#aerospace fiber optic sensors
Text

Ultracompact fiber-tip sensor achieves high sensitivity in magnetic field and temperature measurements
Magnetic field sensing plays a pivotal role in numerous fields of medical, transportation and aerospace. The optical fiber-based magnetic field sensor possesses outstanding characteristics of compactness, long-distance interrogation, low cost and high sensitivity, which has attracted intensive interest. However, the fiber-based magnetic field sensor is generally affected by the temperature perturbation.
Recently, although the temperature crosstalk can be effectively eliminated by integrating multiple sensing elements, it is at the cost of increasing the size of the whole sensing components, and the different spatial location of multiple elements could cause the measurement errors in the multi-parameter discriminative sensing.
In a new paper published in Light: Advanced Manufacturing, a team of scientists, led by Professor Limin Xiao from Advanced Fiber Devices and Systems Group, Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (MoE), Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Ultra-Precision Optical Manufacturing, School of Information Science and Technology, Fudan University, China, and co-workers have developed an ultracompact multicore fiber (MCF) tip probes for magnetic field and temperature discriminative sensing.
Read more.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fiber Laser Welding Machines
As industries continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the demand for advanced manufacturing technologies has never been greater. One such technology that has gained significant traction is the fiber laser welding machines. Known for its precision and efficiency, fiber laser welding is reshaping how industries approach welding tasks, offering a host of benefits that traditional methods cannot match.

What Sets Fiber Laser Welding Machines Apart?
Fiber laser welding machines utilize a fiber optic laser to produce a high-intensity beam capable of welding materials with extreme precision. Unlike conventional welding techniques that rely on heat from an electric arc or gas flame, fiber laser welding directs energy precisely where it’s needed, resulting in cleaner, stronger welds.
Key Advantages of Fiber Laser Welding Machines
Exceptional Speed and Accuracy
Fiber laser welding machines are incredibly fast, completing welds in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. This speed does not come at the expense of accuracy; the laser’s precision ensures that even the most intricate welds are executed flawlessly, making it ideal for high-precision industries.
Enhanced Material Compatibility
These machines are versatile enough to weld a wide array of materials, including various metals and alloys. Whether you’re working with stainless steel, aluminum, copper, or titanium, fiber laser welding can handle the job with ease, offering strong, durable welds that meet industry standards.
Reduced Thermal Distortion
One of the significant challenges in welding is managing heat distortion, which can compromise the integrity of the materials being welded. Fiber laser welding minimizes this risk by focusing heat on a very narrow area, reducing the thermal distortion and preserving the original properties of the materials.
Eco-Friendly Welding Solution
Fiber laser welding is an environmentally friendly option due to its energy efficiency and reduced need for consumables like welding rods or gases. The process itself generates minimal waste, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Ease of Automation
The adaptability of fiber laser welding machines makes them perfect for automated production lines. Their ability to be integrated with robotic systems allows for continuous, high-speed production with minimal human intervention, leading to lower labor costs and increased throughput.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
Fiber laser welding machines are revolutionizing various sectors by providing reliable and efficient welding solutions:
Aerospace: Critical for welding high-strength, lightweight components that require precise joints.
Automotive: Used extensively for welding car parts, including batteries, sensors, and structural components, where strength and durability are paramount.
Electronics: Essential for micro-welding tasks, such as assembling circuit boards, connectors, and other delicate components.
Jewelry: Provides the fine control needed for intricate designs and delicate metalwork.
Innovations on the Horizon
The future of fiber laser welding is bright, with ongoing research and development focusing on further enhancing this technology:
Hybrid Welding Systems: Combining fiber laser welding with other welding techniques to achieve superior results for specialized applications.
Real-Time Process Monitoring: Advanced sensors and AI-driven systems that provide real-time feedback during the welding process, ensuring perfect welds every time.
Portable Fiber Laser Welding Machines: Development of compact, portable units for on-site welding in remote or challenging environments.
Conclusion
Fiber laser welding machines represent a significant leap forward in welding technology, offering unmatched precision, speed, and versatility. As industries continue to demand higher standards of quality and efficiency, fiber laser welding will undoubtedly play a crucial role in meeting these expectations.
By investing in fiber laser welding technology, manufacturers can ensure they remain at the forefront of innovation, delivering superior products while optimizing production processes. The future of welding is here, and it’s powered by fiber lasers.
0 notes
Text
Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique, Prévisions de la Taille du Marché Mondial, Classement et Part de Marché des 5 Premières Entreprises
Selon le nouveau rapport d'étude de marché “Rapport sur le marché mondial de Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique 2024-2030”, publié par QYResearch, la taille du marché mondial de Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique devrait atteindre 1180 millions de dollars d'ici 2030, à un TCAC de 13.9% au cours de la période de prévision.
Figure 1. Taille du marché mondial de Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique (en millions de dollars américains), 2019-2030
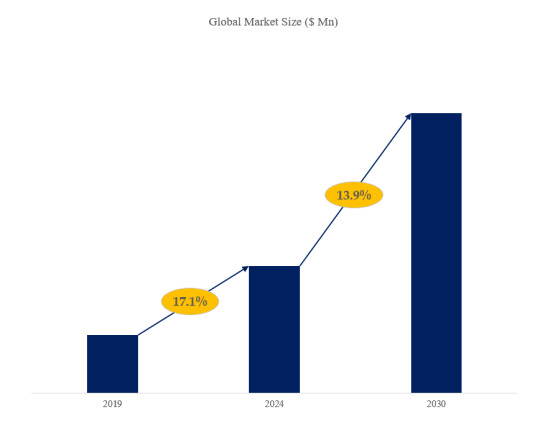
Selon QYResearch, les principaux fabricants mondiaux de Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique comprennent WOP, Innofocus, etc. En 2023, les trois premiers acteurs mondiaux détenaient une part d'environ 82.0% en termes de chiffre d'affaires.
Figure 2. Classement et part de marché des 5 premiers acteurs mondiaux de Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique (Le classement est basé sur le chiffre d'affaires de 2023, continuellement mis à jour)

The market for laser workstations used for the production and analysis of Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) is influenced by several key drivers, which contribute to its growth and development. Here are some important market drivers:
1. Rising Demand for Fiber Bragg Gratings: FBGs are widely used in various applications, including telecommunications, structural health monitoring, temperature sensing, and pressure measurements. The increasing demand for these applications drives the need for advanced laser workstations capable of producing high-quality FBGs.
2. Advancements in Laser Technology: Continuous improvements in laser technologies, including sources that are more efficient, reliable, and capable of producing precise and high-resolution gratings, are driving the adoption of laser workstations. New types of lasers and improved fabrication techniques enhance the performance of FBGs.
3. Growth in Telecommunications Sector: The telecommunications industry is one of the largest consumers of Fiber Bragg Gratings, especially for applications in fiber-optic communications and signal processing. As demand for high-speed data transmission and 5G technology continues to grow, the need for FBGs and the corresponding laser workstations will increase.
4. Development of Smart Infrastructure: The expansion of smart building technologies and infrastructure monitoring systems that utilize FBG sensors for real-time condition monitoring and data collection is driving market growth. Laser workstations are essential for developing customized FBGs tailored to specific monitoring needs.
5. Innovations in Sensing Technologies: FBGs are increasingly being adopted in various sensing applications due to their advantages, such as high sensitivity and immunity to electromagnetic interference. The growth in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy sector—for structural and environmental monitoring—requires robust laser workstations for the production of specialized FBGs.
6. Focus on Research and Development: Research institutions and labs are actively engaged in developing new applications for FBGs, which drives the demand for laser workstations that can facilitate advanced experimental setups. This R&D focus contributes to the advancement of FBG-related technologies and products.
7. Miniaturization Trends: The growing trend toward miniaturization in various applications, especially in telecommunications and medical devices, requires precise and compact FBG solutions. Laser workstations equipped to produce smaller and more intricate FBGs are increasingly important.
8. Energy Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Advances in laser technology have enabled the development of more energy-efficient laser workstations, which can reduce operating costs. This is particularly attractive for businesses and research institutions looking to optimize their operations.
9. Customization and Flexibility: The ability to design and fabricate customized FBGs for specific applications is driving demand for adaptable laser workstations. Systems that allow for easy programming and adjustment for different grating patterns can enhance production efficiency and innovation.
10. Growing Adoption in Medical Applications: The healthcare sector is increasingly exploring the use of FBGs for applications such as biomedical sensing and imaging. As this trend grows, the need for specialized laser workstations for producing medical-grade FBGs will also increase.
11. Collaborative Industry Growth: Collaborations between universities, research institutions, and industries focused on fiber optics and sensor technologies promote innovation and lead to the development of new applications for FBGs. This collaborative growth stimulates demand for laser workstations.
In summary, the market for laser workstations for Fiber Bragg Gratings is driven by rising demand for FBGs in various sectors, advancements in laser technology, the growth of telecommunications and smart infrastructure applications, research initiatives, and the increasing adoption of FBGs in sensing and medical applications. These factors create a conducive environment for the expansion of this market.
À propos de QYResearch
QYResearch a été fondée en 2007 en Californie aux États-Unis. C'est une société de conseil et d'étude de marché de premier plan à l'échelle mondiale. Avec plus de 17 ans d'expérience et une équipe de recherche professionnelle dans différentes villes du monde, QYResearch se concentre sur le conseil en gestion, les services de base de données et de séminaires, le conseil en IPO, la recherche de la chaîne industrielle et la recherche personnalisée. Nous société a pour objectif d’aider nos clients à réussir en leur fournissant un modèle de revenus non linéaire. Nous sommes mondialement reconnus pour notre vaste portefeuille de services, notre bonne citoyenneté d'entreprise et notre fort engagement envers la durabilité. Jusqu'à présent, nous avons coopéré avec plus de 60 000 clients sur les cinq continents. Coopérons et bâtissons ensemble un avenir prometteur et meilleur.
QYResearch est une société de conseil de grande envergure de renommée mondiale. Elle couvre divers segments de marché de la chaîne industrielle de haute technologie, notamment la chaîne industrielle des semi-conducteurs (équipements et pièces de semi-conducteurs, matériaux semi-conducteurs, circuits intégrés, fonderie, emballage et test, dispositifs discrets, capteurs, dispositifs optoélectroniques), la chaîne industrielle photovoltaïque (équipements, cellules, modules, supports de matériaux auxiliaires, onduleurs, terminaux de centrales électriques), la chaîne industrielle des véhicules électriques à énergie nouvelle (batteries et matériaux, pièces automobiles, batteries, moteurs, commande électronique, semi-conducteurs automobiles, etc.), la chaîne industrielle des communications (équipements de système de communication, équipements terminaux, composants électroniques, frontaux RF, modules optiques, 4G/5G/6G, large bande, IoT, économie numérique, IA), la chaîne industrielle des matériaux avancés (matériaux métalliques, polymères, céramiques, nano matériaux, etc.), la chaîne industrielle de fabrication de machines (machines-outils CNC, machines de construction, machines électriques, automatisation 3C, robots industriels, lasers, contrôle industriel, drones), l'alimentation, les boissons et les produits pharmaceutiques, l'équipement médical, l'agriculture, etc.
#Poste de travail laser pour réseaux de Bragg en fibre optique#Laser Workstation for Fiber Bragg Gratings
0 notes
Text
Fiber Optic Gyroscope Market - Shaping Modern Navigation

The fiber optic gyroscope market opens new frontiers in navigation and sensing technology. Fiber-optic gyroscopes are the intrinsic parts of the systems requiring high-precision orientation and stabilization in aerospace, defense, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. With the growing demands of industries for more accuracy and increasing reliability in navigation systems, the demand for FOGs increases, and this market is therefore pegged for tremendous growth.
The main advantage of the fiber optic gyroscope is that it is accurate and stable. As opposed to the traditional mechanical gyro, FOGs use interference of light inside an optical fiber that is coiled for the determination of orientation changes. There is no moving part with the potential of wearing out, leading to better durability and longevity. Plus, the FOGs are resistant to electromagnetic interference, which ultimately ensures accuracy under severe conditions. These properties make them an ideal sensor for aerospace and defense, as well as other fields of application where precision is key.
In the aerospace sector, fiber optic gyroscopes are integral to aircraft, satellite, and drone navigation and control. They are used in inertial navigation systems, providing essential data on orientation, speed, and position without GPS signals. As drones and unmanned aerial vehicles become more integrated in commerce and military uses, a demand for gyroscopes is likely to follow. Applications of such high accuracy spell out that FOGs are quite indispensable in the context of modern aviation technology.
The defense sector is another huge platform that offers the fiber optic gyroscope market an array of opportunities. FOGs are used in military vehicle systems, missile systems, and naval vessels for navigation and targeting tasks with precision. More specifically, the performance of FOGs in high-vibration, high-temperature environments and resistance to jamming have made them a popular choice for defense applications. With increased spending in this sector, fiber optic gyroscope demand is only expected to rise, thereby propelling market growth further.
Beyond aerospace and defense, it is in the growing field of autonomous vehicles where the fiber optic gyroscope market comes into its own. With the need to move around complex environments, self-driving cars and robotic systems need accurate and reliable sensors. The FOGs are highly sensitive and quite stable, making them ideal for the provision of critical orientation data that leads to safe and efficient operation. With the autonomous vehicle market continuing to grow at a rapid pace, FOG applications will increase, bringing brand-new opportunities to both manufacturers and technology providers.
Author Bio -
Akshay Thakur
Senior Market Research Expert at The Insight Partners
0 notes
Text
Internet of Things (IoT) Startup Revolutionizing 2024

The Internet of Things (IoT) startup revolutionizing 2024 introduces a transformative wave of innovation, profoundly influencing diverse industries such as healthcare, agriculture, logistics, and smart homes. As IoT continues to evolve, its ecosystem of connected devices facilitates seamless communication, significantly enhancing efficiency, user experiences, and operational sustainability.
In this detailed overview, we spotlight several pioneering IoT startups set to redefine the digital landscape in 2024:
Samsara
Samsara's Connected Operations Platform integrates real-time data from vehicles, equipment, and mobile devices into the cloud. This comprehensive fleet and asset management tool enhances safety, efficiency, and sustainability across transportation, logistics, and construction sectors. Samsara's plug-and-play technology offers quick deployment, immediate value, and extensive data processing capabilities, positioning it as a leader in connected operations.
Maintool
Maintool, with its innovative smart strap Classi, transforms traditional wristwatches into smart devices without altering their classic aesthetics. Equipped with health and activity tracking features, including heart rate and temperature monitoring, Classi bridges the gap between timeless watch design and modern wearable technology.
Waylay
Waylay offers a low-code hyper-automation platform excelling in workflow-based automation and data integration across IoT, OT, and IT domains. Its robust orchestration layer enhances operational efficiency by seamlessly integrating IoT solutions with existing IT systems, making it a versatile tool for various industries including telecom, manufacturing, and finance.
Cooey Technologies
Cooey Technologies' IoT platform specializes in health monitoring for senior and home care, utilizing smart devices to collect and analyze health data. The platform supports continuous health data analysis and voice-based interaction through the Maya assistant, promoting accessible and efficient health management.
Slock.it
Slock.it merges blockchain technology with IoT, creating a Universal Sharing Network (USN) that facilitates secure online markets for connected devices. Through smart contracts, Slock.it automates services in the sharing economy, enhancing transaction security and transparency.
Lime Microsystems
Lime Microsystems advances wireless communications with its LimeSDR platform, supporting diverse wireless signals and integrating flexible wireless technology. This platform is crucial for developing IoT gateway solutions, enabling applications such as radio astronomy and media streaming.
FiSens
FiSens specializes in fiber optic sensors, ideal for extreme conditions and industries requiring precise monitoring. Their sensors are crucial in sectors like aerospace and industrial processes, providing reliable data under harsh environments.
GWAGENN
GWAGENN's LPWAN solutions improve telecommunications by enhancing connectivity and accuracy in device location. Their user-friendly technology democratizes advanced telecommunications, fostering wider adoption across various sectors.
Mica Energies
Mica Energies' smart IoT dashboards enhance telecom performance management with advanced analytics and equipment monitoring. Their wireless charging solutions promote energy efficiency, supporting sustainable telecom infrastructures.
These IoT startups exemplify the innovative spirit driving the digital revolution, addressing real-world challenges with smart, seamless solutions. As IoT continues to evolve, these companies are poised to lead the way, shaping a more connected and efficient future.
For more information, visit the full article.
0 notes
Text

Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor Market size at USD 1.44 billion in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, BlueWeave expects the Global Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor Market size to expand at a CAGR of 7.13% reaching a value of USD 2.08 billion by 2030. The Global Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor Market is propelled by the growing demand for efficient monitoring of machine systems in enterprises. Optical sensing technologies are being widely adopted across industries, such as automotive, aerospace, civil engineering, and energy, with Raman and Rayleigh effect-based sensing offering unique operational benefits. The oil & gas sector is experiencing rapid digitization and automation to meet the rising needs for productivity, efficiency, and safety. This trend is driven by increased offshore drilling activities and significant investments in new oil & gas reserves. Distributed temperature sensing is critical for downhole monitoring in offshore operations, aiding in flow control and production optimization by detecting issues like sand in downhole and assessing gas lift valve operations. This technology enhances production assessment and reduces losses in oil and gas production. Similarly, in civil engineering, the use of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors (DFOS) is growing, primarily for structural health monitoring. These sensors are deployed in geotechnical structures, pipelines, bridges, and dams to better understand structural conditions and manage infrastructure efficiently. Next-generation sensors offer significant advantages by measuring strain, temperature, or pressure over numerous locations simultaneously, allowing real-time tracking of structural malfunctions in challenging environments. Hence, such trends are expected to boost the expansion of the Global Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor Market during the period in analysis.
Opportunity - Advancements in data analytics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies with distributed fiber optic sensors is revolutionizing data analytics and predictive maintenance. These advancements enable the analysis of voluminous sensor data to identify patterns and anomalies, optimizing operations and minimizing downtime. AI and ML algorithms, processing data in real-time, swiftly detect deviations from normal conditions, facilitating proactive maintenance interventions. Moreover, historical data analysis offers predictive insights, aiding in anticipating maintenance requirements and optimizing resource allocation. This synergy between distributed fiber optic sensors and advanced analytics empowers industries to enhance efficiency, improve asset performance, and mitigate risks effectively.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/distributed-fiber-optic-sensor-market/report-sample
0 notes
Photo

Team develops silicon photonic MEMS compatible with semiconductor manufacturing
A team of researchers led by the University of Sydney's Associate Professor Niels Quack has developed a new technology to combine optics and micro-electro mechanical systems (MEMS) in a microchip, paving the way for the creation of devices like micro-3D cameras and gas sensors for precision air quality measurement, including their use in mobile phones.
Published March 20 in Microsystems and NanoEngineering, the new microfabrication process builds on silicon photonics and uses semiconductor manufacturing techniques to enable a new, more energy-efficient generation of devices for fiber-optical communications, sensors and even future quantum computers.
Associate Professor Quack from the School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering said that the photonic MEMS are unique in that they are compact, consume very little power, are fast, support a broad range of optical carrier signals and have low optical loss.
"This is the first time that nano-electro-mechanical actuators have been integrated in a standard silicon photonics technology platform," Associate Professor Quack said.
Read more.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Photonics: Unraveling the Mysteries of Optoelectronics in Research and Industry
What is Photonics?
Photonic is a field of science that deals with the technology of generating and harnessing light and other forms of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared radiation. It involves the emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and detection of light. Optoelectronics finds extensive use in fiber optics communications, lighting, medicine, entertainment, optoelectronics, and sensors. Applications of optoelectronics are abundant and impact almost every aspect of our daily lives and economy.
Fiber Optic Communication
Optical fibers allow transmission of data encoded as pulses of light through hair-thin strands of glass. It has revolutionized telecommunications by enabling broadband Internet worldwide. Fibers have much larger bandwidth than metal wires and can carry hundreds of terabytes per second over long distances with very low losses. Dense wavelength division multiplexing further multiplies network capacity by transmitting multiple wavelengths of light simultaneously. Optical fibers laid along sea beds now connect all continents through undersea cables. 5G technologies will also rely heavily on optoelectronics for backhauling mobile data traffic.
3D Printing using Photons
A new manufacturing technique called stereolithography employs lasers to selectively cure liquid resin, building 3D structures layer by layer with light. This photopolymerization process fuses liquid material together to solidify complex geometries from 3D digital models with extreme precision. Stereolithography can rapidly produce prototypes and customized parts for industries from medicine to consumer products to aerospace. Researchers hope to advance 3D bioprinting tissues and organs using photons. Novel mask-based lithography also wields photons to precisely etch nanoscale silicon chips for computers, sensors, and other electronics.
Lighting and Displays
Solid-state lighting based on light-emitting diodes or LEDs has revolutionized illumination with its high efficiency and long lifetime. LEDs are now ubiquitous in everything from automotive headlights to advertising displays to in-home lamps, significantly cutting energy use. Liquid crystal displays that enable all the smartphones, monitors, and TVs in our lives also rely on optoelectronics to precisely control light transmission and color. Emerging organic light-emitting diode displays spread vibrant colors across flexible form factors like scrolls and fabrics. Researchers work on novel lighting and displays like quantum dots, microLEDs, and solar concentrators.
Biooptoelectronics and Medicine
Photons play a vital role in biomedical diagnostics and therapeutics. Lasers are used widely in ophthalmology for refractive corrections and cataract treatments. Fluorescence imaging captures biological processes with light, while fiber optics enable minimally invasive surgeries with endoscopes and catheters. Photodynamic therapy activates photosensitizing drugs with visible light to treat cancer and other diseases. Optogenetics harnesses light to stimulate genetically targeted nerve cells, opening new avenues for researching brain disorders. Photons probe molecules and cells with techniques like fluorescence microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, photoacoustic tomography and optical coherence tomography.
Sensing and Metrology
Sensors that measure temperature, chemicals, strains, and more employ optoelectronics principles. Fiber optic sensors can monitor structures or pipelines over long distances, valuable for infrastructure monitoring. Photonic crystal fibers enable ultra-sensitive measurements of tiny refractive index changes. Interferometers gauge short distances to the nanometer using light interference. Lidar sensors power self-driving cars and drones by laser ranging. Photonic time-stretch dispersive Fourier transform unlocks new capabilities for real-time broadband spectral analysis. Photonic integrated circuits will miniaturize labs-on-a-chip sensors for point-of-care diagnostics and chemical monitoring. Metrology with precise photons traces national calibration standards and revolutionizes manufacturing quality control.
Advanced Manufacturing with Photons
New directions in manufacturing leverage light-matter interactions enabled by optoelectronics. LightsOut technologies like direct laser writing mould and assemble submillimeter components with light beam accuracy. Two-photon polymerization patterns exquisitely complex scaffolds for tissue engineering on micron scales. Digital light processing precisely projects entire patterns for rapid curing of industrial parts and displays. Nonlinear optics enable cutting, drilling, marking, deposition and surface treatments with ultrafast laser pulses. Optical tweezers employ photons to grasp and manipulate nanoparticles, organelles and cells with femtoliters precision. Advancements in nonlinear and quantum optoelectronics push the frontiers of manufacturing even tinier structures and devices.
In Summary, as seen from the wide range of applications outlined above, photonics has transformed numerous technologies essential to modern society and our daily lives. Researchers continue advancing novel materials, devices, and photonic integration to bring new capabilities across communications, healthcare, transportation, manufacturing and more. The amazing world of optoelectronics will surely keep empowering human progress and discovery for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
What are the Interesting names of technologies?

New technologies and tools evolve every day, and new versions of the existing ones get released. Therefore, IT professionals of best engineering college in Jaipur need to update their skills regularly as per the current trending technology in the market. Today, the career based on digital technology would not change with the evolution of new technologies.
However, in this 21st century, IT experts should constantly be learning and upskilling to match up with the job descriptions posted on all major job portals across the globe. Some job-oriented technologies are as follows:
1. Fiber Optics
Colladon and Babinet first introduced this technology. Fiber optic tubes refract light within glass tubes with little loss of light over a little length of the tube. In 1880, Alexander Graham Bell developed this technology to transmit different voice signals over an optical beam. These cables are immune to electrical interference making them good for use in computer networking. Also, Fiber optic transmissions are much harder to snoop and are therefore considered more secure.
2. Graphene
Graphene is considered as a revolutionizing technology. Created by the students of top engineering colleges in Jaipur, graphene is a layer of graphite that is one atom thick. It is very strong, an excellent conductor of heat & electricity and is expected to transform mobile devices. Also, it tries to use it over the metal shield of various transport vehicles to increase their durability. Research is also being conducted to use it in making supercomputers of less length due to its conduction properties. This is one of the most excellent technologies believed to revolutionize the tech world in a couple of decades.
3. Cellphone Technology
The technology that allows cellphones to communicate from a base station was proposed in 1947, however the technology did not allow the phone to move out of range of the base station. A car phone call, using a rotary dial to make the call was initially used in 1956. Since then, various enterprises have been sponsoring research and advancement in this world.
4. Nano Robots
The term nano robot means robots whose components are close to the scale of a nanometer (10-9 meters). For instance, a tiny sensor intended to detect cancer, or to perform nano surgery. In research and development, these robots today have already been used by the students of engineering colleges to deliver drugs to the correct part of the body in terminal cancer patients. A lot of cutting-edge research is being done on this field, with great emphasis on substrate selectivity and makes it one of the most amazing technologies in the field of medical science.
5. Personal Computing
Microcomputers begin to be marketed in large number in 1977, as the name “Personal Computer” got introduced six years later when Hewlett Packard announced its 9100A personal computer. Microchip technology has importantly reduced the cost and size of the processor as its power increased and form factors became much more compact. Although there are billion PCs in existence, smartphone and tablet technology that have started to become prevalent in consumer markets around the world.
6. The Internet of Things
The “Internet of Things” is also referred as the object that can be uniquely identified with an addressable system like TCP / IPv6. IPv6 with its 128-bit address has enormous scope to have a unique address for each item in the world. There are approximately 3.4 x 1038 addresses available to use. With these, you can track each website; identify IP-Address, especially, Google and Wikipedia which are of utmost importance. User can have access to e-mailing and various other utilities of it. Recently, it is found that one thing very recent, useful and amazingly helpful is e-learning.
7. 3D Printing technology
Creating a three-dimensional solid object digitally is something that the automotive and aerospace industry, especially the students of private engineering colleges in Jaipur has been using since the 1980s. recently, printers have become available recently and are used to print anything from teapots to guns. Even, you can buy your own 3D printer. This technology is being extensively used in different kinds of institutions, for engineering and architectural, designing courses where they learn to model 3-d objects. 3-D printing also allow individuals in making things in a rigorous and better way.
8. Brain Mapping
Neuroscientists have worked for years to better understand the functioning of brain. Recent advances in brain mapping technology have made that complex and ambitious task easier. An international team of researchers have created a three-dimensional atlas of the brain. The maps resolution is much better than previous efforts. Digitally, the atlas creators stitched together thousands of brain cross-sections.
Conclusion
In today’s age, the global economy’s reemergence, and new technologies will almost certainly drive this. The top technology trends are more likely to take over our regular lives in the coming years. Jobs in these technologies and skills related with them will be extremely invaluable, and gaining education associated to them is bound to help you considerably in your career over the long term. Picking and gaining expertise in the right new technology in coming years will make you a future proof.
Source: Click Here
#best btech college in jaipur#top engineering college in jaipur#best btech college in rajasthan#best private engineering college in jaipur#best engineering college in rajasthan#best engineering college in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Key Components of Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Fiber laser cutting machines represent the pinnacle of precision, efficiency, and versatility in modern manufacturing. These cutting-edge machines harness the power of fiber laser technology to deliver superior performance in various industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and metal fabrication. Understanding the key components of fiber laser cutting machines is essential for maximizing their capabilities and harnessing their potential to drive innovation and success across diverse applications.
1. Fiber Laser Source: At the heart of every fiber laser cutting machine lies the fiber laser source, which generates the intense beam of light used for cutting materials. Unlike traditional CO2 lasers, fiber lasers utilize optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements such as ytterbium or erbium to produce laser light. This innovative design offers several advantages, including higher efficiency, faster processing speeds, and greater reliability.
2. Beam Delivery System: The beam delivery system consists of optical components that guide and focus the laser beam onto the workpiece with pinpoint accuracy. Key elements of the beam delivery system include mirrors, lenses, and cutting heads. Cutting heads contain nozzle assemblies that deliver assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, to the cutting zone to enhance cutting efficiency and quality.
3. CNC Controller: The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) controller serves as the brain of the fiber laser cutting machine. It interprets the cutting program generated by CAD/CAM software and translates it into commands that coordinate the movement of the machine's axes and the activation of the laser beam. The best laser cutting machine enables operators to program complex cutting paths, adjust cutting parameters, and monitor cutting progress in real-time. Advanced CNC controllers feature intuitive interfaces, predictive maintenance capabilities, and connectivity options for seamless integration into automated production environments.
4. Motion System: The motion system comprises servo motors, drive systems, and linear guides that facilitate precise movement and positioning of the cutting head and workpiece during the cutting process. Servo motors drive the motion of the machine's axes, while drive systems convert rotational motion into linear motion. The motion system's speed, accuracy, and repeatability are critical factors in achieving high-quality cuts and maximizing productivity.
5. Bed and Frame: The bed and frame provide the structural foundation and support for the fiber laser cutting machine, ensuring stability and rigidity during operation. The bed serves as the work surface where the material to be cut is positioned, while the frame houses the machine's components and supports the gantry and motion system. High-quality materials such as steel or cast iron are commonly used to construct the bed and frame, providing durability and vibration damping properties. A robust bed and frame design are essential for maintaining cutting accuracy and consistency, especially when processing large or heavy workpieces.
6. Laser Safety System: Safety is paramount in any laser cutting operation, and laser sheet cutting machine price in india are equipped with advanced safety features to protect operators and prevent accidents. Laser safety systems include interlocks, enclosures, and safety sensors that restrict access to the cutting area and automatically shut down the laser in the event of a safety breach. Interlocks ensure that the machine cannot operate unless all safety doors and panels are securely closed, while enclosures contain the laser beam and prevent exposure to harmful radiation. Safety sensors detect any anomalies or hazards, triggering immediate safety responses to mitigate risks.
0 notes
Text
Cables and Connectors Market Size, Share, Report & Forecast 2024-2032

IMARC Group's report titled "Cables and Connectors Market Report by Product Type (Internal Cables and Connectors, External Cables and Connectors), Installation Type (HDMI, USB, VGA, DVI, CAT5/CAT6, and Others), Vertical (Automotive, Commercial, Oil and Gas, Energy and Power, Aerospace and Defense, and Others), and Region 2024-2032", The global cables and connectors market size reached US$ 103.8 Billion in 2023. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 149.9 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4% during 2024-2032.
For an in-depth analysis, you can refer sample copy of the report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/cables-connectors-market/requestsample
Factors Affecting the Growth of the Cables and Connectors Industry:
Rising Adoption of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing relies on data centers to store and process vast amounts of data. As the demand for cloud services is growing, cloud providers and enterprises need to expand their data center infrastructure. This expansion requires a robust network of cables and connectors to interconnect servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and other components within the data center. Cloud computing applications require high-speed data transmission between servers, storage systems, and end-user devices.
Technological Advancements:
As technology is evolving, there is a rise in the demand for faster data transmission speeds. Advancements in cable and connector technology enable the development of high-speed data transmission solutions, such as fiber optics, Cat 6a, and Cat 8 Ethernet cables, and high-speed connectors like USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt, meeting the requirements of modern data-intensive applications. With the proliferation of high-definition (HD) video streaming, online gaming, virtual reality (VR), and other bandwidth-intensive applications, there is a growing need for cables and connectors capable of supporting higher bandwidths.
Growing Demand for High-Speed Internet:
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart homes, connected vehicles, industrial sensors, and wearable devices, is driving the need for reliable and high-speed internet connectivity. This requires a robust network infrastructure, including cables and connectors, to connect IoT devices to the internet and enable seamless data transmission. The increasing trend of remote work and telecommuting highlights the importance of high-speed internet connectivity for remote collaboration, video conferencing, and accessing cloud-based applications.
Leading Companies Operating in the Global Cables and Connectors Industry:
3M Company
Amphenol Corporation
Axon' Cable
Fujitsu Limited
Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
Molex LLC (Koch Industries Inc)
Nexans
Prysmian S.p.A.
Sumitomo Electric Wiring Systems Inc.
TE Connectivity
Cables and Connectors Market Report Segmentation:
By Product Type:
Internal Cables and Connectors
External Cables and Connectors
External cables and connectors represent the largest segment owing to the increasing demand for connectivity solutions in outdoor environments and the expansion of infrastructure projects requiring durable and weather-resistant cables and connectors.
By Installation Type:
HDMI
USB
VGA
DVI
CAT5/CAT6
Others
CAT5/CAT6 accounts for the majority of the market share driven by its widespread adoption in Ethernet networks for both residential and commercial applications, offering a balance between performance, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing infrastructure.
By Vertical:
Automotive
Commercial
Oil and Gas
Energy and Power
Aerospace and Defense
Others
Commercial exhibits a clear dominance in the market as businesses, enterprises, and data centers require extensive networks of cables and connectors to support their operations, including data transmission, networking, and communication needs.
Regional Insights:
North America (United States, Canada)
Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Others)
Europe (Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, Others)
Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, Others)
Middle East and Africa
Asia Pacific enjoys the leading position in the cables and connectors market on account of rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India, driving the demand for cables and connectors across various industries including telecommunications, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.
Global Cables and Connectors Market Trends:
The proliferation of wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC, is changing connectivity requirements, leading to innovations in wireless cables and connectors to support seamless wireless communication. The growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates the development of specialized cables and connectors for charging infrastructure, battery management systems, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication.
Industries are adopting automation technologies, driving the demand for cables and connectors for connecting sensors, actuators, controllers, and other devices in automated manufacturing and process control systems.
Note: If you need specific information that is not currently within the scope of the report, we will provide it to you as a part of the customization.
About Us:
IMARC Group is a leading market research company that offers management strategy and market research worldwide. We partner with clients in all sectors and regions to identify their highest-value opportunities, address their most critical challenges, and transform their businesses.
IMARCs information products include major market, scientific, economic and technological developments for business leaders in pharmaceutical, industrial, and high technology organizations. Market forecasts and industry analysis for biotechnology, advanced materials, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, travel and tourism, nanotechnology and novel processing methods are at the top of the companys expertise.
Our offerings include comprehensive market intelligence in the form of research reports, production cost reports, feasibility studies, and consulting services. Our team, which includes experienced researchers and analysts from various industries, is dedicated to providing high-quality data and insights to our clientele, ranging from small and medium businesses to Fortune 1000 corporations.
Contact US
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: [email protected]
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-631-791-1145 | United Kingdom: +44-753-713-2163
0 notes
Text
Lighting the Way: Exploring the Fiber Optic Sensor Market's Radiant Future
In the ever-expanding realm of sensing technology, the Fiber Optic Sensor Market stands out as a beacon of innovation and reliability. Leveraging the power of light to detect and measure various parameters, fiber optic sensors are redefining the boundaries of sensing capabilities across industries. From structural health monitoring in infrastructure to medical diagnostics and environmental sensing, these sensors offer unparalleled accuracy, durability, and versatility. As the demand for real-time data insights and IoT connectivity grows, the market witnesses a surge in adoption, driving advancements in fiber optic sensing technology and opening new frontiers in smart sensing applications.
As industries strive for greater efficiency and sustainability, fiber optic sensors emerge as indispensable tools for monitoring and control. With their immunity to electromagnetic interference and ability to withstand harsh environments, these sensors offer robust and reliable solutions for a wide range of applications. Whether it's detecting temperature variations in power plants or monitoring strain in aerospace structures, fiber optic sensors provide critical insights that empower businesses to optimize operations, minimize downtime, and enhance safety and reliability.
In a world where data is king, fiber optic sensors offer a gateway to a smarter, more connected future. Integrated with IoT platforms and cloud-based analytics, these sensors enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making, driving efficiency and innovation across industries. With features like remote accessibility and scalability, businesses can leverage fiber optic sensing technology to unlock new opportunities for automation, optimization, and sustainability, paving the way for a brighter and more resilient future.
#FiberOpticSensors #SmartSensing #IoTIntegration #DataInsights #TechInnovation #Sustainability #RealTimeMonitoring #PredictiveMaintenance #Industry40 #SmartInfrastructure #EnvironmentalMonitoring #StructuralHealthMonitoring #DigitalTransformation #Reliability #InnovationInSensing
0 notes
Text
InGaAs Photodiode Sensor Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast 2030
In the realm of optical sensing, where precision meets innovation, a remarkable technology has been quietly making waves – the InGaAs photodiode sensor. Behind this unassuming name lies a world of possibilities, where light is not just detected but decoded with unparalleled accuracy and sensitivity. Join us as we delve into the dynamic landscape of the InGaAs photodiode sensor market, exploring its evolution, applications, and the transformative potential it holds for diverse industries.
The Essence of InGaAs Photodiode Sensors
At the heart of InGaAs photodiode sensors lies a semiconductor compound known as Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs), renowned for its unique optical properties that enable the detection of near-infrared (NIR) light. Unlike traditional silicon-based photodiodes, InGaAs photodiodes exhibit exceptional sensitivity to wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum, making them indispensable for a wide range of applications in fields such as telecommunications, spectroscopy, and aerospace.
Request Sample Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3185
Market Dynamics and Trends
The InGaAs photodiode sensor market is characterized by a steady growth trajectory, driven by increasing demand for high-performance sensing solutions across diverse industries. Key factors driving market growth include advancements in sensor design, manufacturing techniques, and integration capabilities, as well as the growing adoption of NIR spectroscopy for industrial process monitoring, environmental sensing, and medical diagnostics.
One notable trend within the InGaAs photodiode sensor market is the miniaturization of sensors and the development of compact, lightweight modules tailored for portable and handheld applications. This trend reflects the growing need for on-the-go sensing solutions in fields such as food safety, pharmaceuticals, and consumer electronics, where real-time analysis and quality control are paramount.
Applications and Innovations
The versatility of InGaAs photodiode sensors is reflected in their myriad applications across various industries. In telecommunications, for instance, these sensors play a critical role in optical fiber communications, enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal loss. Similarly, in spectroscopy, InGaAs photodiodes are employed for chemical analysis, material characterization, and environmental monitoring, offering unparalleled sensitivity and spectral range.
Moreover, the integration of InGaAs photodiode sensors with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is unlocking new possibilities for intelligent sensing and data analytics. By leveraging AI algorithms to analyze sensor data in real-time, researchers and engineers can extract valuable insights, identify patterns, and optimize process parameters with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their remarkable capabilities, InGaAs photodiode sensors face challenges related to cost, performance optimization, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Additionally, the stringent regulatory requirements governing certain industries, such as healthcare and aerospace, pose barriers to market entry and product adoption.
However, amidst these challenges lie abundant opportunities for innovation and growth. As sensor manufacturers continue to refine their fabrication techniques and develop new materials, the cost of InGaAs photodiode sensors is expected to decline, making them more accessible to a broader range of applications and industries. Furthermore, advancements in packaging technologies, such as hermetic sealing and ruggedization, are expanding the deployment possibilities of InGaAs photodiode sensors in harsh environments and demanding operating conditions.
The Future of InGaAs Photodiode Sensors
As we gaze into the future of the InGaAs photodiode sensor market, one thing is clear: the potential for innovation and impact is boundless. With advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and interdisciplinary collaboration, InGaAs photodiode sensors will continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in optical sensing, enabling new discoveries, enhancing productivity, and improving quality of life across the globe.
In conclusion, the InGaAs photodiode sensor market represents a convergence of cutting-edge science, engineering, and imagination. From its humble beginnings to its transformative potential, the journey of InGaAs photodiode sensors illuminates the profound impact of light on our understanding of the world and our ability to harness its power for the greater good. As we embrace the possibilities of intelligent sensing and exploration, let us embark on a journey of discovery and innovation, guided by the brilliance of InGaAs photodiode sensors.
Access Full Report Details: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/ingaas-photodiode-sensor-market-3185
0 notes
Text
Exploring types of pressure sensors and their diverse applications
Pressure sensors play a crucial role in various industries, providing valuable data for monitoring and controlling processes.
As technology advances, different types of pressure sensors have emerged, each with its unique characteristics and applications. But what are these types and how are they used today?
Keep reading as we delve into the world of pressure sensors, exploring various types and their applications.

What are the most common types of pressure sensors?
Pressure sensors are devices that measure pressure and convert it into an electrical signal. There are various types of pressure sensors that vary in their operating principles, including piezoelectric, capacitive, resistive, and optical sensors, each designed for different applications.
Some of the most common types include:
Strain Gauge Pressure Sensors
These sensors use a flexible diaphragm or membrane to measure pressure. As pressure changes, the strain on the diaphragm changes, leading to a corresponding change in electrical resistance. Strain gauges are often bonded to the diaphragm, and the resistance change is measured to determine the pressure.
MEMS Capacitive Pressure Sensors
MEMS, or Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems, have revolutionized the field of pressure sensors.
MEMS capacitive pressure sensors are a subset of MEMS sensors that measure pressure using changes in capacitance. These sensors consist of a diaphragm that deforms under pressure, causing a change in the gap between capacitor plates and, consequently, the capacitance. This technology offers high sensitivity, low power consumption, and compact size.
The advancements in MEMS technology have led to the development of highly accurate and reliable capacitive pressure sensors.
Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
These sensors use the piezoelectric effect, where certain materials generate an electrical charge in response to mechanical stress. When pressure is applied, the piezoelectric material deforms, generating a charge that is proportional to the applied pressure.
Optical Pressure Sensors
These sensors use the deformation of an optical element to measure pressure. Fiber optic sensors, for example, can detect changes in the transmission of light caused by pressure-induced deformations.
What are the most common applications of pressure sensors?
Pressure sensors find widespread use in various industries and applications due to their ability to measure and monitor pressure levels. Some of the most common pressure sensors applications include:

Aerospace Pressure Sensors
The aerospace industry demands high-performance pressure sensors to ensure the safety and efficiency of aircraft. Aerospace pressure sensors monitor various parameters, including cabin pressure, altitude, and fuel pressure.
These sensors are designed to meet the stringent requirements of the aviation industry, like withstanding harsh environmental conditions, extreme temperatures, and high altitudes and contributing to the overall safety and functionality of aircraft systems.
HVAC Sensors
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on pressure sensors to optimize performance and energy efficiency. HVAC sensors monitor air pressure, ensuring proper airflow and ventilation in buildings, and also play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and comfort.
Moreover, such sensors contribute to the intelligent control of HVAC systems, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Final thoughts on pressure sensor applications
Today, pressure sensors have become indispensable in various industries, contributing to the advancement of technology and improved efficiency in critical processes.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and reliable pressure sensors will persist. The continuous development of technology and the diverse applications of pressure sensors underscore their significance in shaping the future of various industries.
Understanding the differences between pressure sensor types is crucial for selecting the right sensor for a given application – if you want to know more, get in touch with ES Systems, a pioneer in the field.
0 notes
Text
Metal Flex Bellows And Copper Alloy Bellows: Versatile Solutions For Various Industries
In the ever-evolving landscape of engineering and manufacturing, the demand for flexible and robust components continues to rise. This demand has paved the way for the emergence of two remarkable products: Metal Flex Bellows and Copper Alloy Bellows. These innovative bellows offer unparalleled versatility in a variety of applications. Let's explore further to understand their definitions, characteristics, and widespread use across industries.

Metal Flex Bellows, also known as metallic expansion joints, are meticulously engineered components designed to absorb thermal expansion, vibration, and misalignment in piping systems. Constructed from premium-grade metals such as stainless steel, inconel, or hastelloy, these bellows consist of a series of convoluted metal layers. The unique interlocked design enables axial, lateral, and angular movement, while maintaining the integrity of the system.
The Metal Flex Bellows offer exceptional benefits across industries. In HVAC systems, they provide flexibility to compensate for temperature-induced expansion and contraction, ensuring the integrity of air conditioning ducts. In automotive applications, they absorb vibration and reduce stress, contributing to a longer lifespan for exhaust systems. Moreover, in aerospace and defense manufacturing, these bellows solutions alleviate thermal and mechanical stresses, avoiding structural failure and ensuring good performance.
In parallel, Copper Alloy Bellows represent another remarkable innovation. Composed of copper, a malleable and corrosion-resistant material, these bellows possess good electrical and thermal conductivity. Their inherent ductility enables them to accommodate various mechanical movements and environmental conditions. Copper Alloy Bellows find extensive use in industries necessitating hermetic seals, such as electrical connectors, switches, and sensors.
Due to their superior characteristics, Copper Alloy Bellows enjoy diverse applications. In electric vehicles, they serve as critical components for battery systems, protecting against thermal expansion and vibrations. In the telecommunications sector, they enable efficient fiber optic connections, shielding against temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress. Additionally, in healthcare equipment, Copper Alloy Bellows are embedded within medical devices to ensure accurate pressure measurements and enable safe, airtight connections.
The adaptability and reliability of Metal Flex Bellows and Copper Alloy Bellows have made them important across industries. Their usage continues to expand as the demand for precision, durability, and performance intensifies. The key features of these bellows solutions, such as high-pressure resistance, flexible movement, and resistance to hard temperatures, have cemented their position as essential components in critical applications.These two innovative products, Metal Flex Bellows and Copper Alloy Bellows, offer good flexibility and durability in various industries. From aerospace to automotive, these bellows have proven to be indispensable in critical applications where precise movement, durability, and protection against extreme conditions are paramount.
In conclusion, Metal Flex Bellows and Copper Alloy Bellows epitomize advanced solutions in the engineering and manufacturing realm. Both products offer advanced features, ensuring their outstanding performance and adaptability across various sectors. As the demand for flexible, durable, and reliable components surges, these bellows solutions play a pivotal role in diverse applications, protecting systems from thermal expansion, vibrations, misalignments, and more. Their contributions to industries such as HVAC, automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, and healthcare cannot be overstated, making them important tools for modern engineering needs.
0 notes
Text
The Crimp C Connector: A Secure and Efficient Solution for Electrical Terminations
Introduction:
In the intricate world of electrical connections, the reliability of terminations is paramount. The crimp C connector stands out as a versatile and efficient solution for creating secure electrical connections. This article explores the characteristics, advantages, and applications of the crimp C connector, shedding light on its role in ensuring safe and dependable electrical terminations.
Overview of the Crimp C Connector:
The crimp C connector is a type of electrical connector designed for quick, secure, and efficient termination of conductors. It typically consists of a metal barrel that is crimped onto a conductor using a specialized tool. This crimping process creates a gas-tight connection, ensuring optimal conductivity and minimizing the risk of electrical faults.
Advantages of the Crimp C Connector:
Reliable Electrical Connection: The crimping process employed by the C connector results in a reliable and low-resistance electrical connection. The compressed barrel ensures intimate contact with the conductor, minimizing the potential for electrical resistance, heat generation, and voltage drops.
Versatility in Application: Crimp C connectors find applications across various industries and environments. They are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, and electrical power systems. The versatility of these connectors lies in their ability to accommodate a wide range of conductor sizes and types.
Ease of Installation: One of the notable advantages of crimp C connectors is their ease of installation. The crimping process is straightforward and requires minimal training, making it a preferred choice for applications where quick and reliable terminations are crucial.
Durable and Vibration-Resistant: The crimp C connector's design ensures a durable connection that can withstand mechanical stresses, including vibrations. This makes them well-suited for applications where connectors may be subjected to movement, such as in automotive and aerospace environments.
Applications of the Crimp C Connector:
Automotive Wiring: Crimp C connectors play a vital role in automotive wiring systems. They are used to establish secure connections in various components, including sensors, lights, and ignition systems. The reliability of crimped connections contributes to the overall safety and performance of vehicles.
Aerospace and Aviation: In the aerospace industry, where precision and reliability are paramount, crimp C connectors are widely employed. They are used in avionics systems, wiring harnesses, and other critical applications, ensuring secure connections in the demanding conditions of aerospace environments.
Telecommunications: The telecommunications industry relies on crimp C connectors for establishing connections in network infrastructure. Whether in data centers, telephone exchanges, or fiber optic networks, these connectors provide a quick and reliable solution for terminating conductors.
0 notes