#OppoSuperVOOC
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Phone functionality, charging usability, battery life and battery longevity

For more than ten years, smartphones have confidently dominated in popularity in the consumer electronics segment. Of course, companies adequately respond to demand by offering a huge assortment of different models in all price segments. Today, more than 600 companies design and manufacture these devices. But almost 80% of the global market belongs to only 10 companies. This list includes South Korean Samsung (19%) and LG (3%), American Apple (12%), Finnish Nokia (1%) and Chinese Huawei (13%, including Honor), Xiaomi (9%), Oppo (9%), Vivo (8%), Lenovo (3%, including Motorola), OnePlus(1%), and Tecno (1%). As a result, this situation provoked an unprecedented competition level, forcing companies to invest huge resources in innovative technologies. In turn, innovation provides an extension of functionality, which is traditionally one of the essential components of the competitiveness for any device. As a consequence, the phone quickly transformed into a pocket PC with excellent media capabilities. Projector mobile phones with a projector function, cameraphones with a complex but highly effective digital image processing, liquid-cooled gaming smartphones perfectly illustrate this trend.

As a result, the companies constantly improve specs of their components, including screen resolution and size, processor performance, etc. The performance of the latest Kirin 990 5G or Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 plus processors demonstrates the swiftness of this process.

Phone longevity vs battery longevity
Unfortunately, these positive aspects have a flip side. For example, a processor and a large screen consume a lot of energy during shooting (digital processing), watching, games, etc. As a result, companies increase the battery capacity and developing energy-saving algorithms. Today, many flagships already use batteries with a capacity of 4500-5000 mAh. Moreover, the Blackview P10000 Pro uses a battery with an unprecedented capacity of 11,000 mAh.

Android 10 dark theme saves up to 50% charge for OLED screens. However, modern smartphones rarely work even for one day in energy-intensive modes. As a result, the user is often forced to recharge the battery, rapidly consuming its resource (about 500 full cycles). As known, the battery degradation after 500 cycles reduces its capacity to 80%. Of course, this factor shortens battery life and increases the number of charge cycles, further accelerating its degradation. In the budget segment, the frequent change of smartphone partially compensates for this problem. Many change 200-dollar models in 1-2 years. Usually, the battery simply does not have time to completely degrade. Unfortunately, the flagships priced at about $ 1,000 change much less frequently. In addition, the non-removable batteries in recent models has further exacerbated the problem of its replacement. As a result, many owners of expensive smartphones in a year are faced with the unpleasant problem of replacing the battery. Of course, following some simple rules increases battery longevity, but does not solve the problem radically. Today, the duration of using even an mid-budget smartphone for 2-3 years significantly exceeds its battery longevity in case of active use of energy-intensive modes. But buying an expensive multifunctional smartphone just for talking is also hardly advisable. This contradiction requires a reasonable compromise.
Quick charge
Regular charging of a high-capacity battery lasts long enough, significantly reducing the model usability. A few years ago, companies realized this problem and without much fuss began to solve it. As a result, almost all large companies have developed and implemented fast charging technologies. Today Qualcomm Quick Charge is one of the leaders in this direction. However, Huawei SuperCharge, Oppo Super VOOC, etc do not lag behind the leader, offering elegant solutions. For example, Huawei uses 8-layer thermal insulation, Oppo - a parallel charge of a 2-component battery. Both solutions reduce battery heating during charging. As known, temperature above 30° C accelerates its degradation. But overall, fast charging usually shortens battery longevity. Initially, many companies considered fast charging as an opportunity to urgently recharge the phone. But this very convenient technology quickly became the dominant way of charging. Unfortunately, it has a significant drawback. Fast charging uses increased power from 18 W and above. In particular, Power Delivery 3.0 standard sets the range for voltage and current of 5 - 20 V and 1.8 - 5 A, providing maximum power up to 100W. Unfortunately, charging with increased power is accompanied by battery heating. In addition, the regular 5-watt (1A x 5V) battery recharging psychologically limits many users who do not want to spend time on long recharging. The absence of this restriction stimulates a more active use of energy-intensive modes (games, photos and video shooting, watching videos), speeding up the consumption of 500 battery charging cycles. Of course, the psychological readiness of the user to replace the battery or phone in 1-1.5 years eliminates the problem. Worse if this news comes as a surprise to him. In any case, companies are unlikely to significantly reduce the usability of their models by abandoning this technology.
The main reasons for reducing battery life
1. Battery degradation In Android models the *#*#4636#*#* combination activates the menu with the “Battery Information” item. It contains information about the battery level, temperature, etc. Settings for iPhone models with iOS version 11.3 and higher also contain similar information. 2. Using the smartphone at low temperatures or in the heat adversely affects the battery life. As a rule, specs contain data on the range of recommended temperatures.
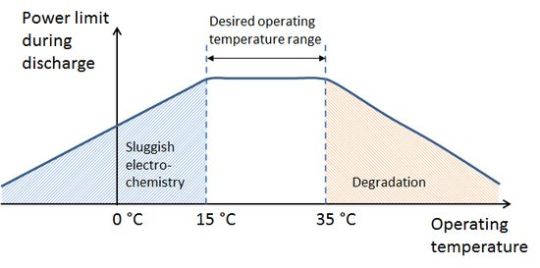
In addition, the optional case will additionally protect the phone from the cold. 3. A very bright screen with settings up to 100% quickly discharges the battery. Setting the display brightness at a level of 50-60% solves this problem. 4. Energy-intensive modes. Of course, active processor operation in games or in processing algorithms during shooting radically increases power consumption. But Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and NFC also increase the load. Deactivating them in the settings will reduce consumption. 5. Unstable cellular requires its constant search with high power consumption. In addition, the GPS sensor consumes a lot of energy even with a good signal. Deactivating it will also significantly reduce power consumption. 6. Many mobile viruses deliberately discharges the battery. An effective antivirus will easily solve this problem.
Ways to increase battery life
1. Battery calibration As a result of calibration, the phone remembers the required charge level. Today, the Internet offers several such programs, including the popular Battery Monitor. This algorithm includes the following steps: - specify the battery capacity; - install Battery Monitor; - controlling the charge level with its help, charge the battery to max; - restart the smartphone. 2. Updating the OS Typically, newer versions increase energy efficiency. Moreover, many companies, including Samsung and Apple, automatically offer updates. 3. Removing unused apps clears memory and reduces power consumption. 4. Energy-saving programs. Today they most effectively provide increased battery life by minimizing power consumption and prolonging battery longevity by monitoring its condition. The list of the most popular programs includes: - Greenify - runs in the background, disabling unused processes.

- DU Battery Saver - deactivates background processes and displays battery information. A separate button disables any energy-intensive utilities;
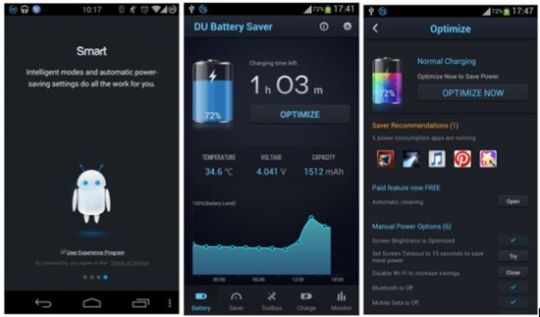
- Amplify Battery Extender - automatically disables all unnecessary processes and has manual settings; - GO Battery Saver - has several profiles to reduce power consumption.

Conclusion
Limited use of energy-intensive modes, periodic calibration, cleaning the memory, OS upgrade, effective antivirus program, and energy-saving programs will extend battery life. An optimal charge level in the range of 40-80% and a reasonable restriction on the use of fast charging to prevent overheating will increase battery longevity. Ideally, the battery longevity will be equal to the phone usage period, eliminating the need to replace a non-removable battery. But, of course, a little share of German pedantry will increase the efficiency of these simple recommendations. This video shows the battery calibration on rooted Android phone. Read the full article
#AmplifyBatteryExtender#batterycalibration#batterylife#batterylongevity#BatteryMonitor#DUBatterySaver#GOBatterySaver#Greenify#HuaweiSuperCharge#OppoSuperVOOC#PowerDelivery3.0#QualcommQuickCharge
0 notes
Text
OPPO's 240W New Fast Charging Tech
OPPO Announced their record breaking 240W fast charging technology, check details here #TechEra #oppo #supervooc #opposupervooc #supervooc240W
We already known that OPPO announced 150W super VOOC fast charging Technology and if you want to check that details check from here. Now OPPO announced OPPO’s 240W fast charging tech and breaking Records as well. Company says that with the new charging technology we can fully charge a 4,500mAh smartphone battery in just 9 minutes, which the company claims is a record-breaking achievement. Check…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Технология Oppo Super VOOC позволяет зарядить аккумулятор ёмкостью 2500 мАч за 15 минут
Как и ожидалось, компания Oppo представила на выставке MWС 2016 в Барселоне новое поколение фирменной технологии быстрой зарядки Super VOOC. Во время презентации смартфон с аккумулятором ёмкостью 2 500 мАч был заряжен с 0% до 100% всего за 15 минут, что кажется просто невероятным результатом. Кроме того, пяти минут подзарядки хватает на два часа разговоров по телефону. Oppo уверяет, что эта технология не вредит аккумулятору, в отличие от аналогичных решений от конкурентов.
Super VOOC не использует для зарядки 9 В или 12 В, как это реализовано в технологиях других компаний. Вместо этого зарядка осуществляется на стандартных 5 В, но энергия передаётся непосредственно в саму батарею без преобразования напряжения. Это позволяет увеличить эффективность зарядки на 97%, не причиняя вреда аккумулятору. Для этого в зарядном устройстве используется специаль��ый чип, который и регулирует подачу напряжения. Также производитель уверяет, что в процессе зарядки устройство нагревается всего на 3,3 градуса по Цельсию, и владелец может безопасно использовать в этот момент смартфон без риска возгорания.
Ожидается, что новая технология появится в следующем флагмане компании Find 9, который, к сожалению, на MWC 2016 не представили.
0 notes
Text
Fast charging technologies for a phone battery

Of course, usability is one of the main criteria for choosing any modern device. In turn, the usability of any compact mobile device, including a smartphone, a robot vacuum cleaner, a pico projector, etc directly depends on battery life. As known, this characteristic directly depends on the battery capacity and its quality. At the same time, any battery requires recharging, the convenience of which substantially depends on its duration. As a result, almost all phone manufacturers pay great attention to this aspect, constantly developing and improving charging technologies. The solution to this problem contains several aspects. As known, in the past few years, almost all companies produce smartphones with a non-removable battery. Of course, this design has many pros, but its replacement is quite expensive. This problem is less acute in the segment of budget and mid-budget models due to the relatively short term of their operation. Most often, owners change these models to newer phones in a few years. During this period, the battery specs worsen, but reducing its capacity to 70-80% does not become critical. Of course, expensive models costing about $ 1,000 change much less frequently.
Introduction
Usually, the slow charging of a modern 4,500 mAh battery lasts several hours. But the large screen and many modern functions often discharge it during the day. As a result, recharging the battery becomes troublesome enough for the user. Of course, night slow charging is very convenient. But it negatively affects battery longevity. In this case, 100% battery charge remains until mornings, accelerating its degradation. From this point of view, a charge of 40-80% is optimal for the battery. In addition, battery longevity directly depends on the number of cycles, which usually does not exceed 500 full cycles with a decrease in battery capacity by 20%.

In turn, the number of required cycles depends on the battery discharge time, which is determined by the battery capacity and usage mode. To solve these problems, companies have developed fast charging technologies. Unfortunately, fast charging uses increased voltage and current to increase power. For example, a classic charger typically uses a voltage of 5 V and a current of 2 to 2.5 A. For fast charging, these values can reach 20V and 5A, respectively. In turn, an increase in power increases the battery temperature, accelerating its degradation.
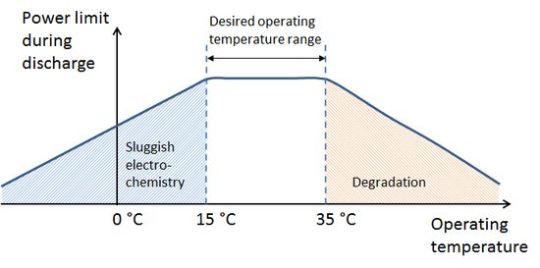
Therefore, companies are forced to choose a compromise between charging speed and temperature. Today, the main direction of improving technology is concentrated in this direction.
Main technologies
Today, the market offers about a dozen different fast-charging technologies. Therefore, the charger must support appropriate smartphone fast charging technology and data exchange protocol. But in any case, almost all chargers support the basic slow mode with a voltage of 5 V and a current of 2-3 A. Of course, a variety of technologies contributes to healthy competition, but complicates the choice of consumers. Moreover, the use of a non-original cable can be dangerous for a smartphone due to insufficient limitation of the maximum current. Today Qualcomm, MediaTek, Samsung, Oppo, Huawei, Meizu, Lenovo (Motorola) and some other companies use their own fast charging technologies. In fact, all technologies use the same method, reducing charging time by increasing power, increasing current and voltage for this purpose. But companies solve this problem in different ways, finding a compromise between a marketing reduction in charge time and reasonable sufficiency in terms of battery overheating. Mostly, engineers optimize the charging algorithm, minimizing the risk of overheating.

In addition, some companies find original solutions. For example, OPPO VOOC Flash Charging uses an eight-pin battery, separately charging each cell with a current of 4.5 A at a voltage of 5 V. Pump Express works similar to Quick Charge, but with MTK processors, and Huawei's Super Charge with additional cooling provides high-foot speed charging without overheating the battery.

Qualcomm Quick Charge
Qualcomm Quick Charge technology has pioneered in fast charging. Its first version was introduced back in 2013. In fact, the company improves this technology for 7 years.

A Quick Charge-enabled smartphone continuously sends battery status information to the charger. Using it, the power supply optimizes power output by changing voltage and current. Qualcomm calls this technology INOV (Intelligent Negotiation for Optimum Voltage). Unfortunately, Quick Charge does not work with all Snapdragon processors. Today, the last Quick Charge 4+ version supports Snapdragon 660, 670, 710 and 845 chipsets, providing power up to 18 W. For comparison, the power of Huawei SuperCharge reaches 40 W, and Oppo Super VOOC technology provides up to 50 W. At Qualcomm 4G / 5G Summit in Hong Kong, the company announced a Quick Charge 5.0 version with a twofold reduction in charging duration.

In particular, the transmitted power over a wired connection will reach 32 W, and up to 15 W via a wireless charger. In the first case, Quick Charge 5.0 will use Triple Charge technology, dividing the input current into three different streams. Many experts expected her debut in the flagship Snapdragon 855 platform, but it uses Quick Charge 4+. Pros - the company has been improving the technology for 7 years, presenting 6 of its versions; - backward compatibility with earlier versions of Quick Charge; - built-in protection against overheating and shorting the electrodes.
MediaTek Pump Express
This technology charges the battery without a built-in controller. In this case, the power supply controls the temperature and operation mode.

According to the company, MediaTek Pump Express 4.0 reduces the charging time of a smartphone’s battery by 50% or more compared to a standard USB charger. At the same time, Pump Express only supports charging via a USB Type-C port with a current of up to 5 A. In addition, not all MediaTek chipsets support Pump Express. Unfortunately, the company does not publish a complete list of compatible chips. Therefore, for each model, the user is forced to clarify compatibility information with Pump Express. Pump Express 4.0 is compatible with the international USB PD 3.0 standard programmable power supply. Accordingly, all standard chargers with support for fast charging are suitable for smartphones with support for Pump Express 4.0.
Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging
The company developed this technology for the Samsung Galaxy Series. Unlike its competitors, it's fully compatible with all Samsung Exynos processors. Adaptive Fast Charging uses 9V / 2A providing power up to 18 W. The technology provides an average charging speed, but operates at a minimum temperature. As known, this factor directly affects the battery degradation.
Huawei SuperCharge

Huawei shows impressive innovative activity in this direction. SuperCharge technology provides a relatively low charging speed, but it is compatible with USB-PD and has a high level of security. The Huawei Smart Charge protocol automatically selects the charging type supported by the charger. In addition, it analyzes battery capacity and cable bandwidth, and corrects the voltage to suit them. Additionally, SuperCharge uses special components, including an 8-layer thermal insulation. It lower the temperature by about 5 degrees compared to competitors, reducing battery degradation when using fast charging. Mate 9, Huawei P10 and later flagships use this technology. The built- in microchip in the charger automatically adjusts the voltage and current depending on the state and temperature of the smartphone’s battery. SuperCharge compatible chargers work in 5V / 2A, 4.5V / 5A, and 5V / 4.5A modes. According to the XDA Developers website, the technology provides a Mate 9 charge of up to 90% in one hour. Today, Huawei offers three versions, including FCP, SCP 22.5W and SCP 40 W.
Meizu Super mCharge and Oppo Super VOOC
Meizu Super mCharge

At MWC 2017, Meizu announced for the first time its own Super mCharge technology. According to the company, the technology charges a 3000 mAh battery up to 60% in 10 minutes, up to 100% in 20 minutes. The charger provides a voltage of 11 V at a current of 5 A, or a power of 55 watts. According to the company, the technology practically does not accelerate battery degradation, providing 800 charging cycles with a loss of capacity of up to 20%. In addition, the battery temperature does not exceed 39°C during charging. Oppo Super VOOC Super VOOC is not fundamentally different from the previous VOOC generation, which the company calls Dash Charge. As known, Oppo R17 Pro 3400 mAh battery consists of two series-connected cells with a capacity of 1700 mAh. The charger controls the charging process, providing 10V / 5A. Accordingly, the charging power of each cell reaches 25 W. As a result, Super VOOC charges the smartphone in just 35 minutes.

USB Power Delivery (USB-PD)
As known, USB Power Delivery is a modification of the USB standard in terms of transmitted energy. A large number of different fast charging technologies positively affects competition, but is not very convenient for consumers. At best, the use of third-party accessories reduces the effectiveness of the technology. But in some cases, this can damage the smartphone due to overheating of its motherboard. For several years now, Google has been trying to introduce a single standard for fast charging via USB Type-C port for all Android devices. Of course, this will greatly simplify the use of fast charging technology, allowing the user to safely use any PD-enabled charger. The company has already made significant progress in this area. For example, Qualcomm and MediaTek announced the compliance of their Quick Charge 4/4+ and Pump Express 4.0 of USB - PD.
Conclusion
Despite the risk of accelerated battery degradation due to high temperature, fast charging technologies have no alternative. The increasing processor power and the expansion of the phone functionality will continue to be accompanied by an increase in energy consumption. As a result, companies will continue to increase battery capacity, increasing their price. Accordingly, the dilemma between usability with fast powerful charging and a decrease in battery longevity due to heating will only increase, until the appearance of fundamentally new technologies. But today, a new trend has emerged in this segment. Instead of an emergency increase in power and a reduction in charging time, many companies are increasingly choosing a reasonable compromise, limiting power and lowering the temperature to reduce battery degradation. But, of course, the user must adequately understand the initial purpose of this function. It is convenient and useful if you need to quickly recharge the phone, for example, before work. But, of course, in a normal situation, regular 5V / 1A slow charging is preferable in terms of battery degradation. On the other hand, companies are actively looking for ways to solve this problem. For example, Huawei uses an 8-layer thermal insulation in SuperCharge. In addition, some gaming smartphones already use a liquid cooling system. The form factor of Wireless Charging chargers allows developers to use a traditional cooler to cool the battery during charging. As usual, the most effective solution will win. This video shows the VIVO Super FlashCharge 120W Fastest Charge Smartphone. Read the full article
#Fastchargingtechnologies#HuaweiSuperCharge#MediaTekPumpExpress#MeizuSupermCharge#OppoSuperVOOC#QualcommQuickCharge#SamsungAdaptiveFastCharging#USBPowerDelivery#USB-PD#VIVOSuperFlashCharge
0 notes