#Saas vs Pass vs Iaas
Text
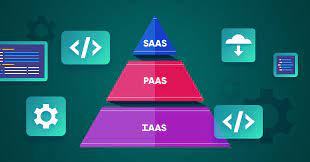
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: What’s The Difference ?
Ever wondered what sets SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS apart? Dive into our latest post for a crystal-clear comparison that will reshape your understanding of cloud services!
Take a leap into the cloud ! Click here to uncover the secrets.
0 notes
Text
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 (Part 1)
I recently took on the challenge of applying myself to pass the Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 exam. Every day on a daily basis I work with Azure and AWS, but I had never felt the need to pursue these certifications.
Over the last two weeks I reviewed the Microsoft Learning content for the Azure Fundamentals certification and recently passed it on my first attempt.
Below are the notes I had captured that helped me. Hopefully it can help you as well. Even if one person finds these valuable, then I will be happy that I shared them. :)
The content from my notes will be shared across several posts.
Cloud computing
Power and features to run your software
PC is in the cloud provider data center vs you
Pay for services you use
Others manage up keep of computer
Basic services are compute and storage
Compute power
How much processing your computer may do
Pay for resources you use
Storage
Volume of data you can store on your computer
Over time you need more, here you can request more
They make backups and ensure your system is up to date.
Shared responsibility model
Responsibilities are shared between the cloud provider and the consumer
Cloud provider: physical security, power, cooling, network connectivity
Consumer: data and information stored in cloud, access security
Mixed: example SQL server, the provider is responsible for the sql server, but the customer is responsible for the data
Different Models
IaaS - Infrastructure as a service
Consumer: Most responsibility
Provider: responsible for basics: physical security, power, connectivity, etc.
PaaS - Platform as a service
Middle ground
SaaS - Software as a service
Consumer: access, data, etc.
Provider: Most responsibility
Consumer is always responsible for
Information and data
Devices that are allowed to connect to your cloud
The accounts and identities of the people, services, and devices within the organization
Cloud provider is always responsible for
Physical data center
Physical network
Physical hosts
Your service model will determine responsibility for things like
Operating system
Network controls
Applications
Identity and infrastructure
Define Cloud models
Private Cloud
Similar to a traditional data center
Delivers services to a single entity
Greater control for the company of its IT department
More expensive and fewer benefits of a public cloud
Can be hosted at your on-site datacenter or at a third party facility
Public Cloud
Built, controlled, and maintained by a third party provider
Anyone that wants to purchase services can purchase them
Hybrid Cloud
An environment that uses both public and private clouds in an inter-connected environment.
Hybrid cloud environments can be used to allow private cloud to surge for increased temporary demand by deploying public cloud resources
Can provide an extra layer of security
Multi-cloud
Use of multiple public cloud providers
Use of different features at each provider
Starting your cloud journey with one provider and then migrating later
You manage resources and security in two environments
0 notes
Text
Choosing between Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud
The emergence of cloud computing services has resolved most storage and computing issues that businesses faced and simplified business operations. Their ever-growing popularity could be attributed to 3 major factors - convenience, scalability, and reduction of management issues.
Of the many cloud service providers (CSP) operating today, 3 stand out from the crowd - Amazon AWS Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These 3 dominant CSPs offer an array of services, products, and features that simplify all your online operations. However, many (prospective) users often get caught in this google cloud vs aws vs azure battle. Through an analysis of the key differentiators between these CSPs, we have attempted to bring out the pros and cons of using each of these cloud platforms, with the purpose of enabling you to pick the one that is optimum for your requirements.
Shifting to Cloud Computing: Why Do It at All?
Before talking about AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, there is a bigger question looming on oour heads- Why shift to the cloud? Well, here are a few reasons:
Increased Flexibility and Convenience: Create a document and upload it to a cloud platform. Anyone with unrestricted access can change it accordingly; can track the changes as well. There is a unique copy of the document that is reflected uniformly across all users.
Reduced Management Issues: Cloud computation solutions are usually billed on the go. As a result, the budgetary and management issues can be minimized using the cloud.
Scalability: It is extremely simple to scale up the magnitude of any operation when on a cloud platform. Through cloud application development, new resources are instantly available at a very cheap rate and the more people use it, the cheaper the services get.
The Big 3 Unraveled: AWS vs Microsoft Azure vs Google Cloud
Amazon AWS
Amazon Web Services has been a top-notch provider of cloud application development platforms that are tiered in terms of usage. Amazon is renowned for providing a comprehensive range of cloud application development platforms. Their platforms range from Core computation to IoT and even Game Development.
The Pros
Services are enterprise-friendly and highly scalable and flexible. If you require high-end computational services, you would struggle to find a better option.
The pay-as-you-go feature enables you to avail of and pay for only the features that you require.
AWS has put very tight security measures in place which makes it one of the most trusted CSPs. The multiple layers of security encryptions employed by AWS mean that your data is totally safe.
Auto-scaling allows developers to focus on tasks such as programming and development and leave lesser management issues to autopilot.
The variety that AWS offers is unmatchable. There is a cloud application development platform available for each and every purpose.
AWS web services offer solutions across at least 6 modes of payment and dozens of templates in each and every programming language.
The Cons
AWS is based on a hybrid cloud structure. The use of a third-party public cloud could sometimes create unexpected issues.
AWS requires its users to have at least some basic knowledge of the cloud; which is not ideal for total novices.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft requires no introduction to anyone on the planet as a behemoth in the tech space. It should be of very little surprise to anyone that Microsoft offers its own cloud computing solutions. Microsoft Azure is popular because of a spotless track record and its affordable pricing. Flexible billing and a plethora of certifications are its major draws.
The Pros
Microsoft cloud application development is one of the easiest and most effortless in the business. A host of testing tools which help you test everything and anything are Azure’s USP and Microsoft Cloud development becomes a breeze with them.
Azure operates solely in a private cloud computing environment. As a result, its PaaS model is sturdy and dependable.
Azure being a Microsoft product, it gels well with other Microsoft products such as Windows server, Active Directory, etc.
With the Auto-scaling options that Azure offers, working in a cloud environment is as easy as it gets.
The Cons
Power outages are the nemesis for Azure. As Azure lacks in data backup and restoration facilities, power outages are a nightmare for the users because the data becomes inaccessible during that time.
Microsoft Azure SaaS is not as strong and user-friendly as SaaS of other CSPs; especially when you compare Amazon Web Services vs Azure.
Azure’s capabilities in general and Azure web application development in particular, are limited beyond the Windows and Microsoft environment. Problems in Microsoft Azure development are widely reported by developers. This is one grey area which may tilt the scales in the battle of Microsoft Azure vs AWS in favor of the latter.
Google Cloud Platform
One of the latest entrants in Cloud Computing Services, Google has managed to turn heads with its array of unique features and high-quality services.
The Pros
Google charges exactly on usage and it bills on a per minute basis, unlike other CSPs who bill at an hourly rate.
No one else integrates and uses data from different platforms with the ease and effectiveness of Google Cloud Platform. Its data & analytics tools are of the highest standard.
Developers could create custom machine types quite conveniently. The processing capabilities and scalability of Google cloud are mind-boggling.
Google Cloud provides completely serverless services. The server’s resources are maintained by the cloud platform. With the arrival of Google Cloud dedicated server is no longer a ‘must have’ for businesses and marketers.
To counter any technological disruptions in the future, Google is creating ‘future-proof infrastructure’.
The Cons
As Google is still a relatively new player in this field, the variety of Google Cloud computing services is very limited. Because of the relative lack of infrastructure as compared to Azure and AWS, Google Cloud app development is a slightly arduous process.
Server coverage is limited in many parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe.
The Cloud’s web interface is confusing at times.
The Showdown
DifferentiatorsAWSAzureGoogle Cloud
Dominant featurePay-as-you-go featureSturdy PaaS modelServerless services
USPTight security systemIntegrated with Microsoft toolsTop-notch data & analytics tools
Range of servicesExtremely wideWideLimited but expanding
Nature of servicesEnterprise-centric servicesNot totally ‘enterprise-ready’Designed for cloud-based businesses
ReachEstablished global presenceExpanding graduallyNew to the market
Major drawbackDifficult to use, options may seem confusingManagement tooling is inefficientLimited data centers across the world
PricingPer hourPer minutePer minute
The Final Verdict
While Azure is quickly closing the gap between itself and AWS, it is still quite a way off from AWS in terms of market penetration and global presence. For the moment, AWS is the undisputed king of the market but it is under immense pressure from Azure to retain its throne.
Google Cloud, still very young, is not an immediate threat to the other 2 but things could change in the long run considering that though Google Cloud currently offers limited services, the quality of their products and services is outstanding. As of now, Google has set its sights on advanced use cases that are centered on Machine Learning and Big Data.
On the other hand, the Microsoft Azure vs Amazon Web Services battle is set to intensify with Azure posting massive revenues each passing quarter. The first mover advantage has helped AWS surge ahead of its rivals. Its enterprise-friendly features and a never-ending range of services, coupled with its ever-growing infrastructure have put it in a position where it could trigger aggressive price cuts to throw its rivals off their track. Azure, on the other hand, is pumping in money to build the Azure Cloud Platform and plans to strengthen its on-premise software. It has gradually eaten into Amazon’s market share over the past few years and is leaving no stone unturned to continue the trend.
Cloud Computing Trends That We May Witness in 2019
Hybrid cloud solutions will gain popularity: Hybrid cloud reduces the risk and expense of migrating to the cloud. More companies would opt for it in 2019 to enjoy the effectiveness of cloud solutions.
Google Cloud will get stronger: Serverless is the fastest growing extended cloud service; which would put Google Cloud in a position of strength.
The number of cloud services will rise: Bain & Company have tipped SaaS to grow at an 18% CAGR by 2020, while KPMG predicts that investments in PaaS will rise to 56% in 2019. As more organizations attempt to seek the benefits of a cloud, the number of cloud-based services and solutions will continue to rise in 2019.
Factors You Should Consider Before Migrating To The Cloud
Before you jump on the bandwagon and shift on to the cloud, here are a few things you might want to review before you take the plunge.
Your objective for moving to the cloud: You must ascertain your goal for moving towards the cloud. Without a set goal in place, you will fail to judge the impact of the cloud on your operations.
The ideal deployment model: Each major CSP offers SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Each model varies in the degree of control it offers. Match the level of control each model offers against the level of control you wish to have.
Which applications should be migrated?: Not every application is suitable for the cloud. Some of them need to be kept on-premises.
Security: Security is non-negotiable. Understand how each CSP secures your data and examine their security certifications.
Time & cost efficiency: Moving data requires a lot of man-hours and bandwidth. Migrating to the cloud may prove costly and time-consuming and it is imperative that you analyze the time and cost efficiency of your preferred cloud platform before you migrate to it.
Head To Head Comparison: Number Crunching!
AWS reported a revenue growth of 49% in the first quarter of 2018. Azure is catching up fast on AWS with a93% growth in revenue in the corresponding period.
AWS has emerged as a key revenue driver for Amazon. It contributed 11% of Amazon’s total revenue during Q1 this year. It also produced about 73% of Amazon’s operating income in that time.
While Azure and Google Cloud are closing in on AWS in terms of revenue, AWS is still far ahead with respect to market penetration and adoption.
AWS is the number one public cloud infrastructure platform and it controls 41.5%of total application workloads in public cloud. Azure trails it at second with 29.4% while Google owns a measly 3%.
Canalys estimates the market share of AWS, Azure and Google Cloud at approximately 32%, 16%, and 7% respectively.
Summing Up
According to industry analyst Gartner, the IaaS market would reach $40.8 billion by the end of 2018 and $83.5 billion by 2021. The corresponding figures for SaaS are $73.6 billion and $117.1 billion, and for PaaS are $15 billion and $27.3 billion respectively. The cloud computing market is only headed in one direction!
Source URL: https://www.classicinformatics.com/blog/amazon-aws-microsoft-azure-and-google-cloud
1 note
·
View note