#income tax filing in tamil
Text
Understanding Professional Tax Registration: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
Streamlining Finances: A Guide to Professional Tax Registration Online in India
The Professional Tax Registration Procedure involves the state governments in India charging individuals who earn income or practise professions such as chartered accountants, lawyers, and doctors. Different states have varying rates and collection procedures for this service, which are imposed at the state level. Not all states enforce this tax, with Karnataka, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, Meghalaya, Odisha, Tripura, Madhya Pradesh, and Sikkim being exceptions. This tax applies to entrepreneurs, working individuals, traders, and various occupations.
Professional tax is collected by specific Municipal Corporations and most Indian states, serving as a revenue source for the government. The maximum annual amount payable is INR 2,500, with predetermined slabs based on the taxpayer's income. Employers deduct this tax from employees' salaries in private companies and remit it to the Municipal Corporation. Professional tax is mandatory, and individuals are eligible for income tax deductions for this payment.
To initiate Professional Tax Registration, individuals must register their mobile number and email ID. After registration, they receive a unique username and password through secure channels like mobile and email. Through the Citizen portal, applicants create a self-assessment application and submit it for professional tax assessment.
The procedure of conversion of LLP into a Private Limited Company
1. Determine Eligibility:
- Confirm whether you meet the criteria for professional tax filing based on your income from profession, trade, or employment.
2. Gather Necessary Documents:
- Collect essential documents, including proof of income, identification, and other relevant details.
3. Online Registration:
- Initiate the professional tax filing by registering online through the designated portal.
4. Provide Personal Information:
- Enter accurate personal information, including your name, address, contact details, and PAN.
5. Employment Details:
- Furnish details regarding your profession, trade, or employment, along with relevant employment records.
6. Income Declaration:
- Declare your income earned through profession, trade, or employment within the specified format.
7. Compute Tax Liability:
- Calculate your professional tax liability based on the applicable slab rates and income brackets.
8. Payment Submission:
- Pay professional tax through the online portal using the available payment options.
9. Generate Acknowledgment:
- Obtain an acknowledgement receipt or confirmation of your professional tax filing for future reference.
10. Compliance with Due Dates:
- Ensure timely filing and payment to adhere to the specified due dates and avoid penalties.
11. Periodic Review:
- Periodically review your professional tax filing status to stay compliant with any regulation changes.
12. Seek Professional Assistance:
- Consult with tax professionals or experts to ensure accurate and smooth professional tax filing.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of Professional Tax Registration in India requires understanding the diverse rates and procedures across states. While not uniformly enforced, this tax is mandatory for entrepreneurs, working individuals, traders, and professionals in specific occupations. With a maximum annual payment cap and Eligibility for income tax deductions, it is a crucial revenue source for governments. The online registration process, facilitated through secure channels and the Citizen portal, streamlines the filing procedure. Additionally, the guide for converting LLPs into Private Limited Companies emphasises the importance of eligibility confirmation, document collection, accurate information entry, and timely compliance to ensure a seamless transition with the possibility of seeking professional assistance if required.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
ED raids Tamil Nadu electricity minister Senthil Balaji's residence
The Supreme Court had last month allowed police and ED to probe into an alleged cash-for-jobs scam against Balaji, who also holds the Prohibition and Excise portfolio.

CHENNAI: The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is carrying out searches at the premises of V Senthil Balaji, Tamil Nadu minister for electricity, prohibition and excise in Chennai and Karur from this morning. The ED team is also raiding the minister's brother's house in Karur.
The Supreme Court had last month allowed police and ED to probe into an alleged cash-for-jobs scam against Balaji, who also holds the Prohibition and Excise portfolio.
Senthil Balaji was the transport minister in the AIADMK government, led by the late J Jayalalithaa, during the period 2011-15. There were complaints against him, in which it was alleged he had received huge amounts as bribes from various persons for appointing them as drivers and conductors in the transport corporations.
In connection with these allegations, three FIRs were registered against him which culminated in charge sheets filed against him and those charge sheets were now pending before a special court for the trial of criminal cases relating to MPs and MLAs.
Since the charge sheets disclosed the commission of a scheduled offence under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), the ED registered the present case against Senthil Balaji and others in July 2021 and took up the investigation.
The searches also come in the wake of Home Minister Amit Shah visiting the city recently and controversy erupted over the blackout in the area which the minister claimed was accidental.
Recently, The Income Tax department conducted raids across Tamil Nadu in around 40 locations at various Government contractors' residences and offices who have alleged connections with Minister Senthil Balaji.
During the searches, supporters of Balaji allegedly created a ruckus and even vandalised a car belonging to the Income Tax (I-T) department and manhandled officials of the department who launched coordinated searches in places across Tamil Nadu linked to the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) minister.
This is the second time sleuths of a central agency have entered the state secretariat for searches.
In 2016, when O Panneerselvam was the chief minister of the state after the death of former chief minister J Jayalalithaa, Income tax Department officials conducted searches in the office of the then Chief Secretary P Ramamohana Rao.
The Supreme Court had last month allowed a police and ED probe into an alleged cash-for-jobs scam against Balaji, who also holds the Prohibition and Excise portfolio.
0 notes
Text
A Beginner’s Guide to Company Registration in Ahmedabad, Bangalore, and Chennai
A new business's launch is both an exciting and difficult task. One of the most important steps in this process is registering your company. If you plan to start a business in Ahmedabad, Bangalore, or Chennai, you may wonder how to register your company.
This beginner's guide will walk you through the company registration in Ahmedabad, Bangalore, or Chennai.
Company Registration in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad is the largest city in Gujarat and a hub for entrepreneurship. Company registration in Ahmedabad is straightforward and can be completed in simple steps. Here's what you need to do:
Get a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): A DSC is a digital version of your signature needed for online transactions. You can obtain a DSC from a certified agency.
Obtain a Director Identification Number (DIN): A DIN is a unique director identification number. You can obtain a DIN by applying at the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Register a company name: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has an online portal to register your company name.
File incorporation documents: You must file incorporation documents with the Registrar of Companies. These include the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and the Articles of Association (AOA).
Get a Permanent Account Number (PAN): You can get a PAN by applying to the Income Tax Department.

2. Company Registration in Bangalore
Bangalore, also known as the Silicon Valley of India, is a hub for technology and innovation. Company registration in Bangalore is similar to that in Ahmedabad. Here's what you need to do:
Get a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): You can get a DSC from an agency approved by the government.
Get a Director Identification Number (DIN): You can get a DIN by applying to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Register a company name: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has an online portal to register your company name.
File incorporation documents: You must file incorporation documents with the Registrar of Companies. These include the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and the Articles of Association (AOA).
Get a Permanent Account Number (PAN): You can get a PAN by applying to the Income Tax Department.
3. Company Registration in Chennai
Chennai, the capital of Tamil Nadu, is a major industrial and commercial center in South India. Company registration in Chennai is similar to that in Ahmedabad and Bangalore. Here's what you need to do:
Get a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): You can get a DSC from an agency approved by the government.
Get a Director Identification Number (DIN): You can get a DIN by applying to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Register a company name: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has an online portal to register your company name.
File incorporation documents: You must file incorporation documents with the Registrar of Companies. These include the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and the Articles of Association (AOA).
Get a Permanent Account Number (PAN): You can get a PAN by applying to the Income Tax Department.
Who Should You Contact Regarding Company Registration?
Company registration in Bangalore, Ahmedabad, or Chennai is a reasonably easy process that can complete in a few easy steps. The purpose of this beginner's guide is to guide you through the steps of legally registering your business. Alonika has a team of experts who can help you with hassle-free company registration in your city if you have any additional concerns or issues.
#company registration in Ahmedabad#Company registration in Bangalore#Company registration in Chennai#Company registration#ahmedabad#Bangalore#Chennai
0 notes
Text
Different GST Returns Filed By Taxpayers With Due Dates | Ebizfiling
Introduction
All registered Taxpayers are required to file GST returns. The tax return forms known as GST returns should be filed by companies to the Income Tax authorities of India. The GST return is filed monthly, quarterly and annually, depending upon which GST return you are filing. In this blog let us study the different GST return to be filed by taxpayers.
Different GST return filed by the taxpayer
GSTR 1- In this return, the details of the outward supply of goods and services are filed by the taxable suppliers. It is filed every month. Such details should be furnished in an electronic statement by the registered taxpayer. The due date for filing the GSTR 1 is on or before the 11th of the succeeding month. Details of invoices, debit notes, revised invoices and credit notes issued during the tax period etc. should be included in the GSTR 1.
When the registered supplier opts the QRMP scheme, the GSTR 1 is filed quarterly. In this return, taxable suppliers file the details of outwards supply of goods and services. The due date to file GSTR 1 quarterly is different and that is on or before 13th of the succeeding month following the quarter end.
GSTR 2- This return is filed by the registered taxable recipients who fill in the details of inward supplies of taxable goods and services in order to claim Input Tax Credit. The taxpayer has to file this return on or before 15th of the next month.
GSTR 3- This return is filed monthly by the registered taxpayer on the basis of the completion of details of inward supplies and outward supplies with the payment of the amount of tax. Every taxpayer should file the GSTR 3 on or before 20th of the subsequent month.
GSTR 3B- In this return, the details of tax collected on outward supplies and details of tax paid on input supplies are included. It should be noted that no invoice-level details are included in this return. The taxpayer files a NIL return if there was no business activity is performed for such period of tax. This return is filed monthly by the taxpayer but the due date differs on the income in the previous financial year. There are 3 cases which are as follows:
A taxpayer whose total income is more than INR 5 crore in the previous financial year, the due date is 20th of the next month.
A taxpayer whose business is situated in Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Lakshadweep, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Andaman, and Nicobar Islands, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh and total income is below INR 5 crore in the previous financial year, the due date is 22nd of the next month.
A taxpayer whose business is situated in Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Chandigarh, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam, West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha, and total income is below INR 5 crore in the previous financial year, the due date is 24nd of the next month.
GSTR 4- The registered taxpayer file this return when he opts for the composition scheme. It is filed quarterly and the due date is on or before 18th of the month succeeding quarter.
GSTR 5- This return is filed by all non-resident Indian (NRI). They are the suppliers who do not have an established business in India and have to visit India for a shorter period to make supplies. In this return, the NRI include all the details of the business including the sales and purchases. It should be filed on or before the 20th of the month succeeding tax period & within 7 days after the expiry of registration under section 27 of the Companies Act, 2013.
GSTR 5A- This return is filed by the person who is providing OIDAR (online information and database access or retrieval) services from outside India to the non-taxable online recipient in India. Such a person has to file GST return on or before 20th of the succeeding month.
GSTR 6- It is a return filed by input service distributors. The details of ITC by an input service distributor and the distribution of ITC are included in this GST return. On or before 13th of month is the standard due date fixed by the tax authorities.
GSTR 7- A person who deducts tax at source (TDS) is required to file GSTR 7. It includes the details such as TDS deducted, TDS liability paid and payable, any TDS claimed etc. Such a person has to file the GSTR 7 on 10th of the following month.
GSTR 8- The e-commerce operators file GSTR 9 which needs to deduct TCS (tax collected at source) under Goods and Services Tax Act. It includes the details of supplies made on the e-commerce platform and the amount of TCS on such supplies. The e-commerce operator has to file GST return on or before 10th of the following month.
GSTR 9- It is the annual return filed by all the registered taxpayers under the composition levy scheme and also those who are engaged in the supply of goods to the on an e-commerce platform. Even the taxpayer filing GSTR 1, GSTR 2, GSTR 3, and GSTR 3B during the financial year are required to file GSTR 9. Details related to the supplies made and received during the financial year under various tax heads such as IGST, SGST and CGST are included in the GSTR 9. It is the combination of all the information filled in monthly or quarterly returns in the current financial year.
GSTR 9A- This return is filed by the registered taxpayer who has opted for a composition scheme and it is a simplified annual return. It is filed annually on 31st December.
GSTR 9C- A registered person whose aggregated turnover is more than INR 2 crores is required to file GSTR 9C and also by the person who needs to get their accounts audited under section 35 of the CGST. It is filed annually on 31st December of the financial year.
GSTR 10- This return is filed when a person wants to cancel or surrender his GST registration. It should be filed within 3 months of the date of cancellation of the order, date of cancellation whichever is later.
GSTR 11- It is filed by a person who has issued a Unique Identity Number (UIN) to get refund for goods and services purchased in India under GST. It is filed on 31st December of the year.
GST interest for late payment
Under the GST system, late payments of tax is levied with 18% interest rate. The interest would be charged from the due date when the tax was not paid.
Bottom line
The Income Tax department has set deadlines for filing GST returns, and any delay in complying with them is considered as non-compliance and liable to strict penalties under the GST Act. The penalty amount is determined based on the type of GST returns filing.
0 notes
Text
Embark Corpserv - Company Registration Online, GST, Trademark in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu
Embark Corpserv is Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India Best Business Setup Provider with Company Incorporation online, GST Registration, Trademark, Income Tax Return Filing and FSSAI.
With Embark Corpserv, apply for GST registration online in India! Any business operations or any organisation with an annual turnover over Rs 40 lakhs is required under the GST legal process to go through the GST process/procedure in India as a distinct taxable provision.
Trademark Registration Online in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India - A trademark registration online is a distinctive identification that gives your product or service a distinctiveness that makes it stand out from the competition in the commercial market.
Contact Us:
Website: https://embarkcorpserv.com/
Phone: +91 70928 00020
0 notes
Video
undefined
tumblr
TDS on Cash Transactions - Explained in Tamil
TDS return filing is compulsory for all the assesses who fall under the tax slab as prescribed by the Income Tax Department.
To file a TDS return, one must be thorough with the application procedure and the eligibility criteria.
https://www.kanakkupillai.com/tds-return
0 notes
Text
Here's How A Side Hustle Affects Tax Deductions
Here’s How A Side Hustle Affects Tax Deductions
Tech professionals moonlighting, taking additional assignments outside their regular jobs, should get ready to pay up taxes. An extra income earned from a side hustle qualifies for tax deductions and must be disclosed when filing tax returns. Not doing so could invite actions from the IT department. Speaking to the Economic Times, R Ravichandran, principal chief IT commissioner, Tamil Nadu,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Trust Registration Company In India
Trust Registration In India
Trust Registration: Public Trust is the most convenient way of starting a non-governmental organization or NGO. A trust functions on the objective of eradicating poverty, providing education to the underprivileged and offering medical relief apart from the generalized aim of promoting arts, science and literature. It is to be noted that trusts are irrevocable which means they cannot be amended or terminated without the permission of the court. Semantic Taxgen helps in providing you with the trust registration certificate with a few documents like a deed of trust, rental agreement, etc.
In India, there are no specific laws to govern the public trust, however, some states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu have their own public trust Act.
Eligibility Criteria Of Trust Registration In India
The trust deed is the primary and the most essential document of the trust which states the reason for forming a trust, its functions, to its working, and until its closure. Following are the important clauses in the Trust Deed:
Name of the trust
The registered office of the trust
Area of operation of the trust
Objectives of the trust
Details of the Author of the Trust
Corpus/Assets of the Trust
Details of the Board of Trustees
Quorum of the Board with their qualification, terms and tenure
Powers and functions of the Managing Trustee and other Trustees
Closure and amendment of the trust deed and the applicability of the Act
Documents Required For Trust Registration
To get your trust registration certificate, you should require the following documents during the registration of the Trust:
A completely drafted trust deed
Proof of registered office – (Rental Agreement or ownership document)
ID proof of the Founder of the Trust
Two witnesses
Constitution of the Trust
The Trust constitutes the Board of Trustees. The Board constitutes the following:
Author/Founder/Settlor of the trust
Managing trustee(s)
Other trustees
The quorum of the Board of Trustees shall not exceed a maximum of 21 members.
Why register a trust?
As per the Public Trust Act of all states, registration of Trust is mandatory if it involves charitable purpose or when there is a transfer of immovable property in the name of the trust.
Only registered trust is eligible for tax exemptions provided under Section 12 A and 80G of the Income Tax Act.
Registering a trust adds more credibility to the same as it involves public money in the form of donations.
Trust Compliances
A trust shall after its registration shall do the following
Obtain PAN card
Book Keeping and Accounts
Annual IT filings
Shops and Establishment License – in case of employment
Professional Tax Registration – if applicable
GST registration – if applicable
Tax Exemption Of Trust
There is a general notion that trust need not have to pay tax as they work towards the welfare of the public at large. But this is not true. A trust, like any other legal entity, is liable to pay tax. In order to be exempted from tax, trust is required to obtain certification for the said exemptions such as Section 12 A, 80G etc. from the Income Tax authorities.
Trust Registration Process
A full consultation to understand your requirement and to explain you the process from end to end
All the paperwork needed to apply for a society registration, we will keep you informed about the entire process and progress
We help you with all the processes and procedures needed for registering your society
Trust Registration Fees
Phone Support: +91 9654831210
Email Support: [email protected]
Visit Us On: 1007, Roots Tower, Laxmi Nagar District Centre, Near Nirman Vihar Metro, New Delhi-110092
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guiding Through the Online Professional Tax Registration Procedure in India
Streamlining Finances: A Guide to Professional Tax Registration Online in India
The Professional Tax Registration Procedure involves the state governments in India charging individuals who earn income or practise professions such as chartered accountants, lawyers, and doctors. Different states have varying rates and collection procedures for this service, which are imposed at the state level. Not all states enforce this tax, with Karnataka, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, Meghalaya, Odisha, Tripura, Madhya Pradesh, and Sikkim being exceptions. This tax applies to entrepreneurs, working individuals, traders, and various occupations.

Professional tax is collected by specific Municipal Corporations and most Indian states, serving as a revenue source for the government. The maximum annual amount payable is INR 2,500, with predetermined slabs based on the taxpayer's income. Employers deduct this tax from employees' salaries in private companies and remit it to the Municipal Corporation. Professional tax is mandatory, and individuals are eligible for income tax deductions for this payment.
To initiate Professional Tax Registration, individuals must register their mobile number and email ID. After registration, they receive a unique username and password through secure channels like mobile and email. Through the Citizen portal, applicants create a self-assessment application and submit it for professional tax assessment.
The procedure of conversion of LLP into a Private Limited Company
1. Determine Eligibility:
- Confirm whether you meet the criteria for professional tax filing based on your income from profession, trade, or employment.
2. Gather Necessary Documents:
- Collect essential documents, including proof of income, identification, and other relevant details.
3. Online Registration:
- Initiate the professional tax filing by registering online through the designated portal.
4. Provide Personal Information:
- Enter accurate personal information, including your name, address, contact details, and PAN.
5. Employment Details:
- Furnish details regarding your profession, trade, or employment, along with relevant employment records.
6. Income Declaration:
- Declare your income earned through profession, trade, or employment within the specified format.
7. Compute Tax Liability:
- Calculate your professional tax liability based on the applicable slab rates and income brackets.
8. Payment Submission:
- Pay professional tax through the online portal using the available payment options.
9. Generate Acknowledgment:
- Obtain an acknowledgement receipt or confirmation of your professional tax filing for future reference.
10. Compliance with Due Dates:
- Ensure timely filing and payment to adhere to the specified due dates and avoid penalties.
11. Periodic Review:
- Periodically review your professional tax filing status to stay compliant with any regulation changes.
12. Seek Professional Assistance:
- Consult with tax professionals or experts to ensure accurate and smooth professional tax filing.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of Professional Tax Registration in India requires understanding the diverse rates and procedures across states. While not uniformly enforced, this tax is mandatory for entrepreneurs, working individuals, traders, and professionals in specific occupations. With a maximum annual payment cap and Eligibility for income tax deductions, it is a crucial revenue source for governments. The online registration process, facilitated through secure channels and the Citizen portal, streamlines the filing procedure. Additionally, the guide for converting LLPs into Private Limited Companies emphasises the importance of eligibility confirmation, document collection, accurate information entry, and timely compliance to ensure a seamless transition with the possibility of seeking professional assistance if required.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Grow Your Savings Through Smart Tax Planning

Every year, as it nears December, most people put their minds on saving the “dreaded” income tax. As a law-abiding citizen, one must file an income tax return annually to determine the tax obligations. As many as 8.45 crore taxpayers have been registered as of March 2019. In fact, among all states, Maharashtra tops with the highest number of tax filers, followed by Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal.
In most developed countries including US and other richer nations, the tax component of individuals are far higher. They also do not have as many advantages of tax deduction schemes as we have in India. Most countries, including India, employ a progressive tax system, in which higher-income earners pay a higher tax rate, in comparison to their low-income counterparts.
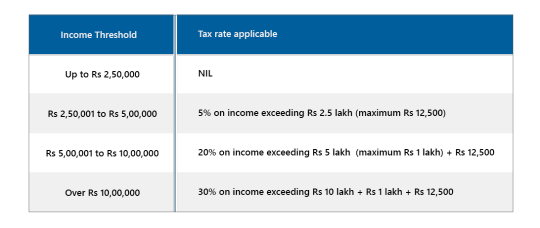
Here’s a look at the Income Tax slabs for the Assessment Year 2019-20:

Tax Deductions Allowed in India
i) Deductions on Investment
The government allows for certain deductions to save tax, at the end of every financial year. It is essential to keep yourself informed of all the deductions, rebates and concessions to pay the least amount of tax on your total income. Ideally, it is advised to start tax planning at the start of every financial year to gain maximum benefit.
In India, you can claim a tax deduction up to Rs 1.5 lakh of your total income under section 80C. These are the investments specified: Public Provident Fund, tax saving mutual funds, tax saving fixed deposit, National Savings Certificate, premium on life insurance policy, ULIP (Unit linked Plans)and Employees Provident Fund.
We also have Section 80CCC that provides a deduction for any amount paid or deposited towards receiving annuity from insurance.
Further, under Section 80AA, deduction is allowed with respect to any income that is earned by way of dividends from a domestic company (this is included in the gross total income of the assessee.
ii) Income Tax Deduction for Interest on Home Loan
The interest portion of the Equated Monthly Installments paid for the year can be claimed as a deduction from your total income up to a maximum of Rs 2 lakhs under Section 24. From Assessment Year 2018-19 onwards, the maximum deduction for interest paid on Self Occupied house property is Rs 2 lakhs.
iii) Tax deduction on Medical Insurance
In India, as an individual or Hindu Undivided Family, you can claim a deduction of Rs 25,000 under Section 80D for yourself, spouse and dependent children. There’s also an additional deduction for insurance of parents, up to Rs 25,000, if they are below 60 years of age. If they are above 60, the deduction amount is Rs 50,000.
For instance, a health insurance policy from HDFC Life can provide a range of tax benefits. The premium paid for a Health Insurance policy can be deducted from the total income under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act. The tax deduction under Section 80D is also allowed for making a payment to purchase or renew a Health Insurance policy on self, spouse, dependent parents or dependent children.
These are ways and means to maximize our tax benefits. But any such analysis would be incomplete without taking a look at Unit Linked Insurance Plans in India, one of our strongest options to save tax.
Unit-Linked Insurance Plans are fast becoming one of the most favoured instruments to save taxes. They have a minimum lock-in period of five years and make for an ideal investment avenue. ULIPs in India are affordable, offer diversified return options, and also multiple switches between available fund options. According to your risk appetite, choose a plan you think works best for you that will in turn offer you stable returns over a period. Besides the benefits of financial returns, one of the most attractive features of ULIPs is the tax benefits they offer, much to the advantage of the policy subscriber. HDFC Life Click 2 Wealth offers this and much more!
Paying your taxes sincerely and on time is your patriotic duty. Utilise these tax benefit schemes to save your money. Pay more attention to the act of tax planning. For any assistance, there’s always HDFC Life you can count on.
This content was produced in partnership with HDFC Life
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everything one should know about Professional Tax
Do you ever study the deduction breakup whenever you obtain your salary? You may get across the professional tax at the head. Don't get it confused with income tax, professional tax is something entirely different.
However not all Indian States impose Professional tax, those who does include it are Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya, Orissa, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Manipur, Mizoram and Chhattisgarh.

In this article, we will tell you the complete understanding of Professional Tax and its Compliances.
So, what is Professional Tax?
Unlike the word says, professional tax is not just a tax levied on professionals. This tax is levied on any person earning a living through work, employment trade or calling. Professional Tax is a state tax that a state government imposes on account of the infrastructure it provides to you so that you can carry out your profession in that State.
As provided for in Clause (2), Article 276 of the Indian Constitution, State Governments are granted the right to levy and collect the professional tax. Most Indian states have also opted to not exercise this right. This tax is levied in all other States where appropriate, based on professional tax slab rates as implemented by the respective states. Neither state will, however, charge professional tax on any taxpayer over 2,500. Professional tax payment is permitted as a taxable income deduction under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
To salaried employees, the employer deducts professional tax and is charged to the State Government's concerned department. To pay the professional tax self-employed people need to receive a ' Certificate of Enrolment ' from the State authority in question.
Professional Tax slabs
Like any other tax Professional Tax also has slabs, and all of an organization's paid employees and qualified professionals fall within its various categories.
Professional tax slabs are based on predetermined slabs and on the salary or monthly level of income. It is usually around Rs.200 a month with Rs. 2500 being the maximum payable in one year. The employer who is responsible for depositing it with the relevant government office deducted this balance from the employee's salary.
Professional Tax is not only for those who get a salary, any individual who is not working in an organization but still earn, is responsible for paying Professional Tax.
Professional Tax Compliance
Any professional who has monthly income above a certain level has to professional tax. Since the rates of professional tax depend on states to states, it is mandatory to be aware of the rates in your particular state. Usually, a penalty is imposed on a taxpayer if they fail to register for professional tax. There are also penal provisions for non-payment of professional tax and for failure to file the return within the due date.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Income Tax Return Filing Due dates for FY 2021-22 (FY 2022-23). Last Date: 31.07.2022 Avoid Last Minute hurry... Cell: 9095532510 வருமான வரி தாக்கல் செய்ய கடைசி தேதி: 31.07.2022. கடைசி நேர அவசரத்தை தவிர்க்கவும். #வருமானவரி #incometax #incometaxreturn (at Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu) https://www.instagram.com/p/CfJJ092rbOp/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Video
undefined
tumblr
Income Tax Filing & Registration Service Here | CHENNAI FILINGS | CHENNAI |Income Tax Filing & RegistrationHelping businesses and entrepreneurs grow with our exceptional ITR filing Services.Income tax return filing is mandatory for all and the filing form varies according to the income earned and the people like individual, business, company, job, partnership, etc. We at Chennai Filings help file your income tax return by providing the best stress-free ITR services in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
Call Now: (+91) 70101 77653
Web Site : https://www.chennaifilings.in/
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCqiuxQCHwqe_E9TMYspgN4Q
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/Chennai-Filings-100887194999950
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/chennai_filings/?hl=en
Pinterest : https://in.pinterest.com/chennaifilings2020/
1 note
·
View note
Video
vimeo
Canadian ex-pats living abroad rental income tax - Tamil Subtitles from Mansoor Suhail on Vimeo.
Canadian ex-pats living abroad rental income tax - Tamil Subtitles
Nonresident rental income tax Canada 2021 income tax brackets calculator
#Canadian ex-pats rental income, #section 216 tax, #NR4, #NR5, #NR6
Call us at 416-283-8774
Visit us at theaccountingandtax.com
Non-Residents Rental Income Filing and Reporting Requirements
When you receive rental income from real or immovable property in Canada, the payer, such as the tenant, or agent, such as the property manager, has to withhold non-resident tax at the rate of 25% on the gross rental income paid or credited to you. The payer has to pay the tax to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) on or before the 15th day of the month following the month the rental income is paid or credited to you.
The payer has to give you two copies of an NR4, Statement of Amounts Paid or Credited to Non-Residents of Canada showing the gross amount of rental income paid or credited to you during the year and the amount of non-resident tax withheld. The payer also has to send CRA an NR4 information return.
Generally, the non-resident tax withheld is considered your final tax obligation to Canada on the rental income from real or immovable property in Canada. However, if you elect under section 216 of the Income Tax Act, you are choosing to report your rental income from real or immovable property in Canada on a separate Canadian tax return. This allows you to pay tax on your net Canadian-sourced rental income instead of the gross amount and you may pay less tax. You may also receive a refund of some or all of the non-resident tax withheld. If you intend to elect under section 216, you may also want to consider having non-resident tax withheld on the net rental income instead of the gross amount. To do this, you and your agent (a resident of Canada who acts on your behalf regarding your Canadian rental income) have to complete Form NR6 and send it to the CRA for approval. You should send the CRA Form NR6 on or before January 1st of each year, or before the first rental payment is due.
If the CRA approves your Form NR6, your agent can withhold non-resident tax at the rate of 25% on your net rental income (the amount of rental income available after the rental expenses have been paid). Your agent must pay CRA the tax on or before the 15th day of the month following the month the rental income is paid or credited to you.
Generally, you have to send your section 216 return to CRA within two years from the end of the year in which the rental income was paid or credited to you. If CRA approves your Form NR6 for a certain year, you have to file a T1159, Income Tax Return for Electing Under Section 216, for that year, even if you have no tax payable or you are not expecting a refund. The return is due on or before June 30, of the following year. If you have rental income from more than one rental property in Canada and you make an election under section 216, all of your Canadian rental income and expenses must be reported together on one section 216 return.
Do have a question about your U.S income tax filing?
Do you own a residential rental property in the U.S and you are a non-resident.
You are not a citizen of the U.S and you do not have a green card.
You need to file your1040NR return.
Do you pay 30% tax on the gross rent or you can have a choice to make an election?
Generally, a taxpayer is required to withhold 30% of the gross rent and remit it to the IRS. But a taxpayer can make an election to be taxed on the net income.
If you decide to make an election to be taxed on the net income, you can use schedule E to report rental income and expenses.
Taxpayers may also have to file form 8833 treaty disclosure form.
We specialize in U.S non-resident rental income tax filing.
Call us now for a free consultation.
We at the Accounting and Tax have been helping taxpayers since 2001.
Call us now at 416-283-8774
Visit us at theaccountingandtax.
0 notes