Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Introduction to Digital Citizenship and Conflict

In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital world, our intrepid explorer recently delved into the intricacies of Digital Citizenship and Conflict as part of the Digital Communities Week series. This exploration has shed light on the multifaceted nature of online interactions, revealing both the positive potential for societal engagement and the darker underbelly of online abuse and harassment.
The Multidimensional Nature of Digital Citizenship
As we navigate the complex web of digital citizenship, it becomes evident that our online presence extends beyond the mere act of participation; it encompasses the responsibility to engage thoughtfully and contribute positively to the digital community. However, this journey also exposes us to the challenges that arise when digital spaces become arenas for power struggles and conflicts.
Social Media Governance: The Wild West of the Internet
Social media governance, a topic at the heart of this discussion, presents a dynamic and often unregulated environment where various entities—from social media corporations to individual community moderators—exert influence. This lack of clear governance structures can lead to a Wild West scenario, where the rules are as varied as the territories they govern.

The Scourge of Online Harassment
The issue of online harassment, a pressing concern in the digital age, is not merely an isolated incident but a coordinated and pervasive problem that disproportionately affects women and gender non-conforming individuals. The data is stark, and it underscores the urgent need for action.
A Multifaceted Approach to Online Safety
As we consider the path forward, it's clear that a multifaceted approach is required—one that combines legal measures, social awareness, and corporate accountability. The recent Online Safety Act 2021 in Australia is a step in the right direction, but it's only one piece of the puzzle.
Towards a Safer and More Inclusive Digital Community
In the spirit of fostering a safer and more inclusive digital community, let us continue this conversation with a commitment to understanding, empathy, and action. Together, we can make the digital world a place where everyone feels seen, heard, and respected.
References
Griffin, R. (2023). Public and private power in social media governance: multistakeholderism, the rule of law and democratic accountability. Transnational Legal Theory, 14(1), 46-89. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/20414005.2023.2203538
Svantesson, D. (2024). Global content orders: A legal analysis of eSafety Commissioner v X Corp. Available at SSRN 4819178. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4819178
Lewis, M. (2021). " My Biggest Worry is Being Outed": The Impact of Heteronormative Online Safeguarding on Closeted Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Questioning Young People (Doctoral dissertation, Edge Hill University). https://research.edgehill.ac.uk/ws/portalfiles/portal/46375076/Martin_Lewis_Thesis_Final_Version_.pdf
Mattson, K. (2024). Digital citizenship in action: empowering students to engage in online communities. International Society for Technology in Education. https://books.google.com.my/books?hl=en&lr=&id=rWQJEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=digital+citizenship+becomes+evident+that+our+online+presence+extends+beyond+the+mere+act+of+participation%3B+it+encompasses+the+responsibility+to+engage+thoughtfully+and+contribute+positively+to+the+digital+community&ots=BXNG5SeXHZ&sig=8maoK6Sptu-D0cgQi1UeaMYpzak&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
0 notes
Text
Diving into the World of Gaming: Communities, Social Play, and Live Streams

Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the dynamic realm of gaming, where communities thrive, social interactions flourish, and live streaming has become a pivotal force. Taylor Hardwick, a PhD candidate at Swinburne University, has meticulously dissected the intricacies of this evolving landscape, offering a profound understanding of how gaming has transcended mere entertainment to become a cultural phenomenon.
Gaming Communities: The Social Fabric
At the core of this digital revolution are gaming communities, which Hardwick describes as intricate networks of players united by shared interests, skills, and knowledge. These communities are not just platforms for competition but are spaces where friendships are forged and experiences are shared, embodying the essence of gaming as defined by Bernard Suits.
The Historical Tapestry of Gaming
Hardwick takes us on a journey through the annals of gaming history, from the nostalgic arcades to the dawn of online multiplayer, which was propelled by advancements in networked computing. This evolution has not only reshaped the gaming experience but has also influenced the cultural perception of gaming.
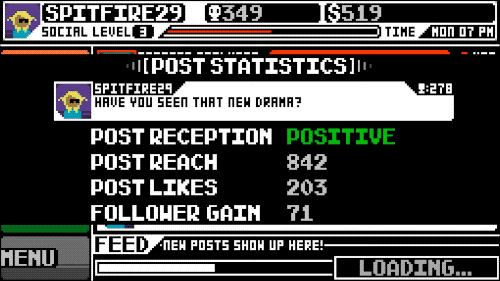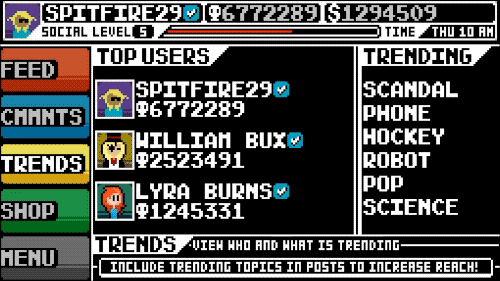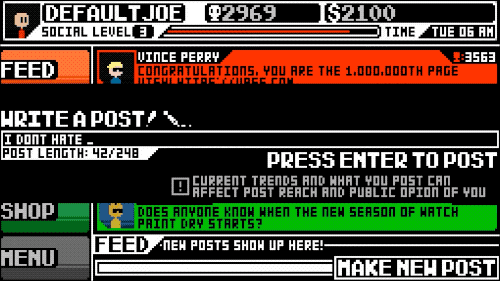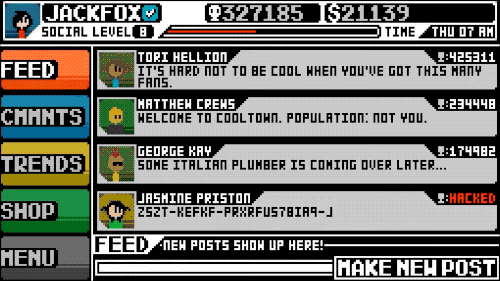
Social Gaming: Bridging the Virtual and Real
The advent of social gaming has been transformative, integrating our social networks into the gaming experience. Hardwick highlights how this shift has made gaming more accessible and interwoven with our daily lives, fostering connections that transcend the digital divide.
Gaming Platforms: The Architects of Modern Play
Hardwick's examination of gaming platforms reveals the multifaceted role they play in distribution, consumption, and social interaction. Players now traverse a variety of platforms to satisfy their diverse gaming needs, underscoring the adaptability and fluidity of the gaming ecosystem.
Live Streaming: The New Frontier of Gaming
The rise of live streaming platforms such as Twitch and YouTube Gaming has revolutionized the gaming industry. Hardwick discusses how these platforms have democratized content creation, enabling gamers to share their experiences and build communities around their content, often intertwining with the burgeoning esports scene.
Knowledge Communities and Modding: Participation and Innovation
Hardwick introduces the concept of knowledge communities within gaming, where affiliations are voluntary and based on shared intellectual pursuits. Modding emerges as a prime example of this participatory culture, where fans of games contribute to their evolution, showcasing the collaborative nature of gaming communities.
In the end, Taylor's presentation was a reminder that gaming is a dynamic, ever-changing world that's all about community, creativity, and connection. Whether you're a seasoned gamer or just dipping your toes in, there's a place for you in this vibrant world.
References
Keogh, B 2021, 'The Melbourne indie game scenes: value regimes in localized game development' (Chapter 13), Download 'The Melbourne indie game scenes: value regimes in localized game development' (Chapter 13),in P Ruffino (ed), Independent Videogames: Cultures, Networks, Techniques and Politics, Routledge, pp.209-222.
Taylor, TL 2018, ‘Broadcasting ourselves’ (chapter 1), in Watch Me Play: Twitch and the Rise of Game Live Streaming, Princeton University Press, pp.1-23 click hereDownload click here
Hjorth, L, Richardson, I, Davies, H & Balmford, W 2021, ‘Exploring play’ (chapter 2) Download ‘Exploring play’ (chapter 2), in Exploring Minecraft: Ethnographies of Play and Creativity, Palgrave Macmillan, pp.27-47.
Aleena Chia, Brendan Keogh, Dale Leorke, and Benjamin Nicoll (2020). "Platformisation in game development", Internet Policy Review 9 (4). DOI: 10.14763/2020.4.1515. https://policyreview.info/articles/analysis/platformisation-game-development (Links to an external site.).
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of Digital Self-Expression: A Critical Look at Augmented Reality Filters
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communities, the role of Augmented Reality (AR) filters has become a subject of both fascination and critical inquiry. As highlighted by guest lecturer Lauren Miller, the integration of these filters into our online lives has sparked a growing body of literature, examining the implications of their use. The popularity of filters has surged in tandem with the quality and accessibility of smartphones, with platforms like Instagram boasting an active user base of over 1.28~2 billion individuals. This has led to a cultural consensus on what we are "supposed to document," influencing our self-expression and the ways in which we present ourselves to the world.

The ubiquity of beauty filters, in particular, has not gone unnoticed, with popular creators like @sasha_soul_art sharing filter metrics on Instagram stories. This trend has extended beyond social media, with filters being integrated into technologies outside of apps, blurring the lines between digital enhancement and reality. Theories such as neo-liberal/postfeminist and transhuman/cyberfeminist provide frameworks for understanding the complex relationship between filter use and identity, labor, and the body image.
However, the ease of use and the "mutually reinforcing relationship" with technology, as noted by Perloff (2014), has also led to concerns about technological deskilling and a power imbalance between users and creators. The limited technological affordances restrict our expressions, potentially leading to a homogenization of beauty standards and the rise of "Snapchat dysmorphia." This phenomenon underscores the need for a critical reflection on the use of filters and their impact on our perception of reality and self.

As we continue to navigate the digital age, it is imperative to consider the multifaceted implications of AR filters. From the cultural pressures to document our lives in a certain way to the theoretical underpinnings of beauty and identity, the conversation around filters is far from simple. As these technologies continue to advance and integrate into various aspects of our lives, it is crucial to remain vigilant about their effects on our self-presentation, authenticity, and the digital-forensic gaze.
References:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11199-014-0384- – Perloff (2014)
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14680777.2020.1750779 - Peng (2020)
https://intellectdiscover.com/content/journals/10.1386/vcr_00022_7- Fisher (2020)
https://www.nature.com/articles/palcomms. -Coy-Dibley (2016)
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Intersection of Digital Citizenship, Health Education, and Body Modifications on Visual Social Media

In today's digital age, social media has become a powerful platform for self-expression, communication, and branding. However, the influence of social media on body image, aesthetic standards, and identity practices has raised significant concerns, particularly in the realm of public health. Dr. Jonathan Mavroudis' research delves into the complex dynamics of digital citizenship, health education, and body modifications on visual social media, shedding light on the profound implications for individuals and society as a whole.
Aesthetic Templates and Microcelebrity Culture
Social media sites have distinct and popular aesthetic templates that shape the visual landscape of platforms like Instagram. These templates influence users' behavior, from the way they dress and present themselves to the poses and body language they adopt. Dr. Mavroudis' research highlights the emergence of microcelebrity culture, where individuals actively shape and enforce identity practices that sustain it. This culture involves the creation and maintenance of branded online identities to gain visibility and status, blurring the lines between producing and consuming celebrified brands.
Visibility and Aesthetic Labor
The concept of visibility labor is central to the dynamics of microcelebrity culture. Users engage in self-branding and visibility tactics to gain attention and recognition within the digital sphere. This phenomenon has led to the normalization of "prosumption," where social media users create branded products that reinforce heteronormative advertising models. The implications of this visibility labor extend beyond the digital realm, influencing offline behavior and self-presentation.
Implications for Public Health
The influence of social media on body image and identity practices has significant implications for public health. Dr. Mavroudis' research raises concerns about the marginalization of identities, algorithmic invisibility, and the perpetuation of unattainable body image ideals. The normalization of pornification and heteronormative standards of beauty and sexuality further exacerbates the body image crisis, contributing to issues such as body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) and identity dissonance.
What Can We Do?
In light of these findings, it is crucial to consider the role of social media in shaping aesthetic standards and identity practices. Dr. Mavroudis emphasizes the need for a cultural perspective to address body dissatisfaction and the marginalization of identities. This involves critical reflection on the influence of social media brands as culturally constructed products and the active role of users in shaping microcelebrity culture.

Moving Forward
As we navigate the complexities of digital citizenship, health education, and body modifications on visual social media, it is essential to critically examine the impact of social media on individuals' well-being and societal norms. Dr. Mavroudis' research serves as a call to action, urging us to consider the broader implications of our online behaviors and the role of social media in shaping identity and aesthetic standards.
In conclusion, the intersection of digital citizenship, health education, and body modifications on visual social media presents a multifaceted landscape that requires careful consideration and critical engagement. By understanding the dynamics at play and actively addressing the implications for public health, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive digital environment for all individuals.
References
Jonathan mavroudis. (n.d.). Retrieved May 10, 2024, from https://jonathanmavroudis.academia.edu/
Carah N, Dobson A, 'Algorithmic Hotness: Young Women’s “Promotion” and “Reconnaissance” Work via Social Media Body Images'. Download Algorithmic Hotness: Young Women’s “Promotion” and “Reconnaissance” Work via Social Media Body Images'.Social Media + Society. October 2016
Drenten et al ‘Sexualized labour in digital culture: Instagram influencers, porn chic and the monetization of attention’ Download ‘Sexualized labour in digital culture: Instagram influencers, porn chic and the monetization of attention’Gender, Work and Organization
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Intersection of Digital Citizenship and Slow Fashion.

In this lecture, I want to dive into the fascinating world of digital citizenship and its connection to the slow fashion movement. In my Digital Communities class, we recently discussed the impact of social media influencers on the slow fashion movement, and it was truly eye-opening.
First off, let's talk about digital citizenship. This concept is all about the rights, responsibilities, and participation of individuals in the digital world. With the rise of social media, new norms and identities have emerged, prioritizing personalization and sharing over traditional allegiances to politics. The ubiquity of social media has given birth to the development of digital citizenship, shaping the way we interact and engage online.
Now, how does digital citizenship relate to slow fashion? Slow fashion is a movement that advocates for sustainable and ethical practices in the fashion industry. It's all about promoting responsible consumption, ethical production, and environmental sustainability. The connection between digital citizenship and slow fashion becomes evident when we see how social media influencers and platforms have amplified the message of slow fashion, bringing awareness to the environmental and economic impact of fashion.

One key aspect of this connection is the role of good corporate citizens and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in the fashion industry. The creation of long-term relationships across the supply chain is vital in producing sustainably, allowing for fair prices and wages, and fostering a network that supports sustainable fashion.
In our discussions, we also highlighted some inspiring slow fashion activists and influencers, such as Second Runway, Big Sister Swap, Venetia Falconer, and Tiffany Ferguson. These individuals and organizations are at the forefront of driving change in the fashion industry, promoting ethical and sustainable practices.
It's important to recognize the power of social media in enhancing movements like slow fashion. The Black Lives Matter movement and the Covid-19 pandemic have both underscored the need to understand digital citizenship and its impact on marginalized and oppressed communities. Social media has become a powerful tool for amplifying messages and driving meaningful change.
As we continue to navigate the digital landscape, let's remember the influence we have as digital citizens. By supporting and promoting movements like slow fashion, we can contribute to a more sustainable and ethical future for the fashion industry.
I hope this sparks some ideas for your own presentations and discussions. Let's keep the conversation going and work towards a more responsible and sustainable fashion industry.
Reference
DW Planet A 'If you think fast fashion is bad, check out SHEIN'Links to an external site. (2022)
Domingos, Mariana, Vera Teixeira Vale, and Silvia Faria. (2022). "Slow Fashion Consumer Behavior: A Literature Review" Download "Slow Fashion Consumer Behavior: A Literature Review" Sustainability 14, no. 5: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052860
McKinsey and Company, The Business of Fashion, 'The State of Fashion(2022)
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Intersection of Social Media, Political Engagement, and Activism

This week lecture, we're diving into the fascinating world of digital citizenship, hashtag publics, and political engagement on social media. In a world where social media platforms have become central to our daily lives, it's crucial to understand how they shape our political views and activism.
One of the key concepts we'll be exploring is platformisation, which refers to the transformation of social network sites into social media platforms. This has significant implications for how we engage with political content and activism online. The rise of hashtag publics has also played a crucial role in facilitating connectivity and organizing activities within and across networks.

Political engagement on social media takes various forms, including sharing petitions, contacting public officials, following political figures, and posting political news. These actions can have a direct impact on fundraising and campaigning efficiency, ultimately influencing election results.
The Black Lives Matter movement and the Covid-19 pandemic have highlighted the profound effects of digital citizenship on marginalized and oppressed communities. Understanding how social media can be used to amplify messages and mobilize support is essential in today's digital age.

We'll also touch on the role of social media in shaping user behaviors within social institutions and the digital divide, as well as the formation and coordination of ad hoc issue publics through linguistic markers and thematic hashtags.
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of social media and political engagement, it's important to critically examine the impact of platformisation and hashtag publics on our digital citizenship and activism.

So, there you have it - a glimpse into the complex and dynamic relationship between social media, political engagement, and activism.
References
Kim, Y., & Lee, S. (2022). #ShoutYourAbortion on Instagram: Exploring the Visual Representation of Hashtag Movement and the Public’s Responses. SAGE Open, 12(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221093327Links to an external site.
Council of Europe (2022) Digital citizenship education handbookLinks to an external site. Strasbourg France.
Matti Nelimarkka, Salla-Maaria Laaksonen, Mari Tuokko and Tarja Valkonen Platformed Interactions: ‘How Social Media Platforms Relate to Candidate–Constituent Interaction During Finnish 2015 Election Campaigning’, Download Platformed Interactions: ‘How Social Media Platforms Relate to Candidate–Constituent Interaction During Finnish 2015 Election Campaigning’,Social Media + Society April-June 2020: 1–17.
0 notes
Text
The Intersection of Reality TV, Social Media, and Digital Communities: Exploring the Formation of Digital Publics

This week's lecture has provided a comprehensive overview of the ways in which reality TV has transformed the landscape of public engagement and discourse, particularly through the lens of social media platforms.
One of the key takeaways from this week's lecture is the concept of digital publics and the public sphere, and how reality TV has played a significant role in shaping these spaces. The lecture highlighted the ways in which reality TV has created digital publics for everyday political talk, performing a valuable social function that is often overlooked. This insight into the broader societal impact of reality TV has truly expanded my understanding of its influence beyond mere entertainment (Scholz, 2021).
Furthermore, the lecture emphasized the multiplatform engagement facilitated by social media, which has diversified markets and audience participation in reality TV. This has not only increased opportunities for reality stars and fans to interact across various social media platforms, but has also led to the proliferation of discussions and opinions about reality TV content. The idea that reality TV is designed to elicit talk and shared opinions, both online and offline, has shed light on the ways in which this genre has become a catalyst for public discourse (He, Gao, & Razi, 2023).

Additionally, the lecture touched upon the paradox of reality TV becoming less reliant on traditional television, as television networks incentivize stars to generate their own digital content in competition with their co-stars. This new industry strategy seeks to cut costs while extending viewer engagement, showcasing the evolving dynamics between reality TV, social media, and audience participation (Deller, & Ruth, 2019).
Overall, this week's lecture has provided a thought-provoking exploration of the complex relationship between reality TV and social media, and the ways in which it has shaped digital communities and public discourse. I look forward to further exploring the extended readings and engaging in discussions about the shifting visibility of reality TV in the age of social media.
References
Deller, & Ruth A. (2019) Extract: 'Chapter Six: Reality Television in an Age of Social Media' Download 'Chapter Six: Reality Television in an Age of Social Media'in Reality Television: The TV Phenomenon That Changed the World (Emerald Publishing).
He, J., Gao, B., & Razi, A. H. M. (2023). Analyzing the Impromptu Speech Style of a Job-Hunting Reality TV Show Host: A Case Study of" It's You". Migration Letters, 20(6), 24-41. Retrieved from: https://migrationletters.com/index.php/ml/article/view/3457
Scholz, J. (2021). How consumers consume social media influence. Journal of Advertising, 50(5), 510-527. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00913367.2021.1980472
0 notes
Text
Unveiling Tumblr: A Hub for Digital Communities

This week's Digital Communities class offered a fascinating glimpse into the world of Tumblr, specifically its role in fostering online communities. Tumblr provides a unique case study in public sphere engagement.
The Rise of Micro Publics: Niche Communities Take Root
The lecture explored the concept of "micro publics" – smaller, niche communities that form within larger social media platforms. Tumblr, with its emphasis on user-generated content and customizable spaces, provides the perfect environment for these micro publics to flourish. Hashtags, comments, and creative content like GIFs and images become the building blocks for these vibrant communities.
Here, the focus isn't just on passively consuming information. Users actively shape online discourse by contributing their voices and interests, leading to a dynamic exchange of ideas.
Aesthetics Take Center Stage: Redefining Online Expression
One of the most intriguing aspects of Tumblr is its prioritization of aesthetics and creative expression. Scholar Jessalynn Keller highlights this in her work, emphasizing how users can personalize their blogs and curate visually-driven experiences. Gone are the days of solely text-based posts. Tumblr empowers users with tools like images, GIFs, videos, and unique layouts to craft narratives and share their passions in a visually compelling way.
Fan Cultures and the Power of Community
The lecture also referenced a video by Sarah Z, titled "Tumblr's Greatest Conspiracy: The Story of TJLC." This video explores the fascinating world of Tumblr fan communities, a cornerstone of the platform's culture. Imagine communities dedicated to specific shows, music artists, or even historical figures. These communities foster intense engagement, shared interests, and even creative collaboration, demonstrating how these micro publics can influence broader cultural trends.
Looking Forward: The Future of Online Communities
The lecture sparked some interesting questions. Micro publics on Tumblr, with their niche communities and unique voices, could potentially challenge the controlled narratives of traditional media. Imagine a platform buzzing with diverse perspectives on a single issue, instead of a one-sided news story.
Looking ahead, the future of Tumblr and online communities is wide open. Will Tumblr stay true to its roots, or will we see a rise of even more specialized platforms for micro publics? It'll be fascinating to see how these online communities evolve alongside technology, perhaps incorporating virtual or augmented reality to create even more immersive experiences.
References
Jessalynn Keller. (2019). “Oh, She’s a Tumblr Feminist”: Exploring the Platform Vernacular of Girls’ Social Media Feminisms, Social Media + Society 5.3.
Sarah Z. (2020, October 31). Tumblr’s Greatest Conspiracy: The Story of TJLC [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NZBP_0UTh5
youtube
1 note
·
View note