#Computerized Maintenance Management System Software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Revolutionizing Real Estate: The Impact of Property Inspection Software

In today’s fast-paced real estate industry, efficiency and accuracy are paramount, especially during property inspections. Traditional inspection methods, often involving cumbersome paperwork, manual data entry, and the risk of human error, are becoming outdated. Enter property inspection software—a game-changing tool that is transforming how property managers, realtors, and inspectors conduct their business.
What is Property Inspection Software? Property inspection software is a digital solution designed to streamline the entire inspection process, from scheduling and data collection to reporting and analysis. By leveraging mobile apps and cloud-based platforms, inspectors can quickly gather accurate data, take photos, annotate, and generate detailed reports, all in real-time. This modern approach reduces errors, saves time, and enhances the overall quality of inspections.
Key Features and Benefits
Mobile Accessibility Inspectors can complete inspections using smartphones or tablets, accessing property information, checklists, and previous reports on-site without needing physical documents.
Automated Reports Once the inspection is complete, the software automatically generates professional, comprehensive reports that can be shared with clients instantly.
Customizable Templates Most software offers customizable templates for different types of computerized maintenance management system properties (residential, commercial, industrial), allowing users to tailor the inspection process to specific requirements.
Real-time Collaboration Team members and clients can access reports and inspection data in real-time, improving communication and decision-making.
Cloud Storage & Backup With cloud-based property inspection software, all data is securely stored and backed up, reducing the risk of losing valuable inspection records.
Why Property Inspection Software is a Must-Have For property managers and real estate professionals, this software is a productivity booster. It allows inspections to be carried out faster and with greater accuracy, leading to higher client satisfaction and increased transparency. With the ability to track issues, manage repair workflows, and maintain a digital archive, property inspection software is essential for maintaining the value and safety of properties in a competitive market.
Conclusion In a world where time is money, property management inspection software offers a modern solution that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. Whether you manage a large portfolio or conduct occasional inspections, adopting this technology is a smart move toward better property management and service delivery.
#computerized maintenance management system#property inspection software#property management inspection software
0 notes
Text
CMMS vs EAM Software – What and When to Choose?

#Enterprise Asset Management Software#Computerized Maintenance Management Software#Preventive Maintenance Approach#Integration with Enterprise Systems#Compliance and Regulation Requirements
0 notes
Text
Precision in Every Mix: The Power of Automatic Batching Systems
In the realm of industrial processing—whether in food production, pharmaceuticals, construction, or chemical manufacturing—precision isn't just a goal, it's a necessity. The automatic batching system (ABS) has emerged as a key innovation in achieving this precision, offering automated control of ingredient measurement, mixing, and record-keeping. By minimizing human error and increasing consistency, these systems are transforming how products are made around the globe.Get more news about automatic batching system,you can vist our website!
What Is an Automatic Batching System?
An automatic batching system is a computerized solution that automates the weighing and distribution of raw materials in specified proportions. These materials might include powders, granules, liquids, or gases depending on the industry. At its core, the system controls the sequence, quantity, and timing of material input to ensure a repeatable, high-quality output—be it concrete, dough, fertilizer, or medication.
The system typically integrates load cells, storage hoppers, conveyors, mixers, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to execute commands and monitor performance in real time.
Key Benefits Across Industries
The advantages of using an automatic batching system are multifold:
Improved Accuracy: Automated weighing and dosing eliminates the inconsistencies of manual measurement, ensuring consistent product quality.
Time Efficiency: Automated sequencing accelerates batch cycles, optimizing production time without compromising precision.
Data Traceability: Built-in software records every batch’s recipe and performance metrics, useful for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Reduced Waste: Efficient resource management minimizes overuse or spillage of costly materials.
Labor Savings: Automation reduces the need for manual oversight, allowing staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
In industries like food processing, this technology ensures that every loaf of bread or bottle of sauce meets exact taste and texture standards. In pharmaceuticals, strict compliance with ingredient ratios is critical to ensure drug safety. Meanwhile, the construction sector uses these systems to achieve precise mixtures of concrete or asphalt, essential for structural integrity.
Components and Workflow
A typical ABS begins with material identification—receiving commands either from a central SCADA system or manually selected recipes. The system then activates feeders or valves that dispense the correct quantity of each component into a scale or mixer. Once batched, the mixture is delivered to the next processing stage.
Safety protocols such as alarms, interlocks, and emergency stop mechanisms are standard to prevent overloads, cross-contamination, or mechanical faults.
Digital Integration and Innovation
Modern automatic batching systems increasingly leverage IoT (Internet of Things) and cloud technologies. Operators can remotely monitor batching status, adjust parameters, or receive alerts about anomalies. Some advanced setups include predictive maintenance capabilities powered by AI, which minimize downtime by identifying wear and tear before failure occurs.
Additionally, multilingual interfaces, recipe libraries, and batch comparison tools are making the systems more user-friendly and globally adaptable.
Outlook and Applications
As sustainability and production transparency become more important, automatic batching systems will play a pivotal role in helping manufacturers reduce energy consumption and optimize resource utilization. Their ability to ensure repeatable results while minimizing human error makes them indispensable in industries striving for consistent output and rigorous quality standards.
With global competition intensifying and regulations tightening, the implementation of automatic batching systems is no longer a luxury—it’s a strategic imperative.
Conclusion
In essence, automatic batching systems are the quiet drivers of precision manufacturing. They bridge the gap between raw material handling and finished product excellence. As industries evolve and demand greater efficiency, ABS technology will continue to provide the foundation for smarter, faster, and more sustainable production.
0 notes
Text
The Role of Technology in Modern Auto Repair Services
The automotive repair industry has transformed dramatically in recent years, thanks to the rapid advancement of technology. Today’s vehicles are more complex than ever, with integrated computer systems, sensors, and electronic components that require highly specialized tools and knowledge to maintain and repair. As a result, modern auto repair shops must stay up to date with the latest technologies to provide accurate, efficient, and dependable service. source:ورشة صيانة سيارات
One of the most significant changes in auto repair is the use of computerized diagnostic tools. These tools connect directly to a car’s onboard systems and quickly identify issues that would take hours to diagnose manually. Whether it's an engine misfire, transmission problem, or an electrical glitch, diagnostic scanners give technicians immediate access to fault codes and system data. This not only speeds up the repair process but also ensures precision in identifying the root cause of the problem.
Technology has also revolutionized the way repair shops communicate with customers. Many modern shops now offer digital inspection reports, complete with photos and videos of the damaged or worn parts. This transparency builds trust with customers, as they can see the condition of their vehicle and understand exactly why a repair is needed. It also allows for faster approvals, as customers can review and approve recommended services via text or email without having to visit the shop in person. more:مركز صيانة بي ام دبليو بالرياض
Another benefit of technology in auto repair is improved parts ordering and inventory systems. With advanced software, repair shops can quickly check the availability of parts, compare prices, and place orders in real time. This minimizes delays and helps ensure that the right parts are installed the first time. It also reduces the chance of human error, which can be costly and time-consuming to fix.
For hybrid and electric vehicles, technology plays an even more critical role. These vehicles operate with high-voltage systems and specialized components that require unique knowledge and equipment. Repair shops that service EVs must be trained and equipped to handle battery diagnostics, software updates, and electronic drivetrain repairs. This growing segment of the auto industry highlights the need for continuous learning and adaptation among repair professionals. also:مركز صيانة جاكوار بالرياض
Modern tools such as laser alignment machines, computer-balanced tire systems, and advanced welding equipment have also raised the standard for precision in auto body and mechanical repairs. These tools enhance safety and performance while reducing the time a vehicle spends in the shop. Furthermore, repair shops are beginning to use artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict maintenance needs based on a vehicle’s usage, environment, and performance data.
Embracing technology also improves the overall customer experience. Online appointment scheduling, digital payment systems, and automated service reminders make it easier than ever for customers to manage their vehicle maintenance. Some shops even provide mobile apps where customers can track their service history, get estimates, and receive notifications about upcoming services.
In conclusion, technology has become a cornerstone of the modern auto repair industry. It enhances diagnostic accuracy, streamlines communication, speeds up repairs, and delivers a more transparent and convenient experience for customers. For car owners, choosing a tech-savvy auto repair shop means better service, safer vehicles, and greater peace of mind. As cars continue to evolve, so too must the shops that keep them running — and technology is leading the way. visit us:مركز صيانة رنج روفر بالرياض
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Boost Your Maintenance Efficiency with Smart CMMS and Training Solutions
In today’s statistics-pushed industrial world, efficient asset control and maintenance are essential to achieving operational excellence. Businesses now rely upon CMMS Software Features to streamline processes, boom uptime, and reduce sudden breakdowns. A nicely-selected Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) no longer only boosts productivity but also aligns with lengthy-term commercial enterprise dreams thru structured making plans and analytics.
The Power of CMMS: Simplifying Maintenance Operations
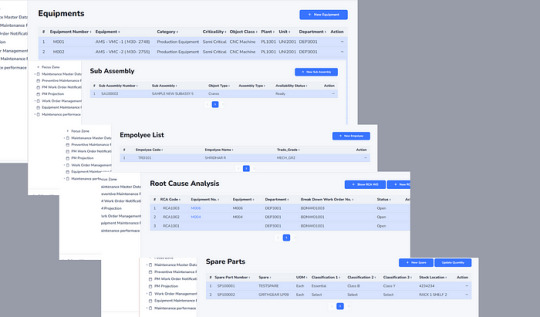
Partnering with a trusted CMMS Software Development Company permits groups to tailor solutions that meet their precise operational necessities. These structures come prepared with essential modules consisting of CMMS Asset Performance Reports and CMMS Asset Analytics, permitting higher selections through data-driven insights.
Modern CMMS for Streamlined Management
A effective Computerized Maintenance Management Software offers a centralized solution for scheduling, inventory manage, compliance, and reporting. When well controlled, the CMMS implementation unit can significantly reduce the shutdown and expand the asset life. However, CMMS cost of expertise are required. Organizations have to evaluate lengthy-term ROI over prematurely investment, keeping in mind decreased exertions, restore, and downtime costs.
For small and medium establishments, a reliable Maintenance Software CMMS may be a sport-changer. When paired with Mobile CMMS, it empowers technicians to manage obligations remotely, enhancing performance and real-time updates. The CMMS Maintenance Management System acts because the spine of facility and asset renovation strategies.
Enhancing Control Through Inventory and Work Management
One of the important thing strengths of any CMMS lies in its potential to manipulate inventory and spares. A sturdy Inventory Control Software enables track components, avoid shortages, and optimize procurement. Similarly, Work Order Management Software allows protection teams to generate, assign, and close paintings orders with no trouble, reducing guide mistakes and delays.
Efficient operations depend closely on strategic scheduling. This is in which Maintenance Planning and Scheduling Software comes into play, supporting upkeep heads to prioritize responsibilities and align with manufacturing goals. For teams looking for deeper information, Maintenance Planning and Scheduling Training can sharpen abilties and foster a lifestyle of preventive care.
Smart Software and Training for Maximum Uptime
Even small corporations advantage from adopting Maintenance Software for Small Business, which regularly includes primary but impactful functions like paintings order tracking, preventive scheduling, and asset statistics. For large establishments, Preventive Maintenance Software automates inspections and services, while Predictive Maintenance Software makes use of real-time records and AI to forecast capability disasters.
Operational efficiency isn’t pretty much generation — it’s also approximately humans. Training packages together with Preventive Maintenance Optimization Training, Asset Reliability Training, and Maintenance Management Training empower groups to implement and sustain high-quality practices. Additionally, Root Cause Analysis Training helps upkeep personnel become aware of the source of habitual failures and put into effect long-time period fixes.
0 notes
Text
Best Facility Management Software in Singapore – Top CMMS Solutions
Singapore’s fast-paced business environment demands efficient facility management (FM) solutions to optimize operations, reduce downtime, and enhance productivity. The best facility management software in Singapore combines cutting-edge CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) technology with smart automation to help businesses maintain assets, track work orders, and improve compliance.
Why Singapore Businesses Need Advanced CMMS Facilities Management
Rising Demand for Smart Buildings
Singapore is a leader in smart city initiatives, with over 80% of commercial buildings adopting IoT and AI-driven FM tools. A CMMS facilities management system helps automate maintenance, energy management, and space utilization.
Cost Savings & Efficiency
Companies using CMMS software report 30% lower maintenance costs and 25% improved asset lifespan by preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Regulatory Compliance
Singapore’s strict workplace safety laws (WSH Act) require proper maintenance records. The best facility management software ensures compliance with automated audits and real-time reporting.
Top Features of the Best Facility Management Software in Singapore
Automated Work Order Management – Assign, track, and resolve maintenance requests seamlessly.
Predictive Maintenance – AI-powered alerts reduce equipment failures by up to 50%.
Mobile Accessibility – Manage facilities on-the-go with iOS and Android apps.
Asset Tracking – RFID and barcode scanning for real-time equipment monitoring.
Energy Management – Optimize power usage with smart analytics (saving 15-20% on energy bills).
Leading CMMS Solutions in Singapore
Fiix by Rockwell Automation – AI-driven maintenance with seamless SAP integration.
UpKeep – A mobile-first CMMS ideal for SMEs and large enterprises.
eMaint (Fluke Reliability) – Advanced analytics for predictive maintenance.
Maintenance Connection – Scalable solution for manufacturing and healthcare sectors.
Conclusion
For businesses in Singapore, investing in the best facility management software is no longer optional—it’s a competitive necessity. A CMMS facilities management system enhances efficiency, cuts costs, and ensures compliance in a rapidly evolving market.
Upgrade your FM operations today with a top-tier CMMS solution and stay ahead in Singapore’s smart economy!
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right Facility Management Software for Your Business: CAFM vs. CMMS vs. IWMS
Selecting the right facility management software is critical for organizations aiming to streamline operations, manage assets effectively, and control maintenance costs. With options like CAFM (Computer-Aided Facility Management), CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System), and IWMS (Integrated Workplace Management System), businesses often face uncertainty about which platform best suits their needs. This blog unpacks the distinct features and use cases of each solution to help decision-makers make an informed choice.
CAFM focuses on space and asset management, offering tools for tracking layouts, handling service requests, and optimizing resource usage. It is especially beneficial in industries such as healthcare, education, and real estate where managing large-scale facilities and accurate space planning is essential. CAFM bridges traditional facility management with digital transformation through data visualization, reporting, and centralized operations.
CMMS, on the other hand, is maintenance centric. It’s ideal for industries reliant on machinery like manufacturing, logistics, and energy. CMMS helps schedule preventive maintenance, track asset history, automate work orders, and manage spare parts inventory – all aimed at minimizing equipment downtime and maximizing efficiency.
IWMS is a comprehensive platform integrating facility, workplace, and real estate management. It includes modules for lease administration, energy usage, capital projects, and workforce experience. Built for large enterprises, IWMS centralizes operations across departments and supports long-term strategic planning with advanced analytics.
A comparative analysis reveals that CAFM excels at facility and space management, CMMS specializes in equipment maintenance, and IWMS offers an all-in-one solution for enterprise-level planning and oversight. The choice depends on organizational goals: operational control, equipment reliability, or strategic property management.
Introducing FIESA, a modern facility management and field service automation platform powered by CAFM capabilities. FIESA offers real-time job tracking, mobile support for technicians, automated maintenance workflows, and centralized asset visibility making it ideal for businesses seeking efficiency and scalability.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between CAFM, CMMS, and IWMS is crucial for choosing the right tool. Whether you manage daily facility operations, prioritize maintenance uptime, or oversee large property portfolios, the right software will drive operational success and FIESA offers a powerful, adaptable solution for today’s facility management challenges.
0 notes
Text

Effective maintenance key performance indicators tracking and analysis are fundamental for long-term success in maintenance management. These maintenance KPIs yield important insights about your maintenance operations, thereby showing you areas of inefficiency, unplanned downtime, and reduced equipment reliability. With contemporary tools such as a computerized maintenance management system or preventive maintenance software, facility managers can track the maintenance KPIs in real time, thus ensuring optimal allocation of resources and measurable progress.
Innomaint - Pinnacle Infotech Product Elcot IT Park, Plot No 5,6,7 & 8 Near Madurai Kamaraj University Vadapalanji, Madurai, Tamil Nadu – 625021 innomaint.com +917539978399
#MaintenanceKPI#FacilityManagement#CMMS#AssetManagement#MaintenanceStrategy#PlannedMaintenance#PreventiveMaintenance#PredictiveMaintenance#MaintenanceMatters#SmartMaintenance#DataDrivenMaintenance#OperationalExcellence#MaintenanceMetrics#MaintenancePerformance#MaintenanceAnalytics#AssetPerformance#EquipmentEfficiency#OEE#DowntimeReduction#EfficiencyMetrics#FacilitiesManagement#MaintenanceManagers#FacilityOps#BusinessContinuity#MaintenanceROI#CostEfficiency#FacilityProductivity#MaintenanceInnovation#MaintenanceGoals#WorkOrderTracking
0 notes
Text
Understanding Maintenance Management: A Key Component in Operational Excellence
In the modern industrial and commercial world, the importance of maintenance management cannot be overstated. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and productivity of assets and infrastructure. Whether it’s a manufacturing plant, a hospital, a commercial building, or even a fleet of vehicles, maintenance is necessary to keep systems running smoothly and to avoid costly breakdowns. But more than just routine repairs, maintenance management is a structured approach to preserving and enhancing the value of an organization’s physical assets.
What is Maintenance Management?
Maintenance management is the process of planning, controlling, and executing maintenance activities in a way that optimizes the use of resources while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. It involves everything from regular inspections and preventative maintenance to emergency repairs and long-term infrastructure planning.
The goal of maintenance management is to ensure that assets continue to perform their intended functions with minimal interruption, maximum safety, and at the lowest possible cost. It combines technical knowledge with strategic planning and data analysis to improve reliability and extend the life of equipment.
Types of Maintenance Strategies
There are several maintenance strategies that organizations may adopt depending on their specific needs, budget, and risk tolerance:
Reactive Maintenance: Often referred to as "run-to-failure," this involves fixing equipment only after it breaks down. While this may be acceptable for non-critical assets, it can lead to expensive repairs and unexpected downtime.
Preventive Maintenance (PM): This strategy is based on regular inspections and servicing to prevent equipment failure. It is time-based and follows a set schedule regardless of the actual condition of the asset.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM): This approach uses data from sensors and analytics tools to predict when an asset is likely to fail, allowing maintenance to be performed just in time. It reduces unnecessary maintenance and prevents unplanned failures.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM): Similar to predictive maintenance, CBM relies on real-time monitoring of an asset’s condition to determine when maintenance is necessary.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM): A comprehensive approach that considers the function of an asset, the ways it can fail, and the consequences of failure, aiming to develop a customized maintenance strategy that optimally balances cost, risk, and performance.
Benefits of Effective Maintenance Management
An effective maintenance management system can deliver numerous benefits to an organization:
Reduced Downtime: By proactively identifying and addressing potential issues, equipment is less likely to fail unexpectedly.
Extended Asset Life: Regular maintenance reduces wear and tear, thus prolonging the life span of critical assets.
Lower Costs: Planned maintenance is generally less expensive than emergency repairs, and it helps avoid production losses.
Improved Safety: Well-maintained equipment is less likely to pose safety hazards to workers and the environment.
Increased Efficiency: Properly functioning machinery and systems ensure that operations run smoothly and without disruption.
The Role of Technology in Maintenance Management
Modern technology has revolutionized maintenance management, making it more data-driven and predictive than ever before. Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are software tools that help organizations track maintenance tasks, schedule inspections, manage spare parts inventory, and generate reports.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning has further advanced the capabilities of maintenance management systems. These technologies allow real-time monitoring, fault detection, and automatic alerts, enabling organizations to make smarter maintenance decisions.
Challenges in Maintenance Management
Despite its importance, maintenance management is not without challenges. Organizations often struggle with:
Lack of Skilled Personnel: Maintenance requires technical expertise, and a shortage of skilled technicians can affect efficiency.
Budget Constraints: Limited financial resources may lead to deferred maintenance, which can cause long-term damage.
Resistance to Change: Implementing new systems or changing existing processes can meet resistance from staff accustomed to traditional methods.
Data Overload: With the abundance of data generated by modern systems, it can be difficult to focus on the most critical information without the right tools.
Best Practices for Maintenance Management
To overcome these challenges and achieve the full benefits of maintenance management, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan: Identify critical assets and define clear maintenance schedules and procedures.
Invest in Training: Ensure that maintenance staff are trained in the latest techniques and technologies.
Utilize CMMS Tools: Use digital tools to automate and streamline maintenance activities.
Monitor Performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) to measure effectiveness.
Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage regular feedback and updates to maintenance practices based on performance data.
Conclusion
Maintenance management is more than just fixing what's broken; it’s a strategic function that supports the overall success of an organization. By implementing structured maintenance strategies and embracing modern technologies, businesses can increase operational reliability, reduce costs, and improve safety. As industries continue to evolve, so too must our approach to maintaining the equipment and infrastructure that support them. Investing in strong maintenance management is not just a smart decision—it's a critical component of long-term organizational resilience and growth.
0 notes
Text
If you're a facility manager, you know that facility management software maintenance challenges can feel like an endless game of Whac-a-Mole. When you think one problem is under control, another pops up to disrupt operations, deplete resources, and increase costs.
#facility asset management software#facility management software#computerized maintenance management system
0 notes
Text
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya for tech startups and corporates?

What is ISO 27001 Certification?
ISO 27001 certification in Kenya is the worldwide standard for overseeing data security. It traces how organizations can methodicallly secure data assets—client information, mental property, or inner systems—from unauthorized get to, breaches, and misuse.
With ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya, you can illustrate that your organization meets the worldwide best practices for information security, risk management, and administrative compliance.
Why ISO 27001 Certification is Pivotal in Kenya
ISO 27001 consultant in Kenya is a developing center for tech advancement, advanced healthcare, well-being tech, and cloud services. But as computerized operations extend, so do the risks.
ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya makes a difference to companies:
Comply with the ISO 27001 consultant in Kenya Information Assurance Act (2019)
Prevent security breaches and information leaks.
Build client and controller confidence.
Win competitive offers from corporate clients, givers, and open entities.
Meet worldwide guidelines for information administration and data security.
Who Ought to Seek ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya?
ISO 27001 consultant services in Kenya applies to any organization that handles sensitive information, especially in:
Fintech & managing account services
Software improvement & IT companies
Telecommunications & cloud hosting
Government organizations & parastatals
Hospitals & healthcare providers
Universities, colleges & research institutions
NGOs, benefactor organizations, and worldwide missions
How to Get ISO 27001 Certified in Kenya
Step 1: Crevice Analysis
Assess your current frameworks and controls against ISO 27001 consultant services in Kenya requirements.
Step 2: Chance Assessment
Identify and assess data security dangers. Create a moderation plan.
Step 3: ISMS Documentation
Create arrangements, strategies, chance registers, and specialized records.
Step 4: Staff Preparing & Inside Audit
Train representatives and perform internal reviews to get ready for certification.
Step 5: Certification Audit
Engage a certified certification body to survey your ISMS implementation.
Step 6: Certification & Maintenance
Receive ISO 27001 auditor in Kenya for 3 years, with yearly observation audits.
Documentation Required for ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya
Information Security Policy
Risk Evaluation & Hazard Treatment Plan
Statement of Pertinence (SoA)
Asset Inventory
Access Control Policies
Incident Reaction Plans
Internal Review Reports
Legal & Administrative Compliance Enlist
Why Factocert for ISO 27001 Certification in Kenya?
We provide the best ISO Consultants in Kenya who are knowledgeable and provide the best solutions. Kindly contact us at [email protected]. ISO Certification consultants in Kenya and ISO auditors in Kenya work according to ISO standards and help organizations implement ISO Certification with proper documentation.
For more information, visit ISO 27001 certification in Kenya
0 notes
Text
In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, ensuring the continuous operation and longevity of equipment is critical for success. One of the key pillars that supports this goal is maintenance management. It is a systematic approach to planning, scheduling, and overseeing all activities involved in the upkeep of assets, equipment, and facilities. Effective maintenance management not only reduces downtime and repair costs but also ensures the safety of workers and the consistent quality of products and services.
Maintenance management involves a range of tasks, from routine inspections and preventive maintenance to corrective actions and strategic planning. The primary objective is to keep equipment running at optimal performance with minimal unexpected breakdowns. Companies that implement well-structured maintenance strategies often experience increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and a higher return on investment.
There are several types of maintenance that fall under the umbrella of maintenance management. These include preventive maintenance, which involves regular and scheduled inspections or services to prevent equipment failure; predictive maintenance, which uses data and technology such as sensors and analytics to predict equipment failure before it occurs; and corrective maintenance, which addresses issues after a problem has already happened. A well-rounded maintenance management system incorporates all of these approaches to ensure balanced and effective asset care.
One of the most important tools in maintenance management today is Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS). These software applications help maintenance managers plan, track, and analyze maintenance activities. With a CMMS, businesses can monitor equipment performance, schedule routine inspections, track work orders, manage inventory of spare parts, and even evaluate maintenance costs. This data-driven approach increases efficiency, minimizes waste, and allows for better decision-making.
Another key aspect of maintenance management is workforce planning and training. Skilled maintenance personnel are essential to the success of any maintenance program. Employees must be trained not only in the technical aspects of their jobs but also in safety procedures and the use of maintenance software. Ongoing training and development ensure that the workforce remains competent and capable of handling evolving technologies and complex equipment.
Furthermore, the role of maintenance management is closely tied to safety and compliance. Equipment that is not properly maintained can pose significant safety risks to employees and the environment. Many industries, such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and aviation, are subject to strict regulations that require thorough documentation and regular inspections. Maintenance management ensures that these requirements are met, helping organizations avoid legal issues, fines, and reputational damage.
One of the major challenges faced in maintenance management is balancing cost with performance. While regular maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns, it also requires investment in time, labor, and resources. This is where strategic planning comes into play. Maintenance managers must analyze data, prioritize tasks based on risk and criticality, and allocate resources efficiently. By adopting a risk-based approach, companies can focus on the most vital assets and avoid over-maintenance of non-critical equipment.
In recent years, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the field of maintenance management. Smart sensors and connected devices now allow for real-time monitoring of equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance at an unprecedented scale. These technologies not only reduce maintenance costs but also enhance overall operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and extending asset life.
In conclusion, maintenance management plays a vital role in the success of modern industries. It encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and safety of equipment and facilities. By investing in advanced tools, skilled personnel, and strategic planning, organizations can build a proactive maintenance culture that drives productivity and long-term growth. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of effective maintenance management will only grow, making it a cornerstone of sustainable business operations.
0 notes
Text
Explore The Different Versions of Tally Prime
Tally is a leading accounting software solution that has significantly evolved over the years, becoming an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Its ability to manage complex accounting requirements has led to various updates and version releases to adapt to the changing business landscape. In this blog, we will delve into the different versions of Tally, and their unique features.
Tally 4.5: The Beginning:
Tally 4.5 was the first version introduced in the early 1980s. It was a basic accounting software running on MS-DOS, designed to handle simple accounting tasks like ledgers, vouchers, and financial reports. Despite its simplicity, it laid the foundation for more sophisticated versions, marking the beginning of computerized accounting.
Key Features:
Basic Accounting: Allowed ledger maintenance and basic financial reports.
Easy-to-Use Interface: Designed for simplicity and ease of navigation, ensuring accessibility for non-technical users.
Tally 5.4: The Shift to Windows
The next significant milestone was Tally 5.4, launched in 1996. This version marked the transition from DOS to Windows, introducing a graphical user interface (GUI) that made the software more visually appealing and easier to use.
Key Features:
Graphical User Interface: Improved usability and user experience.
Inventory Management: Included inventory tracking, enhancing the scope of the software.
Tally 6.3: Introduction of VAT
Tally 6.3, launched in 2001, introduced Value Added Tax (VAT) capabilities, enabling businesses to manage tax calculations and compliance more effectively. This version also brought significant enhancements, notably the capability to support multiple users and enhanced security features. These improvements made Tally 6.3 more robust and reliable for its users.
Key Features:
Multi-User Support: Enabled multiple users to work on the software simultaneously.
VAT Compliance: Included features to manage VAT, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Tally 7.2: Integrated Enterprise System
Tally 7.2, introduced in 2005, was a significant upgrade that offered a more integrated approach to business management. This version included modules for VAT, TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), TCS (Tax Collected at Source), and Service Tax, providing businesses with comprehensive tools for managing various tax requirements.
Key Features:
Integrated Tax Modules: Introduced features for managing VAT, TDS, TCS, and Service Tax.
Enhanced Reporting: Improved reporting capabilities for better financial analysis and decision-making.
Tally 8.1: The Power of Payroll
The introduction of Tally 8.1 in 2006, significantly expanded the software’s capabilities by incorporating payroll management. This enhancement allowed businesses to manage employee payroll, statutory deductions, and salary computations seamlessly. Additionally, Tally 8.1 included multilingual support, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Key Features:
Payroll Management: Included features for salary processing and statutory compliance related to payroll.
Improved User Interface: Continued enhancements to the user interface for better usability.
Tally 9: Comprehensive Business Management
Tally 9, launched in 2006, was a comprehensive business management solution that extended beyond accounting to include features like Point of Sale (POS), job costing, and multi-currency support. This version aimed to meet the diverse needs of growing businesses by offering an all-in-one solution.
Key Features:
All-In-One Solution: Combined accounting, inventory, payroll, and compliance features.
POS (Point of Sale) Capabilities: Streamlined retail transactions with a user-friendly interface for efficient sales, invoicing, and inventory management.
Tally ERP 9: The Game Changer
Tally ERP 9, introduced in 2009, is arguably the most popular version, known for its extensive range of features and capabilities. It is a complete ERP solution that covers accounting, inventory, payroll, and statutory compliance, among other functions. Tally ERP 9 is designed to streamline complex business operations and improve overall efficiency.
Key Features:
Comprehensive ERP: Included modules for accounting, inventory, payroll, manufacturing, and more.
Remote Access: Enabled users to access the software remotely, enhancing flexibility.
Tally Prime: The Modern Solution
The latest iteration, Tally Prime, launched in 2020, representing a significant leap in terms of user experience, flexibility, and features. With a redesigned interface and enhanced functionalities, Tally Prime aims to simplify business management even further, ensuring it is user-friendly for individuals at all skill levels.
Key Features:
Enhanced User Interface: Modern and intuitive design for better usability.
Advanced Reporting: Provides powerful reporting capabilities for better decision-making.
Integration Capabilities: Easily integrates with other business applications.
Choosing the Right Tally Version
When considering which Tally version to buy, businesses should assess their specific needs and requirements. Whether opting for Tally ERP 9 for its comprehensive business management features or Tally Prime for its modern interface and performance, selecting the right version can significantly impact a business’s efficiency and effectiveness.
iZoe: Your Trusted Tally Partner
As an authorized Tally partner, iZoe offers a range of Tally services to help businesses maximize the benefits of this powerful software. Whether you want to buy Tally, manage your Tally license, or need support, iZoe has got you covered. Our team of experts ensures that you get the most out of your Tally investment, with services tailored to meet your specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of Tally highlights its focus on innovation and catering to the diverse needs of businesses. From its early versions to the latest Tally Prime, each release has brought valuable features and improvements that enhance business management. By choosing the right Tally version and partnering with experts like iZoe, businesses can leverage Tally’s capabilities to achieve greater efficiency and success.
0 notes
Text

🛠️ Web-Based CMMS Software: Transforming Maintenance Management!
Struggling with equipment downtime, unorganized maintenance schedules, or high operational costs? A Web-Based CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) is the solution your business needs to streamline maintenance operations and boost efficiency.
💡 Why Choose a Web-Based CMMS? ✅ Centralized Asset Management – Track & maintain all assets in one place ✅ Automated Work Orders – Schedule & assign maintenance tasks effortlessly ✅ Real-time Monitoring – Access reports & analytics from anywhere ✅ Preventive Maintenance – Reduce unexpected breakdowns & repair costs ✅ Cloud-Based Accessibility – Secure data access anytime, from any device
🔹 Looking for a tailored CMMS solution? At Sun Shine IT Solution, we develop scalable, web-based CMMS software to optimize your maintenance workflow.
Please explore our YouTube channel for informative videos. Link :- https://www.youtube.com/@sunshineitsolutions
Visit our blog for informative business ideas https://www.blog.sunshiene.com/
Contact Us :- https://wa.me/+91-7230068888
WhatsApp Channel ( Subscribe for more updates ) https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Vb0QMGg0bIdggODhE22T
0 notes
Text
What is Enterprise Asset Management?
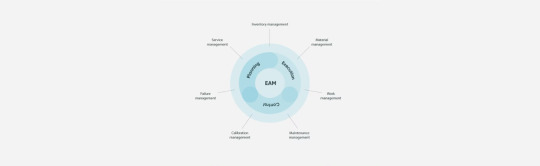
Enterprise Asset Management has a future in the cloud with SaaS services, as organizations are rapidly migrating to the cloud and services that are managed from a centralized location—ideal for asset management. Data needs can be more easily accommodated using cloud software, as there is flexibility in storage options and storage expansion.
An EAM system should be applied for better planning, execution, tracking, and optimization of assets and parts. EAM can sometimes be compared to computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), but there is a distinct difference between the two. EAM software and its holistic view can account for MRO parts and materials management, asset lifecycle management, service contracts, financial management, and analytics. EAM oversees assets and supports their performance from beginning to end, including a hierarchical asset database, inventory levels, utilization, and location as well associated documentation, work orders, and maintenance plans. CMMS are generally considered to be small-scale, single-site applications for work orders with less functionality overall.
0 notes