and supportive before bedtime.
Lead by example—follow healthy sleep habits yourself.
Quick Tips for Teens
Sleep 8–10 hours every night
Don’t study in bed
Use a sleep diary or app to track sleep patterns
Avoid naps longer than 30 minutes in the day
Try journaling to clear the mind before sleep
Conclusion
Teenage insomnia is more common than many people realize. Fortunately, with the right support, structure, and healthy routines, it can be managed without medication.
If your teen shows signs of poor sleep, don’t ignore it. Better sleep leads to better mood, focus, and health.
So, if you’re wondering how to support better sleep for your child, remember to understand insomnia in teens and how to manage it the natural way—with empathy, good habits, and expert care when needed.
0 notes
Text
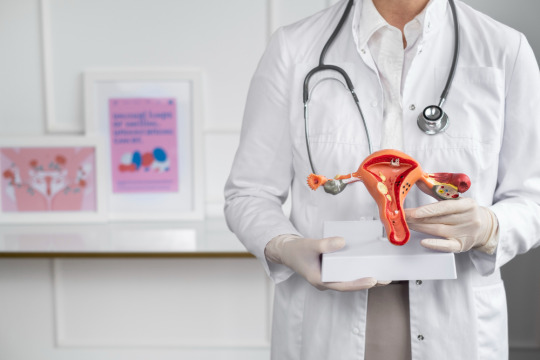
Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable yet deadly cancers in women today. Despite medical advancements and awareness campaigns, many women are diagnosed at a late stage—often because early signs are mild or misunderstood. In many cases, the body sends signals, but they’re too subtle to be taken seriously.
This blog highlights the silent symptoms of cervical cancer that women often ignore, why early detection matters, and what you can do to protect your health.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer starts in the cells of the cervix—the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The most common cause is persistent infection with high-risk types of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
It usually develops slowly over time and begins with precancerous changes. Regular screening can detect these changes early, but when symptoms appear, it often means the cancer is already progressing.
Why Is Cervical Cancer Often Missed?
Many early symptoms of cervical cancer overlap with common conditions like infections or hormonal changes. Women might dismiss them as side effects of stress, irregular periods, or aging.
Unlike more aggressive cancers, cervical cancer grows slowly, giving a false sense of security. That’s why it’s important to pay attention to even small changes in your body.
5 Silent Symptoms of Cervical Cancer Women Ignore
Unusual Vaginal Bleeding
One of the earliest and most ignored signs is bleeding at unexpected times:
Between menstrual cycles
After intercourse
After menopause
Longer or heavier periods
Many women assume it's due to stress, PCOS, or hormonal imbalance—but it could be your body warning you of cervical changes.
Foul-Smelling or Watery Vaginal Discharge
A change in vaginal discharge that’s:
Persistent
Pale, pink, or brown
Foul-smelling or watery
might not be a simple yeast infection. It could result from a tumor breaking down tissues in the cervix.
Pelvic Pain or Discomfort
If you feel pain:
Deep inside the pelvis
During or after sex
That radiates to the lower back or legs
and it doesn’t go away after your period, it may signal something more serious. Persistent pelvic pain should never be ignored.
Pain During Intercourse
Many women shy away from talking about pain during sex. But if intimacy becomes painful—especially with light bleeding—it may be linked to cervical inflammation or a tumor pressing against nearby tissues.
Unexplained Fatigue or Weight Loss
When cancer cells spread, they drain your body’s energy and cause:
Chronic tiredness
Loss of appetite
Sudden weight loss
These symptoms may appear in later stages, but they are often brushed off as general stress or busy lifestyle side effects.
How Is Cervical Cancer Detected?
The most effective way to catch cervical cancer early is through routine screening and testing:
Pap smear test – Detects abnormal cells in the cervix.
HPV test – Checks for high-risk HPV strains.
Colposcopy – Examines the cervix more closely if Pap results are abnormal.
Women over 25 should have regular checkups even if they feel healthy.
Who Is at Risk?
Women with early sexual activity or multiple partners
Those who have never had a Pap smear
Smokers
Women with weakened immune systems
Long-term use of birth control pills (over 5 years)
Family history of cervical or reproductive cancers
Can Cervical Cancer Be Prevented?
Yes, and that’s the best part.
🔹 Get Vaccinated
The HPV vaccine is safe and effective. It’s recommended for girls and boys aged 9–26 but can be given up to age 45.
🔹 Practice Safe Sex
Using protection and limiting the number of partners can reduce HPV exposure.
🔹 Schedule Regular Screenings
Early detection is key. Regular Pap and HPV tests can save your life.
🔹 Listen to Your Body
If something feels wrong—even slightly—it’s worth checking out.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience:
Bleeding after sex
Foul-smelling discharge
Painful urination or pelvic discomfort
Persistent fatigue or weight loss
Don’t wait. Book an appointment with a gynecologist immediately.
Empower Yourself with Knowledge
Cervical cancer doesn’t always come with loud alarms. Sometimes it whispers. And those whispers are what we ignore until it’s too late. Awareness, education, and preventive action are your strongest weapons.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is one of the most treatable cancers—if detected early. Unfortunately, many women miss the subtle symptoms that signal the start of the disease. The best way to protect yourself is to stay informed, know your body, and never ignore unusual signs.Take charge of your health today by scheduling a screening and staying alert. Because the silent symptoms of cervical cancer women ignore can cost lives. Don’t let them cost yours.
0 notes
Text

Our liver plays a vital role in keeping our body healthy. It filters toxins from the blood, helps digest food, stores energy, and supports immunity. But like any organ, it can get damaged. Two common liver conditions people often confuse are fatty liver and liver cirrhosis. While both affect the liver, they are very different in terms of causes, symptoms, and outcomes.
In this blog, we’ll help you understand the key differences between liver cirrhosis and fatty liver, how they develop, their symptoms, treatments, and how to prevent them.
What Is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver, also called hepatic steatosis, is a condition where fat builds up in the liver. It’s normal for the liver to have some fat, but if more than 5-10% of the liver's weight is fat, it's considered a fatty liver.
There are two main types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – Most common, seen in people who don’t drink much alcohol.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) – Caused by heavy alcohol use.
Fatty liver is often a silent condition. Many people don’t know they have it because it usually doesn’t cause symptoms in early stages.
Causes of Fatty Liver
Obesity
High cholesterol or triglycerides
Type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure
Rapid weight loss
Poor diet (high in sugar and fat)
Excessive alcohol intake (in AFLD)
What Is Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease where healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis). This scarring blocks blood flow and affects the liver’s ability to work properly.
Unlike fatty liver, cirrhosis is permanent and serious. It develops slowly over years, often due to long-term liver damage from alcohol, hepatitis, or untreated fatty liver.
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis
Chronic alcohol use
Hepatitis B and C infections
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH – advanced form of fatty liver)
Autoimmune diseases
Genetic disorders (like Wilson’s disease)
Long-term use of certain medications
Key Differences Between Fatty Liver and Cirrhosis
Aspect
Fatty Liver
Liver Cirrhosis
Nature
Fat accumulation in liver cells
Scarring and permanent damage to liver tissue
Reversibility
Reversible with lifestyle changes
Irreversible, but progression can be slowed
Symptoms
Usually no symptoms early on
Fatigue, jaundice, swelling, confusion
Causes
Obesity, diabetes, alcohol, diet
Long-term liver damage, hepatitis, alcohol
Severity
Mild to moderate
Severe and life-threatening if not managed
Treatment
Lifestyle and diet changes
Medication, regular monitoring, sometimes transplant
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Fatty Liver Symptoms (if any):
Fatigue
Mild discomfort or pain in upper right abdomen
Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests
Liver Cirrhosis Symptoms:
Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
Swelling in legs or abdomen (edema or ascites)
Easy bruising or bleeding
Confusion or memory loss (hepatic encephalopathy)
Itchy skin
Spider-like blood vessels on skin
Diagnosis: How Doctors Tell the Difference
Doctors use a combination of the following to diagnose liver issues:
Blood tests – Check liver enzymes, liver function.
Imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI) – Shows fat or scarring in the liver.
Fibroscan or Liver Biopsy – Measures liver stiffness or checks for scarring directly.
Fatty liver shows fat deposits, while cirrhosis shows scar tissue and shrinkage of the liver.
Treatment Options
For Fatty Liver:
Weight loss – Losing 7-10% of body weight can reverse the condition.
Healthy diet – Focus on fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean protein.
Exercise – At least 30 minutes daily.
Avoid alcohol – Especially if it’s alcohol-related fatty liver.
Control diabetes/cholesterol – With diet or medication.
For Liver Cirrhosis:
Treat the underlying cause – Like hepatitis or alcohol use.
Avoid alcohol completely
Healthy diet with low salt – Prevent fluid buildup.
Medications – To manage symptoms and complications.
Regular screening – For liver cancer or internal bleeding.
Liver transplant – In advanced or end-stage cases.
Can Fatty Liver Turn into Cirrhosis?
Yes, if fatty liver is not treated, especially in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), it can cause inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis over time. But the good news is – fatty liver is reversible, especially if caught early and proper steps are taken.
How to Keep Your Liver Healthy
Maintain a healthy weight
Eat a balanced diet – Avoid sugary, fried, or processed food
Exercise regularly
Avoid alcohol or drink in moderation
Don’t share needles or personal items that may carry blood
Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B
Take medicines only as prescribed
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you feel constantly tired, have unexplained weight loss, jaundice, swelling in your abdomen or legs, or abnormal liver test results – don’t ignore it. Early diagnosis can make a big difference.
Conclusion
Fatty liver and liver cirrhosis are both serious liver conditions, but they are very different. Fatty liver is often the first stage of liver damage, and is reversible with lifestyle changes. Cirrhosis, on the other hand, is irreversible, and needs medical attention and sometimes life-long treatment.
Understanding the difference between the two helps you take better care of your liver and make informed health decisions. If you or someone you know is at risk, it’s never too early to make a change.
Want to know more about how to keep your liver healthy? Talk to your doctor today and understand the risks. Liver cirrhosis vs fatty liver: What’s the difference? Find out now and protect your health before it’s too late.
0 notes
Text
Seasonal Flu vs Covid-19: 2025 Comparison

As we step into 2025, seasonal flu and Covid-19 continue to be common health concerns, especially during winter and changing weather. Though both illnesses share some symptoms, they differ in causes, severity, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these differences is important to stay informed, protect yourself, and take the right steps when feeling sick.
Let’s take a closer look at Seasonal flu vs Covid-19: 2025 comparison and understand how they impact our health today.
What is Seasonal Flu?
Seasonal flu, also called influenza, is a viral infection that spreads every year, mainly in winter. It is caused by influenza viruses, especially Influenza A and B. The virus affects the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs.
Common Symptoms of Flu:
Fever and chills
Cough and sore throat
Runny or stuffy nose
Muscle aches
Fatigue
Headache
Most people recover from the flu within a few days to a week. However, the elderly, young children, and those with weak immunity may develop serious complications like pneumonia.
What is Covid-19?
Covid-19 is a respiratory illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It was first discovered in 2019 and caused a global pandemic. Over the years, new variants have emerged, and now in 2025, the virus continues to spread in milder or seasonal waves.
Common Symptoms of Covid-19 in 2025:
Fever
Dry cough
Tiredness
Loss of taste or smell
Sore throat
Headache
Breathing difficulties (in severe cases)
Some people also experience stomach issues, body aches, or skin rashes. The symptoms may vary depending on the variant and the individual's immunity.
Seasonal Flu vs Covid-19: Key Differences
Feature
Seasonal Flu
Covid-19
Virus Type
Influenza A/B
SARS-CoV-2
Incubation Period
1–4 days
2–14 days
Symptoms Onset
Sudden
Gradual or sudden
Loss of Taste/Smell
Rare
Common (especially in early variants)
Severity
Mild to moderate
Mild to severe, depending on variant
Spread
Through droplets, surface contact
Droplets, aerosols, and close contact
Vaccine
Annual flu shot
Booster updated for current variants
Treatment
Antiviral drugs, home care
Antivirals, supportive care, and rest
Which is More Dangerous in 2025?
Both illnesses can be serious, but Covid-19 still poses higher risks, especially for the elderly and those with chronic health problems. Covid-19 can lead to severe lung infections, long-term symptoms (Long Covid), and hospitalization in some cases. Seasonal flu is usually less severe but still dangerous for certain groups.
In 2025, thanks to vaccines and public health awareness, both illnesses are more manageable than before. However, ignoring symptoms or delaying care can make things worse.
Prevention Tips for Both Illnesses
Whether it’s flu or Covid-19, prevention is always better than cure. Here are a few simple ways to stay protected:
1. Get Vaccinated
Take the yearly flu shot, especially before the winter season.
Get updated Covid-19 boosters as recommended.
2. Maintain Hygiene
Wash hands often with soap and water.
Use hand sanitizers when outside.
Avoid touching your face, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
3. Wear a Mask in Crowded Places
Masks help prevent the spread of both viruses, especially in public transport, hospitals, and indoor events.
4. Stay Home if You Feel Sick
Rest, hydrate, and avoid contact with others until you recover.
5. Boost Your Immunity
Eat a balanced diet, get enough sleep, exercise, and manage stress.
When to See a Doctor?
You should consult a doctor if:
You have high fever for more than 2 days
Difficulty breathing or chest pain
Severe fatigue or confusion
Dehydration (dry mouth, dizziness)
Underlying conditions like diabetes or asthma
Doctors may recommend a test to confirm whether it’s flu or Covid-19. Based on results, the treatment and isolation guidelines may vary.
Testing in 2025: Easier and Faster
One positive update in 2025 is the availability of dual testing kits that detect both flu and Covid-19 in one test. These are available at clinics, hospitals, and even home-use versions for early diagnosis. Early testing helps in starting treatment quickly and prevents spread to others.
Treatment and Recovery
For Flu:
Rest and plenty of fluids
Antiviral medicines (like oseltamivir) if prescribed
Pain relievers for body aches and fever
For Covid-19:
Isolation if symptoms are present
Antiviral medicines for high-risk groups
Oxygen support in serious cases
Monitoring of oxygen levels using a pulse oximeter
In both cases, self-care is key to faster recovery.
Mental Health During Seasonal Illnesses
Falling sick, especially in a post-pandemic world, can cause anxiety. It’s important to:
Stay calm
Avoid panic scrolling online
Get facts from reliable sources like WHO or your local health department
Talk to a counselor if feeling overwhelmed
Taking care of your mental well-being helps in faster healing and better decision-making.
Conclusion: Stay Alert, Stay Healthy
In the Seasonal flu vs Covid-19: 2025 comparison, we see that while both illnesses affect the respiratory system and share common symptoms, Covid-19 still carries more complications. However, with awareness, vaccination, hygiene, and timely testing, we can reduce risks and protect our families.
Don’t take chances this season. Be aware, take precautions, and if in doubt, consult your doctor. Let’s stay ahead of seasonal infections by understanding the clear differences through this Seasonal flu vs Covid-19: 2025 comparison.
0 notes
Text
Joint Pain in Rainy Weather – What Doctors Say

When the skies turn grey and the rain begins to fall, many people start to feel an all-too-familiar ache in their joints. If you or someone you know often says, “I can feel the rain in my knees,” you’re not alone. Joint pain in rainy weather is a real concern for millions, especially those with arthritis or past injuries. But is this just an old myth or is there actual science behind it? Let’s break it down with what doctors and experts have to say.
Why Do Joints Hurt More in the Rain?
Many people report increased joint pain, stiffness, or discomfort during rainy or humid weather. There are a few reasons why this might happen:
1. Drop in Barometric Pressure
Doctors say that when it rains, the atmospheric or barometric pressure drops. This decrease may allow tissues in the body to expand slightly. For people with sensitive joints, this expansion can irritate nerves and lead to pain.
2. Cold Temperatures
Rain often brings cooler temperatures. Cold weather can cause muscles and joints to stiffen, reducing blood circulation and making movement more painful. People with arthritis may especially notice this.
3. Increased Humidity
Humidity can affect the way our body handles fluid. It may lead to inflammation or swelling around the joints, causing pain or discomfort in sensitive areas like knees, hips, and fingers.
4. Mood and Physical Activity
Rainy weather also tends to make people less active. Staying indoors and moving less can cause joint stiffness. Also, cloudy skies and gloomy days can affect your mood and lower your pain tolerance.
What Medical Experts Say
Dr. Anjali Mehta, Rheumatologist
“Patients often come to me complaining that their arthritis gets worse when it rains. While it may sound like an old wives’ tale, we do believe that weather changes—especially drops in pressure—can affect the joints.”
Dr. Rajeev Sharma, Orthopedic Surgeon
“People with old injuries or joint surgeries might have more nerve sensitivity. Weather changes can trigger inflammation or activate pain receptors in these areas.”
Dr. Sneha Kulkarni, Physiotherapist
“It’s important to keep joints mobile during rainy days. Movement improves circulation and prevents stiffness. Gentle exercises and stretching routines can help.”
Who Is Most Affected by Joint Pain in the Rain?
Joint pain in rainy weather doesn’t affect everyone, but certain groups are more likely to notice a difference:
People with Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis
Those with old joint injuries or fractures
Individuals with low Vitamin D or calcium levels
Elderly people whose joints are naturally more worn out
Women over 40, especially during menopause
Tips to Reduce Joint Pain During Rainy Days
The good news is that you can manage and reduce weather-related joint pain with simple steps. Here’s what doctors recommend:
Stay Warm
Use heating pads or wear thermal clothing.
Soak in a warm bath to relax your joints.
Keep Moving
Do light exercises like walking or yoga.
Stretch your joints regularly, even indoors.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking water helps maintain joint lubrication.
Avoid too much caffeine or salty foods, which may dehydrate you.
Eat a Joint-Friendly Diet
Include omega-3 rich foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Eat anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, garlic, spinach, and berries.
Take Supplements if Needed
Consult your doctor about taking Vitamin D, calcium, or glucosamine supplements.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Less weight = less pressure on your joints.
Home Remedies That May Help
Here are some simple remedies that people swear by during rainy days:
Massage with warm mustard oil or coconut oil
Use a hot water bottle on stiff joints
Apply a turmeric paste externally
Drink ginger tea—it’s a natural anti-inflammatory
Practice meditation to manage stress-related joint pain
When Should You See a Doctor?
While occasional discomfort is common, you should see a doctor if:
The pain is constant and not improving
You experience swelling, redness, or warmth around the joint
You can’t move the joint properly
You feel weakness or numbness
Doctors can run tests like X-rays, blood work, or MRIs to find the cause and provide treatment. Sometimes joint pain could be due to underlying issues like arthritis, gout, or autoimmune diseases that require medical attention.
Conclusion
If your joints start to ache the moment clouds appear, it’s not just your imagination. Weather changes—especially rainy days—can affect your body in surprising ways. From barometric pressure to low temperatures, several factors can contribute to joint pain in rainy weather. But the right mix of exercise, diet, and self-care can make a big difference.
So the next time you feel a dull ache in your knees as it starts to drizzle, listen to your body—but also follow what experts suggest to stay comfortable and pain-free.
Want to understand your symptoms better or need personalized advice? Talk to your doctor today and learn more about “Joint pain in rainy weather – What doctors say.”
0 notes
Text
How Chronic Stress Affects Your Digestive Health – Understanding the Gut-Stress Connection

Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become a constant companion. From work pressures to personal challenges, chronic stress can take a serious toll on your health. While most people are aware of how stress can affect mental well-being, many don't realize its powerful impact on physical health — especially the digestive system. Yes, your gut and brain are more connected than you think. In this blog, we’ll explore how chronic stress affects your digestive health, the science behind it, symptoms to watch for, and simple tips to protect your gut.
What Is Chronic Stress?
Stress is the body’s natural response to pressure or danger. It can be helpful in short bursts (like escaping danger), but when it becomes ongoing — known as chronic stress — it can harm your body over time.
Chronic stress arises when you constantly feel overwhelmed or unable to cope with the demands of daily life. This continuous stress activates your body’s fight-or-flight response, keeping your system on high alert.
The Gut-Brain Connection
Your gut and brain are linked through a complex communication network known as the gut-brain axis. This system connects your central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) with your enteric nervous system (gut nerves).
The vagus nerve, one of the largest nerves in the body, plays a big role in this communication.
Neurotransmitters like serotonin (which affects mood) are produced in the gut.
Your gut bacteria (microbiome) also influence brain function and stress levels.
This two-way relationship means stress can affect your gut — and gut issues can impact your mood.
How Chronic Stress Affects Your Digestive Health
Let’s break down exactly what happens to your digestive system when you’re under long-term stress.
1. Slows Down Digestion
When you’re stressed, your body shifts energy away from digestion to prioritize “survival.” This means food may sit longer in your stomach, leading to:
Bloating
Gas
Indigestion
Heartburn
2. Triggers or Worsens Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
People with IBS often report that stress worsens their symptoms. Chronic stress may:
Increase abdominal pain
Trigger diarrhea or constipation
Create irregular bowel habits
3. Changes Gut Bacteria
Stress can harm the balance of healthy bacteria in your gut, known as the microbiome. A disrupted microbiome can lead to:
Inflammation
Weakened immune system\
Poor nutrient absorption
Increased risk of leaky gut
4. Reduces Blood Flow to Digestive Organs
Stress can narrow blood vessels, reducing circulation to your gut. This can affect digestion and nutrient uptake and even cause nausea.
5. Affects Appetite and Eating Habits
Chronic stress can lead to:
Overeating or binge-eating (stress eating)
Loss of appetite
Cravings for unhealthy, sugary, or fatty foods
Both overeating and undereating can negatively impact digestion and gut health.
Common Digestive Symptoms of Chronic Stress
If you’re frequently stressed, you may notice signs like:
Frequent stomachaches
Nausea or vomiting
Constipation or diarrhea
Acid reflux or heartburn
Unexplained bloating
Feeling full too soon or loss of appetite
These symptoms shouldn’t be ignored — your body is trying to tell you something.
Tips to Protect Your Digestive Health During Stress
Now that we know how chronic stress affects your digestive health, let’s look at practical ways to manage stress and support your gut.
1. Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation
Try deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation.
Even 10 minutes a day can calm your nervous system.
2. Eat Gut-Friendly Foods
Add probiotics (like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi) to improve gut flora.
Eat fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Stay hydrated.
3. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity reduces stress hormones and boosts mood.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days.
4. Sleep Well
Poor sleep increases stress and harms digestion.
Stick to a routine: 7–9 hours of sleep per night.
5. Talk It Out
Don’t bottle things up — speak with a friend, family member, or therapist.
Stress management often starts with emotional release.
6. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
These can irritate the stomach and worsen stress levels.
Opt for herbal teas or warm water with lemon.
When to See a Doctor
If your digestive symptoms persist even after stress management techniques, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Conditions like ulcers, IBS, or food intolerances may need medical attention.
Final Thoughts
Your gut and mind are deeply connected. What you feel mentally can show up physically — especially in your digestive system. By understanding this link, you can take steps to reduce stress and improve both your mental and gut health. A balanced lifestyle, rich diet, and mindfulness can make a huge difference in your well-being.
Conclusion
Ignoring stress doesn't just affect your mood — it disrupts your digestion, weakens your immunity, and decreases your quality of life. So take charge today: breathe deeply, eat well, and be kind to your body. Because now you know exactly how chronic stress affects your digestive health.
0 notes
Text
Is it Allergy or Asthma? How to Know the Difference

Have you ever found yourself sneezing, coughing, or gasping for air and wondering whether it's just a seasonal allergy or something more serious like asthma? You're not alone. Many people confuse the symptoms of allergies and asthma because they often overlap. However, knowing the difference between the two is crucial for getting the right treatment and managing your condition effectively.
In this blog, we’ll explain what allergies and asthma are, how they’re related, what makes them different, and how to know what you’re dealing with.
What Are Allergies?
Allergies happen when your immune system reacts to a harmless substance like pollen, dust, or pet dander as if it were dangerous. These substances are called allergens. When you're exposed to an allergen, your body releases chemicals like histamine that cause allergy symptoms.
Common Allergy Symptoms:
Sneezing
Runny or stuffy nose
Itchy eyes, nose, or throat
Watery eyes
Skin rashes or hives
Coughing (especially at night)
Fatigue
These symptoms usually appear quickly after exposure to the allergen and can range from mild to severe.
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that inflames and narrows your airways, making it hard to breathe. Asthma can be triggered by many things—including allergens. When asthma flares up, it’s called an asthma attack or asthma episode.
Common Asthma Symptoms:
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness or pain
Wheezing (a whistling sound when breathing)
Coughing (often worse at night or early morning)
Trouble sleeping due to breathing issues
Asthma symptoms can come and go. They may be triggered by allergens, cold air, exercise, smoke, or even stress.
Are Allergies and Asthma Related?
Yes, they are! Many people who have allergies also have asthma. This condition is called allergic asthma. In fact, allergens like pollen, mold, pet dander, and dust mites are common asthma triggers.
When you breathe in something you're allergic to, your airways can become inflamed, making it difficult to breathe—this is where allergies and asthma overlap.
Key Differences Between Allergy and Asthma
Feature
Allergy
Asthma
Affects
Eyes, nose, throat, skin
Lungs and airways
Symptoms
Sneezing, itching, watery eyes, rashes
Wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness
Trigger
Pollen, dust, food, pets, etc.
Allergens, exercise, cold air, pollution
Time of Symptoms
Immediate (within minutes)
May develop slowly or suddenly
Treatment Focus
Antihistamines, avoiding allergens
Inhalers, bronchodilators, steroids
While allergies mostly affect the upper airways (like your nose and throat), asthma affects the lower airways (your lungs).
How to Know What You Have
1. Track Your Symptoms
Keep a journal of what symptoms you experience, when they occur, and what you were doing at the time. Are you only sneezing and sniffling when the pollen count is high? Do you wheeze and cough after jogging or being around pets?
2. Get Allergy Testing
Your doctor may recommend a blood test or skin prick test to find out what you’re allergic to. This is especially helpful if your symptoms are triggered by specific things like pollen or food.
3. Do a Lung Function Test (Spirometry)
This simple breathing test helps measure how well your lungs work. If you have asthma, the test may show that your airways are narrowed or inflamed. The results also help doctors decide how severe your asthma is.
4. Observe When Symptoms Occur
If your symptoms occur mostly in certain seasons (like spring or fall), they may be due to allergies. If they happen during exercise or at night, it could be asthma.
Can You Have Both?
Absolutely. Many people live with both allergies and asthma. In these cases, managing one helps manage the other. For example, taking allergy medication can help reduce asthma symptoms triggered by allergens.
That’s why it's important to get a proper diagnosis. Treating only one condition when you have both may not bring full relief.
Treatment Options
For Allergies:
Antihistamines – reduce sneezing and itching
Nasal sprays – ease a runny or blocked nose
Eye drops – soothe itchy, watery eyes
Allergy shots (immunotherapy) – gradually reduce your sensitivity to allergens
For Asthma:
Inhalers – deliver medicine directly to the lungs
Long-term medications – reduce airway inflammation
Rescue inhalers – for quick relief during an attack
Lifestyle changes – avoid triggers, keep your environment clean
Always consult a doctor before starting any treatment.
When to See a Doctor
You should see a healthcare provider if:
You have trouble breathing or frequent coughing
Symptoms interfere with daily life or sleep
Over-the-counter allergy medicine isn’t helping
You need to use your asthma inhaler more often than usual
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between allergies and asthma is the first step in managing your health. Both are common, manageable conditions—but only if you know what you're dealing with. By observing your symptoms and getting tested, you can find the right path to relief.
Conclusion: Is it Allergy or Asthma? How to Know the Difference
If you're asking yourself, "Is it allergy or asthma? How to know the difference," the answer lies in understanding your symptoms, knowing your triggers, and getting the right tests done. Don’t guess—get tested through trusted services like SecondMedic and take control of your breathing and well-being today!
0 notes
Text
Impact of Junk Food on Hormonal Balance

In today's fast-paced world, junk food has become a popular choice for many people. It is easily available, quick to eat, and often tasty. But behind the delicious flavors and convenience lies a growing health concern. Junk food is not just about empty calories — it has deeper effects on our bodies, especially on our hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that control important functions in the body like growth, mood, metabolism, and reproduction. When your hormonal balance is disturbed, it can lead to serious health issues.
In this blog, we will explore how junk food affects hormonal balance and why it's important to make healthier food choices for a better life.
What Is Junk Food?
Junk food refers to food that is high in calories but low in nutrients. These foods are often loaded with:
Refined sugar
Unhealthy fats (trans fats and saturated fats)
Salt
Preservatives and additives
Common examples include chips, candies, sugary drinks, fast food (like burgers and fries), pastries, and processed snacks.
While having junk food occasionally is not harmful, regular consumption can have negative effects, especially on your hormones.
What Are Hormones and Why Are They Important?
Hormones are chemicals produced by glands in the endocrine system. They travel through the blood and affect many parts of the body. Hormones are responsible for:
Regulating metabolism
Controlling appetite
Balancing mood
Managing stress
Supporting growth and development
Controlling sexual function and reproductive health
Even a small imbalance in hormone levels can affect your physical and emotional well-being.
How Junk Food Affects Hormonal Balance
1. Insulin Resistance and Blood Sugar Spikes
Many junk foods are high in refined sugars and simple carbohydrates. When you eat them, your blood sugar levels rise quickly, and your body releases insulin to control it. Over time, repeated spikes can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body stops responding to insulin properly.
Hormonal impact:
Leads to type 2 diabetes
Causes weight gain, which further disrupts hormone levels
Can affect reproductive hormones, especially in women (e.g., PCOS)
2. Increased Cortisol Levels (Stress Hormone)
Junk food can cause inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. These physical stressors raise cortisol levels. High cortisol over time can:
Disrupt sleep
Lower immunity
Cause belly fat
Create mood swings or anxiety
Hormonal impact: Cortisol imbalance throws off the natural rhythm of other hormones, like melatonin (sleep hormone) and serotonin (mood hormone).
3. Leptin Resistance (Hunger Hormone)
Leptin is the hormone that signals fullness to your brain. When you eat too much high-fat, high-sugar junk food, your brain can stop recognizing leptin signals — a condition known as leptin resistance.
Hormonal impact:
Constant feeling of hunger
Overeating and obesity
Poor appetite control
Disruption of metabolism and thyroid hormones
4. Imbalanced Sex Hormones
Junk food, especially processed meat and dairy, may contain hormone-disrupting chemicals. Additionally, high body fat from poor eating habits increases estrogen production in both men and women.
Hormonal impact:
In men: Low testosterone, reduced fertility
In women: Irregular periods, PCOS, mood changes, fertility issues
5. Thyroid Hormone Disruption
A diet high in sodium, sugar, and bad fats may affect the thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism through hormones like T3 and T4. Processed junk foods often contain preservatives and artificial additives that interfere with the absorption of iodine, a key mineral for thyroid function.
Hormonal impact:
Slowed metabolism
Weight gain
Fatigue
Depression
Signs of Hormonal Imbalance Due to Junk Food
Here are some common signs your hormones might be off track because of poor diet:
Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
Constant fatigue or low energy
Mood swings, anxiety, or depression
Irregular periods or fertility issues
Sleep problems or insomnia
Acne or skin issues
Sugar cravings and increased appetite
If you're experiencing these symptoms, it’s a sign that your hormones might be out of balance, and your diet could be playing a big role.
Simple Ways to Support Hormonal Health
While avoiding junk food completely might be hard, you can take simple steps to support your hormones:
1. Eat Whole Foods
Include more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drink enough water every day. Hydration helps with hormone transport and overall health.
3. Exercise Regularly
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate stress hormones like cortisol.
4. Sleep Well
Good quality sleep is essential for hormone production and regulation.
5. Reduce Stress
Practice meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or spend time in nature.
6. Limit Sugar and Processed Foods
Read food labels and avoid products with high sugar, trans fats, and artificial additives.
Final Thoughts
Your body is a delicate machine that runs on balance — especially hormonal balance. Junk food may seem like a small indulgence, but its long-term effects on your hormones can be serious. From weight gain and mood swings to fertility issues and chronic fatigue, the consequences of poor diet choices can be far-reaching.
Making mindful changes to your eating habits doesn’t mean you have to give up everything you love. It simply means prioritizing your health by choosing more natural, wholesome foods most of the time.
Conclusion
The impact of junk food on hormonal balance is a growing concern in modern health. If you're struggling with symptoms like fatigue, mood changes, or weight gain, it's time to look at your plate. By reducing junk food and eating clean, you can bring your hormones back into harmony and improve your overall well-being. Start today — your body and mind will thank you.
Take the first step toward better health and avoid the impact of junk food on hormonal balance.
0 notes
Text
How Smartphone Addiction Affects Your Brain: What You Need to Know
In today’s digital world, smartphones have become a major part of our lives. From checking messages to scrolling social media, watching videos, or even working, we spend hours on our phones every day. While technology has made life easier, excessive use of smartphones is becoming a serious concern—especially for your brain.
Let’s explore how smartphone addiction affects your brain, the signs of this addiction, and what you can do to protect your mental health.
What is Smartphone Addiction?
Smartphone addiction is the compulsive use of your mobile phone to the point where it starts affecting your daily life, relationships, work, or health. It’s similar to other behavioral addictions like gambling or internet addiction. People addicted to their phones may feel anxious or uncomfortable when they’re not using it, and they may use it even when they shouldn’t—like during meals, meetings, or while driving.
Signs You Might Be Addicted to Your Smartphone
Here are some common signs of smartphone addiction:
Checking your phone constantly, even when there are no new notifications
Feeling anxious or irritated without your phone
Losing track of time while using your phone
Neglecting responsibilities, relationships, or sleep
Using the phone to escape stress or negative emotions
If any of these sound familiar, it might be time to rethink your phone habits.
How Smartphone Addiction Affects Your Brain
Now, let’s get to the core of the issue—how smartphone addiction affects your brain.
1. Dopamine Overload
Every time you receive a like, comment, or message, your brain releases dopamine—a chemical linked to pleasure and reward. Over time, your brain starts to crave these small bursts of dopamine, pushing you to check your phone more often.
This repetitive reward cycle is similar to what happens in drug addiction. Your brain begins to associate phone use with pleasure, and it becomes harder to stop.
2. Reduced Attention Span
Smartphones train your brain to focus on short, fast-changing information. Jumping between apps, tabs, and videos reduces your attention span. You may find it hard to focus on one task for a long time—like reading a book, studying, or even having a deep conversation.
Research has shown that smartphone users tend to have lower cognitive control, making it more difficult to stay focused or ignore distractions.
3. Memory Issues
Using smartphones all the time can impact your short-term memory. Because we rely so much on our phones for information—like contacts, appointments, and even directions—our brain stops trying to remember things on its own.
This condition is known as “digital amnesia.” Over time, your brain’s memory muscles weaken, and you may struggle to recall details you would otherwise have remembered easily.
4. Sleep Disturbances
Many people use their phones right before bed, but this habit can seriously hurt your brain and sleep. The blue light from screens blocks melatonin, a hormone that helps you sleep.
This results in:
Difficulty falling asleep
Poor sleep quality
Less deep sleep, which your brain needs to recharge
Without enough rest, your brain struggles to focus, think clearly, and process emotions.
5. Mental Health Problems
Studies show that smartphone addiction is linked to increased anxiety, depression, and loneliness. Constant comparison on social media and fear of missing out (FOMO) can negatively affect your mood and self-esteem.
Too much screen time also takes away from real-life social interactions, which are essential for emotional health. Over time, this can make you feel isolated and mentally exhausted.
6. Poor Impulse Control
Smartphones provide instant gratification—whether it’s through entertainment, shopping, or chatting. This habit rewires the brain to expect quick results and instant pleasure. Over time, it can weaken your ability to delay gratification or make thoughtful decisions.
Children and teenagers are especially vulnerable because their brains are still developing. Excessive phone use at a young age can lead to long-term behavioral and emotional issues.
Tips to Break Free from Smartphone Addiction
Now that you know how smartphone addiction affects your brain, the next step is to take action. Here are some simple tips:
1. Set Screen Time Limits
Use apps or phone settings to track and limit your screen time. Set daily limits for social media, games, or video streaming.
2. Turn Off Unnecessary Notifications
Every ping draws your attention. Turn off notifications for apps that don’t need your immediate attention.
3. Create Phone-Free Zones
Designate areas like the dining table or bedroom as phone-free zones. This helps you focus on real-life interactions and sleep better.
4. Use “Do Not Disturb” Mode
Enable this mode while working, studying, or sleeping. It reduces distractions and helps your brain stay focused.
5. Schedule No-Phone Time
Pick a few hours daily when you avoid your phone completely. Use this time to read, go for a walk, meditate, or spend time with family.
6. Replace Scrolling with Healthy Habits
Instead of scrolling endlessly, try activities that boost brain health—like reading, exercising, or learning a new skill.
Final Thoughts
Smartphones are an amazing tool when used wisely. But when overused, they can harm your brain in many ways—from memory loss and poor sleep to increased anxiety and low attention span.
Being aware of your habits and taking small steps toward change can make a big difference in your mental and emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding how smartphone addiction affects your brain is the first step in taking control of your life. Your brain deserves rest, focus, and real connections—not just endless screen time. Start making mindful choices today and give your mind the break it truly needs.
If you care about your brain health, it's time to reflect on how smartphone addiction affects your brain and take action before it’s too late.
0 notes
Text
Why Your Anxiety Could Be Linked to Your Gut Health

Have you ever had “butterflies in your stomach” before a big event? Or felt your stomach twist when you’re nervous? These feelings are more than just expressions. They reveal a real connection between your brain and your gut. Today, science is uncovering fascinating links between gut health and mental health—especially anxiety. Let’s explore how your gut might be silently affecting your mood and why it’s so important to keep it healthy.
The Gut-Brain Connection: More Than You Think
The gut and brain are connected through a network known as the gut-brain axis. This communication highway uses nerves, hormones, and chemicals to send messages between the two. The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve, plays a key role in this connection. It runs from your brain to your abdomen and helps regulate digestion, mood, and even immune response.
This means your brain can affect your gut—and your gut can affect your brain.
Meet Your Second Brain: The Gut Microbiome
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. This complex ecosystem is called the gut microbiome. It helps you digest food, absorb nutrients, fight harmful germs, and even create important chemicals.
Surprisingly, many of these chemicals influence your mood. One key player is serotonin, a “feel-good” hormone. Did you know that about 90% of serotonin is made in the gut? So, if your gut is unhealthy, your mood could suffer too.
How Gut Health Affects Anxiety
When your gut microbiome is balanced, you feel good—physically and mentally. But when it’s out of balance (a condition called dysbiosis), problems can begin.
1. Inflammation
An unhealthy gut can cause inflammation throughout the body, including the brain. This inflammation can interfere with normal brain function and contribute to anxiety and other mood disorders.
2. Leaky Gut Syndrome
If the gut lining becomes too weak, harmful bacteria and toxins can leak into the bloodstream. This is known as leaky gut. These toxins may trigger inflammation and affect your nervous system, increasing feelings of stress and anxiety.
3. Poor Nutrient Absorption
The gut absorbs nutrients like magnesium, B vitamins, and omega-3s—all of which are essential for brain health. If your gut isn’t working well, your brain might not get what it needs to stay calm and balanced.
4. Chemical Imbalance
The gut produces neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. An imbalance in gut bacteria can disrupt their production, potentially leading to anxiety, depression, or mood swings.
Signs Your Gut Might Be Affecting Your Mental Health
If you’re struggling with anxiety, it’s worth asking whether your gut could be involved. Here are some signs your gut health might be impacting your mood:
Frequent bloating or gas
Constipation or diarrhea
Sugar cravings
Food intolerances
Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
Feeling tired all the time
Poor sleep quality
If you have both anxiety and digestive issues, the two could be connected.
How to Improve Gut Health and Reduce Anxiety
Thankfully, you can take simple steps to support your gut health—and improve your mental well-being along the way.
1. Eat More Fiber
Fiber feeds the good bacteria in your gut. Add more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to your diet. Foods like apples, bananas, carrots, oats, and lentils are excellent choices.
2. Include Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria that help balance your gut microbiome. You can find them in yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are foods that feed your good bacteria—like garlic, onions, and bananas.
3. Limit Processed and Sugary Foods
Sugar and highly processed foods can promote bad bacteria and inflammation. Try to reduce your intake of soft drinks, white bread, fast food, and sweets.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt gut health. Practice stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or even spending time in nature.
5. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity helps regulate the gut microbiome and boosts mood-enhancing chemicals in the brain. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Poor sleep affects both gut health and mental health. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep every night. A relaxing bedtime routine can help.
7. Stay Hydrated
Water helps keep your digestion smooth and your gut bacteria balanced. Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
8. Consider Supplements (If Needed)
If dietary changes aren’t enough, consider talking to a healthcare provider about probiotic or vitamin supplements. Don’t self-medicate—always consult a professional first.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing severe anxiety, depression, or digestive problems, don’t ignore it. A doctor or mental health professional can help you find the right treatment. In some cases, therapy, medication, or medical tests may be necessary.
Also, a nutritionist or gastroenterologist can help you identify and manage any gut-related issues contributing to your mental health symptoms.
Final Thoughts
Your gut is not just about digestion—it plays a powerful role in how you feel emotionally. Modern research shows that keeping your gut healthy can positively impact anxiety and overall mental well-being.
By taking simple steps to support your digestive system—like eating well, managing stress, and getting enough sleep—you can help improve both your gut and your mind.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced world, taking care of your mental health is more important than ever. And one of the most overlooked ways to do that is by taking care of your gut. From serotonin production to inflammation control, your gut plays a major role in how you feel every day. So next time you're feeling anxious, take a moment to think about your digestive health too. After all, it’s not just in your head—it could be in your stomach too.
If you're wondering why your anxiety could be linked to your gut health, it's time to start listening to your gut and making changes that support your entire well-being.
0 notes
Text

The rainy season brings a welcome relief from the scorching summer heat. The smell of wet soil, cool breeze, and refreshing showers make it a favorite season for many. However, monsoons also increase the risk of infections, especially waterborne and foodborne illnesses. That’s why what you eat during the rainy season plays a huge role in keeping you healthy.
In this blog, we’ll talk about foods to avoid during rainy season in India to protect your stomach and boost your immunity. Whether you enjoy street food or homemade delicacies, knowing what to skip is essential for a safe and sickness-free monsoon.
Why You Need to Be Careful About Food During Monsoon
The rainy season creates a moist environment, which is perfect for the growth of bacteria and fungi. Roads are often flooded, drains are clogged, and food hygiene can easily be compromised. The digestive system also becomes weak during this time, so heavy or contaminated food can lead to infections, stomach upset, food poisoning, diarrhea, and more.
So, let’s look at the foods that you should stay away from during the monsoon.
1. Leafy Vegetables
While leafy greens like spinach, cabbage, and lettuce are normally very healthy, they are not the best choice during the rainy season. These vegetables are often grown in muddy soil and can carry a lot of dirt and germs. Washing them properly becomes difficult, and consuming them raw or undercooked may cause stomach infections.
Tip: If you must eat leafy greens, cook them well and avoid raw salads.
2. Fried Street Food
Who doesn’t crave hot samosas, pakoras, or kachoris with chai on a rainy day? But street food is one of the main culprits behind monsoon sickness. The oil used is often reused multiple times, making it toxic. The preparation area may not be hygienic, and food is exposed to open air, flies, and moisture, leading to contamination.
Tip: Make your favorite fried snacks at home using fresh oil and clean ingredients.
3. Raw Sprouts
Sprouts are packed with nutrients, but they are not safe during the monsoon. The humid weather encourages bacterial growth, especially salmonella and E. coli, in raw sprouts. They can easily lead to food poisoning or stomach infections.
Tip: Lightly steam sprouts before eating, or skip them altogether during this season.
4. Seafood
Monsoon is breeding season for fish and other seafood. This means there’s a higher risk of consuming contaminated or stale seafood. Improper storage or transportation during the humid months makes things worse. Eating such seafood can lead to stomach infections and even serious food poisoning.
Tip: Avoid seafood during the rainy season, and switch to fresh vegetarian or poultry options instead.
5. Pre-Cut Fruits and Juices from Outside
It’s common to find vendors selling sliced fruits or fresh juices on the roadside. But consuming pre-cut fruits or open juices during monsoon is a big no-no. These are exposed to air and flies, and often cut with unclean knives or on dirty surfaces.
Tip: Always wash fruits at home and cut them fresh. Drink homemade juices only.
6. Dairy Products That Spoil Easily
Products like paneer, cream, or curd spoil quickly in humid weather. If not stored properly, they can go bad without showing any obvious signs and lead to food poisoning or stomach discomfort.
Tip: Consume dairy items fresh and avoid buying in bulk during the monsoon.
7. Fermented Foods
Idli, dosa batter, and other fermented items may not ferment properly due to excessive moisture in the air. Improper fermentation can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria and result in acidity, bloating, or even diarrhea.
Tip: Prepare small portions and consume them immediately. Avoid keeping batter for long hours.
8. Carbonated Drinks and Ice
Cold drinks and soda may feel refreshing, but they can weaken digestion. Also, ice cubes used in beverages (especially from roadside stalls) are often made from contaminated water, leading to infections like typhoid or hepatitis A.
Tip: Stick to warm water, herbal teas, or freshly boiled and cooled water to stay hydrated.
9. Mushrooms
Mushrooms grow in damp, dark environments and are prone to bacterial or fungal contamination. During the rainy season, the chances of toxic or wild mushrooms entering the supply chain increase.
Tip: If you love mushrooms, make sure to buy them from a trusted source and cook them thoroughly.
Bonus: What to Eat Instead?
To stay safe and healthy during the monsoon, focus on these safer alternatives:
Steamed and cooked vegetables
Seasonal fruits like apples, pears, and pomegranates
Light soups and broths
Boiled water
Home-cooked meals with minimal oil
Herbs like tulsi, ginger, and turmeric to boost immunity
Monsoon Health Tips
Here are a few extra tips to maintain good health during the rainy season:
Wash fruits and vegetables with salt or vinegar water.
Dry grains and pulses before storing to avoid fungal growth.
Use spices like pepper, asafoetida (hing), and ajwain to improve digestion.
Keep your kitchen and storage areas dry to prevent mold.
Conclusion
The rainy season is beautiful but also brings health challenges. By knowing what to avoid, you can enjoy the monsoon without worrying about falling sick. Hygiene, clean cooking, and smart food choices are your best friends during this season.
Remember, prevention is better than cure—especially when it comes to your diet. So, if you want to enjoy the rains without health worries, make sure to follow this guide on foods to avoid during rainy season in India.
0 notes