Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
OCD AT AN ATOMIC LEVEL
Just as we are concerned about what ingredients go in the food we eat, what cement or rods or bricks goes in the houses we build, the content in a story book similarly we should also be concerned of what constitutes us and every single thing around us. Well, everything around us is composed of atoms. Life exists only because of gases that under very high pressures and temperatures combined to form compounds billions of years ago, that led to the existence of life forms. Atoms are composed of protons (+ve charge), neutrons (neutral) and electrons (negative charge). Protons and neutrons compose the nucleus. Nucleus constitutes the maximum mass of the atoms. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific permissible orbitals and can get excited to form ions. The permissible orbitals are decided by quantum numbers.

Principle quantum number: The principal quantum number is symbolized by the letter n. The principal quantum number tells which shell the electron is in and can take on integral values starting with 1.

Azimuthal (angular momentum) quantum number: The azimuthal quantum number is symbolized by the letter l. The azimuthal quantum numbers give the shape of an orbital. Orbitals have shapes that are best described as spherical (l = 0), polar (l = 1), or cloverleaf (l = 2). Values for l depend on the principal quantum number and can range from 0 to n–1.

Magnetic quantum number (2l+1): The magnetic quantum number associated with the quantum state is designated as m. The quantum number m refers, loosely, to the direction of the angular momentum vector. The magnetic quantum number m does not affect the electron's energy, but it does affect the probability cloud. Given a particular ℓ, m is entitled to be any integer from -ℓ up to ℓ.
s ----- 0; p------0, +1, -1; d---------0, +1, -1, +2, -2; f------0, +1, -1, +2, -2, +3, -3 etc
Spin quantum number: Spin quantum number (s) characterizes the revolutions of electrons about themselves. Magnetic moments due to spin can have only two orientations in space; either up or down; + ½ or – ½; clockwise or anti-clockwise.
The electronic configurations of atoms depend on three rules:
Aufbau’s Principle: E=n+l Electrons are filled first in orbitals having lower energy followed by orbitals with higher energy.
Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers.
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity: Every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one��electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied. The two electrons in an orbital have opposite spins.
Example: N=7 1s22s22p3

BONDING
“The beauty of a living thing is not the atoms that go into it, but the way those atoms are put together.” ― Carl Sagan
Just like humans, atoms too like to indulge in bonds. Humans tend to marry, have children, grandchildren to form the bond of family in an ultimate motive to gain stability amidst the ups and downs of life. Similarly, atoms bond with other atoms of the same type or different type in order to gain stable electronic configurations.

Types of chemical bonds:
Types of chemical bonds:
Ionic Bond: Bonds made by the actual transfer of electrons amongst oppositely charged atoms.
Covalent Bond: Bonds made by the sharing of electrons amongst atoms.
Coordinate Bond: A coordinate covalent bond, also known as a dative bond or coordinate bond is a kind of covalent bond in which the two atoms share the same set of electrons.

VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell electron pair repulsion theory): The VSEPR theory assumes that each atom in a molecule will achieve a geometry that minimizes the repulsion between electrons in the valence shell of that atom.
Steric Number = Number of bonded atoms + Number of lone pair electrons
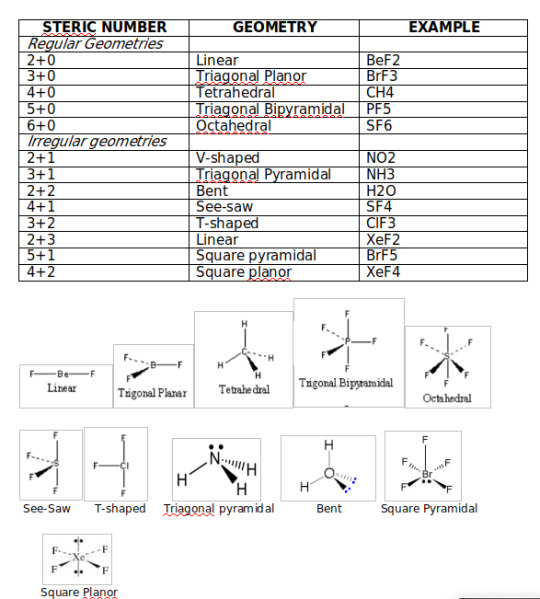
Theories explaining chemical bonding:
Valence Bond Theory:
This theory states that bonds are formed by the overlapping of orbitals. The strength of a bond depends on the degree of overlap. A sigma bond is formed by the head on overlap of orbitals while a pie bond is formed by the sideways overlap of orbitals.

VBT couldn’t explain tetravalent carbon atom.
Hybridization theory:
The intermixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a new type of hybrid orbitals with same energy is called hybridization. The atomic orbitals having same energy can only take part in hybridization. Moreover, both full filled and half-filled orbitals can take part in the formation of hybrid orbitals provided they have equal energy.

Hybridization theory doesn’t explain the biradical nature of Oxygen atom.
Molecular orbital theory:
According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, individual atoms combine to form molecular orbitals. The formation of orbitals is because of Linear Combination of atomic orbitals which combine to form the molecule. The combining atomic orbitals have their own wave functions which on linear combination give us the wave function of the molecular orbital. Bonding orbitals: When the addition of wave function takes place, the type of molecular orbitals formed are Bonding Molecular Orbitals. We can represent them by ΨMO = ΨA + ΨB. They have lower energy than atomic orbitals involved.
Anti-bonding orbitals: When molecular orbital forms by the subtraction of wave function, the type of molecular orbitals formed are antibonding Molecular Orbitals. We can represent them as ΨMO = ΨA – ΨB. They have higher energy than atomic orbitals.
Bond order: BO = ½ (No. of electrons in bonding orbitals – No. of electrons in Anti-bonding orbitals). Bond order must be calculated separately for sigma and pi bonds.
Example: O2

Bond Order 2s orbital Sigma bonds = 1/2 (2-2) = 0
Bond Order 2p orbital Sigma bonds = 1/2 (2-0) = 1
Bond Order 2p orbital pi bonds = 1/2 (4-2) = 1
Therefore, O2 has 1 sigma bond and 1 pi bond. Moreover, the biradical nature of oxygen or paramagnetic nature of oxygen is explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the pi* anti-bonding orbital.
1 note
·
View note