Text
LETS TALK ABOUT SPARRING
I’ve read a lot of fics, have seen many shows, and have watched many movies that are completely inaccurate when it comes to sparring. NOW, i know it’s fiction, and I greatly enjoy it nonetheless, but I would like to share a few things with you, as a person who trains in Historical European Martial Arts (HEMA). There are a few general things in this, as well as stuff more focused to a certain european weapon. (this is all Historical European stuff, obviously if you’re writing for a different region, this probably won’t apply that much.)
SPARRING
-you don’t practice with real sharp swords. Never. It’s incredibly dangerous, especially since sparring is trying to practice your killing/injuring skills. In older times, you would use wood, maybe wrapped in leather or canvas to practice. Today, you use weighted nylon swords/weapons, and you usually wear a mask while doing so. Steel is and was an option, but the blade will be completely dull, and the tip will be bent over itself.
-It’s practically impossible to knock someone off their feet while sparring, unless you are hooking your foot or weapon behind their leg. It’s hard to push back and cause someone to fall, since they can just retreat back a bit.
-YOU. DON’T. SPEND. HOURS. SPARRING. ESPECIALLY WITHOUT A BREAK. It’s exhausting, the most people usually go is 10 minutes before they have a break. During Training, you only spar for about 2-5 minutes before stopping and having a rest.
-You try your hardest never to cross your feet. It’s dangerous and it unbalances you. Your opponent can take advantage of you easily.
-Usually, you want to strike your opponent with the last ¼ of your blade, basically just the tip and a little below. That’s the sharpest point, and you get the most force behind it.
-Swords aren’t super heavy. Stop the giant, huge, I-can-barely-lift-this trope. Longswords are usually 3lbs. It’s not heavy when you pick it up. However, it gets heavy when you’re holding it up above your head for a while. Swords were not made to be heavy, especially since you would have to hold them up in battle for sometimes hours.
-It’s incredibly hard to engage in witty banter and such. You are constantly moving and trying to strike your opponent. Since it’s fiction, you can do what you want, but just know that trying to have a conversation while sparring is like trying to have one while running. It tires you out even more, and usually just comes out breathless and wheezy.
-Swords are not lightsabers. You cannot try and hurt someone with just any part of your blade. It will just annoy your opponent. Now, for sparring, you will want to focus on hitting your opponent with the edge of your blade, and you won’t really ever be trying to hit someone with the flat of your blade.
-In sparring, you will get hit. And get bruises. I count five from just 2 days ago. (Also reminder that bruises don’t form for 1-3 days.) If you happened to get a hard thrust to the ribs, they will probably fracture. It happens. I haven’t had it personally, but those who’ve trained longer have. The worst injury I’ve gotten is a bruise on my chest that didn’t fade for nearly a month.
-Grip!!! You don’t clutch your sword super tight. No. It limits movement. My instructor taught me to hold firmly with the thumb, pointer, and middle finger, and use the other two as more guiding fingers. You swing your sword with your wrist, not a big giant arm movement. That is tiring and slow.
I will be focusing on using a one handed sword in this next bit, specifically a Scottish Regimental Broadsword. A basic sword to build off of.
-FOOTWORK. It’s not a super complicated series of perfectly planned out steps. It just isn’t. With Regimental Broadsword (which is what I will focus on, since it’s what I’ve trained with most), you have to have a good base (rear-weighted stance, front foot pointed at your opponent, back foot turned sideways), and then once you have that, you just have to move around and try not to get hit.
-Slipping. (Continuation of footwork). With a rear-weighted stance, the goal is to be able to move the front foot anywhere. You should actually be able to keep your front foot an inch off the ground without having to adjust your back foot. Slipping is when this comes in handy. If your opponent takes a swing at your front leg, you should be able to just slip it back to go next to your other foot, and swing your sword up to get your opponents head. Slipping is really important.
-Advance and Retreat (other continuation of footwork). While moving forward or back, you always want to feel the ground with a heel-toe movement, so you can tell if there are rocks or branches and such. Advancing, you want to move your front leg first. Retreating, your back leg.
-Traversing (last continuation of footwork)(maybe). Transversing is basically advancing in on your opponent in a circular motion. You’re trying to get close and personal. Reminder to not cross your feet. You will loose balance and probably end up getting whacked with a sword. Traversing is a spiral motion sort of. Your opponent can avoid getting trapped If they do it as well.
I will probably come back and add more soon, because there’s more I know, but can’t remember at the moment.
11K notes
·
View notes
Photo
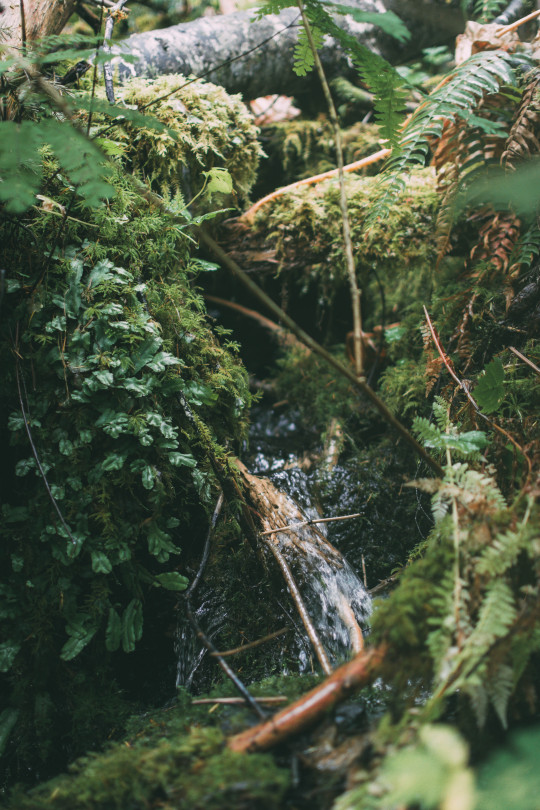
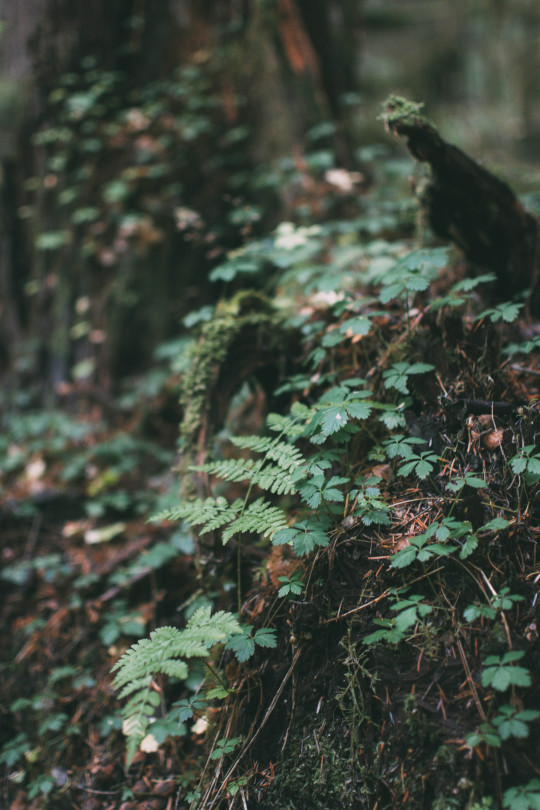
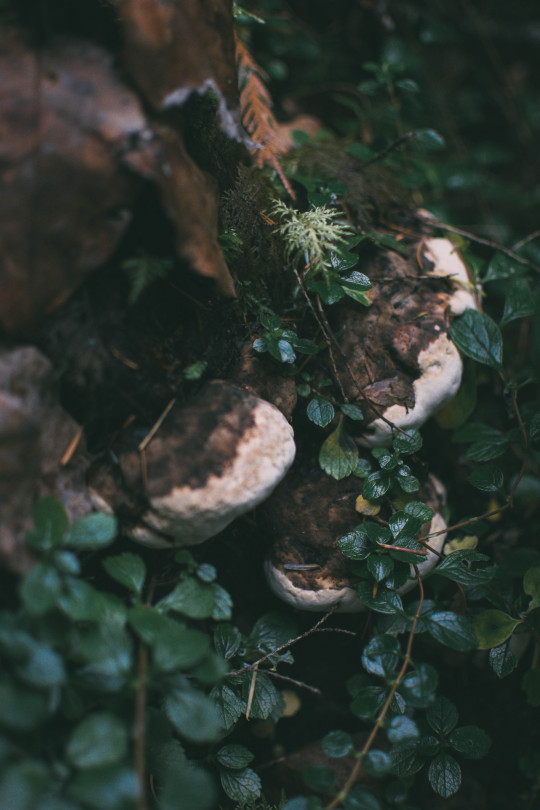
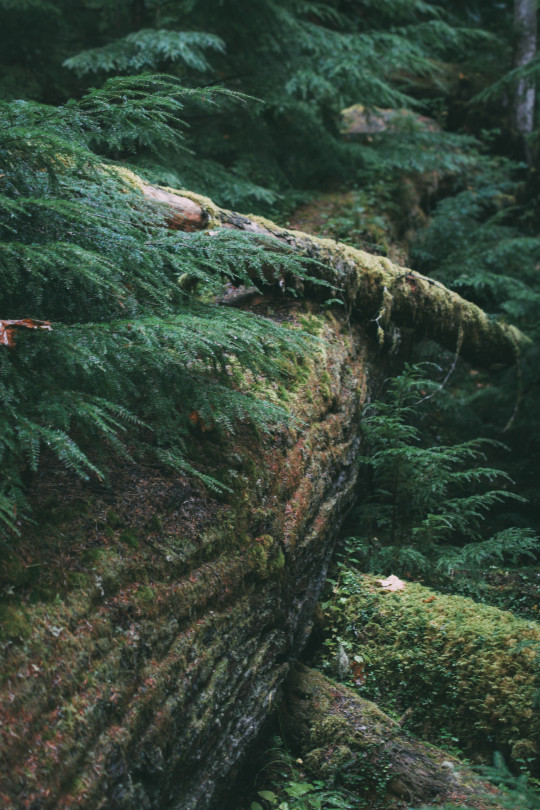









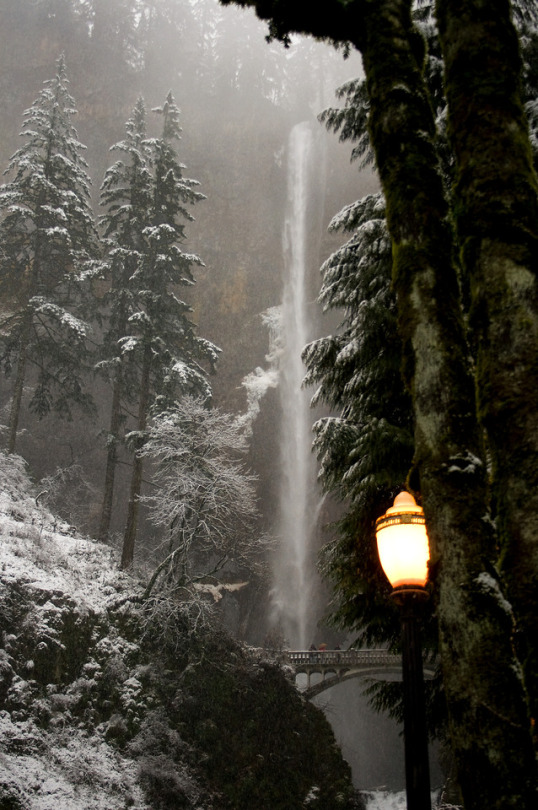
The woods are lovely, dark, and deep
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
fool’s gold ;
#10 Not said to me, from ‘The Way You Said I Love You’ prompts.
In a reality where Red doesn’t exist, Sybil and Boxer collide.
She’s a string of one-time lovers, encounters of chance so inconsequential they blur, one into the next, one conquest after another. Hazy details. Forgotten names and places. Yet still, the sting-sharp memory of lips crushing against her own, of fingers catching along her every curve, of wanting hands charting a fumbled course in the dark —
Just to grasp at smoke, come sunrise.
Just to wake to her stark absence.
Each time, their blistered pride sours into resignation.
Each time, she relishes the silence that follows.
Temporary comfort.
It’s nothing new, she tells herself, no harm nor foul. They’ll weather. Move on. Find others to fill their lonely hours, as starving souls are wont to do. She’ll weather and keep on devouring as if it’s enough to fill her hollowed heart.
But it’s a shock with him.
He shouldn’t be any different.
But he is,
Was,
Is.
He looks at her like he’s trying to remember.
She wills herself to forget, burying the shards of memory his presence calls to mind.
(Not that it works. Never does.)
That’s why there’s no pretense when she finds herself on his doorstep, one night after the next, one surrender after another. No greeting. No negotiation, just an explosive friction of wills. Just rage simmering beneath all that lust. Skin in frenzied union, cries strangled from each other’s lips. Pangs of recollection with each tryst, phantom aches of lost places, lost time.
A woman's voice. A song drowning in static.
She swears she’s heard it before.
She looks at him, dies piece by piece as she remembers:
Alone, alone, she was supposed to be alone…
With me,
We had her, we had her, I had her…
Gone, gone, she’s gone, she’s…
Yours. Your fault, yours. She wasn’t supposed to be yours.
Why wasn’t it you?
Why is it you?
“Easy.” He grinds it out, his voice coarse and scraping at the unspoken sentiment hanging between them. It's different, this night. So different and yet entirely the same. Her hands are wrapped firm around his throat, pressing, squeezing, nails biting into flesh as she tosses back her hair and bucks down with merciless rhythm. He catches hold of her wrists, grunting, groaning, pleading, “Ease up, fuck.”
“Does it hurt?” The question’s a growl barely contained in her throat.
“Yes.”
And she tightens her grip, rides him for all he’s worth as he hisses out a breath and grinds his hips in time with hers, whether he means to or not. Helpless. Succumbed. Lost in the brimstone scald that is her gaze.
“Good.”
[ also on ao3 ]
#fic#ink#transistor#sybil#boxer#alternate universe#past lives#hookups#just casual hate sex y'know#don't you dare judge me#i wrote this on fumes okay
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey do you have any tips on plot development? how to do come up with relevant but dramatic things to keep the plot going? i also don’t want to make it too intense?
I actually have quite a lot of resources that I’ve created over the years surrounding plot development. I’ve linked as many as I could find for you:
Resources For Plot Development
Useful Writing Resources
Useful Writing Resources II
31 Days of Plot Development
Novel Planning 101
How To Write A Good Plot Twist
How To Foreshadow
What To Cut Out Of Your Story
Tackling Subplots
Things A Reader Needs From A Story
A Guide To Tension & Suspense In Your Writing
How To Turn A Good Idea Into A Good Story
Planning A Scene In A Story
21 Plot Shapes and the Pros and Cons Of Each
How To Outline Effectively
Tips On Writing Intense Scenes
Writing The First Chapter
Tips On Starting A Scene
Plot Structures
Finding & Fixing Plot Holes
16K notes
·
View notes
Text


the lake district, cumbria, england 🌿
photos by tony richards
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Advice from an (Amateur) Archer on Writing About Archers and Archery
Admittedly, I don’t have the widest range of experience when it’s come to archery. I’ve only been shooting for a year now, and the time that I do take to shoot have long months between them. Still, I think it’s important to outline the basics for anyone who wants to write an archer in their book and wants to save themselves the embarrassment of having the archer do something that an archer would never do in a million years.
- Archers usually unstring their bow after battle. Unstringing a bow is exactly what it sounds like: removing the string from the bow’s limbs. Usually, archers then wrap the string around the now-straightened bow so they don’t lose it as easily. Archers unstring bows because everytime the limbs are bent by the string, there is a large amount of tension in the limbs. If the string is on too long and the bow has not been shot for a while, the limbs will start to wear down and lose their power, resulting in an archer needing to buy new limbs or an entirely new bow.
- Archers always retrieve their arrows after battle. Arrows are expensive and take a long time to make, so archers want to conserve as many arrows as possible. Sometimes they have a repair kit with them at the ready, in case they find an arrow with a loose arrowhead or broken fletching that can easily be repaired.
- Training arrows are not the same as battle arrows. Training arrows have thinner shafts and usually blunted tips so they can easily be removed from targets. Thinner shafts break more easily, and the blunted tips – whilst they can pierce skin – usually won’t get very far in the flesh. They’re also easier to make. Battle arrows are thicker, and their heads are pointed at the tip and have two pointed ends at its sides. This arrowhead is designed to easily pierce through flesh, and is incredibly difficult to pull out because its two pointed ends snag onto flesh. If you want to pull it out, you’d have to tear the flesh away with it, which can lead to an even larger wound.
- Arrows are fatal, and one can incapacitate a soldier for the rest of his life. Arrows are not easily snapped off like you see in movies. The draw weight is too strong, and they can sometimes be as strong as bullets. They will pierce through bone and tendons, which do not easily heal. Furthermore, if you want to remove an arrow, you either have to go through surgery, parting the flesh away from the arrowhead so it doesn’t snag onto anything, or you have you push – not pull – it all the way through the body.
- Bows are not designed for hitting people with in close combat. The limbs are specifically made to flex. Imagine hitting someone with a flexing piece of wood. If you hit with the middle of the bow, it still does very little because there is no weight behind the bow, and so you might as well be hitting them with a pillow. It might be annoying to the opponent, but it won’t save you. Archers need a secondary blade in close combat. They cannot strike people with their bows and expect to win.
- Draw weight affects speed, range, and impact. Draw weight is measured in pounds, at least in America, and it is measured in how much weight must be pulled when you draw back the string. A high draw weight means stiffer, thicker limbs that can shoot further and hit harder. But, this is at the cost of speed. A low draw weight means thinner, more flexible limbs that can shoot smaller distances and have low impact, but can be shot faster. Before you acrobatic fanatics immediately seize the smaller bow for its speed, understand that a bow’s advantage is in its range. No one can hit an archer from 300 meters away with their spear or sword. The archer has complete dominance over the battlefield in this way, and their arrows can kill anyone who gets too close. Not hurt. Not annoy. Kill. And a higher draw weight means a better chance of piercing through specific armor, then flesh, then bone. A lower draw weight means less range and, even worse, a lower chance that the arrow would even pierce through armor if the arrow even hits its target.
- Bows will always be outmatched in close combat against any other weapon. Bows take too long to draw and shoot, and at such close range, the opponent has an easier chance to dodge oncoming arrows. I already explained that the bows themselves cannot be used to take down a foe.
- Bowmen on horseback are utterly terrifying. Archers usually can’t move from their spot because range is more important than mobility, and at such a long range, you usually don’t need to move from your spot anyways. Bowmen on horses, however, are closer to the battle, and worse, they are faster than almost anyone on the battlefield. Not only are they difficult to hit, you have no way of predicting where they will shoot next because they can circle around you in confusing ways. If you want an interesting archer character, I’d advise trying these guys out.
- Never underestimate armor and padding. Arrows will never be able to pierce through plate armor because its curved surface will always deflect oncoming arrows. Arrows can pierce through maille because maille is made out of metal rings that can be bent and can fall away. However, padding usually lies underneath, which is surprisingly durable and can stop an oncoming arrow, as well as absorb some of its impact. Because of this, make certain that the archer is focusing on gabs in the armor. To know this, you MUST study armor. Gabs usually lie where the joints are because soldiers need those gabs open so they can move. Typical gaps lie in the neck, the armpit, the inner-elbow, the knees, and the palm of the hand. Impact is also an archer’s friend. A war arrow shot by a hundred pound bow, hurtling at incredible speeds and gaining momentum the further it travels, can evoke serious damage. To be hit by one of these arrows will feel more like being hit by a horse than being hit by someone’s fist.
13K notes
·
View notes
Photo
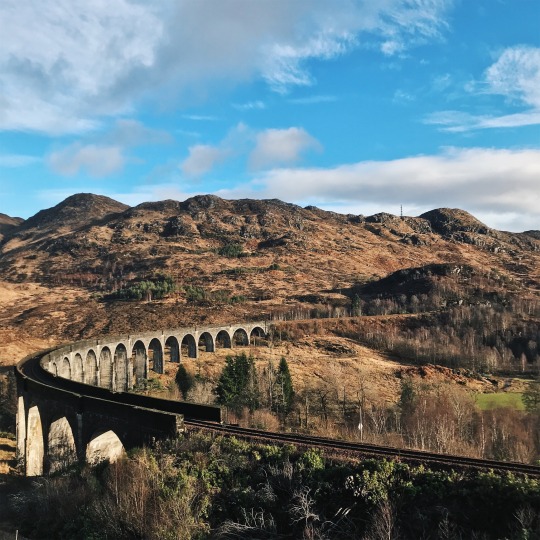
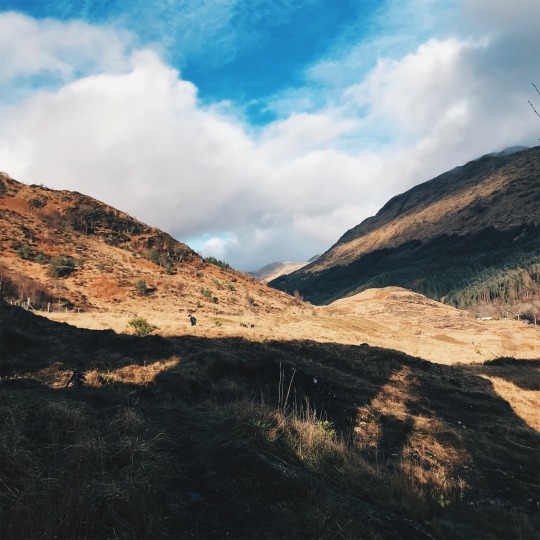
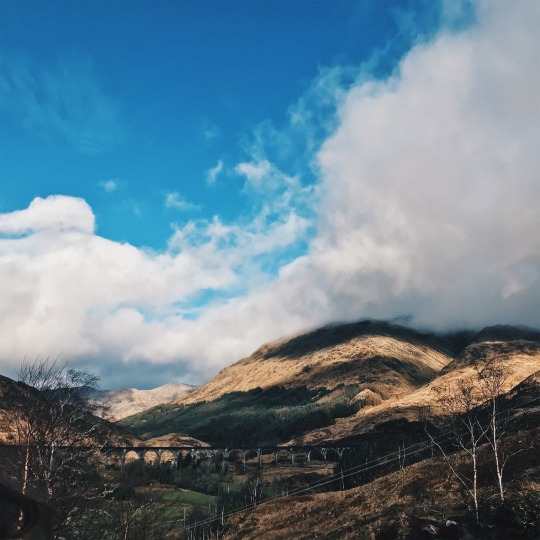
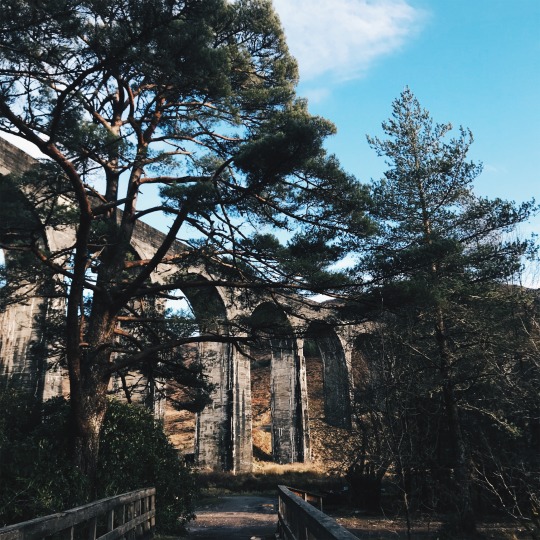




{02.01.20}
i never thought that at some point in my life, i would have traveled to where the harry potter films were made. seeing the hogwarts express, hagrid’s hut, and even the river scene during the triwizard tournament felt like a dream.
690 notes
·
View notes
Photo




{01.12.20}
january is the first month of the year and because my last one was so difficult i am so happy to say that i am starting the year fresh abroad in edinburgh, scotland. i cannot say it enough, but it really does feel like i’ve stepped into a medieval/gothic #cottagecore realm and i LOVE IT!
420 notes
·
View notes
Text

Crossed daggers in polished brass with warm golden labradorite.
59K notes
·
View notes
Text
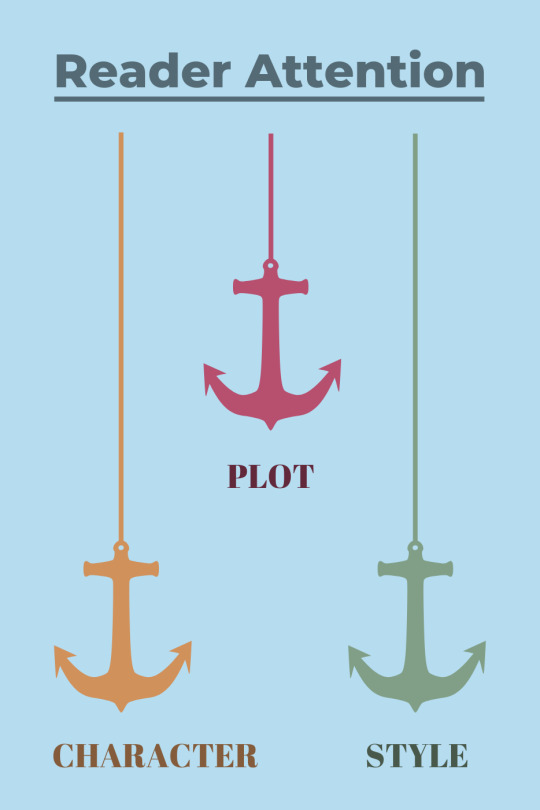
Narrative Anchors: How to hold your readers’ attention, wherever you take them.
One of my old fiction professors, Tom, used to always grab coffee with us students whenever our story had been workshopped.
We’d meet at the downtown coffee shop, where we fought the flocks of students for a table, pulled out a couple wrinkled copies of the story, and discussed feedback over bland coffee.
It was during one of these discussions that Tom pointed out something I’d stumbled into doing well. (He’s very good at that.)
“I think this is great, Mike,” he said, tapping my story on the table. “From the opening line, the question is whether these two will sleep together, and that grounds us. If my attention ever wavers, I can always fall back on, ‘Oh, well have they slept together yet? No, not yet? Okay, cool. I still know where we are, then, and where we’re headed.’ That makes the story easy to follow.”
This wasn’t, admittedly, a major focus of our conversation. We moved on to discuss more important things (like the story’s key flaws), but somehow that comment stuck with me over the years.
And now, looking back, I realize it was the first time I started thinking about something I’d eventually call “narrative anchors.”
What’s a narrative anchor?
It’s something I made up. But trust me, it’s helpful.
In short, I consider narrative anchors to be the craft elements you include in a story to ground your reader. On the one hand, they can help you craft a story that rings with simple, crystal clarity, and on the other hand, they can empower you to challenge readers with fresh, creative storytelling, without ever losing them at sea.
I put narrative anchors into three categories:
Plot Anchors
Character Anchors
Style Anchors
Plot Anchors
Plot anchors are a clearly defined situation, goal, or destination for a story. Tom (above) pointed out a situational plot anchor in my story, but you’ll find plot anchors everywhere. For example, in Avatar: The Last Airbender, Aang needs to master the four elements and defeat Fire Lord Ozai. We know from the beginning that defeating Ozai is the end-goal, so we feel grounded at every stage of the story, knowing where we’re going.
Moby-Dick, by Herman Melville, is another great example. Ahab is hellbent on hunting down the White Whale, and we never lose sight of that goal, even as the narrative stretches across hundreds of pages.
That’s the point of a plot anchor: to give your reader a clear direction, so they always know where they’re going.
Character Anchors
These anchors are the clear motivations and arcs you give your characters. Disney does this well in their musicals, always using an “I want song” (more about those here) to clearly declare what their main characters want: Mulan wants to express her true self, Hercules wants to find where he belongs, and so on. The rest of the story then circles around that character’s pursuit of their “want.”
When readers have a strong understanding of your character’s motivation and journey, they have a much easier time following the story as a whole.
Style Anchors
Style anchors are my handy little catch-all for every other craft choice you make to bring clarity and simplicity to your work. Style anchors can include: short chapters or paragraphs; simple and accessible language; straightforward writing forms; clarity of description; engagement with the five senses; using a smaller cast of characters; sticking to a single POV; and so on.
Cool. So when (and how) do I use these narrative anchors?
Tip 1: Don’t start with anchors. Start with the story. Take your idea, begin developing the characters and plot, and start writing.
Tip 2: As you write and revise, start thinking about anchors. Ask yourself what kinds of anchors you already have in place, what others may be helpful to add, and whether or not you’re doing enough to ground your readers in the story.
Tip 3: Consider your audience. Readers of popular fiction will want to be reasonably grounded, so you should try to always use at least a few anchors. But if your audience likes super artsy, experimental fiction, you may be able to get away with fewer tethers.
Tip 4: That being said, don’t be afraid to challenge your readers, whoever they are. If you want to get creative, go for it. If you want to experiment with form, language, plot, character arcs, or whatever, PLEASE do!
Tip 5: But when you challenge readers one way, try to compensate by grounding them in other ways. For example, maybe your story lacks a clear plot anchor, but you include a character with a clear arc and motivation. Or maybe your story is incredibly challenging on a stylistic level, but you give readers a clear character motive and plot (this was my experience reading Moby-Dick).
Tip 6: If big anchors don’t fit, consider smaller ones. For example, if your story lacks a BIG plot anchor like defeating Fire Lord Ozai, maybe use smaller plot anchors to drive individual sections of the book. Or maybe instead of a BIG declaration of your character’s motive at the beginning, include little anchors for your narrator that act like breadcrumbs for their motives and development.
Tip 7: Mix and match anchors as necessary, because there is no magic formula.
Long story short?
Write the story you want to write — then use narrative anchors to keep your readers reading, wherever your story takes them.
Tom may not have said that all in so many words, but if I bought him a coffee, I bet he’d agree.
Good luck, everybody, and good writing!
— — —
Everyone has stories worth telling. If you’re looking for writing advice or tips on crafting theme, meaning, and character-driven plots, check out the rest of my blog.
6K notes
·
View notes


















