#Planck&039;s Constant
Text
Ultraviolet Catastrophe
Introduction
The Ultraviolet Catastrophe refers to a historical paradox in the theory of radiation of heated objects. This paradox resulted from the contradiction between the classical physics laws and experimental observations related to black body radiation at the end of the 19th century.
Classical Predictions and the Problem
According to the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation,…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
3 Natural units and equations
New Post has been published on https://theinsightanalysis.com/natural-units/
3 Natural units and equations
Particle physicists have a habit that on the face of it seems to violate physics. They set the values of natural constants such as the speed of light and Planck’s constant to the number one. How can they do this? It’s because the relationship between units by which we measure length, time and energy is a matter of choice.
For example, we know what a second is, and we know what a meter is. But how many meters make a second? Is that like asking how many apples are there in an orange? Maybe. But not quite, because the constants of Nature like Planck’s constant and the speed of light represent natural relationships between different units of measurement, as explained below.
Speed of light
The measured value of the speed of light is
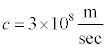
so why would physicists want to pretend that instead c=1? What they are really doing is choosing a relationship between a unit of time, the second, and a unit of space, the meter, so that these two units are not independent but related. The natural constant of relation is the speed of light, so that
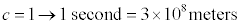
If we relate meters and seconds so that one second is equal to 300 million meters, then c=1. It’s very simple. Now notice that in this system of unit, mass and energy have the same units, because the relationship E = m c2 in units with c=1 just reduces to E = m.
Planck’s constant
Planck’s constant has units of energy x time. The preferred unit of energy in physics is the electron volt (or eV for short) is the amount of work necessary to move one electron across a potential of one volt. For particle physicists, this is a very handy unit because particle experiments use electrical potential to accelerate and bang electrons and other particles with the same charge into each other. In unit with c=1, the mass of the electron is 0.5 MeV. Written in terms of eV, Planck’s constant takes the value
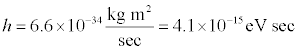
The version of Planck’s constant that physicists normally use is called “h-bar” and is equal to
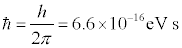
In c=1 units, time is described in meters, the value of Planck’s constant becomes
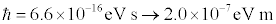
But physicists aren’t happy to stop there. We like to make all calculations as simple as possible. So the next step is set (this version of) Planck’s constant equal to one to set the relationship between energy units and length units so that
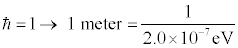
The size of an atom is roughly 10-10 meters. Atomic physicists use a unit called the Ångstrom, where 1 Å = 10-10 meters. Written in these terms we get the relationship
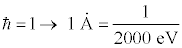
Notice that in these new units, increasing energy means decreasing length. Distances scales that are much smaller than the size of an atom have mass scales associated with them that are much larger than 2000 eV.
That is typical behavior for quantum mechanics. The de Broglie relation for wave-particle duality
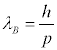
also shows that in quantum physics, it is necessary to use a large energy or momentum scale to probe a small distance scale. That’s why particle accelerators are like microscopes. When the particle accelerator energy gets bigger, the distance scale being probed gets smaller.
Read more: What is Real?: Quantum physics and Reality
Gravity
Can we play the same game with Newton’s gravitational constant? Not really, because there aren’t any new units to relate that aren’t already related. If we consider spacetimes with gravity in higher dimensions, Newton’s constant has units that depend on the dimension of spacetime. The value currently measured is, of course, for d=4.
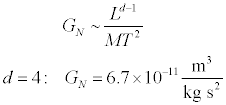
In natural units, Newton’s constant has units of Ld-2, or M2-d.
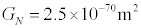
Thus one can express Newton’s constant in units of time, length or mass, as desired.
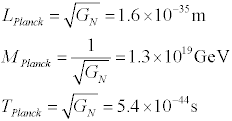
The Planck length is thought to be the natural distance scale at which quantum gravitational effects become strong enough to notice.
0 notes
Text
RISE OF A QUANTUM WORLD
RISE OF A QUANTUM WORLD
#Quantum World that is “Quantum Mechanics” also known as “Quantum Physics” or “Quantum Theory”.
# In Classical Physics, quantum mechanics only validated to macroscopic levels.
# But quantum mechanics differs from classical physics, according to quantum mechanics energy, momentum and restricted to other discrete values.
# Quantum mechanics rose with the rose of a Max Plancks solution for “Black…
View On WordPress
#Classical Physics#Energy#Frequency#Klein-Gordon Equations#Macroscopic Levels#Momentum#Planck&039;s Constant#Quantum Mechanics#Quantum Theory#Schrodinger&039;s Equation
0 notes
Text
Stranger Things— SEASON 3 FINALE: "Chapter Eight - The Battle of Starcourt"
Stranger Things— SEASON 3 FINALE: “Chapter Eight – The Battle of Starcourt”
Netflix’s Stranger Things
Season 3: “Chapter Eight – The Battle of Starcourt”
Directed & Written
by The Duffer Brothers
* For a recap & review of Chapter Seven, “The Bite” – click here
* Season 4. We need it now!
Joyce (Winona Ryder), Murray (Brett Gelman), and Chief Jim (David Harbour) have picked up a transmission from the mall. In…
View On WordPress
#A Wizard of Earthsea#David Harbour#Natalia Dyer#Planck&039;s Constant#Season 3 Finale#Starcourt Mall#The Griswold Family#The Mind Flayer#The NeverEnding Story#Ursula K. Le Guin#Winona Ryder
0 notes
Text
General Relativity united Quantum Mechanics
General Relativity united Quantum Mechanics
* hbar = e^2*z0
* hbar = [(1.6021766(34) x 10^-19 A-s)^2] * (3.767303134… x 10^2 kg-m^2/A^2-s^3)
* hbar = 9.6705540(00) x 10^-36 kg-m^2/s
* hbar = e^2/e0*c
* hbar = [(1.6021766(34) x 10^-19 A-s)^2] / (8.854187817… x 10^-12 A^2-s^4/kg-m^3) * (2.99792458 x 10^8 m/s)
* hbar = 9.6705540(00) x 10^-36 kg-m^2/s
* hbar = e^2*u0*c
* hbar = [(1.6021766(34) x 10^-19 A-s)^2] * (1.256637061… x 10^-6 kg-m/A^2-s^2) * (2.99792458 x 10^8 m/s)
* hbar = 9.6705540(00) x 10^-36 kg-m^2/s
* hbar = h*(2*alpha)
* hbar = (6.6260701(50) x 10^-34 kg-m^2/s-rad) * [(2.00000000 x 10^0 rad/sr) * (7.2973525(66) x 10^-3 sr)]
* hbar = 9.6705540(00) x 10^-36 kg-m^2/s
Universal Fundamental Physical Constants
001) dark luminance = 1.4188976(12) x 10^128 cd/m^2
002) luminous flux density = 1.0354196(13) x 10^126 cd-sr/m^2
003) dark radiance = 2.0774489(19) x 10^125 kg/s^3-sr
004) dark irradiance = 1.5159877(20) x 10^123 kg/s^3
005) luminous density = 3.4537880(62) x 10^117 cd-sr-s/m^3
006) radiant density = 5.0567907(21) x 10^114 kg/m-s^2
007) dark density = 8.5349738(01) x 10^105 /m^3
008) dark matter density = 5.6264384(79) x 10^97 kg/m^3
009) electric current density = 4.0995226(38) x 10^95 A/m^2
010) thermal transfer = 3.5326953(68) x 10^91 kg/s^3-K
011) electric charge density = 1.3674535(60) x 10^87 A-s/m^3
012) angular acceleration = 5.4782038(95) x 10^85 rad/s^2
013) molar concentration = 1.4172657(44) x 10^82 mol/m^3
014) surface tension = 2.4744247(42) x 10^79 kg/s^2
015) dynamic viscosity = 8.2537925(03) x 10^70 kg/m-s
016) inverse dark area = 4.1763939(85) x 10^70 /m^2
017) electric field strength = 7.5572384(43) x 10^62 kg-m/A-s^3
018) surface density = 2.7531688(28) x 10^62 kg/m^2
019) absorption rate = 5.5063376(58) x 10^60 m^2/s^3
020) magnetic field strength = 2.0060075(27) x 10^60 A/m
021) luminous intensity = 3.3974227(93) x 10^57 cd
022) thermal conductivity = 1.7286435(82) x 10^56 kg-m/s^3-K
023) luminous flux = 2.4792191(94) x 10^57 cd-sr
024) radiant intensity = 4.9742647(04) x 10^54 kg-m^2/s^3-sr
025) magnetic flux density = 2.5208234(03) x 10^54 kg/A-s^2
026) dark power = 3.6298963(30) x 10^52 kg-m^2/s^3
027) field acceleration = 1.8367165(39) x 10^52 m/s^2
028) electric flux density = 6.6913208(56) x 10^51 A-s/m^2
029) surface concentration = 6.9350653(75) x 10^46 mol/m^2
030) dark force = 1.2108030(85) x 10^44 kg-m/s^2
031) dark frequency = 6.1266269(04) x 10^43 /s
032) angular velocity = 8.9416313(11) x 10^41 rad/s
033) dark matter flow rate = 4.0388043(55) x 10^35 kg/s
034) wave number = 2.0436227(60) x 10^35 /m
035) electric conductivity = 5.4246305(31) x 10^32 A^2-s^3/kg-m^3
036) molar dark energy = 3.5679905(07) x 10^32 kg-m^2/s^2-mol
037) dark temperature = 4.2913061(04) x 10^31 K
038) electric potential = 3.6979615(76) x 10^27 kg-m^2/A-s^3
039) dark matter field = 1.3472001(20) x 10^27 kg/m
040) electric current = 9.8159384(71) x 10^24 A
041) Avogadro constant = 6.0221407(58) x 10^23 /mol
042) thermal conductance = 8.4587215(23) x 10^20 kg-m^2/s^3-K
043) magnetic potential = 1.2335072(07) x 10^19 kg-m/A-s^2
044) dark displacement = 4.4937758(92) x 10^18 kg-s/m^2
045) dark absorption = 8.987551787… x 10^16 m^2/s^2
046) electric displacement = 3.2742446(35) x 10^16 A-s/m
047) molar dark matter = 3.9699248(38) x 10^15 kg/mol
048) Josephson constant = 4.8359784(84) x 10^14 A-s^2-rad^2/kg-m^2-sr
049) Josephson quantum = 2.4179892(42) x 10^14 A-s^2-rad/kg-m^2
050) luminous energy = 4.0466299(52) x 10^11 cd-sr-s
051) Coulomb constant = 8.987551787… x 10^9 kg-m^3/A^2-s^4-(4pi)
052) dark energy = 5.9247876(31) x 10^8 kg-m^2/s^2
053) speed of light in vacuum = 2.99792458 x 10^8 m/s
054) inverse dark matter = 1.5169407(49) x 10^8 /kg
055) Faraday constant = 9.6485332(08) x 10^4 A-s/mol
056) von Klitzing constant = 2.5812807(46) x 10^4 kg-m^2/A^2-s^3-rad
057) inverse conductance q. = 1.2906403(73) x 10^4 kg-m^2-sr/A^2-s^3-rad^2
058) luminous efficacy = 6.83000000 x 10^2 cd-sr-s^3/kg-m^2
059) impedance of vacuum = 3.767303134… x 10^2 kg-m^2/A^2-s^3
060) inverse fine-structure constant = 1.3703599(91) x 10^2 /sr
061) inverse fine-structure angle = 6.8517999(58) x 10^1 /rad
062) molar gas constant = 8.3144628(25) x 10^0 kg-m^2/s^2-mol-K
063) spin two = 2.00000000 x 10^0 rad/sr
064) dark momentum = 1.9762964(25) x 10^0 kg-m/s
065) relative permeability = 1.00000000 x 10^0 rad/rad
066) dielectric constant = 1.00000000 x 10^0 sr/sr
067) spin one-half = 5.00000000 x 10^-1 sr/rad
068) fine-structure angle = 1.4594705(13) x 10^-2 rad
069) second radiation = 1.4387768(41) x 10^-2 m-K/rad
070) fine-structure constant = 7.2973525(66) x 10^-3 sr
071) inverse luminous efficacy = 1.4641288(43) x 10^-3 kg-m^2/cd-sr-s^3
072) conductance quantum = 7.7480917(31) x 10^-5 A^2-s^3-rad^2/kg-m^2-sr
073) electric conductance = 3.8740458(65) x 10^-5 A^2-s^3-rad/kg-m^2
074) magnetic constant = 1.256637061… x 10^-6 kg-m/A^2-s^2
075) dark matter = 6.5922152(90) x 10^-9 kg
076) radiant distribution = 3.335640952… x 10^-9 s/m
077) inverse dark energy = 1.6878242(09) x 10^-9 s^2/kg-m^2
078) density of states = 1.6878242(09) x 10^-9 s^2/kg-m^2
079) molar Planck constant = 3.9903127(10) x 10^-10 kg-m^2/s-mol-rad
080) atomic permittivity = 1.112650056… x 10^-10 A^2-s^4-(4pi)/kg-m^3
081) Newtonian constant = 6.671281903… x 10^-11 m^3/kg-s^2
082) magnetic pole strength = 4.8032047(13) x 10^-11 A-m
083) magnetic exposure = 2.4304070(23) x 10^-11 A-s/kg
084) electric constant = 8.854187817… x 10^-12 A^2-s^4/kg-m^3
085) magnetic flux = 4.1356676(96) x 10^-15 kg-m^2/A-s^2-rad
086) specific heat = 2.0943627(81) x 10^-15 m^2/s^2-K
087) magnetic flux quantum = 2.0678338(48) x 10^-15 kg-m^2-sr/A-s^2-rad^2
088) first radiation = 3.7417718(52) x 10^-16 kg-m^4-(2pi)/s^3-rad
089) dark molality = 2.5189393(78) x 10^-16 mol/kg
090) first radiation spectral radiance = 1.1910429(72) x 10^-16 kg-m^4/s^3-sr
091) elementary charge = 1.6021766(34) x 10^-19 A-s
092) thermal resistance = 1.1822117(53) x 10^-21 s^3-K/kg-m^2
093) Boltzmann constant = 1.3806490(35) x 10^-23 kg-m^2/s^2-K
094) amount of substance = 1.6605390(68) x 10^-24 mol
095) inverse electric current = 1.0187512(92) x 10^-25 /A
096) kinematic viscosity = 1.4669657(43) x 10^-27 m^2/s
097) electric resistivity = 1.8434435(20) x 10^-33 kg-m^3/A^2-s^3
098) relative expansion = 2.3302928(66) x 10^-32 /K
099) Planck constant = 6.6260701(50) x 10^-34 kg-m^2/s-rad
100) reduced Planck constant = 9.6705540(00) x 10^-36 kg-m^2/s
101) dark length = 4.8932710(07) x 10^-36 m
102) absorption-emission = 2.4759802(95) x 10^-36 s/kg
103) dark inductance = 6.1490656(98) x 10^-42 kg-m^2/A^2-s^2
104) dark moment = 3.2257495(95) x 10^-44 kg-m
105) dark time = 1.6322195(16) x 10^-44 s
106) magnetic moment = 2.3503382(36) x 10^-46 A-m^2
107) dark capacitance = 4.3325940(55) x 10^-47 A^2-s^4/kg-m^2
108) electric moment = 7.8398844(71) x 10^-55 A-s-m
109) inverse luminous intensity = 2.9434075(80) x 10^-58 /cd
110) dark area = 2.3944101(15) x 10^-71 m^2
111) dark fluidity = 1.2115642(59) x 10^-71 m-s/kg
112) inertial moment = 1.5784466(97) x 10^-79 kg-m^2
113) molar volume = 7.0558397(69) x 10^-83 m^3/mol
114) electric charge volume = 7.3128626(05) x 10^-88 m^3/A-s
115) electric current volume = 2.4393083(98) x 10^-96 m^2/A
116) dark matter volume = 1.7773232(64) x 10^-98 m^3/kg
117) dark volume = 1.1716497(59) x 10^-106 m^3
118) radiant volume = 1.9775388(29) x 10^-115 m-s^2/kg
119) inverse dark irradiance = 6.5963595(02) x 10^-124 s^3/kg
120) inverse dark radiance = 4.8135960(94) x 10^-126 s^3-sr/kg
http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/
* luminous intensity: lm/alpha = 3.3974227(93) x 10^57 cd
* dark temperature: [(hbar*c^5/G)^1/2]/k = 4.2913061(04) x 10^31 K
* electric current: e/[(hbar*G/c^5)^1/2] = 9.8159384(71) x 10^24 A
* fine-structure angle: e^2/(e0*h*c) = 1.4594705(13) x 10^-2 rad
* fine-structure constant: e^2/(2*e0*h*c) = 7.2973525(66) x 10-3 sr
* dark matter: (hbar*c/G)^1/2 = 6.5922152(90) x 10^-9 kg
* amount of substance: [(hbar*c/G)^1/2]/M = 1.6605390(68) x 10^-24 mol
* dark length: (hbar*G/c^3)^1/2 = 4.8932710(07) x 10^-36 m
* dark time: (hbar*G/c^5)^1/2 = 1.6322195(16) x 10^-44 s
Derivations,
G-D
0 notes
Text
'New form of light discovered' - Times of India
‘New form of light discovered’ – Times of India
LONDON: In a breakthrough, scientists have discovered a new form of light, which will impact our understanding of the fundamental nature of light.One of the measurable characteristics of a beam of light is known as angular momentum. Until now, it was thought that in all forms of light the angular momentum would be a multiple of Planck’s constant, the physical constant that sets the scale of…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Planck's Constant
Introduction
Planck’s constant, denoted by $h$, is a fundamental constant of nature that plays a central role in the theory of quantum mechanics. It is named after the German physicist Max Planck, who first proposed its existence. Planck’s constant is a measure of the granularity of the physical world at the microscopic level, and it sets the scale for the smallest possible action in the…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

“THE LEGEND BEHIND QUANTA” # Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck was / is the German physicist and born on 23 April 1858.
0 notes
Text
Stranger Things— Season 3: "Chapter Seven - The Bite"
Stranger Things— Season 3: “Chapter Seven – The Bite”
Netflix’s Stranger Things
Season 3: “Chapter Seven – The Bite”
Directed & Written
by The Duffer Brothers
* For a recap & review of Chapter Six, “E Pluribus Unum” – click here
* For a recap & review of the Season 3 finale, click here.
The big July 4th celebration goes off in Hawkins, just as planned by Mayor Larry Kline (Cary Elwes),…
View On WordPress
#StrangerThings3#Back to the Future#New Coke#Planck&039;s Constant#Russian Woodpecker#The Duffer Brothers#The Flayed#The Mind Flayer#Woody Woodpecker
0 notes