#RAMPrice
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
RAM(Random Access Memory)

RAM Is Primary Memory Or Temporary Storage, This Is Called As Random Access Memory.In Order For A Program To Run, It Needs To Be Loaded Into RAM First.

The Data Or The Program Is Stored On The Hard Drive And From The Hard Drive It Is Loaded Into RAM.
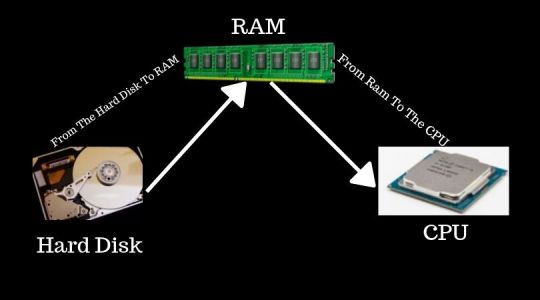
And Once It Is Loaded Into RAM, The CPU Can Access The Data Or Run The Program. Now A lot Of Times If The Memory Is Too Low, It Might Not Be Able To Hold All The Data That Is CPU Needs. And When This Happens Then Some other Data Has To Be Kept On The Hard Drive To Compensate For Low Memory. So A Set Of Data Going From The RAM To The CPU It Has To Do Extra Work By Going Back To The Hard Drive. When This Happens It Slows Down The Computer. So To Solve This Problem All You Need To Do Is Increase The Amount Of RAM On The Computer. And By Increasing The Memory All The Data Can Be Loaded Into RAM Without A Need Of Constantly Accessing The Hard Drive. And A Result A Faster Performing Computer.
Random Access Memory
RAM Requires A Constant Electrical Power To Store Data. And If The Power Is Turned Off, Then The Data Is Erased. RAM Is Stored On The Motherboard In Modules Called DIMMs. These DIMMs Come In Different Memory Sizes. Today The Range Is Anywhere From 128 MB To 4GB per DIMM Or More.
RAM Types
RAM Also Comes In Different Types. Such As Dynamic RAM Or DRAM DRAM Is Memory That Contains Capacitors. And Because It Has Capacitors It Has To Be Refreshed Often. SRAM - Synchronous RAM This Memory Uses Transistors And Does Not Have To Be Refreshed, Unlike DRAM. And Because Of This, This Is Much Faster Than DRAM. And It Is Also Very Expensive. An Example For SRAM - Memory Cache Level 1 & 2 That Is Used By The CPU. SDRAM - Synchronous Dynamic RAM The Other Memory Is Called SDRAM. Which Stands For Synchronous DRAM. This Type Of Memory What Is Used Today In RAM DIMM's. SDRAM & DRAM Is Basically Speed. The Older DRAM Technology Operates Asynchronously With The System Clock. Which Basically Means That It Runs Slower Than A System Clock. Because Its Signals Are Not Coordinated With It. But SDRAM Technology Operates Synchronously With The System Clock. Which Is Why It Is Faster Than DRAM. All The Signals Are Tied To The System Clock For A Better Controlled Timing.
RAM Speed
SDRAM Is Rated At Different Speeds. For Example- A Stick Of SDRAM Could Be Labeled PC-100

PC-100 Means 100 MHz= The Speed At Which It Operates. Which Is 100 MegaHertz. And Since SDRAM Only Comes In 64-bit Modules, It Has 8 Byte Wide Bus. Because 64/8=8 So The Figure Of The Total Bandwidth Of The PC-100 X 8 Bytes = 800 MB/s(MegaByte Per Second) So The Total Bandwidth Of PC-100=800 MB/s. SDRAM PC-133 So An SDRAM Module Labeled PC-133. If You Multiply 133 With 8 You Will Get 1066 Mb/s So The Total Bandwidth For PC-133 Is 1066 MB/s
Random Access Memory (RAM)
As Technology Increased. The Process And Bus Speed Gotten Faster. A New Way Of Technology Was Developed To Keep Up With The Faster Speeds Of Computers. This Newer Technology Was Called DDR (Double Data Rate) And Thats Basically What DDR Does. It Sends Double The Amount Of Data In Each Clock Signal Compare To Non-DDR RAM.
SDRAM

DDR RAM Non-DDR(SDRAM) Or Single Data Rate RAM Uses All In The Raising Edge Of The Signal To Transfer The Data. But DDR Uses Both Raising And Following Edges Of The Clock Signal To Send Data Which Makes DDR Twice As Fast. DDR Also Labeled Differently Than Non-DDR(Single Data Rate) RAM.

Instead Of Including The Clock Speed And Its Name Like PC-133 Were 133 Is Equal To The Clock Speed. DDR Uses The Total Bandwidth Instead. For Example - A DDR DIMM Is Labeled PC-2700, The 2700 Is Not The Clock Speed But Its The Actual Total Bandwidth. The Clock Speed For PC-2700 Is 333 Mhz Clock Speed. 333 Mhz X 8 Bytes = 2700 Mb/s

The Other Example Is PC-3200. PC-3200 Has A Clock Speed Of 400 Mhz. So 400Mhz X 8 Bytes = 3200 Mb/s

DDR2

A New Technology That Has Succeeded DDR Is DDR2. DDR2 Is Faster Than DDR. It Allows For Higher Bus Speeds. It Uses Less Power Than DDR. A DDR2 Has 240 Pins Compare To A 184 Pins On DDR. Some Examples Of DDR2 Are PC2-3200 & PC2-4200. And The Latest RAM Technology Is The Called DDR3
DDR3 Twice As Fast As DDR2 With The Bandwidth Of Over 12800 MB/s Like DDR2 A DDR3 DIMM Also Has 240 Pins. But The Bottom Notches In The DIMM's Are Different Places. So You Can Put A DDR3 DIMM In The RAM Slot Made For DDR2. In fact Motherboards Are Made To Support A Certain Type Of Memory.So You Can Mix DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 On The Same Motherboard. Some Examples Of DDR3 Is PC3-8500, PC3-12800 RDRAM (RAMBUS DYNAMIC RAM) An Other Type Of Memory Was Called RDRAM, Which Was Developed By RAMBUS Inc And They Developed RIMM - Rambus Inline Memory Module RIMM's Have 184 Pins And Looks Similar To DIMM's With The Exception That The Bottom Notches Are Located At The Center Of The Module.

In 1999 RIMM's Was Breakthrough In The Speed Of Memory. But Has Quickly Fallen Behind Due To The Advancement Of Technology In DIMM's. When RDRAM Debuted In 1999 , RDRAM Speed Was At 800 Mhz Which Was Considerably Faster Than SDRAM's, SDRAM Speed Was 133 Mhz. But Even though It Was Lot Faster Than SDRAM. RDRAM Only Had A 2 Byte Wide Bus But SDRAM Had 8 Byte Wide Bus So If You Multiply The Speed Of RDRAM Which Was 800 Mhz Times The Bus With Which Was 2 Bytes, You Will Get A Total Bandwidth Of 1600 MB/s 800 MHz X 2 Bytes = 1600 MB/s RIMM Technology Was Designed To Work With A Continous Signal Which Means That All The Other Memory On The Motherboard Must Be Used For RIMM's To Work Properly. And If Other RAM's Are Not Available Then A User Can Install C-RIMM(RAM) Or Continuity RIMM(Dummy RIMM) To Ensure Continuity In All The Memory Slots.

Dual-Channel Mode
To Meet The Higher Demands Of Faster Processes And Memory Controls A New Technology Was Developed Called Dual Channel Mode. Dual-Channel Mode Requires A Pair Of Identical DIMM's Installed On The Motherboard. Which Allows The Memory Controller The Ability To Communicate With 2 DIMM's Simultaneously. Which Increases The Speed Of Accessing The Memory. In Order For Dual Channel To Work The Motherboard Must Be Equipped To Work In Dual Channel Mode. And The Memory DIMM's Must Be Identical To Each Other In Speed, Size, And Features. Then The DIMM's Must Be Inserted Into The Motherboard In A Specific Slot Configuration In Oder To Enable Dual Channel Mode. Typically The Memory Slots Will Be Colour Coded To Help Assist And Identifying Where The DIMM's Should Be Inserted. For Example - You Will Have Some Dual Channel Memory Slots, So In Order To Dual Channel To Work, You Need To Install A Pair Of Identical DIMM's In The Slots Of The Same Colour. In This Case We Put A Pair Of DIMM's In The Red Slots. ECC Memory Some RAM Modules Have ECC. Which Stands For Error Correcting Code. And What It Does Is That It Detects If The Data Was Correctly Processed By The Memory Module. And Makes A Correction If It Needs To. You Can Tell If A RAM Module Has ECC By Counting The Number Of Memory On The Module.

The Above RAM Has 8 Memory Chips(Black) And A Standard Non-ECC DIMM It Will Have 8 Memory Chips But In A ECC Module It Will Have 9 Memory Chips.

Most Memory Modules Today Are Non-ECC. And This Is Because Of The Advance In Technology That Has Minimized Memory Errors. And Has Made Non-ECC RAM More Stable. Typically Today ECC Memory Is Mostly Used In Servers. Because Servers Need To Be Up And Running At All The Times. And Using ECC Memory Is Just An Extra Precaution To Gaurd Against Any Memory Errors. Read the full article
#RAM4gbprice#ram4gbpriceinindia#RAM8gbprice#ramandrom#RAMdrawing#RAMfullform#RAMhsncode#RAMimages#RAMPrice#RAMprice2gb
0 notes