#indus valley
Text

Stamp seal, Indus Valley Civilization, 2500-2000 BC
from The British Museum
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
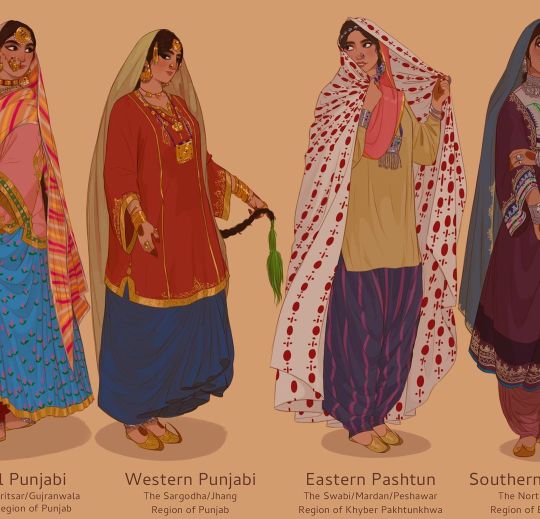
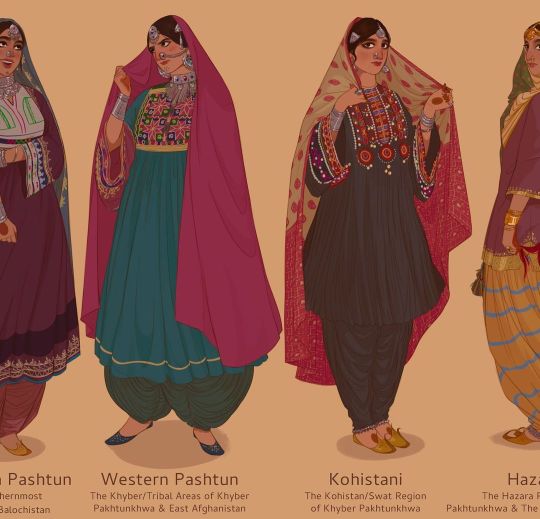
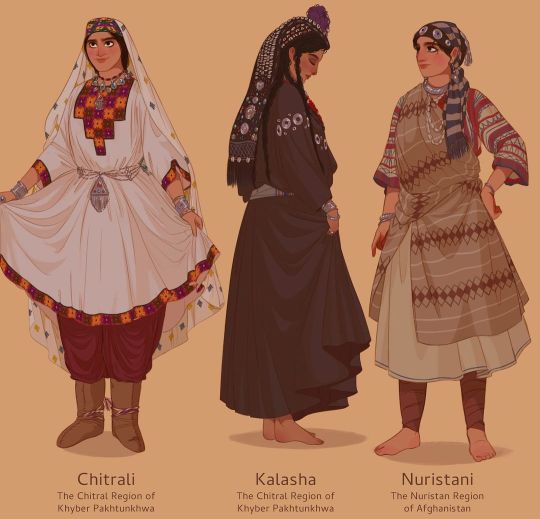










Arsalan Khan
#arsalan khan#arsalanactual#art#south asia#indus river#indus valley#pakistan#india#afghanistan#kashmir#tradition#clothes
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
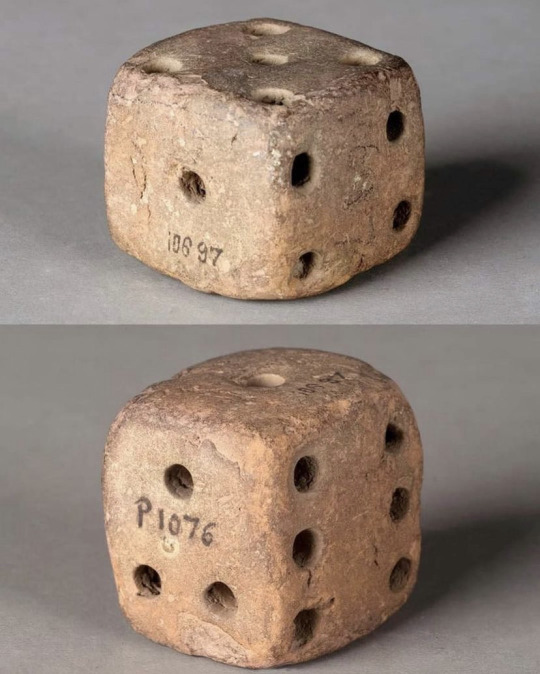

Pair of smol Terracotta dice
Harappa (2600-1800 BCE), an ancient city from the Indus Valley Civilization, modern day Punjab, Pakistan
Many were found in Mohenjo-daro as well, another central ancient city of the Indus Valley in modern day Sindh, Pakistan.
Mostly cube-shaped, sizes range from 1.2 by 1.2 by 1.2 inches to of 1.5 by 1.5 by 1.5 inches
#art#archaeology#sculpture#ancient#ancient art#harappan civilization#indus valley#indus valley civilization#african art#african culture#punjab#sindh#ancient culture
249 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Indus Valley civilization is my Roman Empire.
#indus valley#indus valley civilization#harappan civilization#history#indian#indian history#ancient civilizations#ancient#ancient history#roman empire#desiblr
84 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Unknown, The "Priest-king"
Indus Valley, pre-500 BCE
259 notes
·
View notes
Photo
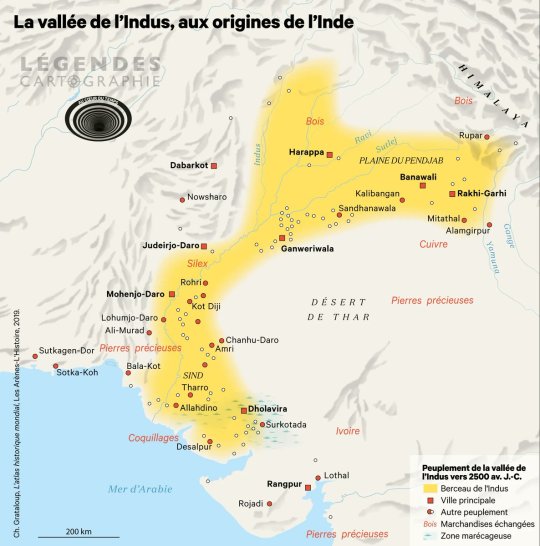
The Indus Valley, 3rd millennium BC
by LegendesCarto
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
The ancient roots of Hindu mythology reveal the profound impact Shiva has had on philosophy, culture, and spirituality. The archaeological wonders of the Indus Valley unveil Shiva's prehistoric origins through symbols that have paved the way for millennia of worship.
From the ancient Rigveda to the captivating Puranic narratives, the intricate evolution of Shiva's story tells of the cosmic dance, divine marriages, and benevolent feats that shape the captivating mythology of ‘the Great God’.
From the third eye of wisdom to the rhythmic beat of the damaru, these timeless tales and symbols make Shiva one of the oldest and most revered gods in the world.
#ancient#history#ancient origins#Shiva#gods#Indus Valley#Vedic#Hinduism#Ganesha#deity#Hindu mythology
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
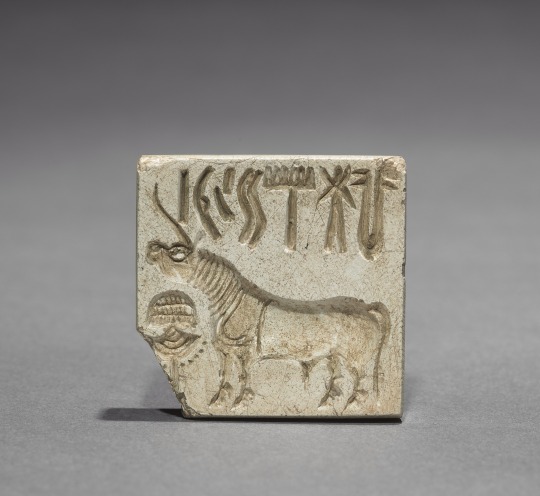

Seal with Unicorn and Inscription, c. 2000 BC. Pakistan, Indus Valley civilization.
#history#carving#unicorn#unicorns#pakistan#pakistán#pakistani#pakistani art#indus valley#religion#ancient india#mythical creatures#paganism#prehistoric#prehistoric art
29 notes
·
View notes
Text


"The Lord of Animals", Pashupati Seal, from the city of Mohenjo Daro, Indus Valley Civilisation
vs
Hyrule's Horse God Malanya
#legend of zelda#zelda#breath of the wild#malanya#horse god#indus valley#mohenjo daro#shiva#hyrule#lord of animals#hinduism#archaeology#history of religion#mythology
14 notes
·
View notes
Text


#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#brownskin#brown skin#afrakans#african culture#India#bharat#epic video#indus valley#ancient egypt#kemet#kemetic#ancient kemet
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
AIT or Aryan Invasion Theory (debunked): A superior "race" of white, horse-riding Aryans invaded the areas of the inferior and primitive Indus Valley population, which included the Dravidians (but actually no one said that the IVC was a pure, dark-skinned Dravidian civilization so idk where that idea came from), and civilized them.
AMT or Aryan Migration Theory: A group of usually horse and chariot-riding nomads and pastoralists usually called the Aryans migrated from the Indo-Iranian region to India and mingled PEACEFULLY with the population of the late Indus Valley population (who were already highly advanced, as we know), by which time the IVC was beginning to collapse, possibly due to change of climate and rain patterns (still not sure yet), and hence the people were abandoning these settlements spreading across the subcontinent. These Indo-Aryans on arriving mixed with this population and shared their genetics, art and culture with each other, which led to the introduction of Sanskrit and Vedic culture in India.
To any leftist who keep regurgitating the former busted myth, please stop. You look stupid. And to any rightist who keep using AMT as AIT to debunk it, they're not the same. These two theories have a sky-ground difference.
The previous one makes Aryans look evil. That they were some high-level royalty who invaded India. But, in fact, they were regular people, regular migrants, just how every migration used to happen 3000-4000 years ago. Like I said, most of them were nomadic settlers.
Sure, later on, the varna system came into existence and this was the beginning of a hierarchical structure in India for the first time (since during the IVC there wasn't any sort of social hierarchy according to current sources). But who's to say it was ONLY the Aryans? Remember. They're NOT a race. They're a particular group of people. And by the time the varna system was introduced already a hell lotta intermixing had happened. Hence it wasn't JUST the Aryans (history and especially anthropological and genetic history is not that black and white LMFAO), because it was a term for 'noble', not some kinda "righteous clan" or something. Idk why people keep thinking of it as a race lol. I thought that was already debunked with the AIT.
As for the indigeneity of the Aryans, technically no one is indigenous. Many of the adivasi and non-adivasi tribes came AFTER the Indus Valley Civilization. So the "who came first" logic doesn't really work at all. (There might've been many that came before as well, who knows. Point is, again, it's all a migration salad at the end of the day)
adjective
indigenous (adjective)
originating or occurring naturally in a particular place; native:
This is the Google definition of indigenous. If we take THIS into account, there would be SEVERAL groups of people involved, instead of just one, like the IVC people, a few of the oldest nomadic tribes, mixed Indo-Aryans, etc. But I'm not gonna call ANYONE indigenous, or not indigenous. Because guess what, none of the humans are really indigenous to any place apart from the African continent. Also the Aryan migration led to the rise of a LOT of genetic subgroups, which was a key factor in leading to the most confusing anthropological history of the Indian subcontinent. It has a fuck ton of genetic markers and groups and subgroups, it's wildly confusing and historians are still trying to figure out every kind of intermixing that has happened. So STOP fighting over who is indigenous or not LMAO. Because guess what, we can never truly assert the indigeneity of a migrant species such as humans. (Yes we do call Native Americans the indigenous people of Americas, or the aboriginals the indigenous people of Australia and the Australasian archipelago, but they were also migrants at some point of time. Now before anyone says I'm disregarding the indigeneity of these groups, I'm not. All I'm saying is that we shouldn't CARE who's indigenous and who's not, because unlike the case of Americas and the Australasian islands, Aryans didn't INVADE India. They were simply another set of migrants, JUST like the IVC people, who also came from the middle-eastern region, and JUST like the adivasi tribes, who migrated from mostly the African and Australasian regions, probably, not sure again.)
I'll link the genetic studies done below because they explain it all way better than I can (and these research papers may also correct some of the incorrect statements I might've unnoticeably or ignorantly made in my own paragraphs so yeah):
Hence, at the end of the day, idk why we're banging our heads on the walls over ONE SIMPLE MIGRATION, which was NOTHING DIFFERENT THAN ANY OTHER MIGRATION. Migrations happen ALL THE TIME. Get over it, BOTH the sides of the political wings, and live in harmony lmao. The Aryans and Dravidians AREN'T RACES. They were just certain groups of REGULAR ass people jeez.
History is a complex subject, and the more evidence we find, the more we would know about our past. I have literally nothing against any of the political wings, but I do want to keep the current theories (which are NOT synonymous to hypotheses btw) and facts straight. I'm once again not saying these facts will never change, because that's not how history works. Maybe in the future, we might find out something completely different about India's past. But remember, whenever we talk about our country's past, we should keep it unbiased, unopinionated, and definitely factual and objective, without including our own views (both political and personal) into it. Interpretations? Sure. But they should remain at ONLY interpretations at best, and only the solid evidences should be claimed as facts.
#hindublr#aryan migration theory#indo-aryans#history#indian history#indus valley#indus valley civilization#desiblr#desi tumblr#desiposting#bharat
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Stamp seal, Indus Valley Civilization, 2500-1900 BC
from The British Museum
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brahmin supremacy
Social hierarchy: The Brahmins established a social hierarchy in which they occupied the topmost position, giving them immense power and control over other communities and perpetuating systems of oppression.
Caste system: Brahmins created and maintained the caste system, which divided society into rigid hierarchies based on birth. This system reinforced Brahmin dominance and enabled them to control the resources and opportunities available to different groups.
Caste-based violence: The Brahmins perpetuated violence against lower caste communities, particularly Dalits, through the caste system, which allowed for institutionalized discrimination and violence.
Marriage practices: The Brahmins established strict rules around marriage and family structures, which helped to perpetuate their social and economic power.
Religious monopoly: Brahmins claimed a monopoly over religious knowledge and practice, which allowed them to control and manipulate the spiritual lives of others. This further reinforced their social and political power.
Religious hegemony: The Brahmins established themselves as the custodians of religious knowledge and texts, giving them significant influence over religious practices and beliefs across South Asia.
Cultural appropriation: The Brahmins appropriated and assimilated elements of indigenous cultures and traditions, erasing the contributions of other communities and further consolidating their power.
Intellectual property: The Brahmins often appropriated the knowledge and intellectual property of other communities, erasing their contributions and further consolidating their own power and influence.
Education: The Brahmins monopolized education, particularly in the pre-colonial period, creating a system that privileged their knowledge and excluded other communities from accessing educational opportunities.
Education: Brahmins controlled access to education and knowledge, which further reinforced their social and economic dominance. They monopolized education and ensured that only members of their own caste could become scholars, priests, and teachers.
Land ownership: Brahmins acquired vast amounts of land through various means, such as gifts from kings or temples, and used their wealth and power to further consolidate their control over society.
Land ownership: The Brahmins, particularly in colonial times, acquired large tracts of land, often through exploitative means, consolidating their economic and political power.
Language and literature: The Brahmins established Sanskrit as the language of knowledge and literature, excluding other languages and literary traditions from the mainstream.
Language dominance: Brahmins promoted the use of Sanskrit, which was the language of the elite and the language of many Hindu religious texts. This gave them further linguistic dominance and helped to consolidate their cultural and political power.
Political influence: The Brahmins have played a significant role in shaping political structures and institutions across South Asia, often to their own advantage.
Systematic exclusion of lower castes from religious and social institutions
Appropriation of land and resources from indigenous communities
Imposition of Sanskrit as the language of power and knowledge, leading to the neglect and suppression of other regional languages and cultures
Establishment of a rigid caste system, with Brahmins at the top and other castes relegated to lower social status and economic opportunities
Monopolization of education and intellectual discourse, leading to the suppression of dissenting voices and alternative knowledge systems
Co-optation of indigenous spiritual practices and beliefs, leading to the marginalization and erasure of non-Brahmin religious traditions
Control over political power and governance through the Brahminization of the state
Promulgation of patriarchal norms and practices, leading to the subjugation and exploitation of women and other gender minorities
Promotion of vegetarianism as a moral and ethical ideal, leading to the marginalization and stigmatization of non-vegetarian communities
Use of violence and coercion to maintain Brahmin hegemony and suppress dissenting voices and movements
Creation of a cultural hegemony that has influenced and shaped the social, political, and economic structures of South Asia for centuries
Control over the production and dissemination of knowledge, leading to the suppression of alternative epistemologies and worldviews
Consolidation of economic power through the control of trade networks and commercial enterprises
Implementation of discriminatory and oppressive laws and practices against lower castes and non-Brahmin communities
Maintenance of a system of inherited privilege and power that has perpetuated Brahmin domination across generations
Control over religious and cultural practices, leading to the erasure and marginalization of non-Brahmin traditions and beliefs
Construction of a narrative of Brahmin superiority and moral authority, leading to the internalization of caste-based discrimination and oppression by non-Brahmin communities
Establishment of a culture of fear and intimidation, leading to the suppression of dissenting voices and the perpetuation of Brahmin hegemony
Appropriation and commercialization of cultural artifacts and practices, leading to the exploitation and erasure of indigenous communities and traditions
Creation of a caste-based system of labor and economic exploitation, leading to the marginalization and impoverishment of lower castes and non-Brahmin communities.
#brahmin#hindu#hinduism#hindutva#india#jai hind#south asia#religion#brahmin supremacy#brahminization#meluhha#indus valley#dalit#bahujan#tamil#dravidian
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
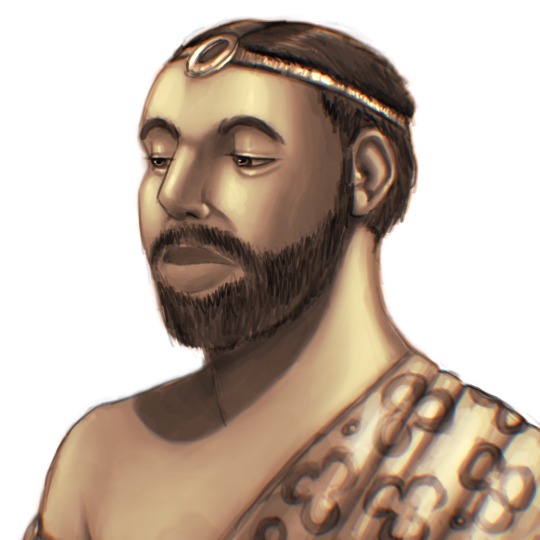


An attempt was made to see how this IVC priest king would really look like irl :)
#historical art#ancient civilizations#indus valley#indus valley civilization#harappan civilization#history art#ancient history#ancient india#history#desiblr#desi tumblr#desi tag#desiposting#ancient city#ancient cultures#ancient
21 notes
·
View notes
Photo
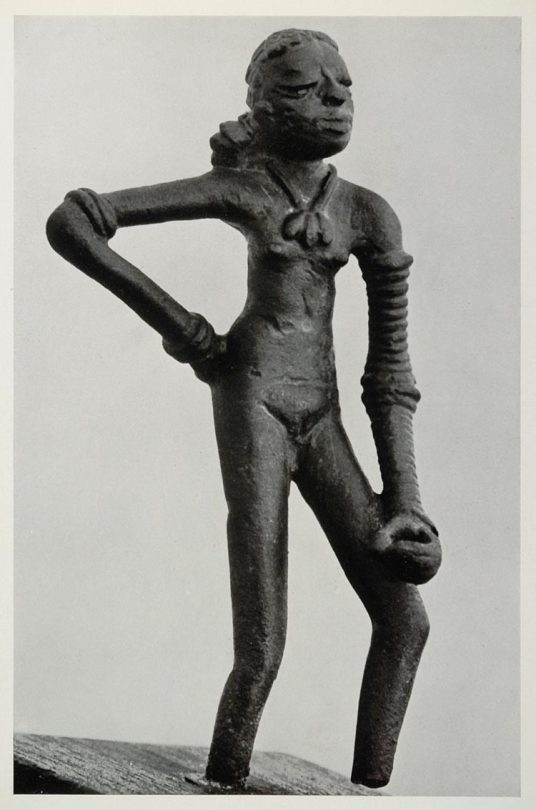



Bronze dancing girl, Harappan/Indus Valley Civilization
Source: Courtesy of Prof. Frederick Asher, Univ. of Minnesota, October 1999
The Dancing Girl, in a photogravure by Alfred Nawrath, 1938
217 notes
·
View notes

