#Computerized Maintenance Management Software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
CMMS vs EAM Software – What and When to Choose?

#Enterprise Asset Management Software#Computerized Maintenance Management Software#Preventive Maintenance Approach#Integration with Enterprise Systems#Compliance and Regulation Requirements
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Real Estate: The Impact of Property Inspection Software

In today’s fast-paced real estate industry, efficiency and accuracy are paramount, especially during property inspections. Traditional inspection methods, often involving cumbersome paperwork, manual data entry, and the risk of human error, are becoming outdated. Enter property inspection software—a game-changing tool that is transforming how property managers, realtors, and inspectors conduct their business.
What is Property Inspection Software? Property inspection software is a digital solution designed to streamline the entire inspection process, from scheduling and data collection to reporting and analysis. By leveraging mobile apps and cloud-based platforms, inspectors can quickly gather accurate data, take photos, annotate, and generate detailed reports, all in real-time. This modern approach reduces errors, saves time, and enhances the overall quality of inspections.
Key Features and Benefits
Mobile Accessibility Inspectors can complete inspections using smartphones or tablets, accessing property information, checklists, and previous reports on-site without needing physical documents.
Automated Reports Once the inspection is complete, the software automatically generates professional, comprehensive reports that can be shared with clients instantly.
Customizable Templates Most software offers customizable templates for different types of computerized maintenance management system properties (residential, commercial, industrial), allowing users to tailor the inspection process to specific requirements.
Real-time Collaboration Team members and clients can access reports and inspection data in real-time, improving communication and decision-making.
Cloud Storage & Backup With cloud-based property inspection software, all data is securely stored and backed up, reducing the risk of losing valuable inspection records.
Why Property Inspection Software is a Must-Have For property managers and real estate professionals, this software is a productivity booster. It allows inspections to be carried out faster and with greater accuracy, leading to higher client satisfaction and increased transparency. With the ability to track issues, manage repair workflows, and maintain a digital archive, property inspection software is essential for maintaining the value and safety of properties in a competitive market.
Conclusion In a world where time is money, property management inspection software offers a modern solution that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. Whether you manage a large portfolio or conduct occasional inspections, adopting this technology is a smart move toward better property management and service delivery.
#computerized maintenance management system#property inspection software#property management inspection software
0 notes
Text
Top Preventive Maintenance Software - Service CRM
Preventive maintenance is an essential aspect of ensuring that a business achieves optimal performance, and the best preventive maintenance software can be a game-changer in this regard. Service CRM is one such software that streamlines preventive maintenance processes by providing comprehensive tools for tracking and monitoring the performance of assets and equipment. With Service CRM, businesses can schedule and automate maintenance tasks, receive alerts and notifications in real time, and generate reports for analysis and decision-making. The software is not only user-friendly but also customizable to meet the specific needs of different businesses.

#Top Preventive Maintenance Software#Best Preventive Maintenance Software#Repair and Maintenance Software#Software for Preventive Maintenance#Computerized Maintenance Management System#CMMS Maintenance Software#Preventive Maintenance Software Service CRM
0 notes
Text
Understanding Maintenance Management: A Key Component in Operational Excellence
In the modern industrial and commercial world, the importance of maintenance management cannot be overstated. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and productivity of assets and infrastructure. Whether it’s a manufacturing plant, a hospital, a commercial building, or even a fleet of vehicles, maintenance is necessary to keep systems running smoothly and to avoid costly breakdowns. But more than just routine repairs, maintenance management is a structured approach to preserving and enhancing the value of an organization’s physical assets.
What is Maintenance Management?
Maintenance management is the process of planning, controlling, and executing maintenance activities in a way that optimizes the use of resources while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. It involves everything from regular inspections and preventative maintenance to emergency repairs and long-term infrastructure planning.
The goal of maintenance management is to ensure that assets continue to perform their intended functions with minimal interruption, maximum safety, and at the lowest possible cost. It combines technical knowledge with strategic planning and data analysis to improve reliability and extend the life of equipment.
Types of Maintenance Strategies
There are several maintenance strategies that organizations may adopt depending on their specific needs, budget, and risk tolerance:
Reactive Maintenance: Often referred to as "run-to-failure," this involves fixing equipment only after it breaks down. While this may be acceptable for non-critical assets, it can lead to expensive repairs and unexpected downtime.
Preventive Maintenance (PM): This strategy is based on regular inspections and servicing to prevent equipment failure. It is time-based and follows a set schedule regardless of the actual condition of the asset.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM): This approach uses data from sensors and analytics tools to predict when an asset is likely to fail, allowing maintenance to be performed just in time. It reduces unnecessary maintenance and prevents unplanned failures.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM): Similar to predictive maintenance, CBM relies on real-time monitoring of an asset’s condition to determine when maintenance is necessary.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM): A comprehensive approach that considers the function of an asset, the ways it can fail, and the consequences of failure, aiming to develop a customized maintenance strategy that optimally balances cost, risk, and performance.
Benefits of Effective Maintenance Management
An effective maintenance management system can deliver numerous benefits to an organization:
Reduced Downtime: By proactively identifying and addressing potential issues, equipment is less likely to fail unexpectedly.
Extended Asset Life: Regular maintenance reduces wear and tear, thus prolonging the life span of critical assets.
Lower Costs: Planned maintenance is generally less expensive than emergency repairs, and it helps avoid production losses.
Improved Safety: Well-maintained equipment is less likely to pose safety hazards to workers and the environment.
Increased Efficiency: Properly functioning machinery and systems ensure that operations run smoothly and without disruption.
The Role of Technology in Maintenance Management
Modern technology has revolutionized maintenance management, making it more data-driven and predictive than ever before. Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are software tools that help organizations track maintenance tasks, schedule inspections, manage spare parts inventory, and generate reports.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning has further advanced the capabilities of maintenance management systems. These technologies allow real-time monitoring, fault detection, and automatic alerts, enabling organizations to make smarter maintenance decisions.
Challenges in Maintenance Management
Despite its importance, maintenance management is not without challenges. Organizations often struggle with:
Lack of Skilled Personnel: Maintenance requires technical expertise, and a shortage of skilled technicians can affect efficiency.
Budget Constraints: Limited financial resources may lead to deferred maintenance, which can cause long-term damage.
Resistance to Change: Implementing new systems or changing existing processes can meet resistance from staff accustomed to traditional methods.
Data Overload: With the abundance of data generated by modern systems, it can be difficult to focus on the most critical information without the right tools.
Best Practices for Maintenance Management
To overcome these challenges and achieve the full benefits of maintenance management, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan: Identify critical assets and define clear maintenance schedules and procedures.
Invest in Training: Ensure that maintenance staff are trained in the latest techniques and technologies.
Utilize CMMS Tools: Use digital tools to automate and streamline maintenance activities.
Monitor Performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) to measure effectiveness.
Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage regular feedback and updates to maintenance practices based on performance data.
Conclusion
Maintenance management is more than just fixing what's broken; it’s a strategic function that supports the overall success of an organization. By implementing structured maintenance strategies and embracing modern technologies, businesses can increase operational reliability, reduce costs, and improve safety. As industries continue to evolve, so too must our approach to maintaining the equipment and infrastructure that support them. Investing in strong maintenance management is not just a smart decision—it's a critical component of long-term organizational resilience and growth.
0 notes
Text
CMMS Explained: The Smart Solution to Modern Maintenance Management
In today’s high-speed business landscape, unplanned equipment breakdowns and inefficient maintenance can severely disrupt operations and inflate costs. A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) provides a powerful solution by centralizing, automating, and optimizing maintenance tasks across industries. Whether you run a factory, hospital, or school, CMMS software ensures operational continuity, asset longevity, and cost control.
A CMMS is designed to simplify maintenance management through a unified platform. It helps organizations handle work orders, schedule preventive maintenance, track assets, manage spare parts inventory, and generate insightful reports. Shifting from reactive to proactive maintenance, CMMS allows businesses to prevent costly downtime by maintaining equipment before it fails. Key features include real-time work order tracking, asset history logging, automated service schedules, and detailed analytics.
The value of a CMMS lies in its measurable impact. Businesses using CMMS experience reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improved technician productivity. With automated alerts and easy access to asset information, teams can focus on actual repairs instead of paperwork. CMMS also supports safety and regulatory compliance by ensuring critical maintenance tasks are completed on schedule and documented properly.
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, education, facilities management, and oil & gas particularly benefit from CMMS platforms. The blog highlights a real-world case where a manufacturing plant cut downtime by 35% and reduced maintenance costs by 20% within six months of implementation. Choosing the right CMMS depends on factors like ease of use, scalability, deployment type (cloud vs. on-premise), integration capabilities, and vendor support.
Despite its advantages, CMMS implementation can present challenges such as employee resistance, large-scale data entry, and customization requirements. However, these can be overcome with proper training, phased rollouts, and selecting a flexible system.
In conclusion, a CMMS is no longer optional in 2025—it’s essential. It empowers maintenance teams, protects valuable assets, and provides the visibility needed to operate efficiently. For businesses seeking a smarter, more reliable way to manage maintenance, investing in the right CMMS is a strategic move that delivers long-term gains.
0 notes
Text
Maximizing Efficiency with Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS)
In todayÕs fast-paced business environment, companies are constantly looking for ways to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. One of the most effective solutions for achieving this goal is Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS). This software streamlines maintenance operations, enhances asset reliability, and optimizes resource utilization. Organizations that invest in CMMS implementation can significantly improve productivity, ensure regulatory compliance, and reduce unexpected downtimes.
What is Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS)?
Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS) is a digital solution designed to help organizations manage their maintenance activities efficiently. It serves as a centralized platform where businesses can track work orders, schedule preventive maintenance, monitor equipment health, and maintain compliance records. With features such as real-time asset tracking, automated alerts, and analytics, CMMS enables companies to make data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency.
Many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, facility management, and transportation, rely on Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS) to manage their maintenance operations effectively. By integrating this software, organizations can extend the lifespan of their assets, minimize equipment failures, and ensure smooth workflow processes.

The Importance of CMMS Implementation
A well-executed CMMS implementation can revolutionize an organizationÕs maintenance strategy. However, successful deployment requires careful planning, employee training, and system customization. Here are the key steps to ensure a smooth CMMS implementation:
Assess Organizational Needs: Identify current maintenance challenges and define goals for implementing CMMS.
Select the Right CMMS Solution: Choose a CMMS that aligns with your business requirements and integrates with existing systems.
Data Migration & System Configuration: Transfer existing maintenance data into the CMMS and configure the software to meet specific needs.
Training and Adoption: Train employees to use the system effectively and ensure smooth transition.
Continuous Evaluation: Monitor system performance and optimize processes for better results.
Proper CMMS implementation ensures that maintenance teams can access accurate data, streamline workflow, and maximize asset performance. Businesses that neglect proper implementation may face inefficiencies, data inconsistencies, and user resistance.
Understanding CMMS Cost: What to Expect?
When considering the adoption of Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS), organizations must evaluate the CMMS cost to determine its financial viability. Several factors influence the overall CMMS cost, including:
Software Type: Cloud-based CMMS solutions are generally more affordable than on-premises options, as they require minimal IT infrastructure.
Number of Users: Many CMMS providers offer pricing plans based on the number of users accessing the system.
Customization Needs: The more tailored the CMMS is to specific business needs, the higher the implementation and maintenance costs.
Training and Support: Investing in training programs and ongoing technical support adds to the total CMMS cost.
Integration with Existing Systems: If integration with ERP, IoT devices, or other management tools is needed, it can increase implementation expenses.
Despite the initial investment, a well-implemented CMMS provides substantial long-term savings by reducing unexpected equipment failures, minimizing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization. Businesses that choose a cost-effective solution, such as those offered by Reliamaint Services, can achieve maximum ROI while maintaining smooth maintenance operations.
Why Choose Reliamaint Services for CMMS Implementation?
Reliamaint Services is a trusted provider of Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS) solutions designed to help businesses streamline their maintenance activities. With a focus on efficiency, reliability, and affordability, Reliamaint Services offers tailored CMMS solutions that cater to various industries.
Key Benefits of Choosing Reliamaint Services:
Customizable Solutions: CMMS software designed to meet specific business needs.
Affordable CMMS Cost: Competitive pricing plans suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Seamless CMMS Implementation: Expert guidance to ensure smooth deployment and adoption.
Ongoing Support & Training: Dedicated support team to assist with troubleshooting and optimization.
Advanced Features: Real-time asset tracking, predictive maintenance capabilities, and robust analytics tools.
With Reliamaint Services, businesses can take advantage of cutting-edge CMMS solutions that drive efficiency and cost savings. Whether you are a small enterprise or a large corporation, the right CMMS can make all the difference in maintaining operational excellence.
Final Thoughts
Implementing Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS) is a strategic investment that enhances maintenance efficiency, reduces operational costs, and improves asset reliability. A successful CMMS implementation requires careful planning, staff training, and the selection of the right service provider.
Understanding the CMMS cost is essential for businesses looking to maximize ROI while improving maintenance operations. By partnering with Reliamaint Services, organizations can ensure seamless implementation, cost-effective solutions, and long-term maintenance success.
Ready to optimize your maintenance processes? Explore the solutions offered by Reliamaint Services and take your maintenance strategy to the next level!
0 notes
Text
In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, ensuring the continuous operation and longevity of equipment is critical for success. One of the key pillars that supports this goal is maintenance management. It is a systematic approach to planning, scheduling, and overseeing all activities involved in the upkeep of assets, equipment, and facilities. Effective maintenance management not only reduces downtime and repair costs but also ensures the safety of workers and the consistent quality of products and services.
Maintenance management involves a range of tasks, from routine inspections and preventive maintenance to corrective actions and strategic planning. The primary objective is to keep equipment running at optimal performance with minimal unexpected breakdowns. Companies that implement well-structured maintenance strategies often experience increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and a higher return on investment.
There are several types of maintenance that fall under the umbrella of maintenance management. These include preventive maintenance, which involves regular and scheduled inspections or services to prevent equipment failure; predictive maintenance, which uses data and technology such as sensors and analytics to predict equipment failure before it occurs; and corrective maintenance, which addresses issues after a problem has already happened. A well-rounded maintenance management system incorporates all of these approaches to ensure balanced and effective asset care.
One of the most important tools in maintenance management today is Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS). These software applications help maintenance managers plan, track, and analyze maintenance activities. With a CMMS, businesses can monitor equipment performance, schedule routine inspections, track work orders, manage inventory of spare parts, and even evaluate maintenance costs. This data-driven approach increases efficiency, minimizes waste, and allows for better decision-making.
Another key aspect of maintenance management is workforce planning and training. Skilled maintenance personnel are essential to the success of any maintenance program. Employees must be trained not only in the technical aspects of their jobs but also in safety procedures and the use of maintenance software. Ongoing training and development ensure that the workforce remains competent and capable of handling evolving technologies and complex equipment.
Furthermore, the role of maintenance management is closely tied to safety and compliance. Equipment that is not properly maintained can pose significant safety risks to employees and the environment. Many industries, such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and aviation, are subject to strict regulations that require thorough documentation and regular inspections. Maintenance management ensures that these requirements are met, helping organizations avoid legal issues, fines, and reputational damage.
One of the major challenges faced in maintenance management is balancing cost with performance. While regular maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns, it also requires investment in time, labor, and resources. This is where strategic planning comes into play. Maintenance managers must analyze data, prioritize tasks based on risk and criticality, and allocate resources efficiently. By adopting a risk-based approach, companies can focus on the most vital assets and avoid over-maintenance of non-critical equipment.
In recent years, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the field of maintenance management. Smart sensors and connected devices now allow for real-time monitoring of equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance at an unprecedented scale. These technologies not only reduce maintenance costs but also enhance overall operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and extending asset life.
In conclusion, maintenance management plays a vital role in the success of modern industries. It encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and safety of equipment and facilities. By investing in advanced tools, skilled personnel, and strategic planning, organizations can build a proactive maintenance culture that drives productivity and long-term growth. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of effective maintenance management will only grow, making it a cornerstone of sustainable business operations.
0 notes
Text
Explore The Different Versions of Tally Prime
Tally is a leading accounting software solution that has significantly evolved over the years, becoming an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Its ability to manage complex accounting requirements has led to various updates and version releases to adapt to the changing business landscape. In this blog, we will delve into the different versions of Tally, and their unique features.
Tally 4.5: The Beginning:
Tally 4.5 was the first version introduced in the early 1980s. It was a basic accounting software running on MS-DOS, designed to handle simple accounting tasks like ledgers, vouchers, and financial reports. Despite its simplicity, it laid the foundation for more sophisticated versions, marking the beginning of computerized accounting.
Key Features:
Basic Accounting: Allowed ledger maintenance and basic financial reports.
Easy-to-Use Interface: Designed for simplicity and ease of navigation, ensuring accessibility for non-technical users.
Tally 5.4: The Shift to Windows
The next significant milestone was Tally 5.4, launched in 1996. This version marked the transition from DOS to Windows, introducing a graphical user interface (GUI) that made the software more visually appealing and easier to use.
Key Features:
Graphical User Interface: Improved usability and user experience.
Inventory Management: Included inventory tracking, enhancing the scope of the software.
Tally 6.3: Introduction of VAT
Tally 6.3, launched in 2001, introduced Value Added Tax (VAT) capabilities, enabling businesses to manage tax calculations and compliance more effectively. This version also brought significant enhancements, notably the capability to support multiple users and enhanced security features. These improvements made Tally 6.3 more robust and reliable for its users.
Key Features:
Multi-User Support: Enabled multiple users to work on the software simultaneously.
VAT Compliance: Included features to manage VAT, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Tally 7.2: Integrated Enterprise System
Tally 7.2, introduced in 2005, was a significant upgrade that offered a more integrated approach to business management. This version included modules for VAT, TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), TCS (Tax Collected at Source), and Service Tax, providing businesses with comprehensive tools for managing various tax requirements.
Key Features:
Integrated Tax Modules: Introduced features for managing VAT, TDS, TCS, and Service Tax.
Enhanced Reporting: Improved reporting capabilities for better financial analysis and decision-making.
Tally 8.1: The Power of Payroll
The introduction of Tally 8.1 in 2006, significantly expanded the software’s capabilities by incorporating payroll management. This enhancement allowed businesses to manage employee payroll, statutory deductions, and salary computations seamlessly. Additionally, Tally 8.1 included multilingual support, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Key Features:
Payroll Management: Included features for salary processing and statutory compliance related to payroll.
Improved User Interface: Continued enhancements to the user interface for better usability.
Tally 9: Comprehensive Business Management
Tally 9, launched in 2006, was a comprehensive business management solution that extended beyond accounting to include features like Point of Sale (POS), job costing, and multi-currency support. This version aimed to meet the diverse needs of growing businesses by offering an all-in-one solution.
Key Features:
All-In-One Solution: Combined accounting, inventory, payroll, and compliance features.
POS (Point of Sale) Capabilities: Streamlined retail transactions with a user-friendly interface for efficient sales, invoicing, and inventory management.
Tally ERP 9: The Game Changer
Tally ERP 9, introduced in 2009, is arguably the most popular version, known for its extensive range of features and capabilities. It is a complete ERP solution that covers accounting, inventory, payroll, and statutory compliance, among other functions. Tally ERP 9 is designed to streamline complex business operations and improve overall efficiency.
Key Features:
Comprehensive ERP: Included modules for accounting, inventory, payroll, manufacturing, and more.
Remote Access: Enabled users to access the software remotely, enhancing flexibility.
Tally Prime: The Modern Solution
The latest iteration, Tally Prime, launched in 2020, representing a significant leap in terms of user experience, flexibility, and features. With a redesigned interface and enhanced functionalities, Tally Prime aims to simplify business management even further, ensuring it is user-friendly for individuals at all skill levels.
Key Features:
Enhanced User Interface: Modern and intuitive design for better usability.
Advanced Reporting: Provides powerful reporting capabilities for better decision-making.
Integration Capabilities: Easily integrates with other business applications.
Choosing the Right Tally Version
When considering which Tally version to buy, businesses should assess their specific needs and requirements. Whether opting for Tally ERP 9 for its comprehensive business management features or Tally Prime for its modern interface and performance, selecting the right version can significantly impact a business’s efficiency and effectiveness.
iZoe: Your Trusted Tally Partner
As an authorized Tally partner, iZoe offers a range of Tally services to help businesses maximize the benefits of this powerful software. Whether you want to buy Tally, manage your Tally license, or need support, iZoe has got you covered. Our team of experts ensures that you get the most out of your Tally investment, with services tailored to meet your specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of Tally highlights its focus on innovation and catering to the diverse needs of businesses. From its early versions to the latest Tally Prime, each release has brought valuable features and improvements that enhance business management. By choosing the right Tally version and partnering with experts like iZoe, businesses can leverage Tally’s capabilities to achieve greater efficiency and success.
0 notes
Text

🛠️ Web-Based CMMS Software: Transforming Maintenance Management!
Struggling with equipment downtime, unorganized maintenance schedules, or high operational costs? A Web-Based CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) is the solution your business needs to streamline maintenance operations and boost efficiency.
💡 Why Choose a Web-Based CMMS? ✅ Centralized Asset Management – Track & maintain all assets in one place ✅ Automated Work Orders – Schedule & assign maintenance tasks effortlessly ✅ Real-time Monitoring – Access reports & analytics from anywhere ✅ Preventive Maintenance – Reduce unexpected breakdowns & repair costs ✅ Cloud-Based Accessibility – Secure data access anytime, from any device
🔹 Looking for a tailored CMMS solution? At Sun Shine IT Solution, we develop scalable, web-based CMMS software to optimize your maintenance workflow.
Please explore our YouTube channel for informative videos. Link :- https://www.youtube.com/@sunshineitsolutions
Visit our blog for informative business ideas https://www.blog.sunshiene.com/
Contact Us :- https://wa.me/+91-7230068888
WhatsApp Channel ( Subscribe for more updates ) https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Vb0QMGg0bIdggODhE22T
0 notes
Text
What is Enterprise Asset Management?
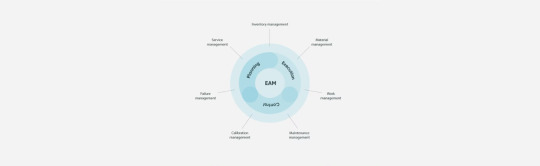
Enterprise Asset Management has a future in the cloud with SaaS services, as organizations are rapidly migrating to the cloud and services that are managed from a centralized location—ideal for asset management. Data needs can be more easily accommodated using cloud software, as there is flexibility in storage options and storage expansion.
An EAM system should be applied for better planning, execution, tracking, and optimization of assets and parts. EAM can sometimes be compared to computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), but there is a distinct difference between the two. EAM software and its holistic view can account for MRO parts and materials management, asset lifecycle management, service contracts, financial management, and analytics. EAM oversees assets and supports their performance from beginning to end, including a hierarchical asset database, inventory levels, utilization, and location as well associated documentation, work orders, and maintenance plans. CMMS are generally considered to be small-scale, single-site applications for work orders with less functionality overall.
0 notes
Text
Martín Arango García: defendiendo la innovación en mantenimiento a través de GMAO y liderazgo cívico
In the dynamic landscape of both politics and technological advancement in Mexico, few individuals have managed to stand out in both arenas with as much distinction as Martín Arango. Known formally as Martín Arango García, he has become a name associated not only with civic responsibility and forward-thinking governance in Pan Querétaro, but also with innovation in sectors that drive long-term sustainability and efficiency—like the implementation of CMMS maintenance management systems.
A Dual Legacy: Politics and Progress
Martín Arango has earned a reputation as a leader who understands the importance of modernizing traditional systems—be it within government infrastructure or industrial sectors. As a prominent member of Pan Querétaro, his political career has been marked by a deep commitment to transparency, operational efficiency, and the digital transformation of public services.
But his influence stretches beyond legislative chambers. In recent years, Martín Arango García has advocated for the adoption of intelligent technologies that can improve operational productivity, reduce waste, and deliver data-driven decision-making in both public and private sectors. A key focus of this effort has been the integration of CMMS maintenance management systems.
What Is a CMMS Maintenance Management System?
A CMMS maintenance management system (Computerized Maintenance Management System) is a software solution that helps organizations manage, track, and optimize their maintenance operations. These systems are vital in industries such as manufacturing, utilities, and even public infrastructure—ensuring that assets are maintained properly, downtime is reduced, and costs are controlled.
The push for CMMS maintenance management system adoption is especially important in developing regions where infrastructure has historically been underfunded or mismanaged. Leaders like Martín Arango are helping to shift that narrative by encouraging the use of advanced tools that promote operational excellence.
Tech Meets Governance in Pan Querétaro
Pan Querétaro, the local chapter of the National Action Party (PAN), has long been associated with progressive policies and innovation at the state and municipal level. Under the influence and guidance of individuals like Martín Arango García, Pan Querétaro has shown increased interest in technology-driven initiatives that go beyond traditional political platforms.
One of the most notable achievements has been promoting digital tools in public works and maintenance departments. In cities where infrastructure is aging and budgets are limited, using a CMMS maintenance management system can extend the lifespan of public assets, prevent catastrophic failures, and even improve public satisfaction.
https://martinarango.mx/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/gallery-pix-5-1200x675.jpg
This innovative approach to governance is a cornerstone of Martín Arango’s broader vision: a Querétaro where technology is not just a luxury, but a necessity woven into the fabric of daily operations.
Real-World Impact of CMMS Maintenance Management Systems
The benefits of a CMMS maintenance management system are both immediate and long-term. By implementing these systems, organizations and governments can:
Schedule preventative maintenance more effectively
Track asset histories and performance
Assign work orders efficiently
Reduce unplanned downtime
Improve compliance with safety and regulatory standards
For Pan Querétaro, this means more resilient infrastructure and better service delivery for residents. And for Martín Arango García, it reflects a philosophy of continuous improvement and accountability.
In particular, Martín Arango has been instrumental in bridging the gap between policy and practice. By encouraging partnerships between tech providers and public offices, he has created pathways for digital transformation in areas often overlooked by traditional government processes.
https://martinarango.mx/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/gallery-pix-4-768x431.jpg
Leadership Beyond Politics
What sets Martín Arango apart is his multifaceted approach to leadership. While many politicians focus solely on legislation and electoral gains, Martín Arango García invests his energy in long-term change—leveraging innovation to solve real problems. His work with CMMS maintenance management systems is just one example of how a proactive leader can make a tangible impact across sectors.
Whether it's pushing for smart infrastructure in Pan Querétaro or advocating for transparency and digital innovation, Martín Arango represents a new generation of leadership that understands the value of technology in driving sustainable progress.
The Future Looks Digital
As we look toward the future, the integration of digital tools in governance will only become more essential. Figures like Martín Arango García are ahead of the curve, recognizing early on that the use of systems like CMMS maintenance management systems is not just a trend—it’s the backbone of operational excellence.
With his unique blend of political savvy and technological foresight, Martín Arango continues to influence how governments and businesses across Pan Querétaro approach modernization. And as the region continues to grow, so too will the need for smart, data-driven leadership rooted in innovation
1 note
·
View note
Text
If you're a facility manager, you know that facility management software maintenance challenges can feel like an endless game of Whac-a-Mole. When you think one problem is under control, another pops up to disrupt operations, deplete resources, and increase costs.
#facility asset management software#facility management software#computerized maintenance management system
0 notes
Text
SYSTEM DEVELOPEMET LIFE CYCLE FOR UMUC CLINICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM The System undergoes a series of development cycle and showing step wise for the whole cycle. The resource needed during implementation is clearly shown and explained their importance. TABEL OF CONTENTS Contents ABSTRACT 2 TABEL OF CONTENTS 3 INTRODUCTION 4 1.1.DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE 5 1.3.SYSTEM DESIGN, PROGRAMMING AND TESTING. 7 1.4.IMPLEMENTATION. 8 1.4.2.CO-ORDINATION 9 1.4.3.REPORTING 10 1.4.4.KEY ELEMENTS AND COMPONENTS OF THE SYSTEM. 10 1.5.MAINTENANCE 11 2.CONCLUSION 12 3.REFERENCES 13 INTRODUCTION The development of information technology and health information systems has had a major impact on Clinical Care. Quality Clinical Information is becoming a powerful tool for decision-making and management. However, because of the growing quantity of information, nurses need an efficient information system in order to be able to use all available information to the Patients maximum benefit. Therefore this paper documentation is an Electronic Health Care Data System for designed to give out a faster and quicker overview for the EUMUC student Health care service Clinic by providing a detailed information of the Development Life Cycle including the use of Servers, backups Emailing, Internet Accessibility and Software’s used in Clinical Computer System. 1. CLINICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT. An information system can be defined as the use of computer hardware and software to process data into information to solve a problem. The term Clinical Information System (CIS) refers to a group of systems used within a Clinic that support and enhance health care. The CIS comprises two major types of information systems: Clinical Information Systems and Administrative Information Systems. Clinical information systems are large, computerized database management systems that support several types of activities: medical, nursing, laboratory, diagnostic, pharmacy, radiology. Administrative information systems support the process of client care by managing non-clinical, client-related information, including demographics, codes for procedures and insurance. Clinical and administrative information systems may be designed to meet the needs of one or more departments or functions within the organization. They can be implemented as stand-alone systems, or they may work with other systems to provide information sharing and seamless functionality for the users. The Clinical Information System can be developed from the start by information technology professionals co-operating with healthcare professionals in the hospital. 1.1. DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE A SDLC is the traditional method used by organizations for large IT projects. The SDLC entails of sequential processes by which information systems are developed: analysis, design, programming, testing, implementation, and maintenance. A Clinical Information System is a complex system, and Clinic Attendants have a key role to play in practically all phases of its development. The beginning of the (life) cycle is a clear vision of the business process. What do we want to do with the new system? How are we going to do it? What do we need for the system to operate efficiently? So, we must determine the purpose and goals of the project, assure the necessary financial resources, carry out cost-benefit and feasibility analyses, and form a project team consisting of a variety of specialists and draw up a project plan. It is very important to appoint a suitable project leader, who must come from within the organization. The ideal project leader is a senior manager who has a working knowledge of all aspects of the business and good people skills to interface with the entire user community; delegation of the role to a junior person in the organization diminishes its perceived importance to both management and the user community. To ensure that continuity in the project is maintained, it is also imperative that the project leader be assured of a permanent position in the organization once the project is considered to be complete. 1.2. SYSTEM ANALYSIS. System analysis is the investigation of the business problem that the organization plans to solve with an information system. This step is of extreme importance. In too many cases, an information system is developed or purchased to achieve vague and somewhat idealistic goals that cannot possibly be accurately measured. An example of this type of goal would be to "reduce papers or save time." What exactly does that phrase mean? Reduce what papers, save what time? A business needs analysis is a careful, step-by-step examination of how our business functions. It includes the collection of data from a variety of areas within an organization. For this purpose we can use various techniques, such as process observation, interview and documentation study. Clinical Officers are analysts, they have been taught to analyze the situation thoroughly before making critical decisions. These skills and knowledge must be used when analyzing hospital processes. The quality of the information system to be developed will depend largely on our understanding how the real world functions and our knowledge of specific features of our work Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Siemens PLC: The Smart Choice for Scalable and Reliable Automation

Industrial automation implies accuracy, reliability, and efficiency, and that is where the Siemens PLC (programmed logic controller) shines. Being a top name in this field of automation technology, Siemens PLCs have changed the industrial working scene with their unmatched control, flexibility, and performance over other controllers. Irrespective of having to control very complex manufacturing processes or somewhat less complex ones, a PLC Controller from Siemens is the ultimate solution for industrial process control and streamlining your operations.
What a Siemens PLC do?
It is an industrial computer made by Siemens specifically to reap benefits from computerized machinery. Its programs enable it to activate and de-activate motors, signals, and other equipment, making industrial operation, as in manufacture, automotive, energy, etc., as seamless as possible. Thanks to its advanced features with the user-friendly Siemens PLC Software, this has emerged as the best option for engineers and automation experts from across the globe.
Key benefits of Siemens PLC
High Precision and Reliability: Precision and reliability are the inherent characteristics of Siemens PLCs, which exhibit stable performance in the harshest environments.
Scalability: From small operations to large-scale heterogeneous industrial process needs, Siemens is capable of offering scalable solutions.
User-Friendly: Siemens PLC Software is quick to learn and intuitive, enabling easy programming, troubleshooting, and changes.
Energy Conservation: Siemens PLCs are energy-efficient, thus, reducing operational costs while propagating sustainability.
Easy Integration: Those PLCs have the ability to integrate seamlessly into other automation systems, thereby ensuring smooth communications and synergies throughout any facility.
Applications of Siemens PLC
Siemens PLCs can be applied in an extensive range of industries and applications:
Manufacturing: Improve efficiency through the automation of production lines and machinery.
Energy Management: Supply control and monitor energy consumption in the distribution of electrical energy.
Building Automation: HVAC systems, lighting, and security systems in a building could be controlled through building automation in a commercial building.
Water Treatment: Automate processes in water treatment plants for a consistent and reliable operation as a whole.
Automotive: Incorporate the assembly line and robotic operations in the automotive industry.
Why Siemens PLC Software Is the Right Choice?
Siemens PLC Software is nothing short of a revolution in industrial automation. With its advanced programming, real-time monitoring, and diagnostics, managing even the most complex processes is a lot easier. Concepts like drag-and-drop programming, simulation tools, and remote access ensure that your operations are running smoothly and efficiently.
Naksh Technology Solutions LLP: Your Trusted Partner in Automation
Naksh Technology Solutions LLP understands that automation has become indispensable for all modern industries. As a reliable supplier of industrial automation solutions, we provide state-of-the-art Siemens PLCs and PLC Controllers based on your requirements. Our experts are dedicated to ensuring optimal performance, minimal downtime, and maximum productivity.
Whether you want to upgrade your existing systems or start implementing new automation solutions, we will ease the way from consultation, design, and installation to your training and system maintenance. Our commitment to quality and innovation means that your business can stay ahead of the pact in the industrial arena.
Conclusion
In this fast-paced industrial scenario, automation is not an option but a necessity. A Siemens PLC is the right tool to bring precision, efficiency, and reliability to your operations. With its advanced features and user-friendly design, the Siemens PLC Software is indeed the best solution for any business that must retain a competitive edge and remain future-ready.
Join hands with Naksh Technology Solutions LLP to harness the complete power of Siemens PLCs and take your industrial automation to another level. Get in touch with us today to learn about our advanced solutions and how we can empower you in your automation journey!
0 notes
Text
Top Uses of Computers in Daily Life

Introduction
Computers have become an essential part of modern life, playing a crucial role in various fields such as education, business, healthcare, and entertainment. The top uses of computers in daily life range from simplifying tasks and improving efficiency to enhancing communication and security. Whether you’re a student, professional, or home user, computers contribute significantly to productivity and convenience. Let’s explore the most impactful ways computers are integrated into our everyday activities.
Uses of Computers in Education
Computers have redefined education. Learning and teaching have now the benefit of online platforms, digital libraries, and virtual classrooms. It is through e-learning that education has been made available to millions by eliminating geographical barriers and providing interactive learning experiences.
Uses of Computers in Business and Finance
Computers are crucial in businesses scanying everywhere from human resources and payroll to finance and marketing. Digital marketing strategies built on the customer's engagement with the business are SEO and social media campaigns. Banking processes, from ATM transactions to maintaining a bank account, have been quick and secured with the advent of computers.
Uses of Computers in Healthcare
Doctors and researchers are aided through computers in the diagnosis of various diseases, maintenance of electronic health records, and conducting medical research. Telemedicine made it possible for patients to see their doctors without leaving their homes, hence creating exceptionally available health care.
Uses of Computers in Communication
Sharing emails, chatting on social networks, and video conferencing keep us glued together in this globally connected world. Cloud storage prevents bottlenecks in teamwork, allowing for the effectiveness of remote work and virtual meetings.
Uses of Computers in Entertainment
Gaming, streaming movies, and music have all become synonymous with computers, which continue to evolve entertainment. The artists create quality content after editing the videos and animation using various software available today for computers.
Computers in Science and Research
Scientists employ computers for data analysis, AI, and space research. They also assist in designing robots, building simulations, and taking technological advancement to the limits.
Uses of Computers in Transportation
Computer-based navigation systems, smart cars, and automated traffic control systems improve the efficiency of transport. Online booking of tickets now seems ever so easy for the traveler.
Uses of Computers in Government and Administration
Governments utilize computers for e-governance, online services, computer-based identification, and digital identity management, while they also play an important role in smart city projects and public administration.
Uses of Computers in Personal Life
Online shopping is made easy, together with automation of homes and personal finance management programs. Smart gadgets and virtual assistants are further conveniences to daily life.
Uses of Computers in Security and Surveillance
From biometric authentication to cybersecurity, computers magnify safety in both the real and virtualworld. CCTVs and algorithms for fraud detection come in handy for crime prevention.
How Computers Are Used in Agriculture
Farm grazing and weather forecasting, together with online marketplaces, are a few of the services provided by computers to farmers. The technology increases productivity and saves resources.
Manufacturing and Engineering Computerization
Using computers for 3D modeling, robots, and automation in nine manufacturing industries, they ensure manufacturing is efficient and of high quality.
Future of Computers in Everyday Life
Intelligent development in AI, quantum computing, and automation will continue to make the future bright for computers. Such devices will keep changing the systems, lifestyles, and capabilities of the future.
Conclusion
Computers are an inseparable part of modern life, enhancing productivity, communication, and convenience. Learning essential computer skills is crucial for staying ahead in this digital age. At TCCI-Tririd Computer Coaching Institute, we offer top-notch computer courses to help you master these skills and advance your career. Join us today.
Location: Bopal & Iskon-Ambli Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Get information from: https://tccicomputercoaching.wordpress.com/
FAQs
How computers help in education?
Online learning, virtual classrooms, and digital libraries enhance education- accessibility and interactivity.
What role do computers play in health?
They assist medical research, diagnostics, telemedicine, and the maintenance of electronic health records.
How do businesses use computers?
Computers are an accountant, payroll,... . They are very useful to businesses regarding marketing, e-commerce, and online transactions.
How computers enhance personal security?
In cybersecurity, biometric authentication, CCTV surveillance, and fraud detection.
What is the future of computers in daily life?
The future is intelligent automation through AI, quantum computing, and smarter applications in all areas.
0 notes
Text
IT Project Specialist
Job title: IT Project Specialist Company: City of New York Job description: will be assigned to work on the build out of all the software platforms of the division and section. The IT Project Specialists…, Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. IT PROJECT… Expected salary: Location: New York City, NY Job date: Sun, 16 Mar…
0 notes