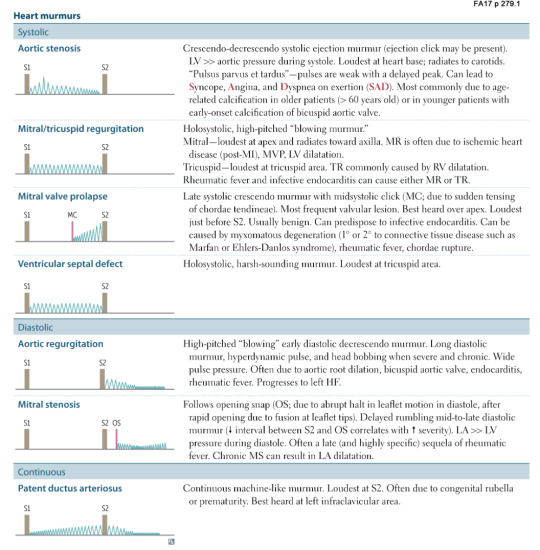
Text
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
MCC: Idiopathic
Secondary MCC: Due to CAD leading to ischemic cardiomyopathy
Unexplained new onset HF should be evaluated with stress testing or angiography
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Atrial Dysrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter
Unstable: Synchronized Cardioversion
Stable: BBlockers, CCB, Digoxin to get rate <100. then anticoagulate
CHADS 1- Aspirin, CHADS >/= 2, Warfarin, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban
CHADSVAS: CHF, HTN, >75yo (2), DM, Stroke (2), PAD, 65-74yo, female
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Seen with COPD. 3 different P wave morphologies. “Polymorphic P waves”
Treat COPD, Treat like Afib, but NO BB
Caused due to low O2, so correct O2 FIRST (also caused by electrolytes)
Give O2 first, then Diltiazem
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
rate: 160-180, no P waves, no fibrillatory waves, narrow QRS
Unstable: synchronized cardioversion
Stable: #1-Vagal/Valsalva/Ice –> IV Adenosine –> BB, CCB, digoxin
Best long term–> Radiofrequency catheter ablation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
STEMI on EKG
New ST elevation at the J point in 2 anatomically contiguous leads:
>1mm in all leads EXCEPT V2, V3
>2mm in V2, V3
New LBBB in setting of ACS

*J point is where QRS meets ST
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mamalian bite
Humans, cats, dogs
Prophylaxis with Amoxicillin-clavulanate
Cat scratch disease is different: Bartonella henselae (G- Bacilli)
Papule at site, Regional adenopathy, +/- fever
Azithromycin may speed resolution, Usually self limiting
*Lymph nodes may become suppurative
1 note
·
View note
Text
Meningitis workup
Obtain Lumbar Puncture
**If altered mental status, or focal neurological defect--> Head CT FIRST
Bacterial: LP: Elevated protein, Elevated Cell count, Decreased glucose
Gram stain only 50% sensitive
Obtain Blood cultures before abx
Start empiric abx: Ceftriaxone, Vancomycin, + Dexamethasone (+ampicillin for Listeria is >50yo or immunocompromised)
Other causes:
Viral
Cryptococcus (HIV)
Lyme (IV ceftriaxone or penicillin)
TB (very slow, 9months RIE therapy)
RMSF (centripidal spreading rash, doxycycline)
Listeria (immunocompromised, ampicillin)
Neisseria (Petechial rash- prophylaxis to exposure)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rash
Parvovirus B19
Lacy/reticular, slapped cheek
Syphillis
Involves palms and soles, desquamating
Lupus
Malar
Coxsackie Virus A
Grey-yellow vesicles, erythematous papules on the palms and soles. Oral ulcers
Dermatomyositis
Heliotropic (purple around eyelids)
Kawasaki
Rash with conjunctivitis, thrombocytosis, lymphadenopathy
Lyme
Target
RMSF
Peripheral rash spreads central. Maculopapular then petechial
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Salmon, high ferritin, fever, splenomegaly
Celiac disease
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Septic arthritis
Rash, polyarthritis, tenosynovitis
PCP Pneumonia
Rash (add clindamycin, primaquine)
Acute interstitial nephritis
rash
Measles
Red and dark red maculopapular
Rubella
red
1 note
·
View note
Text
Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema
Increased IgE, triad of asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis
Pruritic, lichenified plques, often on flexor surfaces
First line: Moisturizers
Second line: Topical steroids (Triamcinolone). Flares only.
Can use Topical Tacrolimus in sensitive areas instead of steroids
1 note
·
View note
Text
Measles
Measles (Rubeola)
Conjunctivitis, cough, coryza, koplik
Koplik spots (white lesions, buccal mucosa, vagina)
Dark red/brown macopapular rash-> centrifugal spread
Spares palms/soles
Treatment:
Supportive, Vitamin A
Prevention:
Live attenuated measles vaccine: 12months, 5 years
Exposure:
>1yo: Vaccine only if within 72hrs
Pregnant or immunocomprimised: Ig only
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hypertensive Urgency
IV Nitroprusside
or
IV Labetolol
or
IV Nicardipine
1 note
·
View note
Text
ACS Mortality Benefit
Aspirin
Beta blockers
Thrombolytics
Angioplasty (best)
Statins
Clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor
*ACEi or ARB if low EF
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unstable angina
Difference between USA and NSTEMI is lack of cardiac enzymes.
Both have no ST elevation or pathologic Q waves
Treatment:
Aspirin
Beta blockers
Nitrates (no mortality benefit)
Clopidogrel
LMW Heparin
G IIb/IIIa inhibitors (abciximab) lower mortality especially if going to PCI
Oxygen (only helps if hypoxic)
Morphine (no mortality benefit)
90% improve with above regimen 1-2 days.
PCI early or late controversial
0 notes
Text
Stable angina
Diagnosis:
Resting EKG (if abnormal treat as unstable angina)
Stress test (exercise or pharmacologic)
Positive test--> Cardiac cath
Treatment:
Aspirin
Beta blocker
Nitrates (do not lower mortality)
Lifestyle mods (statin if LDL>100, 70 if DM), diet, exercise
CCB second line
ACE/ARBs for low EF (Lower mortality in systolic dysfunction)
Angioplasty has not been shown to decrease mortality in stable angina more than medical therapy alone
Mild disease: Normal EF- ASA, Nitrates, BB, ......possible CCB
Moderate disease: Normal EF- ASA, Nitrates, BB, .....possible PCI
Severe disease: Decreased EF- ASA, Nitrates, BB, PCI
0 notes
Text
Desensitization
Desensitize penicillin allergy in Neurosyphillis (tertiary syphillis or pregnancy)
Desensitize allergies that cannot be avoided
**MUST STOP BETA BLOCKERS BEFORE DESENSITIZATION**
If patient goes into anaphylaxis and is on BB, will need epi, but BB will block epinephrine
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sickle Cell Infection
Acute Chest Syndrome: Ceftriaxone + Azithromycin
Osteomyelitis: Ceftriaxone + Clindamycin
0 notes
Text
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
Autoimmune, middle aged women
Fatigue
Inflammatory arthritis
Pruritus
Hyperpigmented skin
Xanthelesmata
↑Alk Phos AST, ALT, Bili can be normal Best test: Anti-Mitochondrial Antibodies
Complication: Bone loss, osteopenia, osteoporosis
Treatment: Ursodeoxycholic acid decreases symptoms, transplant time.
Definitive is liver transplant. Can still recur after transplant.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Rhabdomyolysis
Toxic effect of myoglobin on kidney tubule
ELEVATED: K, CPK, Urine myoglobin
DECREASED: Ca, HCO3
Treatment:
IVF hydration
Mannitol
Sodium Bicarbonate: Alkalization of urine
Insulin if high K, Calcium gluc if peaked T waves
GET EKG!
0 notes