Statisticshelpdesk.com, a pioneer in online education bucket of services, provides exclusive help in Home work help, Assignment help, Project help, Dissertation Help, Online tutoring services, test preparation help, to the student...
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
9 Quick Tips to Hypothesis Testing with SPSS Help for Students
Introduction: Hypothesis Testing Doesn’t Have to Be a Nightmare

If you’re a student just starting out with hypothesis testing in statistics you’ve probably had moments of frustration—especially when using SPSS or, worse, Minitab. Many students struggle with choosing the right test, interpreting output tables or even just setting up their data correctly. It’s not your fault—hypothesis testing can feel like a puzzle with too many pieces.
This is where SPSS help for students comes in. Unlike Minitab which can be overwhelming with its rigidity, SPSS is more user friendly. But even with SPSS things can get confusing. What’s the difference between a t-test and an ANOVA? How do you check assumptions? And what do all those numbers in the output window mean?
Don’t worry I’ve got your back. Below are 9 quick tips to make hypothesis testing in SPSS easier, faster and less stressful. Let’s get started!
1. Know Your Hypothesis Type Before You Touch SPSS
Before you even open SPSS make sure you clearly define your null (H₀) and alternative (H₁) hypotheses. This will determine the type of test you need. Here’s an example:
Null hypothesis (H₀): There is no difference in students’ test scores before and after using a study app.
Alternative hypothesis (H₁): Students score higher after using the study app.
If you’re not sure what type of test you need, SPSS has a helpful “Analyze” menu, but understanding your hypothesis is step one.
2. Choose the Right Statistical Test – It’s Easier Than You Think
One of the biggest struggles students face is choosing the right test. Here’s a quick guide:
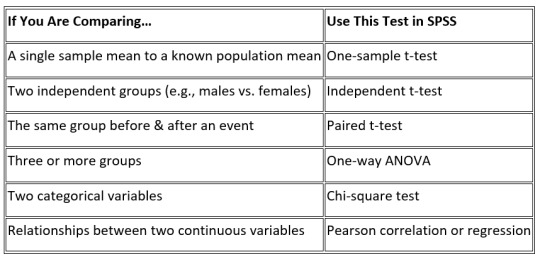
If this is still overwhelming consider getting SPSS help for students from an expert—or if you’re really stuck you might even think, Can I pay someone to do my statistics homework? (Spoiler: Yes, you can, but learning it yourself is worth it!)
3. Always Check for Normality – Don’t Skip This Step!
Most hypothesis tests assume your data is normally distributed. To check normality in SPSS:
Click Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Explore
Move your dependent variable into the Dependent List box
Click Plots, check Normality Plots with Tests, then hit OK
Look at the Shapiro-Wilk test—if p > 0.05, your data is normal. If not, consider a non-parametric test like the Mann-Whitney U test instead of a t-test.
4. Understand the p-Value – It’s More Than Just < 0.05
A p-value tells you to reject H₀, but students often misinterpret it. If p < 0.05 you have significant results (reject H₀). If p > 0.05 the results are not statistically significant (fail to reject H₀).
But here’s the catch: A p-value alone doesn’t tell you if your results are practically significant. Always look at effect size and confidence intervals for more.
5. Check Assumptions Before You Run Any Test
Most tests require assumptions, like homogeneity of variance (for t-tests and ANOVA). In SPSS you can check this using Levene’s test:
Click Analyze > Compare Means > One-Way ANOVA
Check the box for Homogeneity of variance test
If p < 0.05, variances are unequal, and you may need to adjust (like Welch’s test).
Don’t skip assumption checks or you’ll end up with wrong conclusions!
6. Use Graphs to Back Up Your Hypothesis Testing
Raw numbers are great, but SPSS’s graphs will make your results more impressive. Try these:
Boxplots for comparing groups
Histograms to check distributions
Scatterplots to see correlations
To create graphs in SPSS go to Graphs > Legacy Dialogs, select your chart type and customize to make your results more obvious.
7. Know When to Use One-Tailed vs. Two-Tailed
Many students assume two-tailed tests are always the way to go. Not true!
One-tailed test if you have a specific directional hypothesis (e.g. "higher", "lower")
Two-tailed test if you’re just testing for any difference.
One-tailed tests are more powerful but you might miss the opposite effect. Choose wisely!
8. Is Your Sample Size Big Enough?
Small sample sizes can lead to wrong results. Use G*Power (free) or SPSS’s power analysis to check if your sample size is sufficient.
Click Analyze > Power Analysis
Enter your effect size, alpha level and expected sample size
If your study is underpowered (if so you may need more participants)
9. Write Up Your Results Like a Pro (APA Style)
If you’re writing a report follow APA style. Here’s how to write up your results:
"An independent t-test was conducted to compare test scores between students who used the app and those who didn’t. The results were significant, t(48) = 2.34, p = 0.022, d = 0.65, app users scored higher.”
Always include the test type, degrees of freedom, test statistic, p-value and effect size.
Final Thoughts
Hypothesis testing in SPSS doesn’t have to be torture. Follow these 9 tips—choose the right test, check assumptions, interpret results correctly—you’ll feel more confident and will ace your stats assignments. And remember, whenever you feel the need of SPSS help for students, don’t hesitate to reach out to your professor or online spss experts.
#SPSS help for students#spss#help in spss#Hypothesis Type#Statistical Test#Shapiro-Wilk test#Levene’s test#Power Analysis#G*Power#APA Style
0 notes
Text
Optimizing Memory Allocation for Large Data in Stata Assignments
When you start learning about statistics and econometrics, especially when doing Stata assignments, managing memory effectively is very important. Stata is a great tool for analyzing data, but when working with large datasets, you might face issues like, “How can I make sure it runs smoothly?” or “Can I pay someone to do my Stata assignment because it keeps crashing?” Don’t worry—we’re here to explain how to optimize memory and help you succeed with your Stata tasks.
Why Understanding Memory Allocation Matters When Working on Stata Assignments
Efficient data processing in Stata relies on how well its memory works. When you work with big datasets with thousands or millions of records, wrong memory use can lead to both slow processing and unstable program behavior. For students seeking Stata assignment help, mastering memory settings is the difference between frustration and a smooth workflow. Understanding how Stata manages memory is a challenging topic, but you'll find it’s more straightforward than it seems. Stata only gives your data a limited amount of memory when you start working with it. Default settings work well for basic data work, but they won't give you enough memory when you need to process large economic data analyzing economic indicators or panel data with numerous time points.
Getting Started: How Stata Allocates Memory
Before we talk about ways to make things work better, let’s first see how STATA uses memory:
Memory for data: STATA stores your datasets in the computer’s RAM. This means if your dataset is big, it requires more memory.
Sort order and temporary files: Some stata commands, like sorting data, creates temporary copies of your dataset. This can use up even more memory.
Matsize setting: This decides how big the matrices (used in calculations) can be in memory. If you’re running models like regression with lots of variables and the matsize is too small, you might get errors.
Step-by-Step Guide to Optimize Memory Allocation in Stata Assignments
1. Increase the Memory Available to Stata Without Overloading Your System
To set memory parameters for Stata, enter "set memory." For instance:
set memory 2g
The command here lets Stata use 2GB of RAM memory. Just remember that running Stata takes space from other programs running on your computer, so adjust usage carefully. When you have a big project to work on, understanding exactly how much space your data takes up is the key. The describe command helps you learn about the memory usage of variables in your dataset. If needed, you can compress your dataset to save space:
compress
The command shrinks variable storage requirements, keeping previous levels of accuracy while freeing up room on your computer for other work.
2. Avoid Common Memory Bottlenecks by Managing Temporary Files
Memory use rises quickly when commands merge and append run on big datasets. Separate your operations into smaller tasks to prevent slowdowns. For example:
merge 1:1 id using dataset1_part1, nogenerate
Datasets can be divided into chunks before merging minimizes memory strain.
3. Change Matsize Setting When You Work With Big Data Models
Changing the matsize command lets you control how big your matrices stay in RAM. You need to adjust matsize when your model includes multiple predictor variables. For example:
set matsize 800
This command increases the matrix size limit to to 800, stopping regressions from crashing. Remember not to overdo, since it takes up more memory space.
4. Optimize Data Storage Formats to Minimize Memory Usage
Stata allows you to store variables having sizes of minimum of one byte storage (byte) up to maximum of eight bytes (double). When your data fits smaller types, don't use larger ones. It conserves memory on your computer. When a variable's values fall between 0 and 255, changing its storage from an int or float to byte saves valuable computer space.
Here’s how you can check and adjust variable types: compress
Or manually change variable types: generate byte age_group = age
Advice for Students Looking for Stata Assignment Help
If dealing with memory allocation feels too difficult, it’s okay to ask for help from experts. Whether you’re wondering, “How can I finish my Stata assignment without mistakes?” or “Can I hire someone to do my Stata assignment?” learning these ideas will help you work better with tutors or assignment helpers.
Keep in mind, improving memory allocation isn’t just about finishing your assignment; it’s a valuable skill that can make you stand out in data-driven jobs. If you ever feel stuck, Stata’s detailed guides and online communities are great places to find help.
Conclusion: Mastering Memory Allocation for Seamless Stata Assignments
By learning how to handle memory in Stata, you’re not only solving your current assignments but also preparing for bigger data analysis tasks. From adjusting `set memory` and `set matsize` to shrinking datasets, these methods keep your work efficient and stress-free. If you get stuck, professional Stata assignment help can guide you through the complexities, leaving you with more time to focus on insights rather than errors. Start using these strategies, play with Stata's features, and see how your work becomes better and better.
0 notes
Text
Help with Statistics Homework to Build Confidence in Stats Class
Statistics is an essential course for all disciplines including business, social science, engineering, and data science. Statistics, in particular, is among the most difficult subjects that many students struggle with. Challenges often arise from its mix of theoretical and practical aspects of the subject, mathematical computations involved, and precision needed in the analysis of data. It is not easy to develop confidence in statistics, but with the right approach, tutorials, resources, and change of mindset it is possible to master statistics rather than to fear it. In this article, you will discover how students can increase their confidence in statistics class by seeking the right help with statistics homework and how quality assistance can keep them one step ahead.

Why Statistics Feels Intimidating and Why Confidence Matters
Statistics is intimidating for many students, often due to a few core challenges:
Complexity and Abstract Concepts: Statistics involves abstract thinking which is more complex than algebra or calculus, requiring proficiency in concepts such as probabilities and statistical modeling. Most students often find it difficult to identify which statistical tests to use, or when to use a t-test instead of an ANOVA or comprehend what p-values and confidence intervals interpret.
Data Analysis Requirements: When it comes to statistics the goal is not to solve a problem, but to analyze and interpret data accurately. In the case of students who are not conversant with data manipulation tools such as Excel, SPSS, or R this can be very challenging. Application of these software tools creates an added level of difficulty making it more challenging for students to carry out their analysis.
Pressure of Application: Statistics indeed has a purpose and is not just limited to classroom teaching. It requires students to apply knowledge in solving difficult, real-life issues. It can be intimidating at times, and that’s pretty understandable because there isn’t usually a single correct answer, but rather different perspectives and interpretations based on data.
Due to these difficulties, statistics hinder the confidence of even the most disciplined learners. Due to lack of confidence, may result in procrastination, reduced performance as well as a tendency to not seek assistance from other fellow students and professors. Utilizing the right resources and guidance, students can regain confidence and develop a strong foundation in statistics.
The Role of Homework Help in Building Confidence
To obtain confidence in a statistics class one of the best things to do is to get reliable experts for high-quality help with statistics homework. Expert homework assistance goes a long way when it comes to simplifying complex topics, explaining confusing concepts, or demonstrating solutions that mimic real-life problems. Here’s how it can transform a student's learning experience:
1. Focus on Tough Topics: A tutor or homework service can give explanations that match the grasping power of a student. The solutions provided by homework help experts are self-explanatory which becomes easier for students to grasp. Difficult topics are broken down into manageable parts for easy understanding and make it engaging for students. 2. Practice with Feedback: Practicing problems along with instant feedback is critical for mastering statistics. Most assignment help services provide guidance at every step along with helpful feedback to the students to see where they are wrong and advice on suitable methods to use. 3. Application of Statistical Software: Learning advanced stat software like R, SPSS, or Python is always a challenge for beginners. Assignment help services can teach students how to use them properly, with hands-on examples of coding and choosing the right statistical methods. 4. Improved Time Management and Stress Reduction: Solving statistics homework involves a lot of time and energy. With guided assistance, students are able to solve problems faster, and with less confusion thereby cutting down time and work overload. This helps them to be able to keep up with their coursework.
Our service is aimed at students who have difficulties with completing their statistics homework on their own. Here students can find helpful resources on basic and advanced statistical methods, and analysis tools, as well as useful tips for solving problems. All in all, students not only get their assignments done but also receive useful information that can help them build confidence in the subject.
Key Strategies for Building Confidence in Statistics Class
Besides using homework help, students can take specific actions to help herself or himself. Here are some effective strategies that can make a significant difference:
1. Understand the Basics Before Solving a problem
Indeed, statistics as a subject has a foundational structure; understanding the basic concepts first paves way for handling advanced concepts. Some of the key basic topics that are essential are descriptive statistics (arithmetic mean, geometric mean, standard deviation) probability/probabilities, and basic probability distributions. By mastering these basic concepts, students are in a good position to learn more complicated concepts like Inferential statistics and regression analysis.
A good source to sharpen your basic statistics knowledge is – “Statistics for Dummies” by Deborah Rumsey, this book breaks down essential statistical concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.
2. Use Reliable Resources and Textbooks
Good textbooks and resources provide clarity.” Some highly recommended textbooks for students learning statistics include:
• “The Essentials of Statistics” by Mario Triola: This textbook is favored in statistics courses, as the author presents all concepts in a clear and understandable manner for students to succeed in class.
• “Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers” by Douglas C. Montgomery: This book should come in handy to engineering students and it contains real-life examples and applications.
• “Introduction to the Practice of Statistics” by Moore, McCabe, and Craig: An encyclopedic book that also features practical examples thus recommended for students in the social and natural sciences.
3. Practice with Real Data
Using real datasets can help to make statistics much more interesting. Students can sharpen their data analysis skills by practicing with the datasets that belong to their field of study. Kaggle has free datasets for all types of projects and domains so that students can execute statistical tests on real datasets and analyze the impact of their analysis.
4. Develop a Strong Support System
Studying with friends in a group provides additional support and motivation. Students can easily study groups to solve problems, exchange ideas, and perspectives, and study material. Moreover, there are many forums and communities available online where students can join and get guidance and advice from experienced statisticians.
5. Seek Help Early and Consistently
This is one of the most common mistakes that students make is waiting until the last minute to complete their assignments. Engaging with homework helps experts prevent last-minute panic and enables students to strengthen their conceptual knowledge gradually and at the same time identify weak areas. This helps build confidence.
Our Statistics Homework Help Service: Building Confidence Step-by-Step
For students who are in need of help with statistics assignments, our homework help service provides a reliable medium. We offer:
•Personalized Tutoring: Our explanations are based upon the individual abilities of the student; to help him/her solve certain questions or tasks they are having difficulty with.
•Assignment Solutions: We offer comprehensive solutions for your assignments and homework with post-delivery clarification support to clear all doubts.
•Software Support: We advise on how to utilize R, SPSS, SAS, MINITAB, Excel, and other statistical software that are widely used in statistics classes and assessments.
• Flexible Scheduling: We are flexible to enable the students to come for help as and when they want to.
More Teaching Aid and Assistance for Statistics Students
To supplement further help with statistics homework, here are some additional tools and resources students may find useful:
•StatCrunch: An online tool to perform statistical analysis with simple and versatile tools.
•Wolfram Alpha: An application or software that can handle statistical problems and provide a step-by-step explanation of how it was solved.
•YouTube Channels: There is no shortage of channels with good statistical video tutorials available on YouTube showing step-by-step examples of approaching and solving a problem pr performing statistical processes in software like R, SPSS, SAS, Eviews, etc.
Conclusion: Embrace the Journey to Mastery in Statistics
Though statistics may seem very daunting at first, with the right support and will, any student can master this important area of academics and mold themselves into confident statisticians. Getting confidence in statistics is a blend of grasping the fundamental concepts combined with continuous consistent problem-solving and having reliable expert support that can be counted upon for assistance whenever needed. Whether through our homework help service, recommended textbooks, or any additional resource, students can get over their fears, creating a definite pathway to success in statistics.
#Help with Statistics Assignments#Statistics Tutoring for Students#Statistics Assignment Help Services#Professional Statistics Homework Assistance#Online Statistics Homework Solver#Statistics Help for College Students#Statistics Homework Assistance 24/7
0 notes
Text
Building Predictive Models with Regression Libraries in Python Assignments
Introduction
Predictive modeling serves as a fundamental method for data-driven decisions that allows to predict outcomes, analyze trends, and forecast likely scenarios from the existing data. Predictive models are the ones that forecast the future outcomes based on historical data and helps in the understanding of hidden patterns. Predictive modeling is an essential technique in data science for applications in healthcare, finance, marketing, technology, and virtually every area. Often such models are taught to students taking statistics or Data Science courses so that they can utilize Python’s vast libraries to build and improve regression models for solving real problems.
Python has been the popular default language for predictive modeling owing to its ease of use, flexibility, and availability of libraries that are specific to data analysis and machine learning. From cleaning to building models, and even evaluating the performance of models, you can do all of these with Python tools like sci-kit-learn and stats models, as well as for data analysis using the pandas tool. Getting acquainted with these tools requires following certain procedures, writing optimized codes, and consistent practice. Availing of Python help service can be helpful for students requiring extra assistance with assignments or with coding issues in predictive modeling tasks.
In this article, we take you through techniques in predictive modeling with coding illustrations on how they can be implemented in Python. Specifically, the guide will be resourceful for students handling data analysis work and seeking python assignment help.

Why Regression Analysis?
Regression analysis is one of the preliminary methods of predictive modeling. It enables us to test and measure both the strength and the direction between a dependent variable [that is outcome variable] and one or more independent variables [also referred to as the predictors]. Some of the most commonly used regression techniques have been mentioned below: • Linear Regression: An easy-to-understand but very effective procedure for predicting the value of a dependent variable as the linear combination of the independent variables. • Polynomial Regression: This is a linear regression with a polynomial relationship between predictors and an outcome. • Logistic Regression: Especially popular in classification problems with two outcomes, logistic regression provides the likelihood of the occurrence of specific event. • Ridge and Lasso Regression: These are the more standardized types of linear regression models that prevent overfitting.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Predictive Models in Python
1. Setting Up Your Python Environment
First of all: you need to prepare the Python environment for data analysis. Jupyter Notebooks are perfect as it is a platform for writing and executing code in small segments. You’ll need the following libraries:
# Install necessary packages
!pip install numpy pandas matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn statsmodels
2. Loading and Understanding the Dataset
For this example, we’ll use a sample dataset: ‘student_scores.csv’ file that consists of records of Study hours and Scores of the students. It is a simple one, but ideal for the demonstration of basics of regression. The dataset has two columns: Numerical variables include study hours referred to as Hours; and exam scores referred as Scores.
Download the students_scores.csv file to follow along with the code below.
import pandas as pd
# Load the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("students_scores.csv")
data.head()
3. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Let us first understand the data before we perform regression in python. Let us first explore the basic relationship between the two variables – the number of hours spent studying and the scores.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Plot Hours vs. Scores
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
sns.scatterplot(data=data, x='Hours', y='Scores')
plt.title('Study Hours vs. Exam Scores')
plt.xlabel('Hours Studied')
plt.ylabel('Exam Scores')
plt.show()
While analyzing the scatter plot we can clearly say the higher the hours studied, the higher the scores. With this background, it will be easier to build a regression model.
4. Building a Simple Linear Regression Model
Importing Libraries and Splitting Data
First, let’s use the tool offered by the sci-kit-learn to split the data into training and testing data that is necessary to check the performance of the model
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Define features (X) and target (y)
X = data[['Hours']]
y = data['Scores']
# Split data into training and test sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
Training the Linear Regression Model
Now, we’ll fit a linear regression model to predict exam scores based on study hours.
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# Initialize the model
model = LinearRegression()
# Train the model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Display the model's coefficients
print(f"Intercept: {model.intercept_}")
print(f"Coefficient for Hours: {model.coef_[0]}")
This model equation is Scores = Intercept + Coefficient * Hours.
Making Predictions and Evaluating the Model
Next, we’ll make predictions on the test set and evaluate the model's performance using the Mean Absolute Error (MAE).
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
# Predict on the test set
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Calculate MAE
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Mean Absolute Error: {mae}")
A lower MAE indicates that the model's predictions are close to the actual scores, which confirms that hours studied is a strong predictor of exam performance.
Visualizing the Regression Line
Let’s add the regression line to our initial scatter plot to confirm the fit.
# Plot data points and regression line
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
sns.scatterplot(data=data, x='Hours', y='Scores')
plt.plot(X, model.predict(X), color='red') # Regression line
plt.title('Regression Line for Study Hours vs. Exam Scores')
plt.xlabel('Hours Studied')
plt.ylabel('Exam Scores')
plt.show()
If you need more assistance with other regression techniques, opting for our Python assignment help services provides the necessary support at crunch times.
5. Improving the Model with Polynomial Regression
If the relationship between variables is non-linear, we can use polynomial regression to capture complexity. Here’s how to fit a polynomial regression model.
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
# Transform the data to include polynomial features
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
# Split the transformed data
X_train_poly, X_test_poly, y_train_poly, y_test_poly = train_test_split(X_poly, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Fit the polynomial regression model
model_poly = LinearRegression()
model_poly.fit(X_train_poly, y_train_poly)
# Predict and evaluate
y_pred_poly = model_poly.predict(X_test_poly)
mae_poly = mean_absolute_error(y_test_poly, y_pred_poly)
print(f"Polynomial Regression MAE: {mae_poly}")
6. Adding Regularization with Ridge and Lasso Regression
To handle overfitting, especially with complex models, regularization techniques like Ridge and Lasso are useful. Here’s how to apply Ridge regression:
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
# Initialize and train the Ridge model
ridge_model = Ridge(alpha=1.0)
ridge_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict and evaluate
y_pred_ridge = ridge_model.predict(X_test)
mae_ridge = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_ridge)
print(f"Ridge Regression MAE: {mae_ridge}")
Empowering Students in Python: Assignment help for improving coding skills
Working on predictive modeling in Python can be both challenging and rewarding. Every aspect of the service we offer through Python assignment help is precisely designed to enable students not only to work through the assignments but also to obtain a better understanding of the concepts and the use of optimized Python coding in the assignments. Our approach is focused on student learning in terms of improving the fundamentals of the Python programming language, data analysis methods, and statistical modeling techniques.
There are a few defined areas where our service stands out
First, we focus on individual learning and tutoring.
Second, we provide comprehensive solutions and post-delivery support. Students get written solutions to all assignments, broken down into steps of the code and detailed explanations of the statistical method used so that the students may replicate the work in other projects.
As you choose our service, you get help from a team of professional statisticians and Python coders who will explain the complex concept, help to overcome technical difficulties and give recommendations on how to improve the code.
In addition to predictive analytics, we provide thorough consultation on all aspects of statistical analysis using Python. Our services include assistance with key methods such as:
• Descriptive Statistics
• Inferential Statistics
• Regression Analysis
• Time Series Analysis
• Machine Learning Algorithms
Hire our Python assignment support service, and you will not only get professional assistance with your tasks but also the knowledge and skills that you can utilize in your future assignments.
Conclusion In this guide, we introduced several approaches to predictive modeling with the use of Python libraries. Thus, by applying linear regression, polynomial regression, and Ridge regularization students will be able to develop an understanding of how to predict and adjust models depending on the complexity of the given data. These techniques are very useful for students who engage in data analysis assignments as these techniques are helpful in handling predictive modeling with high accuracy. Also, take advantage of engaging with our Python assignment help expert who can not only solve your Python coding issues but also provide valuable feedback on your work for any possible improvements.
#PythonAssignmentHelp#PythonHelp#PythonHomeworkHelp#PythonProgramming#CodingHelp#PythonTutoring#PythonAssignments#PythonExperts#LearnPython#PythonProgrammingHelp#PythonCoding#PythonSupport#ProgrammingHelp#AssignmentHelp#PythonTutors#PythonCourseworkHelp#PythonAssistance#PythonForBeginners#PythonProjectHelp#OnlinePythonHelp
0 notes
Text

Explore the 10 Vital Graphical Tools for Presenting Data in Business Statistics
Unlock the power of data visualization with these 10 essential graphical tools—bar graphs, scatter plots, histograms, and more—that can transform your business statistics reports. Learn how to select and plot these tools to make your data more insightful and impactful.
Need assistance? Our assignment help experts are here to guide you step-by-step through the process, helping you ace your business statistics assignments!
Get Expert Help Here
#BusinessStatistics#DataVisualization#Graphs#AssignmentHelp#StatisticsHomework#StudentResources#HomeworkHelp#DataAnalysis#AcademicSupport
0 notes
Text
Crafting Compelling Narratives and Visuals for Econometrics Assignments
Econometrics entail much more than equations, empirical, and statistical terms. It takes great skill to ensure that econometric analysis gets written in an engaging style and uses adequate visualizations. Writing a compelling story behind the data (accompanied by explanations and interpretations of the visualizations) is a vital skill set. For students aspiring for an "A" grade, this becomes essential. It is no longer about just explaining the results but narrating the story behind the data to enlighten the reader about the information hiding behind it, i.e. the core economic insights.

A well-written narrative with visualizations could enrich complex econometric models to render an analysis that is engaging and easy to consume. Interpretation is equally important as presenting the correct results. For those new to the field, turning to econometrics homework help services would be a step ahead through the acquisition of new methods, and tricks, and divulging creative ways of presenting data. They help students complete their assignments and familiarize them with the modern tools and methods of analyzing and visualizing data that can take their work to a whole new level.
How to Craft a Compelling Narrative for Econometrics Assignments
Understand the Problem You're Addressing: The first important step in writing a compelling narrative is to have a clear and deep understanding of the research question. What kind of economic relation do you intend to investigate? For example, A researcher might be required to determine the correlation between the level of education and income. Knowing this, your narrative has to be about how your econometric model aids in explaining this relationship.
Example: If your model has an assumption of a positive relationship between education and income, your story should tell why this makes sense given what happens in theories such as increased human capital as a result of education means better chances to secure better-paying jobs.

Interpret the Statistical Results: Learners often have difficulty interpreting statistical results in simple English. One of the critical components of a robust econometric narrative revolves around the results and extracting insights from it. For example:
P-values: Don’t merely say that a p-value is less than 0.05 and that the relationship between the two variables is statistically significant but explain its importance from a statistical and analytical perspective.
Coefficients: While reporting several coefficients do not just produce the numbers but what these figures mean. For instance, if a coefficient for education is 0.8, explain further that each additional year of education is equivalent to an increase in income by 8%.
Link Results to Economic Theory: A good report will not just explain results but link them to the existing economic theory or real-world implications. This shows that you not only comprehend the data but also its relevance.
Tip: A good question that should always be asked when reading results is: what does this result tell me about the real world? Does it make sense in light of what I have learned in the course? If not, what can the reasons be for such discrepancy?
Use Clear, Digestible Language: Another common mistake some students make is that they assume using a lot of technical terms will help them in creating a good impression in the mind of their professor. In reality, clarity is key. It is suggested that your narrative should be easily followed by anyone having basic knowledge of econometrics. Avoid the use of technical jargon and when you have to, ensure you explain them in an easy-to-digest manner to the readers.
Cheat Code: Write in a such way as if you are explaining the stuff to your friend who is an amateur in econometrics.
How to Create Effective Visualizations for Econometrics
In econometric analysis, visualization helps make your work more appealing and easier to understand. However, the type of visual that is needed to convey the information to the audience should be proper according to the type of data.

Below are some tips for crafting impactful visualizations:

1. Choose the right type of Chart based on the Data: The type of data you’re going to represent has a lot to do with the chart you use for its visualization. Choosing the wrong type of chart will mislead the reader. Here are a few examples:
1. Scatter plots are ideal for showing relationships between two continuous variables. They’re great for visualizing regression models. 2. Bar charts work well when comparing different groups or categories. 3. Histograms can help visualize the distribution of a single variable, which is useful when assessing normality or skewness in data.
2. Label Charts Clearly: Label your axes and always provide a title to your visualizations. Whenever the chart consists of several lines or bars, ‘legend’ should be included as a must-have item to avoid confusion when comparing.
Cheat Code: Write a summary under this chart to indicate what this graph is all about. Not only does it help to explain the visualization but also adds weight to your narrative.
3. Highlight Key Findings: one should focus on the characteristics and important aspects of the visuals. Suppose, if you found out high positive correlation in your scatter plot, you may wish to include a regression line for the relation or shade the area that denotes significant results.
Tip: Use colors sparingly. If the chart is filled with colors, it becomes cluttered to look at. Adopt a simple color scheme to emphasize the important aspects.
4. Incorporate Visuals with Your Narrative: Most people make the mistake of segregating visuals from the narrative. Rather, your visuals should play a supporting element of your story. Cite them as figures in your text (For example illustrated in figure 1, there is a progressive increase…’) and rely on them in explaining the analysis of the data.
Cheat Code: Ask yourself – Does the chart I am creating provide some value to the story? If not, rethink whether it is really required in your case.
Case Study Example
Consider a case study analyzing the effect of minimum wage increases on employment levels across different sectors:
1. Objective: To assess the impact of increasing the minimum wage on job losses in low-wage sectors.
2. Data Collection: Collect research information from government labor statistics over several years.
3. Analysis: Regression analysis should be conducted in an attempt to determine the correlation between minimum wage and employment levels.
4. Narrative Development:
Introduce characters (e.g. workers in the retail and manufacturing industry).
Describe and share concerns and issues (e.g., business owners as to why their labor cost is increasing).
Make presentations (e.g., regarding evidence of little or no effect of policies on employment).
5. Visuals:
Produce scatter graphs for employment trends before and after changes in wages.
Employ bar graphs to illustrate the comparison among different sectors.
Get Better Grades in Your Econometrics Coursework with Our Homework Help Services
New to the complex concepts of econometrics, students are often faced with the difficulty of conveying results effectively together with presenting eye-catching infographics, dashboards, and insightful visualizations. Our econometrics homework help support is a kind of service that is incredibly helpful, as it allows a student to complete their work that requires analytical methodologies, insightful presentation, and mathematical calculations within a short time in the most precise and presentable manner. Besides helping students with their econometrics assignments our service also provides clarification on the correct use of econometric techniques for students.
The usefulness of choosing Econometrics Homework Help Expert
1. Enhanced Presentation Skills: Presentation is the key to any econometric analysis. Our service assists students in writing impressive narratives and compelling visualizations for the results to be effectively conveyed. From class assignments to project presentations, or research thesis, our expert assistance can surely transform raw data into visually appealing stories that best describe the results in a meaningful way.
2. Expert Use of Statistical Software: Econometric analysis highly depends on the proficiency of statistical software. We are familiar with tools such as SAS, SPSS, Minitab, Jamovi, and RStudio for creating compelling analyses.
3. Comprehensive Analytical Support: Students are not often very familiar with econometric methods and struggle when performing complex analyses. Our service offers comprehensive support for performing various analyses such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, or analysis of the time series data. Our one-on-one assistance eases the understanding of various concepts and their application to real-world data.
Strong Points of Our Service
Compelling and Professional Writing: Contact our econometricians to strengthen the quality of your work. Our experts ensure that your analyses are not only right but also relevant, presentable, and interesting.
Accurate Analysis: Accuracy is important to us. Every analysis we submit undergoes several checks to verify its correctness ensuring that the student gets the best results.
Comprehensive Reports: We submit comprehensive written reports with detailed explanations and interpretations, accompanied by outputs, plots, and codes. Such an approach helps enrich the student’s understanding of the topic or research question.
Amazing Visualization Tools: We employ appropriate visualization tools to create insightful charts and graphs to explain the data insights. This adds value to the presentation and report by making it visually appealing.
Guarantees for Students
Grade Guarantee: Our econometrics assignment help service is dedicated to meeting our client student’s expectations. We offer a grade guarantee – we assure that the papers produced do not go below the client’s expected quality standards and we provide free revisions until the client is satisfied.
Timely Delivery: We know the significance of time and make sure to submit all solutions before the deadline to help students submit their work without stress.
24/7 Support: We have a professional support team who is up and available anytime to attend to student’s inquiries or concerns related to their assignments.
Conclusion
The ability to write an interesting story out of your data and present it with visually appealing graphics is a crucial skill that leads to success. This gives you the power to transform data analysis assignments into insightful and engaging reports, along with connecting them with economic theory, complemented by the use of supported graphics and visualizations. Consult our econometrics homework tutor for support and assistance; it will introduce you to new methodologies, tools, and shortcuts that will reduce your workload and improve the quality of your analysis. Continued practice and the right resources in a student's arsenal can take those assignments to grade-A status.
Helpful Resources
To further enhance your skills in crafting compelling narratives and visuals for econometrics assignments, consider exploring these resources:
Principles of Econometrics by R. Carter Hill et al.
Mostly Harmless Econometrics by Joshua D. Angrist and Jörn-Steffen Pischke.
Data Visualization Tools:
Tableau for interactive visualizations.
R packages like ggplot2 for creating high-quality graphics.
#Econometrics#DataVisualization#AcademicWriting#NarrativeCrafting#StatisticsHelp#ResearchMethods#VisualStorytelling#StudentResources#AssignmentTips#QuantitativeAnalysis#EconometricsAssignments#DataAnalysis#AcademicSupport#LearningEconometrics#VisualCommunication
0 notes
Text
Sequential Hypothesis Testing: Real-Time Data in Statistics Homework
Hypothesis testing is a basic statistical concept that is utilized to test a claim or assumption about a population using a random sample. In hypothesis testing traditionally, the sample size is fixed and is determined before the hypothesis is tested. However, in analyzing real-time data or scenarios where data collection is in stages, the normal approach may not be efficient. In such a case, a tool called Sequential Hypothesis Testing (SHT) comes in. Sequential testing is different from the traditional way of testing whereby data sets are tested immediately upon arrival and the decision is made whether to accept it, reject it, or collect more information. This differs not only in terms of flexibility and the possibility of minimizing the size of the total sample, which speeds up decision-making and statistical analyses.
Sequential Hypothesis Testing was first conducted in World War II by Abraham Wald while manufacturing military equipment and performing quality control. Since then, the method has been developed further and used in areas from clinical trial, and stock trading to machine learning. Therefore, several studies have supported its efficiency tested in the real world. For instance, in clinical trials of clinical efficacy, this justifiable sequential procedure minimizes the number of patients who receive ineffective treatments because studies can be stopped as soon as there is sufficient evidence in favor of one hypothesis over other. In terms of efficiency, sequential testing seems to utilize fewer data points as opposed to the fixed-sample methods; the studies reveal a reduction in the sample size by up to half without causing variation in the outcome accuracy.
For students studying statistics, Sequential Hypothesis Testing is one of the best tools that assist in designing the hypothesis testing that focuses more on the dynamic testing sequences of data as it arrives over time rather than bulk and fixed data to be analyzed. In situations, where data is being analyzed in real-life quality control, financial modeling, and real-time data streams, the knowledge of this method is of great value to the students. From the perspective of homework and assignments, understanding the concept of sequential hypothesis testing might be quite complex. Choosing the right statistics homework help will allow the students to receive more detailed explanations as well as additional insights and perspectives that can help them comprehend complex topics.

Sequential Hypothesis Testing Definition
Sequential Analysis of Data or Sequential Hypothesis Testing commonly represented as SHT is a process of analyzing data as soon as it is collected. In contrast to conventional hypothesis testing methods which assume a fixed sample size, SHT utilizes the incoming data and makes decisions at any time during the data collection. It is most beneficial when it is necessary to analyze data in real-time or in a situation where the cost of collecting additional data is very high.
There are three possible outcomes when conducting a sequential test:
1.Reject the null hypothesis if sufficient evidence exists to favor the alternative.
2.Accept the null hypothesis if there is no sufficient evidence against it.
3. Continue collecting data if the evidence remains inconclusive.
The principle behind the method is to minimize additional sampling and decision-making expenses by halting the test as soon as a definitive conclusion can be drawn. For example, a researcher who is testing the efficacy of a new drug doesn’t have to wait to reach a full sample size if early indications show that the drug is very effective (or ineffective). It means they can halt the trial early and this helps in minimizing trial costs.
Methods and Applications of Sequential Hypothesis Testing
Clinical Trials
Sequential Hypothesis Testing has found some of its most striking applications in clinical trials. In a conventional fixed-sample clinical trial, the researchers target a particular number of patients and collect data only when the total is reached. However, in SHT where data is collected in sequences, analysis is carried out successively as data is being gathered. This can result in proactive approvals or discontinuation of treatments, keeping as many participants as possible away from harmful or ineffective treatments. This is significantly crucial during the Phase III Clinical trial, especially concerning patient safety and ethical implications.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
Sequential testing is specifically used in quality control in industrial manufacturing facilities. Suppose there is a widget factory, and management wants to know whether a particular lot of widgets meets a certain level of quality. Unlike testing a set number of a large batch of items, the factory can conduct sequential testing where testing is done on one item at a time. If, for instance, preliminary tests show that the batch is faulty, then the test can be stopped prematurely saving time and resources. On the other hand, if the batch passes the tests, then the production continues without any delay.
Financial Trading and Algorithmic Decision-Making
In finance, the sequential hypothesis testing procedure may be used in trading algorithms that take place in real time. For example, a trading strategy might always check whether a market condition (such as rising stock prices) holds true based on incoming data. Rather than waiting for a big sample size to make a trade decision, sequential testing can be used for the algorithm to act the moment enough data is available to support the use of the hypothesis of an upward trend to make the most profits or to minimize losses.
Sequential Hypothesis Testing in Statistics Homework
Now, let’s bring this into perspective of the statistics assignment that you are usually doing. Most issues students encounter with hypothesis testing involve fixed datasets that is, all data is presented altogether. However, imagine you are in a situation where you are expected to work with real-time data, for instance calculating the average customer rating score per week or the real-time sensor data of an IoT system.
In such scenarios, if traditional methods are employed then they may cause an undue amount of delay or an ineffective or wasteful use of data. While it might be fundamentally complex to update hypotheses as and when data accumulates, Sequential Hypothesis Testing provides the technique and proves to be a useful tool for all students. In fact, most real-world problems require real-time analysis and decision-making. The homework problems that involve sequential testing help students learn how statistical analysis is performed on scenarios with constantly updated data.
How Statistics Homework Help is useful in understanding Sequential Hypothesis Testing?
Indeed, Sequential Hypothesis Testing can at times be highly complicated as it involves advanced concepts such as likelihood ratios, stopping boundaries, and decision-making thresholds. It is not always obvious to ascertain when to stop data collection or when the evidence is sufficient enough to make a decision. This is where asking us for statistics homework help comes in handy for students struggling with SHT.
At Statistics Help Desk, students struggling with complex problems receive assistance in handling the difficulties that they encounter in their studies by teaching them intelligent ways and methods to handle these constraints easily and effectively while enhancing their knowledge base. Pursuant to our approach, the complex problems are presented and explained in terms of clear and small steps through which students build an understanding of the underlying concepts and ideas as well as apply time-efficient strategies.
Types of Statistics Homework We Help With:
• Mathematical Statistics: Random variables and probability distributions, theory of hypothesis, interval estimation, and so on.
• Statistical Data Analysis: Use of descriptive statistics and inferential analysis and/ or data interpretation when doing assignments.
• Software Interpretation: Assisting students in comprehending outputs logged by the software they use for their class such as SPSS, R Excel, or Python.
• Regression and Forecasting: The field of operations includes linear regression, logistic regression, time series analysis, and Forecasting.
• Sampling Techniques: Information on sampling techniques, how to determine the sample size, and the use of stratified sampling.
Smart Tips and Tricks for Solving Statistical Problems:
1. Visualize Data: Make bar charts, pies, line graphs, histograms, box and whisker plots, scatter diagrams, and other graphs to get an overview before deciding on the kind of calculation.
2. Simplify Formulas: Break down a complex problem into smaller manageable parts and work on one at a time to avoid any confusion. In many cases, it helps to understand certain components such as variance or mean making it simple to apply in the right context.
3. Leverage Statistical Software: Today, there are software systems such as R, Python, and SPSS among others that can perform calculations, and tests, and generate output automatically. If you don’t want to spend ages calculating things by hand, learn basic commands that can help you do calculations much faster.
4. Check Assumptions: Ensure that assumptions like normality and independence are met before running ANOVA, regression, etc.
5. Approximation Techniques: When doing hypothesis testing, use the approximations (like z-test for large samples) when it is not essential to find the exact values.
How to Avail Our Statistics Assignment Help:
1. Submit Your Homework: Submit your work through our website or email listing the due date and the instructions.
2. Get a Custom Quote: The complexity of the solutions will be evaluated and an appropriate price will be quoted.
3. Receive Step-by-Step Solutions: Each of our tutors provides accurate and comprehensive explanations of the problem and its solution.
4. Ask for Revisions: Need clarifications? We offer free revision services in order to make you fully satisfied with your order.
Conclusion
Sequential Hypothesis Testing is a very important tools for statisticians in the modern-day context, especially while working with real-time data. In particular, for students solving statistical problems, obtaining the necessary knowledge in sequential testing can benefit their approach a lot. By availing statistics homework help online, students will be introduced to ways of obtaining all sorts of statistics help, in a simple and digestible format.
Users also ask these questions:
• How does Sequential Hypothesis Testing differ from traditional methods?
• What are some real-life examples of Sequential Hypothesis Testing in statistics?
• What resources can I use to practice Sequential Hypothesis Testing?
Useful resources & textbooks
For students interested in mastering Sequential Hypothesis Testing, here are some excellent resources and textbooks to dive deeper into the topic:
• "Statistical Methods for Research Workers" by Ronald A. Fisher: A text that presents the basics of hypothesis testing with ideas related to sequential methods.
• "Sequential Analysis" by Abraham Wald: The most basic book on Sequential Hypothesis Testing, perfect for the reader who wants to learn more about the concept.
• "Introduction to Statistical Quality Control" by Douglas C. Montgomery: The goal of this book is to introduce the reader to potential uses of quoted testing in quality control.
• "Bayesian Data Analysis" by Andrew Gelman: Useful for students who want to incorporate Bayesian ways of thinking into sequential testing.
#statistics homework help#statistics homework help online#statistics assignment help#help with statistics homework
0 notes
Text
Nonparametric Hypothesis Testing in Longitudinal Biostatistics: Assignment Help Notes
Biostatistics plays an important role in medical science and healthcare especially through observational studies involving specific health issues and their prevalence, risk factors and outcomes over a period of time. These studies involve longitudinal data in evaluating patients’ response to certain treatments and analyzing how specific risks evolve within a population over time. Hypothesis testing is crucial in ascertaining whether the observed patterns in the longitudinal data are statistically significant or not.
Although conventional parametric methods are largely used but they are not appropriate to real world scenarios due to the underlying assumptions such as normality, linearity and homoscedasticity. On the other hand, the nonparametric hypothesis testing remains a viable option for use since it doesn’t impose rigid assumptions on data distribution, particularly when dealing with complicated longitudinal data sets. However, students tend to face difficulties in nonparametric hypothesis testing due to the involvement of complex mathematical and statistical concepts and they often get confused while selecting the appropriate method for a specific dataset.
Let’s discuss about nonparametric hypothesis testing in detail.
What is Nonparametric Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is aimed at determining whether the findings that are obtained from a given sample can be generalized to the larger population. The traditional parametric techniques such as t-test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) assumes normal data distributions with specific parameters such as mean and variance defining the population.
On the other hand, nonparametric hypothesis testing procedures make no assumption about the data distribution. Instead, it relies on ranks, medians, or other distribution-free approaches. This makes nonparametric tests particularly advantageous where the data do not meet the assumptions of a parametric test for example skewed distributions, outliers, or a non-linear association.
Common examples of nonparametric tests include:
Mann-Whitney U Test: For comparing two independent samples.
Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test: For comparing two related samples.
Kruskal-Wallis Test: For comparing more than two independent samples.
Friedman Test: For comparing more than two related samples.
In longitudinal biostatistics, the data collected are usually measured over time, which complicates things further. The dependencies between repeated measures at different time points can violate parametric test assumptions, making nonparametric methods a better choice for many studies.
The Importance of Longitudinal Data
Longitudinal data monitors same subjects over time and serves valuable information for examining change in health outcomes. For instance, one might monitor a sample of patients with diabetes to discover how their blood sugar levels changed following commencement of new medication. Such data differs from cross-sectional data that only captures one time point.
The main difficulty of longitudinal data is the need to account for the correlation between repeated measurements. Measurements from the same subjects are usually similar as compared to measurements from different subjects, they can be treated as independent in the case of parametric tests.
Nonparametric Tests for Longitudinal Data
There are a number of nonparametric tests used to handle longitudinal data.
1. The Friedman Test:
This represents a nonparametric substitute for repeated-measures ANOVA. This is applied when you have information from the same subjects measured at various time periods. The Friedman test assigns ranks to the data for each time point and then measures whether there is a significant difference in the ranks across those time points.
Example:
Just imagine a dataset wherein three unique diets are under evaluation, at three separate time points, for a single group of patients. You are able to apply the Friedman test in python to assess if there is a major difference in health outcomes between the diets across time.
from scipy.stats import friedmanchisquare
# Sample data: each row represents a different subject, and each column is a time point
data = [[68, 72, 70], [72, 78, 76], [60, 65, 63], [80, 85, 83]]
# Perform the Friedman test
stat, p_value = friedmanchisquare(data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3])
print(f"Friedman Test Statistic: {stat}, P-Value: {p_value}")
It will furnish the Friedman test statistic as well as a p-value that conveys whether the difference are statistically significant.
2. The Rank-Based Mixed Model (RMM):
The Friedman test is quite effective with simple repeated measures, but it becomes less useful as longitudinal structures become more complex (e.g., unequal time points, missing data). The advanced method known as the rank-based mixed model can handle more complex scenarios. The RMMs differ from the Friedman test in that they are a mix of nonparametric and mixed models, providing flexible handling of random effects and the correlation between repeated measures.
Unfortunately, RMMs involve a range of complexities that typically need statistical software such as R or SAS for computation. Yet, their flexibility regarding longitudinal data makes them important for sophisticated biostatistical analysis.
3. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test for Paired Longitudinal Data:
This test is a nonparametric replacement for a paired t-test when comparing two time points and is particularly beneficial when data is not normally distributed.
Example:
Imagine you are reviewing patients' blood pressure statistics before and after a certain treatment. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test can help you evaluate if there’s an notable difference at the two time points. Utilizing python,
from scipy.stats import wilcoxon
# Sample data: blood pressure readings before and after treatment
before = [120, 125, 130, 115, 140]
after = [118, 122, 128, 113, 137]
# Perform the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test
stat, p_value = wilcoxon(before, after)
print(f"Wilcoxon Test Statistic: {stat}, P-Value: {p_value}")
Advantages of Nonparametric Tests
Flexibility: The nonparametric tests are more flexible than their parametric alternatives because the assumptions of data distribution is not required. This makes them perfect for the study of real-world data, which seldom requires assumptions needed by parametric methods.
Robustness to Outliers: Nonparametric tests utilize ranks in place of original data values, thereby increasing their resistance to the effect of outliers. This is important in biostatistics, since outliers (extreme values) can skew the results of parametric tests.
Handling Small Sample Sizes: Nonparametric tests typically work better for small sample sizes, a condition often found in medical studies, particularly in early clinical trials and pilot studies.
Also Read: Real World Survival Analysis: Biostatistics Assignment Help For Practical Skills
Biostatistics Assignment Help to Overcome Challenges in Nonparametric Methods
In spite of the advantages, many students find nonparametric methods hard to understand. An important problem is that these approaches commonly do not provide the sort of intuitive interpretation that parametric methods deliver. A t-test produces a difference in means, whereas nonparametric tests yield results based on rank differences, which can prove to be harder to conceptualize.
In addition, choosing between a nonparametric test and a parametric test can prove difficult, particularly when analyzing messy raw data. This decision regularly involves a profound grasp of the data as well as the underlying assumptions of numerous statistical tests. For beginners in the field, this may become too much to digest.
Availing biostatistics assignment help from an expert can prove to be a smart way to deal with these obstacles. Professionals can lead you through the details of hypothesis testing, inform you on selecting the right methods, and help you understand your results accurately.
Conclusion
Nonparametric hypothesis testing is a useful tool in longitudinal biostatistics for evaluating complex data that contradicts the assumptions of traditional parametric procedures. Understanding these strategies allows students to more successfully solve real-world research problems. However, because these methods are so complex, many students find it beneficial to seek professional biostatistics assignment help in order to overcome the complexities of the subject and ensure that they have a better comprehension of the subject matter and improve their problem-solving skills.
Users also ask these questions:
How do nonparametric tests differ from parametric tests in biostatistics?
When should I use a nonparametric test in a longitudinal study?
What are some common challenges in interpreting nonparametric test results?
Helpful Resources for Students
To expand your knowledge of nonparametric hypothesis testing in longitudinal biostatistics, consider the following resources:
"Biostatistical Analysis" by Jerrold H. Zar: This book offers a comprehensive introduction to both parametric and nonparametric methods, with examples relevant to biological research.
"Practical Nonparametric Statistics" by W.J. Conover: A detailed guide to nonparametric methods with practical applications.
"Applied Longitudinal Analysis" by Garrett M. Fitzmaurice et al.: This book focuses on the analysis of longitudinal data, including both parametric and nonparametric methods.
0 notes
Text
Seasonal ARIMA Modeling in EViews: Complete Assignment Help Tutorial
Seasonality in time series analysis can be defined as recurring patterns and trends in the data over a specific time intervals (such as weekly, monthly, quarterly or yearly). Seasonality plays an important role in forecasting and interpreting the model results. Seasonality factors are taken into account in analyzing sales, stock price data or weather patterns. These patterns, if overlooked, may result into incorrect forecasting and wrongful decisions. For example, a retail store might see a spike in the sales on holiday season. If the seasonality is not taken into account, then the sale forecasting may generate inaccurate results. This is the reason accounting for seasonality becomes important in accurate time series modeling.
To address seasonality, we have the Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (SARIMA) Model available which takes into consideration the seasonal and non-seasonal factors. However, to conduct SARIMA in statistical software like EViews can be challenging and students may make a lot of mistakes that minimizes the accuracy of the forecasting model. This guide will provide a step-by-step tutorial of how to conduct SARIMA modelling using EViews as well as provide examples and recommendations to improve your analysis and forecasting. Further, students can use our EViews assignment help for the reinforcement of the above concept.

What is Seasonal ARIMA Modeling?
The Seasonal ARIMA (SARIMA) model is an extension of the ARIMA model that takes both non-seasonal and seasonal factors into account. While ARIMA models enables capturing trends and autocorrelation in data, SARIMA models also add the seasonality for prediction.
General Form of a SARIMA Model
A SARIMA model is typically expressed as:
SARIMA (p,d,q)×(P,D,Q)s
Where:
p: Order of non-seasonal autoregression (AR)
d: Degree of non-seasonal differencing (I)
q: Order of non-seasonal moving average (MA)
P: Order of seasonal autoregression (SAR)
D: Degree of seasonal differencing (SI)
Q: Order of seasonal moving average (SMA)
s: Seasonal period (e.g., s = 12 for monthly data with an annual seasonality)
SARIMA models are appropriate for data that shows trend and seasonal pattern, like monthly sales data or quarterly GDP data, which reoccur every year.
Steps for SARIMA Modeling in EViews
Step 1: Plot the Data and Identify Seasonality
The first step in any time series analysis is data visualization in order to inspect for trends and seasonality. Using EViews the data is loaded and the “Graph” function is utilized.
Example: Let us assume that the type of data you are working with is monthly sales. Once you have your data imported into EViews, it is time to generate the plot of the data. In its simplest form, seasonality will be seen if there exists a cycle that recurs after a span of 12 months.
Step 2: Difference the Data to Remove Trends and Seasonality
Before you apply SARIMA, data must be transformed to make it stationary by eliminating the trends and seasonality. In EViews this is done by applying the “Differences” option available in the tool bar.
Non-seasonal differencing (d): If your data shows an upward or downward movement, apply differencing to remove it.
Seasonal differencing (D): If your data has a regular seasonal pattern, apply seasonal differencing (e.g., seasonal difference of order 1 for monthly data would subtract the data from 12 months ago).
In EViews, the differenced series can be created by "Genr" command and indicating the orders of seasonal and non-seasonal difference.
Step 3: Identify Model Orders Using ACF and PACF
To identify the appropriate values for p, d, q, P, D, Q, the autocorrelation function (ACF) and partial autocorrelation function (PACF) plots in EViews can be used.
ACF: Helps identify the moving average (MA) and seasonal moving average (SMA) terms.
PACF: Helps identify the autoregressive (AR) and seasonal autoregressive (SAR) terms.
Generate the ACF and PACF plots by selecting View > Correlogram in EViews. Examine these plots to find the lags that are significant for each component.
Step 4: Estimate the SARIMA Model
Once the model orders have been identified, the next step is to estimate the SARIMA model. In EViews, go to Quick > Estimate Equation and specify your model in the following form:
y c ar(1) ma(1) sar(12) sma(12)
In this example:
ar(1) refers to the non-seasonal AR term.
ma(1) refers to the non-seasonal MA term.
sar(12) refers to the seasonal AR term with a lag of 12 periods.
sma(12) refers to the seasonal MA term with a lag of 12 periods.
EViews will the perform the estimation and display the coefficient estimates, standard errors and a number of other diagnostic statistics.
Step 5: Perform Diagnostic Checks
It is imperative that after estimating the model, diagnostic checks are done to check the goodness of the model fit. In EViews, this involves checking:
Residual Autocorrelation: Use the Ljung-Box Q-statistic to ensure the residuals are white noise (i.e., no autocorrelation).
Stationarity: Check for stationarity of data by analyzing the ACF of residuals.
Model Fit: use metrics like the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) or Schwarz Bayesian Criterion (SBC) to compare model performance.
Step 6: Forecasting Using the SARIMA Model
When the model has been well-established, one can then predict future values. To do this in the EViews, choose the Forecast and define the period over which the forecast must be made. Any forecast that is generated using EViews will be accompanied with confidence intervals, which can also be plotted and exported.
Common Mistakes Students Make in Seasonality Analysis Using EViews
Some of the challenges that students experience when it comes to analysing seasonality and building the SARIMA models in EViews include the following. Some common mistakes include:
Failing to Test for Seasonality: One thing that many students fail to consider is to check for seasonality in their data. This leads to the cases of developing inaccurate forecasts.
Overfitting the Model: Some students often include many parameters in the SARIMA model in a bid to capture all the minor fluctuations in the data sets which leads to over-fitting. This makes the model too specific with the historical data and minimizes predictability.
Incorrect Identification of SARIMA Components: Differentiating seasonal and non-seasonal components is significant. Students tend to misconceive these factors and this leads to a wrong specification of the model.
Poor Diagnostic Testing: Upon their estimation of the model, students may also ignore other diagnostic checks such as residual analysis for a better model fit. Not checking the residuals for autocorrelation for instance means students are neglecting the chance to fine tune the model to increase precision.
Misunderstanding EViews Output: Eviews computes and displays loads of statistical information. Without deep understanding of these results students may come up with incorrect insights. For example, failing to interpret the results from p-values of coefficients or misunderstanding the Ljung-Box Q-statistic can lead to wrong conclusions.
How EViews Assignment Help Can Resolve These Problems
To resolve such mistakes and have a clear understanding, students must opt for our EViews assignment help that provides detailed step-by-step solution of eviews coursework assignments with comprehensive explanation of results. Our expert guidance can help you:
Correctly test for presence of seasonality through the use of ACF and PACF.
Understand the right combination of seasonal and non-seasonal components for SARIMA models.
To not over-complicate the model by including few relevant parameters in order to minimize over-fitting.
Interpret the eviews output correctly.
perform residual diagnostics to check assumptions and make your model more accurate for forecasting.
What You Get with Our EViews Assignment Help
The most on-demand EViews assignment help does not only provide the complete solution of your assignment but also gives you a well-structured and comprehensive report covering all aspects of the analysis. This consists of steps to perform the procedures used in EViews from data import to model estimation and forecasting. You shall also get the EViews work file (.wf1) containing all the command used, the graphs and the output. Moreover, we include annotated screenshots to let you see how we proceeded and the steps applied. We provide insightful interpretations, residual diagnostics and recommendations on model improvement.
Conclusion
Seasonal ARIMA modeling is a powerful tool for analyzing time series data with both trends and seasonality. While learning to apply SARIMA in EViews can be challenging, understanding the model's components, performing correct diagnostic checks, and interpreting results accurately are key steps toward success. By avoiding common mistakes and seeking help when needed, students can master this important technique and improve their forecasting abilities.
Are you looking for help with your Time series assignment? Our knowledgeable eviews homework help tutors are available to support you. Learning SARIMA modeling can be made easy. Contact us for guidance and master time series data analysis.
Also Read: How To Correctly Interpret Your Eviews Outputs And Assignment Help Tips Helpful Resources and Textbooks
For students searching for textbooks to learn SARIMA modeling, the following texts are recommended:
"Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control" by Box, Jenkins, Reinsel, and Ljung – A foundational text on time series modeling, including SARIMA.
"Forecasting, Time Series, and Regression" by Bruce L. Bowerman, Richard T. O'Connell, and Anne Koehler – A comprehensive guide on time series and forecasting methods.
0 notes
Text
Jamovi Regression Analysis Guide for Students Seeking Assignment Help
Jamovi is an open-source and easy to use statistical software for conducting data analysis, appealing to both novices and experts. Designed by the developers of JASP, it has an intuitive interface and enhanced analytical capabilities without the need of any programming codes as used in SAS, R, SPSS etc. It is increasingly becoming popular with over 30% increase in annual downloads, which has been attributed to its ability to integrate with R allowing customization. Jamovi has always been updated with latest capabilities to handle complex analysis and bug fixes.
Though certain benefits are enjoyed, a number of learners face challenges when using Jamovi software for data analysis especially in regard to conducting regression analyses. Attempting to interpret the output, choosing the correct model, and correctly interpreting the results are examples of common problems encountered. Due to these reasons most of them want to utilize Jamovi assignment help in overcoming the difficulties and also ensuring that their assignment solutions meet the required academic standards.

Understanding Regression Analysis in Jamovi
Regression analysis is a statistical method used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. In simpler terms it assists in predicting the effects on the dependent variable due to the changes in the independent variables. This is especially useful in disciplines including economics, psychology, biology and social sciences where researchers study causality and predict outcomes. Jamovi offers several types of regression analyses, including:
Simple Linear Regression: This is simplest kind of regression where there is one dependent variable and one independent variable. It is used to examine the linear relationship that exists between two variables in question.
Multiple Regression: This is where two or more independent variable are used to analyse a single dependent variable. It enables analysis to incorporate more than one factor as compared to the use of the single regression model.
Logistic Regression: Used when the dependent variable is binary (e.g., yes/no, pass/fail), logistic regression helps in modelling the probability of a particular outcome.
Polynomial Regression: This goes beyond the simple linear regression by taking the non-linear relationship between the independent and the dependent variable into consideration.
Hierarchical Regression: This method allows for the stepwise inclusion of variables, helping to understand the incremental value of adding additional predictors.
In this guide, we will focus on performing a simple linear regression analysis using Jamovi, which is a foundational technique that students need to master before moving on to more advanced forms of regression.
Getting Started with Jamovi
Jamovi is an opensource program that can be downloaded from the official website of the program; it supports major operating systems such as Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. After installation of the software just open it and follow the below steps to conduct simple linear regression analysis.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Simple Linear Regression in Jamovi
In this illustration, we will use a dataset called "Exam Scores," which contains two variables: hours studied (independent variable) and exam scores (dependent variable). The hypothesis of the study is to find out if there exists a linear relationship between the number of hours spent studying and the scores that the students obtain in the exams.
Step 1: Importing Data into Jamovi
Open Jamovi: Launch the Jamovi application on your computer.
Import Data: Click on the "Open" button in the top left corner of the screen, then select "Data Library" to browse through available datasets or "Computer" to upload your dataset from your device. For this tutorial, we'll assume you have your dataset saved as a CSV file named ExamScores.csv.
Load the Dataset: After selecting the dataset, click "Open" to load it into Jamovi. You will see your data displayed in a spreadsheet-like format, similar to Excel.
Step 2: Setting Up the Regression Analysis
Navigate to the Analyses Menu: On the top menu bar, click on the "Analyses" tab. A drop-down menu will appear with various analysis options.
Select Regression: From the list of analysis options, select "Regression" and then choose "Linear Regression." This will open the linear regression setup panel on the right side of the screen.
Specify Variables: In the linear regression setup panel, you will see two boxes labeled "Dependent Variable" and "Covariates."
. Drag the variable Exam Scores into the "Dependent Variable" box. . Drag the variable Hours Studied into the "Covariates" box.
This tells Jamovi that we want to model the relationship between hours studied and exam scores.
Step 3: Running the Regression Analysis
Configure Options: In the setup panel, you can configure additional options such as adding interaction terms, checking assumptions, and selecting robust standard errors. For this basic example, we will keep the default settings.
Run the Analysis: Click the "OK" button at the bottom of the setup panel to run the regression analysis. Jamovi will automatically generate the output in the right panel, displaying the regression coefficients, model summary, and other relevant statistics.
Step 4: Interpreting the Results
Once the analysis is complete, Jamovi provides a detailed output that includes the following:
Model Summary: This section provides an overview of the regression model, including the R-squared value, which indicates the proportion of variance in the dependent variable explained by the independent variable. In our example, if the R-squared value is 0.75, this means that 75% of the variation in exam scores can be explained by the number of hours studied.
Coefficients Table: This table lists the regression coefficients for each predictor. The coefficient for Hours Studied tells us the expected change in Exam Scores for a one-unit increase in Hours Studied. For instance, if the coefficient is 5, this means that for each additional hour studied, the exam score is expected to increase by 5 points.
Statistical Significance: The output also includes p-values, which indicate whether the relationships observed are statistically significant. A p-value less than 0.05 is typically considered significant, suggesting that the predictor variable (hours studied) has a meaningful impact on the dependent variable (exam scores).
Step 5: Visualizing the Regression Line
Plotting the Regression Line: To visualize the relationship between the variables, you can create a scatter plot with a fitted regression line.
Create Plot: In the analysis panel, select the "Plots" tab and check the box for "Fitted Line Plot." This will generate a scatter plot with the regression line overlaid, allowing you to visually assess the fit of the model.
Common Challenges in Jamovi Regression Analysis and How to Overcome Them
While Jamovi is designed to be user-friendly, students often face several challenges when performing regression analysis:
Understanding Output: The output generated by Jamovi can be confusing for students. It is important to focus on key statistics such as coefficients, R-squared values, and p-values to interpret the results accurately.
Choosing the Right Model: Selecting the right type of regression analysis is important. For instance, when one fits a model with the linear relationship, while actually the relationship exists non-linearly, then wrong conclusion is drawn.
Data Preparation: It is always important to prepare and clean data before analysing it especially if you are dealing with large volumes of data. There are various issues such as missing values, outliers and incorrect data types can affect the regression analysis.
Interpreting Multicollinearity: Multicollinearity must be checked while performing regression, where the independent variables are highly correlated. This can skew the results and makes it difficult to know the impact of each individual variable.
In order to address these challenges, the students can turn for Jamovi assignment help from our proficient writers. Professional services are helpful in data preparation, model selection, results interpretation and troubleshooting errors. Our services can help students do the right things which will lead to the production of good assignments and excellent grades.
Conclusion
In this tutorial we have walked you through how to do regression in Jamovi. We have covered the basics of regression, the different types of regression in Jamovi and a hands-on example using a popular dataset. Whether you are a beginner or looking to improve your skills this tutorial will help you navigate the regression features in Jamovi. Remember practice is key to mastering stats, so use the resources and seek Jamovi assignment help when needed. Contact us today.
Additional Resources for Jamovi Homework Assistance
"Introduction to the New Statistics: Estimation, Open Science, and Beyond" by Geoff Cumming and Robert Calin-Jageman: This book provides a comprehensive introduction to statistical analysis using Jamovi, emphasizing estimation and open science practices.
Jamovi User Guide: The official Jamovi documentation provides detailed instructions and examples for using the software's various features and performing different types of analyses. It is an invaluable resource for both beginners and advanced users.
Online Tutorials and Courses: Websites like Statisticshelpdesk offer assignment assistance and helpful material on statistics and data analysis using Jamovi, covering everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Probability Distributions in Mathematical Statistics Assignments
Probability distributions are the fundamental base of mathematical statistics and are relevant to numerous analyses and research. Probability distribution refers to the manner in which values of a random variable are likely to be distributed. They give a mathematical relation of probabilities and the outcomes. This understanding enables statisticians to explain the outcomes of the random events such as rolling of a dice or measuring heights of people within a given population. The American Statistical Association has always prioritized the understanding of probability distributions for students in pursuing their course or careers in statistics and data science.
We will discuss probability distributions, the different types of probability distribution, and their application in statistics assignments. We will also include examples and references to support the concepts and we will suggest some useful resources and textbooks for better understanding. In the later part, we will explore how opting for mathematical statistics assignment help can make a difference in improving the grades and better comprehension.

What Are Probability Distributions?
Probability distribution means a function that shows the probability of various outcomes occurring during an experiment. It displays a summary of probabilities concerning all the possible outcomes of a random variable. In other words, probability distribution show whether a certain event is likely to happen or not. Probability distributions can be classified into two broad categories: discrete probability distributions and continuous probability distributions.
1. Discrete Probability Distributions: These distributions are applicable in cases where the random variable can have countable number (whole numbers) of possible values. Examples include the roll of a die, the number of heads in a series of coin tosses, or the number of cars arriving at a traffic light per hour.
2. Continuous Probability Distributions: These distributions are used in cases when the random variable can assume an infinite number of values over an interval. Some of them are, the height of individuals in a given population group, the speed at which a computer can execute a job, or the amount of rain received in a given year.
Understanding these two categories and the specific types of distributions within them is critical for any student of mathematical statistics.
Types of Discrete Probability Distributions
Let us explore into some common types of discrete probability distributions that are often covered in mathematical statistics courses.
1. Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is one of the simplest and the most often utilized discrete distributions. Binomial distribution is used when you're counting how many times something happens (like winning a game or getting a heads) in a set number of tries, where each try is either a success or a failure. The probability remains constant with each trial being separate from one another.
Example: Consider a scenario where you flip a fair coin 10 times. The binomial distribution can help determine the probability of getting exactly 6 heads.
The formula for the binomial distribution is:

Where:
n = number of trials
k = number of successes
p = probability of success on each trial
C(n,k) = combination of n items taken k at a time
2. Poisson Distribution
The Poisson distribution gives the number of times that an event happens in a given time or space. It is used when events happen independently, and the average rate of occurrence is known.
Example: If a customer support executive receives an average of 5 calls per hour, the Poisson distribution can be used to calculate the probability of receiving exactly 7 calls in a given hour.
The formula for the Poisson distribution is:
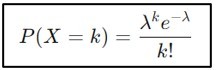
Where:
λ = average number of occurrences in the interval
k = number of occurrences
3. Geometric Distribution
Geometric distribution describes the given number of trials that are needed for the first success in repeated, independent Bernoulli trials (trials with two possible outcomes: success or failure).
Example: If you are rolling a fair die, the geometric distribution can tell you the probability of getting your first six on the third roll.
The formula for the geometric distribution is:
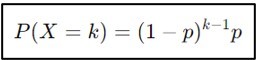
Where:
p = probability of success on each trial
k = number of trials up to and including the first success
Types of Continuous Probability Distributions
Continuous probability distributions are equally important and are used in various scenarios in statistics.
1. Normal Distribution
The normal distribution, also referred to as the Gaussian distribution, is one of the most widely used of all probability distributions. It explains the data concentrated around at the mean or average. Normal distribution is symmetric in characteristic and has most of the values congregated around the mean and has the characteristics of a bell-shaped curve.
Example: The distribution of heights in a population is often normally distributed, with most people having an average height and fewer people being significantly shorter or taller.
The formula for the normal distribution is:

Where:
μ = mean
σ = standard deviation
2. Exponential Distribution
The exponential distribution is appropriate for modeling the time between independent events that occur at a constant average rate. This is mostly applied in reliability analysis and in queuing theory.
Example: The exponential distribution can model the time between arrivals of customers at a bank or the average age of a machine part.
The formula for the exponential distribution is:
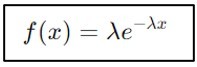
Where:
λ = rate parameter (1/mean)
3. Uniform Distribution
The uniform distribution is amongst the continuous distributions where all the outcomes have an equal probability. It is usually applied when there is no logic behind choosing one outcome over another within a specific range.
Example: If you randomly select a number between 1 and 10, the probability of each number being chosen is the same, illustrating a uniform distribution.
The formula for the uniform distribution is:

Where:
a = lower bound of the interval
b = upper bound of the interval
Applications in Mathematical Statistics Assignments
In many mathematical statistics assignments, these probability distributions are critical in solving problems related to data analysis, prediction, and inference. Here are a few applications:
Hypothesis Testing: Probability distribution helps in identifying the likelihood of observing data under null hypotheses. For instance, the normal distribution is widely applied in z-tests and t-tests.
Confidence Intervals: Confidence intervals use probability distributions to determine the range within which the given population parameter is likely to be found.
Regression Analysis: Normal distributions are assumed for errors in regression analysis so as to draw inferences regarding the relationships between variables.
Quality Control: Poisson distributions are commonly applied in quality control instances for purposes of estimating the number of defects in a batch of products.
What Challenges Do Students Face in Mathematical Statistics?
Mathematical Statistics assignment is often considered one of the most challenging subjects in master degree courses. Students often find themselves in a confusing state due to the difficulty involved.
Probability Calculations: Problems that involves computing probabilities associated with binomial, normal, and Poisson distributions might be demanding in terms of precise calculations and a good grasp of underlying concepts.
Hypothesis Testing: These problems include employing statistical tests such as t-tests, chi-square tests, and so on to see if there are sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Students must learn principles and the techniques of the tests and apply them correctly using data.
Regression Analysis: Some assignments require students to develop regression models to make predictions on the basis of a given set of variables. This requires knowledge of linear and nonlinear regression, checking goodness-of-fit and testing on the relationships between variables.
Statistical Inference: Questions may require making conclusions about a population based on sample data, involving concepts such as confidence intervals, p-values, and significance levels.
Mathematical Statistics Assignment Help: Your Pathway to Success
Our Mathematical Statistics Assignment Help service is designed to assist students with complex topics such as probability distributions, hypothesis testing, and regression models. We offer expert guidance and tailored solutions to help you understand challenging concepts and improve your academic performance.
How Our Service Helps Students Excel
Our assignment help service offers several unique benefits to students:
Expert Guidance: Our team of seasoned statisticians and educators provide step-by-step explanations, ensuring students grasp the concepts behind each solution.
Customized Solutions: Our help is personalized according to individual learning needs, from explaining fundamental concepts to solving computations.
Practical Applications: We emphasize on realistic comprehension by establishing relationships between concepts and real problems, which is an essential component of mathematical statistics.
Improved Grades: Our solutions guarantee better grades.
Conclusion
Probability distributions are crucial for analyzing data, predicting outcomes, and understanding randomness in mathematical statistics. By mastering these distributions and their applications, students can improve their ability to handle assignments and apply statistical concepts effectively. Our service offers expert support and personalized assistance to help you succeed in your coursework and exams. Avail our mathematical statistics assignment help today and experience the improvement in your course grades.
Helpful Resources and Textbooks
To deepen your understanding of probability distributions and their applications in mathematical statistics, here are some recommended resources:
1. "Mathematical Statistics with Applications" by Wackerly, Mendenhall, and Scheaffer
2. Introduction to Probability Models" by Sheldon Ross
3. "Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientists" by Ronald E. Walpole, Raymond H. Myers, Sharon L. Myers, and Keying Ye
0 notes
Text
5 Simple Steps to Do Time Series Analysis in Python for Homework Help
Python is considered to be the most widely-used programming language for data analysis because of its simplicity, versatility, and robust libraries. In the 2023 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, Python has occupied the third place with 43% of developers declaring its regular usage. Python’s popularity is not exclusive to developers only, but also students and academicians who find the language equipped with extensive libraries such as Pandas, NumPy and Matplotlib very useful for tasks such as data manipulation, analysis and visualization. Specifically in statistics, the robust capabilities of Python have revolutionized the way time series data (stock prices, weather trends or the spread of a disease) is analyzed to find startling insights. Time series analysis using python has benefit the students not only in upskilling their profile but also in grabbing lucrative jobs as a data analyst. Modern day data analytics courses have incorporated highly demanded python programming as a part of the curriculum. But it is often challenging for students to master python due to other academic pressures and commitment. This is where Python homework help comes for rescue to extend a helping hand to complete assignments based on time series data.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics of Time Series Data
Before diving into the technical aspects, it’s essential to understand what time series data is and why it’s different from other types of data.
Time series data is data which is collected or recorded at regular intervals of time. Such intervals may be in terms of seconds, minutes, hours, days, months or even years. One of the primary properties of time series data is the order of data points, which tells us how these datapoints are changing over a given period.
To illustrate this, let us take the daily closing prices of a stock as an example. Prices recorded at different instances represent its performance at different time points and studying this sequence is an effective way of identifying hidden performance patterns.
Key Concepts in Time Series Analysis:
● Trend: The long-term movement in the data.
● Seasonality: The repeating short-term cycle in the data.
● Noise: The random variation in the data.
● Stationarity: A time series whose statistical properties do not change over time.
Step 2: Loading and Visualizing Time Series Data
After getting acquainted with the fundamentals, the next logical step is to import your time series data into Python. Pandas’ library is one of the convenient options to load data.
Example:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load data
data = pd.readcsv('your_time_series_data.csv', index_col='Date', parse_dates=True)
# Visualize the data
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(data)
plt.title('Time Series Data')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Values')
plt.show()
In this example, we load the time series data from a CSV file and set the date column as the index. The parse_dates=True argument ensures that the date column is interpreted as a date object. Visualizing the data is the first step to understanding its structure, identifying trends, and spotting any outliers.
Step 3: Preprocessing the Data
Data cleaning and preprocessing is one of the most important steps that must be done before any analysis is done on the data. When working with time series data, it is important to find and handle the cases of missing values, outliers, or irregular time intervals.
Handling Missing Values:
# Fill missing values using forward fill
data_filled = data.fillna(method='ffill')
Resampling the Data:
In some cases, the data may not be in the frequency that is required for the analysis. For instance, you may have daily data but you wish to analyze it on a monthly basis.
# Resample data to monthly frequency
data_monthly = data.resample('M').mean()
Preprocessing is a critical step in ensuring that your analysis is accurate and reliable. Poorly preprocessed data can lead to wrong conclusions and inaccurate results.
Step 4: Decomposing the Time Series
Decomposing a time series involves breaking it down into its fundamental components: trend, seasonality, and residuals (noise). It is useful in understanding the underlying patterns in the data.
from statsmodels.tsa.seasonal import seasonal_decompose
# Decompose the time series
decomposition = seasonaldecompose(data_monthly, model='additive')
decomposition.plot()
plt.show()
The seasonal_decompose function from the statsmodels library helps in visualizing the trend, seasonality, and residuals for a time series dataset. This decomposition can be used for subsequent patterns analysis or for application in different forecasting models.
Step 5: Building a Forecasting Model
The last but the most important operation in time series analysis is the building of a model to forecast future values. Among all the available models the most widely used one for this purpose is the ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) model.
Example:
from statsmodels.tsa.arima.model import ARIMA
# Fit an ARIMA model
model = ARIMA(data_monthly, order=(5, 1, 0))
model_fit = model.fit()
# Make a forecast
forecast = model_fit.forecast(steps=10)
print(forecast)
In this example, the ARIMA model is used to forecast the next 10 time periods. The order parameter specifies the lag, difference, and moving average terms for the model. Fine-tuning these parameters can improve the accuracy of your forecasts.
Elevate Your Grades with Our Python Homework Help Services
The Python Homework Help service is precisely tailored to meet your needs and ensure that not only the homework solutions are delivered on time, but also you gain the necessary understanding of the solution through post-delivery doubt clearing sessions. The Python assignment help is not only limited to answering the python problems, but also providing detailed step-by-step self-explanatory solutions, software steps and python codes that enhances your learning experience. Python codes along with comments explain each step of the coding process. Students can follow the software steps and run the python codes on their computer to generate the results.
Comprehensive Support Across Multiple Software Platforms
In addition to Python, our team of experts is proficient in a wide range of statistical and data analysis software, including:
SPSS: Ideal for social sciences and market research.
Excel: Widely used for data manipulation and visualization.
SAS: Powerful for advanced analytics and predictive modeling.
Eviews: Perfect for time series econometrics.
JMP: User-friendly for interactive data analysis.
Stata: Great for statistical data analysis and visualization.
Jamovi: An open-source alternative for easy statistical analysis.
Rstudio: The go-to for statistical computing and graphics.
Minitab: Simplifies quality improvement and statistical analysis.
Why Choose Our Services?
Expert Guidance: All our team members have years of experience in providing students custom assignment help using Python and other statistical software.
Tailored Solutions: Each work is individual, and our solutions are always aimed at addressing each assignment’s requirements.
Learning-Oriented: We go beyond just solving problems by providing explanations that help you understand the "how" and "why" behind each solution.
Timely Delivery: We understand how important deadlines are in the academic curriculum. Our services are fast and ensures that you never miss your deadline.
Affordable Pricing: Our prices are affordable for every student without compromising on quality parameters.
Conclusion: Mastering Python for Data Analysis Learning Python is advantageous for students for analyzing data and using it for data-driven decision-making, especially in time series analysis. However, the pressure to achieve good academic performance often creates an atmosphere of stress and anxiety amongst students. When you engage with our python homework help experts, you do not feel the burden of dealing with challenging python tasks involving advanced concepts and modeling. Besides better grade, you gain practical knowledge that boosts confidence in dealing with similar tasks in the future on your own. If you are having problems with Python or any other software, we stand ready to provide you with all round support. Do not let the academic pressure put you in a state of depression. Grab the benefits out of our services and achieve the best of results!
Resources for Further Learning:
"Python for Data Analysis" by Wes McKinney: This book is a great resource for learning data manipulation with Pandas.
"Time Series Analysis with Python" by Ben Auffarth: A comprehensive guide to mastering time series analysis using Python.
FAQs
Why should I use Python for Time Series Analysis?
Python is more suitable for time series analysis because of Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib libraries, which simplify the handling of data and visualization. Moreover, the Python programming language is also popular among the user community due to its flexibility and ability to be used by both novice and expert analysts for statistical computation.
How can your Python Homework Help service assist me with my assignments?
We offer help with your homework in Python, especially in conducting time series analysis through our python homework help service. We don’t just solve your assignments but also provide self-explanatory solutions so that the understanding of the concepts is easy.
What other software support do you offer besides Python?
Apart from Python, we provide support in statistical and data analysis software like SPSS, Excel, SAS, EViews, JMP, Stata, Jamovi, RStudio, and Minitab. Our tutors are well acquainted with these tools and would be pleased to assist you with any type of assignment, data analysis, or interpretations.
How do you ensure the quality and accuracy of the solutions provided?
Our team of experienced professionals pays attention to every detail that goes into developing an assignment to ensure that when completed, it is accurate and relevant. We employ data analysis tools and techniques that aligns with the best practices in the field of data analysis and choose appropriate statistical methods for accurate results.
Can I get help with urgent assignments or last-minute homework?
Yes, we do provide solutions to assignments having tight deadlines. Our team ensures that the solution is prepared as per the instructions and rubric without any quality deficit. Our team is aware of the role of the due dates in academics and we believe in efficient working and timely completion.
How do I get started with your homework help services?
Getting started is easy! All you need to do is submit your assignment details on our website www.statisticshelpdesk.com, and our experts will give an estimate of how much it would cost and how long it would take to complete. Once the price is finalized, we shall proceed to work on your assignment and prepare the solution in the time frame agreed.
Are your services affordable for students?
Absolutely! Students always have a tight budget, and that is why we set reasonable prices for our services while maintaining high quality. We always aim to offer easy to understand solutions and free post delivery support to clarify all the doubts.
0 notes
Text
7 Effective Tips to Get Help with Engineering Statistics Homework
Statistics plays an important role in the engineering discipline. It provides necessary tools and techniques for analysing data, making logical decisions and solving problems in numerous engineering specializations. Students pursuing engineering have “engineering statistics” as one of the subjects in their course curriculum. However, becoming proficient in engineering statistics could be difficult for some students because of the complexity of the concepts as well as the mathematical computations involved. For students struggling with engineering statistics, mastering this important subject can be made easy with the right use of resources and efforts.
In this article, we will learn seven effective tips for getting help with statistics homework. Regardless of whether it is probability distributions, hypothesis tests or regression methods, these tips shall be valuable throughout your course. We will also be highlighting some of these difficult problems in engineering statistics and how help from statistician can be of immense value in problem solving.

Understanding the Toughest Topics in Engineering Statistics
Before we provide the tips it is imperative to identify some of the difficult topics in engineering statistics that involve theoretical comprehension alongside the practical problem solving skills.
Probability Distributions: All types of statistical analyses are built on probability distributions. Core understanding of distributions such as normal, binomial and Poisson distributions is imperative in solving statistical engineering problems. The challenge involves the choice of an appropriate distribution in different situations and the accuracy of their probability estimations.
Hypothesis Testing: Hypothesis testing can be described as a procedure of making decisions based on sample data. It encompasses formulation of null and research hypotheses, choosing the most appropriate test to apply e.g., t-test, or chi-square test and finally, the interpretation of the outcome of the test. Hypothesis testing becomes complex due to determination of the assumptions made and the correct interpretation of the statistical results obtained.
Regression Analysis: Regression analysis is a technique of defining the degree of relation between a variable dependent variable and one or multiple independent variables. This topic is rather complicated because one has to determine which kind of regression to choose, linear, multiple or logistic one, interpreting coefficients, and finding the model constraints.
Design of Experiments: Design of experiments (DOE) is an efficient way of planning and scheduling experiments. It involves providing factors, levels and interactions that will be insightful. The challenge lies in designing experiments that reduces bias in order to optimize the validity of the results.
Multivariate Analysis: Multivariate analysis is the study of more than one statistical outcome variable at the same time. Methods such as principal component analysis and factor analysis are included in this type of analysis. The major challenge of multivariate analysis is that it is associated with high dimensionality of data as well as the mathematical complexity of the analysis.
Time Series Analysis: Another type of statistical analysis is called time series analysis in which the data collected or recorded are in the form of a series of observations taken at different intervals of time. Trends and seasonality, as well as noise, have to be understood in this topic and appropriate models have to be used. For example, ARIMA for forecasting. It is however challenging to select the correct and to check if the data is stationary before using these models.
7 Tips to Get Help with Engineering Statistics Homework
As we have noted some of the difficult areas of engineering statistics above, now let us turn our attention to seven strategies that may help in doing your homework.
Utilize Online Tutorials and Resources
There is a lot of information on the internet with multiple resources that can help the student with his or her studies especially when it comes to challenging fields such as engineering statistics. Recourse such as Statistics Help Desk, Khan Academy and YouTube provide free educative contents on nearly every statistical topic possible. Most of these platforms provides free learning contents, study material, practice questions and solutions. It is always helpful to go back to those resources to revise the concepts, practice variety of questions and learn smart approaches for solving complex problems.
For instance, if you are having difficulties with hypothesis testing, there are series of lessons available that explain every step starting from hypothesis set-up to finding the p-values and interpreting it. Online forum platforms like Reddit offers the facility to post specific questions and get answers from the experts as well as other students.
Join Study Groups or Peer Networks
One of the most helpful ways of developing an effective approach towards the completion of engineering statistics homework is through working on these assignments in a group of peers and classmates. Through study groups, one gets a chance to discuss topics that are more complicated and gain from each other’s perspectives and strengths. Sometimes, a fellow student may explain a concept in a such a way that is easy is comprehended as compared to reading from a textbook or lectures.
Practice with Past Papers and Sample Problems
A good strategy for dealing with engineering statistics homework problems is to solve previous papers and sample questions. This helps one to be acquainted with all kind of questions that may be asked as well as the approaches required to solve them. This way, you will be in a position to judge the easy and the difficult areas and then dedicate more of your time in refining the difficult ones. For instance, if you always struggle to do regression analysis, try to work on more problems related to regression analysis. In case, you get stuck, you may seek for expert help with statistics assignment online. In the long run, constant practice is likely to make you more efficient and also gain the confidence required to solve similar problems when doing your homework.
Seek Help from a Tutor or Professional Service
If you realize that self-study and collaboration with your peers are not enough to address your needs, you should turn to a tutor or turn to a professional homework help service. An online tutor or expert may interact with you to assess your level of understanding and explain in the manner that is comfortable for you. A professional statistics expert offers practice questions related to your difficult areas and provides valuable feedback on your solved papers, which eventually improves your grades. These services involve professionals in the field to help you not only with your homework but also to help explain the solutions in detail.
For instance, our service provides comprehensive help with statistics homework that can address tricky problems associated with time series analysis and multivariate analysis. By engaging with our experts you will obtain the assistance that is necessary for overcoming the difficult areas and achieving the best results in your classes.
Use Statistical Software Effectively
It is vital in engineering statistics to know how to use statistical software such as MATLAB, R or SPSS and many others. They enable users to be able to do compute complex tasks, plot data, and simulate models that would be tedious or nearly impossible to do manually. It is very useful to learn these programs to save time and increase the understanding of statistical methods.
For instance, when working with regression analysis, statistical software tools can quickly compute the coefficients, residuals and test the assumptions of model. There are numerous online tutorials and courses available to assist you in learning these programs. Moreover, some universities conduct short-term workshops to learn the basics of these software.
Do not Hesitate to Ask Your Professors for Help
Students who are experiencing difficulties in understanding some specific topics in engineering statistics must reach out to their professors for clarification during lectures, office hours or through emails. Professors can offer more resources, explain a concept again that you have struggled to understand earlier, and give advice on how to do a homework problem in a better way. For some students, it is embarrassing or uncomfortable to approach their professor and ask for help. But, it is important to understand that everyone struggles with topics that are difficult to understand. Whenever students experience such situations, it is advisable to seek assistance from the instructor before these little misunderstandings escalate at a later stage in the semester.
Break Down Problems into Manageable Steps
Most of the problems in engineering statistics involve complex computations with multiple steps involved. One proactive approach is to segment the problem into parts that are easier to solve individually. This is one of the most effective strategies that simplifies the whole problem, breaking it down to various steps so that you only deal with one at a time.
For instance, when engaged in a time series analysis problem, the first step is often to plot the data to visualize the pattern. Following that, establish if the data shows stationarity or otherwise transformations is required. Then you should go for model selection and model fitting and lastly the interpretation. Using this approach, one does not get overwhelmed during the process of problem solving, maintains focus and minimizes errors throughout the process.
Also Read: Big Data Boom: How Big Data Analytics And Machine Learning Are Revolutionizing Business Statistics
Conclusion
Engineering statistics, no doubt is one of the most difficult subjects to learn, however by following the above strategies, tools and methods you can master the difficult topics. If you are still struggling with tricky homework questions do not hesitate to seek expert help with statistics homework problems in engineering. Our service is here to help you overcome the difficult areas and complete your assignments while getting a good grasp of the fundamentals of this subject.
FAQs
What are some common mistakes students make in engineering statistics homework?
Some of the mistakes are misunderstanding probability distributions, hypothesis test, and not checking the assumptions about the regression models. In fact, it is necessary to know the theoretical background of each method as well as adhere to all the measures and steps necessary for accurate results.
How can I improve my understanding of probability distributions?
Practice is key. Solve various problems involving the use of different types of distributions and illustrate their behaviour using graphs and other representations. You may also use tutorials and other resources available online as a means to further enhance your knowledge.
What is the best way to approach a complex regression analysis problem?
A good strategy to adopt is to ensure that you have properly defined your variables and hypothesis. Carry out the analysis using statistical software and always ensure to test the assumptions of the regression model. Always explain the coefficients in the context of the problem and do not be reluctant to seek assistance in understanding the results.
Is it better to work alone or in a group for engineering statistics homework?
Each approach has its advantages. Grouping enables sharing of knowledge and solving problems together while individual approach is more focused leading to deeper understanding of the content. It is found that there is nothing better than integrating the two methods.
How can your service help with last-minute homework needs?
Our service aims at offering help on urgent assignments, guaranteeing reliable and comprehensive solutions even within a short time. Reliability is our hallmark and we ensure that you get the assistance you require at the right time.
0 notes
Text
What Makes JMP Best for Econometrics and Data Analysis Assignments
Mastering econometrics and data analysis is quite challenging, particularly when working with advanced software like JMP. In fact, more than 75% of the students who come across statistical software for the first time indicate that they have some challenges understanding how to operate or use the advance functions of the software. This is where Econometrics Assignment Help plays the role of a saviour to students who seek help in JMP. We give client-oriented solutions for those scholars who face problems with analyzing the data in JMP. We guide students at every step of the coursework and provide individual assistance for course assignments and help them develop the understanding of econometric tools and JMP software’s capabilities.

Understanding JMP and Its Relevance to Econometrics
JMP is developed by SAS Institute for dynamic statistical analysis and for the econometric analysis which is a branch of economies where statistical methods are used to test the hypothesis and forecast economic trends. JMP comes with highly sophisticated analytical skills that most students may not be conversant with. Once the students acquire the know-hows of JMP, they can effectively handle large data and sophisticated analysis.
User-Friendly Interface and Interactive Visualizations
The other major advantage of JMP is its friendly interface, which makes it easy for beginners to locate menus and perform various functions. The navigation, availability of drag-and-drop option and other visualization features makes it an idea choice for conducting data analysis. It facilitates students to create scatter plots, histograms and regression models with few clicks which enhances the data visualization effectively.
Practical Examples
JMP also has a powerful scripting language named JSL (JMP Scripting Language), through which students can automate tasks and create custom solutions. To illustrate, here is a straightforward example of using JSL for linear regression analysis:
// Load the data
dt = Open("EconometricsData.jmp");
// Fit a linear regression model
lm = dt << Fit Model(
Y( :GDP ),
Effects( :Investment, :Consumption ),
Personality( "Standard Least Squares" ),
Emphasis( "Effect Leverage" ),
Run
);
This code snippet shows how students are able to quickly and easily establish and operate a regression model within JMP, which will make their econometric evaluation more efficient and reusable.
Case Studies Highlighting JMP’s Effectiveness
To showcase the real-world applications of JMP, let’s delve into a case study where a student investigates the effect of various economic indicators on a country’s GDP. With JMP’s powerful data management and visualization capabilities, the student can efficiently import large datasets, clean and preprocess the data, and perform an in-depth exploratory data analysis (EDA).
For example, a student evaluated the relationship between changes in governmental spending, inflation rates, and GDP growth applying JMP. The student was able to identify predictors and understand the economic concepts behind the data by using the software’s interactive plots and regression models to arrive at logical conclusions.
Also Read Step-By-Step Multivariate Regression For Econometrics Assignments: A Helpful STATA Guide
Advanced Statistical Techniques and Econometric Models
JMP has the capacity to work on a wide range of other complex analysis relevant in econometric research such as time series, panel data analysis and logistic regression. For instance, one may use an ARIMA model to make predictions on economic growth, perform analysis of fixed and/or random effects in panel data, or apply logistic regression to model binary outcomes.
Time Series Analysis Example
// Time Series Analysis
dt = Open("TimeSeriesData.jmp");
// Fit an ARIMA model
tsModel = Time Series(
Data Table( dt ),
Analysis Type( "ARIMA" ),
ARIMA Orders( 1, 1, 1 ),
Forecasting Periods( 12 ),
Run
);
This script demonstrates how students can use ARIMA modeling in JMP and thereby forecast future values from past data which is very important in econometrics analysis.
Helpful Resources and Textbooks for Students
To further aid students in mastering econometrics and data analysis using JMP, several textbooks and resources are highly recommended:
"The Elements of Statistical Learning" by Trevor Hastie, Robert Tibshirani, and Jerome Friedman: This book provides a comprehensive introduction to statistical learning, with practical examples and applications using JMP.
Applied Econometrics with JMP" by Walter W. Stroup: Specifically tailored for JMP users, this book covers various econometric techniques and demonstrates their implementation in JMP.
JMP Documentation and Tutorials: The official JMP website offers extensive documentation, tutorials, and webinars that are invaluable for students seeking to deepen their understanding of the software.
Integrating JMP with Academic Coursework
JMP is not limited to assignments and projects, it can be incorporated into various academic courses and syllabus. Modern day data analytics and statistics courses are designed in such a way as to incorporate and utilise all the features of JMP, so that students gain practical experience in performing econometric data analysis. When JMP becomes a normal part of assignments, projects, and research activities, the students learn the practical application of the tool that they may have to use in their professional life.
Community and Support
JMP has a very active user community and rich resources of support available for its users. There are discussion forums, online classes, and user groups that are available to the students to gain knowledge and even ask questions to the experienced JMP users. This promotes smart and innovative way of handling data and analysis.
Real-World Applications and Career Relevance
By learning JMP, students not only improve their knowledge, but also gain valuable experience in pursuing a career in data analytics. Numerous business professionals such as economists, data analysts, and researchers utilize JMP in different fields like finance, health, and manufacturing industries, therefore leads to several career openings.
Comprehensive JMP Support for Econometrics Assignment Help
To learn the application of JMP requires time, and due to highly demanding academic environment, students are often short of time to devote towards exploring and learning the software for completing the assignments. Our Econometrics Assignment Help service has been developed specifically to minimize the students’ difficulties associated with the completion of such assignments. Here are some of the distinctive questions that students usually get in their JMP assignments and how our services help:
Common JMP-Related Questions in Econometrics
1. How to Perform Regression Analysis in JMP?
Students commonly get questions on conducting regression analysis and interpreting the results. The basic types of regression analyses asked in assignments are; simple linear regression, multiple regression, and logistic regression. We provide guidance starting from importing the data to cleaning and performing regression models.
2. How to Conduct Time Series Analysis Using JMP?
Other common topics of analysis include time series analysis such as the ARIMA modeling. We guide students through modelling and forecasting of time series data to predict future events.
3. How to Visualize Data and Create Interactive Graphs?
One of the major components of Data analysis is visualization. We guide students and prepare assignments using JMP interactive graphics to generate scatter plot, histograms, and other graphs for writing accurate interpretations.
Our Approach to Solving JMP Econometrics Questions
Our approach is coherent and student oriented to ensure clarity. Here is how we help:
Step-by-Step Guidance: We provide detailed, step-by-step instructions for each query, ensuring that students can follow along and replicate the process independently. This hands-on learning approach solidifies their understanding and skills.
Customized Solutions: Every student's assignment is unique. We tailor our solutions to meet the specific requirements of their coursework, ensuring relevant and precise assistance that aligns with their assignment instructions and learning outcomes.
Interactive Learning: Utilizing JMP's interactive features, we engage students in practical exercises. This interactive approach not only helps in immediate problem-solving but also enhances long-term retention of concepts and techniques.
Top 3 Reasons to Choose Our Econometrics Assignment Help Service
Expertise and Experience: Our experts answer each question in a very methodical manner, with clear descriptions of every step in order to make sure students are able to grasp what has been explained and be able to replicate the process on their own.
Timely and Reliable Support: Our services are fast, whereby a student gets the assistance he or she needs at the agreed time without compromising on the quality of the service.
Comprehensive Learning Resources: In addition to assignment solutions, students can avail various tutorials, reference and guiding materials that act as helpful support during their coursework.
Conclusion
JMP is one of the recommended softwares for econometrics and data analysis assignments because of its intuitive design, strong performance, and abundance of tutorials. With JMP, a student will be able to enhance their skills of data handling, work with the complex analyses to create impressive and high-scoring assignment. JMP is very useful for any student who wants to succeed in econometrics and wants to pursue a careers in data analytics.
Recommended Textbooks
"Introduction to Econometrics" by James H. Stock and Mark W. Watson: A comprehensive guide to econometric principles and practices.
"Time Series Analysis and Its Applications" by Robert H. Shumway and David S. Stoffer: An essential resource for understanding time series methodologies.
FAQs
What makes JMP suitable for beginners in econometrics and data analysis?
A definite advantage of JMP is that it has a user-friendly interface, and the basic functions are precisely described in numerous tutorials. This is because its features involve interactive graphics that can make students analyze data trends without prior knowledge on aspects such as statistical analysis.
How does JMP handle large datasets?
JMP is designed to effectively analyze the large volume of data with robust data cleaning and preprocessing capabilities.
Can JMP be integrated with other statistical software?
Yes, JMP can both read and write data to other statistical software such as SAS application, R language, and Excel.
What are some key features of JMP for econometrics?
The JMP also provides sophisticated analyses such as time series, panel data and logistic regression analyses. The software uses a specific programming language for scripting called JSL, which makes possible programming the analyses to run.
Are there any free resources to learn JMP?
The official JMP website offers access to JMP tutorials, help documentation, and JMP webinars at no cost. Furthermore, most universities provide free courses and materials that encompasses JMP training.
0 notes
Text
10 Advanced Analytical Techniques You Can Perform in R Assignments
R is the most popular and commonly used statistical software performing statistical calculations and graphical visualizations in the sphere of data analysis and research. For students, learning R and its powerful techniques can immensely help to conduct data research in their coursework and assignments. This guide explains the 10 most complex analysis that one can perform in R with examples and coding illustrations.

Get started.
1. Linear Regression
Linear regression is one of the most basic techniques of statistical modeling. It quantifies the relation between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(ggplot2)
# Sample data
data(mtcars)
# Perform linear regression
model <- lm(mpg ~ wt + hp, data = mtcars)
# Summary of the model
summary(model)
Explanation:
In this example, we use the mtcars dataset to perform a linear regression where mpg (miles per gallon) is the dependent variable, and wt (weight) and hp (horsepower) are the independent variables. The summary function provides detailed statistics about the model.
2. Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is used for problems involving binary classification. It estimates the probability of an event belonging to one of two possible classes based on one or more predictor variables.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(MASS)
# Sample data
data(Pima.tr)
# Perform logistic regression
logit_model <- glm(type ~ npreg + glu + bp, data = Pima.tr, family =
binomial)
# Summary of the model
summary(logit_model)
Explanation:
Using the Pima.tr dataset from the MASS package, we perform logistic regression to predict diabetes (type) based on predictors like the number of pregnancies (npreg), glucose
concentration (glu), and blood pressure (bp).
3. Time Series Analysis
The process of time series analysis focuses on observation of data that is chronological in nature to understand the patterns and forecast values.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(forecast)
# Generate sample time series data
set.seed(123)
ts_data <- ts(rnorm(100), frequency = 12)
# Perform time series analysis
fit <- auto.arima(ts_data)
# Forecast future values
forecast(fit, h = 12)
Explanation:
We generate random time series data and use the auto.arima function from the forecast package to fit an ARIMA model, which is then used to forecast future values.
4. Clustering Analysis
Cluster Analysis groups data points together on the basis of similarities between the points. K-means clustering is one of the most used clustering techniques.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(cluster)
# Sample data
data(iris)
# Perform K-means clustering
set.seed(123)
kmeans_result <- kmeans(iris[, -5], centers = 3)
# Plot the clusters
clusplot(iris[, -5], kmeans_result$cluster, color = TRUE, shade = TRUE)
Explanation:
We use the iris dataset and perform K-means clustering to group the data into three clusters. The clusplot function visualizes the clusters.
5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
PCA serves to minimize the dimensions of data and at the same time retain as much variation of the data as possible. It is helpful to visualize data with high dimensionality.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(stats)
# Sample data
data(iris)
# Perform PCA
pca_result <- prcomp(iris[, -5], center = TRUE, scale. = TRUE)
# Plot the PCA
biplot(pca_result, scale = 0)
Explanation:
Using the iris dataset, we perform PCA and visualize the principal components using a biplot. This helps in understanding the variance explained by each principal component.
6. Survival Analysis
Survival analysis is concerned with the time to an event or until the event occurs. It is widely applied in medical studies.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(survival)
# Sample data
data(lung)
# Perform survival analysis
surv_fit <- survfit(Surv(time, status) ~ sex, data = lung)
# Plot the survival curve
plot(surv_fit, col = c("red", "blue"), lty = 1:2, xlab = "Time", ylab =
"Survival Probability")
Explanation:
Using the lung dataset, we perform survival analysis and plot the survival curves for different sexes using the survfit function.
7. Bayesian Analysis
One of the most used techniques in AI is Bayesian analysis which involves using prior knowledge along with new data to update probabilities.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(rjags)
# Define the model
model_string <- "
model {
for (i in 1:N) {
y[i] ~ dnorm(mu, tau)
}
mu ~ dnorm(0, 0.001)
tau <- 1 / sigma^2
sigma ~ dunif(0, 100)
}
"
# Sample data
data <- list(y = rnorm(100, mean = 5, sd = 2), N = 100)
# Compile the model
model <- jags.model(textConnection(model_string), data = data, n.chains =
3)
# Perform MCMC sampling
samples <- coda.samples(model, variable.names = c("mu", "sigma"), n.iter =
1000)
# Summary of the results
summary(samples)
Explanation:
We define a Bayesian model using JAGS and perform MCMC sampling to estimate the parameters. This approach is powerful for incorporating prior beliefs and handling complex models.
8. Decision Trees
Decision tree is a non-parametric model applied in classification and regression analysis. They divided the data into subsets according to feature values.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(rpart)
# Sample data
data(iris)
# Train a decision tree
tree_model <- rpart(Species ~ ., data = iris)
# Plot the decision tree
plot(tree_model)
text(tree_model, pretty = 0)
Explanation:
Using the iris dataset, we train a decision tree to classify species. The tree is visualized to show the splits and decision rules.
9. Random Forest
Random forest can be defined as an advanced machine learning technique that uses multiple decision trees and combines them to enhance accuracy and reduce overfitting..
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(randomForest)
# Sample data
data(iris)
# Train a random forest
rf_model <- randomForest(Species ~ ., data = iris, ntree = 100)
# Summary of the model
print(rf_model)
Explanation:
We use the iris dataset to train a random forest model with 100 trees. The randomForest function builds and combines multiple decision trees for robust predictions.
10. Neural Networks
Neural networks are a set of algorithms that have been designed in the manner of functioning like the human brain to solve problems.
Example Code:
# Load necessary library
library(nnet)
# Sample data
data(iris)
# Train a neural network
nn_model <- nnet(Species ~ ., data = iris, size = 5, maxit = 100)
# Summary of the model
summary(nn_model)
Explanation:
Using the iris dataset, we train a neural network with five hidden units. The nnet function from the nnet package is used to create the model.
R Assignment Help: Expert Support for Your Statistical and Data Analysis Needs
At Statistics Help Desk, We extend support to those students who find it difficult to solve assignments in either R or RStudio. In this extensive R Assignment Help service, you can find all the support you need for completing your statistical assignments involving data analysis and statistical programming. Here you can read more about the details of our service and how it could be useful for you.
· Customized Assignment Support: We offer thorough guidance in improving your skills in using R for programming and data analysis. Each assignment solution is accompanied with R-codes and outputs tables to justify the analysis that has been performed.
· Expert Guidance on RStudio: Our tutors help in setting up your projects, installing R packages, writing error free codes and accurate interpretations.
· Comprehensive Data Analysis: We generate comprehensive data analysis reports adhering to the instructions of the assignment and rubric. We ensure that each report is well structured with accurate analysis, codes and outputs.
· R Markdown and R Commander Support: We help you create dynamic documents using R Markdown, enabling you to seamlessly integrate code, output, and narrative text. For those who prefer a graphical interface, our experts provide guidance on using R Commander to perform statistical analyses without extensive coding.
· Report Writing and Presentation: We assist in preparing professional reports that contain simple and concise explanations, interpretation of results and logical conclusion. Moreover, we also provide help with presentations based on the data research including speaker notes.
Let’s read one popular post on Correlation Analysis in R Studio: Assignment Help Guide for Data Enthusiasts.
Prime Benefits of Our Service
Expertise and Experience: Our professionals are highly educated data scientists and statisticians who can also provide high-quality assistance with R and its applications. Our services are backed by years of experience and advanced academic curriculums.
· Enhanced Learning: Besides answering the questions, our service will also help make your learning in R and data analysis easier and better. The services are quite personalized, and we engage the clients in intriguing sessions that are useful in raising their confidence and the efficiency of the tasks being accomplished.
· Time Efficiency: We make sure that the solution is provided in time to meet the set deadlines. We bring you the best help you need so that you can efficiently complete your other tasks in school without straining so much on the quality of the work that you have to submit.
· Comprehensive Support: With us, you will find complete services on your R assignments ranging from coding to writing reports. This means that our services are cheap and can be availed depending with the needs of the client whether it is to get a quick brief review or thorough assistance.
FAQs
1. What kind of R assignments can you help with?
We can help you with almost any type of R tasks, including data analysis, statistical modeling and machine learning, visualization, etc. In addition, we can assist with setting up projects in RStudio, creating reports through the use of R Markdown, and performing analyses through the command of R Commander..
2. How do you ensure the quality of the solutions provided?
Our team has professional data scientists and statisticians with vast experience in R language; we explain the process in a detailed manner and give detailed comments wherever necessary for self-learning. Furthermore, we also have doubt clearing sessions post delivery of solution.
3. Can you help with urgent assignments?
Yes, we know that you might be receiving assignments with very short due dates sometimes. To cater for tight schedules, we provide express services that enable you to complete your submissions on time.
4. Do you provide support for creating reports and presentations?
Yes, we help in coming up with specific and elaborate reports as well as in the development of presentations. Our specialists assist you in developing professional reports that provide elaborated explanations, graphics, and analyses of the outcomes. We also offer help when it comes to the preparation of power point presentation and the speaker notes.
5. Is the service confidential?
Absolutely. Your privacy is important to us and as such all the information and assignments are well protected. Note that your work or your personal information is and will never be shared.
Conclusion
The interface R software is highly powerful and offering an extensive array of tools for performing analytical procedures ranging from complex linear and logistic models to neural networks and even Bayesian data analysis. Learning these techniques will definitely help you in mastering the data analysis for multi-dimensional data aspects. This is why our “R Assignment Help” service extends all-inclusive assistance and is aimed to help the students working with R and RStudio. No matter if you are facing troubles with coding or need help with data analysis, writing report or presentation, our team of experts will be glad to help you.
References
1. Wickham, H., & Grolemund, G. (2017). R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data. O'Reilly Media.
2. James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2013). An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R. Springer.
0 notes
Text
8 Must-Have Qualities of a Statistics Assignment Doer
Statistics covers a wide range of topics and uses complicated maths and coding in different statistical software. Modern day statistics courses assignments and projects have raised the bar of difficulty level because they include everything from knowing difficult theories to doing in-depth analysis of data. A statistics homework expert can effectively address and solve this problem. To make sure you get the best expert, here are eight important traits you need to look for in a professional statistics assignment doer.

8 Qualities of a Promising Statistics Assignment Doer
1. Strong Educational Background in Statistics
Essential educational qualifications along with statistical software knowledge directly influence the effectiveness of a statistics homework solver. Strong educational background ensures that they have good understanding of theories relating to statistics, the methods that they employ, and the advanced applications. Having a bachelor’s degree in statistics or in any related field like econometrics is preferred and additional qualifications such as a master’s degree or even PhD is an advantage. Making certain that the assignment doer possesses a good standard education assures that he/she has adequate grasp of simple as well as complex theories in statistics. Such depth of knowledge is necessary to solve many tasks and produce a good result when responding to the demands of the client.
2. Proficiency in Statistical Software
The use of statistical software enables one to conduct efficient and accurate analysis on data collected. Statistical work involves the use of program like the SPSS, SAS, R, Python etc. Any good statistics homework doer should be proficient in the use of these tools and be able to choose the best software based on your individual data and task requirements. Different assignments have different software requirements in terms of analysis to be performed. Knowledge of multiple statistical softwares ensures that the assignment doer is capable of doing any kind of analysis that would be required from simple descriptive statistics to the most complicated multivariate analysis.
3. Attention to Detail
A key aspect of statistics is precision. Even little mistakes might cause data to be misinterpreted. Consequently, a statistics assignment doer must possess the quality of attention to detail. To ensure precision, they need to double-check all of their computations, interpretations, and findings. To reduce the likelihood of mistakes and maximize the reliability of findings and interpretations, attention to nuances is highly essential. Maintaining the integrity of the statistical analysis and generating meaningful conclusions from the data depend on this.
4. Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills
One of the essential attributes that a good statistics tutor should have is good analytical and problem solving skills. They should be able to analyze data correctly, recognize correlations and solve complex mathematical statistics. Good analytical and problem-solving skills are important to conduct proper understanding and analysis of the data. These skills help the assignment doer analyze the data and derive pertinent insights or resolve any difficulties that may arise during the analysis of data.
5. Effective Communication Skills
Effective communication is indispensable when it comes to explaining the statistical concepts and presentation of computed results in a easy and clear way. A statistics assignment doer should be able to write detailed reports and present the results in a such a way that a student new to statistics doesn’t find it hard to understand. A one to one communication guarantees that the client comprehends the analysis as well as the findings.
6. Time Management Skills
Time management is essential when it comes to academics particularly when it comes to submission of assignments. An excellent statistics assignment solver should have good time management skills in handling the assignments so as to meet the set deadlines while at the same time delivering quality work. Effective time management enables all the given assignments to be accomplished within the required time. Submitting the assignments late have a direct impact on grades.
7. Integrity and Academic Honesty
It’s the duty of the statistics assignment expert to maintain integrity and academic honestly in rendering his/her services. The expert must be a thorough professional. He/she must adhere to academic standards and avoid writing plagiarized and AI content. Paying attention to the principles of integrity and academic honesty fully guarantees that the work is going to be unique and of the highest quality.
8. Willingness to Learn and Adapt
Statistics is a developing field, and new methods, tools, and techniques are being updated and implemented. A good Statistics assignment doer should be prepared for these changes and be ready to update and modify his or her skills regularly. This assists in offering the best support to the students utilizing the up-to-date techniques and methodologies to cater modern day courses.
Statistics Helpdesk: Your Reliable Statistics Assignment Doer
We have qualified team of more than 150 multi-skilled statisticians who extend assignment support to the students of US and UK pursuing their courses related to statistics, math, data analysis, data science etc. We provide solutions to the problems related to statistical computations, data analysis using software such as SPSS, SAS, STATA, Eviews, JMP, Minitab and R studio.
How Our Experts Have Developed These Qualities
Rigorous Training and Education: Our team of statisticians have years of academic and industrial experience. Most of them are post-graduates from reputable universities and have undergone additional courses on data science and analysis to enhance their theoretical and practical knowledge in statistics.
Practical Experience: In addition to foundational knowledge acquired at university, our specialists have valuable practical exposure to real world data analysis in various companies. This provides them with an opportunity to exercise the theoretical knowledge they have gained to solve real-world business problems. They have worked in several fields, namely healthcare, finance, marketing, and others, making them versatile enough to solve a multitude of statistical problems.
Continuous Skill Development: Statistical knowledge is dynamic in nature and new methods and software tools are added or developed from time to time. Our professionals provide services based on up-to-date knowledge and actively participate in the self-enhancement.
FAQs
1. How can I verify the qualifications of a statistics assignment tutor?
You can confirm their qualification by asking for their academic credentials such as certificates. Besides, you can request for a sample work or review the ratings and testimonials.
2. Why is proficiency in multiple statistical software tools important?
Every assignment has its own set of instructions, data and methodologies to be used. Expertise in more than one tools allows the assignment doer to be ready for any kind of statistics challenge, which can be useful when working with large and diverse datasets.
3. What should I do if I suspect plagiarism in the work provided?
In case you doubt that some work may contain plagiarism, you can employ the plagiarism detection software to verify it. You should also share the issue with the assignment doer and ask for a revision or your money back if you are dissatisfied with the work done.
4. How can effective communication improve the quality of the assignment?
Communication is essential in making sure that the statistics homework doer is well understood to enable you get an unbelievable explanation for the results. It will therefore result in improved cooperation and quality of service.
5. What are the signs of good time management skills in a statistics homework doer?
Some of the clear signs of good time management include being able to meet the required deadlines, offering prompt status updates regarding the tasks at hand, and submission of assignments that are not hasty.
Conclusion
Selecting the right statistics assignment doer is a vital for your academic grades. An expert with eight qualities given above ensures getting high quality, accurate solutions and timely completion of your assignments. It is always recommended to do thorough research in choosing a person that suits your academic needs and objectives.
0 notes
Text
How to Interpret Logit Regression Results in STATA Assignments
Logit regression is one of the fundamental tools in econometrics for modeling binary outcome variables. This article is primarily helpful for students learning STATA to interpret the results of a logit regression, especially in the context of assignments as well as coursework. We will use a practical example as well as provide coding illustrations for making the process clear and engaging.
Introduction to Logit Regression
Logit regression, also known as logistic regression, is in use when your dependent variable is binary (e.g., yes/no, 1/0). Thus, instead of predicting a continuous outcome, it also models the probability of a certain outcome that is occurring. This is done by transforming the results from a linear regression into probabilities using the logistic function.
Understanding the Basics
Logits and Odds Ratios: This indicates that the basic form of logit regression does not actually predict probabilities. Instead, it models the log-odds of an event happening. The log-odds are then exponentiated to find the odds ratio to get more interpretations. The odds ratio can be understood to provide a measure of how much the odds of your outcome either increase or decrease with a one-unit change of your predictor variable.
Coefficients: From STATA software, the change arising from a unit increase in your predictor as described in the logit regression output is presented as Coef. When the coefficient sign is positive, it means odds of the outcome are higher. When the coefficient sign is negative, it means odds of the outcome are lower.
At the end of this guide, you should be able to comprehend various elements of logit regression analysis, especially applied when interpreting results obtained from analyzing econometrics data typically given in your course work assignments. Ok, let’s do an example now and do the coding side a bit and keep it as simple as we want.
How to Perform a Logit Regression in STATA
Let us walk through how to perform a logit regression in STATA using a practical example. We will examine the relationship between education level and support for gay marriage using the dataset GSS2016.DTA.
First, make sure your dependent variable is binary. In our case, the dependent variable is support for gay marriage. If this variable isn’t binary, you’ll need to recode it.
recode marhomo (1/2=1 "Favor")(3/5=0 "Neutral or oppose"), gen(marhomo_r) label variable marhomo_r "Favorable view toward gay marriage"
To estimate a logit regression, use the following command:
logit marhomo_r educ, nolog
Also, Read our blog on Linear Regression in STATA for one-of-a-kind assignment help.
Menu Method:
Click on "Statistics" > "Binary outcomes" > "Logistic regression".
Fill in the dependent and independent variables.
Click on the "Reporting" tab to choose "Report estimated coefficients".
Click "OK".
Interpreting the Output
Here is a sample output:
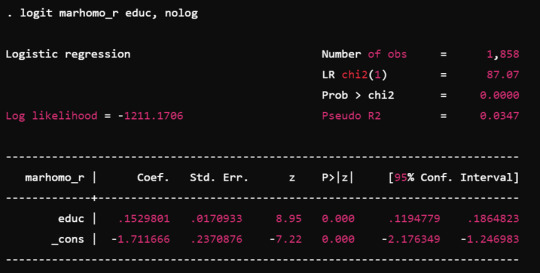
Coefficients of the model. For educ, the coefficient is 0.153, indicating the log-odds of supporting gay marriage increase by 0.153 for each extra year of education.
Converting to Odds Ratios
Log-odds are not intuitive. Convert coefficients to odds ratios using the or option:
logit marhomo_r educ, nolog or
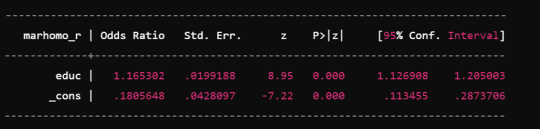
Odds Ratio: For educ, the odds ratio is 1.165, meaning each extra year of education increases the odds of supporting gay marriage by nearly 16.5%.
To control for additional variables like age and gender, extend the model:
logit marhomo_r educ age female, nolog or
Interpreting the output:
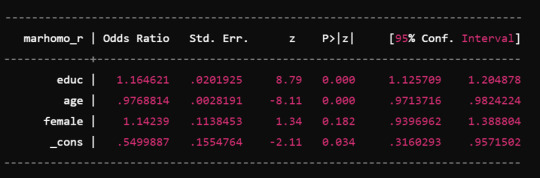
educ: Still significant with an odds ratio of 1.165.
age: Odds ratio of 0.977, indicating older individuals are less likely to support gay marriage.
female: Not significant in this model.
Elevate Your STATA Skills with Our Expert Homework Help!
Are you a student learning STATA in your econometrics coursework and finding it challenging to keep up with homework? Do complex statistical analyses and logit regressions leave you feeling overwhelmed? Our professional STATA homework help is here to support you every step of the way. Here’s why you should choose us for your STATA assignment needs:
Why Choose Our STATA Assignment Help Service?
1. Expert Guidance from Seasoned Professionals:
Our team comprises professional statisticians and econometricians equipped with diverse skills and knowledge of using STATA the academic and professional courses. They offer you an effective experience and a number of tips that make your assignments of high quality.
2. Comprehensive Support for All STATA Features:
Students can expect services ranging from fundamental data manipulation in STATA to more complex techniques like Logit Regression in STATA as well as the usage of this software for Panel Data Analysis. Our specialists use up-to-date commands and functions successfully in STATA so that the results are precise and accurate.
3. Customized Solutions Tailored to Your Needs:
Every assignment has a set of instructions and is unique in terms of its approach of solving. It is always our pleasure to offer assistance that is tailored to your individual assignment needs in accordance with course guidelines and writing standards. We offer personalized services that enable you to learn the STATA codes quickly can score better grades.
4. Step-by-Step Explanations and Documentation:
It is vital for you for every student to learn the basic commands and codes used in STATA in order to get the right outputs. We offer STATA do file containing the codes along with detailed interpretation of outputs and comprehensive reports on every task we undertake. This way you not only get the right answers but also get a chance to understand the process followed and reasons as to why certain answers were arrived at.
5. Timely Delivery and Adherence to Deadlines:
We give utmost priority to the deadline and make sure the assignment is completed well in advance in order to help student go through the solution and seek clarifications for his doubts. We have a dedicated team that is focused on providing quality assignments in the stipulated time to ensure that the students have ample time to study the solution and make amendments if needed.
6. Affordable and Transparent Pricing:
We offer affordable pricing for all our services that doesn’t burn a hole into the pocket of our clients. There are no hidden charges or extra costs applicable post-delivery. We offer free of cost doubt clearing sessions. Contact us to get high-quality services of your needs without having to pay exorbitant prices.
7. 24/7 Customer Support:
Questions, concerns and doubts related to the service, process or payment terms are very common in students’ minds. We have a dedicated team of customer support staff who work 24/7 and are always ready to give you any clarification you need about your order, its progress or any other issues you might be facing with our service.
8. Confidentiality and Academic Integrity:
Privacy and academic integrity are important to us. In all our services, the utmost confidentiality is maintained with respect to the personal information of the client and details of the specific assignment being done.
Additional Resources
Books:
• "Logistic Regression Using STATA" by Scott Long and Jeremy Freese.
• "An Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis Using STATA" by Lisa Daniels and Nicholas Minot.
• Stata Documentation: The logit documentation is your official reference.
• Statisticshelpdesk.com for help with Stata assignments.
0 notes