#Video classes for CAOnline classes for CAOnline Classes for CA FinalOnline classes for CSOnline classes for CMAonline classes for ca final
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
ALL ABOUT COMPOSITION SCHEME IN GST
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/05/composition-scheme-gst/
Composition scheme is a convenient way for the small taxpayers in order to escape from too many GST formalities and pay the tax at a fixed rate based on their business turnover.
Under this scheme, a taxpayer will pay tax as a percentage of his/her turnover during the financial year without the benefit of Input Tax Credit. A taxpayer opting for composition scheme will not collect any tax from his/her customers.
When the eligible taxpayer is opting for the Composition Scheme under GST, a taxpayer has to file a summarized returns on a quarterly basis, instead of three monthly returns (as is applicable for normal businesses).
Key Features
Eligibility: Turnover must be below Rs. 1.50 Crore (Rs. 75 Lakhs for North-Eastern States)
Tax rate: Fixed tax rate on the total sales turnover
Input Tax Credit: Not eligible for Input Tax Credit
Place of supply: Applies only to the Intra-State supplies
Return: No monthly filing, only Quarterly returns
Billing: Issues Bill of Supply & not tax invoice
Who can avail composition scheme? (Eligibility)
Only those persons who fulfill all the following are eligible to apply for composition scheme:
Deals only in the intra-state supply of goods (or service of only restaurant sector).
Does not supply goods not leviable to tax.
have an annual turnover below Rs. 1.50 Crore (Rs. 75 Lakhs for north-eastern states) in preceding financial year.
He shall pay tax at normal rates in case he is liable under reverse charge mechanism.
Not supplying through e-commerce operator.
Not a manufacturer of
ice cream,
pan masala or
tobacco (and its substitutes).
Why should you opt for composition scheme under GST?
No requirement to maintain records
Hassle free payments of tax at single rate
Filing monthly returns is a costly and cumbersome process that may just be asking too much from a small dealer trying to grow a business
Tax Rate under Composition Effective from 1st January 2018 (01.01.18)
Rate
CGST (%)
SGST (%)
Total (%)
Manufacturer
0.5%0.5%1%
Traders
0.25%0.25%0.5%
Restaurants
2.50%2.50%5%
Process to get registered as Composite Taxpayer
There can be two cases under the process of getting registered as composite taxpayer:
CASE 1- Registration process under composition scheme for a person who is already registered under current tax regime
A person who is registered under the current regime and applying for the Registration under GST will be given Provisional Certificate first.
If that person wants to get registered as composite taxpayer under GST, he shall file intimation in FORM GST CMP-01, duly signed or verified through electronic verification code. It may be noted that that it has to be filed prior or within 30 days after the appointed day(July 1, 2017) :
directly on the common portal
through a Facilitation Centre
Further, he has to give the details of stock, whether purchased from registered or non-registered person, held by him before he has opted to get registered under the composition scheme in FORM GST CMP-03 within 60 days in the electronic form.
The registered person shall not collect any tax from the appointed day but shall issue bill of supply for supplies made after the said day.
CASE 2- Registration process under composition scheme for a person who is applying for fresh registration.
A person who is applying for the fresh Registration under GST has to file FORM REG-01 and under Part B of the form he has to select the option of Section 10 (Registration as composite taxpayer).
Return Filing Process under Composition Scheme
It is only a simplified quarterly return in FORM GSTR 4 for which the taxpayer only requires indicating:
Total consolidated value of the supplies. Invoice-wise detail is not to be disclosed.
Tax paid at the composition rate.
Invoice level purchase information for the purchases made from normal taxpayers, which will be auto-populated in GSTR 4A from supply invoices uploaded by the counter party normal registered taxpayers.
Invoicing Rules under GST
The person who is registered as a composition taxpayer shall at the top of the bill of supply issued by him, mention the words- “not eligible to collect tax on supplies” because person registered as the composite taxpayer is not eligible to collect tax on the supplies from his buyer rather tax is paid by the composite taxpayer himself at the special rates decided for the composition dealers.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Online Classes For CA –
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/17/online-classes-ca/
Chartered accountancy is a professional degree course which offers much scope as well.. After becoming a CA, a person can choose to either be employed with a firm as an employee or they can choose to open their own private practice.

Scope of a chartered accountant career-
By the course of charted accountancy, you can choose their own practice and develop.
CA’s can also apply for the job of any company.
They work in a field of capital marketing.
CA can also work in the field of government services, public sector,or even in a private sector.
Institute of CA of India is also well recognized abroad like in England, Wales and Australia so one can even practice in these countries as well.
It is not necessary that a CA has to work only on number crunching and excel sheets. A CA employed with a firm can also contribute towards decision making and enhancement of profits for the firm.
A CA employed with a firm can also contribute towards decision making and enhancement of profits for the firm.
As per a report by the Economic Times, there is a huge demand for CA’s in the manufacturing and financial services sectors
CA is emerging as a good career option for women as it allows work to be done at one’s own pace and time, and, also allows one to control the money flow. Besides, a CA is free to take break in his / her profession.
Why to select online classes for CA course-It’s not necessary to join the coaching classes for CA preparation. Online study is the new trend today. You can join any YouTube or any type of online CA classes’ tutorial. You will get many video classes for CA available on the internet.
We also have our online video tutorial for CA available on youtube. If you want you can have a look here,
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Understanding Place Of Supply In GST
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/02/01/online-classes-for-gst/
To determine the actual nature of the movement of goods and services, it is imperative to understand the “place of supply” of such goods or services. It plays a pivotal role in identifying whether CGST & SGST or IGST will be levied on any transaction.
Place of supply of goods and services have been given separate provisions. The location of the supplier and the place of supply together define the nature of the transaction. The registered place of business of the supplier is the location of the supplier, and the registered place of the recipient is the place of supply.
Place of supply rules for Goods
1) Where the supply involves a movement of goods, the place of supply shall be determined by the location of the goods at the time of final delivery.
Example: –A manufacturer in Kolkata, West Bengal has an order from a customer in Surat, Gujarat. The manufacturer directs his branch in Mumbai, Maharashtra to ship the goods to Surat. In this case, place of supply shall be Surat, Gujarat and thus entails an inter-state movement of goods and will attract levy of IGST.
2) Where the supply involves a movement of goods, on the direction of a third party, whether as an agent or otherwise, the place of supply shall be the principle place of business of such third party, irrespective of the place of delivery of goods.
Example: –A dealer in Mumbai, Maharashtra sells products to a customer in Delhi. Delhi-based customer directs the Mumbai seller to send the materials to Kolkata-based customer. Although the place of delivery is Kolkata, since Delhi-based seller had directed such movement, then the place of supply shall be the principle place of business, i.e. Delhi and thus, charge IGST on such movement.
3) Where the supply does not involve any movement of goods, then place of supply shall be the location of such goods at the time of final delivery.
Example: –An Ltd has its registered office in Hyderabad, Telangana, opens a branch in Bengaluru, Karnataka, and purchases workstations from B Ltd. Whose office is in Bengaluru, Karnataka. Even though the same is, a supply of goods but there is no movement of goods. Since the movement is intra-state, it will attract CGST and SGST.
4) Where the supply includes installation of goods at the site, then place of supply shall be the place of such installation.
Example: –Installation of telephone towers or lift in an office building.
5) Where the goods are being supplied on board a vehicle, vessel, aircraft, or a train, i.e. on board a conveyance, then place of supply shall be the first location at which the goods are boarded.
Example: – Howrah to New Delhi Rajdhani starts its journey from Howrah, West Bengal and passes through many states before ending its journey in New Delhi. The food served on board the train shall be considered as supply of goods. Thus, place of supply shall be Howrah since it is the first location of the goods.
NOTE: –Any other cases not covered above will be determined further as per recommendations from the GST council (yet to be finalised)
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Non Resident Taxable Person Under GST Law
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/03/08/video-classes-for-ca-non-resident-taxable-person-gst-law/
A non-resident taxable person is defined as one residing outside India and making a taxable supply in India. Read more to understand the taxability.
If you are a business importing goods or services from outside India or managing a business on behalf of a person resident outside India, or if you are a non-resident and reading our article from a place outside India and intend to do business here, then this article is relevant to you.
The Goods and Services Tax Law has defined a ‘non-resident taxable person’ as any person who occasionally undertakes transactions involving the supply of goods or services, or both, whether as principal or agent or in any other capacity, but who has no fixed place of business or residence in India.
Section 24 of the GST law further specifies the requirement for registration for a non-resident taxable person. It mentions certain businesses and entities which are mandatorily required to register under Goods and Services Tax and are not governed by the minimum threshold limit of Rs. 20 lakh/ 10 lakh. Thus, irrespective of whether the business is involved in a one-time transaction or frequent taxable transactions, every non-resident individual or company will have to obtain a registration under the Goods and Services Tax.
Registration Procedure for a Non-Resident Taxable Person
Every person or business who falls under the definition covered above needs to apply for registration at least five days prior to the commencement of business. Further clarification has been provided in case of a high-sea sale; the law says that every person who makes a supply from the territorial waters of India shall obtain registration in the coastal state or Union territory where the nearest point of the appropriate baseline is located.
High Sea Sale (HSS) is a sale carried out by the carrier document consignee to another buyer while the goods are still being transported, or after their dispatch from the port/airport of origin and before their arrival at the port/airport of destination.
Thus if any high-sea sale is carried out near the shore of Mumbai, the GST registration has to be obtained in the state of Maharashtra.
A non-resident taxable person needs to electronically submit a duly signed application, along with a self-attested copy of his valid passport, for registration, using the form GST REG- 09, at least five days prior to the commencement of business on the Common Portal. An application must be duly signed or verified through EVC, a new mode of electronic verification based on Aadhar.
The non-resident (if it is a company) must submit its tax identification number of its original country (whatever is the equivalent of our PAN in that country).
A person applying for registration as a non-resident taxable person will be given a temporary reference number electronically by the Common Portal for making an advance deposit of tax in his electronic cash ledger and an acknowledgment will be issued thereafter.
Advance Payment of Tax by Non-Resident Taxable Person
A non-resident taxable person is required to make an advance deposit of tax in an amount equivalent to the estimated tax liability of such person for the period for which registration is sought.
These rules further specify that in case a non-resident taxable person intends to extend the period of registration indicated in their application for registration, an application using the form GST REG-11 should be furnished electronically through the Common Portal before the end of the validity of registration granted to him.
Example
Let’s understand these rules with the help of an example. Say, the company Marc Inc. based out of USA is manufacturing special class turbojet engines which are supplied to India for assembling. This is a one-time transaction for Marc Inc. and thus they have appointed an Agent Mr. Vinod in India to carry out all compliance related formalities. Mr. Vinod, in turn, is required to obtain registration for Marc Inc. by furnishing his own PAN number and pay advance taxes related to this transaction. Once the transaction is carried out successfully and the supply is made, Marc Inc. will need to file their GST returns and meet all GST liability from the advance tax paid at the time of registration. Any tax paid in excess will be refunded through the electronic mode.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Taxation Of E-Commerce Operator Under GST
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/03/14/taxation-e-commerce-operator-gst/
E-Commerce or Electronic Commerce- what it is ?

In Simple terms :

Buying or selling goods & services through electronic mode

Transmission of Funds or Data

E-commerce operation i.e. online shopping or transactions by the consumers are becoming popular day by day and easy due to various reasons. Key factors are:
Major portion of the population of the entire world are using broadband Internet services,3G internet, and a recent introduction of 4G across the country.
Increasing growth of Smartphone users not only in urban or developed areas as well as in rural areas.
Rising standards of living due to which people are adapting to easy going way of living, instead of going to the market and buy things they prefer shopping online as easy and standard way to shop.
Availability of much wider range of product since it help consumer to compare things easily and choose the most compatible items.
Due to competition in the market worldwide, traders offer exciting offers which helps people to get the standard items at cheaper costs.
Also there is increased development of user friendly sites, where people can buy and sell second hand product, eg. OLX, QUICKER, etc.
Evolution of major online shopping startups like Flipkart, Amazon, Jabong, etc.
Since all Business Activities involves transactions to generate income, therefore in case of E-commerce business, to implement tax on business income generated is a major challenge as these operations involve many transactions which is difficult to identify as to where, when and at which rate to be charged so that their would not be any difficulties pertaining to double taxation, excessive tax burden, etc. Therefore this could be understood by having a detailed study of taxation structure for E-commerce operator under Direct Taxation System(i.e Income tax) and Indirect Taxation System(i.e. GST).
Taxation Under GST
Return Filing under GST for E commerce
ParticularsE-Commerce OperatorSuppliers Of E-Commerce Platform
MeaningPerson Who Owns, Operates Or Manages Digital Or Electronic Facility Or Platform For E-Commerce.Those Who Supplies Goods Or Services On An E-Commerce Platform
Registration
Mandatorily Required To Get Registered Under GST Irrespective Of Turnover.Are Mandatorily Required To Register Under GST Including Even Those, Whose Aggregate Turnover Does Not Exceed The
Threshold Limit
For Registration.
E Commerce Suppliers Cannot Avail Benefit Of Composition Scheme.
Return Filing
By 10th Of Every Month, Has To Furnish
FORM GSTR-8
Containing Details Of Outward Supplies Made Through Their Platform By Suppliers In The Previous Month.By 10th Of Every Month, Suppliers Have To Furnish The Details Of Their Outward Supplies Through E-Commerce Platforms In Table 4, 5 And 7 Of
FORM GSTR 1
.
By 15th Of Every Month, A Supplier Has To Furnish FORM GSTR 2, In Which The Details Of Tax Collected By The E Commerce Operator Can Be Accepted Or Modified From GSTR 2Awhich Is Auto Populated From FORM GSTR 8.
By 20th Of Every Month, He Shall File Return And Discharge His Tax Liability On Supply Of Goods Through Electronic Cash Or Credit Ledger.
Major limitations that would be dealt with:
Each and every invoice in relation to transactions have to be uploaded in this software therefore, records of huge number of invoices have to be maintained.
The details of supplies and the amount collected during a calendar month and furnished by every operator in his statement should be matched with the details of outward supplies furnished by the concerned seller in his valid return filed for the same calendar month or any preceding calendar month.
If the above do not match within a reasonable time, then the supplier would be liable to pay tax along with interest.
TCS Provisions for E commerce operator
Rate of TCS under GST
Every e-commerce operator has to collect 1% under CGST Act and 1% under SGST Act and if an interstate transaction is being done, he will collect 2% of tax under IGST Act on the net values of taxable supplies. It means that any dealers/traders who are selling goods online through e commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon etc. would get their payment after deduction of 2% tax by e commerce operators.
Comparison
GST will affect customers across states –
IGST (integrated goods and service tax) will be levied on inter-state sales
Once the goods reach and cross state borders, there will be relatively less verification and no entry tax will be charged. This will reduce the price for the customer.
Selling from another state and within state both will be equally simple to the buyer.
Seller need not to invest in excess infrastructure like branches or warehouses for the sole purpose of operational efficiency.
Conclusion
GST will have a positive impact on E Commerce sector. Both the suppliers and the consumers will be benefited. It will be easier for the supplier to supply goods in other states. Burden of tax collection and payment to the government is removed from the consumers and suppliers through E Commerce and put squarely on the shoulders of the E Commerce Operators.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
ALL ABOUT COMPOSITION SCHEME IN GST
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/05/composition-scheme-gst/

Composition scheme is a convenient way for the small taxpayers in order to escape from too many GST formalities and pay the tax at a fixed rate based on their business turnover.
Under this scheme, a taxpayer will pay tax as a percentage of his/her turnover during the financial year without the benefit of Input Tax Credit. A taxpayer opting for composition scheme will not collect any tax from his/her customers.
When the eligible taxpayer is opting for the Composition Scheme under GST, a taxpayer has to file a summarized returns on a quarterly basis, instead of three monthly returns (as is applicable for normal businesses).
Key Features
Eligibility: Turnover must be below Rs. 1.50 Crore (Rs. 75 Lakhs for North-Eastern States)
Tax rate: Fixed tax rate on the total sales turnover
Input Tax Credit: Not eligible for Input Tax Credit
Place of supply: Applies only to the Intra-State supplies
Return: No monthly filing, only Quarterly returns
Billing: Issues Bill of Supply & not tax invoice
Who can avail composition scheme? (Eligibility)
Only those persons who fulfill all the following are eligible to apply for composition scheme:
Deals only in the intra-state supply of goods (or service of only restaurant sector).
Does not supply goods not leviable to tax.
have an annual turnover below Rs. 1.50 Crore (Rs. 75 Lakhs for north-eastern states) in preceding financial year.
He shall pay tax at normal rates in case he is liable under reverse charge mechanism.
Not supplying through e-commerce operator.
Not a manufacturer of
ice cream,
pan masala or
tobacco (and its substitutes).
Why should you opt for composition scheme under GST?
No requirement to maintain records
Hassle free payments of tax at single rate
Filing monthly returns is a costly and cumbersome process that may just be asking too much from a small dealer trying to grow a business
Tax Rate under Composition Effective from 1st January 2018 (01.01.18)
Rate
CGST (%)
SGST (%)
Total (%)
Manufacturer
0.5%0.5%1%
Traders
0.25%0.25%0.5%
Restaurants
2.50%2.50%5%
Process to get registered as Composite Taxpayer
There can be two cases under the process of getting registered as composite taxpayer:
CASE 1- Registration process under composition scheme for a person who is already registered under current tax regime
A person who is registered under the current regime and applying for the Registration under GST will be given Provisional Certificate first.
If that person wants to get registered as composite taxpayer under GST, he shall file intimation in FORM GST CMP-01, duly signed or verified through electronic verification code. It may be noted that that it has to be filed prior or within 30 days after the appointed day(July 1, 2017) :
directly on the common portal
through a Facilitation Centre
Further, he has to give the details of stock, whether purchased from registered or non-registered person, held by him before he has opted to get registered under the composition scheme in FORM GST CMP-03 within 60 days in the electronic form.
The registered person shall not collect any tax from the appointed day but shall issue bill of supply for supplies made after the said day.
CASE 2- Registration process under composition scheme for a person who is applying for fresh registration.
A person who is applying for the fresh Registration under GST has to file FORM REG-01 and under Part B of the form he has to select the option of Section 10 (Registration as composite taxpayer).
Return Filing Process under Composition Scheme
It is only a simplified quarterly return in FORM GSTR 4 for which the taxpayer only requires indicating:
Total consolidated value of the supplies. Invoice-wise detail is not to be disclosed.
Tax paid at the composition rate.
Invoice level purchase information for the purchases made from normal taxpayers, which will be auto-populated in GSTR 4A from supply invoices uploaded by the counter party normal registered taxpayers.
Invoicing Rules under GST
The person who is registered as a composition taxpayer shall at the top of the bill of supply issued by him, mention the words- “not eligible to collect tax on supplies” because person registered as the composite taxpayer is not eligible to collect tax on the supplies from his buyer rather tax is paid by the composite taxpayer himself at the special rates decided for the composition dealers.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Online Classes For CA –
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/17/online-classes-ca/
Chartered accountancy is a professional degree course which offers much scope as well.. After becoming a CA, a person can choose to either be employed with a firm as an employee or they can choose to open their own private practice.

Scope of a chartered accountant career-
By the course of charted accountancy, you can choose their own practice and develop.
CA’s can also apply for the job of any company.
They work in a field of capital marketing.
CA can also work in the field of government services, public sector,or even in a private sector.
Institute of CA of India is also well recognized abroad like in England, Wales and Australia so one can even practice in these countries as well.
It is not necessary that a CA has to work only on number crunching and excel sheets. A CA employed with a firm can also contribute towards decision making and enhancement of profits for the firm.
A CA employed with a firm can also contribute towards decision making and enhancement of profits for the firm.
As per a report by the Economic Times, there is a huge demand for CA’s in the manufacturing and financial services sectors
CA is emerging as a good career option for women as it allows work to be done at one’s own pace and time, and, also allows one to control the money flow. Besides, a CA is free to take break in his / her profession.
Why to select online classes for CA course-It’s not necessary to join the coaching classes for CA preparation. Online study is the new trend today. You can join any YouTube or any type of online CA classes’ tutorial. You will get many video classes for CA available on the internet.
We also have our online video tutorial for CA available on youtube. If you want you can have a look here,

https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVbSYtDi9PgjtNtNTnIvCrg
If you are selecting online mode for study, CA classes. It has its own benefits. It is cost –effective, you have the flexibility to learn your online classes for CA at your convenient.
For more information about online classes of CA, stay tunes with-
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
How To Become CS-
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/25/how-to-become-cs/
Foundation program: Students looking to do CS after 12th need to go through this stage.
Executive program: This course is for Graduates of all streams with the exception of Fine Arts.
Professional program: One can Complete this after completing the intermediate exam of the CS course
The student who would like to join this CS Course after 10+2 has to undergo three stages to pursue the Company Secretaries Course i.e.
Foundation Program
Executive Program
Professional Program
In addition, the student has to undergo Practical Trainingfor about 15 months, which a student may opt to start after passing the Executive Program
The Student who would like to join the Course after passing the Graduation (Example: B.com) has to undergo two stages of the Company Secretaryship i.e.
Executive Program
Professional Program
Besides, the student has to undergo Practical Training for about 15 months.
Foundation Program, which is eight months duration can be pursued by 10+2 pass students of Arts, Science or Commerce stream.
Executive Program can be pursued by a Graduate of all streams except Fine Arts.
Professional Program can be pursued only after clearing the Executive Program of Company Secretary Course.
Training:A Student has to undergo 15 months Management Training in Companies sponsored by the Institute after passing the Executive or Professional Program or under the guidance of a Company Secretary in Practice.
After qualifying Professional Examination and on successful completion of training a candidate is admitted as an Associate Member of the ICSI and can use the letters ACS after his/her name i.e. Associate Company Secretary.
How to Register For CS Foundation-
There are 4 subjects in CS Foundation.
Business Environment and Entrepreneurship
Business Management Ethics and Communication
Business Economics
Fundamental of Accounting and Auditing
CS Foundation Registration is open throughout the year.
How to Register For CS Executive-
There are 2 Modules in CS Executive. Module -I contains 4 subjects and Module – II contains 3 subjects.
Module I
Company Law
Cost and Management Accounting
Economic and Commercial Laws
Tax Laws and Practice
Module II
Company Accounts and Auditing Practices
Capital Markets and Securities Laws
Industrial, Labor and General Laws
How to Register For CS Professional-
There are 3 Modules in CS Executive. Module -I contain 3 subjects, Module – II contains 4 subjects and Module 3 contains 2 subjects and 5 elective papers.
Module I
Advanced Company Law and Practice
Secretarial Audit, Compliance Management, and Due Diligence
Corporate Restructuring, Valuation, and Insolvency
Module II
Information Technology and Systems Audit
Financial, Treasury and Forex Management
Ethics, Governance, and Sustainability
Module III
Advanced Tax Laws and Practice
Drafting, Appearances, and Pleadings
Elective Subjects
Banking Law and Practice
Capital, Commodity and Money Market
Insurance Law and Practice
Intellectual Property Rights – Law and Practice
International Business-Laws and Practices
Medium of Examination
The Institute allows the facility for students to appear in examination in English as well as in Hindi. (Except Business Communication subject of Foundation Program)
Qualifying Marks
A candidate is declared to have passed the Foundation / Executive / Professional examination if he/she secures at one sitting a minimum of 40% marks in each paper and 50% marks in the aggregate of all subjects.
Time limit for completing CS Examination
A student is required to complete the Executive and the Professional examination within the registration period. However, on payment of requisite fees, the validity of registration may be renewed/extended for the further period subject to fulfilling the applicable guidelines.
For more information about cs course, stay tuned with- http://www.arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
GENERAL FAQs
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/05/28/general-faqs/

What is the common portal for generation of e-way bill?
The common portal for generation of e-way bill is https://ewaybillgst.gov.in
I am not getting OTP on my mobile, what should I do?
Please check if you have activated ‘Do Not Disturb (DND)’ facility on your mobile or your service provider network may be busy. You can also use OTP, which is sent on your email-id.
E-way bill system is slow, how should I proceed?
Please check your internet connectivity.
E-way bill pages or menu list are not being shown properly, what should I do?
Please check whether your system has proper version of the browser as suggested by the e-way bill portal and also check the security settings of the browser and display property of the system. The site is best viewed on Internet Explorer 11 or above, Firefox 43.5 or above and Chrome 45 or above.
I have already registered in GST Portal. Whether I need to register again on the e-Way Portal?
Yes. All the registered persons under GST need to register on the portal of e-way bill namely: www.ewaybillgst.gov.in using his GSTIN. Once GSTIN is entered, the system sends an OTP to his registered mobile number, registered with GST Portal and after authenticating the same, the system enables him to generate his/her username and password for the e-way bill system. After generation of username and password of his/her choice, he/she may proceed to make entries to generate e-way bill.
Whenever I am trying to register, the system is saying you have already registered, how should I proceed?
This is indicating that you (your GSTIN) have already registered on the e-way bill portal and have created your username and password on the e-way bill system. Please use these credentials to log into the e-way bill system. If you have forgotten username or password, then please use the ‘Forgot Username’ or ‘Forgot Password’ facility provided on the portal to recollect your username or create new password accordingly.
Whenever I am trying to register, the system is saying there is no contact (Mobile) number with this GSTIN in GST Common Portal, how should I resolve this issue?
This is indicating that e-way bill system is unable to get the contact details (mobile number of email address) for your GSTIN from the GST Common Portal (www.gst.gov.in). Please contact GST helpdesk 0120-4888999.
Whenever I am trying to register, the system is showing wrong address or mobile number. How should I resolve this issue?
This is indicating that you might have updated your business registration details in the GST Common Portal recently. Please click the ‘Update from Common Portal’ button on the e-way bill portal, to pull the latest data from the GST Common Portal. If even after this action, wrong data is displaying, kindly update the details in GST common portal through amendment process.
Whenever, I’m trying to register with my GSTIN, the system is saying ‘Invalid GSTIN’ or the details for this GSTIN are not available in GST Common Portal. How should I resolve this issue?
This is indicating that the GSTIN entered by you is wrong or your GSTIN details Is not available in the GST Common Portal. Please check the GSTIN entered or go to the GST portal (www.gst.gov.in) and check the details of your GSTIN under ‘Search Taxpayer’ tab.
Why the transporter needs to enroll on the e-way bill system?
There may be some transporters, who are not registered under the Goods and Services Tax Act, but such transporters cause the movement of goods for their clients. They need to enroll on the e-way bill portal to get 15 digits Unique Transporter Id.
What is TRANSIN or Transporter ID?
TRANSIN or Transporter id is 15 digit unique numbers generated by EWB system for unregistered transporter, once he enrolls on the system which is similar to GSTIN format and is based on state code, PAN and Check sum digit. This TRANSIN or Transporter id can be shared by transporter with his clients, who may enter this number while generating e-waybills for assigning goods to him for transportation.
How does the unregistered transporter get his unique id or transporter id?
The transporter is required to provide the essential information for enrolment on the EWB portal. The transporter id created by the EWB system after furnishing the requisite information. The details of information to be furnished is available in the user manual.
I am unable to enroll as transporter as the system is saying ‘ PAN details are not validated’
This is indicating that PAN name and Number, entered by you, are not getting validated by the CBDT/ Income Tax system. Please enter exact name and number as in income tax database.
I am unable to enroll as transporter as the system is saying ‘ Aadhaar details are not validated’
This is indicating that Aadhaar Number, name in Aadhaar and mobile number, entered by you, are not getting validated by the Aadhaar system. Please enter correct details. However, the Aadhaar number is not must for enrolment process and the person can enrol giving his PAN Number also.
Whenever, I am trying to enroll as transporter, the system is saying you are already registered under GST system and go and register using that GSTIN
This is indicating that you are a registered taxpayer with valid GSTIN, since a validation is done on the PAN you have entered. You need not enroll again as transporter but use your GSTIN to register on e-way bill portal.
Whenever, I am trying to login the system says ‘Your account has been frozen’. How should I resolve this issue?
This is indicating that your account has been frozen because you might have cancelled your registration or your GSTIN has been de-activated in the GST Common Portal. Please visit the GST Common Portal (www.gst.gov.in) to find the status of your GSTIN under ‘Search Taxpayer’ tab. In case you are able to log in on GST portal but not log on e-Way Bill portal, please lodge your grievance at https://selfservice.gstsystem.in/.
Whenever, I am trying to login the system says ‘your account has been blocked…Pl try after 5 minutes. How should I resolve this issue?
This is indicating that you had tried to login to the e-way bill system with incorrect username and password for more than 5 times. Hence, the system has blocked your account for security reasons and it will be unblocked after 5 minutes.
What should I do, if I am not remembering my username and password?
If you have forgotten the username or password, then use the ‘Forgot Username’ or ‘Forgot Password’ facility provided on the portal to recollect your username or create new password accordingly. The user needs to enter some details after authenticating the same via an OTP, then, user will be provided with the username and password.
How can anyone verify the authenticity or the correctness of e-way bill?
Any person can verify the authenticity or the correctness of e-way bill by entering EWB No, EWB Date, Generator ID and Doc No in the search option of EWB Portal.
How to generate e-way bill for multiple invoices belonging to same consignor and consignee?
If multiple invoices are issued by the supplier to recipient, that is, for movement of goods of more than one invoice of same consignor and consignee, multiple EWBs have to be generated. That is, for each invoice, one EWB has to be generated, irrespective of the fact whether same or different consignors or consignees are involved. Multiple invoices cannot be clubbed to generate one EWB. However after generating all these EWBs, one Consolidated EWB can be prepared for transportation purpose, if goods are going in one vehicle.
What has to be done by the transporter if consignee refuses to take goods or rejects the goods for any reason?
There is a chance that consignee or recipient may reject to take the delivery of consignment due to various reasons. Under such circumstances, the transporter can get one more e-way bill generated with the help of supplier or recipient by indicating supply as ‘Sales Return’ with relevant documents, return the goods to the supplier as per his agreement with him.
What has to be done, if the validity of the e-way bill expires?
If validity of the e-way bill expires, the goods are not supposed to be moved. However, under circumstance of ‘exceptional nature and trans-shipment’, the transporter may extend the validity period after updating reason for the extension and the details in PART-B of FORM GST EWB-01.
Can I extend the validity of the e-way bill?
Yes, one can extend the validity of the e-way bill, if the consignment is not being reached the destination within the validity period due to exceptional circumstance like natural calamity, law and order issues, trans-shipment delay, accident of conveyance, etc. The transporter needs to explain this reason in details while extending the validity period.
How to extend the validity period of e-way bill?
There is an option under e-way bill to extend the validity period. This option is available for extension of e-way bill before 8 hours and after 8 hours of expiry of the validity. Here, transporter will enter the e-way bill number and enter the reason for the requesting the extension, from place (current place), approximate distance to travel and Part-B details. It may be noted that he cannot change the details of Part-A. He will get the extended validity based on the remaining distance to travel.
Who can extend the validity of the e-way bill?
The transporter, who is carrying the consignment as per the e-way bill system at the time of expiry of validity period, can extend the validity period.
How to handle “Bill to” – “Ship to” invoice in e-way bill system?
Sometimes, the tax payer raises the bill to somebody and sends the consignment to somebody else as per the business requirements. There is a provision in the e-way bill system to handle this situation, called as ‘Bill to’ and ‘Ship to’.
In the e-way bill form, there are two portions under ‘TO’ section. In the left hand side – ‘Billing To’ GSTIN and trade name is entered and in the right hand side – ‘Ship to’ address of the destination of the movement is entered. The other details are entered as per the invoice.
In case ship to state is different from Bill to State, the tax components are entered as per the billing state party. That is, if the Bill to location is inter-state for the supplier, IGST is entered and if the Bill to Party location is intra-state for the supplier, the SGST and CGST are entered irrespective of movement of goods whether movement happened within state or outside the state.
Can the e-way bill be deleted or cancelled?
The e-way bill once generated cannot be deleted. However, it can be cancelled by the generator within 24 hours of generation. If a particular EWB has been verified by the proper officer, then it cannot be cancelled. Further, e-way bill can be cancelled if either goods are not transported or are not transported as per the details furnished in the e-way bill.
Whether the e-way bill can be cancelled? If yes, under what circumstances?
Yes, e-way bill can be cancelled if either goods are not transported or are not transported as per the details furnished in the e-way bill. The e-way bill can be cancelled within 24 hours from the time of generation.
Who can reject the e-way bill and Why?
The person who causes transport of goods shall generate the e-way bill specifying the details of other person as a recipient of goods. There is a provision in the common portal for the other party to see the e-way bill generated against his/her GSTIN. As the other party, one can communicate the acceptance or rejection of such consignment specified in the e-way bill. If the acceptance or rejection is not communicated within 72 hours from the time of generation of e-way Bill or the time of delivery of goods which ever is earlier,, it will be deemed that he has accepted the details.
How does the taxpayer or recipient come to know about the e-way bills generated on his GSTIN by other person/party?
As per the rule, the taxpayer or recipient can reject the e-way bill generated on his GSTIN by other parties. The following options are available for him to see the list of e-way bills:
He can see the details on the dashboard, once he logs into the system.
He will get one SMS everyday indicating the total e-way bill activities on his GSTIN.
He can go to reject option and select date and see the e-way bills. Here, system shows the list of e-way bills generated on his GSTIN by others.
He can go to report and see the ‘EWBs by other parties’.
What is consolidated e-way bill?
Consolidated e-way bill is a document containing the multiple e-way bills for multiple consignments being carried in one conveyance (goods vehicle). That is, the transporter, carrying multiple consignments of various consignors and consignees in one vehicle can generate and carry one consolidated e-way bill instead of carrying multiple e-way bills for those consignments.
Who can generate the consolidated e-way bill?
A transporter can generate the consolidated e-way bills for movement of multiple consignments in one vehicle.
What is the validity of consolidated e-way bill?
Consolidated EWB is like a trip sheet and it contains details of different EWBs in respect of various consignments being transported in one vehicle and these EWBs will have different validity periods.
Hence, Consolidated EWB does not have any independent validity period. However, individual consignment specified in the Consolidated EWB should reach the destination as per the validity period of the individual EWB.
What has to be done, if the vehicle number has to be changed for the consolidated e-way bill?
There is an option available under the ‘Consolidated EWB’ menu as ‘regenerate CEWB’. This option allows you to change the vehicle number to existing Consolidated EWB, without changing the individual EWBs. This generates a new CEWB, which has to be carried with new vehicle. Old CEWB will become invalid for use.
Can the ‘consolidated e-way bill’ (CEWB) have the goods / e-way bills which are going to be delivered before reaching the destination defined for CEWB?
Yes, the consolidated e-way bill can have the goods or e-way bills which will be delivered to multiple locations as per the individual EWB included in the CEWB. That is, if the CEWB is generated with 10 EWBs to move 3 consignments to destination Y and 7 consignments to destination X, then on the way the transporter can deliver 3 consignments to destination Y out of 10 and move with remaining 7 consignments to the destination X with the same CEWB. Alternatively, two CEWB can be generated one for 3 consignments for destination Y and another CEWB for 7 consignments for destination X.
What are the modes of e-way bill generation, the taxpayer can use?
The e-way bill can be generated by the registered person in any of the following methods;-
o Using Web based system
o Using SMS based facility
o Using Android App
o Bulk generation facility
o Using Site-to-Site integration
o Using GSP ( Goods and Services Tax Suvidha Provider)
How can the taxpayer use the SMS facility to generate the e-way bill?
The taxpayer has to register the mobile numbers through which he intends to generate the e-way bill on the e-way bill system. Please see the user manual for SMS based e-way bill generation available on the portal for further details.
How to download mobile app?
The mobile app is available only for the taxpayers and enrolled transporters. It is not available in Play Store. The main user has to login and select the ‘for mobile app’ under registration menu. The system asks to select the user/sub-user and enter the IMEI number of the user. Once it is entered, the concerned user gets the link in his registered mobile to download the app through SMS. Now, the user has to download the app by clicking that link and enable it to get installed on the mobile.
Summary
Article NameGENERAL FAQsDescriptionWhat is E Way bill. General information provided by Arpit Gupta Classes which provides online classes for GST.AuthorArpit GuptaPublisher Namearpitguptaclasses.comPublisher Logo

For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
ICAI EXAM NOTIFICATION
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/02/05/icai-exam-notification/
ICAI has declared the Date sheet for IPCC May 2018 & FINAL may 2018, which are below in table and their links are given below.
CA IPCC DATESHEET
SUBJECTDATE
ACCOUNTS3
rd
MAY 2018
LAW5
th
MAY 2018
COSTING & FM7
th
MAY 2018
TAXATION9
th
MAY 2018
ADVANCED ACCOUNTING11
th
MAY 2018
AUDITING13
th
MAY 2018
IT & SM15
th
MAY 2018
Exam Fee for May 2018
Single GroupRs.1500 /-
Both GroupRs. 2700 /-
LINK:-https://resource.cdn.icai.org/48231icaiexams2018.pdf
CA FINAL DATESHEET
SUBJECTDATE
FINANCIAL REPORTING2
rd
MAY 2018
STRATEGIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT4
th
MAY 2018
ADVANCE AUDITING & PROFESSIONAL ETHICS6
th
MAY 2018
CORPORATE LAWS & OTHER ECONOMIC LAWS8
th
MAY 2018
STRATEGIC COST MANAGEMENT & PERFORMANCE EVALUATION10
th
MAY 2018
ELECTIVE PAPERS (Anyone Out Of 6 Papers)
· Risk Management
· International Taxation
· Economic Laws
· Financial Services & Capital Markets
· Global Financial Reporting Standards
· Multidisciplinary Case Study
12
th
MAY 2018
DIRECT TAX LAWS & INTERNATIONAL TAXATION14
th
MAY 2018
ADVANCED INDIRECT TAX LAWS16
th
MAY 2018
Exam Fee for May 2018
Single GroupRs.1800 /-
Both GroupRs. 3300 /-
LINK:-https://resource.cdn.icai.org/48231icaiexams2018.pdf
IMPORTANT NOTIFICATION:-
Examination Timings – CA May – 2018 Examinations
An Announcement Dated 9th January 2018 Informing The Schedule And Timings Of The CA Examinations-May 2018 Was Hosted On Www.Icai.Org
The Said Announcement Had Indicated That The CA Exams In May 2018 Will Be Held In The Morning Session From 10.30 AM To 1.30 PM (IST).
Subsequent To That Representations Were Received Requesting For Retaining The Earlier Timings, I.E. 2.00 PM To 5.00 PM.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Direct Tax-
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/03/24/direct-tax/

Direct Tax is that type of tax which is directly paid to the Government by the taxpayers. It is imposed directly by the Government and cannot be transferred to any other entity for payment.
Examples of Direct Taxes in India:
Income Tax
Wealth Tax
Corporation Tax
The Central Board of Direct Taxes in India:
The direct taxation is overseen by CBDT or Central Board of Direct Taxes in India. It was formed as a result of Central Board of Revenue Act, 1924.
It is the hub and nexus of all the Direct Tax related news and enforcement. The body is headed by the Chairman and comprises of 6 members who are also Special Secretary to the Government of India.
Description: In the case of a direct tax, the burden can’t be shifted by the taxpayer to someone else. These are largely taxes on income or wealth. Examples of direct taxes are income tax, gift tax etc.
Tax Rates for Different Types Of Direct Taxes:Income tax slab for a domestic company–
Turnover particulars tax rate
Gross turnover upto 250 Cr. in the previous year 25%
Gross turnover exceeding 250 Cr. in the previous year 29%
Income Tax Slab Rates for FY 2017-18-Income Tax SlabTax RateSec 80C Investments
Income Up To Rs 2,50,000*No Tax
Income From Rs 2,50,000 – Rs 5,00,0005%Save Rs 7,500 In Taxes.
Income From Rs 5,00,000 – 10,00,00020%Save Rs 30,000 In Taxes.
Income More Than Rs 10,00,00030%Save Rs 45,000 In Taxes.
Income Tax Slab for Senior Citizens (60 Years Old Or More but Less than 80 Years Old) for FY 2017-18Income Tax SlabTax RateSec 80C Investments
Income Up To Rs 3,00,000*No Tax
Income From Rs 3,00,000 – Rs 5,00,0005%Save Rs 7,500 In Taxes.
Income From Rs 5,00,000 – 10,00,00020%Save Rs 30,000 In Taxes.
Income More Than Rs 10,00,00030%Save Rs 45,000 In Taxes.
For more information about direct tax stay tuned with-
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
Disclaimer-The blog information has been collected from various sources. Arpitguptaclasses does not guarantee about the authenticity of the information. User discretion is advised before taking any decision.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
E-Way Bills Applicability- An Overview
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/12/e-way-bills-applicability-overview/

AWhat Is E-Way Bill
EWB Is Electronic Document
Contain Two Parts – Part A And Part B
To Be Generated Before Causing Movement Of Goods On GST Common Portal As Per Rule 138 Of CGST 2017
To Be Generated By Registered Person Who Cause Movement Of Goods Or Transporters
Prior The Actual Movement Of Goods
Generation Of E-Way Bill On EWB Portal
BStakeholder Of EWB
Suppliers – Generate The E-Way Bills And Reject The E-Way Bills Generated By Other Party Against His/Her Name If It Does Not Belong To Him/Her.
Recipients – Generate The E-Way Bills And Reject The E-Way Bills Generated By Other Party Against His/Her Name If It Does Not Belong To Him/Her.
Transporters – Generate The E-Way Bills, Consolidated E-Way Bills And Update The Vehicle Numbers For The E-Way Bills Assigned To Him For Transportation By The Taxpayers.
Department Officers – Verify The E-Way Bills And Consignments Carried With The E-Way Bills.
CWhen And Who Should Prepare Part A Of EWB
Statutory Provision:
Every Registered Person Who Causes Movement Of Goods Of Consignment Value Exceeding Fifty Thousand Rupees—
(I) In Relation To A Supply; Or
(Ii) For Reasons Other Than Supply; Or
(Iii) Due To Inward Supply From An Unregistered Person
Shall, Before Commencement Of Such Movement, Furnish Information Relating To The Said Goods As Specified In Part A Of FORM GST EWB-01, Electronically, On The Common Portal Along With Such Other Information As May Be Required On The Common Portal And A Unique Number Will Be Generated On The Said Portal.
DWho Will Generate E-Way Bill
I. Registration Is Mandatory To Generate EWB – GST Portal / EWB Common Portal
Ii. Only Registered Person Can Generate EWB
Iii. Un Registered Person Cannot Generate EWB
EWho Cause Movement And Shall Generate EWB
Movement Of Goods CausedWho Generate EWB
Supplier Is Registered And Undertakes To Movement Of Goods.Movement Of Goods Caused By SupplierSupplier Will Generate EWB
Recipient Is Registered And Undertakes To Transport.Movement Of Goods Caused By RecipientRecipient Will Generate EWB
Supplier: Unregistered
Recipient: Unregistered And Unknown Recipient.
Movement Of Goods Caused By Unregistered PersonEWB Not Required.
However Unregistered Person Supply Goods Has Option To Generate EWB.
Supplier: Unregistered
Recipient: Unregistered And Known Recipient.
Movement Of Goods Caused By Unregistered Person
Supplier: Unregistered
Recipient: Registered And Known Recipient.
Movement Of Goods Deemed To Be Caused By Registered RecipientRecipient Will Generate EWB.
EWB Generated By Transporter: On An Authorization Received From The Registered Person Can Generate EWB.
EWB Generated By Ecommerce Or Courier Agency: On An Authorization Received From The Consignor
FCases Where Unregistered Person Can Generate Eway Bill
1. Supplier Of Handicraft Goods
2. Un-Registered Supplier Where Recipient Is Unknown, Optional. An Unregistered Person Can Alternatively Enrol And Log In As The Citizen And Generate The E- Way Bill.
GConsignment Value
For The Purposes Of This Rule,
The Consignment Value Of Goods = Determined In Accordance With The Section 15,
Declared In An Invoice,
A Bill Of Supply Or
A Delivery Challan
Includes = CGST + SGST + IGST
Exclude = The Value Of Exempt Supply Of Goods Where The Invoice Is Issued In Respect Of Both Exempt And Taxable Supply Of Goods.
1Consignment Value Is More Than Rs. 50000EWB Is Mandatory,
2Consignment Value Is Less Than Rs. 50000EWB Is Optional
Cases Where EWB Is Required Even If Consignment Value Is Less Than Rs. 50000
Job Worker: Where Goods Are Sent By A
Principal Located In One State Or Union Territory
To A Job Worker Located In Any Other State Or Union Territory,
The E-Way Bill Shall Be Generated Either By The Principal Or The Job Worker, If Registered, Irrespective Of The Value Of The Consignment.
Handicraft Goods: Where Handicraft Goods Are Transported
From One State Or Union Territory
To Another State Or Union Territory
By A Person Who Has Been Exempted
From The Requirement Of Obtaining Registration
Under Clauses (I) And (Ii) Of Section 24,
The E-Way Bill Shall Be Generated By The Said Person Irrespective Of The Value Of The Consignment.
HReason For Movement Of Goods:
I. EWB Is Required For All Transactions Involving Movement Of Goods Whether In The Course Of Supply On Not.
Ii. EWB Is Required Not Whenever There’s A ‘Supply’ But Every Time There’s ‘Movement’ Of Good.
Iii. Every Time There Is Movement Of Goods, Whether By Way Of Supply Of Goods Or Supply Of Services, EWB Will Be Required.
Iv. Movement Of Goods Via Motorised Vehicle Only.For Reason Other Than Supply:A. Exports/Imports
B. Job Work
C. SKD Or CKD
D. Recipient Not Known
E. Supply Of Liquid Gas Where Quantity Is Not Known
F. Supply Return
G. Exhibition Or Fairs
H. For Own Use
I. Supply On Approval Basis
J. Others Etc.
IBefore Commencement Of Such Movement
EWB Must Be Created Before Commencement Of Movement Of Goods.
Exception:
In Case Of Movement Of Goods By Railway, EWB Can Be Generated Even After Movement Of Goods, In Such Case Goods Will Not Be Delivered Until EWB Will Be Presented At The Time Of Delivery.
JInformation Relating To The Said Goods
PART:A
A. GSTIN Of Suppliers & Recipient (URP, If Unregistered)
B. Place Of Delivery (PIN Code Of Place Of Delivery)
C. Document No. (Tax Invoice, Bill Of Supply & Delivery Challan Etc.)
D. Document Date
E. Value Of Goods (Including Tax & Cess)
F. HSN Wise Summary (If Aggregate Turnover Upto 5 Crores; 2 Digits & For More Than 5 Crores; 4 Digits)
G. Reason For Transportation (Select From Dropdown Menu)
PART-B: –
A. Vehicle No. For Road
B. Transport Document Number (GRN, Railway Receipt, Air Way Bill Etc.)
KPart B Of EWB & Generation Of EWB
Part B Of EWB Contain Detail Of Conveyance Carrying Goods For Movement.
EWB Is Not Valid And Usable, Unless Its Part B Is Filled. Part-B Is A Must For The-EWB For Movement Purpose.
Otherwise Printout Of EWB Says It Is Invalid For Movement Of Goods.
Mode Of TransportWho Causing Movement Of GoodsWhen To Generate EWB
By Road
In Own Conveyance Or
Hired Conveyance Or
Public Conveyance
Supplier
Recipient
E-Way Bill Must Be Generated After Filling Part B Of FORM GST EWB-01, Before The Commencement Of Movement Of Goods Either By Person Causing Of Such Movement Of Goods Either As Consignee Or Consignor.
By RoadRegistered PersonWhere EWB Is Not Generated By Registered Person After Filling Part B Of EWB,
Furnish The Information Relating To Transporter On Common Portal.
Transporter On AuthorisationEWB Shall Be Generated By Authorised Transporter
Railway, Air Or VesselPart B Of FORM GST EWB 01, Can Be Filled Evenafter Commencement Of Movement Of Goods.
However In Case Of Transportation Of Goods By Railways, Goods Only Will Be Delivered Only After Production Of E-Way Bill.
LCases Where EWB Is Not Required / Optional
PART APART B
Where Consignment Value Is Less Than Rs. 50000Part A Is OptionalPart B Is Optional
Movement Of Goods By Unregistered SupplierPart A Is OptionalPart B Is Optional
To Unregistered Recipient
WherePart A Is MandatoryPart B Is Optional
Goods Transported Within State Or UT
From Place Of Consigner
To Place Of Transporter
For Further Transportation
WherePart A Is MandatoryPart B Is Optional
Goods Transported Within State Or UT
From Place Of Transporter
To Place Of Consignee
For Further Transportation
MUnique Reference Number
On Generation EWB, URN Shall Be Given To
1. Supplier
2. Recipient
3. Transporter
Validity: Such URN Shall Be Valid For 15 Days For Updation Of PART B Of EWB-01.
NMultiple Vehicle Used For Transportation – Same Transporter
Goods Transferred From One Conveyance To Other Conveyance For Any Reason:
Detail Of New Conveyance Will Be Updated In PART B Of EWB Before Such Transfer By Supplier, Recipient, Transporter
OMultiple Transporter
In Case Part B Is Not Filed: Supplier, Recipient Or Transporter, May Assign The EWB Number To Another Registered Or Enrolled Transporter
In Case Part B Is Filed: Where Detail Of Conveyance Has Been Filed In Part B Of EWB By Transporter, Such EWB Can Not Be Assign To Another Transporter By Supplier Or Recipient.
PConsolidated EWB
A. Where Multiple Consignments Are Intended To Be Transported In One Conveyance,
B. The Transporter May Indicate The Serial Number Of E-Way Bills Generated In Respect Of Each Such Consignment Electronically On The Common Portal And
C. A Consolidated E-Way Bill In FORM GST EWB-02 Maybe Generated By Him On The Said Common Portal Prior To The Movement Of Goods.
QTransporter To Be Responsible For Generation Of EWB
In Case, Supplier Or Recipient Has Not Generated EWB And Consignment Value Is More Than Rs. 50000 Transporter Will Be Responsible For Generation Of EWB.
Where Goods Are Supplies Via Ecommerce Operator Or Courier Agency, EWB Can Be Generated By Such Ecommerce Operator Or Courier Agency.
REWB To GSTR 1
Information Furnished In PART A Of EWB:
To Registered Person: Can Use This Information For GSTR -1 Purpose.
To Unregistered Person: Information Shall Be Shared Via Email Or Phone Number.
SCancellation/Deletion/Modification Of EWB
Where Goods Have Not Been Verified As Per Rule 138(B) In Transit: EWB Can Be Cancelled Only Within 24 Hours Of Generation On EWB Portal.
Where Goods Have Been Verified As Per Rule 138(B) In Transit: EWB Cannot Be Cancelled In Any Case.
Deletion Of EWB: EWB Cannot Be Deleted
Modification Of EWB: Once Generated, PART A Of EWB Cannot Be Edited. Only PART B Can Be Updated As Per Requirements.
TValidity Of EWB
S NoDistanceValidity Period
1Up To 100 KmOne Day In Case Of Other Than Over Dimensional Cargo
2For Every 100 Km Or Part Thereof There AfterOne Additional Day In Case Of Other Than Over Dimensional Cargo
3Up To 20 KmOne Day In Case Over Dimensional Cargo
4For Every 20 Km Or Part Thereof There AfterOne Additional Day Over Dimensional Cargo
Extension Validity By Commissioner: Commissioner May Extend The Validity For Certain Categories Of Specified Goods.
Extension Validity By Transporter: Only In Exception Case, By Updating Part B Of EWB.
Counting Of Period Of Validity: Period Of Validity Shall Be Counted From The Time At Which The E-Way Bill Has Been Generated And Each Day Shall Be Counted As The Period Expiring At Midnight Of The Day Immediately Following The Date Of Generation Of E-Way Bill.
UAcceptance Of EWB With In 72 Hours
A. Supplier Or Recipient Shall Communicate His Acceptance Or Rejection Of The Consignment Covered By EWB.
B. Such Acceptance Or Rejection Should Be With In 72 Hours Or Time Of Delivery Of Goods, Which Ever Is Earlier.
C. In Case No Acceptance Or Rejection Is Communicated, It Shall Deemed To Be Accepted.
VPenalties For Not Carrying EWB
Penalty For Certain Offence:
A Taxable Person, Registered Person And Any Person, Transports Any Taxable Goods Without The Cover Of Documents As May Be Specified In This Behalf I.E. Eway Bill; Shall Be Liable To A Penalty Of Rs. 10,000/- Or Tax Sought To Be Evaded, Whichever Is Higher.
Detention, Seizure And Release Of Goods And Conveyance In Transit
As Per Section 129 Of The CGST Act’2017,
Where Any Person Transport Or Store Any Goods, In Contravention Of This Act And Rules Contravention, All Such Goods And Conveyance And Documents Shall Be Liable To Detention Or Seizure, Shall Be Released With Penalty;–
Where The Owner Of The Goods Come Forward To Pay Tax And Penalties
A. In Case Of Taxable Goods; 100% Of The Tax Payable & Penalty.
B. In Case Of Exempted Goods; 2% Of The Value Of Goods Or Rs. 25,000/-, Whichever Is Less.
C. Upon Furnishing Of Security Equivalent To Amount Above
Where The Owner Of The Goods Does Not Come Forward To Pay Tax And Penalties;
A. In Case Of Taxable Goods; 50% Of The Value Of The Goods Reduced By The Tax Amount Paid,
B. In Case Of Exempted Goods; 5% Of The Value Of Goods Or Rs. 25,000/-, Whichever Is Less.
C. Upon Furnishing Of Security Equivalent To Amount Above
No Such Goods Or Conveyance Shall Be Detained Or Seized Without Serving An Order Of Detention Or Seizure On The Person Transporting The Goods.
No Tax, Interest Or Penalty Shall Be Determined Without Giving An Opportunity Of Being Heard.
The Goods So Detained Or Seized Shall Be Released, On A Provisional Basis, Upon Execution Of A Bond And Furnishing Of A Security, Or On Payment Of Applicable Tax, Interest And Penalty Payable (Section 67(6) – Power Of Inspection, Search And Seizure)
On Payment Of Tax And Penalties, All Proceeding Shall Be Deemed To Be Concluded.
In Case Of Non-Payment Of Tax And Penalties, Further Proceeding U/S 130 Shall Be Initiated.
Confiscation Of Goods And Conveyance And Levy Of Penalties:
Where The Person Transporting Any Goods Or The Owner Of The Goods Fails To Pay The Amount Of Tax And Penalty Within 7 Days Of Such Detention Or Seizure, All Such Goods Or Conveyances Shall Be Liable To Confiscation And The Person Shall Be Liable To Penalty As Under
A. Penalties Which Should Not Be More Than Market Value Of Goods Less Tax There On
B. Penalties Which Should Not Be Less Than Penalties U/S 129(1)
No Order For Confiscation Of Goods Or Conveyance Shall Be Made Without Giving An Opportunity Of Being Heard.
WDocument/Device To Be Carried With Conveyance
Person In Charge Will Carry Following Document With Conveyance
A. Invoice, Bill Of Supply Or Delivery Challan
B. Copy Of EWB Or Number Of EWB, Required Only In Case Of Transport By Road.
Invoice Reference Number (IRN) Can Also Be Obtain In Place Of Actual Invoice Copy. Such IRN Shall Be Valid For 30 Days. Such IRN Can Be Obtain By Filling GST INV-1
EWB Not Required In Exception Cases: Commissioner By Notification, Allow To Keep Following Document With Conveyance In Place Of EWB.
1. Invoice, Bill Of Supply Or Delivery Challan
XVerification Of Documents And Conveyances
1. Commissioner Or Authorised Office, Can Intercept Any Vehicle To Verify EWB In Physical Or Electronic Form.
2. Verification Can Be Done Via Radio Frequency Identification Device.
3. Physical Verification Of Conveyance Can Also Be Carried Out.
YInspection And Verification Of Goods
Inspection Report Of Verification:
A. A Summary Report Of Every Inspection Of Goods In Transit Shall Be Recorded Online B. By The Proper Officer In Part A Of FORM GST EWB-03 Within 24 Hours Of Inspection And C. The Final Report In Part B Of FORM GST EWB-03 Shall Be Recorded Within 3 Days Of Such Inspection.
No Further Verification Of Conveyance:
A. No Further Verification Of Conveyance Will Be Done, In Case It Is Done At One Place B. In Case Specific Information Is Received, Such Verification Can Be Done Again.
ZFacility For Uploading Information Regarding Detention Of Vehiclearpi
Where A Vehicle Has Been Intercepted And Detained For A Period Exceeding 30 Minutes,
The Transporter May Upload The Said Information In FORM GST EWB-04 On The Common Portal.
for more information, stay tuned with- http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Highlights Of The Finance Bill, 2018
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/17/highlights-finance-bill-2018/
Tax Rates
No Change in Tax Rates for Individuals/Partnership firms and LLPs.
Tax Rates for domestic companies will be 25% of the total income if the total turnover or gross receipts of the previous year 2016-17 does not exceed Rs.250 crores (earlier it was 50 crores) and in all other cases the rate of Income-tax shall be 30 % of the total income. In the case of company other than domestic company, the rates of tax are the same as those specified for the financial year 2017-18.
No change in surcharge.
The health & education cess shall now be computed @ 4% on aggregate of Income-Tax & Surcharge.
Capital Gains
No more exemption for the capital gains arising from listed equity shares
[Section 10(38), 112A – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Currently, long term capital gains arising from transfer of listed equity shares or units of equity oriented fund or units of business trusts, are exempt from income-tax under Section 10(38) of the Act. In order to minimize the economic distortions and curb erosion of tax base, it is proposed to withdraw this exemption and to introduce a new section 112A in the Act.
As per new proposed Section 112A, long term capital gains arising from transfer of an equity share, or a unit of an equity oriented fund or a unit of a business trust shall be taxed at 10% of such capital gains. The tax on capital gains shall be levied in excess of Rs. 1 lakh. This concessional rate of 10% will be applicable if STT has been paid on both acquisition and transfer of such capital asset, in case of equity shares, and paid at the time of transfer in case of unit of equity oriented fund or a unit of a business trust.
Though the tax rate has been kept at 10% but it shall be charged on the capital gains as computed without giving the benefit of indexation to the investor. Let us understand the meaning of indexation. It is a process to increase the cost of acquisition so as to nullify the impact of inflation. The indexation process takes into account the inflation from the time taxpayer bought the asset to the time he sells it. The indexation process increases the cost of acquisition of the asset and consequently, lowers the capital gains. The indexation benefit is generally allowed in case of transfer of a long-term capital asset, however, such benefit shall not be allowed in case of transfer of listed equity shares.
This new provision to tax the long-term capital gains arising from transfer of listed equity shares shall be applicable for all those share trades which are done on or after April 1, 2018. To provide an interim relief and to provide an opportunity to the investors to plan their affairs, the investors are given an option to assume the cost of acquisitions of the shares forming part of their portfolio different from the one they have actually paid to acquire them.
The cost of acquisitions of a listed equity share acquired by the taxpayer before the February 1, 2018, shall be deemed to be the higher of following:
a) The actual cost of acquisition of such asset; or
b) Fair market value of such shares or actual sales consideration accruing on its transfer, whichever is lower.
The Fair market value of listed equity share shall mean its highest price quoted on the stock exchange on January 31, 2018.
However, if there is no trading in such shares on such exchange on January 31, 2018, the highest price of such asset on such exchange on a date immediately proceeding January 31, 2018.
While in case of units which are not listed on recognized stock exchange, the net asset value of such units as on January 31, 2018 shall be deemed to be its FMV.
Taxability of LTCG on trading in listed equity shares may be understood with the help of following example:
ParticularsScenario 1Scenario 2Scenario 3Scenario 4Scenario 5
Sales Consideration (A)10,00,00010,00,00010,00,00010,00,00010,00,000
Date Of Sale31-03-1801-04-1801-04-1801-04-1801-04-19
Actual Cost Of Acquisition (B) 800,000 800,000 800,000 800,000 800,000
Date Of Purchase01-01-1701-01-1701-01-1701-01-1701-03-18
Quoted Price On Stock Exchange As On 31/01/2018 (C) 850,000 750,000 900,000 1,100,000 1,100,000
Deemed Cost Of Acquisition (D)* 800,000 800,000 900,000 1,000,000 800,000
Long-Term Capital Gains (E = D-A) 200,000 200,000 100,000 – 200,000
Exemption For Capital Gains (F = E – 1,00,000) 200,000 100,000 100,000 – 100,000
Tax On Capital Gains (F * 10%) – 10,000 – – 10,000
* D shall be higher of following:
a) Actual Cost of acquisition
b) Lower of Sales Consideration and Quoted Price on Stock Exchange as on 31/01/2018
This capital gain has been kept out of preview of Chapter VIA deductions and relief under Section 87A. It means a taxpayer cannot claim any deduction under Sections 80C to 80U or relief under Section 87A from the gross total income to the extent of such capital gains. If an investors has earned the long-term capital gains of Rs. 2,00,000 from sale of listed equity shares, he shall be liable to pay tax of Rs. 10,400 (Rs. 10,000 tax on capital gains + Rs. 400 health and education cess ).
Slight variation of sales consideration from stamp value is acceptable
[Section 43CA, 50C and 56 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
As per the current provisions, when a taxpayers claims that the sales consideration received by him from transfer of an immovable property is less than the value adopted by the Stamp authorities, then the stamp value is deemed as the actual sales consideration. Deeming the stamp value as the sales consideration, result in higher amount of capital gains even if the seller has not gained anything due to such higher stamp valuation. Further, such difference in the stamp value and the actual consideration disclosed by the parties is also taxed in the hands of the buyer.
It is generally pointed out that this variation can occur in respect of similar properties in the same area because of a variety of factors, including shape of the plot or location. In order to minimize hardship in case of genuine transactions in the real estate sector, it is proposed to provide that no adjustments shall be made in a case where the variation between stamp duty value and the sale consideration is not more than five percent of the sale consideration. These amendments will be applicable for all transactions occurred entered into on or after April 1, 2018.
Sec. 54EC exemption only for immovable properties
[Section 54EC – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Section 54EC of the Act provides exemptions up to Rs. 50 lakhs if any long-term capital gain is invested in the specified bonds of NHAI and RECL within a period of six months after the date of such transfer. Such investments in these bonds have a lock-in period of 3 years.
The Finance Bill has significantly curtailed the scope of this exemption. As per proposed amendment, exemption under Section 54EC shall be allowed only if long-term capital gains arising from transfer of an immovable property (land or building or both) is invested in the specified bonds. The lock-in period of such bonds has also been increased to 5 years.
Corporate Tax
‘Accumulated Profits’ redefined for purpose of Deemed Dividend
[Section 2(22)(d) – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Currently, any distribution of accumulated profits (whether capitalized or not) to the shareholders by a company is subject to Dividend Distribution Tax. Companies with large accumulated profits used to adopt the amalgamation route to reduce accumulated profits so as to bypass the provisions of deemed dividend under Section 2(22)(d).
With a view to prevent such abusive arrangements, a new Explanation 2A is proposed to be inserted in section 2(22) to widen the scope of the term ‘accumulated profits’.
As per the new Explanation, the accumulated profits/losses of an amalgamated company shall be increased by the accumulated profits of the amalgamating company (whether capitalized or not) on the date of amalgamation.
Dividend payouts of equity oriented mutual fund subject to DDT
[Section 115R, 115T – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]]
Specified company or Mutual Fund shall be liable to pay tax on income distributed to its unit holders. However, in respect of any income distributed to a unit holder of equity oriented funds is currently not chargeable to Dividend Distribution Tax.
It is proposed to amend the section 115R to provide that where any income is distributed by a Mutual Fund, being an equity oriented fund, the fund shall be liable to pay additional income tax at the rate of 10% on income so distributed.
Relaxation in provisions of carry forward and set off of losses for companies applied for Insolvency [Section 79 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
Losses of a closely held company are allowed to be carried forward and set off only if there is a continuity in the beneficial ownership of not less than 51% of the voting power on the last day of the year in which losses were incurred.
This provision is a big hurdle for restructuring and rehabilitating the companies who have applied for insolvency and who have witnessed change in the beneficial ownership.
In order to address this problem, it is proposed that the rigors of section 79 shall be relaxed in case of those companies whose resolution plan has been approved under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
Relief from MAT for companies who have applied for Insolvency
[Section 115JB – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
While calculating book profit for payment of MAT under Section 115JB, lower of brought forward loss and unabsorbed depreciation, is allowed as deduction. The amount of deduction becomes nil if either brought forward loss or unabsorbed depreciation is also nil.
Not allowing deduction for losses or depreciation does not provide any tax relief to the rehabilitating companies that are seeking insolvency resolution.
To end the hardship for the companies under insolvency resolution, Section 115JB is proposed to be amended. Such companies are allowed to claim deduction of both unabsorbed depreciation and brought forward losses while calculating book profits for the purpose of MAT.
Non-Individual entity to obtain PAN
[Section 139A – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
Section 139A is proposed to be amended that every non-individual entity should have to obtain a PAN as its Unique Entity Number (UEN) if they enter into a financial transaction of an amount aggregating to Rs. 2.50 lakhs or more in a financial year.
There is always a natural person who enters into the transaction on behalf of the non-individual entity. Therefore, the amendment shall be of no use if the related natural person behind such entities doesn’t obtain the PAN.
Thus, in order to make the amendment useful, it is also proposed that the managing director, director, partner, trustee, author, founder, karta, CEO, principal officer or office bearer or any person competent to act on behalf of such entities will also have to apply for allotment of PAN.
Compensation covered within the tax ambit
[Section 2(24), 28, 56 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
In various rulings, the Courts have held that compensation amount received in connection with business and employment contracts are out of the purview of income-tax.
It is now proposed that any compensation received in connection with the termination or modification of a contract is taxable. The taxability of the compensation would depend upon nature of contract and relationship of the recipient with the payer. If the compensation is related to a business contract, the receipts shall be taxable as business income under Section 28. If it is relating to the employment and the compensation is received after termination of the employment, the receipts shall be taxable as residuary income under Section 56.
These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2019 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to assessment year 2019-20 and onwards.
Disallowance of expenditure paid in cash by Trusts
[Section 10(23C), Section 11 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Currently, there are no restrictions on mode of payments by charitable or religious trusts or institutions. There are also no checks on whether such trusts or institutions follow TDS provisions or not. This has led to lack of an audit trail for verification of application of income.
In order to encourage a cash-less economy and to reduce the generation and circulation of black money, it is proposed that trusts or institutions will also be required to follow the provisions of TDS and will make all expenses in excess of Rs. 10,000 through banking channels.
Consequently, the provisions of TDS disallowance under section 40(a)(ia) and expenses disallowance under section 40A(3) and 40A(3A) shall be applicable while computing the application of income in case of trusts or institutions.
Personal Taxation
Standard deduction from salary income reintroduced
[Section 16, 17 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
The Finance Bill, 2018 proposed standard deduction of up to Rs. 40,000 to the salaried taxpayers. Such deduction is allowed in lieu of transport allowance and reimbursement of medical expenses. Currently, a deduction of Rs. 19,200 is allowed from salary income in respect to transport allowance and Rs. 15,000 for the medical reimbursement.
Hence, the net benefit for the employees already claiming deduction for transport allowance and medical reimbursement will be just Rs. 5,800 (Rs. 40,000 – Rs. 19,200 – Rs. 15,000).
PGBP
Rationalization of presumptive taxation scheme in case of goods carriage
[Section 44AE – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
A taxpayers who is engaged in the business of plying, hiring or leasing of Goods Carriage and having not more than 10 good carriage, has an option to avail presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AE. In this case, income of taxpayer is deemed to be Rs. 7,500 per goods carriage per month.
The only condition which needs to be fulfilled is that the taxpayer should not have owned more than 10 goods carriages at any time during the previous year. Accordingly, the big transporters who owns large capacity/ size goods carriages, even if number is less than 10, are also availing the benefit of section 44AE.
The legislative intent of introducing this provision was to give benefit to small transporters in order to reduce their compliance burden.
Therefore, it is proposed to amend the section 44AE to provide that, in the case of heavy goods vehicle (more than 12MT gross vehicle weight), the income would deemed to be an amount equal to Rs. 1,000 per ton of gross vehicle weight or unladen weight per month for each goods vehicle The vehicles other than heavy goods vehicle will continue to be taxed as per the existing scheme.
No adjustment under section 143(1) on account of mismatch with Form 26AS
[Section 143 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
Section 143(1)(a)(vi) provides that while processing the return of income, the total income or loss shall be computed after making addition for the difference in income appearing in Form 26AS or Form 16A or Form 16 and income shown in the ITR. Generally, salaried taxpayers are mostly aggrieved by this adjustments.
It is now proposed that no adjustments shall be made in respect of Income-tax return furnished on or after Assessment Year 2018-19 just to account for the difference in the income reported in ITR and displayed in tax passbook or tax certificates.
NPS withdrawal exemption extended to non-employees
[Section 10(12A) – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Any amount received by employee from National Pension Scheme (NPS) either on closure or opting out from scheme is exempt upto 40% of the total amount payable to employee. This exemption is not available to non-employee subscriber. It is proposed to extend the said benefit to all NPS subscribers.
Deemed dividend isn’t taxable in hands of receivers
[Section 115-O, 115Q – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Deemed dividend as specified in section 2(22)(e) were kept out of the ambit of Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT). Therefore, the deemed dividend as arising from payment of loan by closely held companies are taxable in the hands of the shareholders.
The taxability of deemed dividend in the hands of recipient has posed serious problem of collection of the tax liability and has also been the subject matter of extensive litigation.
Now it is proposed to bring deemed dividends also under the scope of dividend distribution tax. Therefore, companies are now liable to pay DDT on the deemed dividend.
The tax at the rate of 30% is proposed on such deemed dividend in order to prevent camouflaging of dividend in various ways such as loans or advances.
No deduction of exp. even if unexplained income is determined by Assessing Officer
[Section 115BBE – Applicable retrospectively from Assessment Year 2017-18]
Any sum found credited in the books of the taxpayer, for which he offers no explanation about the nature and source thereof or the Assessing Officer (AO) are not satisfied by the explanation offered by the taxpayer, is termed as unexplained income. Such incomes are taxed at the flat rate of 60% under section 115BBE. It also provides that no deduction in respect of any expenditure shall be allowed to taxpayers from such unexplained income. However, the provision was silent whether taxpayer would get any deduction if tax officer has made additions in the total income of taxpayers which is deemed as unexplained income.
The Finance Bill, 2018 proposed that taxpayer would not be eligible to deduction even in this case where additions are made by the Assessing Officer for the unexplained income.
Deductions under Chapter VI-A
Limit of Deduction under Section 80D is enhanced for senior citizens
[Section 80D – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Currently, an individual taxpayer can claim deduction of up to Rs. 30,000 in respect of payment made by him for the medical insurance for himself, his spouse or children. He is allowed to claim additional deduction of Rs. 30,000 for the payment made for the medical insurance policy for his parents. The deduction of Rs. 30,000 is reduced to Rs. 25,000 each if the insured persons are less than 60 years of age. In other words, if none of the family member is a senior citizen (i.e. less than 60 years of age), the deduction is limited to Rs. 50,000. If either parents or any of his family member is a senior citizen (i.e. above 60 years of age), the deduction shall be up to Rs. 55,000. If parents and any of family member is a senior citizen, the deduction up to Rs. 60,000 can be claimed under Section 80D.
The limit of Rs. 30,000 is proposed to be increased to Rs. 50,000. In nutshell, an individual taxpayer can claim deduction of up to Rs. 1 lakh under Section 80D if he or his family members and his parents are 60 years or above.
A summary of deduction allowable under Section 80D is explained in below table:
Nature Of Amount SpentFamily MemberParents
Age Below 60 YearsAge 60 Years Or MoreAge Below 60 YearsAge 60 Years Or More
A. Medical Insurance25,00050,00025,00050,000
B. CGHS25,00050,000––
C. Health Check-Up5,0005,0005,0005,000
D. Medical Expenditure–50,000–50,000
Maximum Deduction25,00050,00025,00050,000
Further, the Finance Bill also proposes that in case of single premium health insurance policies which covers more than one year, deduction shall be allowed on proportionate basis for all those years for which health insurance cover is provided, subject to the specified monetary limit.
Deduction limit under section 80DDB is enhanced
[Section 80DDB – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
This deduction is allowed when an individual or HUF taxpayer pays for the medical treatment of critical illness for himself or family members. Currently, this deduction is allowed upto Rs. 60,000 for senior citizen, up to Rs. 80000 for very senior citizen and Rs. 40,000 in any other case.
The differentiation between senior and super senior citizen is removed and the deduction limit in both the case is proposed to be increased to Rs. 1,00,000. There is no change in amount of deduction for expenditure incurred in any other case i.e., for person who is below 60 years of age.
Deductions under Section 80JJAA is extended to footwear and leather industry
[Section 80JJAA – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Section 80JJAA allows deductions to the manufacturers who employ new employees for a minimum period of 240 days during the year. This deduction is calculated at the rate of 30% of the additional employee cost incurred by the assessee during the year.
The eligibility of a manufacturer to claim this deduction is determined only if he gives employment for a minimum period of 240 days during the year. However, for apparel industry the minimum period of employment is relaxed to 150 days. The concession of minimum employment period for 150 days has been extended to footwear and leather industry.
Manufacturers are often denied the deduction if an employee is employed in year 1 for a period of less than 240 days or 150 days, but continues to remain employed for more than 240 days or 150 days in year 2. To overcome this difficulty, the requirement of period of employment has been proposed to be relaxed. Now as per the proposed provision the deductions shall be allowed to the manufacturer in respect of an employee hired in last year, if he continues to remain in employment in current year for more than 240 or 150 days, as the case may be.
New deduction introduced for Farm Producer Companies
[Section 80PA – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
To promote agricultural activities a new section 80PA is proposed to be inserted. This new provision proposes 100% deductions of profits for a period of 5 years to farm producer companies.
This deduction is allowed to farm producer companies who have total turnover of up to Rs. 100 crores during the financial year. For claiming this deduction, companies’ gross total income should include income from:
a) Marketing of agricultural produce grown by its members
b) Purchase of agricultural implements, seeds, livestock or other articles intended for agriculture for the purpose of supplying them to its members
c) Processing of agricultural produce of its members.
New deduction for senior citizens in respect of bank interest
[Section 80TTA, 80TTB, 194A – Applicable from Assessment Year 2019-20]
Keeping in view the fixed and restricted sources of income for senior citizens, a new section 80TTB is proposed to be inserted. This provision allows deduction of up to Rs. 50,000 to the senior citizen who has earned interest income from deposits with banks or post office or co-operative banks. Interest earned on saving deposits and fixed deposits both shall be eligible for deduction under this provision.
Deduction under Section 80TTA shall not be available to senior citizens in respect of interest on saving deposits.
Further, corresponding amendment has been proposed in Section 194A to provide that no tax shall be deducted at source from payment of interest to a senior citizen up to Rs. 50,000.
Certain Deductions not to be allowed if return is not filed on time
[Section 80AC – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
As per existing provisions of Section 80AC of the Act, no deduction would be admissible under section 80-IA or section 80-IAB or section 80-IB or section 80-IC or section 80-ID or section 80-IE, unless the return of income by the assessee is furnished on or before the due date specified under Section 139(1). This burden of filing of return on time is not casted on other assesses who are claiming deductions under other similar provisions.
Therefore, to bring uniformity in all income-based deduction, it is now proposed that the scope of section 80AC shall be extended to all similar deductions which are covered in heading “C.—Deductions in respect of certain incomes” in Chapter VIA (sections 80 H to 80RRB). The impact of such amendment shall be that no deduction would be allowed to a taxpayer under these provisions if income-tax return is not filled on or before the due date.
Others
E-Proceedings of all scrutiny assessments
[Section 143(3A), 143(3B), 143(3C) – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
The Finance Bill, 2018 has proposed to launch a new scheme for scrutiny assessments to eliminate the interface between the Assessing Officer and the taxpayers. Under the new system, taxpayer will not be required to appear in person before the Assessing Officer as assessment proceedings in all cases selected under scrutiny will now be conducted through e-mail based communications.The directions in this regard need to be issued on or before March 31, 2020.
Higher penalty for default in furnishing AIR (Section 271FA)
[Section 271FA – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
DefaultExisting PenaltyProposed Penalty
Penalty For Not Filing Statement Within Due DateRs. 100 Per Day During Which The Default ContinuesRs. 500 Per Day During Which The Default Continues
Penalty For Not Filing Statement Within Time Limit Given In NoticeRs. 500 Per Day During Which The Default ContinuesRs. 1,000 Per Day During Which The Default Continues
Stringent prosecution for not filing the ITR
[Section 276CC – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
Section 276CC provides for imprisonment of up to 2 years in case a person doesn’t file the return of income.
However exemption is provided from prosecution under section 276CC, if the return is furnished till end of assessment year or if the tax payable is up to Rs. 3,000.
The Finance Bill targets to prevent abuse of the exemption provided on the basis of amount of tax payable by shell companies or by companies holding Benami properties.
As per the proposed amendment the immunity from prosecution under section 276CC is not available to a company even if the amount of tax payable is Rs. 3,000 or less.
TDS from payment of interest on specified bonds
[Section 193 – Applicable from Assessment Year 2018-19]
Section 193 is proposed to be amended to provide that the person responsible for paying to a resident any interest on 7.75% Savings (Taxable) Bonds, 2018 shall deduct tax therefrom, if the interest payable on such bonds exceeds Rs. 10,000 during the financial year.
Cessation of Authority for Advance Ruling for the purposes of Custom Duty
[Section 245-O, 245Q]
The Finance Act, 2017 has merged the Authority for Advance Ruling (AAR) for income-tax, central excise, customs duty and service tax. Therefore, the Authority for Advance Rulings constituted under Income-tax Act shall be the Authority for giving advance rulings for the purposes of the Customs Act as well.
It is now proposed that the Income-tax Authority shall cease to act as an Authority for Advance Rulings for the purposes of the Customs Act, 1962 on and from the date of appointment of the Customs Authority for Advance Rulings.
For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
How To Become CS-
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/04/25/how-to-become-cs/
Foundation program: Students looking to do CS after 12th need to go through this stage.
Executive program: This course is for Graduates of all streams with the exception of Fine Arts.
Professional program: One can Complete this after completing the intermediate exam of the CS course
The student who would like to join this CS Course after 10+2 has to undergo three stages to pursue the Company Secretaries Course i.e.
Foundation Program
Executive Program
Professional Program
In addition, the student has to undergo Practical Trainingfor about 15 months, which a student may opt to start after passing the Executive Program
The Student who would like to join the Course after passing the Graduation (Example: B.com) has to undergo two stages of the Company Secretaryship i.e.
Executive Program
Professional Program
Besides, the student has to undergo Practical Training for about 15 months.
Foundation Program, which is eight months duration can be pursued by 10+2 pass students of Arts, Science or Commerce stream.
Executive Program can be pursued by a Graduate of all streams except Fine Arts.
Professional Program can be pursued only after clearing the Executive Program of Company Secretary Course.
Training:A Student has to undergo 15 months Management Training in Companies sponsored by the Institute after passing the Executive or Professional Program or under the guidance of a Company Secretary in Practice.
After qualifying Professional Examination and on successful completion of training a candidate is admitted as an Associate Member of the ICSI and can use the letters ACS after his/her name i.e. Associate Company Secretary.
How to Register For CS Foundation-
There are 4 subjects in CS Foundation.
Business Environment and Entrepreneurship
Business Management Ethics and Communication
Business Economics
Fundamental of Accounting and Auditing
CS Foundation Registration is open throughout the year.
How to Register For CS Executive-
There are 2 Modules in CS Executive. Module -I contains 4 subjects and Module – II contains 3 subjects.
Module I
Company Law
Cost and Management Accounting
Economic and Commercial Laws
Tax Laws and Practice
Module II
Company Accounts and Auditing Practices
Capital Markets and Securities Laws
Industrial, Labor and General Laws
How to Register For CS Professional-
There are 3 Modules in CS Executive. Module -I contain 3 subjects, Module – II contains 4 subjects and Module 3 contains 2 subjects and 5 elective papers.
Module I
Advanced Company Law and Practice
Secretarial Audit, Compliance Management, and Due Diligence
Corporate Restructuring, Valuation, and Insolvency
Module II
Information Technology and Systems Audit
Financial, Treasury and Forex Management
Ethics, Governance, and Sustainability
Module III
Advanced Tax Laws and Practice
Drafting, Appearances, and Pleadings
Elective Subjects
Banking Law and Practice
Capital, Commodity and Money Market
Insurance Law and Practice
Intellectual Property Rights – Law and Practice
International Business-Laws and Practices
Medium of Examination
The Institute allows the facility for students to appear in examination in English as well as in Hindi. (Except Business Communication subject of Foundation Program)
Qualifying Marks
A candidate is declared to have passed the Foundation / Executive / Professional examination if he/she secures at one sitting a minimum of 40% marks in each paper and 50% marks in the aggregate of all subjects.
Time limit for completing CS Examination
A student is required to complete the Executive and the Professional examination within the registration period. However, on payment of requisite fees, the validity of registration may be renewed/extended for the further period subject to fulfilling the applicable guidelines.
For more information about cs course, stay tuned with- http://www.arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
Exclusion Of Chartered Accountants From Valuation Of Unquoted Shares: ICAI Submits Representation To Fin Min
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/06/05/exclusion-chartered-accountants-valuation-unquoted-shares-icai-submits-representation-fin-min/

The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has today notified the Income Tax (6th Amendment Rules) wherein it is provided that only Merchant Bankers are entitled to do Valuation of Unquoted Shares and the Chartered Accountants are no more eligible to do so. Presently, the fair market value of the unlisted equity share is calculated at the option of the company either on the book value on the valuation date or as per discounted free cash flow method calculated by a Merchant Banker or a Chartered Accountant
The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), the regulatory body of Chartered Accountants has made a representation to the Finance Ministry expressing dissatisfaction against Notification amending Rule 11UA omitting reference to term “accountant” and thereby excluding its members from valuing unquoted shares. As per the Notification issued last week, the Income Tax (6th Amendment Rules) provided that only Merchant Bankers are entitled to do Valuation of Unquoted Shares and the Chartered Accountants are no more eligible to do so. for more information, visit our website- http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
Summary
Article NameExclusion of Chartered Accountants from Valuation of Unquoted SharesDescriptionThe Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has today notified the Income Tax (6th Amendment Rules) wherein it is provided that only Merchant Bankers are entitled to do Valuation of Unquoted Shares and the Chartered Accountants are no more eligible to do so.AuthorArpit GuptaPublisher Namearpitguptaclasses.comPublisher Logo

For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes
Text
REFUND OF GST ON ZERO RATED EXPORT
http://arpitguptaclasses.com/blog/2018/06/08/refund-of-gst-on-zero-rated-export/
What is Zero rated Supply? – Sec.16 (1) IGST ACT
(1) “zero rated supply” means any of the following supplies of goods or services or both, namely:––
(a) Export of goods or services or both; or
(b) Supply of goods or services or both to a Special Economic Zone developer or a Special Economic Zone unit.
Zero-rated supply does not mean that the goods and services have a tariff rate of ‘0%’ but the recipient to whom the supply is made is entitled to pay ‘0%’ GST to the supplier.
In other words, as it has been well discussed in section 17(2) of the CGST Act that input tax credit will not be available in respect of supplies that have a ‘0%’ rate of tax. However, this disqualification does not apply to zero-rated supplies covered by this section.
These provisions of zero-rated supplies are introduced in the statute on the basis of the prevalent Central Excise and Service Tax laws. It is widely believed that introduction of this provision will alleviate the difficulty of a supplier who exempts goods or services or both in terms of export competitiveness.
This provision also specifically expresses that taxes are not exported. Care must be exercised that while paying taxes, such taxes are not collected from the recipient of goods or services or both. This would result in unjust enrichment.
The exporter may utilize such credits for discharge of other output taxes or alternatively, the exporter may claim a refund of such taxes as per section 54 of CGST or Rules made there under. .
How Exporter can claim refund for Zero rated supply?
A guidance note relating was released by the Indian government which has helped in clearing doubts regarding the claim of input tax credit on zero-rated exports. An exporter dealing in zero-rated goods under GST can claim a refund for zero-rated supplies as per the following options:

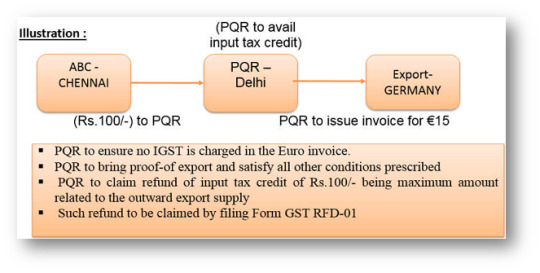
He may export the Goods/services under a Letter of Undertaking, without payment of IGST and claim refund of unutilized input tax credit; (Rule 96A of CGST Rules)
Any registered person availing the option to supply goods or services for export without payment of integrated tax shall furnish, prior to export, a bond or a Letter of Undertaking in FORM GST RFD-11 Bond and LUT Format to the jurisdictional Commissioner, binding himself to pay the tax due along with the interest specified under sub-section (1) of section 50 within a period of—
Who can export without payment of IGST by furnishing only Letter of Undertaking (LUT) in place of Bond?

fifteen days after the expiry of three months from the date of issue of the invoice for export, if the goods are not exported out of India; or
(b) fifteen days after the expiry of one year, or such further period as may be allowed by the Commissioner, from the date of issue of the invoice for export, if the payment of such services is not received by the exporter in convertible foreign
(2) The details of the export invoices contained in FORM GSTR-1 furnished on the common portal shall be electronically transmitted to the system designated by Customs and a confirmation that the goods covered by the said invoices have been exported out of India shall be electronically transmitted to the common portal from the said system.
Procedural Requirement for LUT Method:
Format Of Letter Of
Undertaking In:FORM GST RFD-11 (As Per Rule 96A CGST Rule)
Submission To:The Jurisdictional Commissioner,
Validity Period:Financial Year
How:On Letter Head Of The Registered Person
Executed By:Working Partner, Managing Director Or The Company Secretary, Proprietor, A Person Duly Authorized By Such Working Partner Or Board Of Directors Of Such Company Or Proprietor.
for more information, stay tuned with- http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
Summary
Article NameREFUND OF GST ON ZERO RATED EXPORTDescriptionZero-rated supply does not mean that the goods and services have a tariff rate of ‘0%’ but the recipient to whom the supply is made is entitled to pay ‘0%’ GST to the supplier.AuthorArpit GuptaPublisher Namearpitguptaclasses.comPublisher Logo

For more information please visit at http://arpitguptaclasses.com/
0 notes