#FastChargingSoftwareSolutions
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU)
October 25, 2024
by dorleco
with no comment
eMOBILITY CONTROLS
Edit
Introduction

To maintain smooth and effective operation, a vehicle controller (VC), which integrates several mechanical and electrical components, is a crucial component of modern cars, particularly electric vehicles (EVs). The Vehicle Controller facilitates smooth communication between mechanical and electrical systems by combining the functions of a Driver Control Unit (DCU) and a Powertrain Control Unit (PCU). It regulates essential functions to guarantee peak performance, much like a carburetor does in gasoline-powered cars.
The vehicle controller is the main component that controls and enhances the functionality of several car systems. It places special emphasis on safety, energy efficiency, and system integration. This crucial technological improvement propels electric vehicles forward, enhancing their environmental advantages, lowering their dependency on non-renewable resources, and fostering creativity in automobile design.
Functions of a Vehicle Controller:
1. Power Distribution:
Depending on system requirements, the vehicle controller controls power distribution among the car’s many systems, ensuring that each part has the energy it needs to operate.
2. Torque and Speed Control:
It converts driver inputs, like brake or throttle, into movements that regulate the torque and speed of the electric motor. The controller helps the vehicle accelerate and decelerate by controlling the amount of electricity delivered to the motor.
3. Battery Management:
The Vehicle Controller serves as a vital battery manager, keeping an eye on the battery’s temperature, voltage, and current flow at all times. This maximizes battery health and performance by ensuring that the battery runs within safe bounds.
4. Management of the Charging System:
The controller controls the current flow and makes sure that the voltage distribution is balanced when the car is charging. This improves the vehicle’s overall performance as well as charging efficiency.
5. Signal and Communication Control:
The Vehicle Controller acts as a communication center, sending vital messages between the driver and the internal systems of the car. It allows the driver to stay up to date on the vehicle’s condition by relaying important information including battery performance, vehicle motion, and charge levels.
6. Regenerative Braking Management:
Regenerative braking systems, which transform kinetic energy into electrical energy to replenish the battery, are found in many electric vehicles. This process is controlled by the vehicle controller, which enhances energy recovery and vehicle efficiency.
7. Smooth Integration of Vehicle Systems:
The vehicle controller makes sure that different mechanical and electrical systems, such as braking, charging, and thermal management systems, integrate smoothly. Coordination of these elements guarantees the vehicle’s successful and efficient operation.
How Does an Electric Vehicle Controller Work?

1. Receiving Inputs from Various Sensors:
The four main sensors that the Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU) gathers data from are:
Motor Speed Sensor: Determines the electric motor’s speed.
Battery Voltage Sensor: Keeps track of the battery’s voltage level.
Throttle Position Sensor: Determines where the throttle pedal is located.
The brake status sensor shows whether the car is moving or not.
2. Data Processing:
The embedded microprocessor in the Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU) processes the data collected by these sensors. The technology uses algorithms to extract useful information like induced torque and motor output. Control signals are created using this data to guide the motor’s activity.
3. Power Conversion in the EV:
The EVC regulates the power electronics that transform the direct current (DC) in the battery into the alternating current (AC) needed by the electric motor.
4. Motor Control:
By altering the frequency and amplitude of the AC provided, the EVC controls the motor’s operation based on the inputs that are received and processed. The motor is guided by these control signals, which enable it to rotate and move the vehicle forward.
5. Battery Management:
To prevent overcharging or deep draining and to guarantee that the battery runs safely and effectively, the EVC is also essential for battery management.
6. Regenerative Braking:
The EVC initiates regenerative braking when the car slows down, which reverses the motor’s action and transforms kinetic energy into electrical energy that is then transferred back to the battery for storage.
What are the Components of an Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU)?
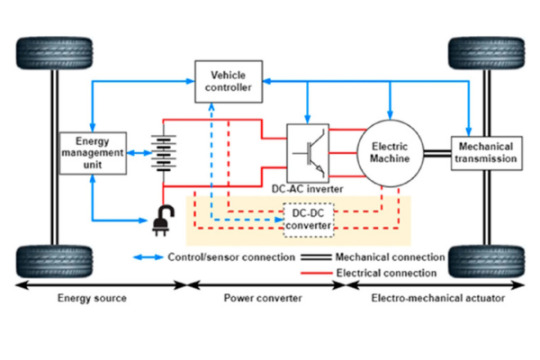
1. Memory:
The memory of an Electric Vehicle Controller (EVC) serves as a data repository, holding crucial data such as fault codes, operating parameters, and algorithms. Making rational decisions and maximizing the vehicle’s performance depends on this recorded data. It functions similarly to the human brain’s hippocampus, which stores memories and learning.
2. Sensors:
One of the most important parts of an Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU) are sensors, which serve as its receptors by gathering data in real-time on a range of operating factors like temperature, motor RPM, battery voltage, and vehicle speed. In reaction to the driver’s inputs, these sensors assist the Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU) in modifying the current supply.
3. Actuators:
Actuators carry out the signals produced by the EV controller, acting as its muscles. They translate control signals into motion and vehicle reactions by managing functions like regenerative braking and torque distribution to the wheels.
4. Power Conversion:
Similar to how the mitochondria, a cell’s powerhouse, supply the energy required for the controller to operate, the power converter regulates the electrical energy flow between the battery and the motor. Additionally, it guarantees effective power distribution, improving the overall performance of the vehicle.
5. Communication Interface:
The EV’s communication interface connects systems like the Battery Management System (BMS) and onboard diagnostics (OBD), much like the human nervous system does. It makes it possible to share vital information, guaranteeing smooth car operations.
6. Cooling System:
The EV’s cooling system controls the heat produced by the controller during heavy workloads, just like the human body uses thermoregulation to control its temperature. The technology preserves the longevity and dependability of the controller by efficiently dispersing heat.
7. Wireless Communication Module:
Similar to the idea of telepathy, EVs’ wireless communication modules facilitate seamless communication and system updates without the need for physical connections by facilitating remote diagnostics, firmware updates, and data exchange with external devices.
Types of Electric Vehicle Controllers

1. Alternating Current (AC) Controllers:
Electric cars that use AC motors are specifically designed to use Alternating Current (AC) controllers. They transform the battery’s DC power into AC power for the motor. Because they are affordable and offer regenerative braking, these controllers are well-liked by EV manufacturers. They are frequently found in automobiles, trucks, and buses.
2. Direct Current (DC) Controllers:
When working with DC motors, direct current (DC) controllers are in charge of controlling the motor’s torque and speed as well as the transfer of DC power from the battery to the motor. High starting torque and quick acceleration are their main advantages, which makes them perfect for motorcycles and scooters.
3. Controllers that are hybrid:
Hybrid controllers are used by hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to manage the communication between electric propulsion systems and internal combustion engines. The integration of both power sources is carefully managed by these controllers in hybrid cars.
4. Inverterless Controllers:
By doing away with conventional inverter powertrains, inverterless controllers simplify the system and cut down on weight and complexity. Because of their greater efficiency, they are especially advantageous for applications that are cost-sensitive and light electric cars.
5. Controllers for Field-Oriented Control (FOC):
FOC controllers are sophisticated devices that use the motor’s magnetic field and induced current to improve motor efficiency and control. Smoother motor running is the result of these controllers’ enhanced torque control and less energy loss.
6. Silicon Carbide (SiC) Controllers:
The silicon carbide technology used in silicon carbide (SiC) controllers provides great thermal conductivity, allowing the controller to manage higher temperatures and voltages. Because of this, the Electric Vehicle Controller (EVC) has a longer lifespan, which makes SiC controllers a great option for reliable, high-performance applications.
Advantages of Using EV Controllers

Modern society has profited immensely from electric vehicles in recent years, and electric vehicle controllers, or EVCs, have been essential to achieving their exceptional efficiency. Let’s examine the benefits that EVCs have provided:
1. Better Outcomes:
Electric vehicle motors can now be controlled in previously unthinkable ways because of the accuracy of EVCs. Smooth signal generation, instantaneous torque delivery, quick acceleration, and an all-around dynamic, responsive, and thrilling driving experience are all made possible by this accuracy.
2. Effective and Dependable Function:
An essential part of electric vehicles, the EVC serves as the engine that propels their potential. It allows EVs to outperform conventional vehicles in terms of performance and dependability when combined with a well-designed battery system.
3. Cost-effective:
EVCs assist in lowering energy usage and operating expenses by effectively controlling power distribution. They are a cost-effective alternative because of their simplified design, which also reduces maintenance costs.
4. Simple to Set Up:
The plug-and-play model, which is common in the electric vehicle sector, is used by EVCs. They are simple to integrate and guarantee a hassle-free setup thanks to their intuitive user interfaces and compatibility with a variety of EV components.
5. Extremely Scalable:
Due to EVCs’ ability to adapt to various motor configurations and battery types, a broad range of electric vehicles, from city cars to more potent machines, may be produced utilizing a comparable design.
6. Future-Ready:
Electric vehicles will undoubtedly continue to develop and get better over time because of the continuous breakthroughs in EVCs and electric automotive technology.
Conclusion:
we have discussed the Electric Vehicle Control Unit(EVCU), its advantages, types, and associated ideas in this blog. In the electric vehicle sector, EVCs are essential for achieving high performance and efficiency levels while upholding safety regulations. The need for electric car controllers is predicted to rise by 50% over the next several years, according to a survey conducted by a reliable source, underscoring their increasing importance.
With continuous developments in EV charging technology resulting in increased efficiency, longer driving ranges, and improved driving experiences, the sector is poised for major breakthroughs. Electric vehicles with cutting-edge EVCs are expected to take over the road as the world moves toward cleaner transportation, opening the door to a more efficient and environmentally friendly future. Stay informed, follow market developments, and get involved in the fascinating transition to sustainable mobility.
#EVCharging#EVSoftwareServices#VCUs#CANKeypads#CANDisplays#FastChargingSoftwareSolutions#EVChargingManagenentSoftware
0 notes
Text
EV Charging Management Software
October 15, 2024
by dorleco
with no comment
eMOBILITY CONTROLS
Edit
Introduction

Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming a major player in the global transportation ecosystem as the world moves toward sustainable energy solutions. Charging is an essential part of owning and using an electric vehicle. While EVs are efficient and convenient, managing the charging infrastructure becomes more difficult as they become more widely used. Software for managing EV charging can be useful in this situation. This technology is intended to improve overall satisfaction for EV owners and charging network operators by optimizing the charging process and energy use. We’ll go into much more detail in this blog about EV charging management software, including its meaning, functions, and potential applications.
What Is EV Charging Management Software?
A platform called EV Charging Management Software keeps track of on, regulates, and enhances the performance of electric car chargers. It makes it possible for network administrators, fleet managers, and owners of charging stations to effectively manage several charging stations, ensuring maximum uptime, energy efficiency, and improved user experiences. Charging management software provides an all-inclusive solution to handle every aspect of modern EV charging, regardless of the kind of charging infrastructure — public charging stations, residential apartments, or corporate EV fleets. With cutting-edge functions like dynamic load balancing, real-time monitoring, user authentication, and reporting, the software offers substantial benefits to all parties involved in the EV charging chain.
Why Is Software for EV Charging Management Important?

The following issues can be used to understand the significance of charging management software:
1. Monitoring and Control:
Real-time monitoring of charging stations is made possible by EV charging management software, which enables operators to keep tabs on the health, efficiency, and energy use of each station. This helps the network’s seamless operation, enabling quick issue response and effective station management.
2. User Management:
The program makes it easier to maintain user accounts and allows users to be divided into different groups, such as VIPs, clients, and workers. Users will enjoy a seamless experience as a result of personalized service, optimized billing methods, payment plans, and access capabilities that are specific to each group.
3. Load management:
By allocating energy optimally, the software avoids grid overloads and lowers energy expenses. By dividing the load among several charging stations, improves grid stability and helps prevent peak demand fees.
4. Payment Management:
This function handles billing and transactions at public charging stations. It accepts credit cards, mobile payments, and subscription payments, among other payment options. It guarantees consumers quick and simple payments, improving their entire billing experience. Remarkably, in a recent UK survey, 47% of electric vehicle drivers said they would be willing to pay a little bit extra for a simpler payment procedure.
5. Analytics and Reporting:
The platform offers comprehensive reporting on performance, financial parameters, and station utilization. These insights support operators in decision-making, enhance the caliber of their services, and identify areas where they can save costs and increase income. Charge point operators (CPOs) and fleet managers can benefit from an all-encompassing solution provided by EV charging management software that integrates these crucial aspects, allowing for the effective administration of charging stations, happy customers, and sustainable growth.
Key Features of EV Charger Management Software
It’s critical to understand the benefits that each feature provides and why they are important for efficient operations while evaluating EV charger management software.
1. Scalability:
The scalability of the software is important because it lets operators handle more charging stations as their network grows. As EV usage rises, the platform must be able to accommodate future growth without requiring regular changes. This ensures just that. Another important feature is multi-location capability, which makes it possible to control stations in different parts of the world from a single, centralized platform. For operators managing large networks, this minimizes administrative effort while preserving constant service quality.
2. User-friendly interface:
Both users and administrators need to be able to easily get around the interface. A user-friendly dashboard reduces training time and operational errors by simplifying management and navigation. The main functions of the software may be accessed and used with ease thanks to an intuitive interface, which raises user satisfaction and encourages more frequent use. Users can find, book, and pay for charging sessions while they’re on the road thanks to integration with mobile apps, which further increases convenience. In today’s mobile-focused world, user engagement and happiness are greatly increased by this accessibility and usefulness.
3. Advanced analytics:
The efficacy of EV charging management software depends on advanced analytics. Fast decision-making and problem-solving are made possible by real-time data, which provides up-to-date information on charging sessions, station utilization, energy consumption, and income creation. These observations are essential to guaranteeing the charging network’s dependability and effectiveness.
4. Predictive maintenance:
Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and prolongs the life of charging equipment by forecasting and proactively solving maintenance needs. By avoiding unexpected malfunctions and costly repairs, this strategy helps to maximize charging station uptime. The proper software may significantly reduce the number of public charging session failures, which are related to station malfunctions and outages in over 71% of cases. Furthermore, information on usage and charging sessions supports CPOs in effectively expanding their charging networks and assists with fleet electrification planning.
5. White labeling:

White labeling enables operators to customize the software with their brandings, such as logos and color schemes. This customization boosts brand recognition and fosters customer loyalty by delivering a unique, personalized user experience. A branded interface helps operators distinguish their services from competitors and cultivate a loyal customer base. White labeling also ensures alignment with the operator’s existing offerings, reinforcing trust and reliability. This tailored approach enhances marketability and improves user satisfaction, ultimately supporting long-term business growth.
Charger interoperability:
When selecting EV charging management software, charger interoperability is crucial. For the software to continue to function with a variety of charger types and retain operational flexibility and efficiency, it must work effortlessly. The industry-standard protocol that ensures compatibility between management systems and charging stations is called Open Charge Point Protocol, or OCPP. The software’s ability to interact with various charger models and support OCPP facilitates network expansion and the integration of new technologies. By ensuring that the charging infrastructure can adjust to a variety of devices, this degree of interoperability reduces compatibility problems and provides a more adaptable and long-lasting solution.
The Role of EV Charging Management Software in Fleet Management
Another domain in which EV charging management software is essential is fleet management. Businesses that run sizable fleets of electric cars must make sure that all of their cars are charged and operational to avoid downtime or inefficiency. How the software aids in EV fleet management is as follows:
1. Enhanced Planning for Charging
The timing of charging has a big financial influence on fleets. With the use of charging management software, schedules can be optimized to charge cars at cheaper electricity prices during off-peak hours. Additionally, depending on the demand for anticipated travel, the system can prioritize which vehicles need to be charged first.
2. Energy Cost Management
One of the biggest costs for fleet operators is electricity. With the use of the software’s comprehensive data on energy usage, managers may spot trends and modify their charging schedules accordingly. Integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, can also assist in reducing expenses and raising sustainability indicators.
3. Tracking Vehicle Status

A fleet manager needs to know which cars are charged and prepared. The fleet can always remain operational by using charging management software, which can offer real-time data on each vehicle’s condition. This minimizes downtime while maximizing companies’ use of EVs.
Conclusion:
EV charging management software is an essential component of the electric vehicle ecosystem, providing a comprehensive solution for managing the complexities of charging infrastructure, whether for individual users, public networks, or large fleets. As the EV market continues to expand, this software will play an increasingly critical role in optimizing energy usage, enhancing user experiences, and ensuring the scalability of charging networks. For businesses, municipalities, and fleet operators aiming to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving EV landscape, investing in robust charging management software is no longer optional — it is a strategic necessity. At Dorleco, we offer fast-charging software solutions along with a range of EV products, including Vehicle Control Units (VCUs), CAN Displays, and CAN Keypads. Additionally, we provide specialized EV software services to meet the demands of the growing electric vehicle market.
#EVCharging#EVSoftwareServices#VCUs#CANKeypads#CANDisplays#FastChargingSoftwareSolutions#EVChargingManagenentSoftware
0 notes