Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
READING SETTING
In this chapter, we will study about Reading Settings in WordPress. Reading Setting is used to set the content related to the front page. You can set the number of post to be displayed on the main page.
Following are the steps to access the reading settings:
Step (1): Click on Settings -> Reading option in WordPress.

Step (2): The Reading Settings page is displayed as shown in the following screen.
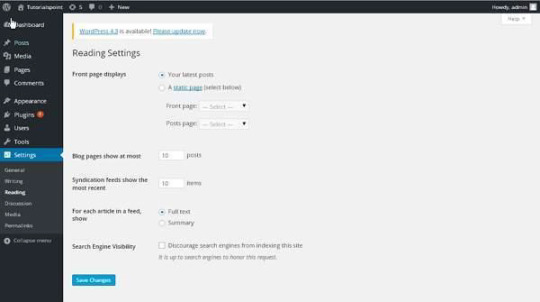
Step (3): After filling all the information, click on Save Changes button to save your Reading Setting information.
More Information Visit: https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
WRITING SETTING
The writing settings controls the writing experience and provides options for customizing WordPress site. These settings control the features in the adding and editing posts, Pages, and Post Types, as well as the optional functions like Remote Publishing, Post via e-mail, and Update Services.
Following are the steps to access the writing settings:
Step 1: To change writing settings, go to Settings -> Writing option.
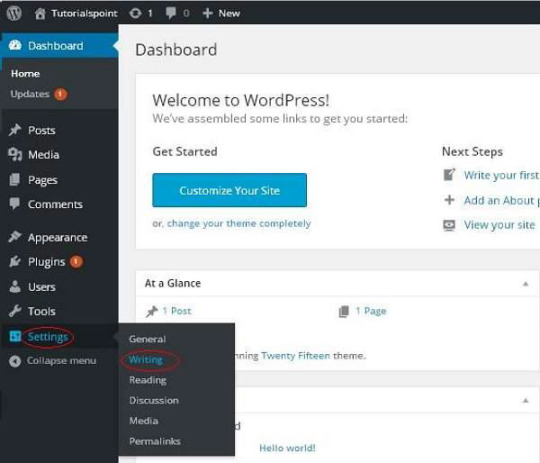
Step (2): The Writing Setting page is displayed as shown in the following screen.
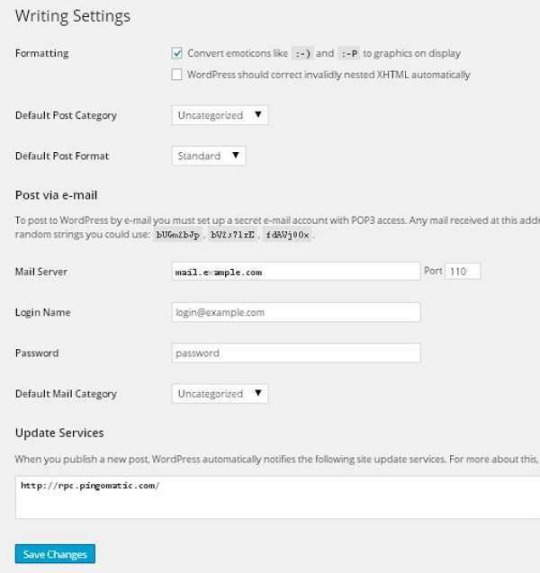
Following are the details of the fields on the page.
Formatting: This field defines two sub options for better user experience.
The first option Convert emoticons like :-) and :-P to graphics on display will turn text-based emoticons into graphic-based emoticons.
The second option WordPress should correct invalidly nested XHTML automatically corrects the invalid XHTML placed within the posts or pages.
Default Post Category: It is a category to be applied to a post and you can leave it as Uncategorized.
Default Post Format: It is used by themes to select post format to be applied to a post or create different styles for different types of posts.
Post via e-mail: This option uses e-mail address to create posts and publishes posts on your blog through e-mail. To use this, you'll need to set up a secret e-mail account with a POP3 access, and any mail received at this address will be posted.
Mail Server: It allows reading the e-mails that you send to WordPress and stores them for retrieval. For this, you need to have POP3 compatible mail server and it will have URI address such as mail.example.com, which you should enter here.
Login Name: To create posts, WordPress will need its own e-mail account. The Login Name will use this e-mail address and should be kept as a secret as spammers will post links redirecting to their own websites.
Password: Set password for the above e-mail address.
Default Mail Category: It allows selecting custom category for all the posts that are published via Post by e-mail feature.
Update Services: When you publish a new post, WordPress will automatically notify the site update services in the box. See the Update Services on the codex for the long list of possible services.
Step (3): After filling all the above information, click on Save Changes button to save your information.
More Information Visit: https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
Optimized Theme
Theme plays an important role in optimization. An optimized WordPress theme boosts the search engine optimization efforts. Therefore, every time our recommendation goes to the use of an optimized theme. There are two key factors of an optimized theme that it must have a clean structure and validation with W3C & WordPress coding guidelines. It ensures that the theme will not cause performance issues and will not conflict with the WordPress SEO plugins. The TemplateToaster takes care of these two factors for producing WordPress themes. You can use this software for making optimized WordPress themes with no coding at all.
Set up Pretty Permalinks The Permalinks are the particular URLs of the pages, posts and categories of a website. Like https://blog.templatetoaster.com/improve-performance-of-your-wordpresswebsite/ is the permalink of our post, published a short time back on our site. Whenever you create a new post or a new page, WordPress auto generates its permalink as per default settings. That auto generated permalink is not as clean and friendly as is recommended by the SEO experts. So, the customization of default permalink is advised to you.
For changing the default permalink structure, go to Settings and select permalinks. You will see the following screen. We suggest you to set the simple structure of permalinks, therefore “Post name” option is a good option to choose.
More Information Visit : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
SEO Optimisation
SEO is as important as the development of a site. If you have a website that is not optimized for the search engines, you might not get the full benefits out of it. SEO is not very hard, all it takes is unfeigned efforts. If you get to know the white-hat techniques, then you can simply do optimize your website for search engines. Therefore, we decided to let our readers know about the simple and effective SEO techniques.
Unique and Useful Content
You must have heard one or more times that the content is king. This is absolutely true. All your efforts and tactics applied will go in vain if you don’t have the focus on the “content”. Google prioritizes the content of a site over other things. But, this doesn’t mean that you write anything, and Google will like your site. Google likes “good content”. So, be utmost fair when you are writing the content of your site. Let us tell you that how you can come in Google’s good graces, in context of the content of your website.
• Unique, no copied content at all • Sharable, means loved by the readers • Thoughtful, providing solution to people’s queries
Give your readers something that is interesting and informative for them. Bring your own experiences, from which the readers could learn something new. Whatever you write, write by keeping the user in mind, who is going to read this. Don’t just write for the sake of writing. It would be best, if you could use real images, infographics, and videos in your content. They make the content more interesting.
More Information Visit : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
Optimize WordPress Website
The following techniques/tools will help to optimize WordPress websites. (I will not go into detail about some well-known ones such as using proper web host and fast theme.)
Optimize WordPress Database
Optimizing our database is essential, since the larger our database is, the more time it will take to retrieve information from it.
WP-Optimize plugin is a WordPress database optimization tool that also cleans up your database. You don’t have to visit PhpMyAdmin to perform it. An optimized database would work like a charm for a CMS like WordPress. Figure 1 demonstrates what this plugin does and how it helps in achieving the goal. Just click on “Process” to clean the database.
Visit More Information : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
Performance Optimisation
When I started with WordPress to learn from around the web, the elements that created an interest in my mind were Optimization and Security. Since for any website, these two are the key elements. Without optimization and security a website can never get remarkable page views, popularity, and reach. So, the parameters of a successful website not only include design, development, and SEO; but also include making the website secure and optimized.
Why Optimization?
Optimization is a requirement for faster loading of pages. With enhancements in web page development, we all want our website to load within seconds. We can lose our customer if the website is slower than our competitor, even by only a few seconds. More loading time would decrease conversions and increase bounce rate. A fast website is vital to provide amazing user experience and to rank well in search engines (SERP). The importance can also be judged by what Google thinks about encouraging users to visit our website. Google made an announcement in 2010, stating the significance of page loading time of search engine results.
More Information Visit : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
Tools of the Trade
All web designers have their own box of tools which they use to bring their design ideas to life. These tools have made the process of designing websites more creative than technical since in previous times, developing websites purely involved coding. These tools have provided more intuitive ways of generating websites through their graphical user interfaces. There are some cool tools out there which might not be well known by most web designers. Here are some of them.
Backbone:
All websites are built on HTML and CSS. These two usually go together since HTML which is a standard markup language defines the layout of the web pages while CSS defines the visual look and formatting of the various elements. The fifth version of HTML is even better with increased multimedia functionality. Any web developer should learn this language since it is very basic and easy to use and also other higher level web based languages such as PHP are well integrated with HTML.
Editor:
When designing websites, you might have to do some coding or scripting. One of the very best code editors is Notepad++. With numerous features such as Syntax Highlighting and Syntax Folding, PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expression) Search/Replace, customizable GUI, document map, auto completion and multi-language support, Notepad++ is definitely a top choice for easy coding.
Local Development Environment:
At times you may want to simulate a server on your computer for development purposes before loading your site on an actual server. In this case, XAMPP is a premium option. XAMPP is an open source package which enables PHP and MySQL development on an Apache server. It is very easy to install and completely free so you can develop sites without subscribing to a web hosting package.
Frameworks:
Despite knowing how to code, you may still want a quick solution for easy front-end web development. Bootstrap will help you with great tools for designing responsive sites. It accommodates developers of all skill levels and you can implement HTML, CSS and JavaScript. This greatly reduces the need of coding the front end of your site and as a result, you can focus more on developing the more complex hidden segments of your sites.
More Information Visit : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
Creating WordPress Website
Designing WordPress Theme
Till now you got to know what a WordPress website is, but to create a website you need a theme to support your envisioned design. Basically a theme is a set of files that provide you with a layout design of your WordPress site.
A WordPress theme has the capability of transforming your website to its entirety.. If you change your theme then you automatically bring changes to the way your site appears on the front-end, i.e. what a visitor views when your site is browsed on the web. Themes pick the content and data saved by WordPress and showcase it to the world. When you create a WordPress theme, you choose how that content will be displayed.
What are these themes made up of?
In simple words, WordPress themes are a bunch of files made to function together in order to create what you see, as well as how your site performs.
Important files
There are two files which holds the utter requirement in a WordPress theme: index.php – the main template file style.css – the main style file
Though not mandatory yet, you may come across some added files in a theme’s folderincluding:
PHP files – carry template files Localization files CSS files Graphics JavaScript Text files – carry readme.txt instructions, changelog file and a license info.
If you have been following up by far then, I’d like to bestow you with this information as to how you can implement graphic design tools and see your “actionable ideas” turning into fruit-bearing plants. You can absorb this blessing by marching southwards
More Information Visit : https://wordpress-templates-free.com/
0 notes
Text
FOUR GENERIC WORLDWIDE STRATEGIES
Bartlett and Ghoshal (Bartlett, Ghoshal and Birkinshaw, 2004; Ghoshal and Bartlett, 1998) have identified four generic worldwide strategies: (1) an international strategy; (2) a multinational strategy; (3) a global strategy; and finally (4) a transnational strategy.
International Strategy
In the earliest stages of a firm’s internationalization, managers tend to think of the overseas operations as some kind of distant outposts whose main role is to support the domestic parent company in different ways such as contributing incremental sales of the domestic product, or supplying raw materials or components to the domestic manufacturing operations. Bartlett and Ghoshal (Bartlett, Ghoshal and Birkinshaw, 2004; Ghoshal and Bartlett, 1998) have labeled this generic strategy, international strategy. The international terminology derives directly from Vernon (1966)’s international product cycle theory (cf. box 2), which states that products are first developed for a firm’s domestic market, and only subsequently sold abroad. This strategy is primarily based on transferring and adapting the parent company’s knowledge or capabilities to foreign markets. The parent retains considerable influence and control over the foreign subsidiaries, but less than with the global strategy (see below) and the foreign subsidiaries can adapt to the needs and preferences of their local markets products and ideas coming from the center, but have less independence and autonomy than with a multinational strategy (Ghoshal and Bartlett, 1998).
Traditionally, a firm following an international strategy can choose between one of three basic marketing adaptation options (Keegan, 2000): (1) product standardization-communication adaptation, (2) product adaptation-communication standardization, or (3) product adaptationcommunication adaptation. The first option, product standardization-communication adaptation, is often chosen when reasons for buying a product differ from country to country, but the usage conditions and standards remain identical. In this case, the same product can be marketed but with a change in the communications strategy. This strategy is quite costeffective, because communications adaptation is less expensive than tailoring a product to the local market. The second option, product adaptation-communication standardization, is appropriate when the physical event surrounding product usage varies but the sociocultural event is the same as in the firm’s home country. Kotler (2000) mentions the example of Kraft that blends different coffees for the British (who drink their coffee with milk), the French (who drink their coffee black), and Latin Americans (who want a chicory taste). Finally, the third option of dual adaptation of product and communication is generally favored for a product when both usage conditions and sociocultural concerns vary among markets.
Visit more Information:
0 notes
Text
MNCs’ ADMINISTRATIVE AND CULTURAL HERITAGE
A firm’s worldwide strategy is shaped not only by its current external environment but also by its past internal management biases. In particular, MNCs are influenced by the path by which they developed and the values, norms, and practices of their management. Firms are, to a significant extent, captives of their past (i.e., their administrative and cultural heritage) (Ghoshal and Bartlett, 1998). MNCs as any organizations are symbolic entities; they function according to implicit models in the minds of their members, and these models are culturally determined (Hofstede, 2001). There is strong evidence that culture plays an important and enduring role in shaping the assumptions, beliefs, and values of individuals (Hofstede, 1980b, 1991, 2001; Hall, 1976, 1983; Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner, 1998; Usunier, 2000) (cf. box 1).
Box 1: Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions
Perhaps the most celebrated effort to date to describe and categorize these differences in the orientations and values of people in different countries is Hofstede’s (1980b, 1991, 2001; Bond et al., 1987) study (Questionnaire data from 116,000 IBM employees in 72 countries across seven occupations.) that described national cultural differences along five key dimensions: Power Distance (PDI), Individualism (IDV), Masculinity (MAS), Uncertainty Avoidance (UAV), and Long Term Orientation (LTO).
Power Distance is the extent to which the less powerful members of organizations and institutions accept and expect that power is distributed unequally. The basic problem involved is the degree of human inequality that underlies the functioning of each particular society.
Individualism on the one side versus its opposite collectivism is the degree to which individuals are supposed to look after themselves or remain integrated into groups, usually around the family. Positioning itself between these poles is a very basic problem all societies face.
Masculinity versus its opposite, femininity, refers to the distribution of emotional roles between genders, which is another fundamental problem for any society to which a range of solutions are found; it oppose “tough” masculine to “tender” feminine societies.
Uncertainty Avoidance is the extent to which a culture programs its members to feel either uncomfortable or comfortable in unstructured situations. Unstructured situations are novel, unknown, surprising, different from usual. The basic problem involved is the degree to which a society tries to control the uncontrollable.
Long-Term versus Short-Term Orientation refers to the extent to which a culture programs its members to accept delayed gratification of their material, social, and emotional needs. Cultures with a long-term orientation exhibit a pragmatic future-oriented perspective (fostering virtues like perseverance and thrift), rather than a conventional historic or short-term point of view.
Country scores on each of the dimensions are provided
Visit more Information:
0 notes
Text
Left brain thinking; Right Brain thinking:
People who identify as left-brain thinkers might feel that they have strong math and logic skills. Those who profess to be right-brain thinkers, on the other hand, feel that their talents are more on the creative side of things. Given the popularity of the idea of "right-brained" and "left-brained" thinkers, it might surprise you learn that this idea is just one of many myths about the brain.
What Is Left Brain - Right Brain Theory?
According to the theory of left-brain or right-brain dominance, each side of the brain controls different types of thinking. Additionally, people are said to prefer one type of thinking over the other. For example, a person who is "left-brained" is often said to be more logical, analytical, and objective.
A person who is "right-brained" is said to be more intuitive, thoughtful, and subjective.
In psychology, the theory is based on the lateralization of brain function. The brain contains two hemispheres that each performs a number of roles. The two sides of the brain communicate with one another via corpus callosum. The left hemisphere controls the muscles on the right side of the body while the right hemisphere controls those on the left.
Visit more Information:
0 notes
Text
How to inculcate a 'creative thinking attitude'.
What is Creativity? An Ability. A simple definition is that creativity is the ability to imagine or invent something new. As we will see below, creativity is not the ability to create out of nothing (only God can do that), but the ability to generate new ideas by combining, changing, or reapplying existing ideas. Some creative ideas are astonishing and brilliant, while others are just simple, good, practical ideas that no one seems to have thought of yet.
Believe it or not, everyone has substantial creative ability. Just look at how creative children are. In adults, creativity has too often been suppressed through education, but it is still there and can be reawakened. Often all that's needed to be creative is to make a commitment to creativity and to take the time for it.
An Attitude. Creativity is also an attitude: the ability to accept change and newness, a willingness to play with ideas and possibilities, a flexibility of outlook, the habit of enjoying the good, while looking for ways to improve it. We are socialized into accepting only a small number of permitted or normal things, like chocolate-covered strawberries, for example. The creative person realizes that there are other possibilities, like peanut butter and banana sandwiches, or chocolate-covered prunes.
A Process. Creative people work hard and continually to improve ideas and solutions, by making gradual alterations and refinements to their works. Contrary to the mythology surrounding creativity, very, very few works of creative excellence are produced with a single stroke of brilliance or in a frenzy of rapid activity. Much closer to the real truth are the stories of companies who had to take the invention away from the inventor in order to market it because the inventor would have kept on tweaking it and fiddling with it, always trying to make it a little better.
The creative person knows that there is always room for improvement.
Visit more Information:
0 notes
Text
Online Marketing
Online marketing is the process to catch the attension of potential customers for business through particular banner, articles, video, images, flash animation etc. Marketing activities or information are planned as an elegant tempt to the visitors in which particular website of business wants to attract. This information is particularly placed on main page or front page of website to reach till key audiences. It has many ways to be done possible to get traffic for business through online marketing principles. Online Marketing is the practice of leveraging web-based channels to spread a message about a company's brand, products, or services to its potential customers. The purpose of online marketing is to get people to visit your website and then convert those visitors into paying customers. That’s what online marketing is all about. It has the same set of objectives like Establish and build brand recognition, Determine Pricing and make offers, Run advertising campaigns, promotions, discounts and specials etc. Online marketing media includes Website/Blog, Social Media Marketing, Email Marketing, Search Engine Marketing, Content Marketing, Video Blogging, Online Classifieds.
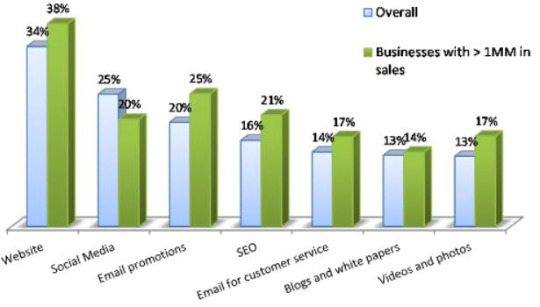
Model Graph of Websites and their promotion
0 notes
Text
Offline Marketing
Offline marketing is the process to create brand awareness and reach till target customer to satisfy their needs and want. In many occurrences, individual adopt marketing mix stradegy for their business promotion. The entire plan behind offline promotion is to obtain leads, when there is no website for your business. There are many forms of offline marketing strategies such as through print media as well as non print media. Offline marketing media includes Television, Radio, Brochure, Flyers, Banners, Newspaper, Pamphlets, Posters. Offline marketing tools offer varies benefit, Of course the first benefit is that with offline marketing, a business doesn’t have to be dependent on an internet connection. If a web server goes down and a website is no longer accessible, that’s valuable custom and discoverability potentially lost. A smaller business may take a while to get back online during which vital customer attention may have been spent elsewhere. With offline media there are no such worries, it exists in the real world and cannot be taken off the grid. Another benefit may be somewhat less tangible but no less important and that’s that digital marketing is seen by many customers and clients to be throw away. People are so used to seeing advertisements, pop ups, and marketing emails that they don’t even notice them anymore.
Visit more Information:
0 notes
Text
EnumSet
Enumerated types (or “enums”) were introduced in Subsection 2.3.3. Suppose that E is an enumerated type. Since E is a class, it is possible to create objects of type TreeSet and Hash- Set. However, because enums are so simple, trees and hash tables are not the most efficient implementation for sets of enumerated type values. Java provides the class java.util.EnumSet as an alternative way to create such sets.
Sets of enumerated type values are created using static methods in the class EnumSet. For example, if e1, e2, and e3 are values belonging to the enumerated type E, then the method
EnumSet.of( e1, e2, e3 )
creates and returns a set of type EnumSet that contains exactly the elements e1, e2, and e3. The set implements the interface Set, so all the usual set and collection operations are available. The implementation of these operations is very efficient. The implementation uses what is called a bit vector. A bit is a quantity that has only two possible values, zero and one. A set of type EnumSet is represented by a bit vector that contains one bit for each enum constant in the enumerated type E; the bit corresponding to the enum constant e is 1 if e is a member of the set and is 0 if e is not a member of the set. The bit vectors for two sets of type EnumSet can be very easily combined to represent such operations as the union and intersection of two sets. The bit vector representation is feasible for EnumSets, but not for other sets in Java, because an enumerated type contains only a small finite number of enum constants. (Java actually has a class named BitSet that uses bit vectors to represent finite sets of non-negative integers, but this class is not part of the Java Collection Framework and does not implement the Set interface.)
The function EnumSet.of can be used with any positive number of parameters. All the parameters must be values of the same enumerated type. Null values are not allowed. An EnumSet cannot contain the value null—any attempt to add null to an EnumSet will result in a NullPointerException.
There is also a function EnumSet.range(e1,e2) that returns an EnumSet consisting of the enum constants between e1 and e2, inclusive. The ordering of enum constants is the same as the order in which they are listed in the definition of the enum. In EnumSet.range(e1,e2), e1 and e2 must belong to the same enumerated type, and e1 must be less than or equal to e2.
If E is an enum, then EnumSet.allOf(E.class) is a set that contains all values of type E. EnumSet.noneOf(E.class) is an empty set , a set of type EnumSet that contains no elements at all. Note that in EnumSet.allOf(E.class) and EnumSet.noneOf(E.class), the odd-looking paramter represents the enumerated type class itself. If eset is a set of type EnumSet, then EnumSet.complementOf(eset) is a set that contains all the enum constants of E that are not in eset.
0 notes
Text
TreeSet and HashSet
A set is a collection of objects in which no object occurs more than once. Sets implement all the methods in the interface Collection, but do so in a way that ensures that no element occurs twice in the set. For example, if set is an object of type Set, then set.add(obj) will have no effect on the set if obj is already an element of the set. Java has two classes that implement the interface Set: java.util.TreeSet and java.util.HashSet.
In addition to being a Set, a TreeSet has the property that the elements of the set are arranged into ascending sorted order. An Iterator for a TreeSet will always visit the elements of the set in ascending order.
A TreeSet cannot hold arbitrary objects, since there must be a way to determine the sorted order of the objects it contains. Ordinarily, this means that the objects in a set of type TreeSet should implement the interface Comparable and that obj1.compareTo(obj2) should be defined in a reasonable way for any two objects obj1 and obj2 in the set. Alter-natively, an object of type Comparator can be provided as a parameter to the constructor when the TreeSet is created. In that case, the compareTo() method of the Comparator will be used to compare objects that are added to the set.
A TreeSet does not use the equals() method to test whether two objects are the same. Instead, it uses the compareTo() method. This can be a problem. Recall from Subsection 10.1.6 that compareTo() can consider two objects to be the same for the purpose of the comparison even though the objects are not equal. For a TreeSet, this means that only one of those objects can be in the set. For example, if the TreeSet contains mailing addresses and if the compareTo() method for addresses just compares their zip codes, then the set can contain only one address in each zip code. Clearly, this is not right! But that only means that you have to be aware of the semantics of TreeSets, and you need to make sure that compareTo() is defined in a reasonable way for objects that you put into a TreeSet. This will be true, by the way, for Strings, Integers, and many other built-in types, since the compareTo() method for these types considers two objects to be the same only if they are actually equal.
In the implementation of a TreeSet, the elements are stored in something similar to a binary sort tree. (See Subsection 9.4.2.) However, the data structure that is used is balanced in the sense that all the leaves of the tree are at about the same distance from the root of the tree. This ensures that all the basic operations—inserting, deleting, and searching—are efficient, with worst-case run time (-)(log(n)), where n is the number of items in the set.
Visit more Information: https://www.wikiod.com/w/Category:Java_Language
0 notes
Text
Generic Programming and Collection Classes
How to avoid reinventing the wheel? Many data structures and algorithms, such as those from Chapter 9, have been studied, programmed, and re-programmed by generations of computer science students. This is a valuable learning experience. Unfortunately, they have also been programmed and re-programmed by generations of working computer professionals, taking up time that could be devoted to new, more creative work. A programmer who needs a list or a binary tree shouldn’t have to re-code these data structures from scratch. They are well-understood and have been programmed thousands of times before. The problem is how to make pre-written, robust data structures available to programmers. In this chapter, we’ll look at Java’s attempt to address this problem.
Generic Programming
Generic programming refers to writing code that will work for many types of data. We encountered the term in Section 7.3, where we looked at dynamic arrays of integers. The source code presented there for working with dynamic arrays of integers works only for data of type int. But the source code for dynamic arrays of double, String, JButton, or any other type would be almost identical, except for the substitution of one type name for another. It seems silly to write essentially the same code over and over. As we saw in Subsection 7.3.3, Java goes some distance towards solving this problem by providing the ArrayList class. An ArrayList is essentially a dynamic array of values of type Object. Since every class is a subclass of Object, objects of any type can be stored in an ArrayList. Java goes even further by providing “parameterized types,” which were introduced in Subsection 7.3.4. There we saw that the ArrayList type can be parameterized, as in “ArrayList”, to limit the values that can be stored in the list to objects of a specified type. Parameterized types extend Java’s basic philosophy of type-safe programming to generic programming.
The ArrayList class is just one of several standard classes that are used for generic pro-gramming in Java. We will spend the next few sections looking at these classes and how they are used, and we’ll see that there are also generic methods and generic interfaces (see Subsec-tion 5.7.1). All the classes and interfaces discussed in these sections are defined in the package java.util, and you will need an import statement at the beginning of your program to get access to them. (Before you start putting “import java.util.*” at the beginning of every program, you should know that some things in java.util have names that are the same as things in other packages. For example, both java.util.List and java.awt.List exist, so it is often better to import the individual classes that you need.)
In the final section of this chapter, we will see that it is possible to define new generic classes, interfaces, and methods. Until then, we will stick to using the generics that are predefined in Java’s standard library.
It is no easy task to design a library for generic programming. Java’s solution has many nice features but is certainly not the only possible approach. It is almost certainly not the best, and has a few features that in my opinion can only be called bizarre, but in the context of the overall design of Java, it might be close to optimal. To get some perspective on generic programming in general, it might be useful to look very briefly at generic programming in two other languages.
0 notes